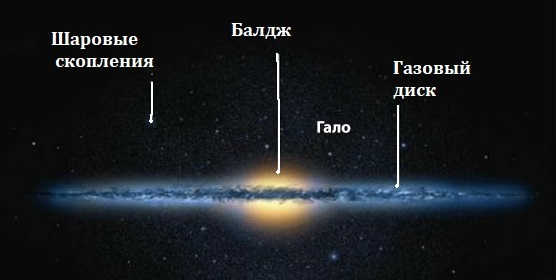
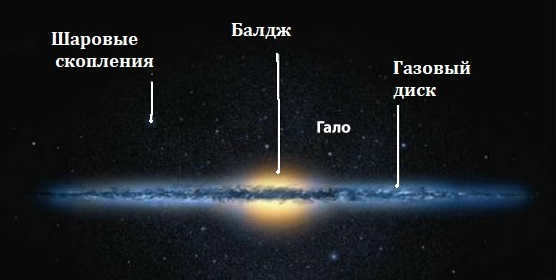
Let’s remember that our galaxy falls into the category of spiral galaxies. It’s clear that the Milky Way has a disk-like shape. Within this disk, we can find a central bulge, galactic arcs, and spiral arms.
The configuration of the Milky Way galaxy
The Milky Way galaxy is filled with a significant quantity of cosmic dust. As a result, the visibility of stellar emissions is considerably limited. Consequently, not all of the objects within our galaxy can be observed and comprehensively studied.
Astronomers have effectively resolved this predicament. They have devised specialized radio telescopes for this very purpose. It is important to note that the utilization of radio waves has partially facilitated exploration through the veil of dust. Consequently, scientists have been able to refine their understanding of the spiral arms.
Undoubtedly, this groundbreaking technique has broadened the horizons of extraterrestrial investigation. Nevertheless, the configuration and characteristics of the Milky Way remain a subject of active examination.
In conclusion, the Milky Way takes on the shape of a disk, housing a vast number of stars, gas, and dust.

The arms of the Milky Way
Is it possible to observe the Milky Way without any instruments?
Given that we are located within the galaxy, it is not feasible to observe it from an external perspective. However, it is possible to view the Milky Way without any telescopes or binoculars from virtually any location on Earth. To be more specific, only a portion of the galaxy is visible to the naked eye.
Where is the best place to see the Milky Way?
As mentioned previously, the Milky Way can be observed in almost any location on Earth. However, it is important to note that it becomes increasingly challenging to see the Milky Way from areas above 50 degrees north latitude. For the best viewing experience, it is recommended to look towards the southern hemisphere. Additionally, during the summer months, it is advised to face south, whereas in spring, west, and in fall, east. It is not recommended to attempt observation during the winter season.
Optimal conditions for observing the Milky Way are during the summer months. During this time, the Milky Way is further away from the Sun, resulting in less interference with its light.

The Milky Way can be observed in the solar system of the Milky Way galaxy.
How can we spot the Milky Way?
As mentioned before, the key factor is the timing for observing the galaxy.
It is obviously necessary to wait for the darkness. Moreover, it is recommended to choose a night without the moon and clouds. Experienced astronomers suggest selecting a time frame two hours before or after sunset.
Keep in mind that urban lighting poses a significant obstacle to observing celestial objects. Therefore, the best location would be the most remote areas away from populated regions.


The Milky Way
To observe the Milky Way in greater detail and clarity, a telescope is necessary. Alternatively, binoculars can be used.
For guidance on selecting a telescope, refer to this guide.
Firstly, determine the direction of the south. A compass can assist with this task. It is worth noting that a compass is readily available on most smartphones nowadays.
Next, locate a dense cluster of stars within the core. Within this cluster, several dark spots can be observed. These are clouds that partially obscure portions of the Milky Way, known as the Great Divide.
Eventually, a slender band of stars will reveal itself across the sky, showcasing the full glory of the Milky Way.

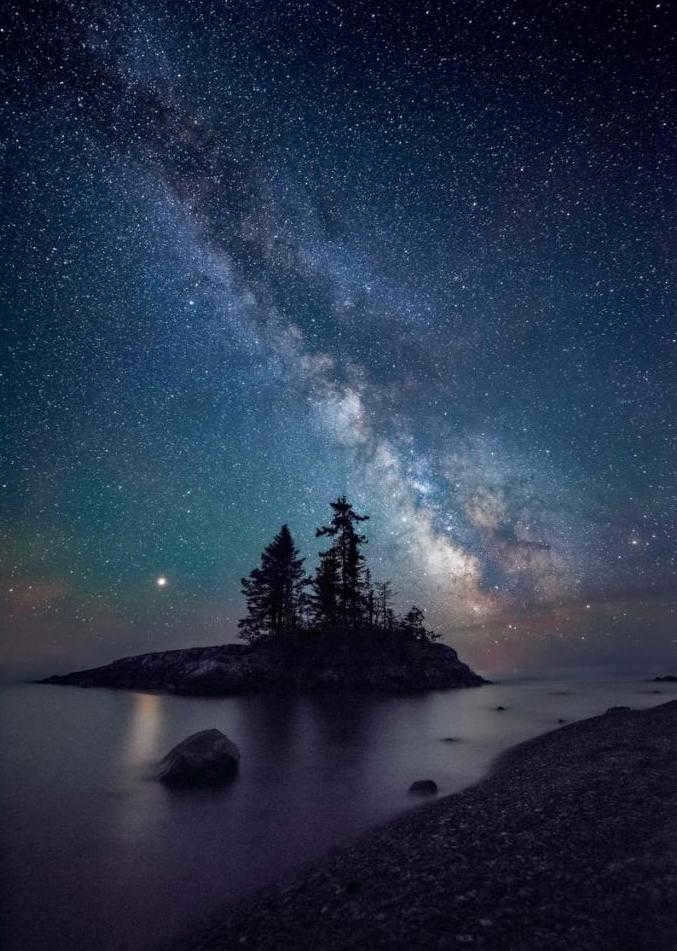
The Milky Way can be observed in remote areas of Russia (Fig. 2). However, due to the rapid growth and increasing illumination of cities, it is becoming more challenging to view the cosmos with the naked eye or through a telescope. Nevertheless, it is still possible to do so.
In conclusion, I recommend selecting a favorable time and location to witness the awe-inspiring sight of the Milky Way. It is important to remember that this is our own galaxy, and it is undeniably breathtaking. Moreover, it is an experience that can truly be enjoyed.
One in three people on Earth are unaware of the location where the Milky Way can be observed

The people of Babylon in ancient times associated the group of bright reflections in the night sky with their revered deity Tiamat, considering it to be the tail of their goddess. Communities in ancient Greece believed that this luminous plume was the source of Hercules’ divine power. However, it wasn’t until the 17th century, in the 10th year, when Galileo provided a solution to the intriguing question. He discovered the optimal location to observe the Milky Way through a telescope. Upon examining it, the thinker arrived at an unequivocal conclusion: it is comprised entirely of stars.
The night sky and the Milky Way


Scientists believe that the Milky Way, a spiral galaxy, has a central bar. The Milky Way consists of:
- Earth;
- the solar system;
- other stars (200-400 billion) that can be seen with the naked eye.
The diameter of the Milky Way is approximately 100,000 light-years, with an average thickness of 1,000 light-years. The shape of the galaxy resembles a flat disk. The structure of the Milky Way includes:
- a disk (the galaxy’s diameter) that rotates faster than the halo, containing most of the stars;
- a nucleus located in the Sagittarius constellation, housing a massive black hole;
- spiral arms, one of which is the Orion arm that contains the Sun’s system, positioned on the inside edge.
- The spherical dark matter extending beyond the Galaxy is referred to as the halo.
There is a speculation that the Milky Way will eventually engulf the Magellanic clouds (both small and large) in approximately 250 million years, and in another billion years, the Andromeda Galaxy will consume our great Milky Way. This event will result in the Milky Way being swallowed up by the Andromeda Nebula. However, it is important to note that this is purely speculative.
Ways to Prevent Losing the Cosmic Path

Essential gear for night photography

The most fascinating locations in Russia
The never-ending enigma of the stars beckons us to seek answers to the questions that arise within us on our humble planet. Hasn’t each and every one of us pondered, at least once, why we are here and not on some distant celestial body? Who are we and what is our purpose? Perhaps astrotourism holds the key to someone’s eternal quest for knowledge. In recent times, this phenomenon has evolved into something more diverse and enlightening than it initially appears. The optimal conditions for stargazing can be found in mountainous areas. In Russia, the top three regions for observing the Milky Way are Altai, Crimea, and the Caucasus. Siberia is also a popular destination, as it boasts numerous remote locations far from the lights of civilization. The best and most accessible option is to choose a less-traveled route and embark on a hiking adventure. However, this does not mean that in other, already partially inhabited places, one cannot enjoy the splendor of the night sky. The only potential hindrance may be light pollution.
According to contemporary scientists, the presence of artificial light has caused a significant distortion in our perception of the night sky, making it increasingly difficult to find a location where we can observe the magnificent beauty of the Milky Way. While it may seem that humanity has lost its connection to the stars, there are dedicated individuals who are actively exploring “astro-routes” and working towards the preservation of our celestial heritage, ensuring that future generations will have the opportunity to experience the awe-inspiring cosmic narrative.
How to Observe the Milky Way in the Night Sky
Regrettably, the majority of individuals have long lost the memory of what the Milky Way appears like! We inhabit urban areas where the nocturnal firmament is tragically concealed by street lamps, luminous advertisements, and automobile headlights. Additionally, in metropolises, there is often a presence of air pollution, which reflects the illumination from street lamps quite effectively. Consequently, the nighttime sky in urban regions is not dark and transparent, but rather overcast and illuminated, resembling the coloration of coffee mixed with milk. It is no surprise that countless individuals have never laid eyes upon the Milky Way in their lifetimes! This leads to the inquiry: is it even feasible to view it? Or rather, how does one go about observing the Milky Way in the celestial expanse?
The straightforward response is to search for the dark sky! Another aspect to consider is that it is not as simple to accomplish this now as it was two or three decades ago. There are progressively fewer locations on our planet that have not yet been illuminated by artificial light. And that is precisely the type of dark and unclouded sky that is necessary to fully appreciate the Milky Way. Where can you find such a sky? Before delving into this inquiry, let us first examine the optimal time to observe the Milky Way.
Optimal Time for Observing the Milky Way
The visibility of the Milky Way varies depending on the season. During spring, particularly in the month of April, it becomes very low in the northern hemisphere, appearing as a faint arc peeking out from the horizon. This is due to the fact that during this time, the night side of Earth is facing away from the Milky Way, resulting in a dark and starless sky.
In winter, the Milky Way can be spotted passing through prominent constellations such as Ascendant, Taurus, Orion, and the Lesser Dog. However, even during this season, its visibility is limited. This is because, in winter, our line of sight is directed towards the outer regions of the Galaxy, where the Milky Way appears faint and lacks distinct shape.
So, when is the best time to catch a glimpse of the Milky Way?
The optimal time to observe the Milky Way in Russia is during the months of August and September. During this period, we have the opportunity to witness the brilliance of its most prominent sections while looking towards the constellations of Cygnus, Scutum, and Sagittarius. It is worth noting that the Milky Way can also be observed in the earlier months of summer, although the nights are shorter and brighter throughout Russia during this time.
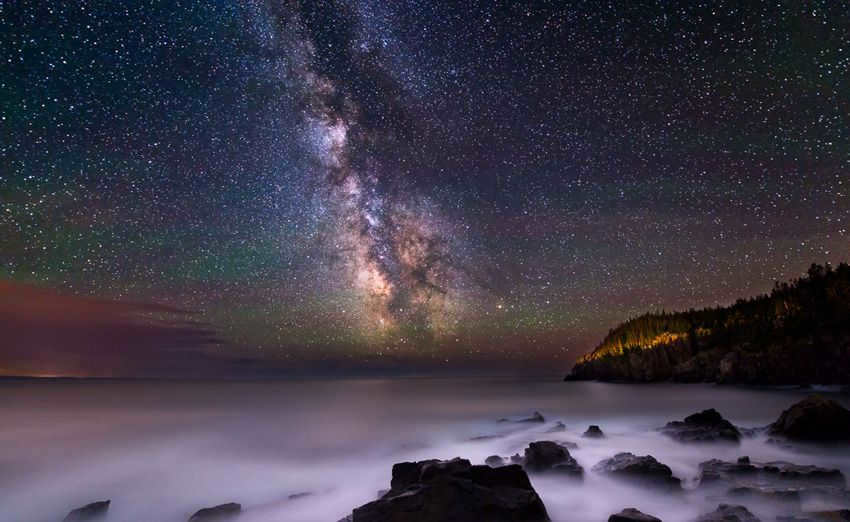

The Milky Way can be observed in the direction of the constellations Shield and Sagittarius. This stunning image was captured in August 2013 in Canada by the talented photographer, Adam Woodworth.
How can you locate the Milky Way in the night sky?
Now, let’s discuss the steps to easily spot the Milky Way without any optical aids. Follow these simple guidelines:
- First and foremost, it is crucial to escape the bright urban lights! As you may know, metropolitan areas emit a strong luminance that can be visible from miles away. Try to find a location where the light pollution is minimal or non-existent.
- To locate areas with minimal light pollution, utilize the light maps found at lightpollutionmap.info. In certain cases, it may be necessary to travel a distance of 50 or even 100 kilometers to discover a sufficiently dark sky, particularly for individuals residing in Moscow or St. Petersburg. Please note: A country house is not ideal for stargazing as it is typically still affected by nearby street lighting. The optimal locations for observing the stunning Milky Way are forest edges, remote countryside, steppes, mountains, and seashores. The most challenging part is finding the perfect spot, but it becomes easier from there!
- One crucial consideration: your observation site should be situated away from roads frequented by vehicles. The glare from passing car headlights can impair your vision.
- It is advisable to observe only during a night without moonlight! The moon has a similar negative impact in the sky as streetlights. Therefore, it is recommended to look for the Milky Way when: a) the Moon is close to the new moon phase; b) the Moon has not yet risen (for instance, in the evening, after the full moon phase and during its decline); c) the moon has already set (this occurs during the waxing phase of the month, when the Moon is visible in the evenings). How can I determine the current position of the moon in the sky? There are numerous free and paid mobile applications available in the App Store. You can choose the one that suits you the best.
- Clear skies are essential for observing the Milky Way. The atmospheric conditions can be less than ideal. Wispy clouds, light fog, high humidity – all these factors will not completely obscure the Milky Way, but they will make it less distinct.
- Before you begin your observation, it is important to spend about 15-20 minutes in complete darkness.
- Avoid looking at your phone screen or using a flashlight, as well as any other sources of light.
- This period of darkness will help your eyes adjust and become more sensitive to the surroundings.
What the Milky Way looks like without any aid
During the months of August and September, the Milky Way can be observed in the southern sky during the evenings and in the southwest during the night.
To locate it, you can use the Grand Summer Triangle as a reference point. This figure is formed by three bright stars: Vega, Deneb, and Altair.
The Milky Way can be seen following the line connecting Deneb and Altair. It appears as a hazy, glowing river with soft, indistinct edges.
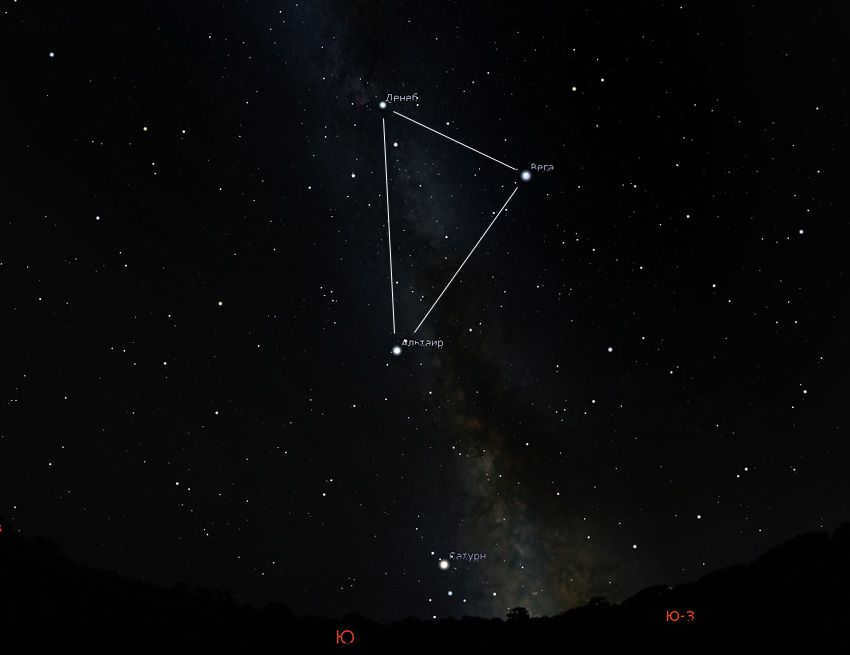
The dark country sky offers a breathtaking sight of the Great Summer Triangle and the Milky Way. This celestial display is particularly captivating in the Swan constellation where the Milky Way splits into two streams that gracefully descend towards the horizon. The interstellar space between these streams is filled with darkness, absorbing the light emitted by distant stars and nebulae.
The constellation of Shields provides a truly awe-inspiring view of the Milky Way, adorned with a dense and radiant stellar cloud. Additionally, the constellations of Sagittarius and Scorpius leave a grandiose impression, albeit unfortunately being too low in the Russian sky. However, those fortunate enough to be in the Caucasus region can witness these magnificent regions of the sky in all their glory.
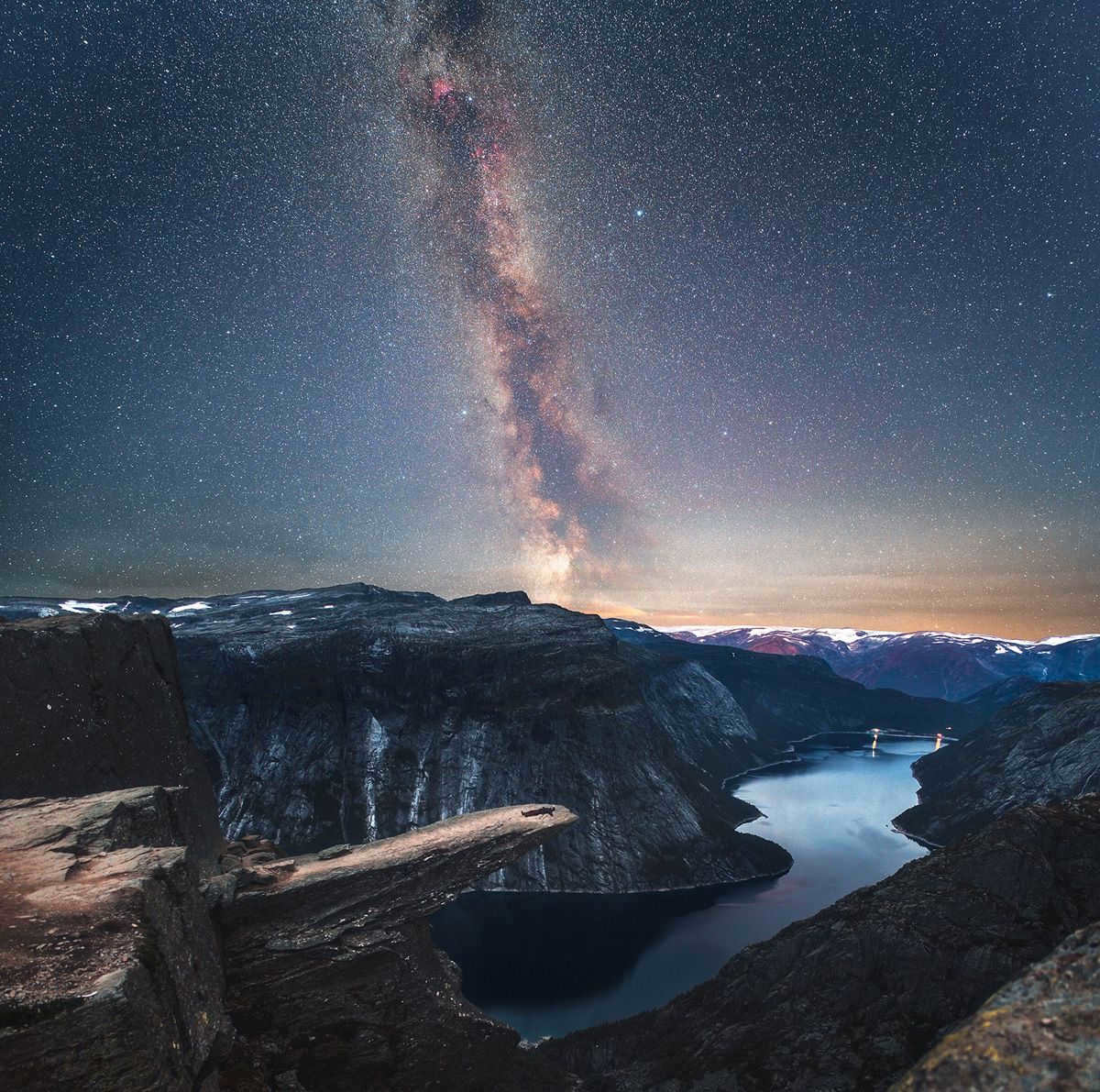

The view of the Milky Way in the direction of the Summer Triangle and the constellations Shield and Sagittarius is truly breathtaking: its intricate and ethereal formation is truly remarkable, with vibrant star clusters intertwined with reddish hydrogen nebulas and deep cosmic dust lanes. Photo: Ruslan Merzlyakov/APOD
The Milky Way’s intricate formation becomes even more evident when observed through compact binoculars. The wide field of vision provided by binoculars allows for the observation of vast nebular structures, chains of stars, and clusters of stars interspersed with enigmatic dark patches.
Undoubtedly, the Milky Way is among the most breathtaking sights that can be observed in the celestial sphere without the aid of any instruments. Naturally, proper preparation is necessary for its observation, but I am confident that the effort put into it will be well worth it! The starry expanse unveils its treasures to only a select few.
PS. In the dark skies of August or September, not only can the Milky Way be spotted with the naked eye, but also a handful of other faint nebulous entities. Particularly noteworthy is the renowned Andromeda Nebula, which happens to be the nearest large spiral galaxy to us. Further information on how to spot it can be found here.

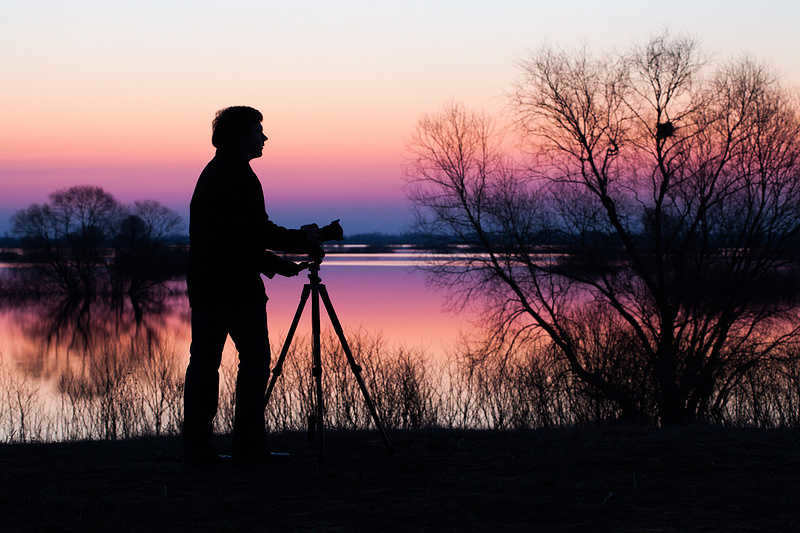
Only in photographs can you truly appreciate the beauty of the night sky. Unfortunately, the human eye cannot capture all the vibrant colors that a camera’s sensor can. Nevertheless, anyone can take such a photograph. Victor Malyshchits, an astrophotographer, has generously shared his tips for capturing stellar images and has explained the importance of finding the perfect vantage point, even if it means venturing to the top of a mountain – but not too high.
The photographer’s craving for the stars knows no bounds
Viktor Malyshchitz and his team embarked on a mission to capture the beauty of the North Caucasus night sky. Inspired by the ESO UltraHD project, they sought to create their own stunning images. Back in 2014, a group of esteemed astrophotographers embarked on a similar journey through Chile’s Atacama Desert, aiming to capture the stars from the European Southern Observatory (ESO).

– Naturally, the sky in the Caucasus is quite different from that in the Atacama Desert,” Victor explains. “The extremely clear and dry air of the desert allows us to capture celestial objects that are incredibly faint. Additionally, the southern hemisphere sky itself offers a more captivating view compared to our own. However, the landscapes of the Atacama are rather monotonous, resembling the Martian terrain with its lack of steep variations in height. This is not the case in the Caucasus, which boasts cliffs, valleys, forests, rivers, and snowy peaks.
While astrophotographers certainly require stars, Victor believes that capturing famous landmarks, architectural wonders, or natural phenomena against a starry backdrop adds a level of intrigue that surpasses a simple starry sky.
– I wouldn’t argue that the sky holds more significance than the landscape. It’s simply that the sky often serves as the focal point of a photograph. However, the stars and constellations remain constant regardless of location, yet it is far more captivating to witness a particular place beneath these celestial bodies. We specifically selected these locations as they offer a stunning view of the illuminated sections of the Milky Way juxtaposed against the majestic snow-capped peaks of the Main Caucasus Range.
The night sky appears much more vibrant than what meets the eye
When you look at pictures of the night sky, you see a bright and colorful display of stars. However, in reality, our eyes are not able to perceive all the different cosmic glows. This is why most people only see a multitude of bright stars against a plain black background. Even if you were to venture up into the mountains, you still wouldn’t be able to witness the full splendor that astrophotographers capture and share with us, unless you have the necessary photographic equipment.
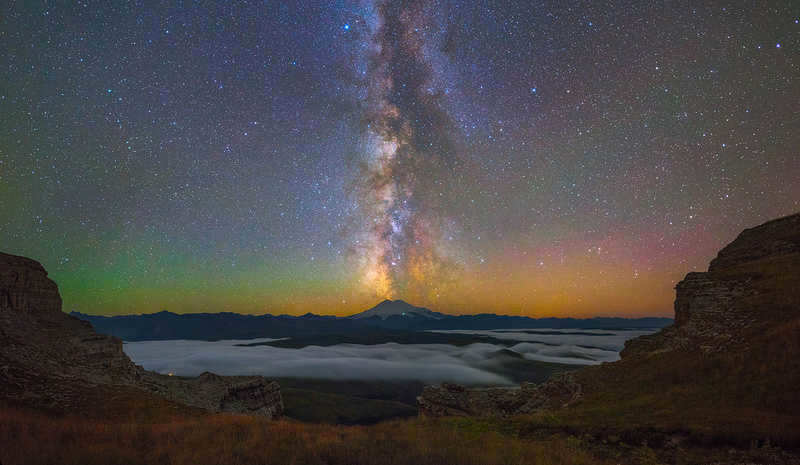

– The human eye lacks the ability to retain light for an extended period, whereas a camera can. This is why photos taken with 20-30 seconds of exposure time capture more stars than what is visible to the naked eye,” explains Victor. – In essence, nighttime photographs reveal a world that is beyond our natural sight.
Victor advises us not to be disheartened by this. “According to him, the dark starry sky is even more awe-inspiring in person.
– It is particularly breathtaking in the mountains, where the transparency of the sky unveils the glow of our atmosphere: frequently, green, red, or yellow streaks, waves, and spots can be seen in my starry sky photos. Take note, they appear in nearly all of my pictures.
Unveiling the Mysteries of Night Sky Photography
Unlocking the secrets of capturing the breathtaking night sky is no easy task. While compact cameras, superzooms, and smartphones cannot do justice to this celestial spectacle, fear not! With an affordable DSLR or mirrorless camera in hand, you can embark on an exhilarating journey to capture a stunning image. Be prepared to click countless frames in pursuit of that one perfect shot.

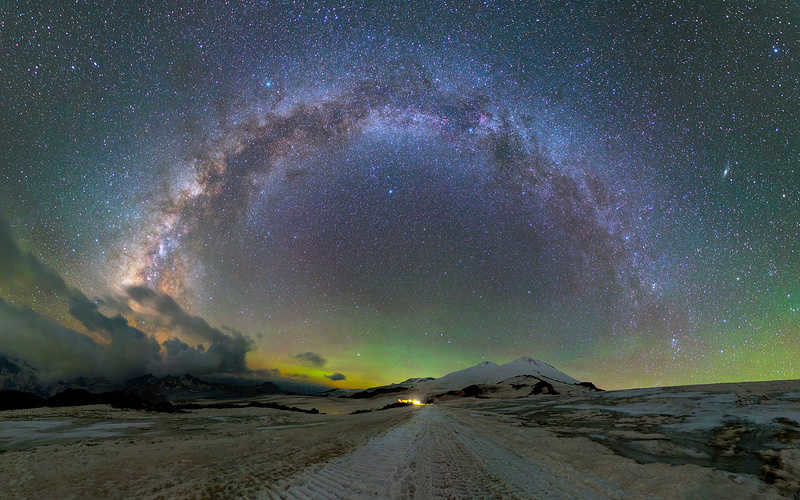
– There are a few key elements that contribute to a successful photograph. Firstly, having a camera with a high-sensitivity sensor and fast lenses is crucial. Secondly, I typically capture multiple frames to create a mosaic, which allows for reduction of digital noise. Thirdly, to enhance the visibility of objects on the ground and minimize camera noise, I often take multiple identical shots and average them on the computer. While this technique may not be effective for the sky, it significantly improves the details on the ground.
Most of the photographs in the article were captured with exposure times ranging from 20 to 30 seconds and an ISO sensitivity of 4000. The lens used had a focal length of 24 mm and an aperture of 1.4. Each image is a combination of multiple shots. Vertical shots featuring the Milky Way typically consisted of 3-4 frames, while panoramas showcasing the arch of our Galaxy could include up to 15 frames.
The elevation of the shooting location also plays a role in the quality of the sky. The higher the vantage point, the better the sky will look. However, finding interesting landscapes may become more challenging at higher altitudes, such as on Mount Elbrus. Nevertheless, this does not imply that other locations will have the same limitations.
– We were shooting a film on the northern side of Mount Elbrus, situated at an elevation of 4000 meters. Naturally, we lacked both the necessary mountaineering expertise and equipment. Furthermore, transporting heavy equipment to the summit proved to be quite a challenging task. Nevertheless, the crucial factor is that as you ascend this mountain, the landscapes gradually lose their appeal for astrophotography. After all, such photographs typically require a wide perspective, and the foreground is dominated by vast expanses of snow fields. Consequently, I had no desire to continue climbing any higher.

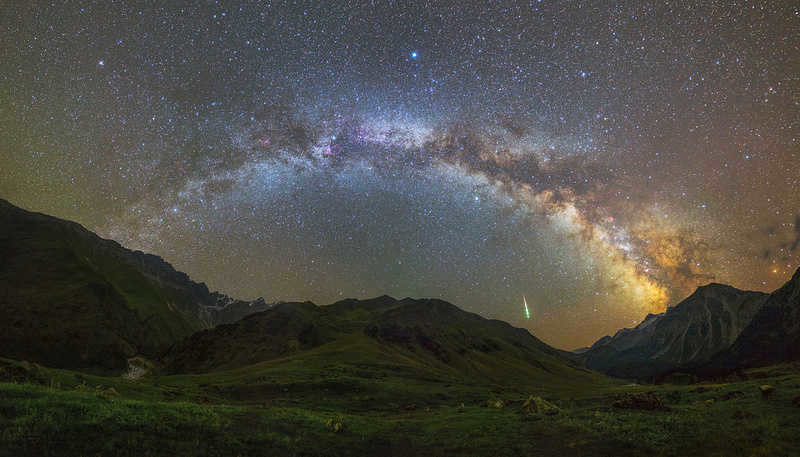
It’s fascinating how visibility actually improves with height, yet the human eye is designed in such a way that it perceives less effectively in areas with thin oxygen.
– Those who have gazed at the stars from an altitude of 5000 meters and above claim that due to oxygen deprivation, the retina’s sensitivity decreases, resulting in a diminished view of the stars. However, once you connect to an oxygen tank, the entire sky starts to sparkle with countless diamonds.
Beginner photographers who are learning the principles of composition are well acquainted with the rule of thirds: the horizon line in a landscape should occupy one-third of the frame above or below. In nighttime landscapes, this rule is typically followed, but a larger portion of the frame is dedicated to the sky.
Escaping the Glow of the City
– Venturing into the mountains is a worthwhile endeavor not only in the Caucasus, but in any mountain range. As we ascend, the sky above becomes darker and clearer. Typically, the main pollutants such as haze, dust, and aerosols are concentrated within the first two kilometers of the atmosphere. Therefore, the higher we go, the more captivating the sky becomes. However, during our journey through the Caucasus, I was left disappointed by the sky. Throughout the three weeks, a faint haze persisted in the atmosphere. It is possible that air masses carried dust from the deserts of Central Asia. Occasionally, we could even discern a stark contrast between the dusty and transparent air.

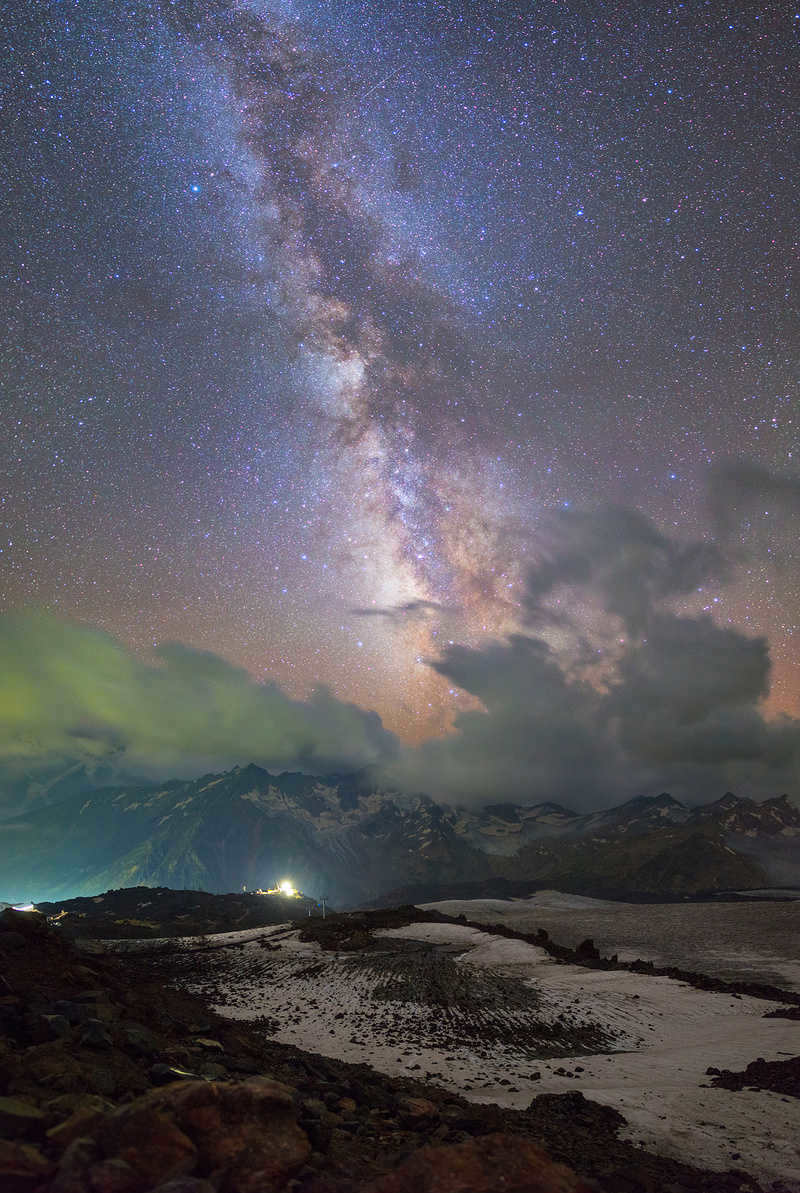
The visibility of various stars and constellations changes throughout the year. The movement of the sun against the backdrop of the stars causes different constellations to be hidden from our view at different times of the year.
– I particularly enjoy the latter half of summer and the beginning of autumn, as well as the middle of winter. During summer, we can see the brightest sections of the Milky Way. At latitudes in the Caucasus region, we can even have a fantastic view of the areas towards the center of our Galaxy – during the summer, these luminous star clusters are visible low in the southern sky. Conversely, in winter, the Milky Way appears very faint, but the winter sky is filled with vibrant and stunning stars, and the snowy scenery only accentuates the splendor of the celestial bodies.

When starting out as an astrophotographer, it is important to keep in mind a crucial detail. Star photography takes place at night, which means that you will need to spend the night in the mountains, camping in tents. As a result, before embarking on such a journey, it is advisable to first research the potential hazards that may be encountered along the route.
– In the Caucasus, there are numerous locations where one might come across bears and other large predators during the nighttime. A friend of mine captured starry skies in the mountains while listening to the grunting of a whole herd of wild boars in the nearby bushes. However, it is worth noting that such encounters are highly unlikely and rarely pose any danger to humans.