This webpage provides details about the present and projected position of Mars in the solar system and in the sky based on your location, along with its apparent brightness, size, luminosity, and more.
Discover where Mars is currently located in the sky
The chart displays the altitude of Mars above the horizon (—°) at different times of the day. The shaded regions ( ) represent the nighttime, while the dashed line ( — ) indicates the present time.
Latest Mars News
New evidence has emerged supporting the existence of a subglacial lake on Mars.
The Chinese rover has discovered indications of past flooding in the Utopia Planitia region.
Scientists have identified a “promising” landing site for the Chinese rover named “Zhurong”.
A peculiar rock formation was captured in a photograph taken by the Mars rover “Curiosity”.
Contrary to previous claims, scientists have refuted the existence of a subsurface lake on Mars.
The InSight module continues to unveil the inner structure of the Red Planet.
Chinese rover “Zhurong” successfully roved away from its landing platform.
The first images captured by the Chinese rover “Zhurong” have been released to the public.
The landing of the Chinese rover on Mars is anticipated to occur on May 15.
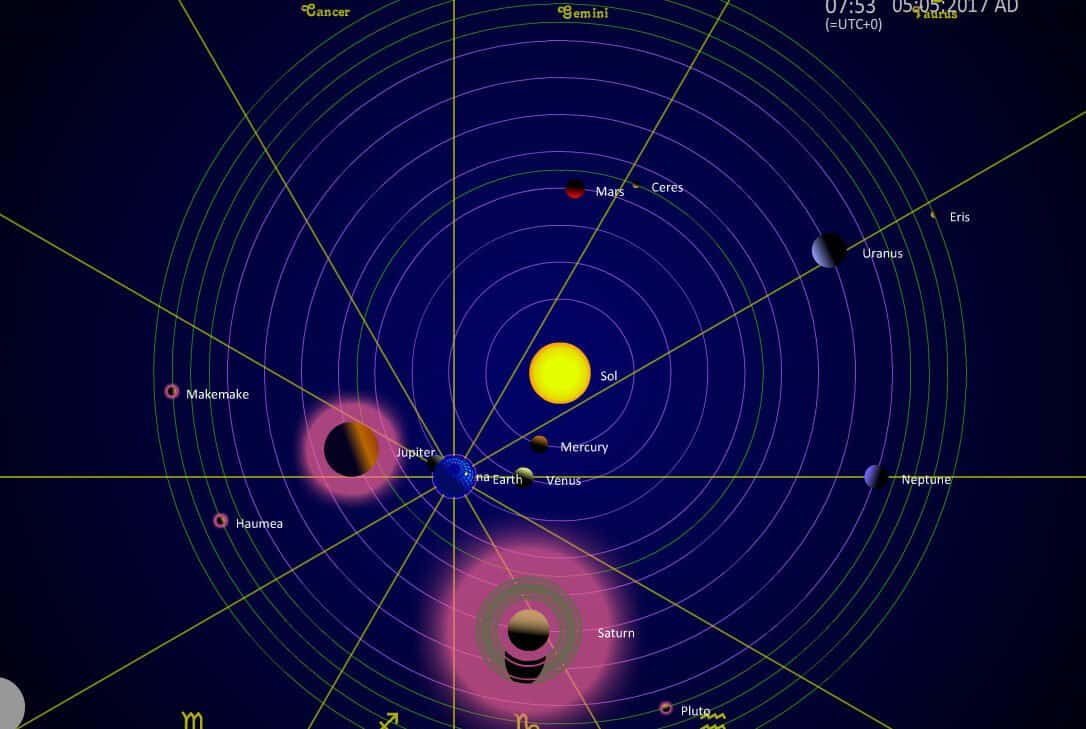
Current Position of Mars in the Solar System
Displayed in the diagram is the present whereabouts of Mars, Earth, and the Sun, as well as their projected locations in half a year.
The current position of Mars in the sky can be seen in the image above.
The current distance from the Sun to Mars is unknown.
The current distance from Earth to Mars is unknown.
The animation demonstrates the movement of a photon from Earth to Mars, traveling at a velocity of 299,792,458 meters per second. It will cover the current distance of 365.6 million kilometers in a time of 20 minutes and 18 seconds.
Visibility of Mars in the sky over the next half-year
The chart presents the fluctuation in the duration (in hours) of Mars’ visibility in the sky before sunrise and after sunset on specific days.
The luminosity of Mars in the sky over the next six months
The graph illustrates the variation in Mars’ luminosity (—) based on the stellar magnitude (m).
Details about the other planets in the Solar System
© 2015-2023 In-Space. All rights reserved.
Any use of the text materials, without any modifications, is allowed only if there is an active hyperlink to In-Space. All audiovisual works are owned by their respective authors and copyright holders, and are solely used for educational and informational purposes.
The online edition of In-Space is officially registered with the Federal Service for Supervision in the Sphere of Communications, Information Technologies, and Mass Communications (Roskomnadzor) on May 04, 2018. The registration certificate is numbered FS 77 – 72684.
This site may contain content that is not suitable for individuals under the age of 18.
Observing the planet Mars in the sky: how to locate and when to observe, the moment of opposition, Mars’ orbit around the Sun, choosing a telescope, surface mapping, and its satellites.
Mars, also known as the Red Planet, is positioned fourth in line from the Sun and is named after the violent god of war, Mars. It is located at a distance 1.5 times greater than that of Earth from the Sun. Mars completes its revolution around the Sun in approximately 687 Earth days. The average yearly temperature on Mars is -60˚C, with the highest recorded air temperature reaching no higher than +10˚C. In addition, Mars is accompanied by two natural satellites, Deimos and Phobos, which orbit around it.
What is the best time to observe Mars?
The ideal time to observe the Red Planet is during its opposition periods, which occur when it is closest to Earth. These opposition periods happen regularly every 2 years and 50 days. During this time, Mars appears at an apparent angular size of 13′-14” and has a stellar magnitude of -1.3. The most recent Mars opposition occurred on April 9, 2014.

However, the moment of true delight for astronomers comes around only once every 15-17 years. We are referring to the incredible Mars Encounter, set to take place in 2018.
Mars has a more elongated orbit compared to Earth’s, and the Great Encounters occur when the planet reaches its perihelion. The least favorable times for observations are when Mars is positioned at aphelion.

Mars at its nearest oppositions:
The transition of seasons on Mars
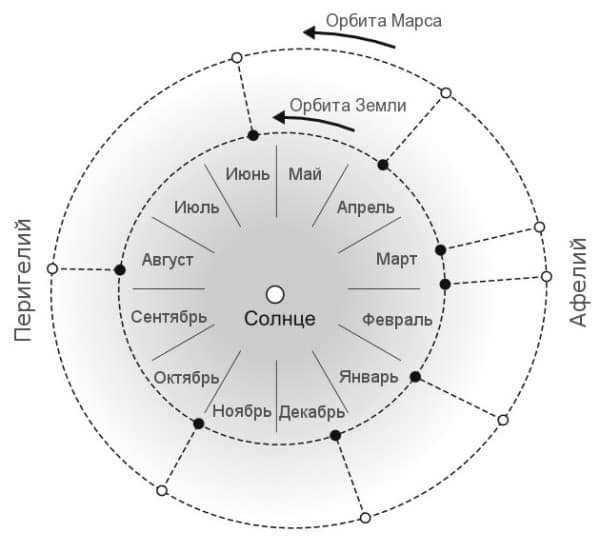
Illustration depicting the cyclical pattern of seasons on Mars
Similar to Earth, Mars undergoes seasonal changes due to its equatorial tilt in relation to its orbit. The seasonal transitions on Mars closely resemble those experienced on Earth.
Just like on Earth, the onset of summer in the northern hemisphere of Mars coincides with winter in the southern hemisphere, and vice versa. However, there are notable differences. In the northern hemisphere of Mars, summers are lengthy and cold, while winters are brief and warm. Conversely, in the southern hemisphere, summers are brief and warm, while winters are long and freezing. Summer in the southern hemisphere of Mars aligns with the planet’s journey through perihelion, while in the northern hemisphere, it aligns with aphelion.
Equipment needed
If the weather conditions are favorable for observing, a 60-millimeter telescope will allow you to see the small disk of Mars, but you won’t be able to observe its details. That’s why the most suitable instruments for studying the Red Planet are a 150 mm reflector telescope and a 100 mm refractor. However, it is recommended to have a Newtonian reflector of 250-300 mm for the best results.
It is not advisable to purchase a large amateur telescope with a lens larger than 350 mm, as such equipment is affected by atmospheric turbulence and requires a long time to stabilize thermally. These larger telescopes can only be effective in extremely calm weather conditions, when the fully cooled device can reveal a wealth of details and nuances on the planet’s surface.
The Celestron Advanced VX 8″ N telescope
is a unique and innovative telescope that offers advanced features and capabilities. This telescope is perfect for both amateur and professional astronomers, as it provides high-quality images and precise tracking. With its 8″ aperture and advanced VX mount, this telescope is able to capture detailed views of the night sky. Whether you’re interested in observing planets, stars, or deep-sky objects, the Celestron Advanced VX 8″ N telescope is the perfect choice.
Introducing the Celestron Omni XLT 150 Telescope
The Celestron NEXSTAR 102SLT Telescope
Bresser Pollux 150/1400 EQ2 Telescope
Rephrase: Explore the Universe with the Bresser Pollux 150/1400 EQ2 Telescope
The Bresser Messier AR-152S/760 EXOS-2/EQ5 Telescope
combines high-quality optics and a sturdy mount to provide excellent views of the night sky.
The Bresser Messier NT-150S/750 EXOS-1 Telescope
is a unique piece of equipment for astronomers.
Synta Sky-Watcher Dobsonian 8″ telescope (200/1200)
The Sky-Watcher Dob 8″ (200/1200) Telescope Retractable by Synta
A stable clockwork mount is necessary for a telescope designed for exploring Mars, as it allows the planet to remain within the field of view for an extended period of time.
When observing Mars, the utilization of color filters is essential as they aid in examining the planet’s surface with greater precision. Additionally, they enable the observation of various atmospheric phenomena.


When observing Mars, a set of color filters is an essential tool.
The red filter enhances the contrast between light-colored land regions and dark seas, particularly noticeable at low magnifications and in calm atmospheric conditions.
Among the most effective filters for observing Mars are orange and yellow filters. They effectively highlight fine details in the red areas of the planet and are also great for enhancing visibility in dark areas, providing a stable image.
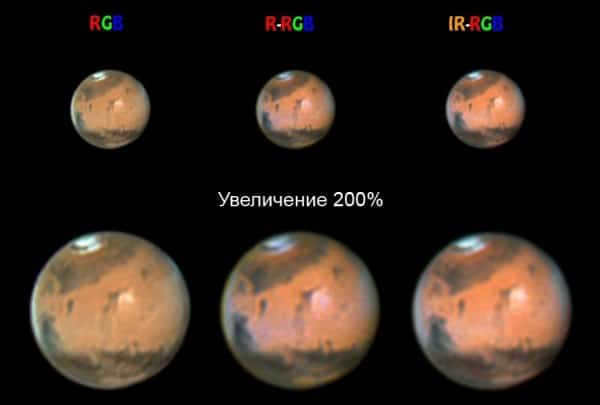

An illustration showcasing the utilization of diverse filters during the observation of Mars
The green filter is employed in the examination of dark regions in close proximity to the polar caps, and it is particularly effective in enhancing the visibility of yellow dust storms. Furthermore, this filter efficiently accentuates white areas on Mars’ red surface.
The blue filter is specifically crafted to highlight the violet regions of the planet, making it highly proficient in the detection of water clouds within Mars’ atmosphere.
The violet filter effectively emphasizes fogs and clouds that manifest during the melting of the polar caps.
What can be observed through a telescope on Mars
Mars presents a unique and challenging opportunity for observation. Traditionally depicted as a tiny dot devoid of any discernible features, it is understandable that novice astronomers might feel disappointed by the lack of visible continents and polar caps through their lenses.
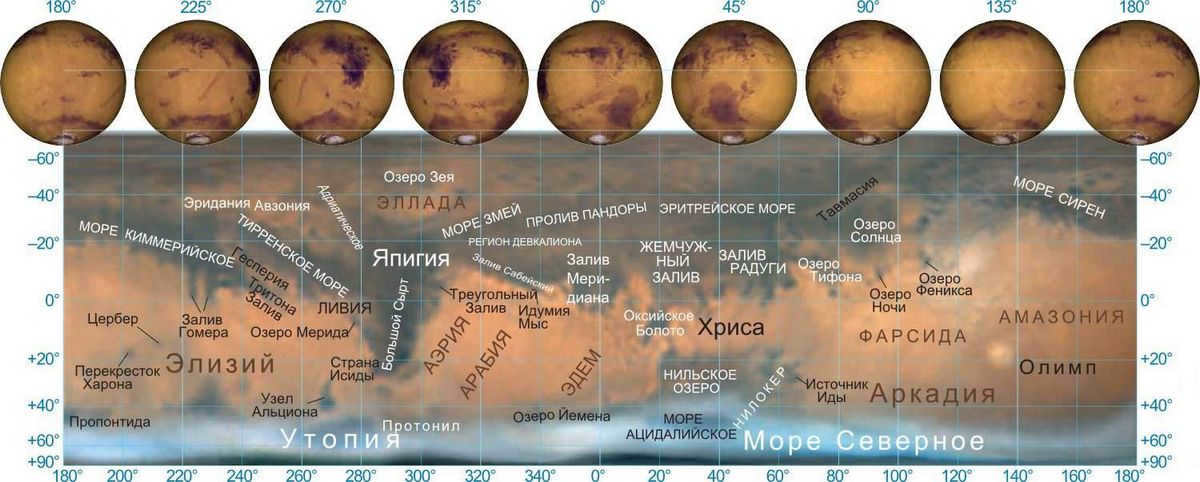
A map depicting the topography of Mars. Feel free to click on the image to enlarge it.
During periods of opposition, the viewing conditions are slightly improved, allowing for a remarkable observation of the receding polar caps using a high-quality 100mm refractor. Moreover, this instrument enables the examination of the distinct dark outlines of the continents present on the surface of the Red Planet. The lens of a 150-millimeter telescope reveals the presence of greenish-gray areas on the Martian disk, which were mistakenly identified as flourishing vegetation by astronomers in the twentieth century. It is now known that these areas are merely composed of dust and rocks, reflecting sunlight in a peculiar manner.

Comparing the photo of Mars captured through an amateur telescope with a computer model can provide valuable insights. However, it is important to note that the true joy of exploring Mars can only be experienced with larger or medium-sized amateur telescopes. These telescopes, when coupled with favorable atmospheric conditions, allow observers to closely examine the planet’s surface and observe changes in its appearance brought about by weather patterns and seasonal variations.
Tips for observing Mars
Typically, the period of Mars observation begins 40 days prior to the opposition and continues for 40 days afterwards. This is because the angular diameter of Mars is at its maximum during this time. However, astronomers with telescopes that have lenses larger than 250 mm can extend their observation time frame to 4 months before and after the opposition. Within this extended period, one can witness fascinating changes, meteorological transformations, and the melting of the polar caps. Additionally, it is possible to observe the different phases of Mars.
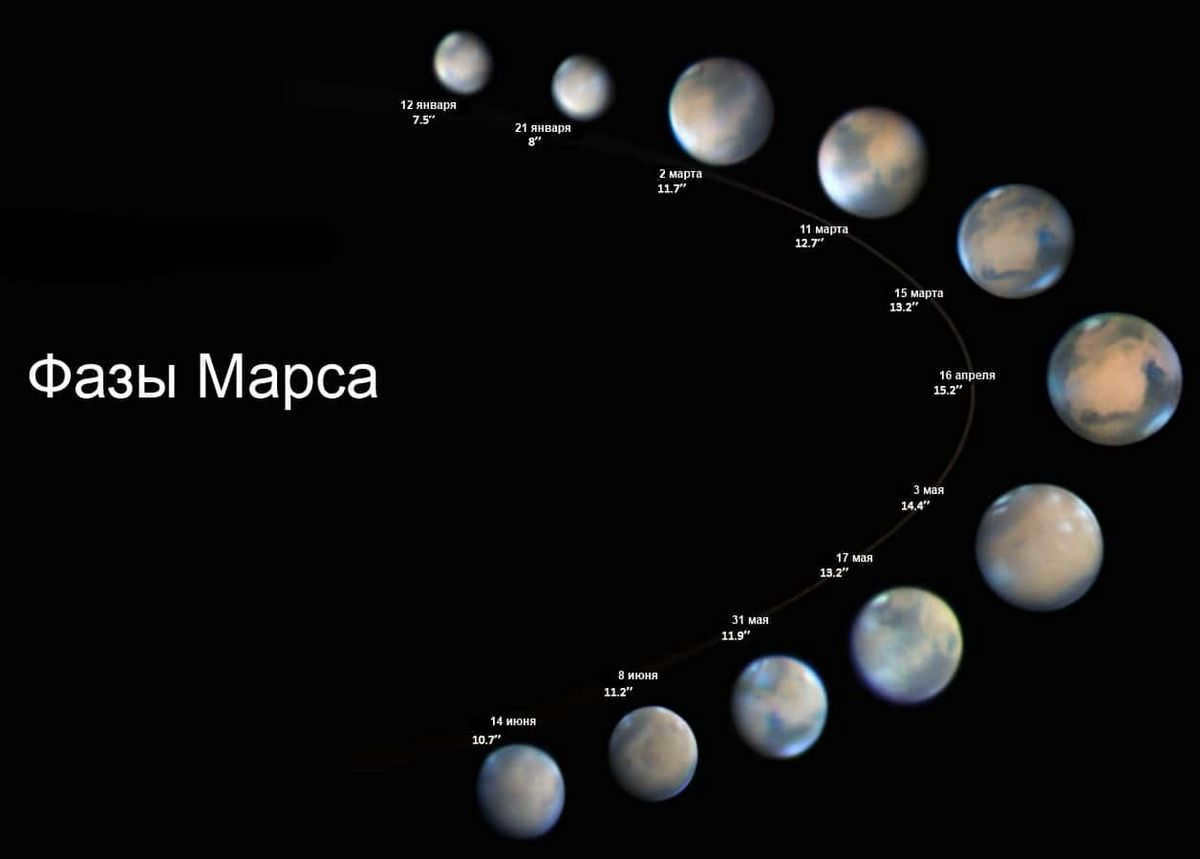

Phases of Mars. The picture was captured during the 2015 observations
If you regularly make sketches of the appearance of Mars, you can easily uncover the most intriguing details on its surface. This approach allows for a more thoughtful and comprehensive study. Even rough representations of what you see in the telescope can be beneficial. They encourage the researcher and aid in identifying the features observed.
If you start making regular observations of Mars, you will soon discover the elusive nature of its features. That’s why achieving a high-quality focus with your telescope is crucial in this scenario. However, with Mars, the difficulty of this task becomes ten times greater. To ensure success, it is essential to remember the following rule: focus on the polar cap, as it is the most distinct feature on the planet’s surface.


An example of a picture of Mars captured using a Celestron C8XLT + Celestron x2 Barlow Ultima 200-millimeter telescope
Don’t anticipate Mars to immediately reveal all of its mysteries to you. As you commence your observations, take a moment to relax fully. Allow your breath to be as steady and tranquil as possible. Give your eyes a couple of minutes to identify the features you are witnessing. The first thing you will notice is the polar cap. It stands out easily due to its stark contrast with the surrounding surface: a bluish-white region on an orange disc.
Gradually, your attention will be drawn to the faded greenish-gray spots – the Martian seas. Whenever you get the chance, aim your telescope lens towards Mars. Once you gain enough expertise, you will uncover the enchanting beauty of the Red Planet.
As a point of comparison, here is a photograph of Mars captured through a Celestron Nexstar 127 SLT 127-millimeter telescope.
Keep in mind that it takes Mars 1 day and 37 minutes to complete a full revolution on its axis, according to Earth time. This is why if you observe the planet at the same time each day, you will notice that surface features from the previous day appear 37 minutes later. By observing Mars consistently at the same time for 6 weeks, you can track the complete axial rotation of the Red Planet.
What can be observed on Mars
Polar caps
The polar caps are the most distinctive features on the surface of Mars. They are visible to any amateur astronomer. The appearance of the polar caps varies with the seasons. During the spring and summer, the caps undergo active melting. Their edges gradually shift towards the poles. Your objective is to monitor these changes.
The southern polar cap can be easily observed using a basic telescope, especially during opposition periods when Mars reaches its closest point to the Sun. In the spring and summer months, the southern cap undergoes significant changes in both size and shape. It is particularly fascinating to witness the cap splitting into two distinct halves. This phenomenon is caused by the gradual melting of the snow on the peak of the Mitchell Mountain Range. As the snow thaws and cracks, these changes become clearly visible along the southern edge of the cap.

The most striking feature of Mars’ surface is its south polar cap.
The north polar cap, on the other hand, lacks the dramatic seasonal changes that fascinate astronomers. Even in the summer, it does not completely disappear, leaving observers intrigued by its unpredictable behavior. When autumn arrives on Mars, fog forms in the northern hemisphere’s polar region. This fog can also appear in the spring, adding to the mystery. At the same time, the melting of the north polar cap halts and it gradually starts to grow again.
Martian seas and their seasonal transformations
The transformation of the Martian surface during the change of seasons also has an impact on the dark regions known as seas. Typically, these changes begin in the middle of the spectrum and continue until the polar cap disappears. At that point, the dark zones encompass the entire area between the equator and the polar region. Throughout the spring and summer periods, the gray seas become noticeably darker and undergo changes in size and shape. To fully observe these transformations, a detailed understanding of Mars’ topography is necessary.
Among the areas of the planet that are most affected by seasonal changes are the Gulf of Pearls (Margaritifer Sinus), Syrtis Major, Pandorae Strait (Pandorae Fretum), and Lake of the Sun (Solis Lacus). All of these locations are featured on an extensive Mars map.
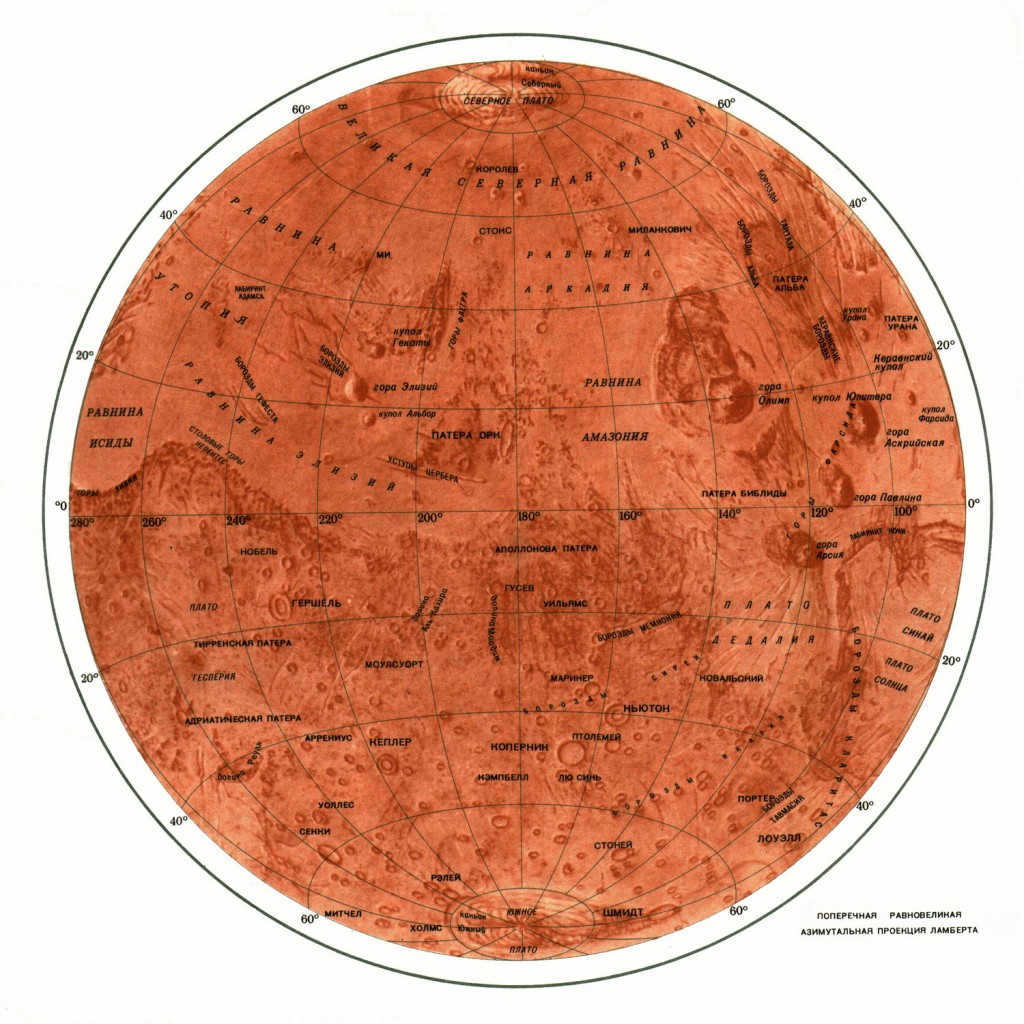

Check out this map of the Martian surface. Simply click on the image to get a closer look.
The Atmosphere and Phenomena of Mars
The presence of white fog and bluish clouds on Mars is believed to be a result of seasonal changes. These formations typically occur during the spring months and disappear completely by winter. It is thought that the melting of the polar ice caps may contribute to this phenomenon.
To accurately identify fog and clouds on Mars, a solid understanding of Martian cartography and appearance, as well as significant observational experience, is required. One can recognize clouds by observing their changing shape and size as they move across the Martian seas. The use of colored filters such as green #58, blue #38, 38, 38A, 80A can greatly assist in this task.


The use of different filters offers a distinct benefit when studying the atmospheric phenomena of Mars.
Mists and clouds can persist above the surface of Mars for a considerable duration, lasting up to a full day on Earth.
Dust storms and yellow clouds are examples of atmospheric phenomena that can be studied using a telescope at an amateur level. Typically, these phenomena are formed on the planet during its perihelion passage, coinciding with the observation of the summer opposition in the southern hemisphere.
Dust storms and yellow clouds are the result of solar activity, leading to the creation of powerful wind currents. These occurrences occur unexpectedly and swiftly envelop vast regions. They frequently obscure entire oceans and continents from view. To enhance contrast, one can employ filters in shades of orange or yellow.
Observing Phobos and Deimos
Not every amateur astronomer has the opportunity to observe the moons of Mars. These moons of Mars – Deimos and Phobos – are like elusive apparitions. However, there are a few simple techniques that can assist in studying the moons of Mars even with an amateur telescope.
Firstly, it is ideal to conduct observations during the Mars opposition, as the close proximity of Mars to Earth makes its moons appear brighter. During this time, Deimos has a stellar magnitude of 12, and Phobos has a magnitude of 11. They can be observed using a 4-5 inch telescope. Of course, the clarity of the view is affected by the brightness of Mars. This is particularly true for Phobos, as its orbit is in close proximity to Mars.

Observing Mars satellites with an amateur telescope
Experienced astronomers are aware of a useful technique for observing dim objects near bright stars: simply remove the bright star from the field of view. This technique can be applied when studying the moons of Mars, Phobos and Deimos. To optimize your observations, it is recommended to use an eyepiece with a narrow field of view, such as an orthoscopic eyepiece. Before observing, it is advisable to calculate the time when the moons will be farthest from Mars, as this will provide the best conditions for observation. Computer programs such as SkyTools 3 or Guide 9.0 can assist in this calculation.
When the specified time comes, direct the telescope towards Mars and gradually move it out of the field of view. This will prevent its brightness from affecting your observations. Once you have the opportunity to observe Phobos and Deimos, attempt to bring the planet back into the field of view. It’s possible that you may still be able to spot the satellites. If not, take a moment to admire these stunning photographs of Mars captured by amateur astronomers.
Images of Mars captured by hobbyist astronomers:






- Methods for solar observation
- Approaches to lunar observation;
- 100 features on the lunar surface
- Ways to observe Mercury and Venus;
- Techniques for observing Mars;
- Procedures for observing Jupiter;
- Tips for observing Saturn;
- Observing Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto
- How to view a solar eclipse;
- How to view a lunar eclipse
- How to observe dark nebulae;
- Observing globular clusters: a guide
- The fundamentals of double stars
- Exploring the beauty of the Polar Lights
- Silver clouds: uncovering their secrets

During the beginning of December, the planet Mars will be directly opposite to the Sun, creating a perfect opportunity to witness this spectacular celestial event. Discover the compelling reasons why you should make sure not to miss observing the captivating Red Planet during this time.
On December 8, 2022 at 08:35 MSC (05:35 GMT), Mars will be at opposition. During this time, Mars, Earth, and the Sun will align in a nearly straight line, with Mars and the Sun positioned on opposite sides of the Earth.
What does this mean for you as an observer? It means that in the upcoming days, you will have a great opportunity to spot Mars in the sky! Here are a few reasons why you should take advantage of this:
- Mars will be fully illuminated by the Sun and reach its maximum brightness in 2022. The red planet will be shining with a star magnitude of -1.9 – making it the brightest star in the sky!
- During the opposition, the apparent size of Mars will be at its peak. The planet will have an angular diameter of 17″, which is almost three times larger than its size in May. This increase in size is due to the fact that Mars recently reached perigee, the point in its orbit closest to Earth, on December 1. The accompanying image illustrates how Mars’ size changes throughout the year.
- This year, Mars’ perigee will be the closest it has been in the past decade. The Red Planet will be 0.54 a.u. (or 80 million kilometers) away from Earth.
- You will have ample opportunity to observe Mars as it will rise at sunset, reach its highest point in the sky around midnight, and remain visible for the rest of the night.
- During the opposition, viewers in North America, Western Europe, and northwest Africa will have the opportunity to witness Mars being covered by the Moon. As the full Moon passes in front of the Red Planet, it will create a spectacular sight!
- The Mars opposition is an infrequent occurrence, happening approximately once every two years. Don’t miss out!
You don’t have to wait for the opposition to start observing Mars. The planet is currently visible and will continue to grow brighter until December 8. Take a look at our infographic for more fascinating facts about the 2022 Mars opposition.

Are you a fan of observing Mars? Then get ready for its opposition in December 2022. We will explain why this is the ultimate opportunity to witness the Red Planet until 2033.
How can you spot Mars in the sky?
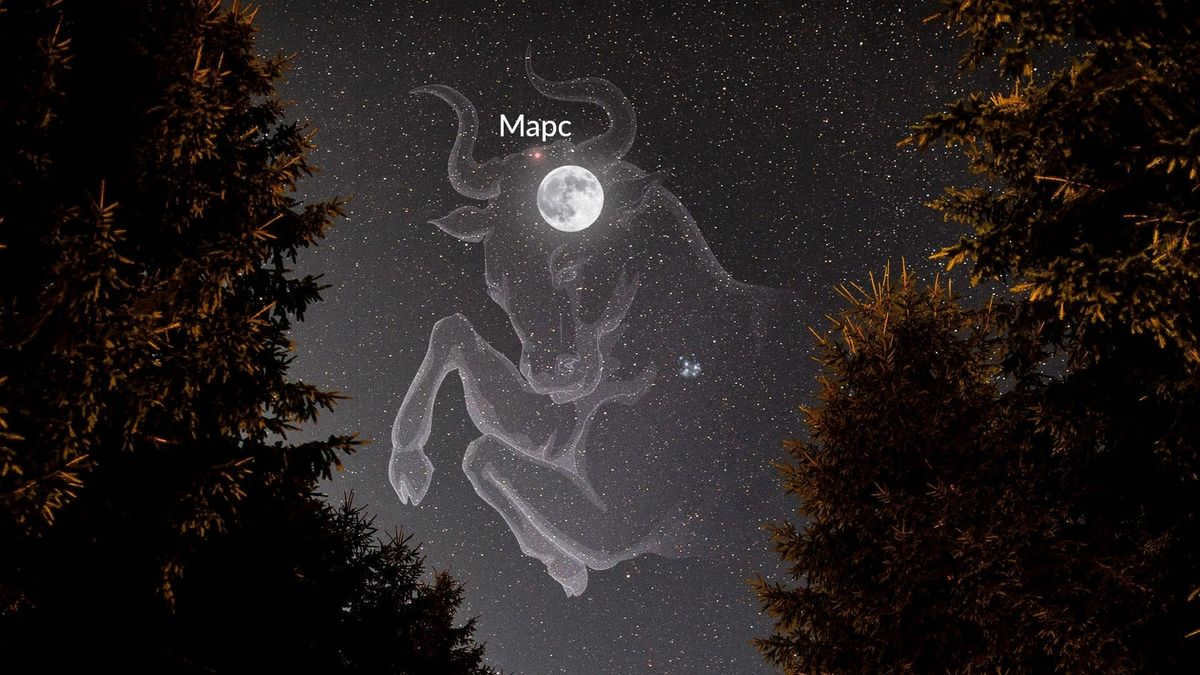
Mars is quite easy to locate and differentiate from other celestial objects, especially during the opposition. It will appear as a vivid reddish spot in [the constellation Taurus]. The planet will emerge above the northeastern horizon at sunset and reach its highest point in the southeastern part of the sky around midnight.
The optimum viewing conditions for the Mars opposition in 2022 are in the Northern Hemisphere, where the positioning of the planet will be significantly higher in the sky compared to the Southern Hemisphere. While Mars is visible to the naked eye, it can also be observed using binoculars or a telescope. During this particular year, Mars will be tilted towards Earth, providing the opportunity to view both of its polar regions through a telescope. However, it is important to note that the ice caps will not be visible: the north polar cap is currently concealed beneath a thick layer of clouds, while the south polar cap has significantly diminished in size over the summer months.
To easily locate Mars in the night sky, it is recommended to utilize a stargazing application such as Sky Tonight or Star Walk 2.like Sky Tonight or Star Walk 2.
To start, you can get the Sky Tonight app on your iOS or Android device.
To search for the event:
- Tap on the magnifying glass icon located at the bottom of the screen;
- In the “Popular” section, search for the “Mars Confrontation” event;
- Click on the blue telescope icon to view the position of Mars in the sky during the confrontation;
- In the “Popular” section, you can also click on the telescope icon next to the “Mars” object to see its current location.
To use the calendar:
- Click on the calendar icon at the bottom of the screen and choose December 8 from the “Events” tab;
- Locate the “Mars Confrontation” event in the list of events below the calendar;
- Click on the blue telescope icon to view Mars’s position in the sky during the confrontation.
How to locate Mars during the confrontation using Star Walk 2
First, download Star Walk 2 on your iOS or Android device.
Utilize the search feature:
- Tap the magnifying glass icon located in the bottom left corner of the screen;
- Type “Mars” in the search box and select the corresponding result;
- The app will display the current position of Mars in the sky.
Utilize the calendar feature:
- Tap the menu icon located in the lower right corner of the screen;
- Access the Astronomical Calendar;
- Search for December 8 and select the “Confrontation: Mars” event;
- The application will display the position of Mars in the sky during the opposition.
Mars will be in close proximity to the Moon on December 8, 2022
During the Mars opposition, you will have the opportunity to witness another remarkable celestial event – the conjunction of the Moon and Mars. The Full Moon will pass just 0°32′ away from the Red Planet in the constellation Taurus.
Observers in North America, Europe, and North Africa will be particularly fortunate. On that very same night, they will have the chance to witness the Moon obscuring Mars. The Moon will completely cover Mars during the occultation!
When is the upcoming Mars confrontation?
The next time Mars will be in opposition to Earth is on January 16, 2025. This event won’t be as impressive as the one happening this year because Mars will be farther away from our planet, resulting in a slightly dimmer appearance (star magnitude -1.4) and a smaller size (angular size 14.6”) in the night sky. So, make sure not to miss the Mars opposition in 2022!
To sum up: On December 8, 2022, Mars will reach opposition, making it shine the brightest and appear almost at its largest size for the entire year. After that, the next Mars opposition won’t occur until 2025.
Which planets can be observed in the sky during July 2023? All planets will be visible during mid-summer, but their visibility conditions vary greatly for different regions of Russia. In the northern regions, where the phenomenon of white nights still persists, only Venus (in the first half of the month during the evenings) and Jupiter (in the morning towards the east) will be visible to the naked eye. In the central regions of Russia, both Venus and Jupiter will be much more visible, and Saturn will also be visible. Mercury and Mars can only be seen at the limit of visibility during the evenings in the southernmost regions of Russia. Uranus and Neptune can be observed through a telescope, especially if you are in the southern part of the country. Now, let’s examine the visibility conditions of the planets in more detail.
Mercury’s Position in July 2023
On July 1, Mercury is in a close alignment with the Sun, and then it transitions into the evening sky. However, this does not immediately result in its visibility during the evening. The gap between Mercury and the Sun in the sky gradually widens, and it only reaches 15° by the middle of the month.
By the end of July, the planet will be positioned 25° to the east of the Sun. However, despite this considerable distance, it will still be challenging to spot the planet with the naked eye in most parts of Russia, except for the southernmost regions. This is because the ecliptic, which is the path the Sun appears to travel along throughout the year, has a shallow angle to the horizon in the western sky during summer. Consequently, even though the planet will be significantly further east than the Sun by late July, its height above the horizon will only differ slightly from that of the Sun. As a result, the planet will set during the early twilight hours. The same is true for Venus and Mars, which are also located nearby.
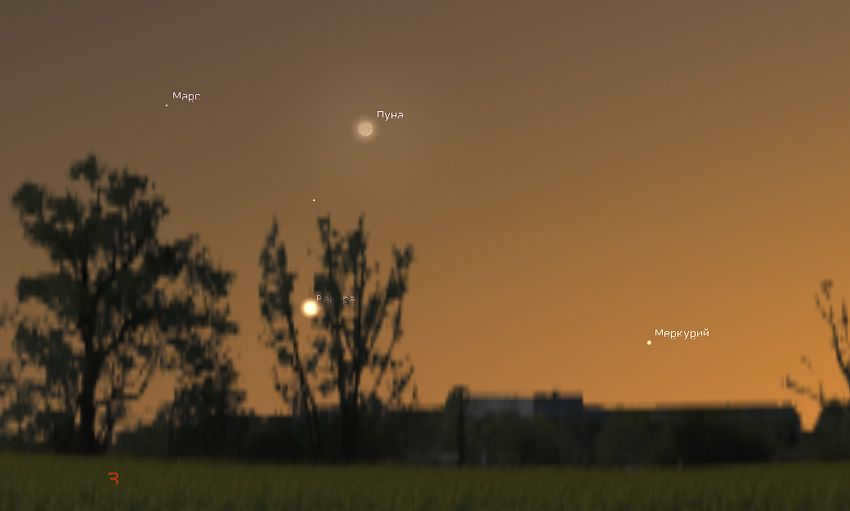

In July, Mercury sets so early during twilight that it becomes challenging to observe, even in the Caucasus region. The image shown here depicts the sky on July 20, 2023, at the latitude of Sochi. On that evening, the crescent of the young Moon will be in close proximity to Mercury and Venus. Image source: Stellarium
Bright Venus continues to sparkle in the evening sky. However, in June, the presence of the planet disappeared for residents of the middle and northern regions of Russia: despite being almost 50° east of the Sun, it disappears at twilight. Nevertheless, even in areas with white nights, Venus remains observable! Its luminosity is what distinguishes it from Mercury and enables it to be visible to the naked eye even when the Sun is still below the horizon. However, if you reside, for instance, at the latitude of St. Petersburg or Petrozavodsk, don’t anticipate Venus to shine as brilliantly as it does in April and May. You will need to search for it!
How to locate Venus in the sky during July?
- If you reside in an urban area, locate an unobstructed western horizon. Ensure that there are no buildings or trees blocking the view.
- About 30 to 40 minutes after sunset, direct your gaze towards the west. Venus will be positioned a few degrees above the horizon. In the central region of Russia, the planet’s elevation will be approximately 8°. The closer you are to the southern hemisphere, the higher Venus will appear above the horizon.
- In a bright twilight sky, the planet may not stand out immediately, but it can be easily spotted. It might take a couple of minutes for you to locate it. With the naked eye, Venus appears as a small white dot. However, when observed through a telescope, even at low magnification, it exhibits a snow-white crescent shape resembling the moon.
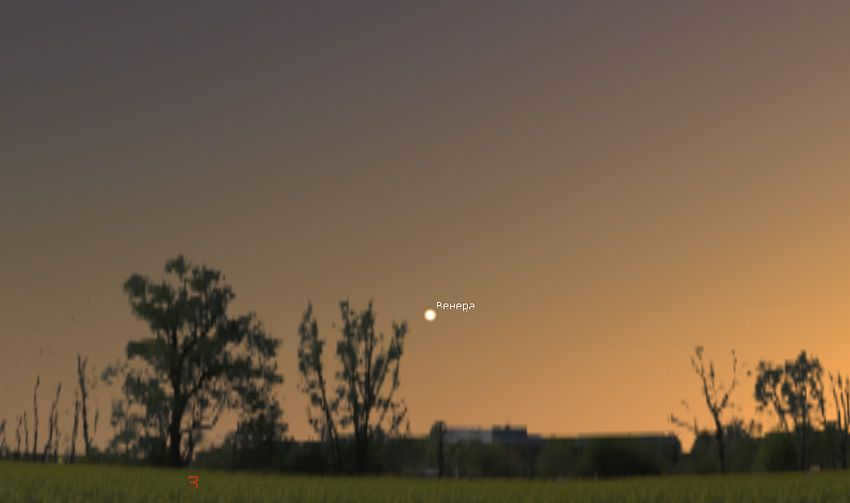

You should definitely take the opportunity to observe Venus through a telescope before it becomes less visible. The planet’s visibility is decreasing, and in the middle zone of Russia, it will only be observable until mid-July. After that, it will only be visible in the southern part of the country. By August, Venus will enter into conjunction with the Sun and transition to the morning sky. For more information on Venus’ visibility in the fall and winter, check out the article “Venus in 2023.”
Mars in July 2023
Throughout the entire month of July, the planet Mars can be seen in the evening sky in close proximity to Venus. Unfortunately, its brightness is such that it is hardly visible to the naked eye in most parts of Russia, except for the southernmost regions. In July, Mars appears with a magnitude of 1.7 m, which is roughly equivalent to the brightness of the stars in the handle of the Big Dipper. It’s important to note that the luminosity of celestial bodies can decrease by 1 star magnitude or more at the horizon due to atmospheric extinction. All of these factors make it challenging to observe the Red Planet from the latitude of Moscow and especially St. Petersburg.
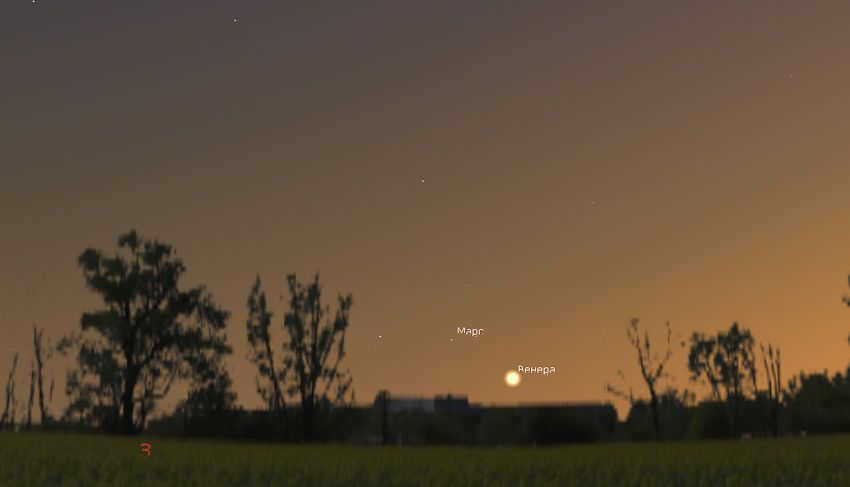

In early July, about an hour after sunset, Mars and Venus can be observed in the evening sky of Moscow. This information is based on data from Stellarium.
In the southern region of Russia, Mars can still be seen against the backdrop of a dark sky. To locate Venus, one must simply look for the brightest object in the evening sky. In regions such as the Caucasus or Primorye, Venus becomes easily visible as early as an hour after sunset.
As the night progresses, two stars of similar brightness will become visible to the left of Venus. The star closest to Venus is actually the planet Mars! The other star, located farther away, is Regulus, the brightest star in the constellation Leo.
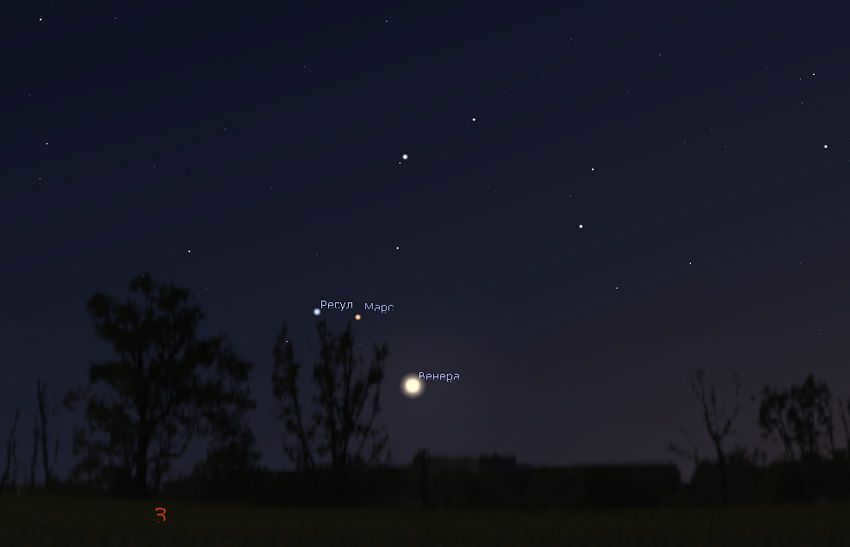

In early July, the evening sky of Sochi offers a captivating view of Mars and Venus. The planets can be seen low above the horizon, but keep in mind that they only remain visible for about an hour before setting behind the horizon. Therefore, it is crucial to have an unobstructed view of the western horizon in order to observe Mars.
Jupiter in July 2023
Jupiter can be seen in the morning sky during the month of July. It first rises around 2 a.m. at the beginning of the month and around 1 a.m. towards the end of the month in the eastern direction. It remains visible in the sky until sunrise. The visibility of Jupiter varies depending on the latitude.
In the southern region of Russia, Jupiter is easily visible in the morning sky. However, in Moscow and its surrounding areas, the visibility is not as good. In early July, Jupiter rises against the bright morning dawn. However, as the month progresses, it can still be observed for an hour or more against a relatively darker sky background.
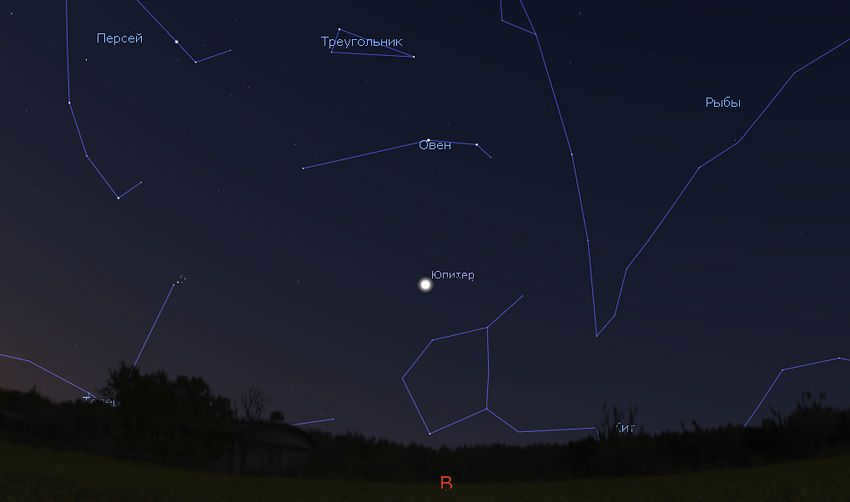
In mid-July, Jupiter can be seen in the morning sky of Moscow. The planet is located in the constellation Aries, surrounded by the constellations of Cetus, Pisces, and Taurus. To the east, the direction is marked with the red letter B. Image: Stellarium
Seeing Jupiter in early July at the latitude of St. Petersburg can be a bit challenging. Although the planet rises during the morning twilight, it is still bright enough to be visible in the sky. The main difficulty is that Jupiter rises and becomes visible late at night. However, the period of white nights ends in mid-July, and the conditions for observing Jupiter will gradually improve every night. The same applies to higher latitudes.
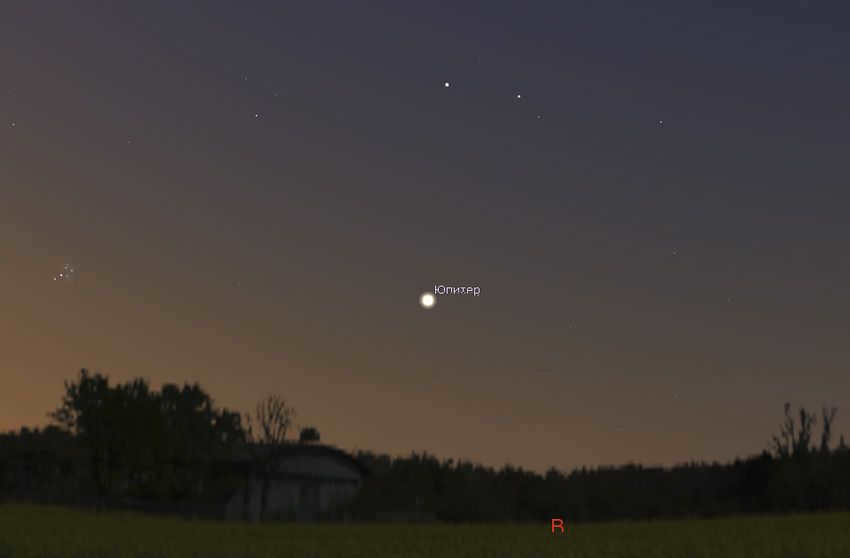

In mid-July, residents of St. Petersburg can observe Jupiter in the morning sky. On the left side, the Pleiades, a stunning star cluster in the constellation Taurus, can be seen. This information is provided by Stellarium.
It’s worth noting that on the mornings of July 11th and 12th, the Moon will be in the last quarter phase and will be located near Jupiter. This will make it easier for observers to locate this magnificent planet!
Exploring Jupiter with a Telescope
Jupiter is undeniably one of the most captivating planets to observe through a telescope. One of its remarkable qualities is its consistent brightness and angular size throughout the year. Jupiter always shines brightly, making it easily distinguishable from the surrounding stars. The only planet that can rival its brilliance is Venus, although these two planets are rarely visible simultaneously.
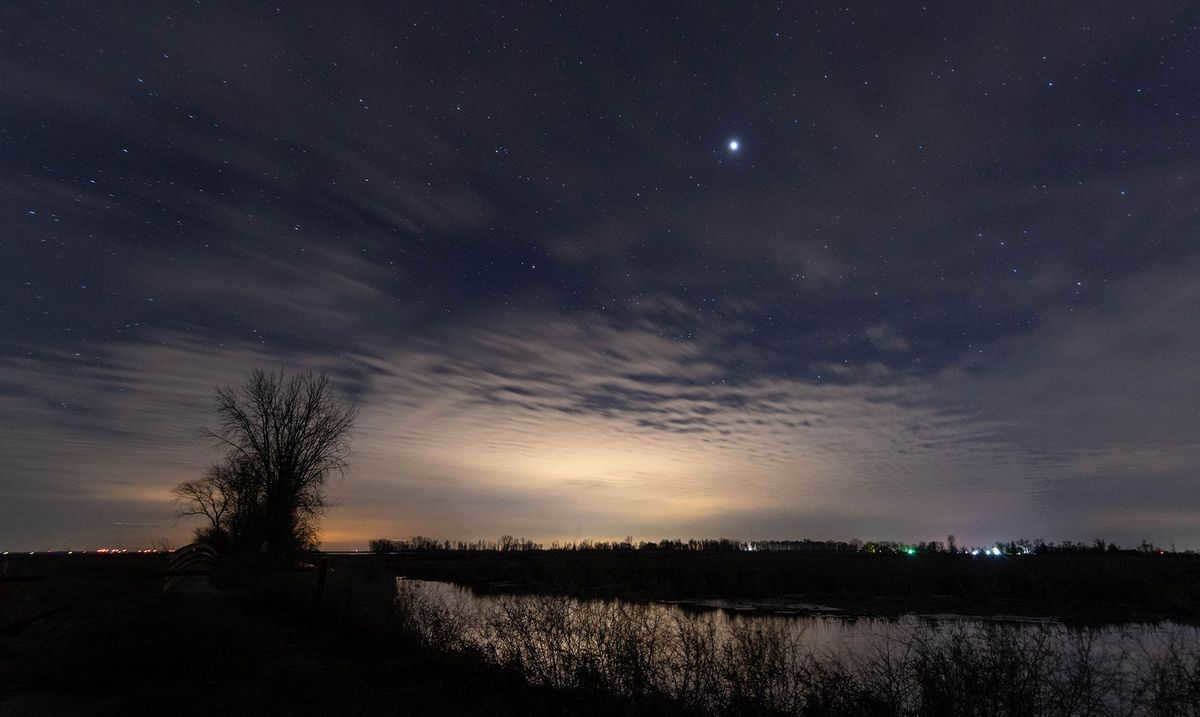

When looking at the sky before dawn, Jupiter appears as a brilliantly shining star. Photo: Joshua L. Smith
There is always something interesting to observe on Jupiter: with a small telescope, you can see its cloud belts, the Great Red Spot, and its four largest moons – Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto.
However, for optimal observations, Jupiter needs to be at least 20° above the horizon (ideally 40°). In the latter half of July, the planet will have reached this altitude before disappearing into the morning twilight.
Saturn in July 2023
Saturn is a planet that offers stunning views in July, particularly during the night and morning hours.
In the early part of the month, Saturn can be seen rising around 1am and remains visible until dawn in the southeastern part of the sky. The length of time that Saturn is observable varies depending on the latitude of the observer, with those located further south enjoying a longer viewing period.
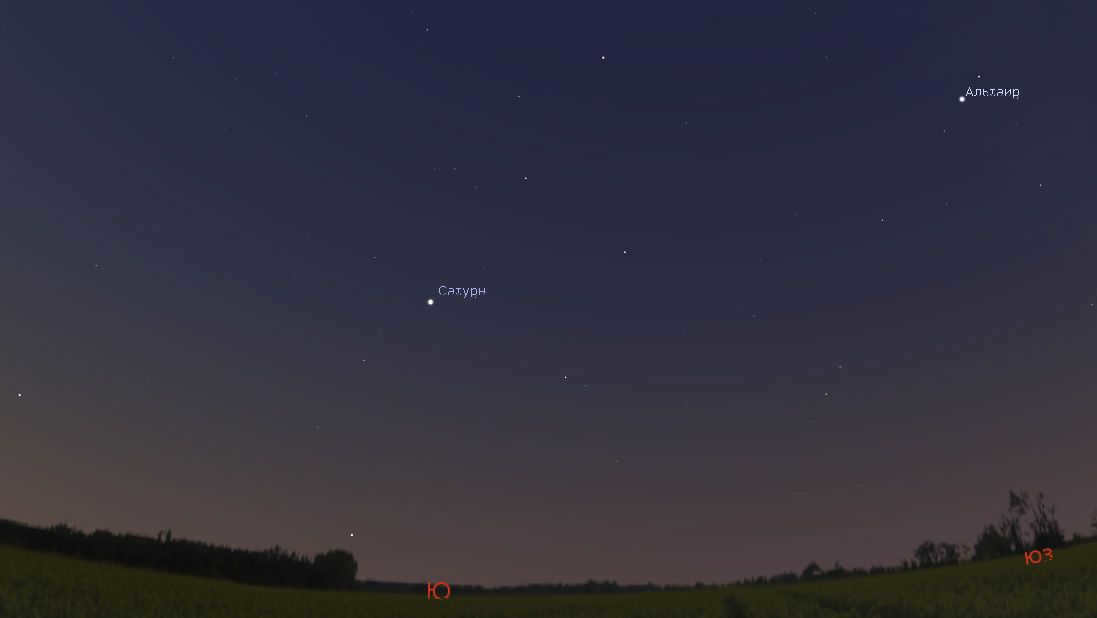

In the early morning of late July, Saturn can be seen in the southern part of the sky. Keep an eye out for the star Altair, which is located to the right of Saturn. Altair is one of the stars that make up the Summer Triangle asterism, which can serve as a guide to finding Saturn. Image: Stellarium
By the end of July, Saturn will rise around 11 PM in the southeast and remain visible throughout the night in the southeastern and southern regions of the sky. In Moscow, for example, the planet will be visible for approximately 5.5 hours!
Saturn’s brightness is equivalent to 0.6 m for a month, which is similar to the brightest stars in the sky. To locate it, you can refer to the stars of the Summer Triangle. The planet can be found 30° to the left (east) and below this group of stars. It is worth noting that on the night of July 6-7, the waning Moon will be in close proximity to Saturn.
In the summer of 2023, Saturn can be found in the constellation Aquarius, gradually ascending along the ecliptic. In July, Saturn will reach a maximum altitude of 20° or higher in the middle part of Russia. These conditions provide a favorable opportunity for observing the planet through a telescope.
Saturn in a telescope
When observed through a telescope, Saturn appears much smaller in size compared to Jupiter. The planet’s disk, which has a yellowish color, lacks the same level of detail as Jupiter’s disk and appears more blurred and low-contrast. However, the rings of Saturn, which are its main attraction, can be easily seen even with small telescopes. In 2023, the angle of the rings may be smaller, but they still capture immediate attention.

This is approximately how Saturn and its largest moons appear when observed through a non-professional telescope equipped with a 200mm lens. Image: Stellarium
Another notable feature is the planet’s flattened shape at the poles. Saturn, as we know, is a giant gas planet. Due to its fast rotation (a Saturn day lasts about 10 hours on Earth), centrifugal forces cause the planet to bulge at the equator, where the rotational velocity is highest. This is why Saturn’s equatorial diameter is about 1/10 larger than its polar diameter.
In July, the morning sky presents a unique opportunity to observe the farthest and least visible planets, Uranus and Neptune. Due to the short and bright nights in the middle part of Russia, it can be challenging to spot them in the first half of the month. However, from the 20th of July onward, they will become more easily accessible for observation using binoculars or a small telescope.
Uranus in July 2023
The planet Uranus can be found in the Aries constellation, close to the border with Taurus. It has a luminosity of 5.8 m. Under exceptional circumstances, it can be visible to the naked eye, provided that the sky is dark and moonless, away from any light pollution, and the air clarity is exceptional. However, even with just a pair of binoculars, Uranus can be observed with great clarity.
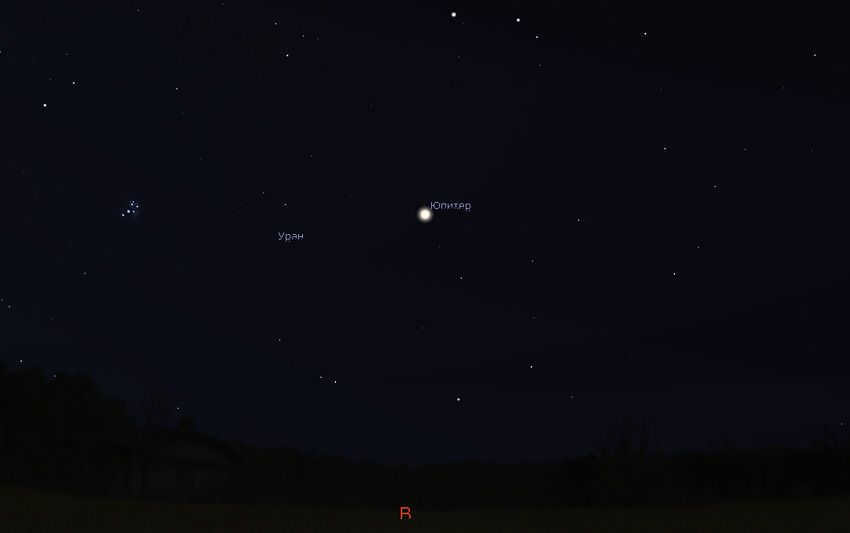

The morning sky on July 28, 2023, will showcase the presence of Uranus, Jupiter, and the Pleiades. This celestial scene can be observed by referring to the Stellarium figure provided.
In order to locate Uranus, it is necessary to first locate the bright planet Jupiter, which is currently positioned in the Aries constellation. However, Jupiter is situated 10° west (to the right) of Uranus. Additionally, another point of reference is the well-known Pleiades cluster, which is often mistaken for the Little Dipper and is best observed during winter evenings. The Pleiades cluster is positioned 8.5° east (left) of Uranus.
The planet is not directly aligned with Jupiter and the Pleiades, but is positioned slightly below them, creating an obtuse triangle with these celestial bodies. If you have a pair of small binoculars, you can easily locate the planet. Simply aim your binoculars at the area of the sky between Jupiter and Saturn, and then adjust them downward. The planet can be found 2° south (below) a star called Bothein or delta Aries, which has a magnitude of 4 stars out of 4 stars.
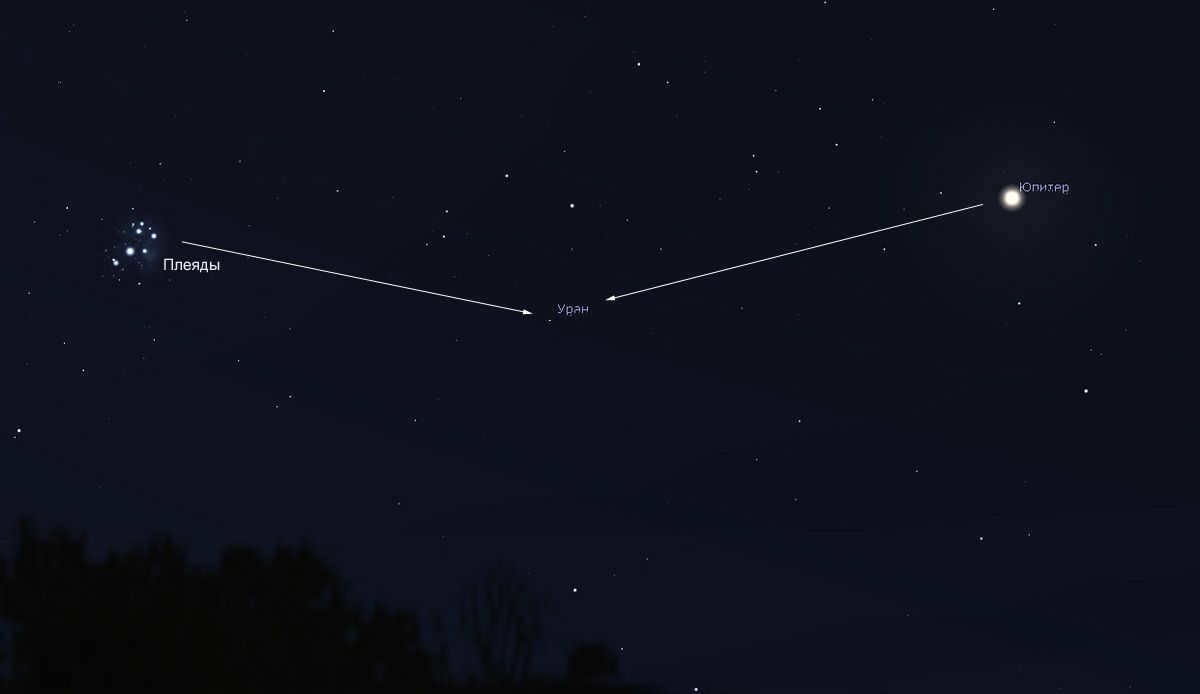

A detailed map showing the area around Uranus in July 2023. Image credit: Stellarium
When observed through binoculars, Uranus appears as a nondescript bluish star. The planet has a similar appearance when viewed through a small amateur telescope. To observe the planet’s disk, a telescope with a lens larger than 80 mm and an eyepiece providing a magnification of 80x or higher is required. Naturally, the atmospheric conditions should be as close to perfect as possible.
Neptune is significantly more challenging to observe in comparison to Uranus. With a luminosity of 7.7 m, Neptune demands a keen eye for star charts in order to differentiate it from the numerous comparable stars in its vicinity.
In the month of July in the year 2023, Neptune can be found in the constellation of Pisces, positioned 20° to the east of Saturn. Another important reference point is the star known as Deneb Caitos, also referred to as beta Cetus, with a magnitude of 2 stars. This star is located 30° to the southeast of Saturn.
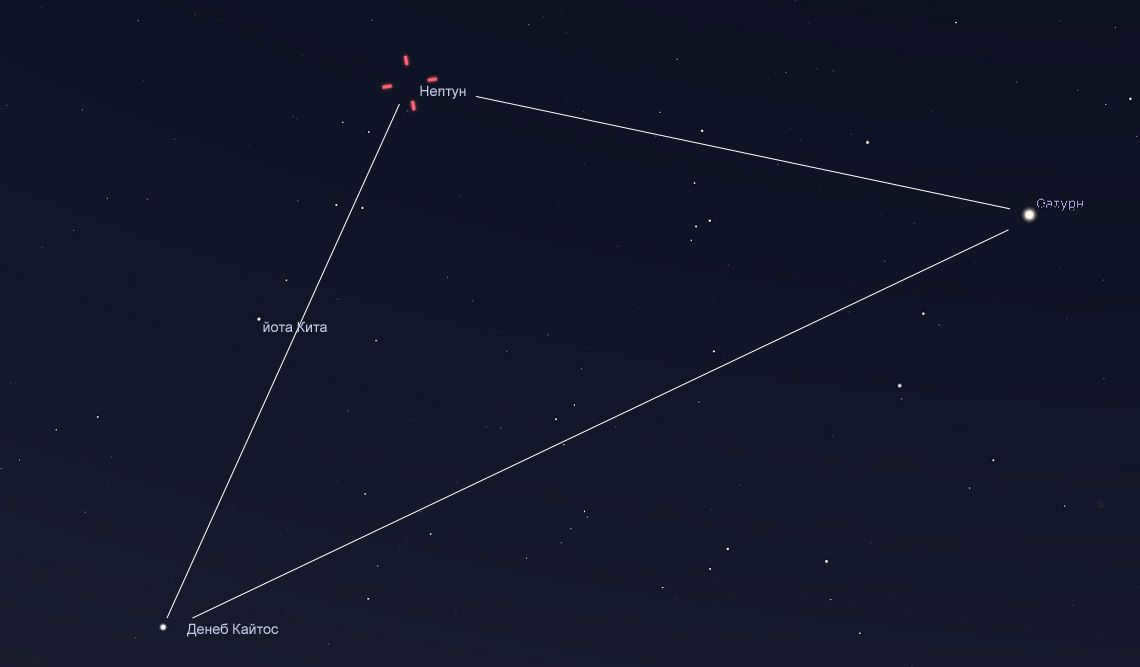
To locate Neptune in the sky, you can start by identifying the area between Saturn and the star Deneb Caitos. Follow the path from Saturn to this star, and then continue upward through a series of fainter stars. Neptune forms an almost isosceles triangle with these two stars, with Neptune being at the apex. This information is shown in the figure from Stellarium.
Another way to find Neptune is by locating Keith’s beta and then finding the 4th magnitude star labeled as Keith’s iota. Once you have identified this star, use binoculars to continue moving upward. After about 5 degrees from Jota Kita, you will come across an irregular quadrangle of 5th magnitude stars. Neptune can be found 2 degrees above and to the right of this quadrangle.
In summary, Neptune can be located by envisioning it as the apex of an isosceles triangle, with Saturn-Deneb Caitos forming the base of the triangle.
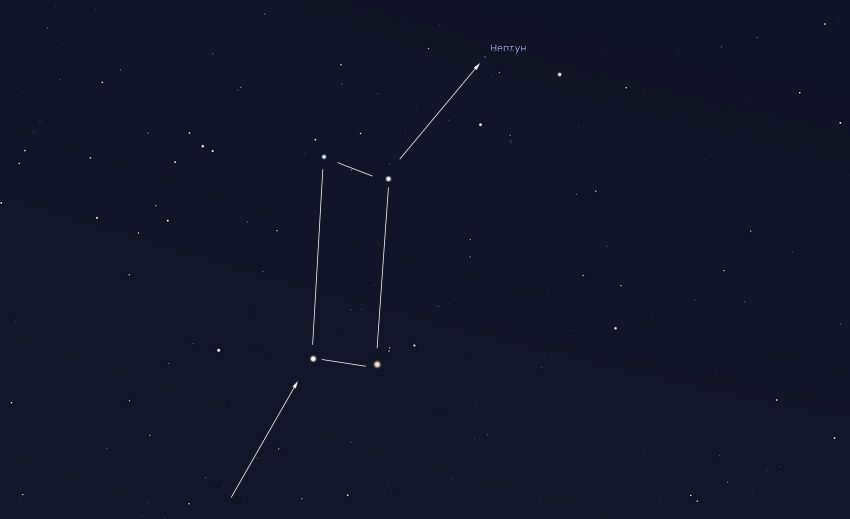
An elaborate depiction of the vicinity of Neptune during the month of July in the year 2023. Illustration: Stellarium
When viewed through a pair of binoculars, Neptune appears as a faint pinpoint of light, almost indistinguishable from the surrounding stars. To observe Neptune’s disc, a dedicated amateur telescope with a magnification of at least 100x is required.
Summary of Planets in July 2023
In July, three planets will be visible in the evening sky: Venus, Mars, and Mercury. These planets can be found close together in the western part of the sky. Venus will be easily observable with the naked eye during the first half of the month. Mars will be visible throughout the entire month, but only in southern Russia. Mercury can be attempted to be spotted at the end of July in the sky of southern Russia.
There will be two other planets visible as well: Saturn and Neptune. They can be observed during the night and morning hours in the southeast, and before dawn in the southern part of the sky. Saturn will appear as a bright star low above the horizon, but finding Neptune will require binoculars, star charts, and sky navigation skills at a minimum.
Jupiter and Uranus can be seen in the eastern sky in the morning during the month of July. At the start of the month in the central region of Russia, they appear against the backdrop of the dawn, while towards the end of the month, they can also be observed against a dark sky.
In general, July is a favorable month for planet observation in southern Russia. However, due to the shorter nights, it may not be as ideal for residents in the middle and northern regions of the country.
The Red Planet – is one of the most enigmatic and captivating celestial bodies in our solar system. Not too long ago, there were speculations about the existence of not only life, but also an advanced civilization on Mars! The stories of Martian canals, although now considered to be mere myths, still linger in our collective consciousness. Mars is not only the most Earth-like planet, but also the only planet in our solar system that can be observed in intricate detail through a telescope. And what a sight it is! From its crimson deserts to its shadowy “seas,” polar caps and wisps of clouds drifting in its tenuous atmosphere, there is so much to behold. However, before one can marvel at Mars through a telescope, it is essential to know how to locate it. What does the planet Mars appear like in the night sky? How can it be spotted with the naked eye? These are the questions that this article seeks to address.
The Red Planet in the Twinkling Sky
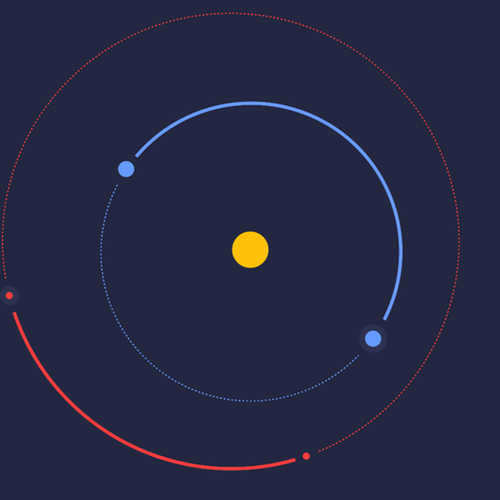
Mars is one of the celestial bodies in the outer regions of our solar system. As it journeys through the vast expanse of the universe, Mars goes through various configurations in relation to the backdrop of twinkling stars.
- Solar Conjunction: During this phase, Mars is not visible to the naked eye as it is positioned too close to the brilliant Sun in the sky.
- Eastern Quadrature: Mars is situated at an angular distance of 90° from the Sun, appearing in the morning sky for observation.
- Opposition: Also known as opposition, Mars occupies the opposite part of the celestial sphere from the Sun, making it observable during all the hours of darkness.
- Western Quadrature: Positioned at an angular distance of 90° from the Sun, Mars becomes visible in the evening sky.
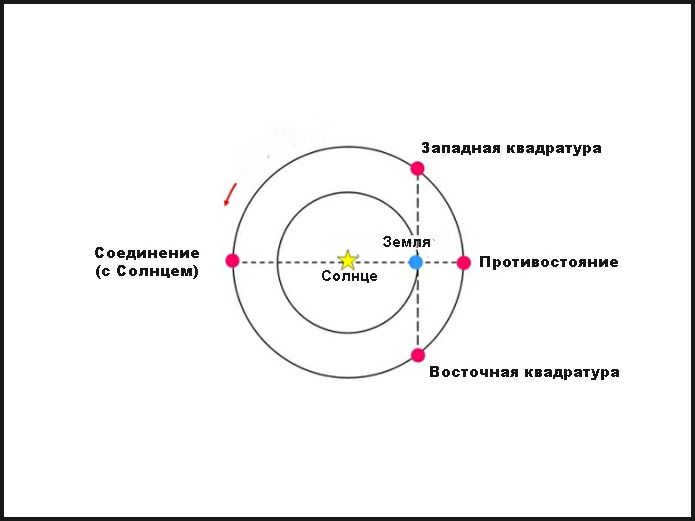
The fundamental formations of Mars and the rest of the outer planets.
The duration of Mars’ presence in the sky follows a two-year pattern. Throughout this period, the planet transitions from the morning sky to the night sky, and finally to the evening sky. Simultaneously, its luminosity undergoes a highly dramatic transformation. In the initial and concluding stages of visibility, Mars remains relatively inconspicuous in the sky, while during oppositions it becomes one of the most brilliant celestial entities.
Mars in the morning sky
After about a month of being in conjunction with the Sun, Mars makes its first appearance in the sky. It can be seen during the early morning hours, when the sky is just starting to light up in the east. Spotting Mars during this time can be quite challenging, as it is not very bright and can easily blend in with the brightening sky.
As time goes on, Mars starts to rise earlier and earlier, although it still lags behind the Sun. If you observe it closely, you’ll notice that it moves in the same direction as the Sun, from west to east, against the backdrop of the stars. This is known as direct motion, which is the typical motion of planets.
This apparent lag is caused by the difference in the angular velocities of the Earth and Mars as they orbit the Sun. If we were able to rise above the Solar System and observe it from above, we would see that it is actually the Earth, orbiting Mars, that is catching up with the Sun, not Mars lagging behind.
The process of “catching up” is not rapid and takes over a year in the sky. During the first 8 or 9 months after it becomes visible in the sky, Mars is not very noticeable. The planet can only be observed in the mornings, and its visibility (from planetrise to dawn) is only a few hours. At this time, Mars appears like a typical 2nd magnitude star. Its brightness is similar to that of the stars in the Big Dipper constellation.
Mars in a westerly square
Ten and a half months after conjunction, Mars is positioned in a westerly square. This signifies that the angular separation between Mars and the Sun in the celestial sphere reaches 90°.
During the square, face Mars and extend your arms outwards. If the square is in the western direction (morning), your left hand will be pointing towards the Sun. If it is in the eastern direction (evening), your right hand will be pointing towards the Sun.
When Mars is in square, it rises around midnight and remains visible in the sky until dawn.
Following the westerly square, it is a favorable time to observe the Red Planet, including using a telescope. However, the optimal time for observing Mars begins approximately one month before the opposition and continues until the planet reaches the eastern square.
The Curious Path of Mars in the Sky
The trajectory of Mars is quite complex. Eleven months after its alignment with other stars, the planet comes to a halt in the sky, creating a standstill. Mars then begins to move in the opposite direction, from east to west. This movement is known as retrograde motion.
The retrograde motion of Mars lasts for two months and two weeks, after which the planet resumes its direct motion. If we were to plot the trajectory of Mars against the backdrop of the stars during this period, we would observe an intricate curve, often resembling a loop.
There is a variety of forms that loops of Mars can take – they can be closed, zigzag (open loops), or a combination of both. The specific shape depends on the planet’s position in the sky – whether it is above the ecliptic, below it, or crossing it. Closed loops are the most common, while Z-shaped loops are the rarest.
The looping motion of Mars occurs because the Earth is catching up with the Red Planet as it orbits around the Sun. Since the Earth is moving faster than Mars, there comes a point where we observe Mars moving in a curved pattern against the backdrop of distant stars.
Imagine yourself on a rapidly moving train, passing a person walking in the same direction as the train. Despite both of you moving in the same direction, it would seem to you that the person is moving in the opposite direction towards the distant forest.
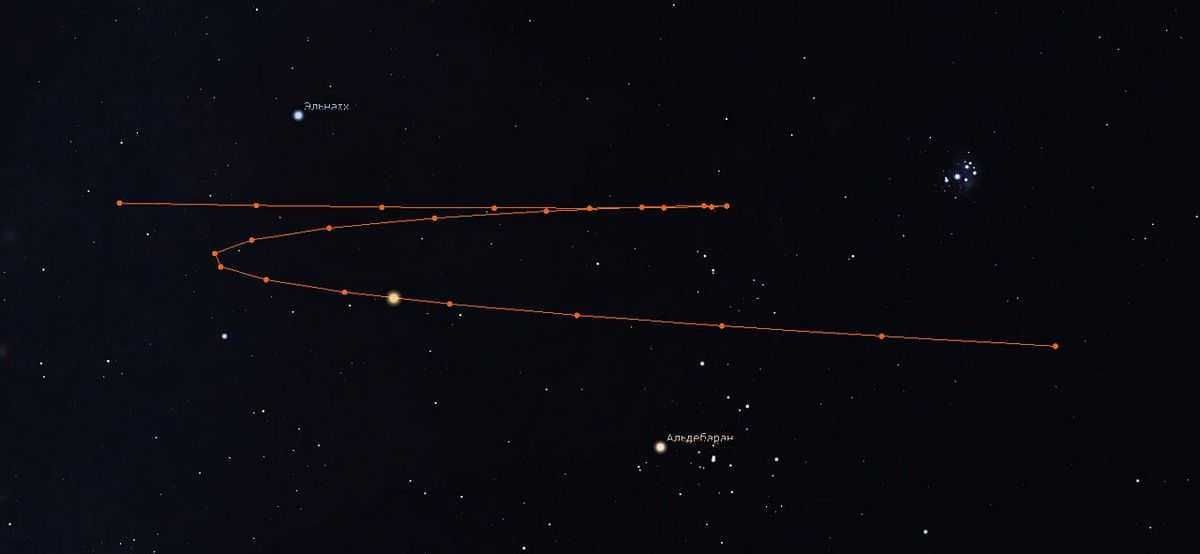
Mars creates a unique loop in the sky during the year 2022. The planet’s path forms a closed loop and an unclosed Z-shaped loop. This phenomenon can be observed using Stellarium software.
The Mars opposition occurs when the planet is approximately halfway through its retrograde motion.
Mars oppositions
The Mars opposition occurs 14 months after conjunction. This is when the Earth, while orbiting the Sun, finally catches up with Mars.
During this event, the Sun, Earth, and Mars are all aligned in a straight line.
What does this mean for the position of Mars in the sky? Well, during the opposition, the angular longitude of the Sun and Mars is 180° – the two celestial bodies are completely opposite each other in the sky.
The opposition of Mars is without a doubt the perfect time to observe this fascinating planet. And here’s why:
- When Earth and Mars are in opposition, Mars is at its closest distance to Earth for the entire year. This means that when we look at Mars through a telescope, it appears at its brightest and largest size in the sky.
- During and around the time of opposition, Mars is visible in the sky all night long. It rises at sunset and sets at dawn, giving us plenty of time to observe it.
- Additionally, during opposition, the side of Mars that is fully illuminated by the Sun is facing us, giving the planet a phase of 1.0. This is significant for Mars because it causes the planet to appear not as a perfect disk, but as an oval shape.
The upcoming Mars opposition is scheduled to take place on December 1, 2022 at 2:18 World Time (5:18 Moscow time). Further information on this significant occurrence can be found here.
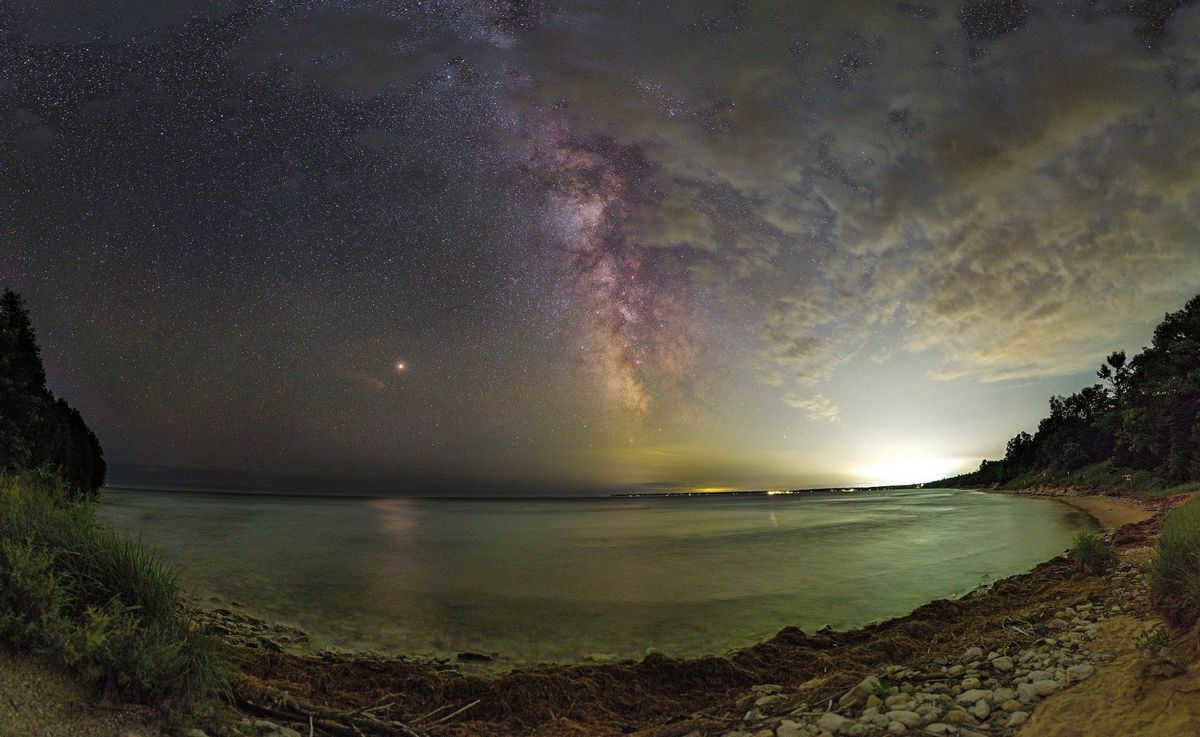

Mars and the Milky Way were captured in a stunning photo by Tom Masterson shortly after the remarkable opposition in 2018.
On average, Mars’ oppositions occur every 2 years and 2 months. Following the upcoming opposition in 2022, the next one will take place during the winter of 2025. Each Mars opposition is unique, with some being considered less favorable while others are more favorable. However, there are also special occurrences known as the great oppositions, during which Mars comes closest to Earth. For more detailed information on Mars oppositions, please refer to the dedicated article.
The 2022 opposition is expected to be relatively favorable. Interestingly, it will coincide with a rare event on December 1, when Mars will be covered by the Moon!
Mars in the Eastern Square
Following the opposition, Mars gradually starts moving away from Earth. The planet’s brightness and apparent size through a telescope begin to decrease. It moves into the evening sky.
Nonetheless, Mars remains bright enough and visible in the eastern square, which occurs 3.5 months after the opposition. It continues to be visible in the evening sky for a few more months, appearing after sunset in the west for a few hours.
After 7 months from the eastern square, Mars disappears, getting lost in the dawn’s rays. The visibility cycle of Mars comes to an end. A month later, the planet aligns with the Sun, marking the beginning of a new visibility cycle.
The best opportunities to observe Mars’ conjunctions with other planets are near the evening square.
The luminosity of Mars
The luminosity of Mars is heavily influenced by its planetary configuration. Initially, when it first appears in the sky, Mars resembles a typical star with a magnitude of 1.5m. However, as it approaches the square, its luminosity becomes comparable to that of the brightest stars.
Mars reaches its peak brightness during opposition, when it is closest to Earth. During this time, Mars is typically much brighter than any star in the sky. In fact, during great oppositions, Mars may even outshine Jupiter! (The planet’s luminosity during oppositions ranges from -1.5m to -2.9m.)
Mars stands out from other celestial bodies due to its significant variations in brightness throughout its visibility period.