Where is the World’s Longest River Located in Terms of Climate Zone?
The Amazon River, which is the longest river in the world, is situated in the tropical climate zone of South America. The climate in this area is known for its high humidity and consistent air temperature, creating perfect conditions for the thriving and preservation of diverse flora and fauna. . Read more
Is the word “no” real?
Yes, it is. We all occasionally use it in spoken form, even though it is considered incorrect. I often say “no” in phrases like “I don’t have any soda” or “I don’t have the energy to go out today,” but technically, it can be used in conversation. In written form… Read more
What is the composition of the base of a regular quadrilateral pyramid?
In order to determine the composition of the base of a regular quadrilateral pyramid, it is important to understand that this type of pyramid has a base that consists of four equal sides and four vertices. Therefore, the base of a regular quadrilateral pyramid is composed of a quadrilateral. Typically, these figures are referred to as quadrilaterals. Read more
Understanding the size of the solar system can be a challenging task. At the foundation of this system lies the sun, a star around which all the planets orbit. While these planets may appear to be incredibly distant, scientists are able to calculate their positions in their orbits at any given moment and the number of light-years they are away from Earth.
Calculating astronomical distances
Due to the immense size of the galaxy, astronomers needed to devise a unit of measurement that could accurately represent such a vast distance. This led to the creation of the light-year, which represents the distance that light can travel in the span of one year. This distance amounts to nearly 6 trillion miles, but the light-year primarily serves as a measure of time rather than a direct measure of distance. To put it into perspective, when you’re running late to meet a friend, you would likely say, “I’m 20 minutes away” rather than “3.2 miles away.”
This simplifies the comprehension of the distance between Earth or the Sun and planets, stars, asteroids, and comets. Instead of grappling with the meaning of distances in trillions and trillions of miles, conceptualizing in terms of light years enables one to visualize the time it takes for light to travel from one location to another. For instance, if you come across an image of a galaxy that is situated 90 million light-years away, you can actually envision what that galaxy appeared like 90 million years ago.
Distances between the Sun and the Planets
When observing planets through a telescope or in photographs, we must remember that they are much closer to Earth than galaxies, which means that the images we see are not from a distant past. To better comprehend the distances, scientists often measure the distances from the Sun to the planets in terms of light minutes or light hours, rather than light years. This makes the numbers more manageable and easier to grasp. Take Mercury, for example. It is the closest planet to the Sun and, on average, is approximately 36 million miles away. In light years, this would equate to a distance of 0.00000612383880620837039 light years. It is much simpler to express it as roughly 3.3 light minutes away, indicating that it would take light about 3.3 minutes to travel between Mercury and the Sun.
Here are the average distances from the Sun to the other planets:
Venus is located approximately 0,00001139722222266557821 light years away from the Sun, which is equivalent to about 6 light minutes.
Earth is situated around 0,0000158200249371616235 light years away from the Sun, or about 8.3 light minutes.
Mars can be found at a distance of about 0,000024155306893301653 light years from the Sun, which is approximately 12.7 light minutes.
Jupiter is positioned roughly 0,00008233217279125351 light years away from the Sun, or about 43 light minutes.
Saturn is located at a distance of about 0,000150545545398595955772 light years from the Sun, which is equivalent to about 1.3 light hours.
Uranus is situated approximately 0,0003027918751413869 light years away from the Sun, or about 2.7 light hours.
Neptune can be found at a distance of about 0,00047460060074811487044 light years from the Sun, which is approximately 4.2 light hours.
Calculating Age in Lunar Years: A Step-by-Step Guide

To determine your age in lunar years, it is necessary to calculate the number of moon phases you have experienced. This can be done by dividing the time between lunar phases, known as the “synodic month,” which is approximately 29,530 Earth days. Typically, there are twelve phases in a lunar year, as observed in the Islamic calendar.
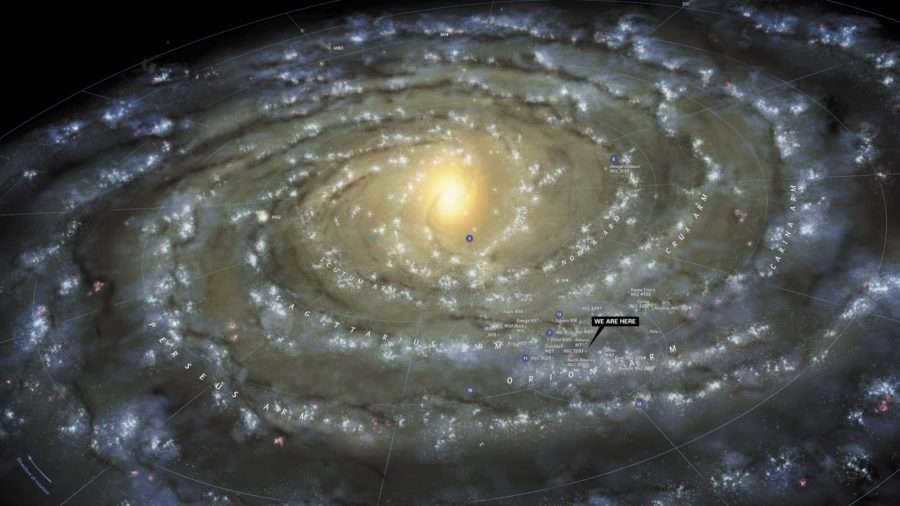
Arrangement of planets in terms of their proximity to the sun

There are a total of eight planets in our solar system. Out of these, four are classified as terrestrial planets with rocky surfaces, while the other four are known as gas giants or ice giants due to their composition mainly consisting of various gases and ice.
The Sun’s gravitational pull and the planets’ inertia

When studying the fundamentals of astrophysics, it is crucial to comprehend the forces that keep the planets in orbit around the Sun.
Astronomy, like any scientific field, has its own unique terminology that can be perplexing to those who are unfamiliar with it. What exactly is elongation? And what about perigee? Are pulsars and quasars one and the same? One question that frequently arises among individuals interested in astronomy is: what exactly is a light year?
Both words, “light-year,” may individually seem clear, but when combined, they create confusion. What exactly does “light-year” measure? Is it a unit of time? If so, it would be helpful to know the duration of a light-year. In other words, how many of our standard Earth years are equivalent to one light-year? On the other hand, many people have observed that this term is used when discussing distances to celestial objects. For instance, phrases like “the center of the Galaxy is 30,000 light-years away” or “Sirius is 8.6 light-years from us” are commonly used. This raises the question: how can distance be quantified in terms of time?
Let’s attempt to answer this query in the simplest manner possible.
Scaling

- Let’s assume that a contemporary spacecraft departs from the boundaries of our solar system at a velocity of 16.7 kilometers per second. It would take approximately 18,000 years to cover the distance of the first light-year!
- If the spacecraft aims to reach the nearest star system, Alpha Centauri, which is about 4.36 light-years away, it will take approximately 78,000 years!
- Considering the vastness of our Milky Way galaxy, which spans approximately 100,000 light years, the spacecraft would need approximately 1 billion, 780 million years to traverse it.
Read also: Growing Moon in April 2020: money, work and career, love and relationships, health, emotions and mood during the period of the growing Moon from April 6 to 18, 2020
Video
Sources
We often receive fascinating questions that have unconventional answers.
One of these inquiries is the topic of this article. How many Earth years are equivalent to one light year? Unfortunately, there is no definitive answer.
This is because a light year is not a unit of time, but rather a unit of distance. Specifically, a light year represents the distance that light travels in a vacuum without the influence of gravity fields over the span of one Julian year (equivalent to 365.25 standard days or 31,557,600 seconds) as defined by the International Astronomical Union.
Now, let’s attempt to calculate the distance of a light year.
To calculate this, we can take the speed of light, which is 300,000 kilometers per second, and multiply it by 31.56 million seconds (the number of seconds in a year). This gives us a massive number of 9,460,800,000,000 kilometers, which is equivalent to 9.46 million kilometers. This incredible distance is known as a light-year.
- 1 light month is approximately 788,333,000,000,000 kilometers
- 1 light week is approximately 197,083,000 kilometers
- 1 light day is approximately 26,277 million kilometers
- 1 light hour is approximately 1,094 million kilometers
- 1 light minute is approximately 18 million kilometers
- 1 light second is approximately 300,000 kilometers
To determine the number of kilometers per light-year, you can use a simple web calculator.
To convert a number of light years, enter the desired value in the left field. The calculation result will be displayed in the field on the right. Simply click on the corresponding link to convert light years or miles to different units of measurement.
How much is a light year?

The notion of a light year is also intimately connected to the field of relativistic physics, which emerged in the early 20th century as the principles of Newtonian mechanics began to crumble under scrutiny. Before then, the measurement of distance was primarily based on larger units within the system, with little consideration for the intertwined relationship between space and time.


That’s an incredible span. Astrophysics offers an even more expansive measure of space. A light-year corresponds to roughly one-third of a parsec, which is an even more substantial unit for gauging interstellar distances.
The velocity at which light moves under varying circumstances
Incidentally, there is also a unique feature where photons can travel at varying speeds in different mediums. We already understand how quickly they move in a vacuum. And when they state that a light year is the distance light travels in one year, they are referring to empty space. However, it’s intriguing to note that in other circumstances, the speed of light may be lower. For instance, in the air medium, photons disperse at a slightly reduced speed compared to a vacuum. The exact reduction depends on the specific atmospheric conditions. Consequently, in a gas-filled medium, the value of a light year would be slightly lower. Nevertheless, it would not deviate significantly from the accepted value.
What is a “luminous summer”
The luminous year of a one-way system (St., ly) is equivalent to the distance covered by light in a vacuum during a single July year (365.25 days).
The term is primarily utilized in scientific and fictional contexts, and within professional circles, the term “parsecs” with the prefix “kilo” and “mega” has been adopted.
It wasn’t until 1984 that the luminous year came to be understood as the distance covered by light during a tropical year. The value has since changed by 0.002%, but the practical significance of this difference is minimal since precise measurements are not typically made in luminous years. The speed of light is approximately 300,000.
One kilometer per second is equivalent to about 10 trillion kilometers (or 9,460.8800 million km) in a light year. When it comes to measuring distances, for instance, Sirius is located approximately 8 light years away, while the closest star to Earth, Proxima Centauri, is about 4.22 light years away. The diameter of our galaxy, the Roman Road, is a staggering 100,000 light years.
A light year represents the number of Earth years it takes for light to travel
An astronomical year is a measurement of time that signifies the duration of one complete orbit of the Earth around the Sun.

The measurement unit used to calculate distances between planets is called a light-year.
Due to this fact, it is not possible to determine the measurement of one object using another.
Similarly, it is possible to determine the power of a nuclear explosion in liters. The power of an explosion is measured in terms of TNT equivalent, while the volume is measured in liters.
An astronomical year consists of 365 days, and a light-year represents the distance that light travels within this time frame.
Distance Measurement in Light Years
Categories: Education and ScienceGet: Math Popularity
For centuries, humans have developed various systems to measure distances. Eventually, a universal unit of measurement, the meter, was established, and kilometers became the standard for longer distances.
However, in the twentieth century, a new challenge arose as scientists started exploring the vastness of the universe. They discovered that the size of the universe was so immense that traditional units, such as miles, became inadequate.
While it is possible to express the distance from Earth to the Moon or Mars using conventional units, determining the distance to the nearest star requires a much larger number that grows exponentially with each decimal place.
What does 1 light-year mean?
It became evident that a new measure of space exploration was necessary – and that measure came to be known as the light-year.
In just one second, light can travel 300,000 kilometers. A light-year
—
is the distance that light can travel in exactly one year, and when converted into a more familiar numerical system, that distance amounts to 9,460,730,472,580, 8 kilometers.
It is evident that the use of the concise “simple flight” is much more convenient than having to deal with incredibly large numbers in calculations.
Out of all the stars that are closest to us – Proxima Centauri – it happens to be only “4.2 light-years” away. Naturally, when considering the distance in kilometers, the figure becomes unimaginable. However, everything is relative – especially when you consider that the nearest galaxy, Andromeda, is separated from the Roman road by a whopping 2.5 million light years. In comparison, Proxima Centauri starts to feel like a very close neighbor.
By the way, using light-years helps scientists determine which parts of space are worth searching for intelligent life and which areas would be a waste of time sending radio signals to.
Considering that the velocity of a radio signal is comparable to the velocity of light, it is reasonable to anticipate that a salutation transmitted towards a remote galaxy will arrive at its intended location after millions of years. It is logical to anticipate a reply from nearby “neighbors” – entities whose hypothetical response signals will reach Earthly devices within the span of a human lifetime.
Light-years as a Measure of Distance
The light-year serves as a useful tool for comprehending the vast distances involved in astronomy.
| Scale | Value (sv. years) | Description |
| Seconds | 4·10−8 | The average distance to the Moon is approximately 380,000 km. This implies that a ray of light emitted from the surface of the Earth would take approximately 1.3 seconds to reach the surface of the Moon. |
| Minutes | 1,6·10−5 | One astronomical unit is equivalent to approximately 150 million kilometers. Therefore, it takes about 500 seconds (8 minutes and 20 seconds) for light to travel from the Sun to the Earth. |
| Hours | 0,0006 | The average distance from the Sun to Pluto is approximately 5.25 light hours. |
| 0,0016 | The Pioneer and Voyager series of spacecraft traveling outside the solar system have traveled about one hundred astronomical units from the Sun in the approximately 30 years since launch, and their response time to requests from Earth is approximately 14 hours. | |
| Year | 1,6 | The inner edge of the hypothetical Oort cloud is 50,000 a.u. from the Sun, and the outer edge is 100,000 a.u. It would take light about a year and a half to travel from the Sun to the outer edge of the cloud. |
| 2,0 | The maximum radius of the region of the Sun’s gravitational influence (the “Hill Sphere”) is about 125,000 a.u. | |
| 4,2 | The closest star to us (other than the Sun), Proxima Centauri, is 4.2 sv. years away. | |
| Millennia | 26,000 | The center of our Galaxy is approximately 26,000 light-years away from the Sun. |
| 100,000 | The diameter of our Galaxy’s disk is 100,000 light years. | |
| Millions of years | 2.5·106 | The closest spiral galaxy to us, M31, the famous Andromeda Galaxy, is 2.5 million light-years away. |
| 3.14·106 | The Triangle Galaxy (M33) is 3.14 million light-years away and is the most distant stationary object visible to the naked eye. | |
| 5.8·107 | The nearest cluster of galaxies, the Virgo cluster, is 58 million light-years away. | |
| Tens of millions of light years | Characteristic size of galaxy clusters in terms of diameter[4]. | |
| 1.5·108 — 2.5·108 | The Great Attractor gravitational anomaly is located 150-250 million light-years away from us. | |
| Billions of years | 1.2·109 | The Great Wall of Sloan is one of the largest formations in the Universe, about 350 Mpc in size. It would take about a billion years for light to travel from end to end. |
| 1.4·1010 | The size of the causal region of the Universe. Calculated from the age of the Universe and the maximum speed of information transmission – the speed of light. | |
| 4.57·1010 | The associated distance from the Earth to the edge of the observable Universe in any direction; the associated radius of the observable Universe (within the standard Lambda-CDM cosmological model). |
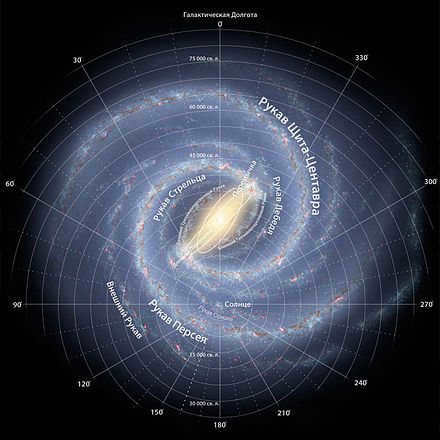
Distances in the galaxy

This Wednesday marked a significant milestone in the field of astronomy as scientists have confirmed the existence of a planet that shares similar conditions to Earth. Known as the “c” planet, it revolves around the red dwarf star Gliese 581, which is located a mere two hundred trillion kilometers from our solar system.
Explorers
The celestial body’s condition is evaluated by scientists based on the fact that all stellar systems conform to the same laws. The actual observation of the planet itself has never occurred. Its existence is deduced from variations in the star’s parameters around which it revolves.
The telescope at the La Silla Observatory in Chile (La Silla) discovered Planet 581. This telescope is one of the instruments of the European Southern Observatory and is specifically designed to detect planets by monitoring changes in star brightness across different wavelengths.
It is evident that in the near future, the most powerful telescopes will be directed towards this newly discovered object, and the data obtained will undergo thorough analysis. Currently, there is no more information available about the Gliese 581 system than there is about many other nearby stars.
A celestial body named Gliese 581
Gliese 581, a red dwarf star, is one of the numerous stars in close proximity to our Sun, situated at a distance of 20.4 light-years.
Initially documented by Friedrich Wilhelm August Argelander, a Prussian astronomer, in 1863, Gliese 581 is positioned in the Libra constellation. This star is smaller and cooler in comparison to our Sun, rendering it invisible to the naked eye.
Red dwarfs, such as Gliese 581, have longer lifespans compared to yellow dwarfs, which includes our Sun. These red dwarfs make up approximately 80 percent of the stars closest to us.
Gliese 581 is accompanied by a minimum of three planets. Apart from the recently popularized planet c, there is also planet b, akin to Neptune, and planet d, which was the first to be discovered. Planet d has a mass eight times that of Earth and completes its orbit around Gliese 581 in a period of 84 days.
Until recently, the prevailing belief was that red dwarfs were incapable of having planets that could support life similar to Earth. However, this notion has been debunked, both in theory and in practice.
Similar to Earth

Up until now, astronomers have identified 220 exoplanets. Gliese 581 c is among the first of these planets to be considered potentially habitable. However, this does not necessarily mean that the conditions on Gliese 581 c would allow hypothetical Earth travelers to casually explore the distant planet wearing jeans and a T-shirt.
Gliese 581 c is approximately five times more massive than Earth and has a diameter that is one and a half times larger. It completes an orbit around its star in just 13 days.
Most likely, the planet that has been discovered is a solid mass of rock. It is possible that it may be covered in a layer of ice. The temperature on the surface likely ranges between 0 and +40 degrees Celsius. It is currently unknown whether the planet undergoes rotation on its axis. There is a possibility that the planet is tidally locked to its star, meaning that one hemisphere is constantly exposed to extreme heat, while the opposite side remains cold. This same characteristic was previously mistakenly attributed to Mercury by astronomers.
Scientists have not yet determined the composition of the planet’s atmosphere, including whether it exists at all. The presence of water on the planet is currently only a hypothesis.






