Betelgeuse
Betelgeuse is a red supergiant star located in the constellation of Orion. It is one of the largest and brightest stars visible to the naked eye from Earth. Betelgeuse has a diameter about 1,000 times that of our Sun and is roughly 700 light-years away from us. It is nearing the end of its life and is expected to explode as a supernova in the next few thousand years. Despite its immense size, Betelgeuse is only about 10 million years old, which is relatively young for a star. Its red color is due to its relatively cool surface temperature compared to other stars. Betelgeuse is a fascinating object for astronomers to study and continues to captivate the imagination of people around the world.
Ahernar
Rewrite the text to make it unique, using the English language while preserving the HTML markup:
Ahernar

SN 1987A
SN 1987A is the designation given to a supernova that was observed in 1987 in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a nearby galaxy. It was the first supernova to be observed with modern telescopes and provided a wealth of information about the death of massive stars. The explosion was so bright that it could be seen with the naked eye from Earth, and astronomers were able to study its evolution in great detail. The observations of SN 1987A have helped to refine our understanding of supernovae and their role in the universe.

A star that went supernova, exploding at a relatively close distance from Earth, approximately 168,000 light-years away. The brightness from the explosion, which occurred on the outer edges of the Tarantula Nebula, didn’t reach our planet until 1987. It’s worth noting that the explosion, which reached its maximum brightness in May 1987, was visible to the naked eye. The magnificence of SN 1987A is enhanced by the presence of two faint rings. These rings are symmetrically positioned in space at the location where the predecessor star, a blue supergiant named Sanduleak, exploded. As these rings cool down, the atoms of carbon, silicon, and oxygen within them will come together to form molecules and dust. Astronomers are closely monitoring the site of the explosion, but so far, no neutron star or black hole has been detected by scientists.
Procyon A
can be rephrased as
Procyon Alpha
.

The Lesser Dog’s brightest star, known as Procyon, appears to move in front of Sirius from our perspective on Earth, which is why it was given the name “in front of the dog.” This stunning star is relatively close to our solar system, located 3.5 parsecs away. Procyon A is accompanied by its dim companion, Procyon B, creating a double star system. Over time, the Little Dog’s star is steadily increasing in size and is projected to reach 130-150 times its current size. Procyon A has been observed and revered by ancient civilizations such as the Sumerians, Egyptians, and Babylonians, who regarded it as a divine entity. Interestingly, in the scientific community, the animal known as the raccoon is also named Procyon, meaning “pre-dog.” 5
Rigel
can be paraphrased as
The star Rigel
.

Capella
Capella is a star located in the constellation Auriga. It is one of the brightest stars in the night sky and has a visual magnitude of 0.08. Capella is actually a system of four stars, with two pairs of binary stars orbiting each other. The primary component of the system is a yellow giant star, while the secondary component is a red dwarf star. Capella is easily visible in the northern hemisphere and is often used as a reference point for navigational purposes.

G1.9+0.3
can be rephrased as “The celestial object known as G1.9+0.3.”
G1.9+0.3, a star located in the Sagittarius constellation, underwent a supernova explosion in our Galaxy. This event occurred approximately 25,000 years ago, making it the most recent star explosion known to date. The light from this explosion, which took place 25,000 light years away from Earth, reached our planet in 1868. However, the presence of gas and dust clouds hindered a thorough observation at that time. In 1985, G1.9+0.3 was identified by astronomers as a prominent radio source. By comparing images, scientists discovered that the remnants of this supernova star are rapidly dispersing through space at a staggering speed of up to 56 million kilometers per hour.
Vega
Vega is a star in the constellation Lyra. It is one of the brightest stars in the night sky and is easily visible from both the northern and southern hemispheres.
Known as the “Falling Eagle” in Arabic, Vega has been a prominent star in various cultures throughout history. It has been used as a navigational aid and has even been referenced in literature and music.
In addition to its cultural significance, Vega is also an important star for astronomers. It is relatively close to Earth, only about 25 light-years away, and is one of the closest stars to have a known exoplanetary system.
Overall, Vega is a fascinating star that continues to captivate both scientists and stargazers alike.
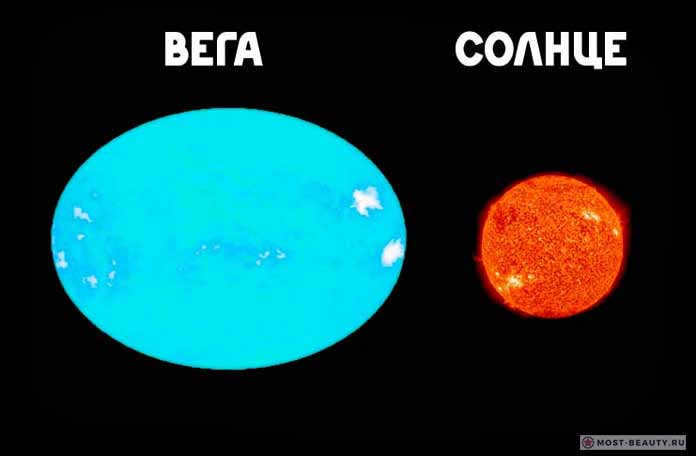

- Firstly, Vega is the most extensively studied among all stars known in the universe.
- Secondly, it was the first star to be captured using a television camera (following the Sun).
- Thirdly, scientists were the pioneers in determining the spectral analysis of Vega.
- Lastly, Vega became the first star to have its distance measured through scientific methods rather than theoretical calculations.
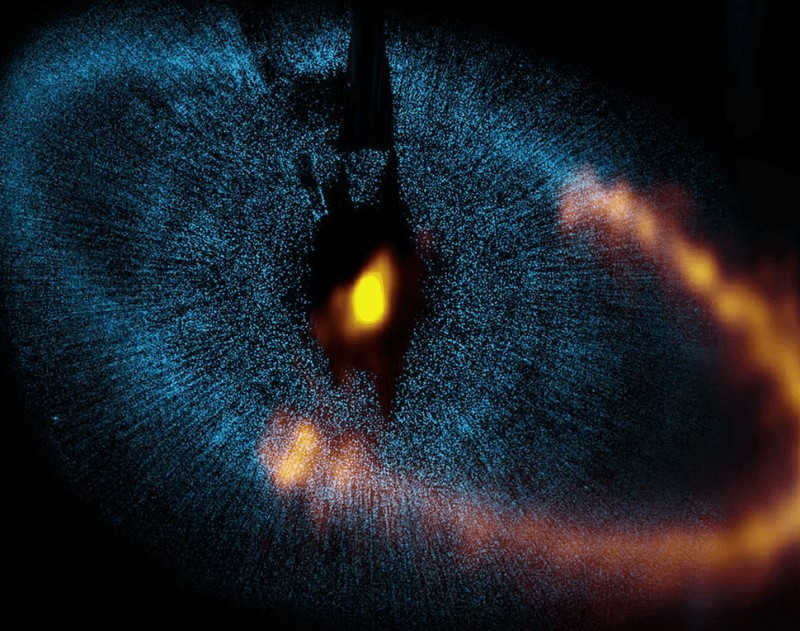
Surrounding this star, which captivates the imagination with its uniqueness, is a disk of dust. This disk may have formed due to the collision of two celestial bodies in close proximity to Vega, with the star subsequently attracting the remnants of this cosmic catastrophe.
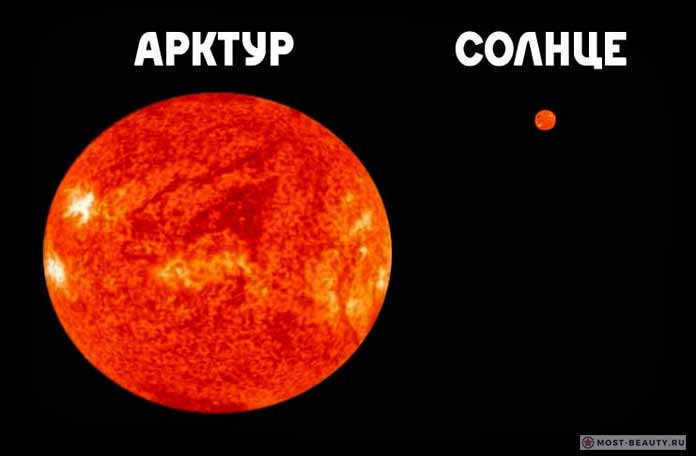

Pictured: Comparative size of Arcturus and the Sun.
The most luminous star in the Northern Hemisphere seamlessly blends into the intricate network of stars in the constellation Volopassus. This exquisite celestial body can be observed from any location on our planet.
The star’s impressive radiance stems from its substantial size of 25.7? and relatively close proximity to Earth, at 11.3 parsecs. This places Arcturus in the category of red giants, with its brightness surpassing that of our Sun by 110 times. Arcturus has a mass of approximately 1-1.5?
The visible motion of Arcturus, as it traverses the cosmos at a high velocity, was first documented in 1718.
In mythology, this star assumes the role of a guardian. In ancient Greek, Arcturus is known as the “Guardian of the Bear,” while in Arabic it is referred to as Haris-as-sama, meaning “Guardian of the Heavens.”
Diamond Star PSR J2222-0137
Imagine a radiant celestial object in the vast expanse of the universe known as Diamond Star PSR J2222-0137. This remarkable entity captivates astronomers and stargazers alike with its dazzling brilliance and enigmatic nature. Its name, Diamond Star, evokes images of a rare and precious gemstone, reflecting the intense light emitted by this celestial wonder.
PSR J2222-0137 is not just any ordinary star; it is a pulsar, a highly magnetized, rotating neutron star. Pulsars are remnants of massive stars that have undergone a supernova explosion, leaving behind a dense core composed primarily of neutrons. What sets PSR J2222-0137 apart is its incredibly rapid rotation, completing a full revolution in a mere 1.64 milliseconds.
The diamond-like quality of this pulsar lies in its intense electromagnetic emissions, which create a mesmerizing display of light and energy. As the neutron star rotates, beams of radiation are emitted from its magnetic poles, sweeping across space like a cosmic lighthouse. These beams can be detected on Earth as regular pulses of radio waves, hence the name “pulsar.”
PSR J2222-0137’s unique characteristics have made it a subject of great interest for scientists studying the mysteries of the universe. Its rapid rotation and pulsating nature provide valuable insights into the fundamental properties of matter and the behavior of extreme gravitational fields. Additionally, its intense magnetic field offers a testing ground for theories of magnetism and particle physics.
In the vast expanse of the cosmos, Diamond Star PSR J2222-0137 shines as a beacon of cosmic beauty and scientific intrigue. As we continue to explore the wonders of the universe, this remarkable celestial gem reminds us of the infinite possibilities that await us in the depths of space.
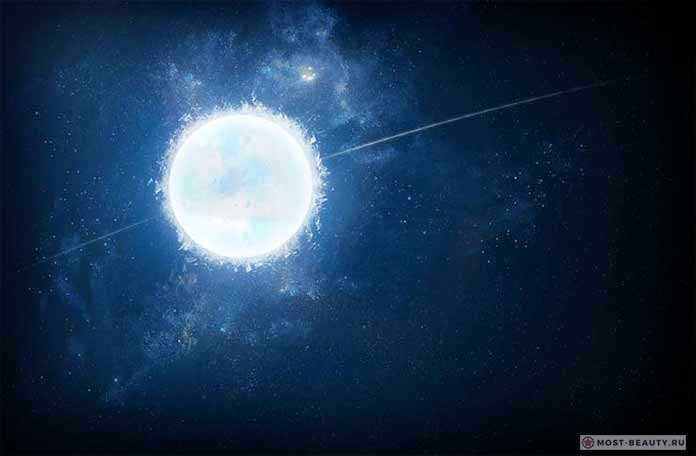

PSR J2222-0137, the coldest and most unique star in terms of composition, is situated approximately 900 light-years away from our planet. This extraordinary star is part of a binary star system, orbiting around a common center along with a pulsar.
This star has surpassed its expected lifespan and is composed of crystallized carbon, which, due to gravitational forces, has transformed into a massive diamond. Just imagine, a colossal cosmic diamond equivalent in size to Earth, traversing the vast expanse of the universe. The white dwarf can be found within the constellation Aquarius.
Having completed its life cycle and reaching the age of 11 billion years, the planet-diamond’s existence is similar to that of the Sun. Currently, it is known to the scientific community as the coldest star in the cosmos.
Due to its faint luminosity, detecting this star was challenging and its discovery occurred as recently as 2013. Scientists were even able to calculate the temperature of the extinct star, which is approximately 2,700 degrees Celsius.
Theoretically, astronomers have predicted the existence of similar celestial bodies in the cosmos, but their detection is hindered by their extremely low brightness.
For more fascinating discoveries made by scientists in space, check out the article on most-beauty.ru.
Toliman
Toliman, also known as Alpha Centauri B, is a star system located in the constellation of Centaurus. It is one of the closest star systems to our solar system, located at a distance of about 4.37 light-years. Toliman is a binary star system, meaning it consists of two stars orbiting around a common center of mass. The two stars in Toliman are named Alpha Centauri A and Alpha Centauri B. Alpha Centauri B, or Toliman, is slightly smaller and cooler than its companion star, Alpha Centauri A. Despite its smaller size, Toliman is still a main-sequence star, meaning it is in the stage of its life cycle where it is fusing hydrogen into helium in its core. The proximity of Toliman to our solar system has made it a target of interest for astronomers and scientists studying exoplanets and the potential for habitable worlds. In fact, in 2016, an Earth-sized exoplanet was discovered orbiting around Proxima Centauri, which is the third star in the Alpha Centauri system. This discovery has sparked even more interest in the search for potentially habitable planets in the Toliman system.
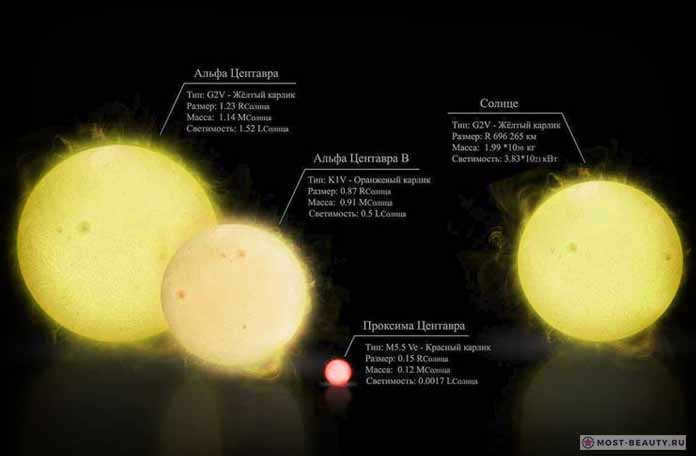
The picture shows the relative size of the Centauri system and the Sun
In our daily lives, we are more familiar with the alternate name of the star – Alpha Centauri. For some reason, in all the children’s games involving aliens, they always came from this star. The Centauri star system, which is the closest to us, is widely depicted in science fiction literature and on the big screen.
The binary stars in the Centauri constellation have a unique structure. The two stars, Alpha and Beta, appear as one star when viewed from Earth. Toliman closely resembles the Sun in terms of its structure and characteristics. Its mass is 10% greater than that of the Sun, and its radius is 22% larger.
The unique star system has existed for approximately 6 billion years, making it 2.5 billion years older than our solar system. This star system also includes another star in orbit, known as the red dwarf Proxima Centauri. Proxima Centauri is located at a significant distance from the two stars in the Centauri system and completes one orbit around them every half a million years.
Scientists, astronauts, and space engineers speculate that Alpha Centauri may be the first interstellar destination for spacecraft. Most-Beauty eagerly anticipates the launch of these groundbreaking spacecraft.
Canopus
Canopus is a bright star in the southern constellation of Carina, and it is the second brightest star in the night sky after Sirius. It is located about 310 light-years from Earth and has a visual magnitude of -0.72, making it easily visible to the naked eye. Canopus is a supergiant star with a diameter about 71 times that of the Sun and a mass about 8.5 times that of the Sun. It is estimated to be about 9 million years old and is nearing the end of its life cycle. In the future, Canopus will likely explode as a supernova, leaving behind a remnant such as a neutron star or black hole.

Shown here is a comparison of the sizes of Canopus and the Sun.
Canopus is a star located in the constellation Lyra and is known to be one of the brightest stars in the Southern Hemisphere. This white-yellow supergiant star has been extensively studied by astronauts.
Canopus is located at a considerable distance from our solar system, about 310 light years away. Not only is its distance impressive, but the size of this celestial object is also remarkable. Canopus has a mass that is 9 times greater than the Sun and a radius that is 65 times greater than our own star.
Prior to the invention of the compass, Canopus served as a navigational landmark for ships. The star’s name is derived from the helmsman of one of Menelaus’ ships, a hero of the Trojan War.
There exists an intriguing historical detail regarding the star. In the film “The Magic Lamp of Aladdin,” a sorcerer in the desert beseeches the star Canopus for assistance in locating Aladdin.
Sirius
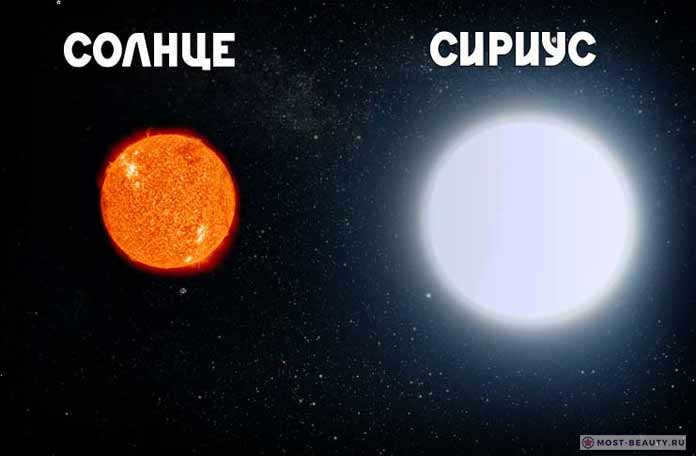

Pictured: The comparative size of Sirius and the Sun.
The magnificent star from the constellation Canis Major is situated 8.6 light years away from us and serves as the most brilliant star in the celestial expanse. It possesses a mass of 2?, a radius of 1.7?, and a luminosity that surpasses our ? by 25 times.
Sirius has always held a significant role in the annals of humanity. The star aided sailors in traversing the open ocean, the ancient Egyptians and Sumerians attributed their principal deities to it, the Kazakhs long relied on it to determine the changing of seasons, and the African Dogon tribe continues to worship it as a divine being in our modern era.
The natural star complex Sirius, voyaging through the cosmos, is steadily approaching our solar system at a velocity of 7.6 kilometers per second, thereby causing the star’s apparent brightness to augment as time progresses.
It has been forecasted by scientists that Sirius will transform into a red dwarf in approximately 660 million years. Eventually, after a period of time, it will shed its dust shell and evolve into a white dwarf.
The Sun

In the vast expanse of space, there are countless stars, each with its own unique beauty. However, when it comes to our own planet, there is one star that stands out among the rest – the Sun. Whether it’s the mesmerizing colors of a sunset or the gentle glow of a sunrise, the Sun never fails to captivate us.
While we may admire the Sun from the safety of Earth, it’s important to remember that directly observing it without the proper equipment can be extremely dangerous for our eyesight. The Sun’s intense brightness can cause permanent damage, so it’s always best to take precautions.
As we gaze up at the Sun, it’s fascinating to think about its age. Scientists estimate that the Sun is approximately 4.6 billion years old, making it a relatively young star in the grand scheme of the universe. In fact, based on our knowledge of similar celestial objects, it’s believed that the Sun is currently in the middle of its life cycle.
What sets the Sun apart from other stars is not only its beauty but also its significance to our solar system. It’s the only star in our system and plays a crucial role in keeping everything in balance. From the planets to the satellites to the comets, everything revolves around the Sun’s gravitational field.
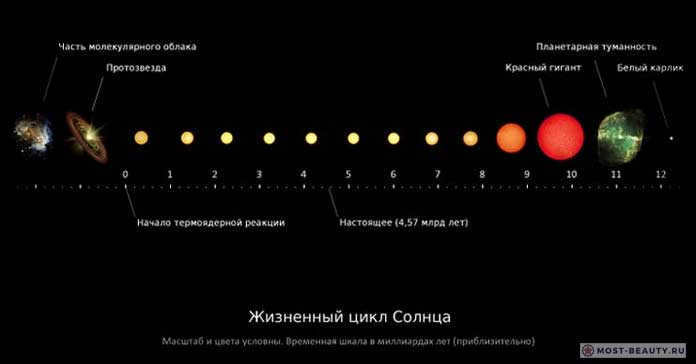
By the time it reaches an age of 10-12.5 billion years, the star will have undergone enough heating to transform into a red giant. At this stage in its development, the Sun will have expanded to the point where it will reach the orbit of the Earth.
One of the most captivating occurrences that can be witnessed by the inhabitants of Earth are solar eclipses.
Being the closest star to us, the Sun has become an object of adoration for all the people residing on the planet. In Slavic mythology, there is the God of the Sun, known as Dazhbog, and the solar disk, named Khors. The origin of the former deity can be traced back to the phrase “Life-giving God,” which signifies the Sun.
There is also a fascinating tale associated with the Sun, featuring Phaeton, who met his demise in outer space while riding a solar chariot.
LP 40-365
can be rephrased as “LP 40-365” or “LP 40-365” is another way to say LP 40-365.
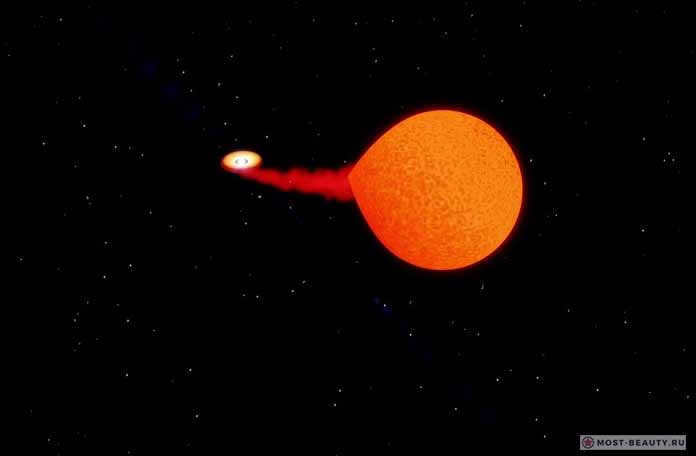

In the vast expanse of the cosmos, it is a common occurrence for celestial bodies to come together and form binary star systems, engaging in an elegant cosmic dance. Occasionally, these stellar partners become increasingly drawn towards each other, resulting in a fascinating phenomenon where one star gradually exerts its gravitational pull on the other, causing a transfer of matter between them.
In the video, you can observe a simulation of a binary star explosion resembling LP 40-365.
LP 40-365 has been the pioneering star of its kind, providing solid evidence for the previously hypothesized occurrence of such phenomena. With a mass 6.5 times smaller than that of our Sun, LP 40-365 is located approximately 1,000 light-years away.
Galaxy z8 GND 5296
The model Galaxy z8 GND 5296 is a new addition to the Galaxy series. It offers innovative features and advanced technology that make it stand out from other smartphones in the market. With its sleek design and powerful performance, the Galaxy z8 GND 5296 is a must-have for tech enthusiasts. Its high-resolution display and impressive camera capabilities ensure a truly immersive and enjoyable user experience. Whether you’re a professional photographer or a casual smartphone user, the Galaxy z8 GND 5296 is sure to impress with its stunning image quality and versatile shooting modes. Stay connected and productive with the Galaxy z8 GND 5296’s fast and reliable network connectivity. Its long-lasting battery ensures that you can enjoy all the features of this amazing device without worrying about running out of power. Upgrade to the Galaxy z8 GND 5296 and experience the future of smartphones today.
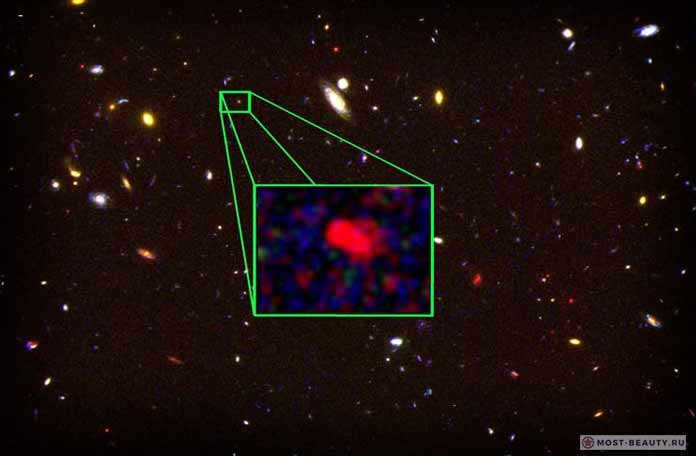

This is a picture of a distant galaxy.
Our final entry is not about a single star, but an entire galaxy. Astronomers discovered this cluster of stars, known as z8 GND 5296, in the Big Dipper constellation in 2013.
The distance from z8 GND 5296 to Earth is 30 billion light years. We can currently observe the light that these faraway stars emitted 700 million years after the universe’s creation. Essentially, when we look at the sky, we are seeing the past.
It’s an incredible phenomenon that there is an ongoing formation of new stars within our Galaxy. Assuming that one star is born in the Milky Way annually, it means that z8 GND 5296 witnesses the birth of 300 new celestial bodies each year. However, it should be noted that these objects might no longer exist, and the process of star formation in this distant galaxy might have already concluded.
Summing up

Human beings are inherently peculiar. Indeed, we can only envision the magnificence of the stars in our minds, as well as through images captured by space exploration vehicles. However, men, when expressing affection towards a woman, often refer to her as a “Star” or a “Sun”. It’s a common practice for mothers to use these same epithets when praising their children. The romantic image of distant celestial bodies has firmly established itself in our lives.
Despite the fact that there is a saying “cold as a star”, these cosmic entities above us provide our lives with purpose and inspire us to continuously pursue knowledge.

Expanding our knowledge of the Cosmos and the mechanisms that occur in interstellar and interplanetary regions, we can anticipate forthcoming transformations in the Universe and roughly outline the future cosmic chronicles of our planet.
We are confident that there exist other equally captivating and extraordinary stars in existence. Eventually, humanity will acquire knowledge about them, but for the time being, we bring our narrative to a close. Thank you for your kind attention. The editorial team at most-beauty eagerly awaits your comments. Please feel free to express your thoughts on stars, space; share your musings, conjectures, and observations.

What does a star look like in outer space? What is the concept of a star in the field of astronomy? These inquiries trouble not just the present generation, but have also been a concern for individuals in the past. Let’s provide a precise explanation of what constitutes a star.
An object in the night sky
An object in the night sky is a highly heated sphere of gas, with temperatures reaching several million degrees at its core, enough to trigger nuclear reactions, and several thousand degrees on its surface.
It is a celestial body composed mainly of hydrogen and helium, held together by gravity and existing in a plasma state. In essence, it is a gaseous sphere that rotates around itself.
The appearance of stars in space can vary greatly depending on their stage of life.
Each individual has their own personal stars. For some, these stars act as guiding lights, leading them on their path. For others, they are simply points of light. Antoine de Saint Exupery.
Balance of forces within a star
To maintain the gas within a star in a spherical shape, there are two opposing forces at play: gravity and pressure. Gravity pulls matter towards the center, while the internal pressure pushes it outward. In other words, the compressing force of stellar gravity is counteracted by a repulsive force.
Consider a gas bubble located at the edge of the star. It is initially attracted towards the center due to gravitational forces. However, as it moves inward, it encounters increasing pressure forces that push it back towards the surface. This delicate balance of forces is known as hydrostatic equilibrium, which enables a star to remain stable for millions, if not billions, of years.
The life cycle of a star
Stars have a limited lifespan: once they exhaust all of their hydrogen and begin fusing helium (which can last for billions of years), they expand and transform into red giants.
Depending on their initial mass, stars will either gradually fade away, becoming white dwarfs, or experience a sudden and explosive end as supernovae. In the event of a supernova, they may even go on to form black holes.


Stars with greater mass consume their hydrogen at a faster rate, such as the Sun. The Sun, for example, has a lifespan of approximately 10 billion years.
As a star grows larger, it becomes brighter but also has a shorter lifespan. When a star’s core runs out of nuclear fuel, typically hydrogen, fusion reactions cease. Without the pressure generated by these reactions to counteract gravity, the star collapses inward. This collapse triggers an explosion, resulting in the formation of a supernova star.

Romantics are drawn to the sky, with its vastness and mystery. We are captivated by the question: what lies beyond? We understand that the planets and stars are incredibly distant, but we can’t help but dream of a future where scientists create a spaceship capable of venturing even farther. Of course, by that time, many things will have changed, but for now, we can be satisfied with what is available to us.
In our modern era, the Earth is illuminated by electric lights, making the Milky Way nearly invisible to those living in cities. The only way to truly appreciate its splendor is to escape the urban areas, particularly during the months of June to August. In the Southern Hemisphere, it will be winter, while in the Northern Hemisphere, it will be summer. If you long to witness this breathtaking beauty, venture into the wilderness!
Meanwhile, we recommend taking a closer look at what’s right under your nose! Explore the stunning photographs of the most breathtaking stars in outer space, and let’s discover their names and a brief overview of each.
1.

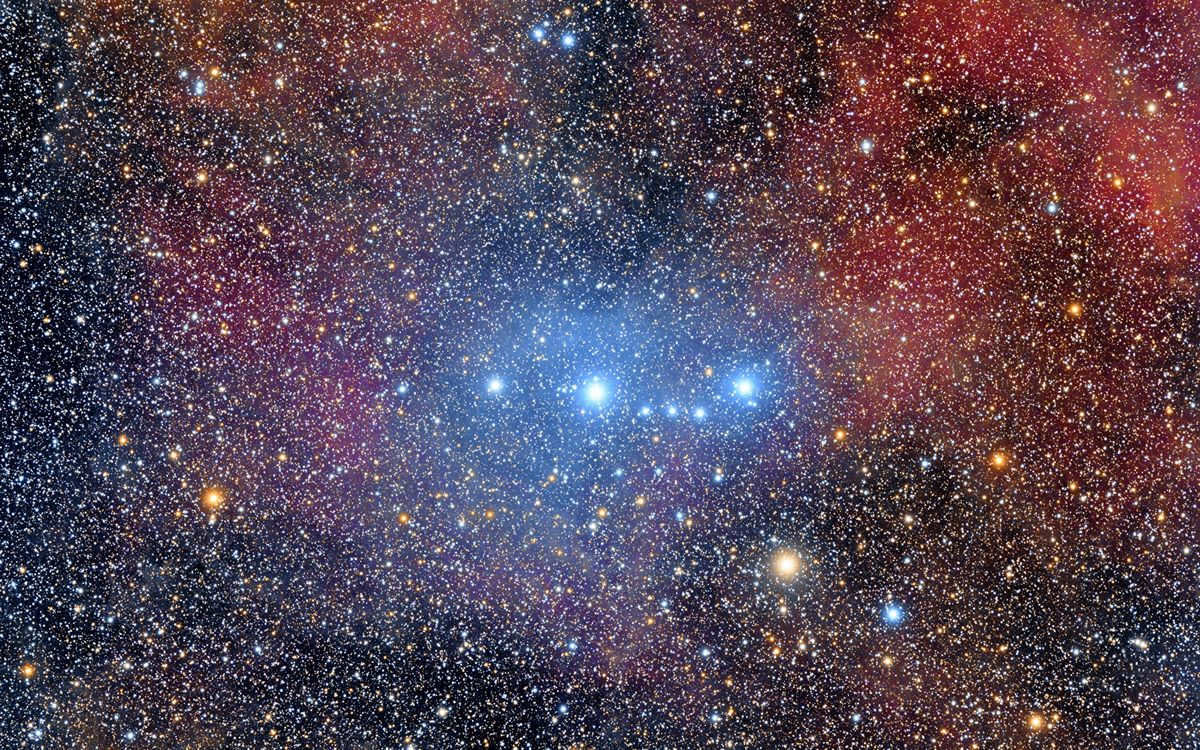
Gakruks
The star Gakruks shines brilliantly, captivating observers with its luminosity. It ranks as the 24th brightest star, drawing in all those with a romantic spirit. Much like the Southern Cross constellation, it serves as a symbol for many countries in the Southern Hemisphere. Gakruks is a binary star, comprising two components that are separated by a distance of 400 light years.
At first glance, Gakruks may appear to be a solitary star, but it is actually composed of Gakruks-A and Gakruks-B. While this star is not visible from Russia, it can be observed with a telescope in the Southern Hemisphere. This includes countries such as Brazil, Australia, New Zealand, and others.

Antares
Inhabitants of the Northern Hemisphere have the opportunity to admire the magnificent and most brilliant star Antares from late spring to early fall. To locate it in the sky, it is necessary to navigate through the constellation of Scorpius – it is situated at the position of the conventional head. Astronomers have assigned different names to this star: Satevis, Selkite, but Antares is the most renowned.
This star is a constituent of the Scorpius constellation and serves as its brightest entity. The star’s name was determined by its color. Since ancient times, people have been captivated by it – the star captures attention with its reddish hue and radiant gleam. Positioned 600 light years away from our planet – if you compare this giant with our Sun, this star is significantly more luminous and larger.
3.
Rephrase the text to make it unique, using the English language and preserving the HTML markup:
3.

Pollux
Pollux is the second brightest star in space. It is known for its intense brightness and is ranked as the 17th brightest star in the night sky. Its name is derived from the dioscurus twins, who were prominent figures in ancient Greek mythology. According to ancient texts, Pollux, along with his twin brother Castor, were the sons of Leda and Zeus.
Pollux’s luminosity surpasses that of the Sun, and it is located in the Gemini constellation. It is approximately 40 light years away from Earth. Astronomical calculations suggest that the star’s helium reserves will eventually deplete in around 100,000,000 years, causing it to transform into a white dwarf. In 2006, an exoplanet was discovered orbiting Pollux.
4.
Reword the text, making it unique, using the English language and preserving the HTML markup:
4.

Rigel
One of the most brilliant stars in close proximity to our solar system is Rigel. Its luminosity is immense, shining 85,000 times brighter than the Sun, a concept that is truly mind-boggling. Located in the constellation of Orion, Rigel emits a radiant light that can be compared to that of bright lamps, illuminating the surrounding nebulae.
This celestial giant is not a solitary entity, but rather a triple star system consisting of stars A, B, and C. Together, they emit a dazzling blue-white light. Locating Rigel is relatively easy, as it is situated in the constellation of Orion. If one looks down from the top star of Orion’s belt and glances to the side, the brightest point will be none other than Rigel itself.

Capella
Capella, a bright yellow star located 41 light-years away from Earth, is recognized as one of the most prominent stars in the Ascendant constellation. Although it appears as a solitary star to the naked eye, it is actually a binary system composed of four individual components. The optimal period to observe Capella is during the winter months, although there is also a possibility to view it in the autumn.
To locate Capella, you can utilize the Big Dipper – simply mentally trace a line connecting Dubhe and Megrez, and continue until you reach the star. Ranking as the 6th brightest star in the nighttime sky, Capella is projected to reach the end of its lifespan gradually, although this event is considered imminent in human terms.
6.
Rewrite the text, making it unique, using the English language and preserving the HTML markup:
6.
Fomalgaut
There is no star in the constellation of South Pisces that shines brighter than Fomalgaut. Fomalgaut, which means “mouth of the whale” in Arabic, is known as the 18th brightest star. It was first observed by the Persians, Arabs, and Chinese, who named it accordingly. This star is particularly fascinating and relatively young. In Russia, it can be observed in the southern regions.
Fomalgaut has always been a subject of fascination and deemed enigmatic. Despite its youthful age, it shines with a luminosity that is 16 times greater than that of the Sun. This star possesses a formidable transformative power, serving as a reminder of the impermanence of all things in this world. Situated at a relatively close distance of 25 light years from Earth, it can be easily observed through astronomical instruments.
7.
Rewrite the text, making it unique, using the English language and preserving the HTML markup:
7.

The Appearance of Hadar
Hadar star is a stunningly bright and blue celestial body, which is prominently featured on the Australian flag. It occupies the second position in terms of brightness among the stars in the Centauri constellation and is located at a distance of 530 light-years away from our planet Earth. This remarkable star holds the 11th spot in the list of the brightest stars. A closer observation of Hadar reveals that it is actually a cluster of three distinct stars.
According to the accounts of astronauts, it is predicted that at some point in the future, two of these stars will undergo supernova explosions. Unfortunately, Hadar cannot be observed from Russia, unless one is situated in the southern latitudes. The star exhibits a bluish hue and possesses a stellar magnitude, also known as luminosity, of 0.61. The name Hadar is believed to have a meaning of “low” in translation, possibly alluding to the star’s appearance as it appears low on the horizon.

Adara
Adara, situated in the constellation of Canis Major, is the most resplendent and magnificent star in the night sky. It is positioned in close proximity to other luminous celestial bodies, including Rigel, Procyon, Sirius, and others. When gazing at the heavens, it is effortlessly discernible as the most brilliant star beneath Sirius. Its astronomical distance from Earth amounts to 430 light years.
The luminosity of this star surpasses that of the Sun by 20,000 times, which accounts for its visibility from our planet. Adara is not a solitary star, but rather a binary star system, with its companion being Adara B. Presently, the star can be observed in the central regions of Russia. Emitting an exceedingly radiant light, Adara never fails to astonish with its grandeur.
9.
Rewrite the text, making it unique, using the English language and preserving the HTML markup:
9.

Spica
There are numerous stunning stars in the celestial sky, and Spica stands out among them. This particular star is situated in the Virgo constellation and its symbol was adopted for the Brazilian flag. Alongside Spica, the Virgo constellation incorporates a multitude of other luminous stars (at least 190). Nevertheless, Spica shines with greater brilliance compared to the rest, making it truly remarkable.
The star holds the 16th position in terms of brightness in the night sky. Based on calculations made by astronomers, it outshines the Sun by a remarkable 12100 times. This brightest star is situated at a distance of 262 light years from Earth, but it is easily visible and can be easily spotted. It is closely associated with the constellation known as the Big Dipper. To have a clearer view of this star, one must venture outside the city limits where there is no urban light pollution.
10.
Rewrite the text, making it unique and preserving the HTML markup:
10.

Procyon
Procyon, the star that shines twice as bright as the Sun, is an exquisite celestial body. It has captivated the attention of humans since ancient times and is renowned for its remarkable luminosity. Procyon is located within the constellation Canis Minor and owes its name to the Greeks, as it translates to “in front of the dog”. This magnificent star lies 11.4 light years away from our planet.
Astronomers predict that Procyon will undergo a transformation and emit a vivid red hue in approximately 150 years. The best time to observe this stellar beauty is during winter in the southern regions of Russia, where it shines prominently despite its greater distance from the Sun. Procyon is a binary system composed of two stars: Procyon A and Procyon B. The primary star, Procyon A, is characterized by its radiant yellow color.

Every individual has had the opportunity to gaze at the magnificent starry sky at least once in their lifetime. However, for those living in urban areas, such experiences are few and far between. The presence of street lights and advertisements often obstruct the view of the night sky, making the stars appear small and dim in comparison. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of stars in space.
However, when one ventures outside of the city, away from the omnipresent artificial lighting, a mesmerizing sight awaits: the true beauty of stars in their natural environment. Have you ever pondered the purpose and significance of stars in space? Who are they meant for and what role do they play?
What is the definition of the word “star”?
In the Russian language, the term “star” has multiple meanings. It can refer to:
- a radiant point visible in the nighttime sky;
- in the field of astronomy, a celestial body with specific characteristics;
- a polygonal shape on a plane formed by numerous triangular rays originating from a central point;
- a star-shaped marine invertebrate creature; metaphorically, it can represent a well-known individual in the public sphere, such as an artist, singer, or musician;
- metaphorically, it can symbolize luck, happiness, or destiny.
What exactly constitutes a star?

When referring to stars as celestial bodies, science defines them as luminous masses of matter with immense size, where active thermonuclear processes occur. These processes are responsible for the thermal and light radiation emitted by stars, allowing us to observe them during the night.
Stars are situated at vast distances from us, which makes them appear small. However, in reality, most of the stars visible in the sky are much larger in mass and volume compared to our Sun, which is classified as a yellow dwarf star.
Interestingly, individuals with good eyesight can see approximately 3,000 stars in the sky, while the total number of stars in the Universe is believed to be infinite. Stars are grouped together in vast clusters known as galaxies, often taking the form of spiral structures with multiple arms.
During the time when astronomers only had access to optical telescopes, the primary criterion for categorizing stars was their level of brightness.
Once it became possible to gather spectra from stars, a classification system was developed based on spectral analysis. This method provides a more comprehensive understanding of stars, as it allows for the determination of their chemical composition, mass, and stage of development.
Stars are categorized into classes based on their temperature, using the spectral composition as a guide. Each class is assigned a letter from the Latin alphabet. The highest class, O, consists of the hottest stars, with temperatures ranging from 30-60 thousand degrees Kelvin. Following this, with decreasing temperatures, are classes B, A, F, and G. Stars with temperatures below 2-3.5 thousand degrees Kelvin are denoted by letters from M to T.
Furthermore, astronomers categorize stars into the following classifications:
- A brown dwarf is a star where nuclear processes are insufficient to offset energy losses from radiation;
- A white dwarf is a star in a phase of structural rearrangement, which can ultimately result in a transition to a neutron star or a black hole;
- A red giant is a star with low density and a massive volume and luminosity, emitting most strongly in the infrared part of the spectrum;
- A variable star is a luminary that exhibits varying intensity of radiation;
- A double star is a binary system consisting of two glowing gas spheres of similar mass. Interestingly, they orbit each other along a complex trajectory, forming a cohesive unit;
- A new or supernova star is a celestial body that has completed its development cycle. It culminates with a powerful explosion that results in a brief but intense increase in brightness.
- A neutron star is a celestial body in the late stages of evolution, characterized by a highly compressed core. As a result, it does not emit visible light waves but rather emits radiation in the form of neutrons, X-rays, or radio waves.
- A black hole is a star that has undergone such extreme core compression that its gravitational field at the surface is incredibly strong, preventing even the escape of radiation.
What are stars composed of?
Every star visible in the night sky is a luminous sphere made up of gas. Due to its immense mass, the gas is subjected to colossal gravitational fields, causing it to undergo compression.
Within the star’s core, where the compression is most intense, a thermonuclear process is triggered. This process releases vast amounts of energy. However, while the surface temperature reaches a few thousand or tens of thousands of degrees Kelvin, the interior temperature soars into the millions.
By the way, the gas comprising stars is primarily hydrogen. Through the thermonuclear reaction, hydrogen is transformed into helium and various other chemical elements. Young stars, which are in the early stages of their life cycle, have relatively small amounts of helium.
Furthermore, there can be trace amounts of metals in the gas and plasma, which can have a substantial impact on the pace of fusion reactions within the star’s core. The composition of a star evolves over time, with older stars containing a greater variety of chemical elements.
What is the purpose of stars?

Stars are the primary celestial objects in the Universe. They emit both light and heat energy, which spreads through space as radiation. The Sun, located at the center of our solar system, serves as the source of life and warmth for our planet.
It is highly likely that numerous stars in our galaxy and others are accompanied by planets. Furthermore, it is possible that life has originated and developed on some of these planets.
If the Sun were to suddenly go out or disappear, all life on Earth would perish due to the extreme cold within a matter of two or three weeks.
The celestial bodies served as the foundation for the mythology of numerous civilizations across the globe. The stars inspired poets to compose verses, while science fiction authors imagined them as the dwelling places of strange and enigmatic beings. Artists, on the other hand, captured the vast and extraordinary landscapes of cosmic disasters.

The exploration of the universe is still incomplete, even in the present day. How many of us have gazed up at the night sky, pondering the allure of those shimmering little specks? In reality, those specks are thousands, tens of thousands, and even hundreds of thousands of times larger than our beloved Earth.
Stars come in various sizes and formations, and they behave uniquely within the vast expanse of the Universe. Some drift alone through cosmic expanses, while others have their own orbiting planets. There are stars that have long since perished, yet their light still reaches us. However, every single star is remarkable and one-of-a-kind.
Among all the celestial objects in the vast galaxy, let us examine the most extraordinary, stunning, and exceptionally peculiar stars.
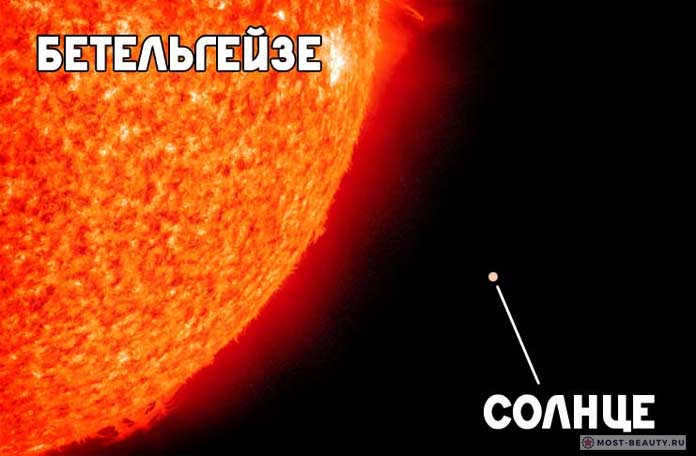
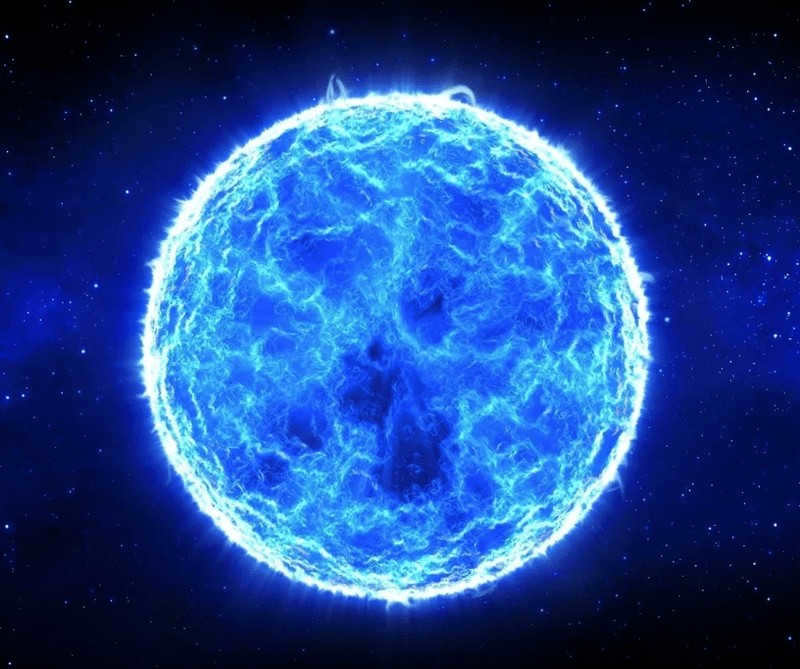
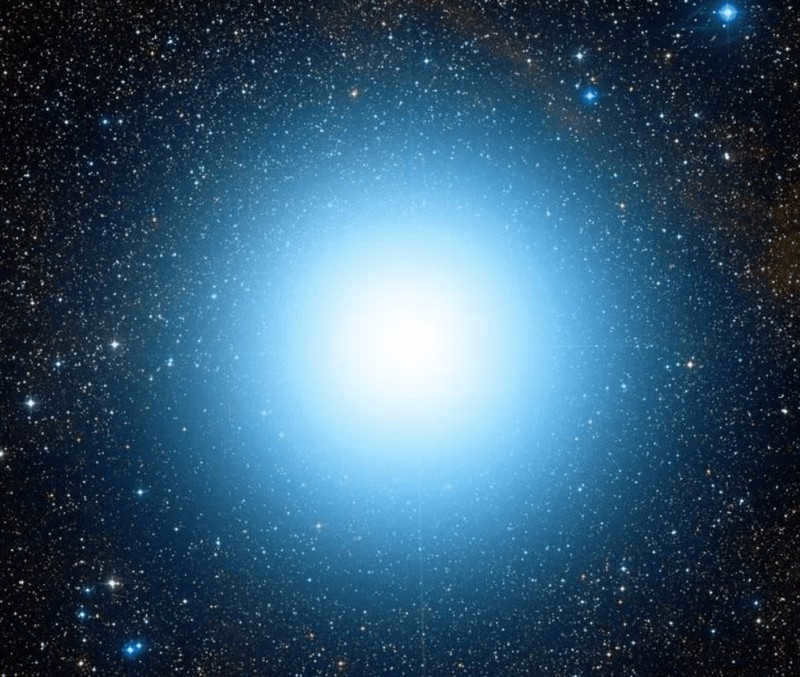
1. Betelgeuse
Betelgeuse, also known as Alpha Orionis, is one of the brightest and most recognizable stars in the night sky. It is located in the constellation Orion and is a red supergiant. Betelgeuse is approximately 640 light-years away from Earth and has a diameter about 700 times that of the Sun. Its name comes from the Arabic phrase “yad al-jauza,” which means “the hand of Orion.” Betelgeuse is a variable star, meaning its brightness fluctuates over time. In recent years, astronomers have observed a significant dimming of Betelgeuse, leading to speculation about its future. Despite its distance and size, Betelgeuse will one day explode as a supernova, an event that will be visible from Earth and will likely have a significant impact on the night sky for a short period of time.
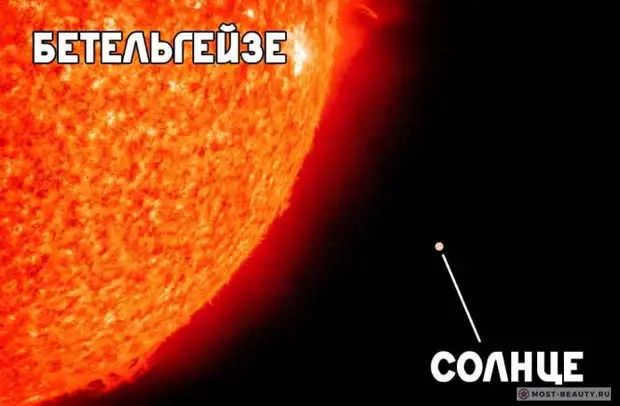
Comparing the size of Betelgeuse and the Sun, they are similar in size.
Betelgeuse, located in the Orion constellation, is one of the most enigmatic stars in outer space. It is often referred to as Orion due to its position in the constellation.
This red supergiant star is known by more than 8 different names in various languages around the world, but the commonly accepted translation from Arabic, Yad al-Jawzah, is “Twin Hand”.
The brilliant star is unwilling to disclose its mysteries to astronomers. One of the astonishing phenomena occurring to it is the reduction in the star’s diameter. While observing Betelgeuse, it experienced a “weight loss” of 15%, shrinking from 5.5 to 4.5 astronomical units. Its current size is approximately 1,000 times that of the Sun.
Researchers anticipate that in the future, this star will go through an explosion and possibly transform into a white dwarf after shedding the Orion planetary nebula. If such an explosion occurs soon, then Most-Beauty assures you of a breathtaking spectacle, as Betelgeuse will be visible during daylight hours. Scientists are unable to provide any specific timing for the star’s explosion, but it could happen at any moment.
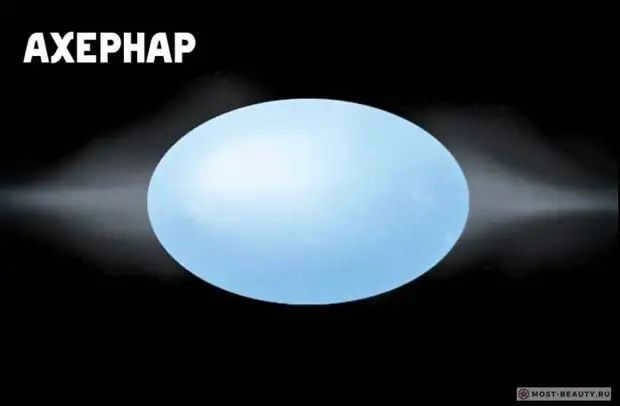

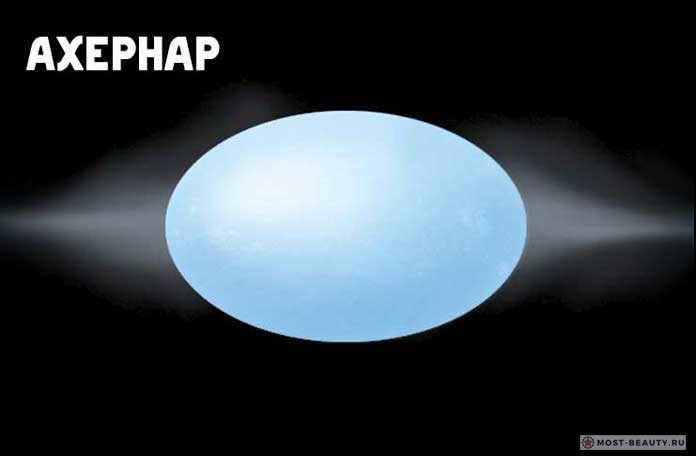
Ahernar, the brightest star in the distant constellation of Eridanus, stands out not only for its brightness but also for its striking blue color and extreme heat. This massive star, which is about ten times larger than our own sun, is a true marvel in the vastness of space.
Situated at the farthest end of the constellation, Ahernar earned the nickname “The End of the River” in ancient times. Its prominence and mystical allure have made it a popular subject in works of science fiction.
Known as Eridana in astronomy reference books, Ahernar is actually a double star. Its unique shape is a result of its rapid rotation around its axis, causing it to appear flattened. Additionally, it boasts an orbital velocity of approximately 300 kilometers per second.
This extraordinary blue star, which shines a thousand times brighter than our Sun, has a companion satellite. This satellite completes a full orbit around Eridanus every 14-15 Earth years.
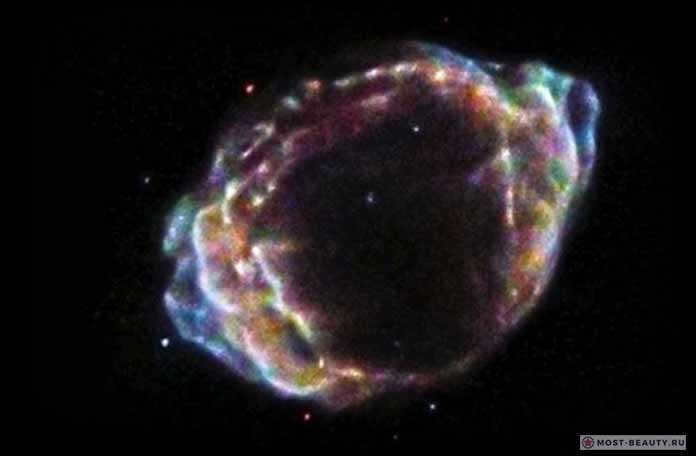
3. SN 1987A.
SN 1987A is the name of a supernova that occurred in the year 1987. It was the first supernova that was visible to the naked eye since the invention of the telescope. The supernova was located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, which is a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. The event was significant because it provided scientists with a rare opportunity to study the explosion of a star in detail. The explosion of SN 1987A produced a burst of neutrinos, which are subatomic particles that are extremely difficult to detect. This detection confirmed some of the predictions of the theory of stellar nucleosynthesis, which describes how elements are created in the cores of stars. Overall, SN 1987A was a groundbreaking event in the field of astrophysics and continues to be studied by scientists to this day.

An explosion of a star known as a supernova occurred relatively close to Earth, approximately 168,000 light-years away. The light emitted from this event, which took place on the outskirts of the Tarantula Nebula, did not reach our planet until the year 1987.
It is worth mentioning that this explosion, which reached its maximum brightness in May 1987, was visible to the naked eye.
The magnificence of SN 1987A is heightened by a pair of delicate rings. These rings are positioned symmetrically in the vastness of space, marking the location where the blue supergiant Sanduleak, the precursor star, experienced its catastrophic explosion. As the rings gradually cool, the atoms of carbon, silicon, and oxygen within them will undergo chemical bonding, resulting in the formation of molecules and dust particles. The astronomical community is diligently observing this fascinating celestial event, yet to this day, no evidence of a neutron star or a black hole has been detected by the scientific community.
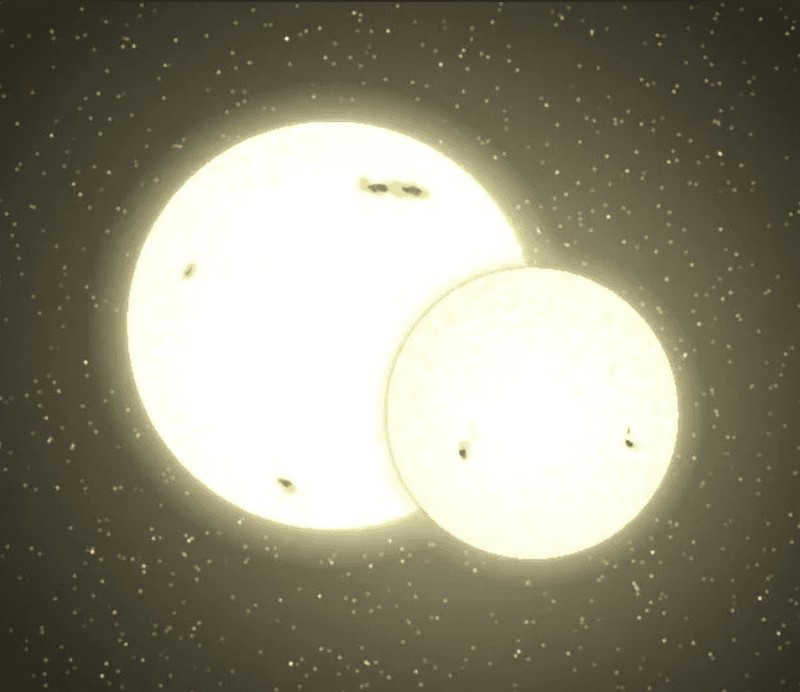
4. Procyon A.
Procyon A is the primary star of the Procyon system, which is located approximately 11.46 light-years away from Earth. It is a binary star system, with Procyon B being its companion star. Procyon A is a main-sequence star that belongs to the spectral class F5 IV-V. It has a mass that is about 1.5 times that of the Sun and a radius that is about 1.9 times that of the Sun. Procyon A is also brighter than the Sun, with a luminosity that is about 7.5 times that of the Sun. It has a surface temperature of about 6,530 Kelvin. Procyon A is known for its high proper motion, which means it moves across the sky at a relatively fast pace. This motion is caused by its close proximity to the Sun and its high velocity through space. Procyon A is also a relatively young star, with an estimated age of about 1 billion years. It is believed to have formed from the same molecular cloud as the Sun, making it a sibling star to our own Sun.

Shown in the picture: Comparison of the size of Procyon A and the Sun.
The most brilliant star in the Lesser Dog constellation appears to move in front of Sirius, earning it the name “in front of the dog.”
This stunning star is relatively near to our solar system, at a distance of 3.5 parsecs. Procyon A has a faint companion, Procyon B, together forming a binary star system.
The star in the Little Dog constellation is constantly expanding, and in the future, it will be around 130-150 times its current size.
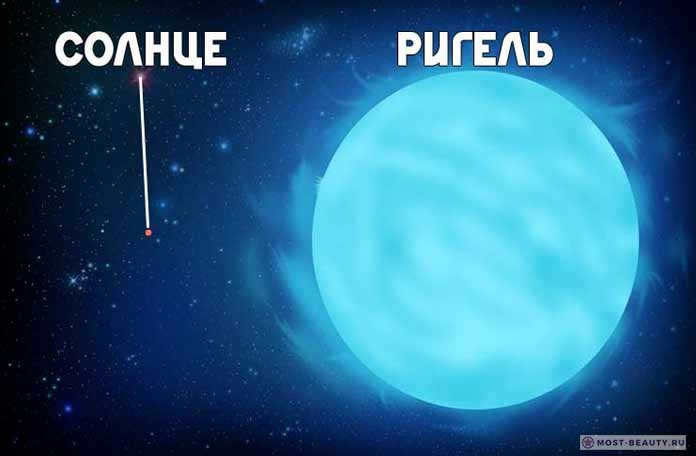
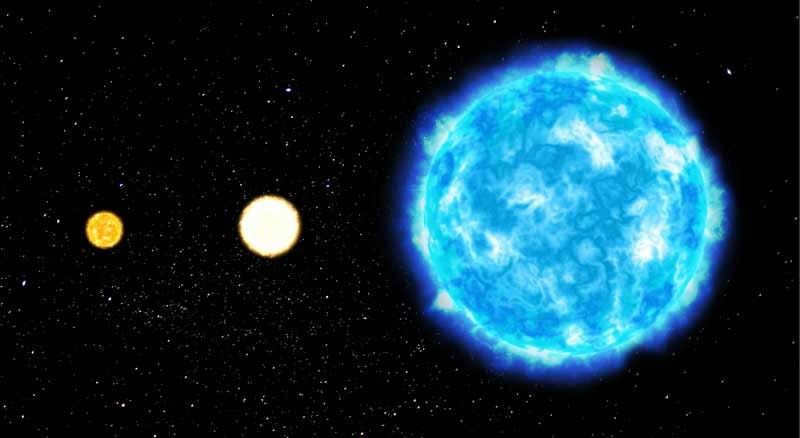
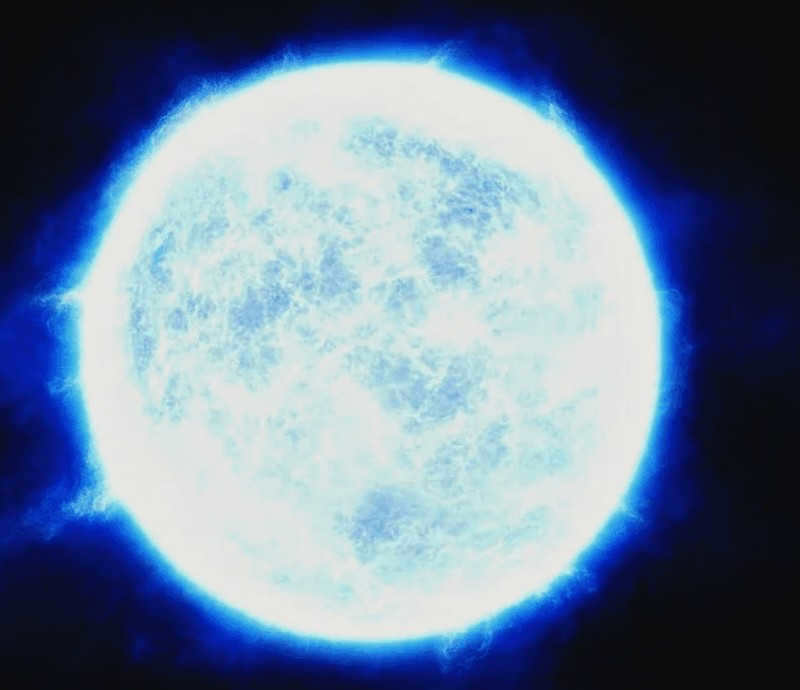
5. Rigel
Rigel, also known as Beta Orionis, is the brightest star in the constellation Orion. It is a blue supergiant, located approximately 860 light-years away from Earth. Rigel has a mass about 17 times that of the Sun and is around 40,000 times more luminous. It is one of the most prominent stars in the night sky and is easily recognizable due to its blue-white color. Rigel is a young star, estimated to be only about 10 million years old. It is believed to have formed from the gas and dust of a larger molecular cloud. Rigel is a variable star, meaning its brightness can fluctuate over time. It is also a binary star, with a companion star that is much smaller and dimmer. The two stars orbit each other every 9.8 days. Rigel is an important reference star for astronomers and has been used to calibrate the brightness scale of other stars. Its name comes from the Arabic word for “foot,” as it represents the foot of Orion in the constellation’s depiction.

Shown in the picture: Comparison of Rigel’s size to the Sun’s.
An exquisite supergiant with a captivating blue-white hue situated in the mesmerizing constellation Orion. The name of this radiant star near the equator means “Foot”.
Rigel’s luminosity is 130,000 times greater than that of the Sun. This makes it the most potent star in the roster of the most brilliant stars in the vastness of space. Rigel surpasses the Sun in mass by 18 times and in size by 74 times. Additionally, Rigel is the nearest star to us with such an immensely immense luminosity.
In the Milky Way, where Rigel is situated, it is a truly stunning location. The star’s luminous radiance illuminates the nearby dust clouds, creating a mesmerizing sight.
In ancient Egyptian legends, Rigel was revered as the protector of the deceased and was regarded as the ruler of all celestial bodies. Over time, this star became closely linked with Osiris. The Maori people marked the arrival of the new year by observing the ascent of Rigel in the heavens.





