It is common knowledge that the sun is the central star around which the Earth and other planets orbit. Most people are aware that this celestial object rises in the East and sets in the West. However, not everyone is familiar with the exact location of the sun’s setting and the reasons behind it. In the following article, we will explore the topic of where the sun appears and disappears in the sky.
How the sun travels
Once the sun rises above the horizon, it embarks on its uninterrupted journey. Throughout the day, we can witness the sun’s movement across the sky. However, it is not actually the sun that moves, but rather the Earth that revolves around the star. This entire process takes approximately 24 hours.
Explaining why rooms located on the southern side of an apartment are always brighter than those on other sides is quite simple. This is due to the sun’s path following a projection along the southern horizon, eventually reaching its highest point. This entire process is scientifically referred to as the culmination of the celestial body.
Shadow and navigation on the ground
There is an alternative method for orienting oneself using shadows. When in unfamiliar surroundings and faced with this need, one should consider different celestial bodies. During the night, this could be the North Star, and during the day, it could be the sun.
By understanding the direction in which the sun sets, one can determine the other cardinal directions and choose the correct travel route. For instance, in northern latitudes during summer nights, the setting sun is closer to the horizon, resulting in a brighter sky on the northern side compared to the southern side.
It is common knowledge that the position of the sun can be determined by the length of its shadow. The shortest shadow indicates that it is noon, and the direction of this shadow points to the north. The same principle applies to the moon: when it is full and at its highest point in the sky, it is located in the south. This is when there is sufficient light to clearly see shadows. Similarly, during a full moon, the shadow is shortest at midnight, with its direction pointing to the north.
How the duration of the day is influenced by the sunset
It is a commonly acknowledged fact that the length of the day varies significantly between the winter and summer seasons. In the warmer months, the daylight hours appear much longer compared to winter. Surprisingly, this phenomenon can be easily explained. The duration of daylight hours is directly influenced by the sun. Individuals who are unaware of this information might mistakenly believe that the duration of the day is determined by the speed of the celestial luminary’s movement. However, this is a complete misconception. In reality, the length of the day is determined by the sunrise and sunset points of the star. It is not difficult to deduce that these points change throughout the calendar year.

What is the importance of registering your pregnancy?
No, it is not mandatory to register your pregnancy. However, there are some challenges that may arise. The majority of women who are on maternity leave highly value every single cash receipt, no matter how small it may be. By not registering your pregnancy, you will not have a birth certificate, which is necessary for applying to any women’s consultation for pregnancy registration and later on, to any municipal maternity hospital for receiving free medical care during childbirth. Additionally, you will not have the benefit of constant medical supervision throughout your pregnancy, which may hinder timely assistance in case of any emerging health issues for both you and your future baby.
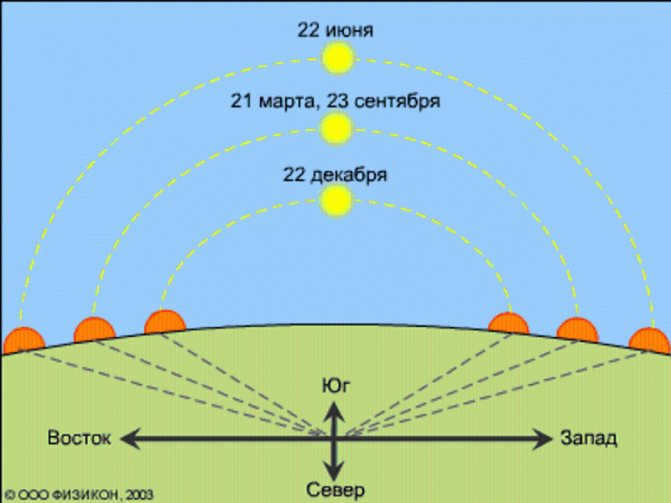
Sunset point movement
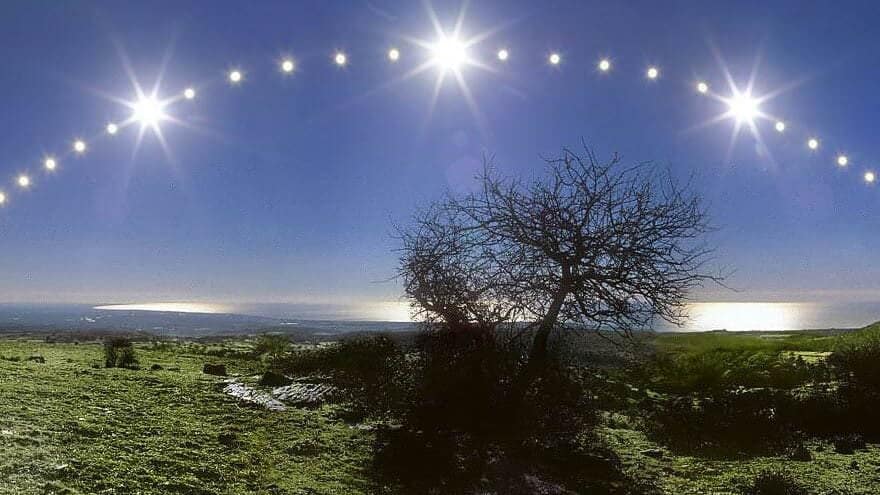
The sun sets in the West only twice a year. These dates, known as the equinox days, occur on March 20 and 21, and September 22 and 23. During these times, the sun sets exactly in the West, and the length of the day is twelve hours. These particular dates may be the only instances when the sun truly sets in the Western part of the horizon.
Following the vernal equinox, the sun gradually moves higher in the sky, causing the days to become longer. As a result, the points of sunset and sunrise shift closer and closer to the north each day. This process continues until June 21, which marks the solstice. On this day, the point of sunset is at its maximum shift to the north, and the day is longer in duration.
In cities located above the Arctic Circle, the convergence of the sunset and sunrise points occurs, resulting in the sun never leaving the horizon and the occurrence of polar day.
Starting from June 22, the sunset point of the Sun gradually moves to the west, while the sunrise point also shifts. As a result, the length of the day decreases. After September 23, the sunrise and sunset points begin to merge, appearing to the south of the horizon. This pattern continues until the winter solstice, when the sun rises and sets south of its previous positions, resulting in the longest night of the year.

Did you know that on this day the polar day is replaced by the polar night? It’s a fascinating phenomenon where the Sun does not appear above the horizon. This happens because the points where the Sun sets and rises converge in the south. As we move past the winter solstice, everything starts to change gradually. The points of sunset and sunrise begin to shift in the opposite direction, resulting in longer daylight hours.
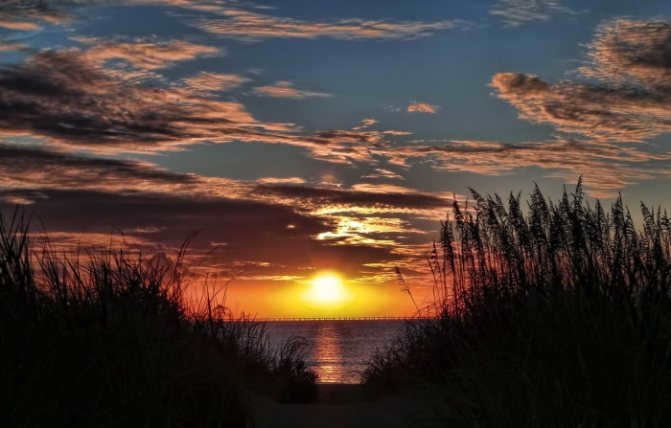




An experienced explorer is aware that the compass arrow always points north. This knowledge can be utilized to ascertain the location of the object in question at various times of the day.
- During the morning, the object known as the Luminary can be found to the left of the directional arrow. Direct your attention in that direction. It is positioned precisely in the east solely during the spring and fall equinoxes.
- During daylight hours, specifically at noon, the star that our solar system revolves around can be located in the southern part of the sky, directly behind you. However, it’s important to note that noon doesn’t always align with 12 o’clock, with a variation of plus or minus 15 minutes. The term “noon” refers to the moment when the sun reaches its highest point in the sky (zenith). This method of orientation is most accurate for regions with moderate latitudes, rather than the entirety of Russia. For those closer to the poles, a more precise way to determine the position of the sun is by examining one’s own shadow. If the shadow disappears, it indicates that it is noon. If the shadow is long and shrinking, it is the time period from sunrise to noon. If the shadow reappears and grows, it is the period from noon to sunset. In the Polar Regions, after the spring equinox, daylight hours increase rapidly while nights shorten. This marks the beginning of the first period of white nights. Instead of setting below the horizon, the sun touches it at the northern point and rises again, completing a full 360-degree rotation in the sky. At the poles themselves, the sun remains unseen for six months at a time.
Characteristics of Daylight Hours in the Southern Hemisphere
Contrary to the norm, in the southern hemisphere, things happen in the opposite way. When the northern hemisphere experiences its longest day of the year, the southern hemisphere experiences shorter daylight hours. These contrasting phenomena are evident in various aspects. While we have the autumnal equinox, they have the spring equinox in the southern hemisphere. The sun’s zenith also occurs at the opposite point: in the northern hemisphere. However, just like us, the sun sets directly in the western part of the sky.

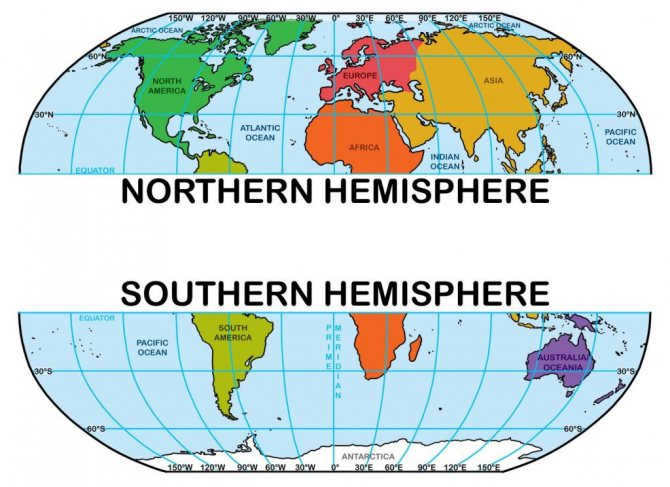
Different Types of Hemispheres and Their Contrasts
There are a total of four types of hemispheres – Northern and Southern, Eastern and Western. To briefly explain the Eastern and Western hemispheres, it should be noted that they differ in terms of time zones. In other words, when it is daytime in the Western Hemisphere, it is nighttime in the Eastern Hemisphere and vice versa. This phenomenon occurs due to the Earth’s rotation on its axis. Throughout the day, different parts of the Earth are exposed to the sunlight.
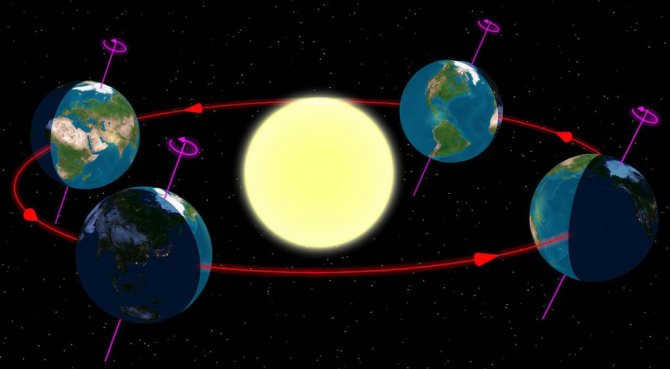
However, our focus lies on the Northern and Southern hemispheres. They exhibit contrasting seasons. In other words, when the Northern Hemisphere experiences winter, the Southern Hemisphere enjoys summer and vice versa. Similarly, spring and fall are also reversed. These variations occur because of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun and the uneven distribution of sunlight.
Fascinating information about the sun and its sunset
Throughout history, mankind has always been captivated by the sun and its position in the sky. There exist intriguing facts that highlight the captivating and enigmatic nature of this celestial body.
- As the sun sets, the temperature gradually decreases, resulting in a noticeable chill in the air. However, it is quite surprising that the temperature during the night does not reach its lowest point. The coldest period is actually considered to be the morning, just before sunrise.
- People all around the world witness the beauty of the sunset every single day. However, those living near the poles can only experience this phenomenon once a year.
- In ancient times, people relied on the sun to measure time, with the position of the celestial luminary serving as a cue for different times of the day. The use of shadows, cast by specific objects, allowed for the creation of the earliest clocks and calendars.
- By using a camera, it is possible to track the sun’s path throughout the day. Simply taking pictures from a fixed point on Earth at consistent time intervals allows for the observation of the sun’s movement over days and even months.

To summarize, it should be mentioned that the sun, which provides us with warmth and light on a daily basis, is actually a star. It is challenging to determine the exact location where this celestial body sets. The position of the sunset changes daily, influenced by the time of year.
Twilight
The period of time just before sunrise and after sunset is known as twilight. It is a remarkably beautiful sight to behold. The celestial body’s disk is positioned very near to the horizon, causing some of the rays to penetrate the upper layers of the atmosphere and reflect onto the Earth’s surface. This vibrant spectacle typically lasts for approximately two hours, although in temperate latitudes. However, in the circumpolar regions, twilight can extend for several hours before sunset. In fact, at the poles, this period can last anywhere from two to three weeks! Conversely, at the equator, twilight lasts a mere 20-25 minutes before sunrise.
During this time, we are treated to a breathtaking display as the sun’s rays bathe the Earth’s surface and the sky in a myriad of colorful hues, thanks to the optical effect.

What to Expect During Your First Visit to the Gynecologist
During your initial visit to the gynecologist, you will be provided with a special medical card that will document the entirety of your pregnancy. Additionally, you will receive an exchange card that you will keep and bring with you to the maternity hospital when it’s time for delivery. This exchange card will also record important information such as the progress of your pregnancy, any tests or examinations conducted, and any necessary referrals.
Aside from these documents, there are a few other items you will need for your first visit:
- A list of any medications or supplements you are currently taking
- Any previous medical records or test results related to your pregnancy
- A form of identification
During the appointment, the doctor will ask you various questions about your medical history and perform a thorough examination. They may also provide you with referrals for additional tests or examinations to be conducted by specialists.
As part of the examination, your weight and blood pressure will be measured. Additionally, the doctor will take measurements of your height, ankles, arms, thighs, waist, fingers, and toes to track your physical changes throughout your pregnancy.
What is the optimal timing for pregnancy registration?
The best time to register for pregnancy is typically between 8 and 12 weeks. However, if there are any concerns about well-being or previous miscarriages, it is advisable to register earlier.
If a woman chooses to register at a later stage, she will not lose anything officially, except for the fee for early pregnancy registration. However, from a medical perspective, this situation may not be ideal. Early examinations and tests can identify potential abnormalities in fetal development and placenta health at an early stage of pregnancy. In some cases, addressing these issues early can prevent complications and ensure the well-being of both the mother and the future child.
Where to apply for pregnancy registration
The antenatal clinic where you have received previous care is the recommended place to register for pregnancy. However, it is within your rights to choose any counseling center for this purpose. When selecting the institution, there are two key factors to consider:
- Whether the institution provides an exchange card (which will be necessary at the maternity hospital);
- and whether they issue a birth certificate (which will enable the expectant mother to receive free prenatal care and give birth at the chosen antenatal clinic and maternity hospital).

Photo source: shutterstock.com
How to register for pregnancy without having a registered address
If a woman does not have a registered address, she should submit an application to the head doctor of the medical institution where she wants to register. The application should be accompanied by a copy of the registration at the place of residence. If there is no registration, a copy of the rental agreement or, if no agreement has been made, a copy of the landlord’s passport should be attached. Regardless, it is important to provide the address of your current residence.
It is important to note that the absence of a registered address does not result in a refusal to register for pregnancy!
What does the medical examination involve when registering for pregnancy?
The initial examination during pregnancy registration includes:
- Visual examination of the vagina using a mirror;
- Visual examination of the cervix, also using a mirror;
- Sampling to assess vaginal cleanliness;
- Collection of a smear for cytological analysis;
- Palpation using two hands to determine the size of the uterus and its appendages.

Photo source: shutterstock.com
What tests are recommended during pregnancy registration
During the initial appointment, the doctor will provide a list of the following tests:
- complete blood count;
- blood test for biochemistry;
- blood coagulation test (coagulogram);
- determination of blood type and Rh factor;
- tests for THORCH infections (rubella, herpes, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, etc.);
- tests for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis B and C.
- An electrocardiogram (ECG) will also be ordered.
An ultrasound of the pelvic organs will also be scheduled. The ultrasound will help identify any fetal and placental abnormalities during the early stages of pregnancy.
What are the necessary documents for pregnancy registration?
When registering for pregnancy, you will need to provide two essential documents:
- A valid passport or any other form of identification.
- A current health insurance policy that has not expired and contains accurate information such as name and address.
Occasionally, additional documents may be required by the healthcare facility, such as the SNILS. Therefore, it is advisable to inquire beforehand at the registration office about the specific documents required for pregnancy registration at that particular medical institution.

The natural processes of sunrise and sunset occur regularly in our universe. However, it is important to note that the Sun does not actually rise and set, but rather remains stationary. Contrary to the beliefs of our ancient ancestors, it is not the celestial luminary that revolves around our planet, but rather the Earth, along with the other seven planets, revolves around the Sun while also rotating on its axis in a west to east direction.
Knowing the direction from which the Sun rises can be beneficial for tourists, as it can help them orient themselves in their surroundings and even serve as a substitute for a compass. Additionally, there are many people who enjoy watching and admiring the beauty of sunsets. This article provides readers with information on where the Sun sets and rises.
General information
If you were to ask individuals, “From which direction does the Sun ascend?”, the majority would likely respond to this seemingly foolish question with, “The Sun ascends from the East”. However, this response is not entirely accurate. The same can be said for the customary response to the inquiry, “Where does the Sun descend?”. Both replies are flawed. More precisely, they are correct, but only on two specific days of the year. These days are September 23 and March 21, commonly referred to as the autumn and vernal equinoxes. As their names imply, on these particular days, daylight and darkness are evenly split, with 12 hours of each. Consequently, during these periods, the Sun distinctly rises in the east and sets in the west.

At different times, the Sun follows a completely different path through the sky, resulting in either a shorter trajectory (when the night is longer than the day) or a longer trajectory (when the day is longer than the night).
It is also important to mention two more significant dates – December 22 and June 21. These dates mark the winter and summer solstice respectively. As the name suggests, on these days the sun is in the sky for the longest period of time. However, this is true for the Southern Hemisphere on the day of the winter solstice, and for the Northern Hemisphere on the day of the summer solstice. But why is that?



Summer and Winter Solstice
The summer and winter solstice occur on June 22 and December 22, respectively. The winter solstice, which falls on December 22, is known for having the shortest day and the longest night in the Northern Hemisphere. On this day, the winter sun is positioned at its lowest point above the horizon throughout the entire year.
In areas above latitude 66.5 degrees, the sun remains below the horizon and does not rise. This phenomenon is referred to as the polar night, where the winter sun does not appear on the horizon. The shortest night lasts only 2 days at latitude 67 degrees, while the longest night occurs at the poles and lasts for a staggering 6 months!

December is the month of the year when the Northern Hemisphere experiences the longest nights. In Central Russia, people wake up and return home from work in darkness, making it a challenging month for many. The lack of sunlight during this time affects both physical and mental well-being, and can even lead to depression.
In Moscow in 2021, on December 1st, the sunrise is expected at 08.33, while the daylight will only last for 7 hours and 29 minutes. The sunset will occur very early at 16.03, resulting in a night duration of 16 hours and 31 minutes. This means that the night is twice as long as the day!
This year, the winter solstice falls on December 21st. On this day, the daylight will last for exactly 7 hours. This situation will persist for the following two days. However, starting from December 24th, the daylight will gradually increase, bringing more hours of sunlight.
Every day, one additional minute of daylight is added on average. By the end of the month, the sunrise in December will occur precisely at 9 o’clock, which is 27 minutes later than on December 1st.
June 22nd marks the summer solstice, a day when everything happens in the opposite way. On this date, the Northern Hemisphere experiences the longest day and the shortest night of the year.
Conversely, in the Southern Hemisphere, the opposite occurs. This day is associated with interesting natural phenomena. Beyond the Arctic Circle, the polar day begins, where the sun remains above the horizon for 6 months at the North Pole. In St. Petersburg, June brings the start of the mysterious White Nights, which last for approximately two or three weeks starting in the middle of the month.
All of these four astrological dates can vary by 1-2 days, as the solar year does not always align with the calendar year. Additionally, shifts may occur during leap years.

Types of hemispheres and their distinctions
There are a total of four types of hemispheres – Northern, Southern, Western, and Eastern. When it comes to the Western and Eastern hemispheres, one notable difference between them is their time zones. In other words, while it is daytime in the Western Hemisphere, it is nighttime in the Eastern Hemisphere, and vice versa. This phenomenon occurs due to the Earth’s rotation on its axis. As the Earth rotates, different parts of it are exposed to the Sun at different times of the day.
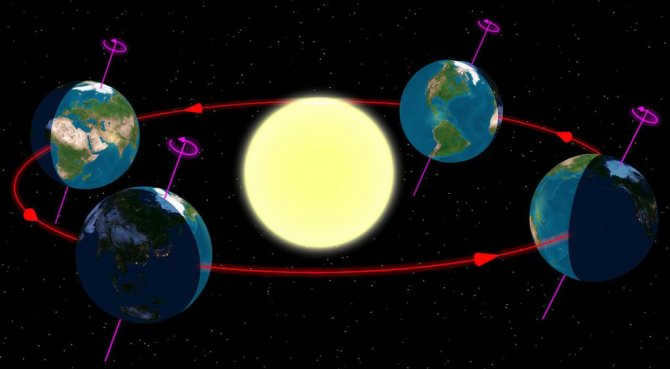
However, our focus lies on the Northern and Southern hemispheres. These two regions exhibit distinct seasons. For instance, when it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere, it is summer in the Southern Hemisphere, and vice versa. Likewise, spring and fall are reversed in these hemispheres. This phenomenon can be attributed to the Earth’s rotation around the Sun and the resulting uneven illumination.
The height of the Sun above the horizon determines the angle at which its rays strike the Earth
The amount of sunlight and heat that reaches the Earth’s surface is directly influenced by the angle at which the Sun’s rays hit. The Sun’s rays can hit the Earth at angles ranging from 0 to 90 degrees due to the spherical shape of our planet. The larger the angle, the brighter and warmer it is.
For instance, when the angle is 0 degrees, the rays only graze the Earth’s surface without providing much heat. This angle of incidence is observed at the North and South Poles as well as above the Arctic Circle. At 90 degrees, the Sun’s rays fall directly on the equator and the region between the South and North Tropics.
Therefore, the angle at which rays hit the surface of the Earth and the elevation of the sun above the horizon are identical. These factors are determined by the geographical latitude. As the latitude approaches zero, the angle at which rays hit the surface becomes closer to 90 degrees, and the sun rises higher above the horizon. This results in warmer and brighter conditions.
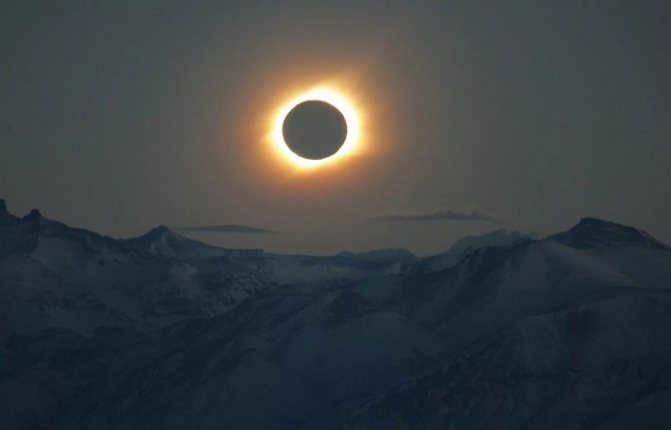
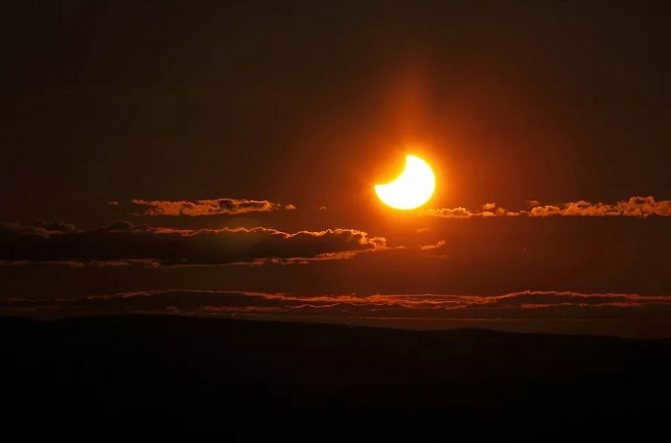




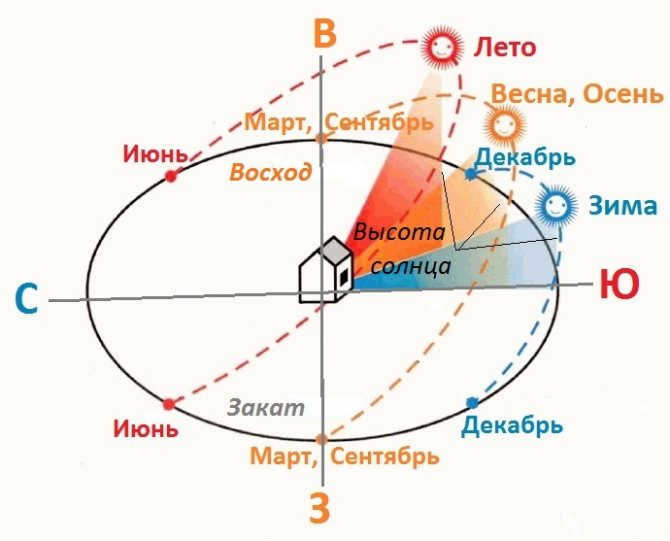
If we analyze the Northern Hemisphere, during the summer season, the Sun ascends in the direction between north and east, and descends in the direction between north and west. Conversely, in winter, it ascends between south and east and descends between west and south. In autumn and spring, the Sun ascends between northeast and southeast, and descends between northwest and southwest. On the days of the autumn and spring equinoxes, as already mentioned, it ascends and descends precisely in the east and west, respectively.
In the Southern Hemisphere, the situation is completely opposite. This discrepancy accounts for the disparity in the seasons.
It is worth noting that the distinction between night and day becomes more pronounced the further north a region is located in the Northern Hemisphere, and the further south it is in the Southern Hemisphere. In other words, a general rule can be formulated as follows: the closer a territory is to the pole, the greater the contrast between night and day. Conversely, the closer a territory is to the equator, the less pronounced the difference between day and night will be.
For example, at the poles, nights can last for several months, just like days. On the other hand, at the equator, there is hardly any distinction between night and day. Because of this, the equator experiences a consistent level of illumination throughout the year, with no distinct winter or summer seasons.
Characteristics of the annual movement of the Sun
Even ancient observers noted the irregularity of the apparent motion of the Sun across the celestial sphere throughout the year. During the autumn and winter seasons, the Sun appears to move at a faster pace compared to the spring and summer months.
The Sun’s speed is at its highest around January 3rd (approximately 1° 1′ per day), and slows down around July 4th (57′ per day). As a result, spring and summer each span 186 days, while fall and winter each span 179 days.
The apparent diameter of the Sun’s disk also varies throughout the year. It reaches its maximum size (32.5′) when the Sun moves at its fastest, namely in January, and its minimum size (31.5′) in July. This indicates that the distance to the Sun is shorter during winter compared to summer.
The Earth reaches its closest point to the Sun, known as perihelion, on January 3.
Conversely, the Earth reaches its farthest point from the Sun, known as aphelion, on July 4.
Due to gravitational disturbances, the positions of perihelion and aphelion are slightly shifted along the Earth’s orbit, resulting in the average dates of Earth’s passage through these points during our era. The closest distance between the Earth and the Sun occurs between January 2 and January 5, while the greatest distance occurs between July 1 and July 5.


The Autumn Sun’s Behavior in the Sky

It’s also quite disheartening! Why? It’s simply due to the fact that the Sun has distanced itself further from the Earth. This increased distance, which we perceive through the decrease in heat intensity, is interpreted differently. It appears as though the Sun yearns for the green planet. The celestial body longs for the radiance emitted by its inhabitants. And on a gloomy and overcast day, what comes to mind? How does the sun appear during the autumn season? It’s absolutely delightful! It peeks out from behind the clouds like a smile on the face of a whimsical child. It ignites a desire to live and create. Autumn is transitioning into winter. The gloomy days pass by in an unbroken succession. And it almost seems as if the sun has forsaken the planet during the fall. “What sun?” – you may ask. – “We have forgotten what it even looks like.” So, is the autumn sun being stingy? It visits us so rarely.

Discovering the beauty of Norway under the sun
The phenomenon of white nights is a delightful experience for tourists in various cities across Norway. Certain regions in the country enjoy several months of continuous sunlight. One of the most sought-after destinations for travelers is Cape Nordkap, where the sun graces the sky for a minimum of 1800 hours annually.

Undoubtedly, these phenomena are considered normal for the locals, unlike the astonished travelers. When visiting such cities, every individual naturally wonders about the unique aspects of living under constant daylight.
It appears that these conditions do not lead to sleep disorders, as the people of Norway have long adapted to these circumstances and can sleep easily even with sunlight streaming through the windows. Unfortunately, travelers cannot fall asleep as easily, as they begin to confuse day and night due to the continuous daylight.
What is the phenomenon of sunset?
As the sun sets and moves towards the western horizon, its brightness gradually diminishes. The sun’s disk undergoes a stunning transformation, starting from a vibrant yellow hue and shifting to a warm orange shade, eventually transitioning into various shades of red. Simultaneously, the surrounding sky undergoes a mesmerizing change, transitioning from a golden color to a deep blood red, against a backdrop of blue, and sometimes even greenish tones.
When beholding the beauty of a sunset, it is essential to also observe the exact opposite side of the sky. At this point, the shadow of the Earth becomes visible in the form of a strip of bluish ash color, while above it, a bright segment known as the Belt of Venus emerges. This remarkable phenomenon can be witnessed anywhere in the world, as long as the sky remains unclouded.
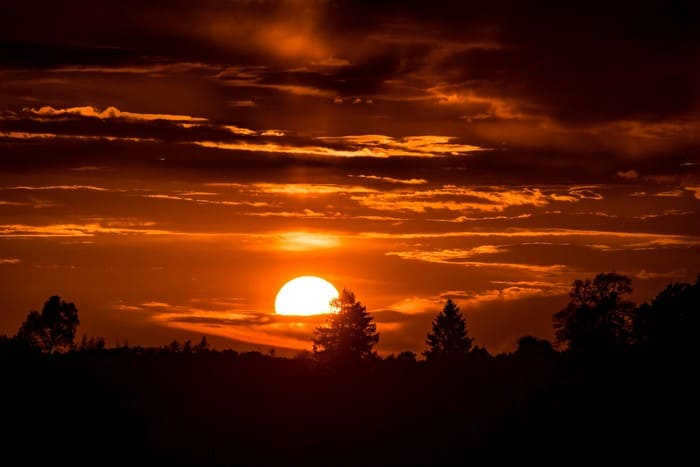

As the Sun descends beneath the horizon, the hues become more vibrant. As the luminary fades from view, the Buddha Rays emerge, initially strong and then diminishing with each passing minute until they merge with streaks of crimson. Conversely, the Belt of Venus dissipates, making way for the Moon to rise, and darkness descends.
How to differentiate between sunset and sunrise
Sunrise and sunset are both indicators of the Earth’s rotation around its axis. At first glance, they may seem identical. However, those who wake up early have the chance to compare the two: the rays of the rising sun are more vibrant, and the colors of the surroundings take on delicate shades. On the other hand, during sunset, the sun and the sky surrounding it are painted in tones of red. This evening coloring is caused by the visibility of dust particles, which become more apparent in the evening due to lower humidity and stronger air currents.
Autumn Sunset
Each evening farewell to the radiant sun feels like a bittersweet parting with a cherished companion. There is always a hint of uncertainty, a lingering doubt that it may not grace us with its presence the following day. The sun, much like a temperamental diva, may choose to hide behind a veil of clouds, sulking and refusing to accept our adoration. And so, it departs from the earthly stage, retreating behind the protective embrace of the atmosphere. Alternatively, it may take its time, leisurely traversing the vast expanse of the sky, meticulously observing the world below like a diligent master, carefully planning its next appearance.
In autumn, our luminary transforms into a more polite and significant presence. It has expended all of its warmth and affection during the summer. Now, it requires some rest and care. Have you ever noticed this phenomenon? During the summer, people often complain about the heat, become irritable, and express their frustrations. But where does all that anger go when fall arrives? During this season, everyone seems to fall in love with the occasional ray of sunshine, quickly learning to appreciate and thank the magnificent luminary for each visit. Its gentleness and grace during the autumn months are particularly enchanting!
A lunar eclipse is a rare event that amateur photographers have the opportunity to capture. It is a captivating phenomenon where a circular, red object, resembling a colossal colored glass disk, slowly moves across the silvery surface of the full Moon over the span of an hour. Eventually, the entire Moon becomes engulfed in this vibrant red hue. The Moon remains in this state for an extended period before the crimson circle gradually recedes from its right side.
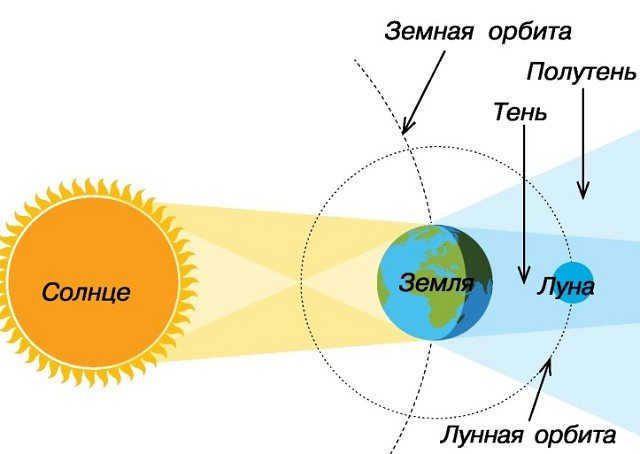
Lunar eclipse
Thousands of years ago, Eastern sages began to understand the cause of lunar eclipses. However, this knowledge was kept as a secret among priests. It was not until Greek scientists came along that the Chaldean wisdom was comprehended and revealed.
Aristotle clearly stated this truth and drew a significant conclusion: the round cross-section of the shadow cone during an eclipse indicates that our Earth is round and spherical. This was the first, but not the only, evidence of the Earth’s sphericity.
If the Moon’s orbit were aligned with the Earth’s orbit (the ecliptic plane), lunar eclipses would occur every full moon, which happens approximately every 29.5 days. However, the Moon’s path is inclined by 5° to the ecliptic plane, causing it to only intersect with the “circle” twice a month at specific points known as the nodes of its orbit. Therefore, for a lunar eclipse to take place, two conditions must coincide: there must be a full moon and the Moon must be positioned at or near its node at that particular time.
Depending on the proximity of the Moon to the orbital node during the eclipse, it can either pass through the center of the shadow cone, resulting in a total lunar eclipse, or it can pass through the outer edge of the shadow, causing a partial lunar eclipse. The shadow cone of the Earth is surrounded by a penumbra, which only receives a fraction of the sunlight that is not obstructed by the Earth. This is why penumbral eclipses occur. Although these eclipses are listed in astronomical calendars, they cannot be discerned with the naked eye, only cameras and photometers can detect the darkening of the Moon during the penumbral phase or penumbral eclipse. If a full moon occurs far from the nodes of the lunar orbit, the Moon will pass either above or below the shadow, resulting in no eclipse.
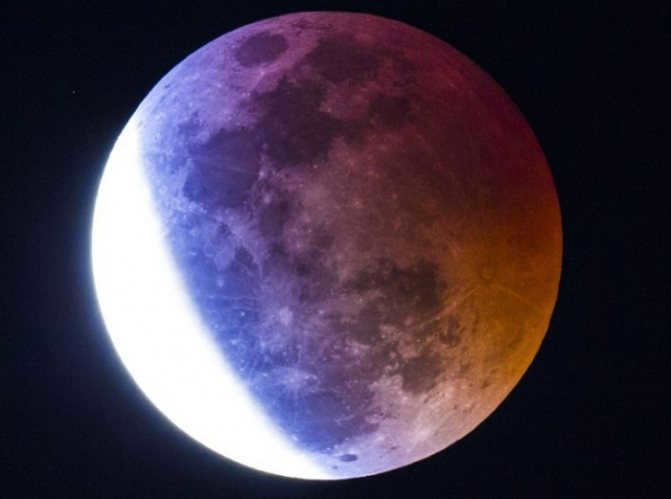

Lunar eclipses occur during full moons, when the Earth is directly between the Moon and the Sun, causing the Earth’s shadow to cover the Moon and block out sunlight.
Eastern priests, although lacking a clear understanding of this phenomenon, diligently recorded both total and partial eclipses for centuries. Upon initial examination, there appears to be no discernible pattern in the occurrence of eclipses. Some years may have three lunar eclipses, while other years may have none at all. Additionally, the visibility of a lunar eclipse is limited to the half of the Earth where the Moon is above the horizon at that particular time. This means that from any given location on Earth, such as Egypt, only slightly more than half of all lunar eclipses can be observed.
When astronomers gained a more precise understanding of the Moon’s orbit, they were able to not only determine the date of an eclipse, as the saros method had done, but also the exact time when it would begin.
Autumn Sunrise
When the magnificent star, weary from the toils of summer, graces the sky, it is truly a cause for celebration. It no longer casts its rays gently upon the world, but instead surveys from its lofty perch the fruits of its labor. From its vantage point high above, it scrutinizes every nook and cranny of the Earth, assessing what requires immediate attention and where its presence may not be necessary. Have you ever observed that on occasion, the Sun briefly disappears, withholding its radiance for an entire day? This signifies that nature does not currently require its magnificence. However, there are days when it displays a level of vigor akin to that of summer. This indicates that it has resolved to continue its efforts, feeling as though it has not done enough. Nature yearns for its life-giving energy. In the autumn, the radiant star emerges from beyond the horizon, emanating both energy and contentment.
Does the Sun have a “reverse” movement in the Southern Hemisphere?
We are all aware, from our geography classes and nature walks, that the Sun moves across the sky from east to west (clockwise) and points south at noon. These facts may seem almost absolute. In fact, some experienced individuals can even estimate the time based on the Sun’s position.
However, a simple question can easily perplex the minds of those living in the Northern Hemisphere. What direction does the Sun move in the Southern Hemisphere?
Considering that the antipodes observe the sky from a completely different perspective, it is conceivable that all celestial bodies would move in the opposite direction – from west to east. Let’s explore this further…
Which direction does the Sun move?
If you rotate any circular object in the light of a lamp, you will observe that at one point, the bottom and top of the object are simultaneously illuminated. This phenomenon applies to the Sun and its rays on Earth as well. When New York experiences daylight, so does Buenos Aires, which is located below it.
Interestingly, despite being located in different hemispheres, both cities witness the sunrise in the same direction – the east. This suggests that the Sun traverses the sky from east to west for both locations. You might think this settles the matter, but there is more to it than meets the eye…
Clockwise or counterclockwise?
Let’s rotate the first image from the article by 90 degrees and observe how the Sun’s movement across the sky is perceived by an American and an Indonesian.
Based on the image, it becomes apparent that for someone residing in the Northern Hemisphere, the Sun ascends in the east, faces south at noon, and descends in the west, following a path that goes in a clockwise direction.
Its opposite point also rises in the east and disappears over the horizon in the west, except for one significant difference: at noon, the Sun reaches its highest point in the north and traverses the sky in a counterclockwise manner.
Did you enjoy the article? Remember to give it a thumbs up and subscribe to my channel.
What about Uranus? Neptune? And what about Pluto?
Uranus is located too far away to be visible to the naked eye. With the help of a telescope, we can observe it if we know its location, but due to its immense distance, it is challenging to see any details.
As for Neptune, the situation is even more complex. Interestingly, this planet was actually discovered through calculations before it was visually observed using a telescope. Astronomers noticed irregularities in Uranus’ orbit, which led them to theorize the existence of another planet. They then proceeded to calculate its position based on the observed anomalies in Uranus’ trajectory. Eventually, in 1846, Neptune was officially discovered, slightly deviating from its predicted location!

In a 24-hour day, there are a total of 24 hours, which are further divided into daytime and nighttime, as well as morning and evening. To explore the reason behind the phenomenon of light during the day and darkness at night, one can observe the sky. During the hours of daylight, the Earth is illuminated by the Sun, resulting in a bright planet. However, as night falls, the Sun disappears from view.
The Sun in various cultures throughout history
In ancient civilizations, the Sun was revered as a divine entity and held in high regard. The warmth and illumination that the celestial body bestowed upon the Earth were seen as blessings from the heavens. Among the Slavic people, the Sun was worshipped as the god Yaril, depicted as a masculine figure with radiant golden hair, traversing the sky on a majestic white steed each day.

In the realm of the heavens, the Sun God Helios of ancient Greece traverses the celestial expanse atop his majestic steeds. These four horses, pure as the driven snow, are adorned with golden harnesses as they pull his chariot of gilded splendor. Helios himself embodies youthful beauty, with his flowing locks cascading down and a regal crown adorning his head.
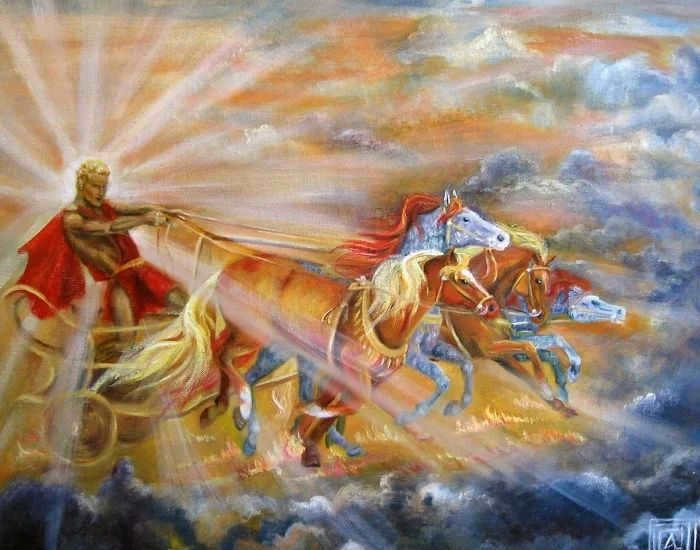

The Sun in ancient Egyptian mythology was personified as the god Ra. Ra was often depicted as a falcon, a majestic feline, or a man with the head of a bird. The Sun itself was symbolized by a vibrant red disk. According to popular belief, Ra would travel across the sky during the day, riding in a boat on the Nile River and casting his radiant light upon the entire Earth. However, at night, Ra would transfer to another boat and navigate the underground Nile, concealing his light from view.
Each nation has its own name for the blazing ball of the Sun, and they have transformed it into a deity. The Romans worship the Sun as the God Apollo, the Persians revere it as Mithra, and the Japanese honor it as the girl-goddess Amaterasu.
So, what exactly is the Sun?
All of these beliefs and legends are not supported by scientific evidence. The scientific concept of the Sun was first proposed by the Greek scientist and philosopher Anaxagoras. He argued that the Sun is a massive, luminous sphere. However, his theory was considered pseudoscientific, and as a result, Anaxagoras was imprisoned.
The Sun is, in fact, a sphere that the Earth orbits around. In the daytime, the presence of sunlight causes other celestial bodies such as stars and the Moon to become invisible. The reason for this is that sunlight is significantly more powerful and luminous compared to starlight. It surpasses the radiance of the stars as soon as the morning arrives. However, as night falls, these celestial objects reemerge in the nocturnal sky.

Is the sun a star or a planet?
Contrary to popular belief, the Sun is not a planet but rather a star. Its surface temperature is extremely high, a characteristic feature of stars rather than planets. In fact, the color of a star can indicate its temperature. A blue star, for example, is very hot, while a red star is relatively cooler. The Sun, with its average temperature, appears yellow. Additionally, the Sun’s mass surpasses that of all the other planets combined. It undergoes nuclear reactions, a phenomenon not observed on any of the other planets in the solar system, but typical of stars. These distinctive attributes clearly classify the Sun as a star. Moreover, it is the nearest star to our planet.
The solar system is composed of the Sun at its center, with the other planets orbiting around it. In addition to planets, there are also comets, asteroids, and other celestial bodies that orbit around this radiant star.
The Solar System
The planets within the solar system are arranged in a specific order. Mercury, the smallest and closest planet to the Sun, is followed by Earth, which is the third farthest from the Sun. Neptune and Pluto are the farthest planets from this fiery celestial body.
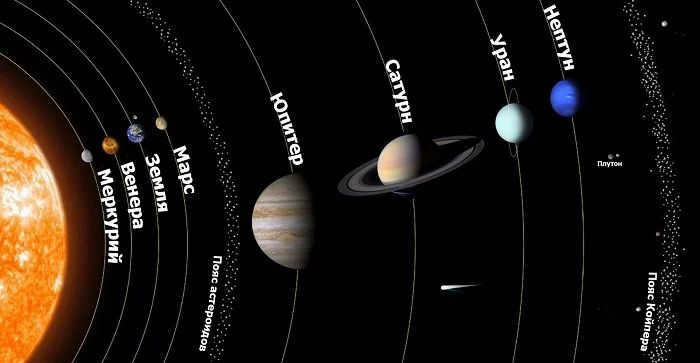
In comparison, the planet Earth is relatively small when compared to the Sun. If you were to place numerous Earth-sized planets inside the Sun, there would be an astonishing one million of them.
However, the Sun’s significance goes beyond its size. It serves as the primary source of heat and light for all life on Earth. Additionally, its consistent rotation plays a crucial role in supporting the existence of life. If the Earth were constantly facing the Sun on one side, the first half of the Earth would experience scorching temperatures, while the other half would endure freezing cold temperatures.

Why the day and night change
The change of day and night is caused by the enormous hot star known as the sun. The Earth revolves around its axis, completing a full rotation in 24 hours.
As the planet spins, different parts of it are exposed to the sun’s light. The illuminated half experiences daylight, hence it is daytime. On the other side, the absence of sunlight results in darkness, creating nighttime. This occurs because the sun’s rays do not reach the Earth’s surface, leaving it in shadow.

The occurrence of equal night and day is a rare phenomenon that happens only twice a year, during the spring and fall equinoxes. It is interesting to note that there are certain locations on Earth where night and day are always of equal length. This phenomenon is observed at the equator.
Stars and constellations
During the night, the sky is adorned with countless luminous dots known as stars. However, these stars may appear small when viewed from Earth. In reality, there are stars that are so massive that their size equals that of the entire solar system, while there are others that are so small that they cannot be observed even with the aid of a telescope.

What is a star?
A star is defined as a celestial object consisting of a ball of gas that is able to maintain its shape due to the force of gravity. The high temperatures within a star cause it to emit light, which is why we can see these twinkling balls in the night sky.
When stars are grouped together, they can form patterns that resemble drawings or figures of animals and people. These groupings are known as constellations and have been recognized since ancient times. In astronomy, constellations refer to specific areas of celestial space where certain groups of stars are found.

The exact count of constellations known in the field of science is indeterminate. Over the course of several centuries, the number has fluctuated as constellations were merged or divided. A prime example of this is the constellation known as the Ship of Argo. It was once considered the largest, but in the 13th century, it was split into three separate constellations. Additionally, another constellation, the Compass, was introduced. As a result, four new groups of stars emerged from the original Ship of Argo.
It wasn’t until 1930 that the precise tally of constellations in the sky was established within the scientific community. Scientists concluded that there are a total of 88 constellations, which includes 13 constellations that fall under the zodiacal category.
What do we understand by the term “zodiacal constellations”?
The term “zodiacal constellations” refers to the constellations that the Sun moves through throughout the year.


The Big Dipper and the Little Dipper
The most well-known star formations visible in the night sky are the Big Dipper and the Little Dipper.
The Big Dipper constellation consists of seven stars arranged in the shape of a ladle with a handle. It can be seen in the northern hemisphere. Each star has its own name. This is one of the largest constellations among the three.
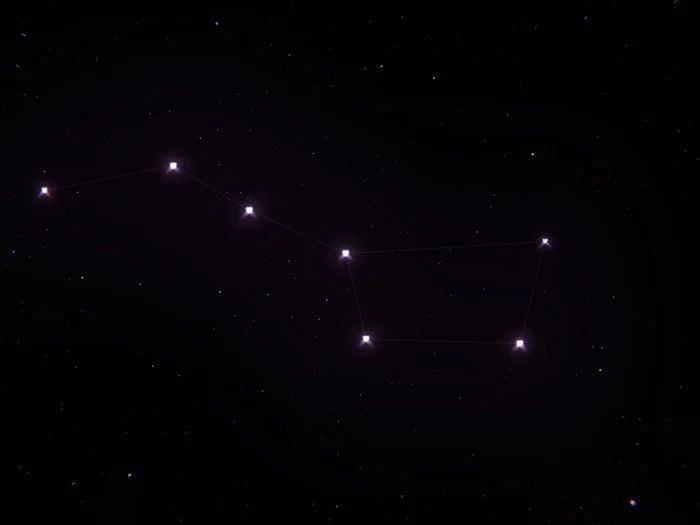

What is the reason behind the dipper being referred to as the bear?
Actually, there are numerous other stars within the constellation, but they are all quite faint, and some cannot even be observed with astronomical instruments. The section that looks like a dipper corresponds to the bear’s tail and half of its back. The entire constellation simply resembles this predatory creature.
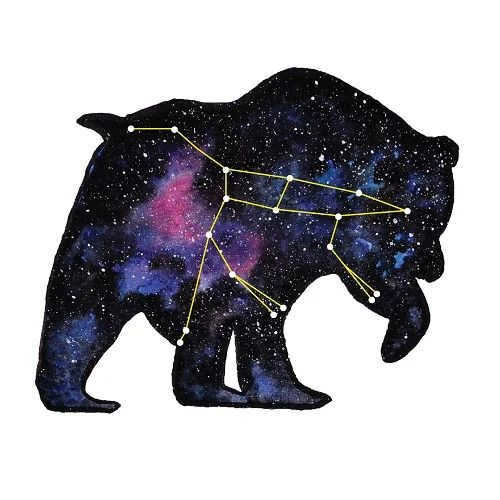

From the constellation Ursa Major, you can locate Ursa Minor and Polaris within it. To accomplish this, simply draw a straight line from the brightest star in Ursa Major, known as Dubhe. This line will lead you to the brightest star in the entire night sky, which is Polaris.
What is the significance of Polaris being called the guiding star?
Its ability to consistently point towards the North gives Polaris its name as the guiding star. This makes it a valuable tool for lost travelers who can use Polaris to orient themselves. Polaris is situated in the constellation Ursa Minor.
According to ancient Greek mythology, there is a fascinating legend behind the origins of these constellations. The story revolves around a queen named Callisto who resided in the state of Arcadia. Renowned for her extraordinary beauty, Callisto incurred the wrath of Zeus’ wife, who decided to cast a spell on her. As a result, the once-glorious queen was transformed into a majestic bear and left to wander through the enchanting woods. One fateful day, Callisto stumbled upon a hunter, and to her astonishment, she recognized him as her own son. Overwhelmed with joy and longing after her prolonged journey, Callisto approached her son, yearning to embrace him. However, the son failed to recognize his mother and, consumed by the hunter’s instinct, aimed his spear at her. Fortunately, the mighty Zeus intervened at the last moment, preventing the tragic fate from unfolding. In a bid to avert the impending disaster, Zeus transformed the young man into a bear cub. To commemorate this extraordinary tale, Zeus decided to immortalize Callisto and her son in the heavens, placing them in close proximity to one another.
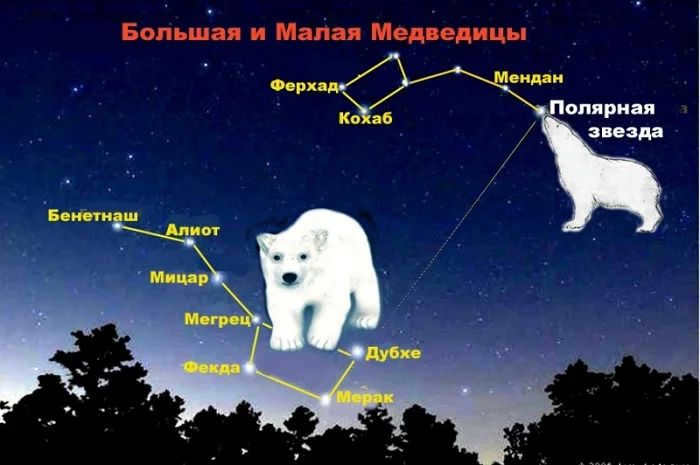
Source
Some well-known constellations include:
Legends about Scorpio and the Swan constellations
Scorpio is a widely recognized zodiacal constellation.
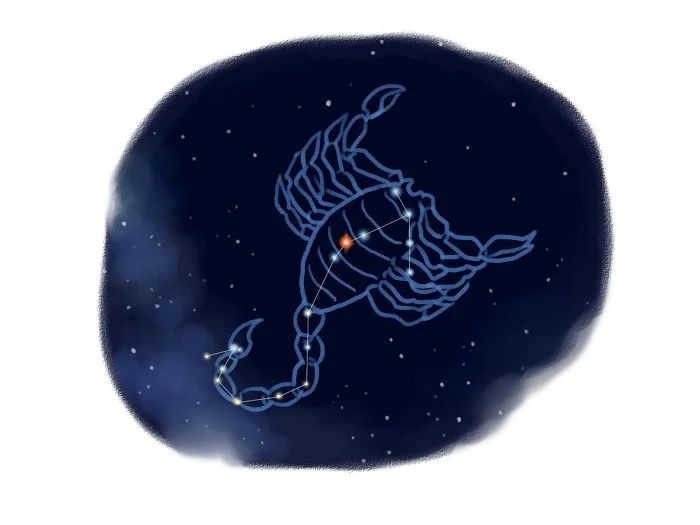

The constellation has 162 stars that are visible to the naked eye. There is a myth surrounding Artemis, the goddess of hunting. Artemis had a dispute with Orion, who claimed to be a superior hunter. Apollo, Artemis’ brother, took her side and decided to defend her honor. Apollo found a scorpion and sent it to Orion, who he was angry with.
Zeus intervened and placed Scorpion and Orion in the sky, but kept them separated so they would never cross paths and Scorpion couldn’t harm Orion.
That’s why when the Scorpio constellation appears in the east, Orion becomes visible in the west.
The Swan constellation also has an intriguing history and is considered one of the oldest constellations.
In ancient depictions, the avian creature gracefully glides through the atmosphere, extending its wings and elongating its neck. The prevailing legend surrounding this group of stars is intertwined with the renowned figure of Zeus. Enamored with Leda, the god transformed into a swan to win her affection. Afterward, he soared into the heavens, metamorphosing into a constellation.
The notion of a constellation remains a fluid concept. Over time, stars undergo shifts in their celestial positions. Astronomers propose that even the configuration of the highly popular Big Dipper will alter within a few decades.
The Milky Way
The Milky Way traverses numerous constellations and is visible to the naked eye. This vast expanse of white haze is filled with countless luminous stars, constituting what we refer to as a galaxy. When observing the Milky Way through a telescope, one can discern that it is not a nebula, but rather a collection of billions of stars, both large and small. Scientists have estimated that the approximate number of stars in the Milky Way is a staggering 400 billion.

In addition to the stars, the moon can be seen in the night sky. However, it is not a star like the Sun. So why does it have a yellow glow? In ancient times, when people had limited knowledge about celestial objects and relied heavily on religion, the explanation was simple – the moon was believed to be a source of light that dispelled the darkness of night.
The moon itself cannot emit light, but it can reflect the light of the Sun. This is because its surface is partially composed of glass rocks. These rocks act like mirrors, reflecting the Sun’s rays and directing them back towards Earth.
The movement of the sun is responsible for the transition between day and night as well as the changing of seasons. In addition to its rotation on its own axis, the Earth also orbits around the Sun. This journey takes approximately 365 days to complete. Throughout this time, winter gives way to spring, spring transitions to summer, summer transforms into fall, and fall eventually returns to winter. The planet’s path is not a perfect circle, but rather an oval, resulting in varying distances from the Sun, the celestial body that provides heat and light.
However, the primary factor behind the changing seasons is not solely the distance to the Sun. The presence of warmth or coldness depends on the angle at which the Earth’s axis is inclined in relation to its rotation. This axis is an imaginary line and does not physically exist. As the Earth tilts at different angles, different parts of its surface are exposed to the rays of the sun.
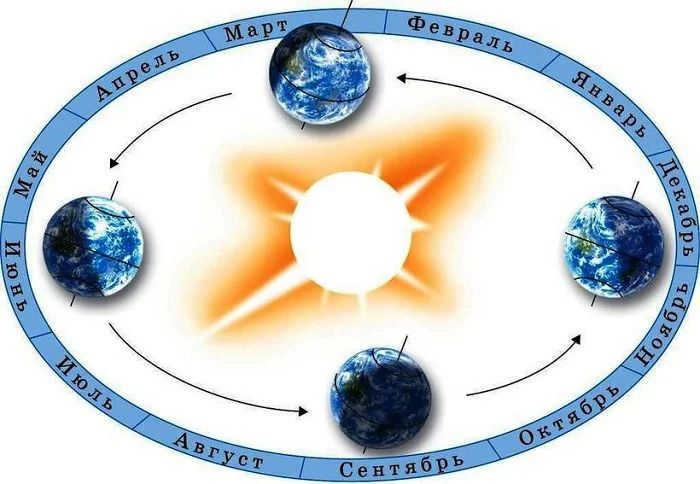
Source
The Sun is the closest star to Earth. It is responsible for providing heat and light, which are essential for all living beings on our planet. Although the Sun becomes invisible at night, there are other stars that also emit light.
The sky holds numerous enigmas and secrets. Outer space remains largely uncharted territory for astronomers and scientists.
Our planet is a part of a system, with the Sun at its center. The Sun remains fixed in one position, while other celestial bodies orbit around it. The Earth experiences different seasons due to the uneven illumination it receives from varying angles. Additionally, the rotation of the Earth on its axis causes periods of day and night, with alternating periods of light and darkness. Traditionally, it is believed that the Sun rises in the east and sets in the west, with the east being the stable location of its appearance and the west being where it disappears every evening. However, this is only true on two specific days of the year: March 21 and September 23, known as the spring and fall equinoxes. On these days, the Sun’s rays illuminate the Earth’s surface equally from the Far North to the South Pole. During all other times, the Sun moves from north to south. Let’s explore why the Sun rises and sets in different locations, and why the rising rays no longer shine directly into a room as they did before.
What is the phenomenon of sunrise?
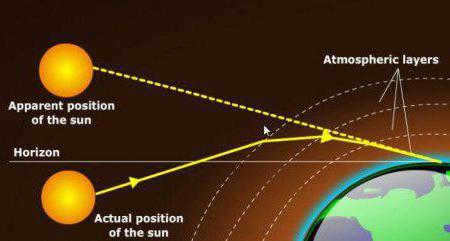
The period when the upper edge of the solar disk appears on the horizon is referred to by various names: birth, the start of a new day, or the morning dawn. However, astronomers define sunrise as the moment when the sun completely crosses the horizon line. The presence of the atmosphere plays a role in determining the exact timing of this phenomenon, due to atmospheric refraction – the bending of light rays as they pass through different layers of the atmosphere. As a result of this refraction, an observer on Earth sees the sunrise slightly earlier than the actual moment, and certain regions experience a longer duration of daylight:
Fun fact! In the polar regions, the transition from polar night to polar day takes approximately 2 days.
Understanding the Phenomenon of Sunset
As the sun descends towards the western horizon, its radiant disk gradually loses its luminosity. Initially, it takes on a yellow hue, then transitions to orange before finally transforming into various shades of red. Simultaneously, the surrounding sky undergoes a remarkable transformation, transitioning from a golden hue to a deep blood-red color against a backdrop of blue or occasionally green.
While beholding the breathtaking spectacle of a sunset, it is worth diverting one’s attention to the exact opposite side, where a peculiar phenomenon occurs. Here, the Earth’s shadow manifests as a strip of bluish ash color, with a vibrant segment known as the Belt of Venus appearing just above it. This awe-inspiring spectacle can be observed anywhere in the world, provided the sky is clear and devoid of clouds.

Sunset
The colors become more intense as the Sun sinks below the horizon. As soon as the Sun is no longer visible, the Buddha Rays emerge, initially vibrant and gradually fading with each passing minute until they transform into red streaks. Meanwhile, the Belt of Venus dissipates on the opposite side, making way for the Moon to rise and night to descend.
How to differentiate between a sunset and a sunrise
Sunrises and sunsets serve as evidence of the Earth’s rotation around its axis. At first glance, they may appear to be identical. However, those who wake up early have the opportunity to compare them: the rays of the rising sun are brighter and the surrounding colors take on delicate shades. On the other hand, sunsets are characterized by the luminary and the surrounding sky disk being tinged with shades of red. The reason for this evening coloring is the visibility of dust particles that become more noticeable in the lower humidity conditions of the evening, due to the strengthening of air currents.
Enchanting dates of equinoxes and solstices
Twice a year, the Earth aligns with our celestial body at a 90-degree angle. This year, this celestial event will occur on March 19 and September 22. On these remarkable days, regardless of your location on the planet, the sun will rise and set precisely at six o’clock in the morning and evening, respectively. These moments provide a convenient opportunity to accurately determine the local time. In the northern regions, twilight and dawn linger in the sky, painting mesmerizing landscapes. In tropical latitudes, the sun swiftly descends below the horizon, casting a breathtaking spectacle. However, the true essence lies beyond these phenomena. It is worth noting that the perceived length of daylight can be visually diminished by the presence of clouds, creating a unique atmospheric ambiance.
There are two additional dates that should be kept in mind: the winter and summer solstice. In the northern hemisphere, December 21 marks the day with the longest night. Conversely, on June 21, the sun lingers in the sky without haste. During this date, the night does not arrive within the northern polar circle, while December 21 does not transition into daytime. However, when does dawn arrive during the summer and winter solstice in the region of our concern?

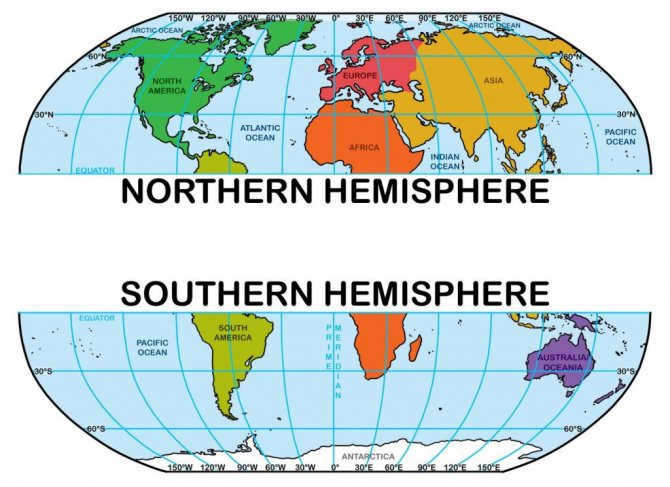
The Various Types of Hemispheres and Their Distinctions
Our vibrant planet is conventionally partitioned into four hemispheres: the Northern and Southern hemispheres, which divide the Earth along the equator, and the Western and Eastern hemispheres, which are demarcated by the Greenwich and 180⁰ meridians. The Northern and Southern hemispheres play a crucial role in regulating the seasons. These seasonal variations are a consequence of our planet’s rotation around the Sun and the unequal distribution of sunlight. During the winter months in the Northern Hemisphere, the Southern Hemisphere experiences summer, and vice versa. Likewise, when the Southern Hemisphere is blanketed in snow, the Northern Hemisphere is basking in warmth.
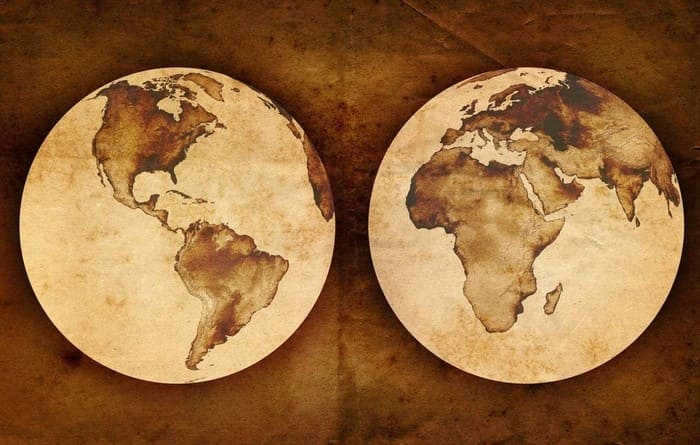
Types of hemispheres
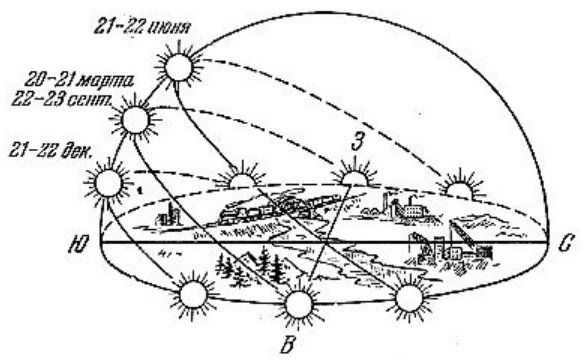
The directions of sunrise and sunset in the Northern Hemisphere are as follows:
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
| Sunrise | Northeast | Northeast | Southeast | Southeast |
| Sunset | Northwest | Northwest | Southwest | Southwest |
In order to see the sunrise directly in the east and the sunset in the west, one must wait until the vernal or autumnal equinox, which falls on March 20 or September 23.
There are two additional significant days to remember: the “solstice days”. These are the days when the sun is at its highest or lowest point above the Earth. The winter solstice occurs on December 21-22, while the summer solstice occurs on June 20-21.
Orienteering is a valuable skill not just for tourists, but for anyone interested in basic navigation. Here’s a guide on how to determine the correct direction when in either the Northern or Southern Hemisphere:
| Position yourself with your back to the Sun, facing your own shadow | ||
| Northern Hemisphere | Southern Hemisphere | |
| Front | North | South |
| Behind | South | North |
| Left | West | East |
| Right | East | West |
Movement of the point where the sun sets
The sun only sets in the West twice a year. These dates are March 20th and 21st, and September 22nd and 23rd. They are also known as the equinox days. During these days, the sun sets exactly in the West, and the length of the day is twelve hours. These dates might be the only ones when the sun truly sets in the Western part of the horizon.
Once the vernal equinox is over, the sun starts to move higher in the sky, causing the days to become longer. As a result, the points where the sun rises and sets gradually shift towards the north each day. This process continues until June 21st, which is the summer solstice. On this day, the point where the sun sets is at its maximum northern position, and the duration of the day is the longest.
Starting from June 22nd, the position of the sunset shifts gradually towards the west, while the sunrise point moves towards the east. As a result, the duration of daylight decreases. From September 23rd onwards, the position where the sun rises starts to align with the point where it sets, happening south of the horizon. This pattern continues until the winter solstice. During this time, the sun appears and disappears south of its previous positions, making the night on this day the longest of the year.

It’s fascinating to note that on this particular day, the polar day transitions into the polar night. The Sun remains hidden below the horizon throughout the day. This occurrence is mainly attributed to the convergence of the points where the Sun sets and rises in the southern region. Following the winter solstice, a gradual transformation takes place. The locations of sunset and sunrise start shifting in the opposite direction, resulting in the lengthening of daylight hours.
Approximately 30% of the global population holds the belief that the Earth remains stationary while the Sun traverses the sky. This belief stems from the concept of relativity, where the perception of movement depends on the chosen frame of reference. Whether an object is considered to be in motion or not, and the direction and destination of its movement, are all subjectively evaluated based on one’s perspective.
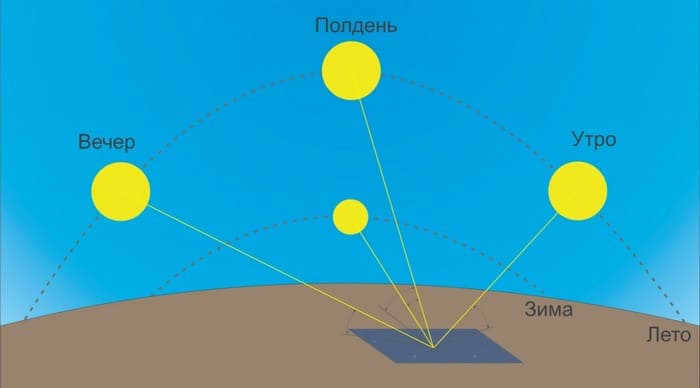
The movement of the sun
The Sun is the center of our solar system, and the Earth revolves around it while also rotating on its own axis. This rotation takes approximately 24 hours, which is known as a day. It is important to note that these rotations occur counterclockwise. As a result, the commonly held belief that the sun always rises in the east and sets in the west is not entirely accurate. The points at which the sun becomes visible are constantly changing. Depending on the season, the specific location where the sun rises will vary. Following the spring solstice, the sunrise and sunset points gradually shift towards the north. This shift continues until the fall equinox. Additionally, the further north one is located, the more the sunrise point shifts towards the west.
Let’s examine the algorithm for computing the duration of daylight and, consequently, the times of sunrise and sunset using the case of the capital city. On March 19th in Moscow, similar to everywhere else on the planet, the daylight will last for twelve hours. However, since the metropolis is situated slightly to the east of the UTC +3 hour meridian, the sun will rise there not at 6:00 but at 6:38, and it will set at 18:38. The duration of daylight continues to increase, reaching its peak at seventeen hours and twenty-five minutes on June 20th. We can conveniently determine the sunrise and sunset times for Moscow on this particular date. At noon, it will be 12:38. Consequently, the sun will rise at 3:48 and set at 21:13. Are you already aware of the difference from the meridian in your area? When is the actual noon there?
Where does the Sun go?
Imagine a completely flat and stationary planet. The source of light would always be directly above, and there would be no such thing as a sunrise or sunset. However, because the sun rises in the east and sets in the west, our life has become cyclical and filled with these beautiful events.
Every morning, the sun’s disk appears on the eastern side of the sky and follows a predictable path. The spot on the horizon where the sun disappears is commonly referred to as the west. In reality, the sun doesn’t actually set anywhere; it remains stationary while the Earth rotates towards or away from it. Once the Earth completes one full rotation, it’s daylight again. In astronomy, the moment of sunset is when the top of the sun’s disk becomes completely invisible over the horizon.
How the Sun’s Movement Works
When observing the Sun during the daytime (with the appropriate filter, of course!), it may seem stationary. However, it is important to mark a reference point, as within a few minutes, you will notice the movement of the shadow and the change in its length. You will also observe that the Sun has moved to the right, towards the west, relative to the object.
The Earth’s axis of rotation is not perpendicular to the plane of its orbit around the Sun, nor is it parallel to the axis of rotation of the Sun. The angle of inclination between these axes is 23 degrees. As a result, when transitioning from the Southern Hemisphere to the Northern Hemisphere, the Earth tilts upward by 23 degrees, and when transitioning back, it tilts downward by the same amount. Without this angle, our planet would not experience the change of seasons.
Motion of the Sun
The brightness of our planet at different times of the year relies directly on its distance from the Sun and the side that is facing it at any given moment. Here is how the Sun travels throughout the day:
The primary source of warmth emerges in the east at approximately 6 am, shifting westwards by 6 pm. Around midday, it reaches its highest point, known as its zenith, which aligns with the geographic south. However, it is important to consider the disparity between actual time and astronomical time in order to accurately determine the direction of the Sun, estimate the time, and locate a specific spot on a map. These are the essential factors to know in order to identify where the Sun rises and sets, as well as its daily and annual movement.
Here is one of the simplest and most popular methods to orient oneself using the Sun:
- The longitude of the location. The astronomical noon, which is the true noon, may not always align with the official noon recognized in a specific area. It is common to consider 12 o’clock as the midpoint of the day, disregarding the fact that the Sun has not yet reached the zenith (the highest point in its trajectory). When observing from the Earth’s surface, the sunrise always appears in the east, regardless of whether it is in the northern or southern hemisphere. Two individuals located at different longitudes will witness the Sun at its zenith at different times: first the person farther east, and then the person observing from the west.
- The movement of the Earth around the Sun is an interesting phenomenon. Instead of following a perfect circle, the Earth’s orbit is actually an ellipse. This means that the distance between the Earth and the Sun varies as the planet moves closer and farther away. As a result, the length of a solar day, which is the time between two consecutive solar noons, also differs. Another factor to consider is the Earth’s tilt relative to its axis of rotation. This tilt leads to a fascinating observation in the middle latitudes of the northern hemisphere. When marking the position of the sun at 12:00 each day, the path forms a figure-eight shape. This shape represents the sun’s location, sometimes on the southern side and sometimes on the northern side. Failing to account for these deviations can result in errors of up to 4⁰ in the middle latitudes and even more in the tropics.
- The sun is directly overhead at the zenith.
- During the solstice days, the sun is at its highest point at noon.
- In the mid-latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere, summer is in the north.
- In the southern hemisphere, the upper boundary of the tropics is in the south, and summer is strictly overhead.
- In the southern hemisphere, the lower boundary of the tropics is in the north, and winter is strictly overhead.
- At the equator, the sun is directly overhead during summer and winter, and from fall to spring equinox in the south, and from spring to fall equinox in the north.
- During winter, the days are shorter.
- In summer, the days are longer.
- Above the Arctic Circle, the sun does not appear for days or weeks during winter.
- Above the Arctic Circle, in summer, the sun does not set for days or weeks.
- when the northern hemisphere experiences the longest day, the southern hemisphere experiences the shortest day.
- when it’s winter in the northern hemisphere, it’s summer in the southern hemisphere.
- In the equatorial zone, twilight lasts for about 30 minutes.
- In temperate latitudes, twilight lasts for approximately 2 hours.
- In subpolar regions, twilight can last for several days.
- The biological rhythms of living organisms are influenced by the sun.
- By studying solar flares and magnetic storms, we can predict and prepare for weather-related events that may affect the population.
- The movement of the sun serves as a reliable guide for navigation.
- Astronomical calculations rely on key indicators of solar activity.
– Find a straight stick that is approximately 1 meter in length and insert it into the ground where the shadow is clearly visible.
– Make a mark at the end of the shadow.
– Wait for about 15 minutes, during which time the shadow will move.
– Set a second point at the new location of the shadow.
– Connect the two points with a straight line and extend it by 30 cm.
– Place your left foot on the first mark and your right foot on the second mark.
– In the Northern Hemisphere, this method will give you the Nordic direction.
EAST and WEST …
Like many others, I too learned about the different parts of the world through associations during my childhood. My parents used to tell me that;
When the Sun is directly overhead
It is commonly believed that at exactly 12 noon, the Sun is positioned in the southern sky. This assumption forms the foundation of orienteering, but it should be noted that it provides only a rough estimation of location.
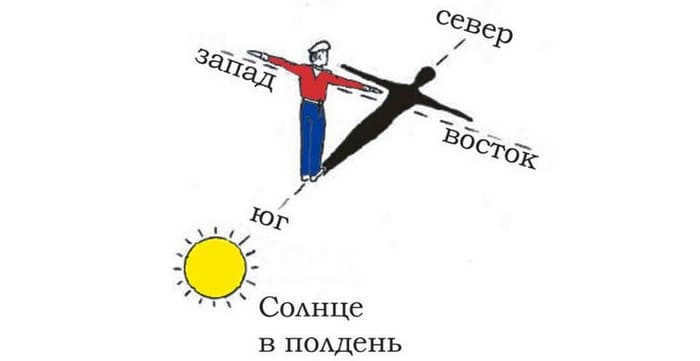
The position of the Sun at noon
There are various factors that influence the position of the Sun, proving that it is not always in the south at noon:
| The sun at the zenith | Solstice days, sun at noon | |
| Southern Hemisphere mid-latitudes | South | Summer is in the north |
| Upper boundary of the tropics S/hemisphere | South | Summer – strictly overhead |
| Lower boundary of the tropics S/hemisphere | North | Winter – strictly overhead |
| Equator | South (fall to spring equinox) North (spring to fall equinox) | Summer, winter, strictly overhead. |
So, when the tropical zones transition into temperate zones, the zenith (when the sun gives no shade) occurs once a year. Closer to the equator, this phenomenon is observed twice a year.
The table disputes the incorrect judgement of the time of day when the sun rises and sets.
Perspective from outer space
Not everyone has the opportunity to ascend into the atmosphere and witness the magnificence of the celestial bodies and observe their movement. Astronauts who have ventured into space describe their observations as follows: all planets rotate in a counterclockwise direction as they orbit the sun, traveling from west to east. Uranus is spinning in a unique orientation, possibly due to a shifted center of gravity, and Venus is rotating in the opposite direction, perhaps due to a collision with a meteorite thousands of years ago.
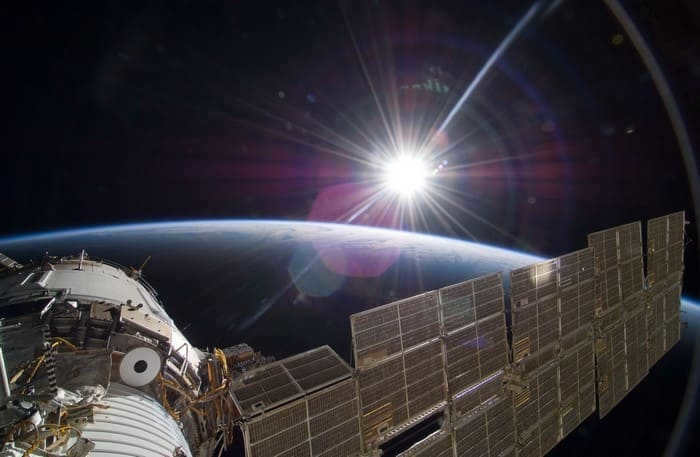

Observing the Sun from the International Space Station provides a unique perspective. Due to the ISS’s orbit around the Earth, astronauts have the opportunity to witness the sunrise of the solar disk multiple times a day, as the station completes its journey in just an hour and a half.
Fascinating fact! Interestingly, in space, the sunrise lasts only a few seconds. Captured by NASA astronauts, the photos showcase a breathtaking image of the sunrise: moments before the Sun emerges, the water surface takes on a stunning golden hue, and the clouds appear exceptionally captivating.
Polar explorers have made a fascinating discovery: while at the North Pole and observing the sunset, they have noticed that the sun moves from east to west, contrary to its usual movement from west to east. The North Pole is a unique location where day and night periods can last for up to six months. During the autumn equinox, the sun completes a full circle on the horizon. Each new day, it gradually rises higher in a spiral motion, reaching a maximum angle of 23-27⁰ during the summer solstice. The process then reverses, leading up to the fall equinox. At this point, the sun circles the entire horizon, and subsequently sinks deeper and deeper below it. The dawn can last anywhere from a week to a month and is visible from all directions. The phenomenon known as the white night gradually dims as it transitions into the middle of the polar night. However, the sun never goes below 23-27⁰ below the horizon, resulting in a constant brightness where the morning star can still be seen.
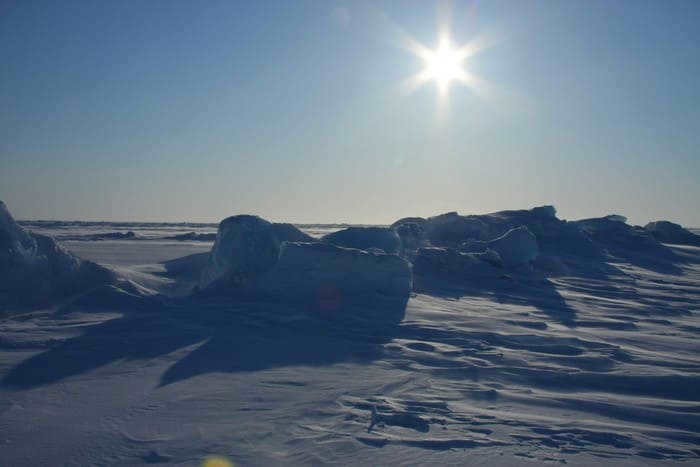

The position of the Sun in the sky at the North Pole is quite unique. If we compare it to a geographical point in the Southern Hemisphere that is at the same distance from the equator, we can observe a significant difference. At noon in the North, the Sun appears in the southern part of the sky, while in the Southern Hemisphere, it moves towards the north. Meanwhile, at the equator, the Sun’s position at noon varies throughout the year. For half of the year, it can be observed in the North, while for the other half, it is in the South. Interestingly, there are two days in a year when the Sun passes directly overhead at the equator.
Does the Sun really rise in the East and set in the West?
Contrary to popular belief, the Sun does not always rise in the East and set in the West. This phenomenon only occurs during the equinoxes, which happen twice a year.
In order to witness this rare occurrence of the Sun rising directly from the East, one must be located within the equatorial belt, anywhere between the two tropics. A perfect example of such a location is Reunion Island. To experience the Sun rising exactly in the East and setting exactly in the West, the observer must be at the equator during the equinoxes!
On any other day of the year, the Sun deviates from its East-West trajectory. Its farthest point from this position is reached during the solstice.
The sun reaches its highest point above the southern horizon, a phenomenon known as culmination. This is the moment when the sun passes over a point to the south, marking its peak position above the horizon.
Have you ever noticed how the length of daylight hours changes?
Does the sun move slower across the sky in summer and faster in winter? Absolutely not! It simply has different points of sunrise and sunset. After the vernal equinox, these points gradually shift northward, resulting in longer days.
On the day of the summer solstice, the Sun rises in the northeast and sets in the northwest, causing the convergence of the sunrise and sunset points. In regions near the poles, these points merge into a single position, right at the point north, resulting in the phenomenon known as polar day where the Sun remains above the horizon without setting. In temperate latitudes, on the day of the summer solstice, when the points of sunrise and sunset are closest to the point north, the duration of daylight is the longest, making it the peak of the year in terms of daylight hours.
This is what sunrise looks like at the North Pole.
Contrary to the northern hemisphere, in the southern hemisphere:
Unlike the northern hemisphere, in the southern hemisphere, the Sun reaches its highest point in the northern part, not the southern part. However, the Sun still rises and sets in the same manner in both hemispheres – in the eastern part of the sky and the western part of the sky, respectively.
If someone tells you that the Sun rises in the East and sets in the West, confidently correct them as this is inaccurate.
Twilight, also known as the hour periods in the evening before the main star has finally set and in the morning before it rises, is a captivating time of day. It has been the subject of inspiration for poets and filmmakers, who have sought to capture its mysterious essence. Lasting for approximately 2 hours, this enchanting phenomenon occurs when the rising and setting luminary casts its final rays onto the earth, which are then reflected in the upper atmosphere. However, it’s important to note that this duration of twilight is specific to Russia and temperate latitudes.

Twilight
The duration of twilight varies depending on the calendar and the observer’s location:
Note! Twilight is divided into three periods. Civil twilight occurs when the sun is 6⁰ below the horizon. Nautical twilight occurs when the sun is 6-12⁰ below the horizon. Astronomical twilight occurs when the sun is 12-18⁰ below the horizon. This is the darkest period before nightfall.
For a long time, people have observed a correlation between the movement of celestial bodies and events on Earth. This observation led to the creation of the first calendars, which were based on the movements of the sun and the moon. Today, our understanding of these celestial movements is based on scientific research of our hot planet:





