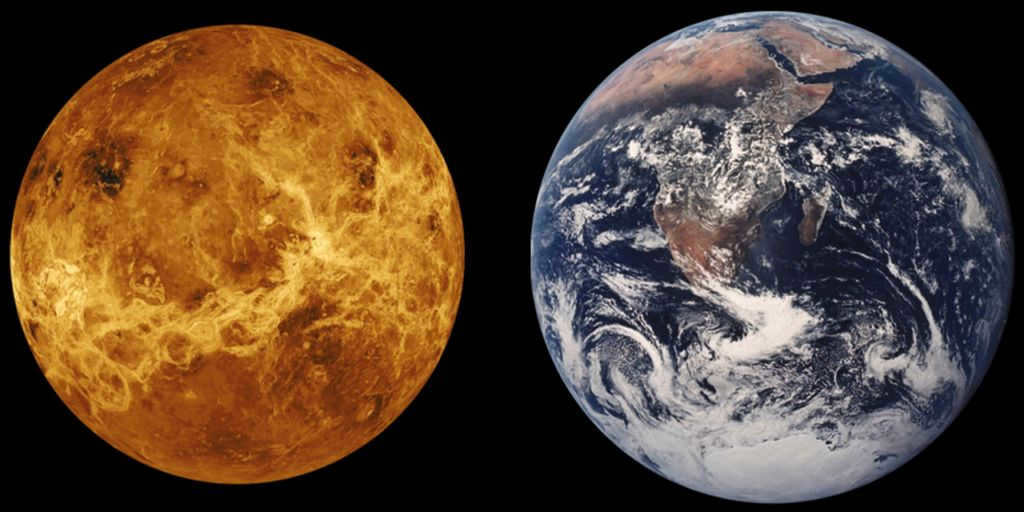
The question of whether Venus or Earth is the larger planet can only be answered through mathematical calculations. Even if these two celestial bodies were directly compared, it would not be possible to determine their relative size with the naked eye, as their diameters vary by a mere 5%. Although Venus and Earth share similarities in terms of mass and size, they differ significantly in temperature and other factors that could impact the potential for life to develop.

Comparison of Physical Characteristics of Venus and Earth
To facilitate comparison, the following table summarizes the main physical characteristics of Venus and Earth:
| Parameter | Venus | Earth |
| Radius, km | 6 052 | 6 371 |
| Mass in kilograms multiplied by 10 to the power of 21 | 4867.5 | 5972.37 |
| Volume in cubic meters multiplied by 10 to the power of 11 | 9.2843 | 10.8321 |
| Atmospheric pressure, kPa | 101 325 | 9200 |
| Average temperature, Celsius | 462 | 15 |
The orbit of Venus is situated at a shorter distance from the Sun compared to the Earth’s orbit, resulting in a higher average speed of the celestial body. Specifically, Venus travels at a speed of 35 km/sec while the Earth moves at 30 km/sec. Consequently, a year on Venus is shorter, spanning only 224.7 days in contrast to the Earth’s 365 days.
Comparison between Venus and Earth
By examining the table in the previous section, it becomes evident that Venus and Earth share numerous similarities. These types of celestial bodies are referred to as Earth-like planets. Apart from having almost identical mass and volume, the classification is based on the structural composition of these celestial objects.
Within their structure, the main elements can be clearly distinguished:
- The crust, which is considered to be denser than Earth’s crust;
- The mantle, estimated to be 3,300 kilometers thick;
- The core, which is further divided into solid and liquid components.
- tectonic movements;
- magnetic field presence;
- absence of surface water;
- a planet’s satellite orbiting it.
One more dissimilarity between Earth and Venus is the heightened volcanic activity. Instead of water, the Venusian surface is predominantly covered by solidified basaltic lava, which encompasses over 90% of the planet’s surface.
Both celestial bodies experience the alternation of day and night as a result of their rotation around their respective axes.
Nevertheless, based on this standard, the nearby celestial body presents a stark contrast to our own:
Venus, in terms of its day and year length, is more similar to Mercury than Earth. A day on Venus is longer than the time it takes for the planet to complete one orbit around the Sun. Unlike Earth, Venus lacks axial tilt, resulting in the absence of seasonal changes.
Planetary Atmospheres and Their Various Characteristics
The composition of the atmospheres on these planets exhibits significant variations. Nitrogen and oxygen are the primary components of Earth’s air. Conversely, carbon dioxide dominates the atmosphere of Venus, accounting for over 96% of its total mass. Additionally, trace amounts of nitrogen have been detected.
The clouds on Venus consist of sulfuric acid, resulting in an atmosphere that is nearly opaque to visible light. To observe its concealed surface, scientists employ radio waves and microwave radiation.
While Earth’s atmosphere experiences relatively calm air masses, Venus is characterized by intense circulation and rotation patterns. Consequently, the Venusian atmosphere completes a full revolution around the planet in just 96 Earth hours, whereas the planet itself takes 243 Earth days to complete its orbit.
One of the main distinctions between the two atmospheres lies in the pressure they generate. On Venus, the pressure is 93 times higher. This results in another significant distinction in the properties of the planet – the surface temperature. Venus reaches an average temperature of 462°C. This measurement aligns with the temperature recorded on the Sun-facing side of Mercury. The presence of the greenhouse effect contributes to this intense heat.
Venus is a celestial body that holds familiarity for every human being, situated near the Sun and the Moon. It is not coincidental that the planet is often referred to as Earth’s sister, as it shares certain characteristics such as mass and size. However, how does it differ from other entities within the solar system and what unique features does it possess?

The planet of the Roman goddess of beauty and love was given an unusually beautiful name. The Romans chose this name based on the planet’s high visibility and brightness, as they did not have advanced space exploration technology at that time and had limited knowledge about Venus. Ever since, the planet has been associated with femininity, love, and tenderness, reflecting the feminine characteristics of the celestial body. Ancient scholars even believed that the entire surface of Venus, like Earth, was covered in swampy forests and harbored life.
Venus is one of the eight main planets in our solar system and is the second closest to the Sun. The distance between Venus and the Sun is always greater than 48 degrees. Its average distance from the Sun is about 108 million kilometers. The distance between Venus and Earth can vary from 37 to 261 million kilometers. Venus takes approximately 225 Earth days to complete one orbit around the Sun, with an average orbital velocity of 35 km/s. In terms of size, Venus is very similar to Earth, with a radius that is 95% of Earth’s and a mass that is approximately 82% of Earth’s.
The luminous celestial body has captivated the attention of humanity throughout various historical eras. The exploration commenced with the Babylonians, who referred to the planet as Ishtar. However, it was the renowned Italian scientist and astronomer Galileo Galilei who made the most significant and pioneering observations of this celestial body using a rudimentary apparatus – a telescope. His scientific endeavors provided a fresh and genuine understanding of the planet. Subsequently, with the introduction of more advanced optical instruments like telescopes in 1610, individuals began to document the phases of Venus, which bore resemblance to the lunar phases. The initial observations unveiled certain similarities between the planet and our own Earth.
The positions of Venus change as it orbits around the Sun. During the full phase, the planet is behind the brightest object in outer space. The quaternary phase indicates the furthest elongation. The phases of Venus can be observed using a regular telescope. At a certain point in the study of the planet, its phases provided strong evidence for the heliocentric model of the solar system, as the celestial body directly rotates around the Sun.
Until the mid-twentieth century, scientists conducting research hoped to find signs of life on the surface of Venus, but space missions conducted by the USSR and the United States proved otherwise.
Venus’ atmosphere is still experiencing the ongoing loss of hydrogen and oxygen. Additionally, the planet exhibits evident signs of volcanic activity and contains traces of sulfur. The limited presence of craters indicates that Venus is relatively youthful, with an estimated age of around 500 million years. Notably, there is an absence of water on the planet. Furthermore, the lithosphere of Venus is characterized by its high viscosity and lack of mobility.
In terms of exploring Venus, the Soviet Union was the pioneering nation in constructing a spacecraft specifically designed for studying Venus. This satellite was launched on February 12, 1961. Subsequently, a multitude of satellites from the Soviet Union, United States, Europe, and Japan were sent to the planet’s surface. However, the research conducted using these specialized space devices was limited due to the harsh conditions on Venus, allowing for only a short period of operation, typically lasting two to three hours. Roscosmos has plans to send a new device to Venus that will be capable of conducting research for an entire month.
Comparison of the Sizes of Venus and Earth
Due to their close proximity to each other, Venus and Earth share some similarities in terms of structure and size, leading to an eternal rivalry between the two planets. However, it would be incorrect to claim that they are identical, as these celestial bodies are actually quite different. Despite this, there is a similarity in terms of size. The diameter of Venus is 12,100 kilometers, while the Earth has a diameter of 12,742 kilometers. In terms of mass, Venus weighs 4.867E24 kilograms, whereas Earth has a mass of 5.972E24 kilograms. Based on statistical data, the gravitational forces exerted by these planets also exhibit similarities.
Comparative features of the planets
Here are the main characteristics of Venus:
- Each planet has a core, crust, and mantle in its internal structure.
- Venus, unlike Earth, does not have plate tectonic rocks.
- The surface of Venus experiences a pressure 92 times greater than that of Earth.
- Unlike Earth, Venus does not have life-supporting elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, and other important elements. Its temperature is so high that it can melt even the strongest metals, with concentrations ranging from 95% to 97%.
- Venus does not have any moons.
- Venus is the nearest planet to Earth in the solar system.
- Venus and Uranus are the only two planets in the solar system that rotate clockwise.
- While a day on Earth lasts 24 hours, a day on Venus lasts longer than a year because it takes the planet 243 Earth days to complete one rotation on its axis.
- Venus is known for its constant thunderstorms, with rainfall consisting of sulfuric acid unlike Earth’s rain.
- Venus has a unique landscape with three large plateaus and a surrounding plain. Observing Venus is challenging due to its thick cloud layer, but scientists have managed to detect the plateaus using radar technology.
- One notable characteristic that sets Venus apart from the other planets in the solar system is its abundance of lava. The entire surface of the planet is comprised of this molten rock, unable to cool quickly due to the extreme temperatures. Venus is home to thousands of active volcanoes.
- The climate on Venus is extremely dry and hot, far surpassing the heat experienced on Earth, where temperatures reach a scorching 470 degrees Celsius. Venus is in a perpetual state of drought.
- The wind on the planet is a force to be reckoned with, as even the slightest breeze can escalate into a full-blown storm.
- Venus takes on a perfect spherical shape.
- The seasons on Venus remain constant, with no noticeable changes.
A Brief Overview of Venus
- Venus has a year that is 224.7 Earth days long.
- The planet takes 243 Earth days to complete one rotation around its axis.
- Unlike Earth, Venus does not have any natural satellites like the Moon.
- Venus and the Moon share similarities in terms of saturation and degree of illumination, but Venus ranks third in brightness, falling behind the Sun and Earth’s satellite.
- Venus has a dense atmosphere composed of 96-97% carbon dioxide.
- The atmospheric pressure on Venus is significantly higher than that on Earth, comparable to the pressure at a depth of 900 meters underwater.
- The average surface temperature on Venus is a scorching 735 Kelvin (462 Celsius).
- Venus exhibits a greenhouse effect.
- The distance between the planet and the Sun never exceeds 47.8 degrees.
- The hottest planet lacks a magnetic field on its surface.
- The celestial body’s atmosphere consists mainly of carbon dioxide (over 96%) and nitrogen (over 3%), with small amounts of sulfur dioxide, argon, and water vapor.
- At an altitude of 100 kilometers, there is an ozone layer.
- The planet is composed of seven layers: exosphere, thermosphere, mesopause, upper mesosphere, lower mesosphere, tropopause, and troposphere.
- The equator of the planet rotates at a speed of 6.52 kilometers per hour.
- Clouds cover the entire planet, providing significant protection from sunlight and preventing some light from reaching the surface.
The Milky Way galaxy is home to the eight largest planets that humans have discovered, and one of these planets, Venus, holds a significant position in this group. Venus is an extraordinary and unparalleled planet, and while it can be compared to other celestial giants like Mercury and Earth, it possesses a multitude of unique qualities that set it apart. For instance, Venus boasts large-scale winds and a landscape covered in volcanic activity, distinguishing it from its counterparts. With its vast uncharted territory, Venus remains a captivating and enigmatic planet. It is possible that in the coming centuries, humanity will gain a deeper understanding of its fascinating characteristics.
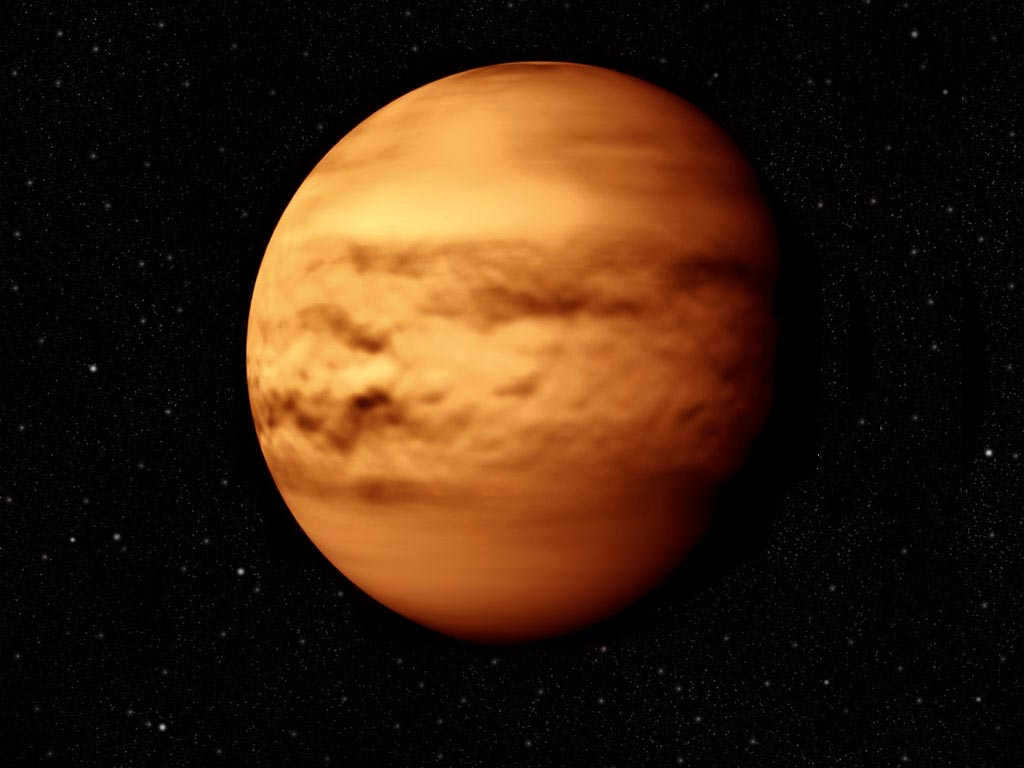

Venus, the second planet from the Sun, is the closest neighbor to Earth. However, this is not the only characteristic that sets it apart. While Venus and Earth have similar masses and diameters, they also possess notable distinctions.
Astronomy has been a known scientific field for a very long time. In ancient times, people developed an interest in celestial bodies and began to speculate about the existence of planets and stars. One of the first celestial bodies to be noticed was Venus, due to its brightness. However, it took nearly 3,000 years to observe Venus through a telescope. As early as 1600 BC, the Egyptians referred to it as the morning and evening star. However, active research on Venus only began in the early 1960s.
Both American and Soviet scientists made various attempts to explore Venus, with some being successful and others not. These efforts involved the launch of spacecraft that provided valuable information about the planet. As a result of successful missions, humanity gained knowledge about Venus’ mass, structure, density, volume, and diameter. Notable successful missions include the Soviet Venera-3 and Venera-4.
The missions of Venus 5 and 6 were equally fruitful, as they yielded additional data. However, their fate was sealed, as they succumbed to the immense atmospheric pressure a mere 20 kilometers away from the planet’s rugged terrain. On the other hand, the Venus Express endeavor triumphed and remains in orbit to this day.
The weight of the planet
The planet Venus has a mass of 4.87*10 24 kilograms. Venus is known for its heavy weight, which is not proportional to its size. This is because of the high density of its surface. The atmosphere of Venus is also very dense, with 96% carbon dioxide. This dense atmosphere creates a greenhouse effect, causing the temperature on Venus to rise to 462 degrees Celsius.
Researchers determined the weight of Venus by analyzing data sent by space stations. Since it is impossible to weigh a planet in the conventional sense, scientists calculated its mass based on information about its density and volume. The volume of Venus is 9.38*10 11 cubic kilometers, and the mass was calculated using this information.
Man has acquired knowledge about approximately 95% of the surface of Venus, the second planet from the Sun, at the start of the 21st century. This extensive research ensures that the data obtained is highly accurate, allowing us to confidently state that Venus has a mass of 4.87*10 21 tons.
Diameter and Radius
Due to Venus’ slow rotational speed, it maintains a nearly perfect spherical shape and does not experience significant stretching at the equator. As a result, the diameter of Venus remains consistent regardless of which point is measured.
The distance between the two farthest points on Venus is 12100 km or 12.1*10 6 meters. Consequently, the radius of Venus is 6050 kilometers, which is the distance one would need to travel to reach its core. Scientists hypothesize that Venus, similar to Earth, possesses a core.
Density
The high density of this celestial body is responsible for its relatively heavy weight. It is estimated to be around 5.2 grams per cubic centimeter. This is a result of a unique combination of rocks and metals. This explanation can be considered factual, assuming that there is a glowing metallic core surrounded by a rocky mantle within the planet. However, proving this theory is extremely challenging due to the difficulty in conducting appropriate analyses.
In addition to its density, Venus also possesses another notable characteristic – its atmosphere. The atmosphere of Venus is significantly denser compared to that of Earth. The atmospheric pressure on Venus is 93 times higher than what we experience on our own planet.
The normal viewing conditions on Venus are hindered by its height, density, and atmospheric composition. However, this also has its advantages, as meteorites are unable to reach the surface. The atmosphere is made up of carbon dioxide and clouds of sulfuric acid, which destroy anything that enters. Only bodies with a diameter of at least 50 km have a chance of surviving, but even they would lose a significant amount of mass upon impact.
Despite having a similar density to Earth, Venus is devoid of life and likely incapable of supporting it. None of Earth’s living creatures could survive on Venus, mainly due to the peculiarities of its atmosphere, extreme temperatures, and powerful winds that can reach speeds of up to 360 km/h. Venus is currently a lifeless planet, although it may have harbored life around three hundred million years ago when there was water present.
Comparison of Venus and Earth’s Size
Venus, often referred to as Earth’s sister planet, shares many similarities with its celestial relative:
- Venus has a radius of 6050km, while Earth’s radius measures 6371km;
- The mass ratio of Venus to Earth is approximately 4.87*10^24 kg to 5.97*10^24 kg;
- Venus has a volume of approximately 9.38*10^11 cubic kilometers, whereas Earth’s volume is about 1083.21*10^11 cubic kilometers.
However, despite these similarities, Venus and Earth have taken different evolutionary paths, resulting in significant differences. In terms of their orbits, Earth has greater distances, being approximately 40 million km farther away. On average, Earth is about 149 million km from the Sun (with aphelion at 152 million km and perihelion at 147 million km), while Venus is situated around 108 million km away (with aphelion at 107 million km and perihelion at 109 million km).
Comparison of planetary characteristics
When comparing Venus to other planets in the solar system, it is clear that Venus shares some similarities with Earth due to its high density. This is why Venus, the second closest planet to the Sun, is often grouped together with Earth. However, there are also several notable differences between Venus and the other planets:
- Venus rotates on its axis in a clockwise direction, which is opposite to the rotation of most other planets. This unique rotation is referred to as retrograde.
- Venus does not have any natural satellites, unlike Jupiter (which has 63), Uranus (which has 27), Mars (which has 2), and Neptune (which has 14).
- In terms of density, Venus has a higher density compared to other planets. Uranus, for example, is considered an ice planet, while Jupiter is classified as a gas giant.
- Jupiter has a perfect round shape due to its slow revolution around its axis, which takes 243 Earth days. This sets it apart from Venus, which has a “wide waist” because its complete revolution only takes 10 hours, despite being 1400 times larger in size.
- Venus shares some similarities with Mercury in terms of temperature. While Mercury can heat up to 425 degrees, Venus maintains a temperature of 462 degrees Celsius.
- When it comes to mass, Venus ranks third among all the planets in the solar system.
- Jupiter is also the largest planet in terms of physical size among all the celestial bodies in the solar system.
The exciting part about admiring the brightest star in the evening sky is the fact that you are observing a different planet while being on one yourself.
To avoid any confusion, the planet you are currently on is Earth, while the brightest star you see is actually Venus. It’s common for us to mix up the two.
Major discoveries
- While Earth possesses an atmosphere that supports life, Venus is characterized by an atmosphere that is highly toxic, primarily composed of carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid clouds.
- Unlike Earth, which maintains an average temperature of 15°C (59°F), Venus experiences surface temperatures that soar to a scorching 467°C (872°F).
- Earth benefits from a robust magnetic field that shields it from solar radiation, whereas Venus lacks this protective magnetic field.
Comparison of Earth and Venus
Earth, the third planet in our solar system, is known for its unique ability to support life. This is due to the favorable conditions for human existence found on our planet. Venus, on the other hand, is the second planet in our solar system. It is situated closer to the sun, resulting in extremely high temperatures that make life unsustainable. In fact, the scorching heat on Venus makes it impossible for any form of life to exist. Additionally, Venus has a much longer day compared to Earth, with one day on Venus lasting as long as 243 Earth days.

Life thrives on Earth, and its beauty is often celebrated.
We have all experienced this phenomenon at some point in our existence. The Earth’s surface is predominantly covered by water, which is crucial for supporting life.
Furthermore, Earth is positioned as the third planet from the Sun, strategically located to sustain diverse life forms. Conversely, Venus, despite being Earth’s twin, diverges from it in almost every aspect, if not all.
Venus, the brightest planet, resides as the second planet from the Sun.
One distinctive feature that sets this planet apart from our own is its “clockwise” rotation. As a result, the sun appears to set in the east and rise in the west, contrary to Earth’s rotation.
What is the Earth?
There is not much to be said about the beauty of the Earth. We have all witnessed it at some point during our existence.
The Earth’s surface is mainly covered by water, which is crucial for sustaining life on this planet. It also holds the position of being the third planet from the Sun, strategically located to support various life forms.
Life thrives on Earth due to the abundance of nitrogen and oxygen present in our atmosphere. These gases are essential for supporting life as we know it.
If the atmosphere consisted of different gases, like the ones found on other planets, it would be evident that sustaining life in such an environment would be impossible. However, this is not the only characteristic that sets our planet apart.
Besides the issue of climate change, the temperature is perfect for sustaining all types of organisms. Consequently, the combination of various factors renders this planet suitable for living, incredibly awe-inspiring, and enigmatic.
It possesses numerous components that add vibrancy to an otherwise ordinary and expansive landmass. Mountains, deserts, and other natural features all merit admiration.
But why limit ourselves to just the Earth? The Earth’s bodies of water would be dull and unremarkable without the presence of lagoons, oceans, rivers, and more.

What is Venus?
Venus stands out from our planet in several ways. One notable difference is its clockwise rotation, which means that the sun appears to set in the east and rise in the west.
Additionally, the speed at which Venus rotates is significantly different from that of Earth. Thankfully, we can appreciate the relatively faster rotation of our own planet.
Furthermore, the length of days and nights on Venus is much longer due to its slower rotation.
However, the extreme heat on Venus presents a major obstacle for potential inhabitants. The surface temperature there is nearly nine times hotter than on Earth!
Moreover, the atmospheric composition of Venus is also cause for concern, with high levels of carbon dioxide and clouds of sulfuric acid.
If the extreme temperatures don’t do us in, this will surely be the end of us. These aforementioned gases are causing the planet’s surface temperature to skyrocket.
And there’s more to include on the roster. It doesn’t even have a natural satellite.
To put it simply, it lacks a moon that orbits around it like our own planet does. It differs from our planet in terms of size, weight, and many other factors.

Venus and Earth exhibit several significant disparities. One notable distinction lies in their respective axial tilts.
Key Contrasts: Earth vs. Venus

- Earth and Venus have contrasting weights, with Venus being heavier due to its proximity to the Sun and higher temperature.
- The rotation of Earth is characterized as clockwise, whereas Venus rotates counterclockwise. This unique rotation direction sets Venus apart from Earth, resulting in the sun setting in the east and rising in the west on Venus.
- While Earth’s atmosphere consists of nitrogen and oxygen, Venus has a carbon dioxide-dominated atmosphere, with clouds composed of sulfuric acid.
- Another notable distinction is the surface temperature of the two planets. Earth is significantly colder, while Venus is scorching hot and capable of melting us before we even reach its atmosphere.
- These planets also have variations in the quantity of their satellites. While Earth possesses a single one, Venus is completely devoid of any.
I have dedicated a significant amount of effort to crafting this blog post in order to provide you with valuable information. It would greatly benefit me if you would consider sharing it on social media or with your friends and family. SHARE WITH ♥️
Throughout history, humans have always been intrigued by the vastness of space that remains unexplored. The exploration of other planets has captivated numerous scientific minds, while the general public is curious about what lies beyond our own planet. The planets within our solar system are the primary focus of scientific research, as they are the closest to Earth and therefore more accessible for study. Among these planets, Mars, known as the mysterious red planet, has garnered significant attention. In this article, we will compare the sizes of Mars and Earth and explore the reasons why this celestial body holds such a strong fascination for us.
When observed from our planet, the planets in our solar system appear as tiny, glowing specks that are difficult to perceive without magnification. However, Mars stands out among all of them – it appears larger than the other celestial objects and occasionally emits an orange glow that can even be seen without the aid of a telescope.
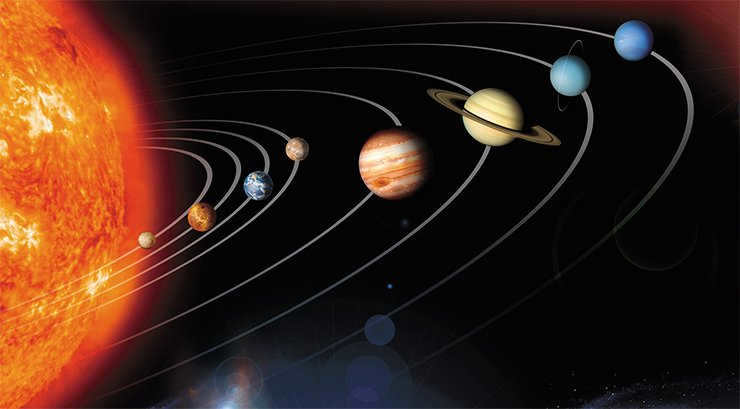
Is Mars bigger than Earth or is it smaller? Is Mars more visible because of its larger size or because it is closer to us? Let’s find the answer to this question. To do that, let’s take a look at the sizes of all the planets in the solar system. They can be divided into two groups.
The Earth: A Unique Member of the Planetary Group
Mercury, the smallest planet in our solar system, holds the distinction of being the closest to the Sun. With a diameter of 4878 kilometers, it is a remarkable celestial body.
Venus, the second planet from the Sun, is not only the closest to Earth but also the next farthest from the Sun. With its scorching surface temperature reaching up to +5000 degrees Celsius, Venus is a fascinating planet. Its diameter measures 12103 kilometers, making it larger than Mercury.
Unlike its neighboring planets, Earth stands out due to its unique features. With its atmosphere and water reserves, Earth has provided a favorable environment for the origin and flourishing of life. It surpasses Venus in size, with a diameter of 12,765 kilometers.
Mars, the fourth planet from the Sun, is smaller than Earth and possesses an equatorial diameter of 6786 kilometers. Its atmosphere is predominantly composed of carbon dioxide, accounting for almost 96% of its composition. Mars follows a more elongated rotational orbit compared to Earth.

Enormous planets
Jupiter is the most massive among all the planets in the entire solar system. It boasts a diameter of 143,000 kilometers. Composed mainly of swirling gas, Jupiter rotates on its axis at an incredibly fast rate, completing a full revolution in just 10 Earth hours. This massive planet is also orbited by a total of 16 satellites.
Saturn is a truly extraordinary planet. It possesses the lowest density among all the planets. Saturn is best known for its magnificent rings, which measure 115,000 kilometers in width and 5 kilometers in thickness. As the second largest planet in the solar system, Saturn has a size of 120,000 kilometers.
Neptune comprises a blend of gases, primarily methane, which gives the planet its distinctive blue hue. The surface of Neptune is enshrouded in clouds consisting of ammonia and water. The planet measures 49,528 kilometers in size.
Pluto, the farthest planet from the Sun, does not fall into any of the established planetary groups within the solar system. With a diameter half that of Mercury, it spans 2320 km.
Distinctive Traits of Mars: Comparing its Size to Earth
In this discussion, we will explore the dimensions of various celestial bodies within our solar system. Consequently, we can determine whether Mars or Earth boasts a larger size. By conducting a straightforward analysis of their respective diameters, we can easily make a comparison. Essentially, Mars is approximately half the size of Earth, earning it the title of the “Red Planet”.


Mars is an intriguing celestial body to investigate. Its planetary mass accounts for a mere 11% of Earth’s mass. The surface temperature on Mars fluctuates between +270 and -700 degrees Celsius throughout the day. This drastic variation is attributed to Mars’ less dense atmosphere, which primarily consists of carbon dioxide.
Describing Mars begins by highlighting its striking deep red hue. One might wonder what causes this distinctive coloration. The answer is rather straightforward – the composition of Mars’ soil, abundant in iron oxides, and the heightened concentration of carbon dioxide in its atmosphere. Due to this particular shade, ancient civilizations referred to the planet as “bloody” and named it after Ares, the Roman god of war.
The majority of the planet’s surface is comprised of deserts, although there are also areas of darker terrain that have yet to be fully explored. The northern hemisphere of Mars is relatively flat, while the southern hemisphere is slightly elevated compared to the average terrain and features numerous craters scattered across its surface.
It is not widely known, but Mars is home to the tallest mountain in the entire solar system, Olympus Mons. This colossal mountain reaches a height of 21 kilometers from its base to its summit and spans an impressive width of 500 kilometers.
The primary objective of astronomers is the quest for evidence of life in the vastness of the cosmos. To investigate Mars and determine the existence of living cells and organisms on its surface, Mars rovers have made multiple visits to the planet.

Multiple expeditions have already demonstrated that there was water present on the Red Planet in the past. It still exists, albeit in the form of ice, and is concealed beneath a thin layer of rocky soil. The presence of water is also evidenced by images that clearly depict the beds of Martian rivers.
Many scientists are eager to establish that humans can adapt to living on Mars. The following facts are presented as evidence to support this theory:
- The velocity of Mars and Earth is nearly identical.
- The gravitational fields are similar.
- Carbon dioxide can be utilized to generate essential oxygen.





