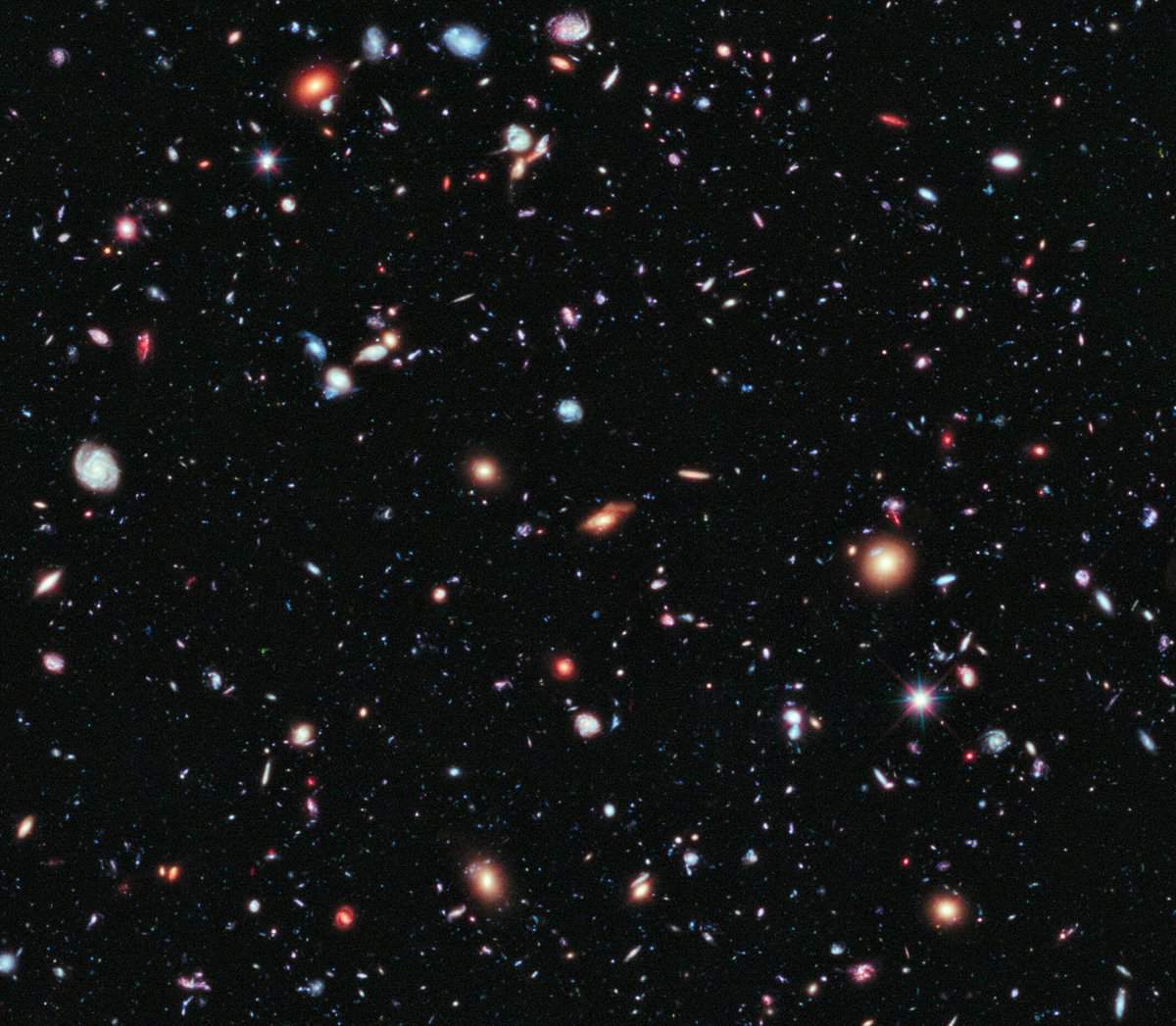
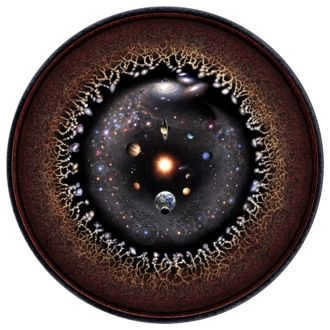
The Hubble Deep Field extreme (XDF) project was finalized in September 2012 and presents a collection of the farthest galaxies ever captured in a photograph. With the exclusion of a small number of stars located in the foreground (which are distinguishable due to their bright appearance and diffraction peaks), each individual entity depicted in the image represents a distinct galaxy, some of which are estimated to be as old as 13.2 billion years. It is believed that the observable universe encompasses over 2 trillion galaxies.
Cosmology (derived from the Greek word Κόσμος, kosmos meaning “world” and -λογία, -logia meaning “study”) is a field within astronomy dedicated to the examination of the timeline of the universe. Physical cosmology explores the origins of the universe, its large-scale structures and dynamics, and the eventual destiny of the universe, encompassing the scientific laws that govern these domains.
The term cosmology was initially introduced in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount’s ” Glossography,” and was later employed in Latin by the German philosopher Christian Wolff in his work ” Cosmologia Generalis.”
Religious or mythological cosmology refers to a system of beliefs rooted in mythological, religious, and esoteric literature and traditions, encompassing creation myths and eschatology.
Physical cosmology is the subject of study for scientists such as astronomers and physicists, as well as philosophers like metaphysicians, philosophers of physics, and philosophers of space and time. Due to its close relationship with philosophy, theories in physical cosmology may contain both scientific and non-scientific statements, and may rely on assumptions that cannot be empirically tested. While astronomy focuses on individual celestial objects, cosmology examines the universe as a whole. The Big Bang theory, which seeks to reconcile observational astronomy with particle physics, is the dominant theory in modern physical cosmology. Specifically, the Lambda-CDM model, which incorporates dark matter and dark energy, is the standard parameterization of the Big Bang.
The field of cosmology can be described as a “historical science,” according to theoretical astrophysicist David N. Spergel. This is because when we observe objects in space, we are actually looking back in time due to the finite speed of light.
Areas of Study
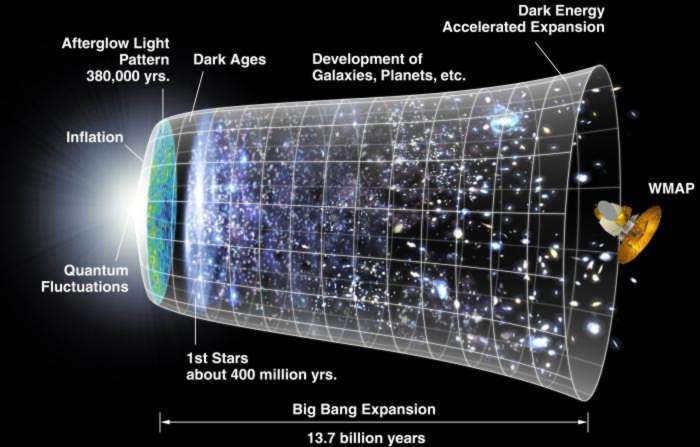
Physics and astrophysics have played key roles in advancing our understanding of the universe through scientific observation and experimentation. The study of physical cosmology relies on both mathematical analysis and observational data to explore the entire universe. It is widely accepted that the universe began with the Big Bang, followed by a period of cosmic inflation, during which space expanded rapidly. This event is believed to have occurred approximately 13.799 ± 0.021 billion years ago. Cosmogony investigates the origins of the universe, while cosmography focuses on mapping its various features.
Metaphysical cosmology is often defined as the positioning of human beings within the universe in relation to all other beings. One instance of this can be found in Marcus Aurelius’ contemplation on the role of humanity in this grand scheme: “A person who lacks understanding of the nature of the world will also lack knowledge of their own place within it, and someone who remains oblivious to the purpose of the world’s existence will struggle to comprehend their own identity or the true essence of the world itself.”
Explorations
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology is the field of physics and astrophysics that investigates the origins and development of the universe. It also examines the characteristics of the universe on a large scale. Initially, it encompassed what is now referred to as “celestial mechanics,” the study of celestial bodies. The ancient Greek philosophers Aristarchus of Samos, Aristotle, and Ptolemy put forth various cosmological hypotheses. Ptolemy’s geocentric model remained the prevailing belief until the 16th century when Copernicus, followed by Johannes Kepler and Galileo Galilei, proposed the heliocentric system. This example highlights one of the most well-known instances of the epistemological divide in physical cosmology.
“Foundations of Mathematics Isaac Newton’s ‘Foundations of Mathematics’, which was published in 1687, was the initial exposition of the concept of universal gravitation. This discovery offered a theoretical framework for understanding Kepler’s laws and also provided explanations for inconsistencies in earlier models that were caused by gravitational interactions among planets. The key distinction between Newton’s cosmology and its predecessors was the adoption of the Copernican principle, which asserted that the laws governing celestial bodies also applied to Earth. This revolutionary philosophical shift had a profound impact on the field of physical cosmology.”
The advent of modern scientific cosmology can be traced back to 1917 when Albert Einstein published his latest modification of the general theory of relativity in his article “Cosmological Considerations of the General Theory of Relativity” (although this article was not widely accessible outside Germany until after World War I). This breakthrough prompted cosmologists like Willem de Sitter, Karl Schwarzschild, and Arthur Eddington to explore its astronomical implications, enabling astronomers to study distant objects with greater precision. The prevailing notion of a static and unchanging universe began to shift. In 1922, Alexander Friedmann proposed the concept of an expanding universe populated by moving matter. Concurrently (between 1917 and 1922), the Great Debate took place, during which early cosmologists such as Heber Curtis and Ernst Epic determined that certain nebulae observed through telescopes were actually separate galaxies located far beyond our own.
In addition to the dynamic approach to cosmology, there was a long-standing discussion about the structure of the universe that was approaching a critical point. Harlow Shapley, an astronomer at Mt. Wilson, proposed a model in which the cosmos consisted solely of the Milky Way star system. On the other hand, Heber D. Curtis argued that spiral nebulae were independent star systems, comparable to island universes. This divergence of opinions came to a head with the organization of the Great Debate on April 26, 1920, during a meeting of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences in Washington, D.C. The debate was ultimately settled when Edwin Hubble discovered variable Cepheids in the Andromeda galaxy in 1923-1924. It became clear that the spiral nebulae were actually formed well beyond the confines of the Milky Way.
Since approximately 1990, cosmology has undergone a series of extraordinary advancements in observational science, transitioning from a primarily speculative field to a predictive one that exhibits precise alignment between theory and observation. These advancements encompass various breakthroughs, such as the examination of the microwave background through the utilization of COBE, WMAP, and Planck satellites, extensive redshift surveys of galaxies including 2dfGRS and SDSS, and the study of distant supernovae and gravitational lensing. Remarkably, these observations have corresponded with the predictions put forth by cosmic inflation theory, modified Big Bang theory, and a specific variant known as the Lambda-CDM model. As a result, this period has been widely regarded as the “golden age of cosmology”.
Gravitational waves were discovered by astronomers from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics on March 17, 2014, providing compelling evidence for inflation and the Big Bang. However, on June 19, 2014, it was reported that confidence in the verification of the cosmic inflation findings had decreased.
During the Planck 2014 conference in Ferrara, Italy, on December 1, 2014, astronomers revealed that the universe is approximately 13.8 billion years old and consists of 4.9% atomic matter, 26.6% dark matter, and 68.5% dark energy.
Religious or mythological cosmology
Religious or mythological cosmology encompasses a collection of beliefs rooted in mythological, religious, and esoteric writings, along with creation and eschatological traditions.
Philosophical cosmology
Cosmology explores the entirety of space, time, and all phenomena. Throughout history, it has possessed a wide-ranging focus and has often been intertwined with religious beliefs. In contemporary discourse, metaphysical cosmology delves into inquiries about the universe that surpass scientific explanations. Unlike religious cosmology, it approaches these inquiries through philosophical practices like dialectic. Modern metaphysical cosmology endeavors to provide answers to questions such as:
- What caused the universe to come into existence? Is its existence essential? (Refer to monism, pantheism, emanationism, and creationism)
- What are the fundamental building blocks of the universe? (Consider mechanism, dynamism, hylomorphism, and atomism)
- What is the fundamental cause for the presence of the universe? Is there a specific intention behind the cosmos? (refer to teleology)
- Does the presence of consciousness serve a purpose? How do we acquire knowledge about the entire cosmos? Does cosmological reasoning uncover metaphysical realities? (refer to epistemology)
k is equal to zero; Λ is equal to zero, representing the critical density.

Astronomy is a paradoxical field of study that humanity has created almost as if to challenge itself. It provides us with the opportunity to continuously make new breakthroughs through observations and calculations, yet these discoveries only serve to highlight how little we truly comprehend about the vast expanse of the Universe. We remain ignorant about the stars, the planets in our Solar System, and the Universe itself. Presently, there are several distinct branches within the realm of astronomy, with the most prominent ones being galactic and extragalactic astronomy, stellar physics, astrophysics, exobiology, astrochemistry, and cosmology. It is the latter discipline that we shall delve into and explore in great detail.

Definition of the concept
Two educational institutions, sharing a common belief
In contemporary times, the field of cosmology can be divided into two distinct branches, each with its own group of scientists. Empiricists, in their research, rely solely on observations of celestial bodies and matter. They do not create models or simulations of alternate realities in earthly conditions, as they believe that any such results would be far from the truth. Theorists, on the other hand, utilize calculations and the findings of various studies. Their work often involves constructing models of specific regions of space, such as black holes or other celestial objects. It is important to note that cosmology is a scientific discipline that explores the universe from both practical and theoretical perspectives. Despite their differences, both branches of cosmology share a common framework – the Big Bang Theory. This theory suggests that all of space and time originated from a highly dense and hot state. In contrast to the Big Bang Theory, there exists a lesser-known but still significant theory that posits the universe as a constant entity with no definitive beginning or end, devoid of any moments of birth or decline.
The fundamental principles underlying scientific knowledge
Cosmology relies on six fundamental principles that describe the structure of the universe:
- Space is isotropic, which means that all celestial objects, including planets, asteroids, galaxies, and black holes, exhibit chaotic motion. Cosmology aims to study this motion, which can lead to the accumulation of matter and the formation of regions with distorted space, high pressure, and temperature, or dispersion and the thinning of space in other areas.
- Continuous expansion of limits. The primary focus of cosmology is the study of the Universe’s evolution, and this progression can be considered as occurring right in front of our eyes. All celestial objects, particularly galaxies, are moving apart from one another. Additionally, as their dimensions increase, the rate at which distances grow also accelerates.
- The space encompassing our planet is likewise uniform. This implies that the Earth, as well as its orbit, is a typical constituent of the Universe, which in its composition will vary only slightly from, for instance, the regions near the planet Kepler-36B.
- The immense secrets of the Universe lie within its tiniest particles – atoms. As mentioned earlier, any given section of space will have the same composition as the previous one, as determined by researchers. For every 10 hydrogen atoms, there is 1 helium atom.
- On the other hand, a fact that further supports the theory of the universe’s constant expansion is that there are significantly more quasars found at greater distances from the Solar System. These distant quasars lead more active lives.

Cosmological Theories Exploring the Universe as a Unified Entity
The famous Big Bang theory encapsulates a concise history of the universe. It originated from Einstein’s general theory of relativity, which laid the foundation for the work of astronomers who constructed a model of expanding matter. This hypothesis was subsequently confirmed when scientist Hubble compared the distances between galaxies and the velocities at which they are receding from one another. The third confirmation arose from G. Gamowy, who discovered relic radiation. This pervasive phenomenon exists throughout the cosmos and resembles an “echo” from the epoch of the explosion.

Unveiling the astonishing temperatures of the cosmic detonation
When attempting to elucidate the origins of the cosmos to young minds, it is often explained that it was once smaller than a pea, yet contained unimaginable levels of temperature and pressure. In actuality, the concise history of the universe bears striking similarities to this toy-like model. The age of our surrounding world is estimated to be around 20 billion years. During the time when the universe was merely a singularity, the pressure within it reached an astounding 10^90 kg/cm^3. It is at this point that gravity came into existence. Interestingly, scientists argue that gravity is not a separate or distinct force, but rather a distortion of space that arises from the density of matter. This explains why solid celestial bodies possess a (albeit minimal) atmosphere encircling them, while gaseous objects and stars lack such a field. As a result, over the course of centuries, the cosmos has expanded, giving rise to distinct gravitational fields.

Alternative models of reality have been developed based on the Big Bang concept, which are equally valid as the main model. The conflict arises from the fact that the singularity of space during the moment of nucleation and the isotropy in the present can be theorized based on the study of the SS. However, beyond the known planetary orbits, there exist different conditions that may not be isotropic. This has led scientists to identify three cosmological problems that remain unsolved, but which stimulate further thinking and research. We will now discuss these problems in greater detail.
The concept of singularity
The notion that matter possessed a state of singularity at the very inception of existence is often dismissed as mere science fiction. The extraordinary density, warped spacetime, and unimaginable temperatures associated with this state have been theorized and calculated, but attempts to replicate such conditions on Earth have proven futile, even on a small scale. Consequently, cosmology’s primary challenge lies in refuting the notion of a singular world at the moment of its birth. Instead, it is proposed that the universe began in a different state of matter.
Isotropy Deficiency
The consensus among theorists is that the entirety of space within the cosmos is uniform, however observations indicate otherwise. Investigations into the depths of the Universe reveal the existence of extraordinary galaxy clusters in some regions, while others remain largely empty. It is evident that the density of matter in these distinct parts of space cannot be equal. Thus, it can be concluded that the Universe is characterized by anisotropy, and its chemical composition exhibits variations across different regions.
In today’s world, scientists are fascinated by the enigmas of the cosmos that can be found within its microscopic components, as these hold the key to determining the course of future events. By calculating the average density of matter, researchers can determine whether the universe will undergo a contraction or an expansion. If the density surpasses a critical threshold, the universe will shrink and a cataclysmic explosion will be imminent. Conversely, if the density falls below this threshold, the universe will continue to expand indefinitely, making it impossible to measure its vast expanse, volume, and duration.
A different framework explaining the beginning and development of the Universe
The field of scientific cosmology is constantly evolving, with new discoveries and theories being generated on a daily basis. One such theory is the concept of asymmetry, which explores the interaction between matter and antimatter. It is hypothesized that relic radiation in the cosmos is a result of this interaction, with both matter and antimatter playing important roles. However, it is important to note that matter is much more prevalent in the universe, while antimatter exists primarily in calculations. Scientists believe that during the first ten seconds of the universe’s existence, a symmetry breakdown occurred, leaving antiparticles in the minority compared to particles. The exact reasons for this asymmetry remain unknown.
Concluding Remarks
Cosmology is an area of study dedicated to understanding the entirety of the universe. It is a theoretical discipline that seeks to provide logical explanations for the various phenomena observed in the cosmos, elucidating the movements of galaxies and stars.

The vastness and variety of the world around us can captivate anyone’s imagination. Everything and everyone that surrounds us, from the natural world to the microscopic realm, is filled with wonder.

Currently, the inquiry regarding the definition of the singularity is causing a great deal of curiosity among not only science enthusiasts but also the most prominent researchers globally. This concept can be found in various fields such as mathematics, physics, astronomy, cosmology, and other precise disciplines. The way it is understood and explained may differ depending on the context.
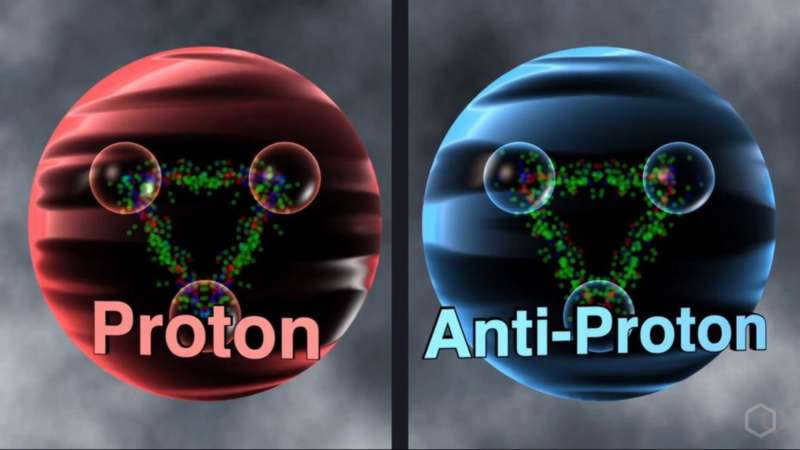

Antimatter is a unique substance composed of antiparticles. It is an intriguing concept in the field of physics, where matter and antimatter play crucial roles. Throughout history, scientists have made remarkable progress in the experimental detection of antimatter. The applications of antimatter are extensive and diverse. However, one question that often arises is the cost and storage of antimatter. Understanding the value and proper handling of this extraordinary substance is of utmost importance.

Being fascinated by cosmic processes and phenomena, an astronomer is an individual who explores the mysteries of the sky. The origins of astronomy can be traced back to ancient times when the first inquisitive minds started pondering the enigmas of the celestial realm. Delve into our enlightening article to discover the pioneering figures who paved the way for the captivating field of astronomy.

The clash between Giordano Bruno and the Roman Catholic Church has, in its own right, become one of the most remarkable and extensively examined conflicts in history. This philosopher and intellectual was executed by being burned at the stake, not only for his scientific theories, but also for his heretical religious declarations.

The vibrations of strings and branes are responsible for the formation of all substances in our universe. The superstring theory, which encompasses these vibrations, also introduces the concept of gravity. This is why scientists consider it to hold the answer to the unification of all known forces.
Copernicus introduced the heliocentric system of the universe, which was a groundbreaking revolution in the field of astronomy. This article aims to provide an introduction to Copernicus and shed light on his significant contributions to the scientific community. However, prior to Copernicus, Ptolemy had put forward an alternative model, which we will briefly discuss.

Cosmogonic myths are a kind of stories that describe the process of chaos turning into space. The term “cosmogony” is derived from two Greek words: “cosmos” meaning world or universe, and “gony” meaning arising. In the myths, chaos (also known as emptiness, derived from the Greek word “khao” which means to yawn) represents the primal state, the shapeless substance from which the world is formed.

At present, there are extra aggregated discounts (ranging from 2% to 25%) that can be availed by 58,754 educational establishments. To determine the specific discount applicable to all staff members in your educational institution, kindly access your personal Infoworks account.


Are you looking to enhance your skills and knowledge in the field of librarian activity? Join our professional retraining course and learn about the organization of librarian activity in professional education.
Get Discount for Your Educational Institution
We are pleased to offer a special discount for your educational institution. The discount amount depends on the number of your colleagues who have already taken the Infoworks course. By adding your educational institution’s discount, you can save even more.
Currently, we have additional cumulative discounts available for 58,754 educational institutions. To find out the exact discount that applies to all employees of your educational institution, simply log in to your personal Infoworks account.




Advanced training program
Expert in occupational safety
We have the ability to include your school’s discount along with this promotion (this will depend on the number of your colleagues who have completed Infowork courses).
At present, there are 58,754 educational institutions eligible for additional discounts (ranging from 2% to 25%). To find out the specific discount available to all employees of your educational institution, please log in to your personal Infoworks account.


Effective software solutions for the production of interactive multimedia presentations
Breakdown of the presentation based on individual slides:

Slide 1: Natural Science Picture of the World (ENCM)
Lecture topic #4 (part 1)
Overview of the Universe
Presenter: Oksana Vladimirovna Silakova, Associate Professor at the Chair of Life Safety Education Methodology

2 slide
The cosmos is the surrounding world, boundless in space, time, and diversity of matter and its transformations. The entire cosmos is explored through the field of astronomy.
Astronomy (derived from the Greek words astron meaning “star” and nomos meaning “science”) is the discipline that investigates the movement, structure, origin, and evolution of celestial bodies, their systems, and the cosmos as a whole. The primary means of acquiring astronomical knowledge is through observation, as experimental methods are generally infeasible for studying the cosmos.

Slide 3: Cosmology is a scientific discipline that focuses on understanding the Universe as a unified entity and its various cosmic systems. By examining the ancient Greek interpretation of the word “cosmos” as “order” or “harmony,” it becomes clear that cosmology seeks to uncover the underlying order in our world and identify the principles governing its operations. Ultimately, the objective of studying the Universe as a cohesive entity is to uncover these fundamental laws.

Slide 4 Cosmology and cosmogony are closely intertwined disciplines within astronomy that explore the origins of cosmic objects and systems.
However, cosmology and cosmogony approach the study of these phenomena differently – cosmology focuses on understanding the overall laws and patterns of the entire Universe, while cosmogony examines the formation and development of specific celestial bodies and systems.


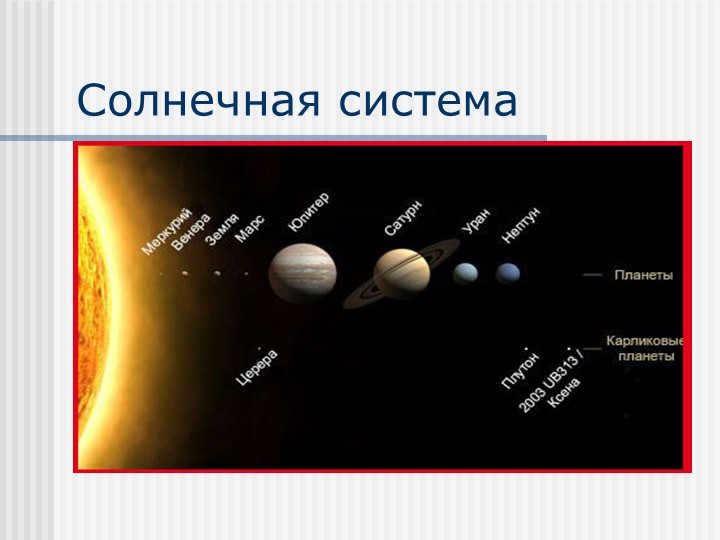
Slide 5 showcases stars, which are massive glowing self-luminous celestial objects. Planets, on the other hand, are chilly celestial bodies that revolve around a star and emit light that is reflected from the star. Satellites, which orbit planets, are also cold celestial bodies that shine light reflected from stars. Consequently, the solar system (or planetary system) is a collection of celestial bodies – planets, their satellites, asteroids, comets – that orbit around the Sun due to its gravitational force. The Solar System consists of 9 planets, their satellites, over 100 thousand asteroids, and numerous comets.

Asteroids (also known as minor planets) are small frigid celestial objects that form part of the Solar System. They range in diameter from 800 km to less than 1 km and orbit the Sun in accordance with the same principles that govern the movement of larger planets.
Comets, on the other hand, are celestial bodies that are also part of the solar system. They are characterized by their hazy, nebulous appearance with a luminous core known as the nucleus. The nuclei of comets are relatively small, measuring just a few kilometers in size.


Slide 8: A galaxy is an enormous star system that consists of more than 100 billion stars revolving around its central point.
Star clusters are collections of stars that are closer to each other compared to the typical distances between stars in interstellar space. These stars are bound together by their shared motion in space and have a common origin.

Slide 9: A metagalaxy is a magnificent collection of separate galaxies and clusters of galaxies.
In the modern understanding, the terms “Metagalaxy” and “Universe” are often used interchangeably.
However, sometimes the Metagalaxy is only considered as the visible portion of the Universe, while the Universe is thought to be infinite.


Slide number 10: When exploring entities within the cosmos, individuals confront exceedingly immense distances.
To facilitate the measurement of incredibly vast distances in cosmology, specialized units are employed:
– the astronomical unit (a.e.) represents the distance from Earth to the Sun, which is approximately 150 million kilometers.
This unit is typically utilized for determining cosmic distances within our Solar System. For instance, the distance from the Sun to Pluto, the farthest planet, is 40 a.u.;
– a light-year represents the distance traveled by a beam of light moving at a speed of 300,000 km/s in the span of one year. This equates to roughly 10^13 km.
1 a.u. is equivalent to 8.3 light minutes. Distances to stars and other cosmic entities beyond our Solar System are expressed in light-years;
– a parsec (pc) is a distance equivalent to 3.3 light-years. It is employed to measure distances within and between star systems.

Slide 11: The tasks of contemporary astronomy encompass more than just explaining astronomical observations. They also involve investigating the unfolding and development of the Universe. This field of study, known as cosmology, is currently experiencing rapid growth and advancement.
Understanding the evolution of the Universe is predicated on several key principles:
– The assumption that universal physical laws hold true throughout the entire cosmos.
– Recognizing that conclusions drawn from astronomical observations are applicable to the entirety of the universe.
– Accepting as true only those conclusions that do not contradict the possibility of human existence, known as the anthropic principle.


12 slide
A model (derived from the Latin word modulus, meaning sample or norm) serves as a representation of a particular section of the natural or social reality (the original) and provides a possible explanation for it.
Modern cosmology follows an evolutionary approach to understanding the origins and development of the Universe. In accordance with this approach, a model of an expanding Universe has been constructed.

Slide 13 The model of the evolving expanding Universe was developed based on the general theory of relativity proposed by A. Einstein, a German physicist, in 1915. According to this model, the Universe exhibits the following characteristics:
– Homogeneity, meaning it has the same properties at all points.
– Isotropy, meaning it has the same properties in all directions.
– Nonstationarity.
In 1922, A.A. Fridman, a Russian physicist and mathematician, was the first to conclude that the Universe is non-stationary.


On 14th slide of 1929, Edwin Hubble, an American astronomer, made a significant discovery called the “redshift”. This term refers to the decrease in the frequencies of electromagnetic radiation, specifically in the visible part of the spectrum where the lines are shifted towards the red end.
Based on his research findings, Edwin Hubble formulated a crucial law for cosmology, known as Hubble’s law. This law states that galaxies that are farther apart from each other move away at a faster rate. Consequently, this indicates that the Universe is constantly expanding and not in a stable state.
The “Singular point” represents the initial state of the Universe, characterized by:
Volume – 10-33 cm3
Density – 1093 g/cm3
Temperature – 1027 K


Slide 15: According to Hubble’s law, the velocity at which a galaxy V is moving away from us is directly proportional to its distance from us. In other words, the farther a galaxy is from us, the faster it is moving away from us. This relationship can be expressed as V = Hr, where V is the velocity of the galaxy, H is the Hubble constant, and r is the distance to the galaxy.

Slide 16: The model of the hot Universe
From this model, two conclusions can be drawn:
1). The matter that gave rise to the first stars consisted primarily of hydrogen (75%) and helium (25%);
2). In the present-day Universe, a faint electromagnetic radiation should be observed, which preserves the memory of the initial stage of the Universe’s development and is therefore called relic radiation.


Slide 17: The discovery of relic radiation in 1965 provided observational proof for the existence of a hot Universe.
Based on the theory of relativity, the expanding Universe can be described as:
– homogeneous
– isotropic
– unsteady
– hot

There are 18 slide Convincing arguments supporting the validity of the cosmological model of an expanding universe that are established facts.
These facts include the following:
– The universe is expanding according to Hubble’s law;
– Luminous matter is homogeneous at distances of about 100 megaparsecs;
– There is a relic background radiation with a thermal spectrum corresponding to a temperature of 2.7K.

Slide 19: The estimated age of the Universe, based on the modern cosmological theory of its formation and evolution, is roughly 13-15 billion years, calculated from the start of the expansion.
In two billion years after the birth of the universe, quasi-stars known as quasars emerged. These celestial objects are rapidly moving away from our planet at a staggering velocity of 100,000 kilometers per second and serve as potent sources of X-rays. Moreover, quasars emit intense infrared and radio radiation. Scientists believe that quasars serve as the central nuclei for future galaxies.
Approximately one billion years after the advent of quasars, galaxies began to take shape. These galaxies are clusters composed of numerous stars.
Five billion years following the big bang, the formation of the Milky Way galaxy occurred. Within this galaxy, our Sun is just one of the many stars. The Sun itself came into existence eight billion years after the big bang and has persisted for a duration of 7-9 billion years. Meanwhile, Earth has been in existence for five billion years, with the first traces of life appearing three billion years ago.


Quasars, which are believed to be the brightest and most distant celestial objects currently known, are highly powerful sources of cosmic radio emissions.
Neutron stars are stars composed of neutrons that are suspected to be formed by supernova outbursts.
Black holes, also known as “frozen stars” or “gravitational graves,” are objects that stars are thought to transform into at the final stage of their existence. The space within a black hole is like being ripped out of the Metagalaxy’s space: matter and radiation fall into it and cannot escape.

Slide 21 – THE THEORY REGARDING BLACK HOLES
In the event that a certain mass of material emerges within a comparatively limited space that is crucial for its existence, said material will begin to uncontrollably condense as a result of the gravitational forces it exerts upon itself. This leads to a gravitational catastrophe, commonly referred to as gravitational collapse.
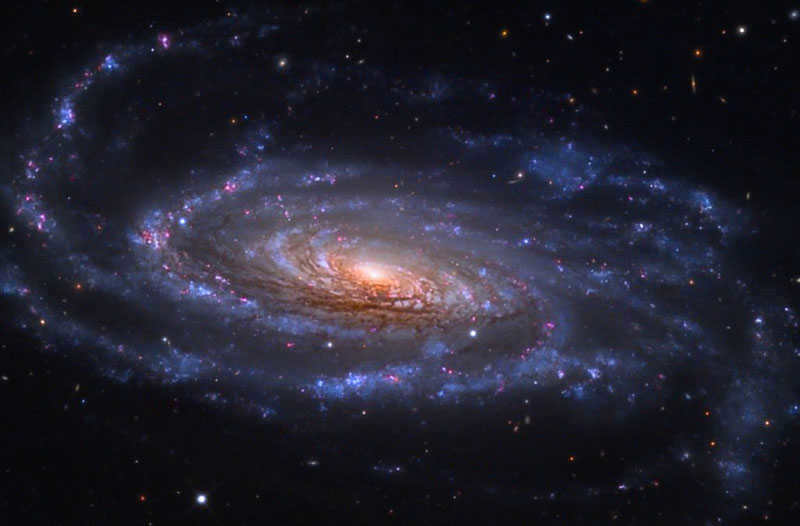

Today, our focus is on the Universe. It so happens that one fateful day, it emerged into existence, and now, here we all are. Some of us are engrossed in reading this article, while others are diligently preparing for an exam, venting their frustrations about everything under the sun. Airplanes soar through the skies, trains traverse vast distances, planets rotate on their axis; there’s always something happening somewhere. Throughout history, people have perpetually sought to uncover one intricate answer to a seemingly simple question: How did it all originate, and how did we arrive at this point? In essence, how did the universe come into being?
Thus, we delve into various theories and models that attempt to explain the genesis of our vast cosmos.
Creationism: God is the creator of all things

This theory of the origin of the universe was the first to emerge and continues to hold significance. It is a highly plausible and convenient explanation that has stood the test of time. Interestingly, many physicists, despite the perceived dichotomy between science and religion, have expressed their belief in a higher power. Albert Einstein, for instance, famously stated:

The Theory of the Origin of the Universe
The Big Bang Theory is perhaps the most widely known and accepted model explaining the beginning of our universe. This concept is familiar to almost everyone. What is the essence of the Big Bang Theory? It suggests that approximately 14 billion years ago, there was no space or time, and all the matter in the universe was concentrated in an incredibly dense point known as a singularity. At some point, this singularity experienced a failure due to the emergence of inhomogeneity within it, resulting in a phenomenon called the Big Bang. Since that moment (although time did not exist yet), the universe has been continuously expanding and cooling down.
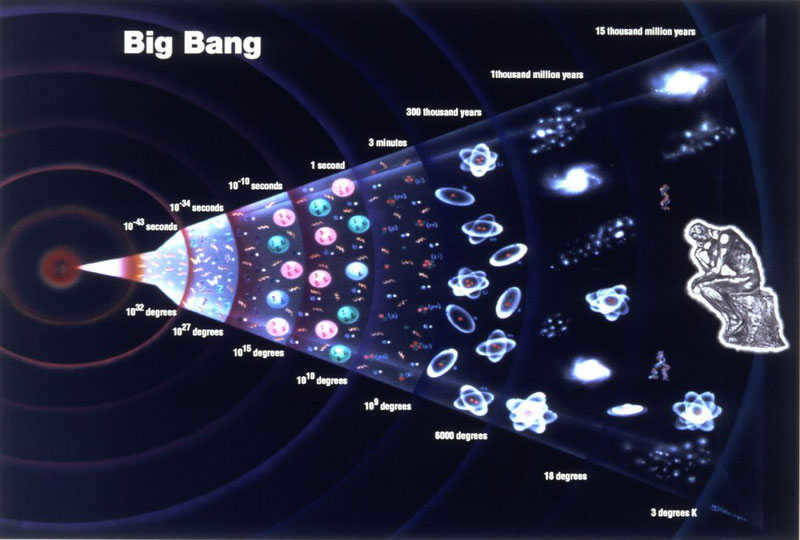
The Expanding Universe Model
It is now widely accepted that galaxies and other cosmic objects are moving away from each other, indicating the expansion of the universe. In the 20th century, there were various alternative theories concerning the origins of the universe. One of the most prominent theories was the stationary Universe model, which was supported by Einstein himself. According to this model, the Universe is not expanding but instead remains stationary due to a mysterious force that keeps it together.
The discovery of the cosmological redshift, red shift, and relic radiation further solidified the foundation of the Big Bang theory. These two occurrences serve as the most compelling evidence in support of the accuracy of the theory. Additionally, you may find an article on creating a presentation in Word to be beneficial.
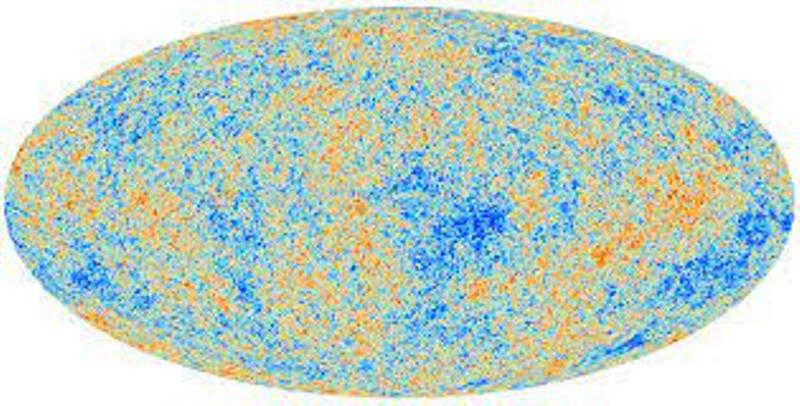
Redshift refers to a phenomenon where the frequencies of radiation observed from distant sources decrease. This decrease can be explained by the distances between these sources, such as galaxies and quasars. It provides evidence for the expansion of the Universe.
Relict radiation can be thought of as echoes from the moment of the big bang. During its early stages, the Universe existed as a hot plasma that gradually cooled down. Even today, there are residual photons in the Universe from that ancient time, which contribute to the cosmic background radiation. This radiation was much more intense during the higher temperatures of the early Universe. Now, its spectrum resembles that of a solid object with a temperature of only 2.7 Kelvin.
The exploration of the evolution of the Universe in contemporary times necessitates its integration with quantum theory. Consequently, within the scope of string theory (a theory founded on the postulation that all elementary particles and their fundamental interactions manifest as a result of vibrations and interactions of ultramicroscopic quantum strings), the concept of a multiple universe model is posited. Granted, a Big Bang event did transpire, but it did not materialize ex nihilo; rather, it potentially arose from the collision of our Universe with another, distinct Universe.
In fact, not only did the Big Bang give rise to our Universe, but numerous other Big Bangs occurred within the multiple Universe framework, giving birth to a multitude of other Universes that evolve according to their own unique laws of physics.

The exact details of how, where, or why the Universe came into existence may forever remain a mystery. However, there is ample opportunity for contemplation and exploration on this subject. To provide you with plenty of food for thought, we invite you to watch an intriguing video regarding the current theories surrounding the origins of the Universe.





