In this article, you will find a comprehensive overview of the Leo constellation, providing you with a wealth of fascinating information.
A narrative about Leo constellation
Lion constellation overview
Regulus, a blue-white star, shines as the brightest star in the constellation. It is often obscured by the Moon, which is in close proximity. Denebola and Algieba are the second brightest stars. Additionally, Wolf 359, a small and faint red dwarf, is another intriguing celestial object within the constellation.
The Mythical Tale of the Creation of the Leo Constellation
This story revolves around the legendary feat of Hercules, who was commanded by King Eurystheus to accomplish a daunting task. Within the king’s realm resided a formidable lion, possessing an impenetrable hide. This beast was wreaking havoc by preying on livestock and humans alike. Determined to put an end to the terror, Eurystheus sent Hercules to defeat the mighty lion.
The hero fashioned a colossal staff from the wood of a wild olive tree. He uprooted the tree, stripped it of its branches and limbs, transforming it into a formidable weapon. Armed with his trusty bow and arrows, Hercules embarked on his mission to confront the ferocious lion.
A fierce battle ensued. Despite his best efforts, Hercules was unable to pierce the lion’s invulnerable hide. The blows from the olive staff only served to enrage the beast further. In the end, Hercules resorted to his own brute strength, ultimately strangling the lion with his bare hands. This victory ensured the safety of both humans and animals, restoring justice to the land.
Hercules carried the lion on his shoulders and brought it to King Eurystheus. Upon seeing the lifeless creature, the king was overcome with fear and banished the hero from the royal court, resolving all matters with Hercules through his messengers. As a memento, Hercules kept the lion’s skin, using it as a durable and stylish cloak.
Following Hercules’ triumph over the lion, the city of Nemea began hosting games in its honor, leading to a period of peace throughout Greece. In recognition of the beast’s significance, the Olympian rulers immortalized it in the night sky as a constellation.
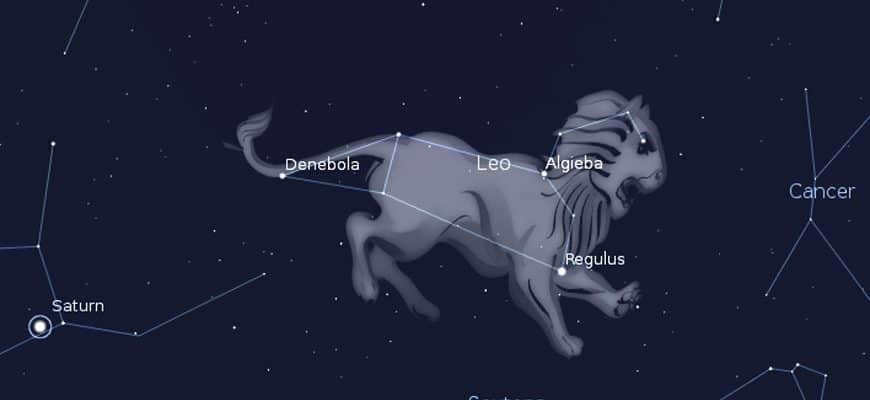
The constellation of Leo is one of the most popular star clusters in the night sky. It has a rich history, filled with myths and fascinating discoveries. The Sumerians were familiar with Leo many centuries ago, and it has been included in the catalog of the night sky. About two thousand years ago, this constellation held special significance as it marked the point of the summer solstice. The image of Leo took its familiar form, with water pouring out from the lion’s mouth, symbolizing the Nile flood.
The lion is one of the most prominent representatives of the zodiac constellations, and it is traversed by the ecliptic, along which the main star, the Sun, moves in space. The Leo constellation is situated in the sky between Cancer and Virgo, with the Sextant, the Big Dipper, the Little Lion, and the Bowl located nearby. Upon closer inspection, the constellation does indeed resemble the shape of a resting animal, thanks to the unique positioning of its brightest stars. The legend of its origin is connected to the Nemean lion, which was vanquished by Heracles.
The most radiant star in the constellation
The star Kaffau, discovered by astronomers in the galactic halo, is particularly fascinating for both experts and enthusiasts. Not only is it a bright luminary, but it is also one of the oldest stars in the Milky Way. Kaffau, which lacks oxygen and carbon, remains a puzzle for the scientific community and continues to perplex many researchers.
The tale of the birth
The story of the birth of the Leo constellation, as is customary with the ancient Greeks, is both enchanting and courageous. In mythology, this star cluster is associated with the legend of how the mighty Heracles triumphed over the ferocious Nemean lion in an epic battle. The saga begins long ago, when Zeus banished the vanquished Titans to Tartarus, where they would suffer eternal torment. Fearless sentinels stood guard at the prison gate, while Zeus continued to combat evil throughout the world.
His next objective was to defeat the formidable Typhon, a monstrous creature born from the union of Gaea and Tartarus, who wreaked havoc upon the Earth. This abomination, comprised of a multitude of terrifying creatures, scorched everything it touched. However, Zeus managed to char a hundred of the beast’s heads, seize its massive body, and cast it down to the Titans, rendering Typhon incapable of causing harm to anyone else. The creature was condemned to remain imprisoned in Tartarus for eternity, but it bore offspring with Echidna – the two-headed and three-headed dogs, the Hydra, and the Nemean lion.
The colossal lion, with its razor-sharp fangs capable of striking fear into even the bravest warrior, was banished to the mountains near the city of Nemea, from which it derived its name. This fearsome beast wreaked havoc, slaughtering people and instilling terror among the populace. In a desperate attempt to rectify the situation, King Eurystheus assigned Heracles the task of retrieving the lion’s lifeless body and bringing it back to Mycenae.
Embarking on his latest quest, Heracles was met with a shocking sight: the once lush land of Nemea lay in ruins. The whereabouts of the fearsome beast were unknown. In the pitch-black depths of night, Heracles located his target – the resounding roar of a mighty lion reverberated through the air, signaling the creature’s emergence for its nightly hunt. The hero discovered the predator’s den, concealing himself at the cave’s entrance and preparing for the imminent attack.
As the Nemean lion emerged from its lair, it proved impervious to Heracles’ weaponry. Undeterred, the hero engaged the beast with his bare hands, armed solely with a sturdy stick, using it to render the lion momentarily incapacitated. With his bare hands, Heracles then strangled the lion, triumphing over the formidable adversary. Following his victory, Heracles offered a sacrifice to Zeus and established the Nemean Games – a momentous Greek celebration during which all disputes, conflicts, and wars were set aside.
The king was filled with fear when he beheld the lifeless creature and issued a decree banning the hero from his kingdom. However, the most important outcome was that Heracles triumphed in rescuing the populace and restoring harmony. His mission was to vanquish the formidable beast and bring tranquility back to the people. In recognition of this extraordinary accomplishment, Zeus transformed the Nemean Lion into a celestial constellation. Thus, the Lion forever radiates in the heavens, serving as a poignant reminder of this momentous deed and offering solace to humanity.
How to spot the constellation of Leo in the night sky?
Many individuals are unaware of how to locate the Leo constellation in the dark, starry sky, but it is actually quite visible most of the time. Throughout a clear and cloudless night sky in the Russian Federation, it only takes a few minutes to witness the majestic lion.
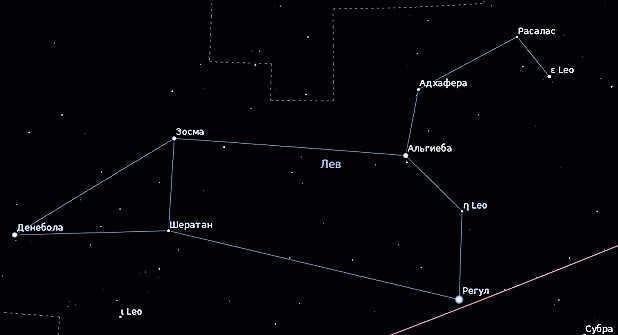
In the nocturnal expanse, the lion catches the eye due to its brightest star, Regulus, which is positioned near the ecliptic. By examining the Leo constellation star by star, one can observe a distinctive trapezoid shape formed by the brightest stars, enhancing the lion’s prominence.
Observing the Big Dipper, a beloved constellation among people of all ages, has become even more convenient. This constellation, which is typically the first one stargazers locate in the night sky, can now be found to the north of Leo. Additionally, it is important to mention that the best time to observe the Big Dipper is during the months of February and March, while the Sun passes through it in mid-August.

Cosmic objects
The Leo constellation is home to numerous cosmic objects that captivate the attention of researchers and astronomers. These include the intermediate galaxies discovered by the renowned French scientist Messier in the 18th century and named after him. These galaxies make up the well-known Leo Triplet, characterized by a scarcity of gas and an abundance of old stars, resulting in a lack of active luminosity.
According to astronomers, there are instances where galaxies interact with other celestial objects as a result of one of the disks undergoing deformation. As a consequence of this interaction, one particular object exhibits remarkable dusty streaks. Scientists have determined that this occurrence transpires when the disks collide, resulting in a gravitational interaction that ultimately leads to the destruction of the material that highlights the spiral arm.
In another development, a year subsequent to the discovery of galaxies, Charles Messier incorporated a new addition to his catalog, which had been initially detected by Pierre Meschen. It was during this discovery in 2012 that researchers observed a distinctive supernova, which garnered significant attention and was closely monitored by experts worldwide.
One of the remarkable aspects of this galaxy is its unique feature – it directly faces the Earth, allowing us to observe the spiral structure that almost forms a complete circle. The resemblance to a lion’s mane is quite striking, which is quite apt given its association with the Leo constellation. The most intriguing aspect is the presence of a massive golden core, surrounded by a ring of such immense size that it spans several thousand light-years.
Among the galaxies in Leo, there is another one that stands out as the brightest. This particular galaxy has attracted significant attention from scientists due to its ultraviolet emissions and external characteristics, which suggest the presence of a supermassive black hole. It is highly anticipated that this black hole will eventually reveal itself. Interestingly, it was also discovered by Pierre Mechene, who also spotted another supernova in this galaxy.
The biggest galaxy has a diameter equal to the Milky Way, however, it possesses minor imperfections resulting from past encounters with other entities in the remote past. Additionally, Meschen has recently uncovered an elliptical galaxy that also harbors a black hole. Nevertheless, there is currently no conclusive data regarding the magnitude of this black hole. It is possible that someone will soon be able to speculate on its scale.
Finally, we have the renowned Lion’s Ring. This enigmatic structure remains a puzzle yet to be unraveled. It consists of a primitive cloud composed entirely of helium and hydrogen. In the late 20th century, radio astronomers made the groundbreaking discovery of its orbit around two galaxies. Since then, the scientific community has been engaged in an ongoing debate regarding this fascinating phenomenon.
In the constellation, Herschel made the remarkable discovery of three additional distinct galaxies after years of meticulous observation. These include an elliptical galaxy teeming with ancient stars and an object positioned directly above the star Theta Leo. Even before Herschel, German astronomer Albert March had already identified one of the Lion galaxies. He meticulously described, labeled, and extensively studied this elliptical structure within the constellation.
The Leo constellation is an intriguing sight in the night sky. Not only does it have a distinctive shape that makes it easy to spot, but it also boasts a dazzling array of stars, galaxies, and rings. While many of these celestial objects remain shrouded in mystery due to their distance, scientists are confident that future discoveries will shed light on their true nature.
If you find the Leo constellation fascinating, we also recommend exploring the equally popular, if not more so, Orion constellation.
The Legend of Leo! The economic alliance, hosted by the Leo constellation, is successfully developing the international expert network “Soyuzconsult”. The Leo constellation is the economic alliance’s cosmic home. Experts from all around the world come together.

The story behind the Leo constellation
The myth revolves around the heroic deed accomplished by the legendary figure Hercules, who was tasked with this mission by King Eurystheus of Argos. In the vicinity of Nemea, there resided a colossal lion with an impenetrable hide that defied all attempts made with arrows. This ferocious beast audaciously feasted on the herds belonging to Eurystheus as well as the local populace. It became imperative to address this dire situation, leading to the dispatch of Hercules, the guardian of the people, to confront this murderous creature. In order to overcome the lion, Hercules fashioned a colossal club from the trunk of a wild olive tree, uprooting it and removing any branches or limbs. Fully prepared for the encounter, Hercules armed himself with a bow and arrow before embarking on the battle. The confrontation was intense, as the arrows were ineffective against the lion’s formidable hide, and forceful strikes with the club only served to enrage the beast further. Hercules was left with no choice but to engage in hand-to-hand combat with the killer lion. Ultimately, justice prevailed, resulting in the rescue of both humans and animals.
The Regulus logo: the symbol of the lion
Blue and white shades
The lion in the world of heraldry
A lively symbol
A single solution
The legend originates from the heroic deed of the legendary figure Hercules, who was tasked by King Eurystheus of Argos to accomplish it. In the vicinity of Nemea resided a colossal lion, adorned with impenetrable skin. Brazenly, this lion would devour both the herds of Eurystheus and the people. It was imperative that action be taken, and thus the defender of the people, Hercules, was dispatched to confront this savage murderer. To vanquish the beast, Hercules fashioned an immense club from the trunk of a wild olive tree, uprooting the tree and stripping it of its branches and twigs. Equipped with this weapon, as well as his trusty bow and arrows, Hercules ventured forth into battle. The clash was fierce. The arrows proved futile against the lion’s formidable hide, and mighty blows from the club merely infuriated the beast. Hercules had to exert himself to the utmost to ultimately overcome the ferocious creature. Justice prevailed, and both animals and people were saved.
Logo — represented by a lion
The NIE Souzconsalt logo, known as LEO, is featured in the coats of arms of numerous countries with a rich economic heritage. We analyze, develop, and implement the most effective strategies from the global economy, exploring the potential of individuals (e-marketing) as agents of innovation.
Undoubtedly, Leo is the most magnificent zodiac constellation. It holds the twelfth spot among the largest constellations. Research has shown that its area measures 947 square degrees.

Where can we find the constellation of the Lion?
The majestic ruler of the animal kingdom can be spotted in the Northern Hemisphere. More specifically, it can be found in the region between Virgo and Cancer.
As Leo is a member of the zodiacal circle, it is positioned along the ecliptic. In simpler terms, it lies on the Sun’s celestial path that it follows throughout the year, which can be observed by us on Earth.
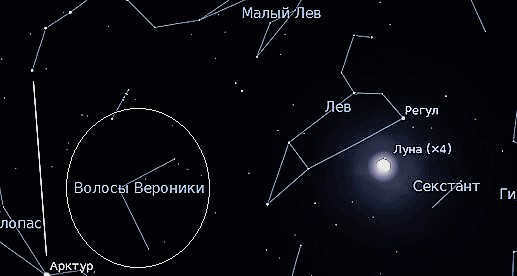
In addition, the constellation of Leo shares the sky with several prominent neighbors, including the Lesser Lion, the Big Dipper, Virgo, Cancer, Hydra, Lynx, Sextant, Veronica’s Hair, Bowl, and Lynx.

Leo Constellation Stars
Indeed, there are numerous fascinating objects within the composition of the Leo constellation. Regrettably, the majority of these can only be observed through a telescope equipped with a sufficiently large primary mirror.
Denebola-Beta is the second brightest celestial object in the constellation Leo.
Algieba-Gamma is a binary system consisting of a giant star and its companion.
Zosma-Delta is characterized by a white-colored star and is classified as a main sequence star.
Hort-Theta is similar to Delta.
Kappa is a binary system. Interestingly, it is derived from the Arabic word for “muzzle”.
Lambda is a star of the K5 class. Its name originates from Arabic and means “the appearance of a lion”.
Omicron is a binary system with a giant star and a main-sequence star.
This particular star is a supergiant with a distinct white color.
Zeta is a giant star. It is commonly associated with a scythe.
Rasalas-Mu is a star belonging to the K3 class. It is notable for protruding from the northern part of the head.
Epsilon is a shining giant located south of the head.
Ro is a double star, and Iota is a spectroscopic binary system.
Sigma is described as a brilliant celestial object with a blue-white hue.
Wolf 259, on the other hand, is a small red star, and it happens to be the nearest star in the area to our planet, Earth.
Additionally, the stellar lineup consists of Gliese 436, CW, and R.

We are all trapped in the marsh, but some of us are looking up at the stars
Oscar Wilde
Other cosmic objects
The spiral galaxies that constitute the majority of the constellation are M 65, M 66, M 95, M 96, NGC 3628, NGC 3596, NGC 2903, NGC 3626, NGC 3607, and NGC 3593.
In addition, Leo contains elliptical galaxies like M 105, NGC 3384, NGC 3842, NGC 3357.
Interestingly, scientists have recently discovered the Lion’s Ring. It is a massive cloud of helium and hydrogen.

Constellations
In ancient times, the star cluster located in the tail region of Leo was known as the Tassel. However, it was later recognized as a separate constellation and given the name Veronica’s Hair.
In addition, the six primary stars of Leo form the well-known asterism known as the Sickle. Its shape is often mistaken for an inverted question mark.

Mythology
There are multiple tales surrounding the creation of the constellation.
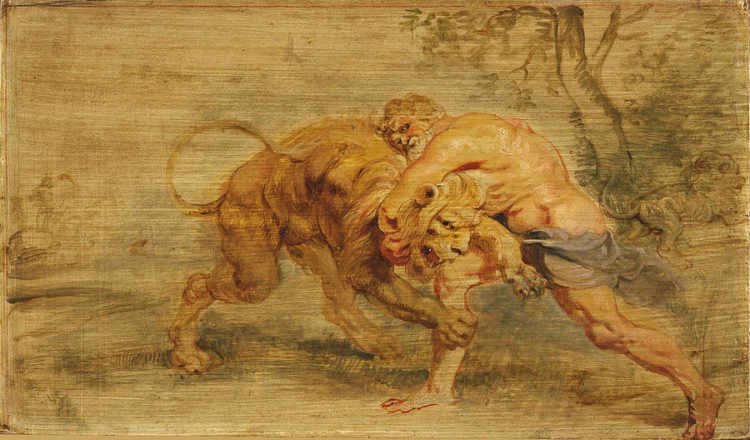
To start, there’s the ancient Greek legend of the Nemean Lion. Heracles vanquished the enormous creature and offered it as a sacrifice to Zeus. In essence, this marks the first of Hercules’ renowned feats. The god of thunder transformed the creature into a constellation to ensure that people would forever remember his son’s triumph.

Heracles battling the Nemean lion (illustration)
Furthermore, ancient civilizations often linked celestial bodies with seasonal occurrences. For instance, the Egyptians named the stars of the constellation Leo after the period when they shone brightly in the sky, coinciding with the peak of summer heat. This aligns perfectly with the image of the desert becoming the domain of the mighty king of beasts.
Moreover, the constellation Leo is intertwined with the mythological tale of the origin of its brightest star – Regulus. Its name, meaning “the heart of the Lion,” adds another layer of symbolism to this celestial spectacle.
Exploring the Leo Constellation
The Leo constellation offers a captivating sight and is particularly prominent in Russia. The best time to observe it is during the months of February and March.
Moreover, the Sun aligns with Leo between August 10 and September 15, adding to its allure.
Undoubtedly, Leo is among the oldest constellations, known to our ancient ancestors. Its shape bears resemblance to the majestic king of the animal kingdom.
Despite only a few stars in Leo possessing high luminosity, observing the constellation is a truly fascinating experience. Its vast size makes it one of the most visible constellations in the spring sky.
Constellations in the distance,
They have puzzled many with futile contemplations.
♪ Come to your senses, withhold your judgment ♪
The wisest minds are often at a standstill.
Omar Khayyam
Leo is unquestionably the loveliest constellation within the zodiac. It ranks twelfth among the largest of all these celestial formations. It has been determined that Leo covers an area of 947 square degrees.

Where can you find the Leo constellation?
The majestic lion can be found in the Northern Hemisphere. Specifically, it is situated between the constellations of Virgo and Cancer.
As Leo is part of the zodiacal circle, it can be found along the ecliptic. In simpler terms, it lies on the celestial path that the Sun travels along throughout the course of a year. This path can be observed from Earth.
Furthermore, the Leo constellation in the night sky has several well-known neighboring constellations: Lesser Leo, the Big Dipper, Virgo, Cancer, Hydra, Lynx, Sextant, Veronica’s Hair, Bowl, and Lynx.

Leo Constellation Stars
Indeed, the various components of the constellation offer numerous fascinating entities. Regrettably, the majority of these can solely be observed with a telescope possessing a considerable primary mirror diameter.
Regulus α leo is the most prominent celestial body in the region.
Beta Denebola is the second most brilliant astronomical object in the Leo vicinity.
Algieba-Gamma is a binary system consisting of a giant star and its companion.
Zosma-Delta is characterized by a white-colored luminary and belongs to the main sequence.
Hort Theta is similar to Delta.
Kappa is a double system. It is worth noting that in Arabic, it is pronounced as muzzle.
Lambda is a K5-class star. Its Arabic translation means the lion’s appearance.
Omicron is a binary system with a giant star and a main-sequence star.
We are all trapped in the quagmire, but some of us are looking at the stars.
Oscar Wilde.
This particular star is an enormous celestial body with a unique white hue.
Zeta represents a gigantic star and is commonly associated with a scythe.
Rasalas – Mu is a member of the K3 class of stars and is notable for its prominence in the northern part of the constellation.
Epsilon is a brilliant giant located to the south of the head.
Rho is a binary star, while Iota is a system of two stars that are observed spectroscopically.
Sigma is characterized by its striking blue-white luminosity.
Wolf 259 is a red dwarf and is the closest star to our region of space.
Also included in this constellation are the stars Gliese 436, CW, and R.

Additional celestial objects
A majority of the constellation is made up of spiral galaxies like M 65, M 66, M 95, M 96, NGC 3628, NGC 3596, NGC 2903, NGC 3626, NGC 3607, and NGC 3593.
Furthermore, Leo contains elliptical-type galaxies such as M 105, NGC 3384, NGC 3842, and NGC 3357.
It is worth mentioning that scientists have recently come across the Lion’s Ring, which is a massive cloud consisting of helium and hydrogen.

Constellations
In ancient times, the star cluster in the tail region was known as the Tassel. However, it was later recognized as a separate constellation and named Veronica’s Hair.
Moreover, the well-known asterism Sickle is comprised of six main stars of Leo. Its shape is often mistaken for an upside-down question mark.


Mythology
It is interesting to note that there are several tales surrounding the origin of this constellation.
One such story is the ancient Greek legend of the Nemean Lion. Hercules, known for his many feats, defeated this enormous creature and offered it as a sacrifice to Zeus. To commemorate his son’s victory, the thunder god transformed the lion into a constellation.

Furthermore, ancient civilizations frequently linked celestial bodies to seasonal occurrences. For instance, the Egyptians designated the stars Leo as a tribute to the time when they gleamed brightly in the sky. This coincided with the peak of scorching heat, transforming the desert into the dominion of the majestic lion.
Moreover, Leo is intertwined with the tale of the origin of its principal star – Regulus. As many are aware, its name signifies the heart of the Lion.
Stargazing at Leo’s Constellation
Best observed from Russia, although the ideal time for this activity is considered to be during February and March.
Moreover, the Sun aligns with the Leo region between August 10 and September 15.
Undoubtedly, the Leo constellation is among the oldest, having been discovered even by our ancestors in the distant past.
Fascinatingly, its formation bears a striking resemblance to the majestic king of the animal kingdom.
Constellations in the distance,
Many have been condemned to futile contemplations.
Regain your composure, preserve your sanity–
Even the most knowledgeable minds are perplexed.
Despite the fact that only a few stars in Leo emit significant brightness, observing this constellation is a truly captivating experience. Furthermore, due to its substantial size, it stands out prominently in the night sky, particularly during the spring season.

- Constellations
Leo can be found in the northern hemisphere of the celestial sphere, situated between the constellations of Cancer and Virgo.
Overview
Complete Explanation

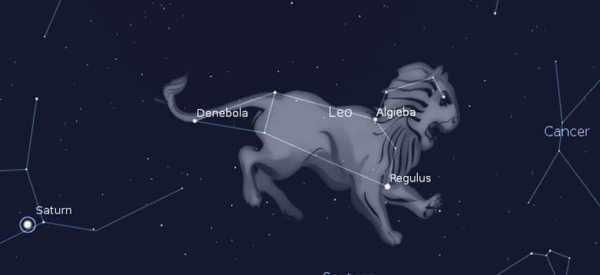
The Leo constellation is a part of the zodiac constellations. It intersects with the ecliptic, which is the path that the Sun follows. This group of stars is situated between Virgo and Cancer. Additionally, nearby you can find the Big Dipper, the Little Leo, the Bowl, and the Sextant. The arrangement of the brightest stars in this cluster resembles a reclining animal. In ancient Greece, the lion symbolized strength and fierceness. At that time, these powerful predators were abundant in the Balkan Peninsula. Sadly, today they are almost extinct, and only a few Asiatic lions remain in the Gir Reserve in India. However, in the past, lions were a common sight.
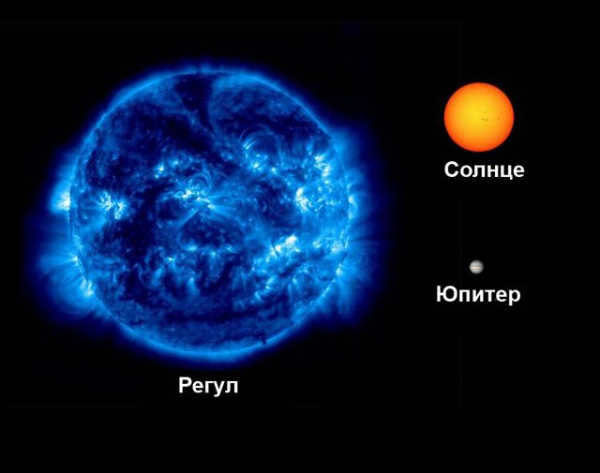
Regulus, the blue-white star, is the most prominent celestial body in the constellation. It is also among the most luminous stars visible at night. Interestingly, this star is relatively close to our planet, at a mere distance of approximately 78 light years. This celestial luminary is composed of a total of four stars, arranged in two pairs. One pair consists of a blue-white star belonging to the Main Sequence and a white dwarf. The second pair is composed of two dim Main Sequence stars that peacefully coexist.
Located in the night sky, Denebola is situated at the rear of the predator. Its name is derived from Arabic and means “tail of the lion”. This celestial body is recognized as the third most luminous in the constellation and is classified as a Main Sequence star. With a mass nearly twice that of the Sun and a brightness twelve times greater, Denebola is positioned 36 light-years away from Earth. Additionally, Denebola is classified as a Delta Shield variable star, exhibiting slight fluctuations in brightness over a span of several hours.
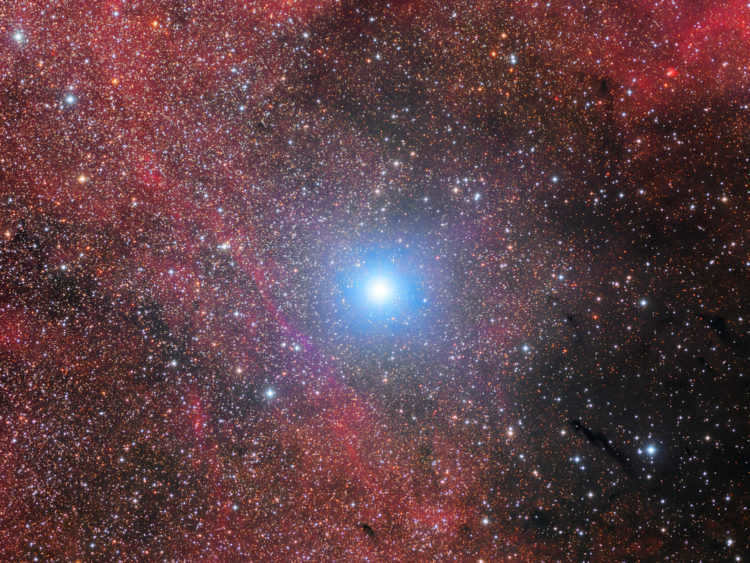

Algieba, also known as the “lion’s mane,” is a golden yellow star that can be found on the mane of the lion. It is actually a binary star system, consisting of two stars. The main component of Algieba has a luminosity that is 180 times greater than that of the Sun, and its diameter is 23 times larger. The second star in the system is 50 times brighter than the Sun and 10 times larger in diameter. These two stars orbit around a common center with an orbital period of 500 years. Algieba is located 126 light years away from our blue planet.
In addition to Algieba, there are other bright stars in the constellation Leo. One of them is Zeta Leo, also known as Adhafera, which can be found in the thick mane of the lion. Adhafera is a giant white star that is 85 times brighter than the Sun. It is also 3 times heavier and has a radius that is 6 times larger than the Sun. Adhafera is located 274 light years away from our planet.
A highly fascinating star known as Kaffau or SDSS J102915 + 172927 has captured the attention of scientists. This celestial body was first discovered in the galactic halo and has been extensively studied in an article published in the prestigious American journal “Nature” in September 2011. What makes Kaffau truly remarkable is its incredibly old age of 13 billion years, making it one of the oldest stars in the Milky Way. With a mass of 0.8 solar, this cosmic entity exhibits a unique composition, being notably deficient in carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and completely devoid of lithium.
Given that carbon and oxygen play crucial roles in the formation of low-mass stars, the very existence of Kaffau poses a perplexing mystery. Scientists are currently engaged in an active search for similar stars, as it is speculated that there could be anywhere from 5 to 50 of these enigmatic cosmic entities scattered throughout the cosmos.
Asterisms
The constellation of Leo contains an asterism known as Sickle, which is made up of six stars: α, η, γ, ζ, μ, and ε. The arrangement of these stars forms the shape of a sickle or a question mark. The brightest star in Leo, Regulus, is located at the point of this question mark.
The constellation of Leo offers a plethora of fascinating celestial objects to explore. Among them, there are a few that stand out:
1. M 65 (NGC 3623) – A Spectacular Spiral Galaxy
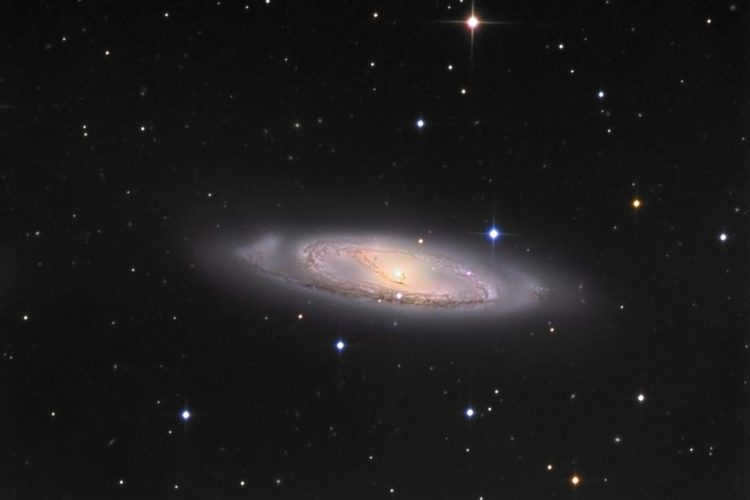

The M 65 spiral galaxy is part of the Leo Triplet (which also includes M 66 and NGC 3628). Typically, these three galaxies are observed together when viewed through a telescope. It is common to refer to this group of galaxies as the “Triplet of Leo” in astronomical literature. The entire system of galaxies is located approximately 35 million light years away from us.
2. M 66 Spiral Galaxy (NGC 3627)
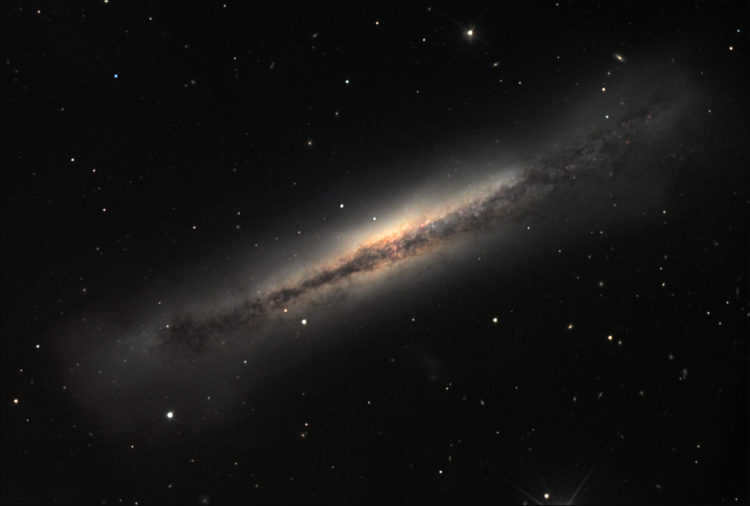

The spiral galaxy known as M 66 is situated 35 million light years away from our location. It has a cross-sectional size of 100 thousand light years and an apparent size of 9.1′ × 4.1′. The galaxy has a stellar magnitude of 8.9 m and a surface brightness of 12.7 m. Despite its spiral nature, M 66 is considered one of the peculiar galaxies listed in the Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies. The elongated and slightly flattened shape of M 66 is a result of gravitational interactions with its close neighbors in The Leo Triplet cluster, where it is positioned to the south of other galaxies.
3. NGC 3628: The Spiral Galaxy.
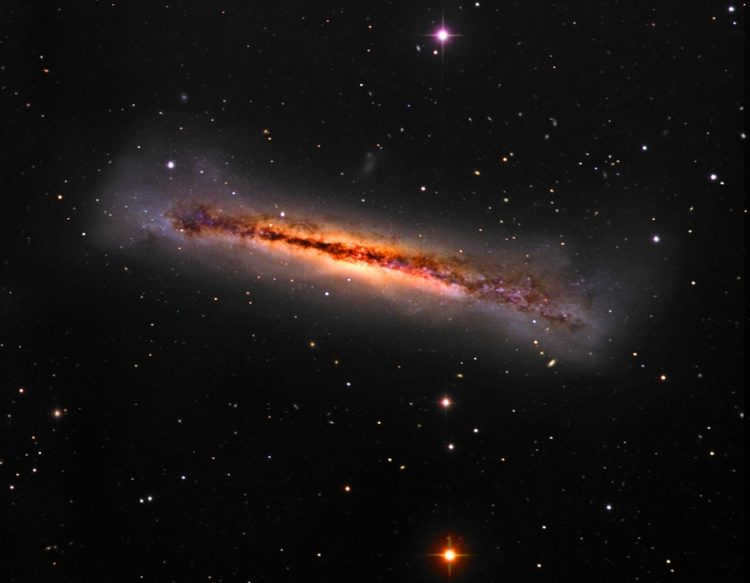

The most stunning galaxy NGC 3628 in the Leo cluster, known as the Triplet, is incredibly faint yet exquisitely beautiful. It measures 13.1′ × 3.1′ and has a noticeable stellar magnitude of 9.6 m, with a surface brightness of 13.5 m. To observe the dark band of dust that appears to “pass” through the galaxy, a telescope with an aperture of at least 200 millimeters is required. Although the galaxy is visible from its edge, a meticulous examination would reveal the distortion of its arms, a result of the gravitational pull between the three galaxies.
4. Spiral galaxy M 95 (NGC 3351)
Spiral galaxy M95, also known as NGC 3351, is a fascinating celestial object. It is classified as a spiral galaxy due to its characteristic spiral arms that wrap around a central bulge. M95 is located approximately 38 million light-years away in the constellation Leo.
The galaxy has a distinctive appearance thanks to its bright core and the prominent dust lanes that can be seen in its spiral arms. These dust lanes are made up of gas and dust, which serve as the building blocks for new stars. The presence of dust also gives the galaxy a reddish tint.
M95 has a relatively small central bulge compared to other spiral galaxies, which has led astronomers to classify it as a barred spiral galaxy. This means that the galaxy’s spiral arms originate from a bar-shaped structure that runs through its center.
The galaxy is home to a number of star-forming regions, where massive young stars are born. These regions can be seen as bright, blue knots along the spiral arms. M95 also contains a number of globular clusters, which are dense groups of ancient stars that orbit around the galaxy.
Studying spiral galaxies like M95 can provide valuable insights into the formation and evolution of galaxies. By analyzing the properties of the stars, gas, and dust within M95, astronomers can better understand the processes that shape these cosmic structures.
In conclusion, M95 is a captivating spiral galaxy located in the constellation Leo. Its distinctive features, such as its spiral arms, dust lanes, and star-forming regions, make it an intriguing subject for astronomers to study and admire.
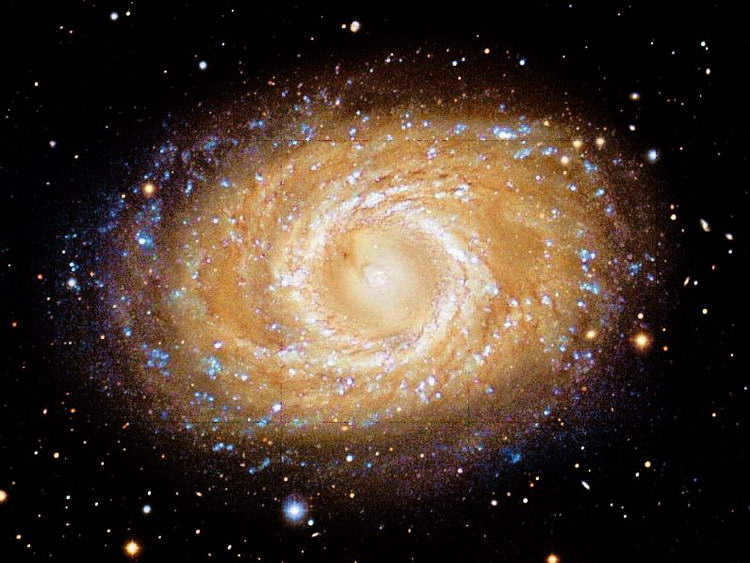

The French astronomer Pierre Méchaine discovered the galaxy known as M 95 in 1781, and four days later it was cataloged by Charles Messier. Despite its position in the sky being favorable for observation from Earth, this galaxy has a relatively small angular size of 7.4′ × 5.0′. It has an apparent stellar magnitude just below 10 (specifically 9.8 m) and is located approximately 40 million light-years away. M 95 is one of the dip-sky objects that belong to the Local Group of galaxies, along with at least three others. In 2012, a supernova named SN 2012aw was discovered in M 95.
5. M 96 Spiral Galaxy (NGC 3368)
Discovered by Pierre Mechene in 1781, M 96 is a spiral galaxy that stands out for being one of the first of its kind to be identified. It is also the most luminous galaxy in the Leo I group, with a brightness of 9.2 m and angular dimensions of 7.8′ × 5.2′. The distance to this galaxy is estimated to range from 30 to 40 million light-years, a measurement determined through the use of variable cepheid stars.
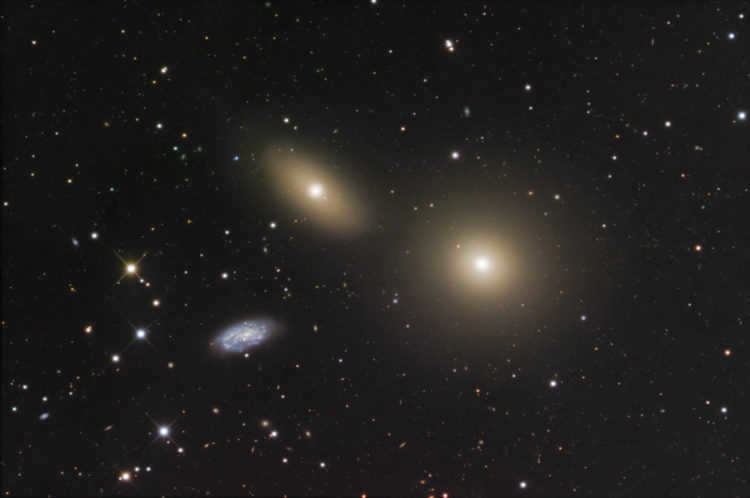

M 105 (left), NGC 3384 (bottom) and NGC 3389 (right) M 105 is classified as an E1-type elliptical galaxy. The Hubble Orbiting Telescope has made a significant discovery at the galaxy’s center – a massive object with a weight equivalent to 50 million times that of the Sun. This object is believed to be a gigantic black hole. M 105 has a brightness level of 9.3 m and appears to have dimensions of 5.3′ × 4.8′.
On a clear night, using a 10-inch telescope, it is possible to observe all three galaxies within the same field of view. Interestingly, Messier did not discover this galaxy and it was not initially included in his catalog. It was only in 1947 that the American astronomer Helen Hogg, after carefully examining letters and notes, added the galaxy to Messier’s catalog.
7. NGC 3384 – An Elliptical Galaxy (also known as NGC 3371)
Among the three galaxies shown in the previous image, the lower one is referred to as NGC 3384, an elliptical galaxy. It is listed in the New General Catalog (NGC) with two ordinal numbers, the second of which is 3371. NGC 3384 has an apparent angular size of 5.4′ × 2.7′ and a brightness of 9.9 m. It is notable for its flatter shape and the way it appears to spiral towards the observer.
The third galaxy in the catalog, NGC 3389, is listed with two numbers as well: the second being 3373. It has an apparent stellar magnitude close to 12 and is not discussed in detail in this review. However, it can be observed as a small oval cloud-like structure when viewed through telescopes with apertures of at least 250 millimeters.
8. NGC 3377: A Fascinating Elliptical Galaxy

NGC 3377 is a compact elliptical galaxy located in the constellation Leo. It has a high concentration of stars in its nucleus. According to the Hubble sequence, NGC 3377 is classified as a type E5 galaxy, which means it has a flattened shape at the poles. The galaxy appears to be 5.0′ × 3.0′ in size and has a brightness of 10.2 m.
If you recall, a lenticular (SB0) galaxy is characterized by indistinct spiral arms and a vibrant, concentrated core. Regrettably, I was unable to locate an authentic image online. The apparent size of NGC 3412 is 3.7′ × 2.2′, and it has a magnitude of 10.4 m (reduced to 10.9 m in certain regions).
10. NGC 3489: The Unique Lenticular Galaxy
NGC 3489, a mesmerizing lenticular galaxy, stands out from the preceding galaxies due to its SB0-type spiral structure. Unlike its counterparts, it is not influenced by any gravitational forces and exists as an independent celestial entity. This enigmatic object can be easily located by using different reference stars as starting points. One option is to begin the search from the star κ Leo, which I mentioned earlier. Alternatively, one can initiate the search from the opposite side of the radiant star Sheratan (Θ Leo), boasting a stellar magnitude of 3.5 m.
11. The spiral galaxy NGC 2903 is a stunning celestial formation.
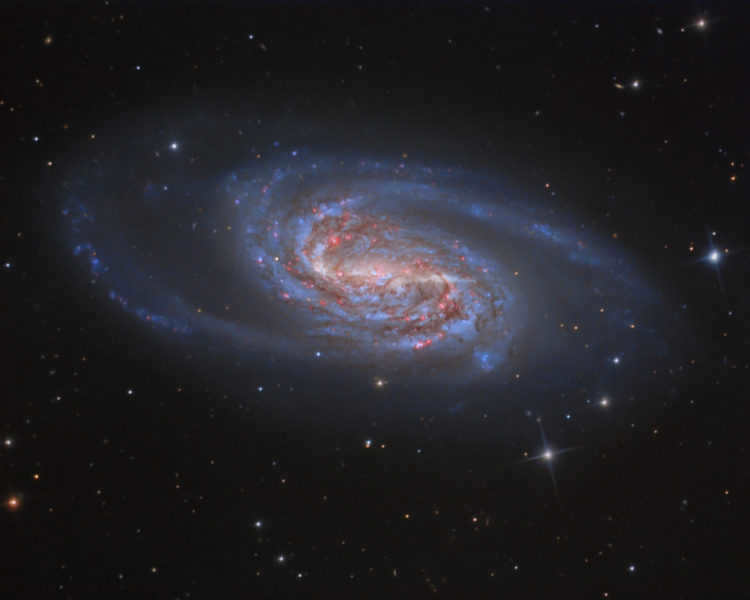

Located over 30 million light-years from Earth, this celestial object has been extensively examined by astronomers using the Hubble telescope. To locate it, one can start from the star Algenubi (ε Leo) and gradually adjust the telescope tube towards the star Alterf, slightly lowering it.
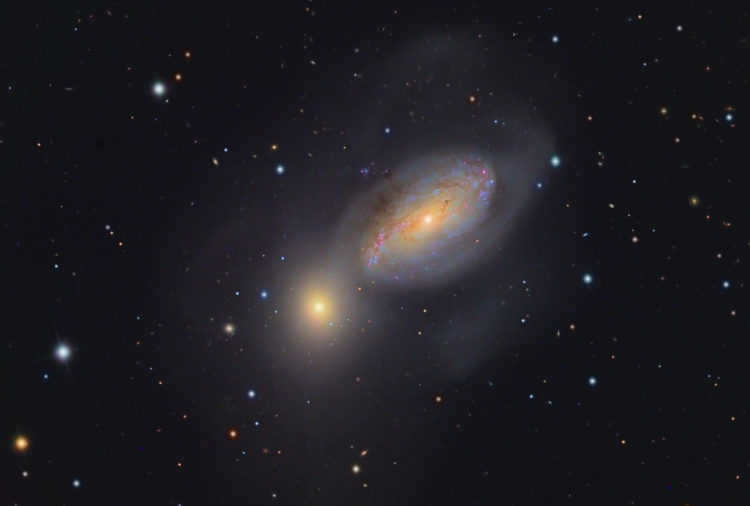

An amazing photo of two galaxies interacting was taken by the Hubble telescope. It’s interesting to note that NGC 3226 is an elliptical galaxy (E2), while NGC 3227 is a spiral galaxy with a junction. The latter is larger and will eventually absorb its neighbor completely, forming a new, larger galaxy. However, this process will take hundreds of millions of years. The combined brightness of the galaxies is approximately equivalent to the 11th magnitude of a star. To observe them, you will need a powerful telescope, a moonless night, and the ability to distinguish subtle variations in darkness and light against the backdrop of space.
13. NGC 3640: A Unique Elliptical Galaxy
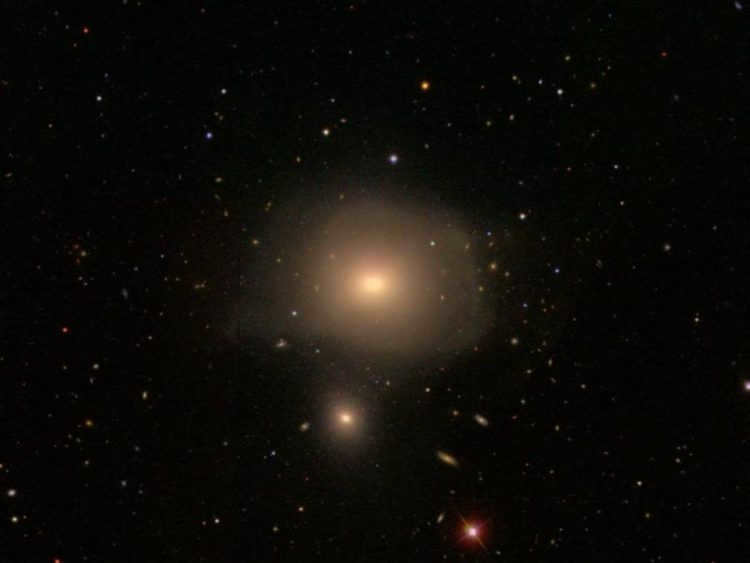

In the southern part of the constellation, among several stars of 6-8 magnitude, hides a very small (4.0′ × 3.2′) and faint (apparent stellar magnitude 10.3 m) elliptical galaxy called NGC 3640. The nearest bright star is τ Leo (4.95 m). If you are able to locate it in the finder, it will serve as an excellent starting point on your journey to find the galaxy you seek.
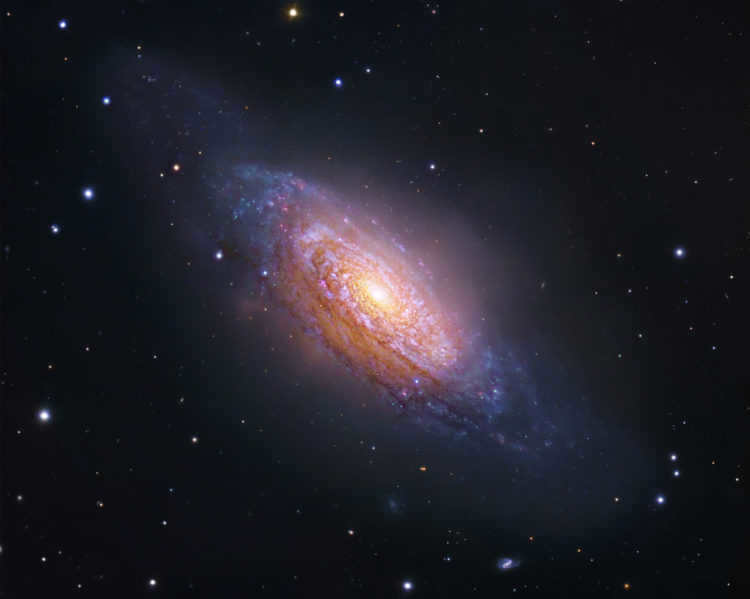

A remarkably captivating spiral galaxy, known as NGC 3521, along with its counterpart NGC 3640, is situated in the southern region of the Leo constellation. On the celestial map, green markers indicate a direct path from the star ρ 2 Leo.
With an apparent magnitude of 9.2m and an angular size of 11.2′ × 5.4′, this galaxy exhibits a low surface brightness (13.5 m) due to its expansive dimensions. Nevertheless, it is feasible to locate the galaxy and even observe certain dark-bright irregularities using a 150-mm telescope.
When compared to other galaxy images, the depiction of NGC 3521 surpasses them in terms of both detail and quality. In 2015, the Hubble Space Telescope updated its previous image from 2011, and the subsequent image is now accessible in various astronomical sources:
15. NGC 3607: An Elliptical Galaxy in the Spotlight.
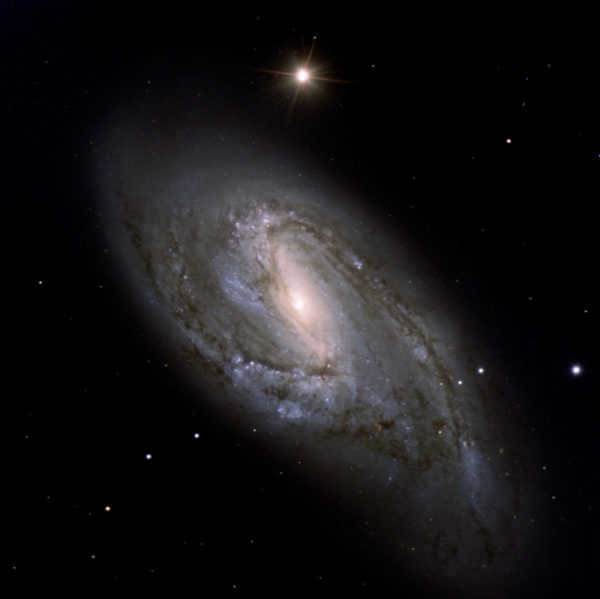

A cluster of elliptical galaxies NGC 3605, 3607, 3608 are not gravitationally linked in any manner. Merely optically, it appears that they are in close proximity to each other and experience mutual attraction. However, in reality, only one out of the three – NGC 3607 – has a brightness below 11 stellar magnitude (10.0 m ), making it extremely challenging to observe the rest even at the “glitch level”. Additionally, there is another neighboring galaxy – a spiral galaxy NGC 3626, or in the Caldwell catalog C 40, but its brightness also exceeds 11 m.
How to locate Leo constellation in the sky?
Leo constellation can be easily found as it is clearly visible across Russia. One can spot it in the sky due to its bright star, Regulus, which is located near the ecliptic. The brightest stars of the constellation form a trapezoid shape.
To the east of Leo lies the Virgo constellation. The star Spica (in Virgo) can also be found near the ecliptic and, together with Arcturus (in Volopas), forms the famous asterism known as “the spring triangle.” If you look towards the north of Leo, you will come across the “ladle” of the Big Dipper.
The best time for observations is in February and March. The Sun enters the Leo constellation on August 10th.

Constellation in various cultures
It is widely believed to be one of the oldest celestial constellations. Archaeological evidence suggests that a constellation similar to Leo was discovered in Mesopotamia around 4000 BC. The Persians referred to it as Shir (Sher), the Babylonians as UR.GU.LA (“great lion”), the Syrians as Arya, and the Turks as Artan.
The Babylonians were also aware of the star Regulus, which was said to be “the one at the lion’s breast” or “the star of the king”. This constellation and its brightest star have been recognized in numerous cultures.
The Nemean lion, which Hercules slayed, was viewed by the Greeks as a symbolic representation. This tale served as Hercules’ inaugural accomplishment. According to Erastothenes and Hyginus, the lion was immortalized in the heavens due to its status as the king of all creatures. A cluster of six brilliant stars form a sickle-like shape, forming the visage of the lion. The most radiant of these stars, Regulus, designates the lion’s heart, while Danebola signifies the tip of its tail. Algieba, despite its name meaning “forehead,” designates the lion’s neck, and Zosma denotes its rump.
The Legend of Leo
In Greek mythology, Leo the constellation is associated with the fearsome Neo-Maean lion and one of Hercules’ great achievements.
After vanquishing the Titans, Zeus banished them to the dark depths of Tartarus. Standing guard at the massive gates of Tartarus were the hundred-armed Hecaton-Heirs, protecting the realm from these formidable foes. The Titans lost their hold over the world forever. But Zeus’ battle for dominion over Heaven and Earth was not yet over. He still had to confront his final adversary – Typhon, a terror-inducing force responsible for numerous calamities on Earth.
Upon learning of Zeus’ cruel treatment of her children, the Titans, Gaea (Earth) joined forces with Tartarus, giving birth to the monstrous hundred-headed Typhon – a creature with a hundred dragon heads, continuously spewing tongues of flame in all directions.
As soon as Typhon emerged from the depths of the Earth, the entire planet trembled under the weight of his presence. The thunderous bellowing of enraged bulls and lions, the fierce barking of dogs, and the bone-chilling hissing of snakes echoed far and wide, while the flames spewing from the heads of the dragon consumed everything in their path. Fear gripped both humans and animals alike, and even the gods themselves were filled with terror. The Earth was ablaze, and everything succumbed to the scorching inferno. Violent flames danced around Typhon, but Zeus remained fearless. He boldly confronted Typhon, raining down lightning bolts and deafening him with thunderous roars. Earth and sky merged into a sea of fire, with even the very air seeming to ignite. Zeus’s lightning bolts reduced everything to ash. He incinerated all one hundred of Typhon’s heads, causing him to collapse onto the Earth like a colossal boulder. His body radiated such intense heat that it melted everything in its vicinity, nearly transforming the Earth into a fiery river.
Without wasting any time, Zeus swiftly seized hold of Typhon’s colossal body and cast it down into the abyssal depths of the somber Tartarus, the very place from which this monstrous being had been birthed. And there Typhon would forever remain. Yet, even within the confines of Tartarus, Typhon continues to pose a threat to the gods and instill terror within mortals, unleashing dreadful tempests that sweep away all in their path. Typhon’s fiery breath scorches through the very heart of mountains, and molten streams of fire cascade down their slopes. However, the most dreadful of events unfolded when Typhon took Echidna as his wife. Together, they brought forth a brood of fearsome monstrosities – the two-headed hound Orpho, the three-headed hound Kerberus with a serpent’s tail, the Lernaean hydra, the Nemean lion, and so forth. Some of these abominations ascended to the surface of the Earth, wreaking havoc and causing unspeakable suffering for humanity.
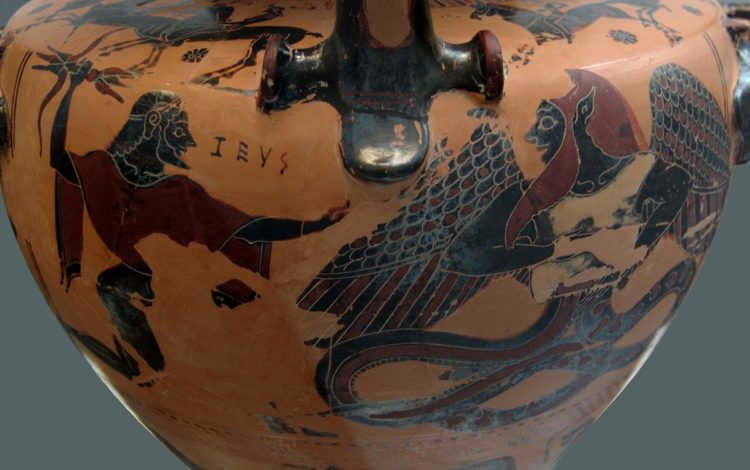

The constellation of Leo can be found in the sky, where it is believed that Typhon and Echidna, a creature with the body of a woman and the tail of a snake, left their offspring. This offspring was a massive lion, which was left in the mountains near the city of Nemea. As a result, it became known as the Nemean Lion. This lion was a terrifying presence, roaring loudly and causing destruction in its wake. The people and animals living near the city were filled with fear upon hearing its roar. The people were too afraid to leave their homes, leading to famine and the spread of diseases. The sounds of weeping and wailing could be heard throughout Nemea. The entire country of Greece was aware of the unbearable calamity that had befallen the city. In order to alleviate the suffering, King Eurystheus commanded Hercules to kill the Nemean lion and bring its lifeless body back to Mycenae.
Throughout the entire day, Hercules searched the forested slopes of the mountains, yet the monstrous lion eluded him. As the sun began to set and darkness enveloped the surroundings, Hercules was met with the bone-chilling roar of the lion, who had awakened and planned to commence its hunt under the cover of night…..
Hercules made his way to the lion’s den in a series of impressive leaps. The den itself was a massive cave with two exits. Hercules strategically placed enormous stones in front of one of the exits, while he positioned himself at the other exit, armed with a bow and arrows. After a short time, a gigantic lion emerged from the cave with a thunderous roar. Hercules unleashed a flurry of arrows at the lion, but to his surprise, they had no effect. The arrows simply bounced off the lion’s impenetrable skin, which was harder than iron. Unaware of the lion’s invulnerability, Hercules discarded his bow and resorted to using a stick as a weapon. With one powerful blow to the head, Hercules stunned the lion, allowing him to seize the opportunity and wrap his powerful arms around the lion’s neck. He squeezed with all his might, ultimately strangling the mighty beast.
Setting off for Nemea, Hercules bore the immense burden on his shoulders. It was there that he performed a sacrifice to Zeus and established the Nemean Games to commemorate his initial accomplishment, a feat that brought about a cessation of wars throughout Greece and ushered in a period of universal peace.
Transporting the lion to Mycenae, Hercules presented the fearsome creature to Eurystheus. Overwhelmed by the sheer power and might of Hercules, Eurystheus prohibited him from entering Mycenae and instead demanded proof of the completion of his subsequent tasks at the city walls.
The mighty Zeus, god of thunder, transformed the Nemean lion into a constellation, forever illuminating the sky as a reminder of the heroic deed performed by his son Hercules, who saved humanity from this formidable catastrophe.
Video footage
Star formations
Leo is one of the most popular constellations in the night sky. It has a fascinating history, with numerous myths and intriguing discoveries. Leo has been known to the Sumerians for centuries and is included in the celestial catalog. Around two thousand years ago, this constellation held great significance as it marked the summer solstice, and its depiction took on its current form. The lion’s mouth was portrayed as pouring out streams of water, symbolizing the flooding of the Nile.
The lion is an outstanding representative of the zodiac constellations, and it is traversed by the ecliptic, along which the main star – the Sun – moves in space. The Leo constellation is situated in the sky between Cancer and Virgo, and nearby, you can observe the Sextant, the Big Dipper, the Little Lion, and the Bowl. Upon closer inspection of the constellation, it truly resembles the form of a resting animal due to the unique arrangement of its brightest stars. Its origin is linked to the Nemean lion, which was vanquished by Heracles.
The most brilliant celestial body in the astrological grouping
Regulus, the most luminous star within the Leo zodiac grouping, stands out as one of the most radiant entities in the entire nocturnal expanse due to its close proximity to our planet. However, observing Regulus can be quite challenging due to its position on the ecliptic and its frequent concealment by celestial bodies such as the Moon, Venus, and Mercury. Additionally, this primary star shines 160 times brighter than our own Sun. The Arabs referred to Regulus as the “Heart of the Lion,” while its Latin name translates to “little king.”
In addition to its “predatory” celestial bodies, the constellation of Leo conceals one of the nearest stars to Earth. Meet the Wolf, or Wolf, a red dwarf that exhibits intermittent flares. Within a matter of minutes, the Wolf can suddenly ignite and just as quickly extinguish, sometimes indefinitely. This youthful and captivating star has yet to reach its full luminosity.
Of particular interest to both experts and enthusiasts is the Kaffau star, which astronomers have recently discovered in the galactic halo. Not only is it a powerful celestial body, but it is also one of the oldest stars in the Milky Way. Almost devoid of oxygen and carbon, Kaffau remains an enigma in the scientific community, leaving many researchers puzzled and curious.
The tale of the birth
The story of the origination of the Leo constellation, as per usual with the ancient Greeks, is mesmerizing and valiant. Folklore intertwines the group of stars with the narrative of how the mighty Heracles triumphed over the Nemean lion in a fierce battle. It all commenced when Zeus banished the vanquished Titans to Tartarus, where they would endure eternal torment. Dauntless sentinels stood watch over the captives at the entrance of the prison, while Zeus persisted in combating malevolence across the world.
His next objective was to defeat the fearsome Typhon, the monstrous offspring of Gaea and Tartarus, who unleashed chaos upon the Earth. A grotesque amalgamation of terrifying creatures, Typhon scorched everything in his path. However, Zeus swiftly vanquished the hundred-headed beast, seizing its colossal body and consigning it to the titans, ensuring that Typhon would never again pose a threat. The creature remained imprisoned in Tartarus for eternity, yet it spawned new monstrosities in conjunction with Echidna – the two-headed and three-headed dogs, the hydra, and the Nemean lion.
The colossal lion, whose razor-sharp fangs could strike fear into even the bravest warrior, was banished to the mountains near the city of Nemea, from which it derived its name. The beast laid waste to everything in its vicinity, slaughtering humans and instilling terror in the population. In a desperate bid to restore peace, King Eurystheus tasked Heracles with the mission of bringing the slain lion’s carcass to Mycenae.
Embarking on his latest task, Heracles was filled with horror as he gazed upon the desolate land of Nemea. The whereabouts of the fearsome beast remained unknown. In the deep darkness of the night, Heracles pinpointed his target – the resounding roar of a mighty lion reverberated through the area, signifying the creature’s emergence for its hunt. Taking cover at the cave entrance, the hero located the predator’s den and prepared himself for the imminent attack.
As the Nemean lion emerged from its lair, it proved impervious to Heracles’ weaponry. Undeterred, the hero engaged the beast with nothing but his bare hands and a simple stick, using it to incapacitate the lion before ultimately strangling it. Having vanquished the creature, Heracles made a sacrificial offering to Zeus and instituted the Nemean Games – a significant Greek celebration during which all disputes, conflicts, and wars were temporarily halted.
How to Spot the Lion Constellation in the Sky?
Many individuals are unaware of how to locate the Leo constellation in the dark, starry sky; however, it is actually quite visible most of the time. Throughout most of the Russian Federation, on a clear and cloudless night, it only takes a few minutes to admire the majestic lion.
In the nighttime sky, the lion stands out due to its brightest star, Regulus, which is situated near the ecliptic. By carefully examining the Leo constellation, one will notice that its brightest stars form a distinct trapezoid shape, which sets the lion apart.
There is another method to detect the celestial predator by using other constellations. The constellation Virgo, which has a star called Spica located near the ecliptic, is situated to the east of the predator. When combined with Arthur, it forms an asterism known as the “spring triangle” that can be easily seen even in unfavorable weather conditions.
It is even simpler to locate the Big Dipper, a beloved constellation for both adults and children, which is typically the first one to be spotted by stargazers. Currently, the Big Dipper is positioned north of Leo. Additionally, it is worth mentioning that the best time to observe this constellation is in February – March, and the Sun enters it in mid-August.
Comparing Star Regulus
Astronomical entities
The constellation Leo encompasses numerous astronomical entities that captivate the attention of researchers and astronomers. These include the intermediate galaxies discovered by the renowned French scientist Messier in the 18th century, which bear his name. These galaxies constitute the famous Leo Triplet, consisting primarily of old stars and containing minimal amounts of gas, rendering them devoid of active luminosity.
Astronomers have observed that certain galaxies engage in interactions with other objects as a result of the distortion of one of their disks. As a consequence of these interactions, some of these galaxies possess fascinating dusty streaks. Scientists have determined that these streaks were formed as a result of the collision of the disks, which caused a gravitational interaction that disrupted the material responsible for highlighting the spiral arm.
A year following the discovery of these galaxies, Charles Messier included a newly discovered galaxy in his catalog, which had been observed by Pierre Meschen. In 2012, researchers at this galaxy made an exciting observation of a unique supernova, which attracted global attention and was closely monitored by scientists worldwide.
One of the galaxies in Leo stands out as the most luminous among them. Scientists are particularly interested in this galaxy due to its ultraviolet radiation and external features that suggest the presence of a supermassive black hole, which is expected to reveal itself in the future. Pierre Mechene was the one who discovered this galaxy, and there has also been a sighting of another supernova in this area.
The largest galaxy in Leo has a diameter similar to that of the Milky Way, but it has some minor imperfections resulting from past collisions with other celestial objects. Mechen also discovered an elliptical galaxy in Leo, which is known to have a black hole. However, there is still no definitive information regarding the size of this black hole. Hopefully, in the near future, someone will be able to estimate its magnitude.
Renowned explorer William Herschel played a vital role in the discovery of a spiral galaxy that possesses a distinctive “tail” and a wide streak of dust. This galaxy is also part of the Leo Triplet, making it one of the most prominent and captivating celestial bodies in the sky. The streak traverses the disk’s plane and is a source of fascination for young stars. It was designated as a unique galaxy in the 20th century due to its inability to be classified using conventional criteria.
Additionally, the Lion Ring in this constellation is an enigmatic phenomenon that continues to puzzle scientists. This extraordinary object consists entirely of helium and hydrogen and is believed to be a primordial cloud. Radio astronomers discovered its presence orbiting two galaxies in the late 20th century, and the scientific community is still actively engaged in debating its nature and origins.
In just a few years of meticulous work on the constellation, Herschel discovered three additional galaxies that were completely unique. Among them was an elliptical galaxy filled with ancient stars, as well as an object situated directly above the star Theta Leo. Prior to Herschel, the German astronomer Albert March had also stumbled upon one of the Lion galaxies. March took the time to describe, label, and study this elliptical object within the constellation.
The constellation Leo is undeniably one of the most captivating sights in the night sky. Not only is its distinctive shape easily recognizable, but the brightness and abundance of its celestial components also add to its allure. While many of the stars, galaxies, and rings within Leo remain enigmatic due to their vast distances, it is only a matter of time before these mysteries are unravelled and explained.