It is not uncommon for individuals who are distant from the field of astronomy to feel inspired by the captivating images captured by the Hubble Telescope or the James Webb Telescope, and subsequently decide to purchase an amateur telescope. The prospect of gazing upon the surfaces of distant planets, passing icy comets, or observing nebulae millions of light years away from Earth with one’s own eyes is undeniably fascinating. With bated breath, one approaches the telescope’s eyepiece, eagerly anticipating a journey into the enigmatic realm of space, brimming with hidden details and vibrant colors. However, reality often diverges significantly from these lofty expectations. Nevertheless, this does not negate the value of owning a telescope. Simply peruse these photographs, and you will gain a newfound understanding.

The view of space through a telescope is not what many people envision.
What sets apart an expensive telescope from a budget one
When browsing through various online retailers, it becomes evident that amateur telescopes for stargazing come in a wide range of prices, starting as low as $50 or even $25 (approximately 1560 rubles) and reaching several thousand dollars. It doesn’t require an expert to recognize that the pricier the telescope, the superior its ability to observe celestial objects. However, the extent and significance of this disparity deserve closer examination.
From a technical standpoint, there are various differences among telescopes in terms of their optics, construction type, lens diameter, and, of course, size. There are lenticular, lenticular-mirror, and mirror models available for amateur astronomers. When purchasing a more affordable telescope with a diameter of up to 100 mm, it is advisable to favor a lenticular or lenticular-mirror design. However, if you are interested in a telescope with a lens diameter exceeding 100 mm, it would be preferable for it to be a mirror-based model.


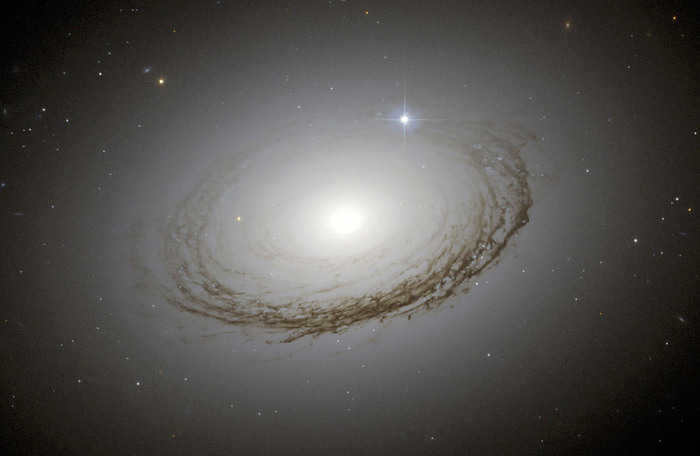
In an expensive telescope, objects appear clearer and more detailed.
How much do the characteristics of cheap telescopes differ from expensive ones, and is it worth spending more? Planets can be observed even with a low-cost telescope. The only question is what will be visible and how it will appear.
Many individuals believe that in an expensive telescope, objects will appear larger because it provides stronger magnification, allowing for the observation of small details. However, this is not entirely true. While expensive telescopes do offer stronger magnification, the difference is not as significant as the difference in price. This is particularly true for objects located at a significant distance.
The factors influencing the visibility of objects
The visibility of objects is determined by various factors, including the quality of the telescope and external conditions. However, it is important to note that it is not solely dependent on cloudy weather. Other significant factors that affect visibility include light pollution and atmospheric pollution. This is because urban lighting scatters in the atmosphere and reflects off dust particles in the air.


Comparing the visibility of the Andromeda Galaxy under different conditions
In certain circumstances, objects may appear blurry and indistinct even when observed through high-end telescopes. Hence, attempting to pursue astronomy from one’s own balcony, particularly in urban areas, is not advisable. To observe planets and other celestial objects, one must venture outside the city limits, where there is minimal street lighting and atmospheric pollution. This is why observatories are typically established in remote mountainous regions, far from civilization.
What can you observe with a telescope?
There is a common misconception that when looking through a telescope, you can see the planets of the solar system in great detail, resembling the images published by NASA. However, amateur astronomers often face disappointment as many planets appear as small, blurry dots even through high-quality telescopes. Nevertheless, this does not imply that amateur telescopes are incapable of revealing anything interesting.


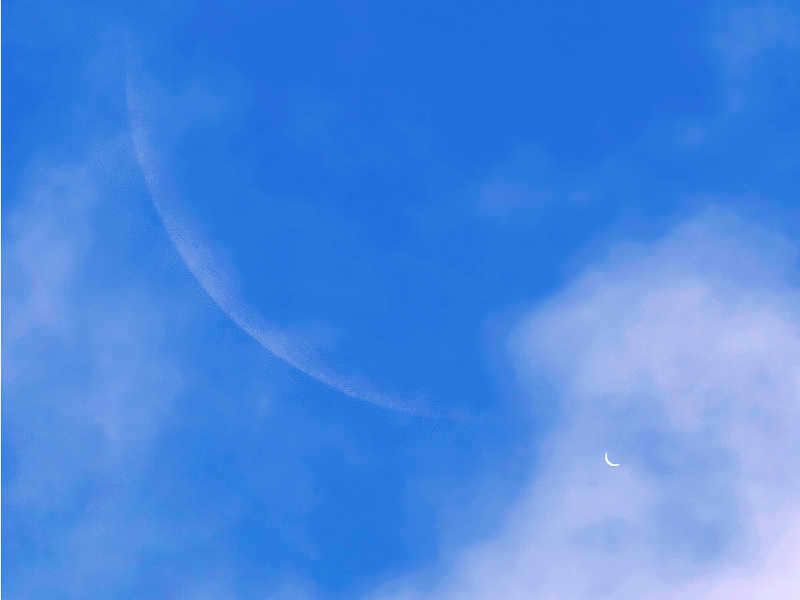
This is the view of Venus through an affordable telescope.
Mercury and Venus
Due to its close proximity to the Sun, Mercury is challenging to observe and can only be seen very rarely. Even if it is visible through the telescope, it will appear as a small, blurred spot.

Observing Venus through a high-end amateur telescope
When it comes to Venus, the experience is more favorable as it can be observed through an affordable telescope. However, the view may not be particularly impressive as it appears as a small, silver crescent-shaped object. There are no discernible details, even when observing Venus through a more expensive telescope.
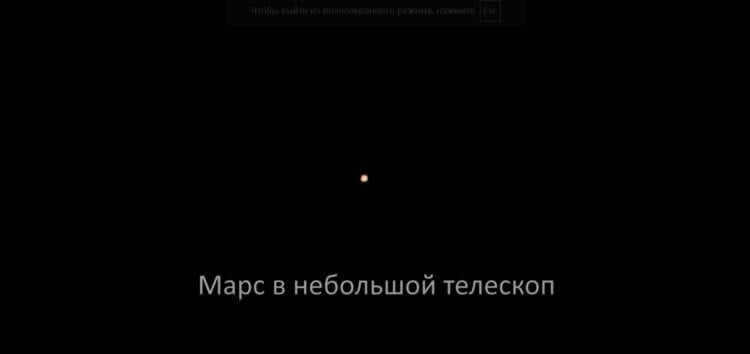

This blurred reddish spot is Mars – this is how it appears in a reasonably priced telescope.
Mars
While Venus and Mercury may not capture the interest of most individuals, Mars continues to intrigue scientists who are tirelessly searching for signs of life, or any remnants thereof, that may have once thrived on the red planet. Some even speculate that these traces of life may have contributed to Mars’ supposed “demise”. Unfortunately, obtaining a clear view of Mars is no easy feat. Even during its closest approach to Earth, the planet appears as nothing more than a red spot with indistinct edges when observed through an inexpensive telescope. When Mars is far from our planet, it becomes virtually invisible to the naked eye.

Mars appears more captivating when observed through a high-end telescope.
With the aid of a top-notch telescope, one can discern more intricate features, such as the polar caps, if fortunate. However, it is important to note that the image obtained may deviate from the conventional perception of Mars held by many individuals.

This is a guide on how to observe Jupiter using an affordable telescope
Jupiter and Saturn
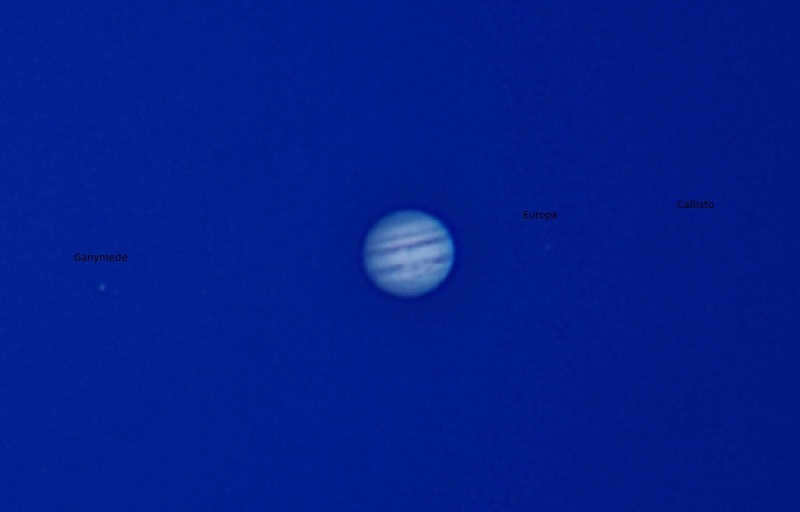
Observing Jupiter can be a fascinating experience. Even with a basic telescope, like the one used by Gallileo Gallilei, you can still observe this planet. A high-end telescope is not necessary. With an inexpensive device, you will be able to see Jupiter’s equatorial bands. In a more advanced telescope, the image will be sharper, allowing you to distinguish the boundaries between the equatorial bands more clearly. You can also observe Jupiter’s four satellites using any telescope. However, it is unfortunate that the satellite Enceladus, which could potentially harbor life, is not visible through amateur telescopes.

This is the appearance of Saturn when observed through a high-end telescope
Saturn is truly remarkable. Its well-known rings and satellites are visible through any telescope. Moreover, when viewed with an expensive instrument, one can also distinguish the equatorial bands on the planet.
Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto
When it comes to Pluto, observing it with either a budget-friendly or high-end telescope is impractical. Its vast distance from Earth, coupled with its small size, makes it nearly impossible to see in a meaningful way.

Despite the use of a pricy telescope, the visibility of Uranus remains limited.
While Uranus and Neptune are technically observable, even with a high-end telescope, their appearance would resemble faint, indistinct dots. Hence, these planets hold little fascination for amateur stargazers.
Exploring the Depths of Outer Space
When it comes to observing the wonders of deep space, it may seem counterintuitive, but high magnification is not necessarily required. The crucial factor is the diameter of the telescope’s lens, as it determines the amount of light it can gather. In other words, the larger the lens diameter, the more light it can capture. This ability to capture light is what allows us to glimpse galaxies and nebulae in the night sky.
Thus, the difference between inexpensive and expensive telescopes becomes more evident when observing deep space objects. However, even more critical is the absence of light pollution. Attempting to view deep space objects from the heart of a bustling city would be futile, regardless of the telescope used.

Amateur telescopes of various price ranges provide different views of the Hercules cluster in deep space.

This is a visual representation of stars through a telescope
Stars compared to the Sun
Observing stars may not be particularly exciting, as they appear no different through a telescope than they do to the naked eye. However, it is worth noting that what may initially seem like a single star can actually be a cluster of multiple stars when viewed through a telescope. This phenomenon can be observed with any telescope.


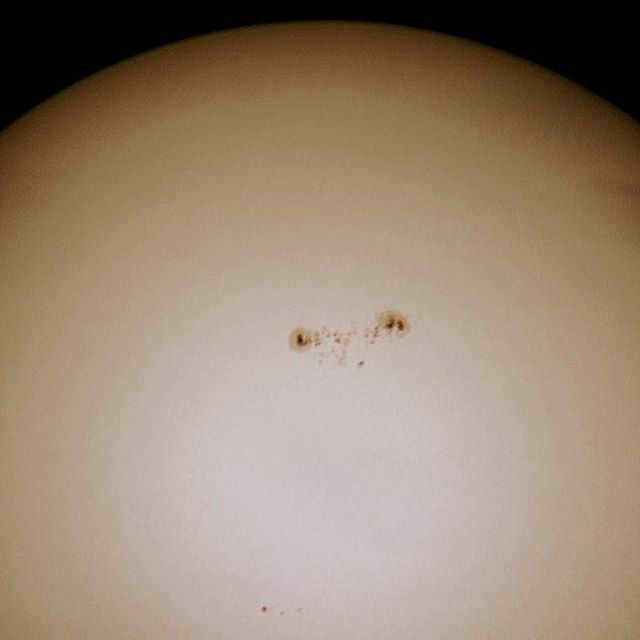
Here’s how you can observe the Sun through a high-quality filter in a costly telescope
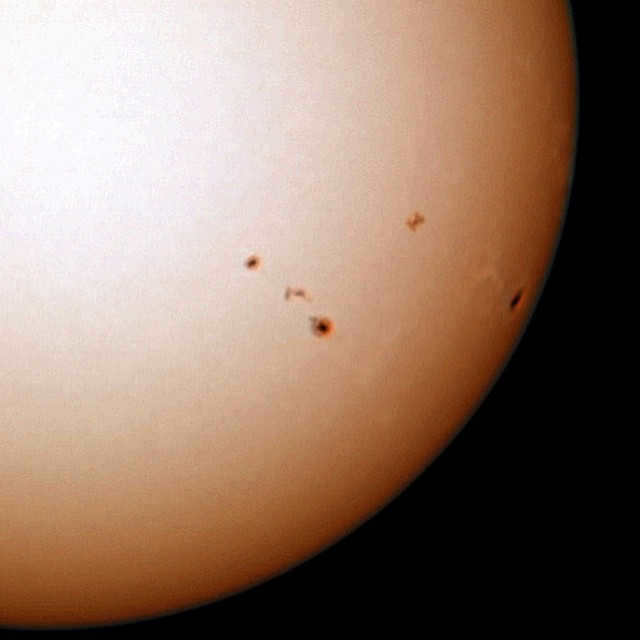
Regarding the Sun, it is only possible to observe it through a telescope twice in a lifetime – with the left eye and the right eye. And there is indeed a punchline in this joke. Without special equipment, it is impossible to gaze at our star. However, you can purchase a special filter, which functions similarly to sunglasses. Even in the most affordable telescope, with the aid of a filter, you can observe sunspots on the Sun. In a pricey telescope, as expected, there will be more intricate details.

This is the view of the Moon through an affordable telescope
Moon
It is not difficult to understand that the Moon can be observed through a telescope with great clarity. It is important to note that significant details of the Moon’s surface can be observed even with a basic telescope or binoculars.


A high-priced telescope offers the opportunity to observe the Moon with more precision.
With a telescope, you can even observe relatively small craters and various irregularities on the satellite. An expensive telescope will reveal an abundance of details. However, it is important to note that even with such a telescope, it is not possible to view the American flag or the lunar rover due to the limitations of the telescope’s capabilities.

Comets are visible even through a low-cost telescope
Comets, supernovae, and man-made satellites
On occasion, when comets approach the Sun closely, they become visible through any telescope. Typically, they appear as a hazy envelope with a tiny luminous point at the center. However, there are instances when comets come in proximity to Earth, enabling observers to discern them with greater clarity. Additionally, it is possible to observe man-made satellites, including the International Space Station (ISS), through a telescope.

With a high-quality telescope, it is possible to observe even the smallest details of the International Space Station (ISS).
If one takes space observation more seriously, they may occasionally witness extraordinary events such as supernova explosions and stars being eclipsed by asteroids. Additionally, the observation of variable stars that undergo changes in brightness over time is also possible.
Be sure to subscribe to the YANDEX.ZEN CHANNEL, where you will discover truly captivating material.
Although observing space objects through a telescope may not be as visually stunning as some might imagine, it still remains a fascinating and thrilling experience.
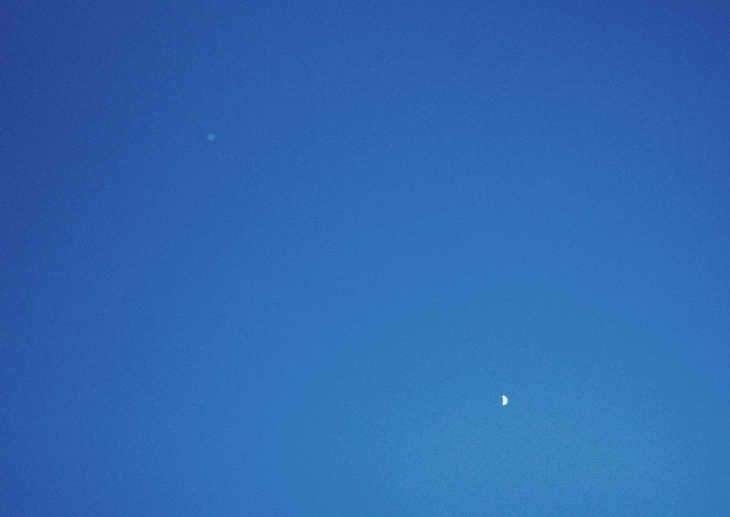
It is common knowledge that astronomical observations are typically conducted during the dark hours, preferably in locations far from the glare of city lights. However, there are still plenty of fascinating sights to behold in the daytime sky, even with the presence of bright sunlight. And it’s not just limited to the Sun. During daylight hours, one can observe the Moon with great clarity, and with a certain level of expertise, it is even possible to spot and capture images of certain planets and spacecraft! This article contains a multitude of photographs and videos showcasing various celestial objects captured in broad daylight.


Daytime view of the Moon and Venus. Image credit: Astronomy Picture of the Day, by David Cortner.
I have made an effort to acknowledge the creators of all the images I have included in this article. The authors of YouTube videos can be found on YouTube. In cases where the author is not specified, I have used my own photographs.
The Sun is the most prominent object for observing during the daytime, as it is not visible at night. To safely view the Sun, it is important to use a dense light filter to protect your eyesight. You have the option to create your own filter using specialized film or purchase a pre-made glass filter. In certain instances, atmospheric haze can act as a natural filter, allowing for the observation of large sunspots even without any additional protection. In the provided photograph, a cluster of sunspots known as AR 2396 can be seen below and to the left of the center of the Sun’s disk.

So, when observing the sun through a compact telescope and using a special filter, the sunspots appear in the following manner:

By using basic techniques in the image editing software, you can uncover faint flares that are invisible to the naked eye – these are luminous formations that surround the spots.
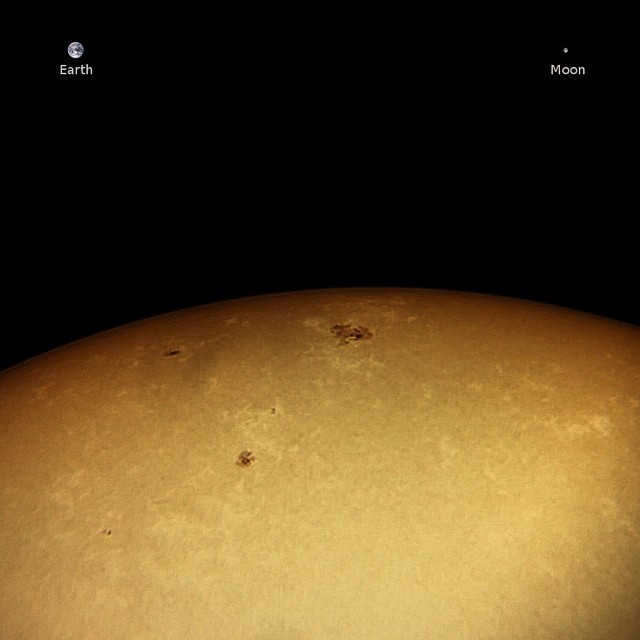
To illustrate the size, I have included an image of the Earth and the Moon in proper proportions at the top of the picture.
Lunar Satellite
Many individuals are unaware that the Moon can be observed during daylight hours. It is visible on most days, except for those near the new and full moon phases. The waxing Moon can be seen in the latter part of the day, while the waning Moon is visible in the earlier part. Presently, it is an opportune moment to observe the waning Moon, as it can be easily spotted in the morning while commuting to work. You can even capture a photo of the Moon during the day using your smartphone:


You can observe lunar craters during the day through a telescope, and capturing photos of them against a vibrant blue sky can create an even more stunning effect compared to traditional night photos with a dark black backdrop.

If you capture multiple images with a 24-hour gap, you will be able to observe not only the alteration in lunar phases, but also the phenomenon of libration.
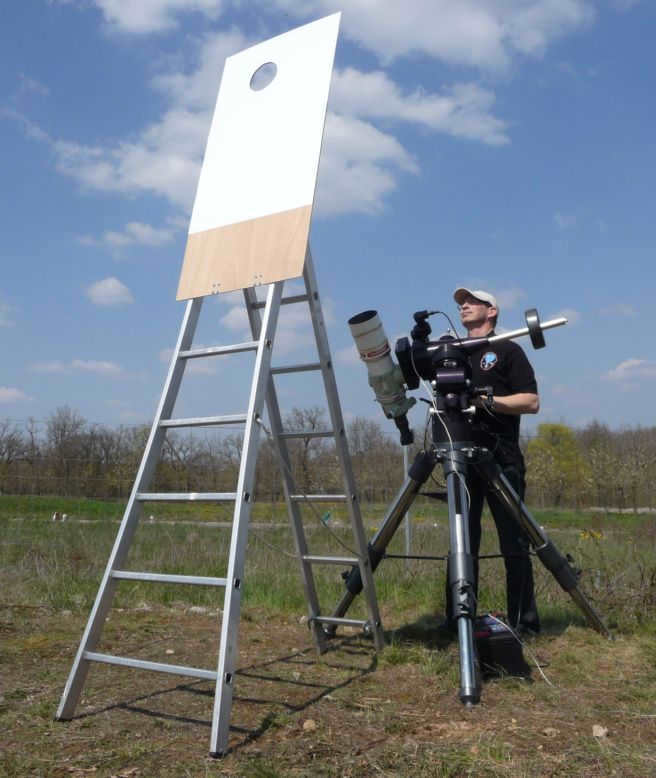
Furthermore, presented here is an impressive photograph by Thierry Legault, showcasing the thinnest crescent moon ever captured.

At the moment the photo was taken, the Moon was a mere four degrees away from the Sun. To capture the image without interference from the bright light, the photographer had to construct a special contraption for protection.

Lastly, when it comes to the Moon, it is impossible not to consider solar eclipses, when the Moon moves in front of our primary source of daylight.
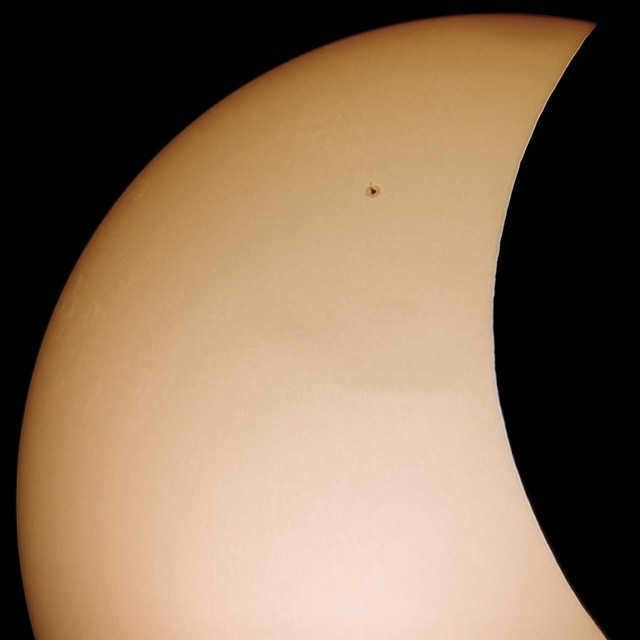

If you are interested in seeing more images of the recent solar eclipse, I encourage you to check out my article titled Watching the Solar Eclipse Together. It features a collection of captivating photographs that captured the beauty and wonder of this celestial event.
Discover the Enchanting Venus
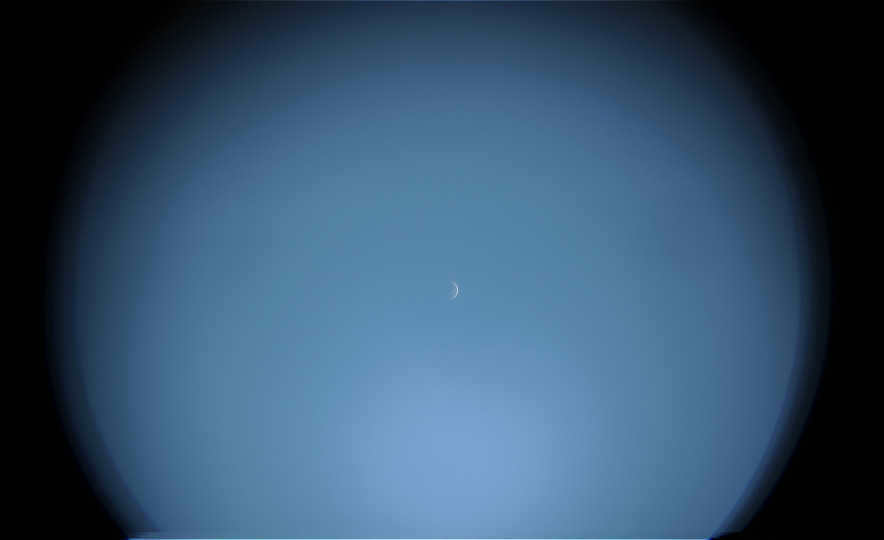

The narrow sickle is incredibly luminous, illuminating even the lightest clouds, as evidenced by the captivating videos below.
#Daytime #planet #Venus piercing through the #clouds.
A video shared by @lunogram on Aug 30, 2015 at 4:56am PDT
Another mesmerizing video showcasing #daytime #Venus.
A video shared by @lunogram on Aug 30, 2015 at 5:02am PDT
Jupiter
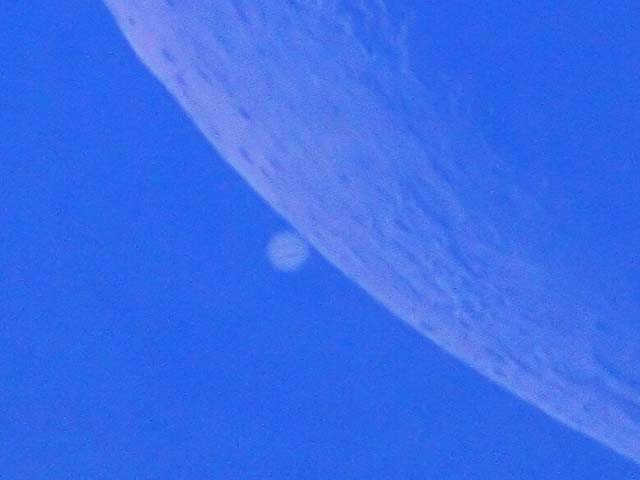
Jupiter is situated at a significantly greater distance from the Sun. During daylight hours, it poses a considerable challenge to observe Jupiter with the unaided eye, as it appears fainter compared to Venus.

Francisco Diego from spaceweathergallery.com captured the conjunction of Jupiter and Venus.
It bears a resemblance to the Moon’s crescent in terms of surface brightness.

Text source: Sky and Telescope, written by Gary Seronik.

Nonetheless, certain photographers are able to capture a daytime image that reveals the intricate features of Jupiter’s surface and even its orbiting satellites.
Source: Stargazers Lounge, by Steve Ward.
Mars
On occasion, during periods of intense opposition, Mars can shine as brightly as Jupiter. However, Mars is not visible during these confrontations – it rises at sunset and sets at dawn. Therefore, during daylight hours, it can only be observed in this manner:

Image source: spaceweathergallery.com by Philip Romanoff.
Mercury
Locating Mercury in the sky can be challenging due to its proximity to the Sun. Can you spot Mercury in this photograph?

Venus and Mercury. Author: Emil Ivanov.
If you’re unable to, click to view a bigger image.
An excellent opportunity to observe Mercury during daylight hours will occur on May 9, 2016, as the planet will cross the Sun’s disk. An intriguing fact is that Mercury and Venus will both transit the Sun together on July 26, 69163. The last time this dual transit occurred was in 373,173 BC.
Artificial satellites
I have previously mentioned that the International Space Station (ISS) is as bright as Venus, making it visible during the daytime. During the day, it appears as a white dot floating in the blue sky. By using a telescope equipped with a motorized mount and specialized software to track satellites, you can capture its magnificent presence on video.
At times, the ISS comes near the Moon or even crosses its disk. When this occurs, it becomes much easier to observe and film the ISS, as the Moon serves as a visible reference point.
If the ISS passes in front of the sun, you can observe its dark silhouette using the same methods employed for observing sunspots.

For information on when the ISS will pass near other celestial objects, you can visit calsky.com.
Iridium flashes can outshine the ISS and are of short duration, usually lasting only a few seconds.
If you are unable to see anything, try opening the video in full screen mode.
Dipskai
It’s hard to believe, but with the help of an H-alpha filter, it is possible to capture the image of a luminous nebula in the sunlight. I created a captivating animation by combining a series of shots of the M42 nebula. The initial photograph, which showcases the finest details, was captured at the break of dawn, while the final one was taken forty minutes after sunrise.

Clusters of young stars are surrounded by dark nebulae. This specific region belongs to the star cluster located in the Eagle Nebula, which came into existence approximately 5.5 million years ago and is positioned 6500 light-years away from our planet.


Located in the Indian constellation, the NGC 7049 is a massive galaxy that is situated 100 million light-years away from our planet.

Situated at a distance of two thousand light-years from our planet, the Sh2-106 emission nebula is a small yet active area where new stars are being formed. In the midst of this nebula lies the star S106 IR, which is surrounded by a combination of dust and hydrogen. In the photograph, this region is depicted as conventionally blue in color.

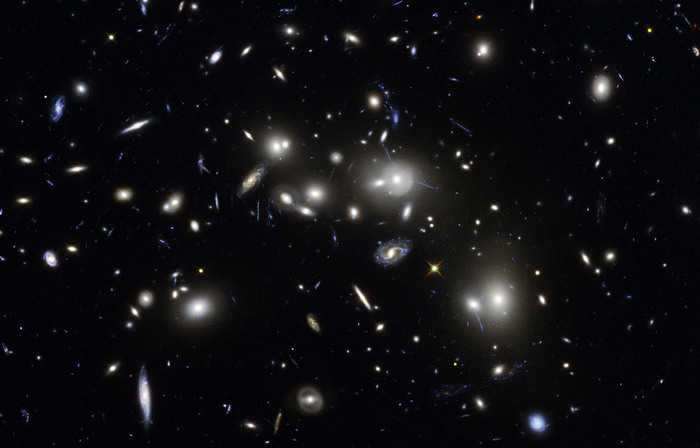
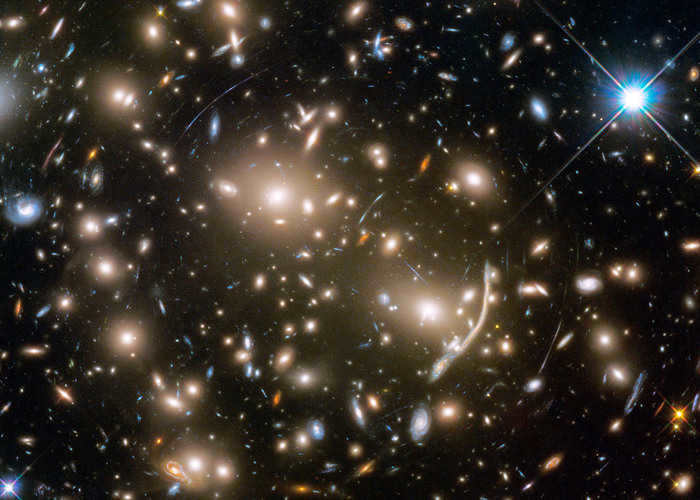
The Pandora cluster, also referred to as Abell 2744, is a massive assemblage of galaxies formed from the simultaneous convergence of at least four distinct clusters of smaller galaxies that took place over a span of 350 million years. The galaxies within the cluster contribute to less than five percent of its total mass, while the gas component (approximately 20 percent) emits X-ray radiation due to its intense heating. The enigmatic dark matter constitutes approximately 75 percent of the cluster’s overall mass.

The constellation Kiel is home to the Kiel Emission Nebula, also known as the “Caterpillar”. This stunning region is filled with ionized hydrogen, creating a beautiful display in the night sky.

NGC 1566, situated in the constellation Goldfish, is a spiral galaxy with a SBbc junction. It is positioned at a distance of 40 million light-years.
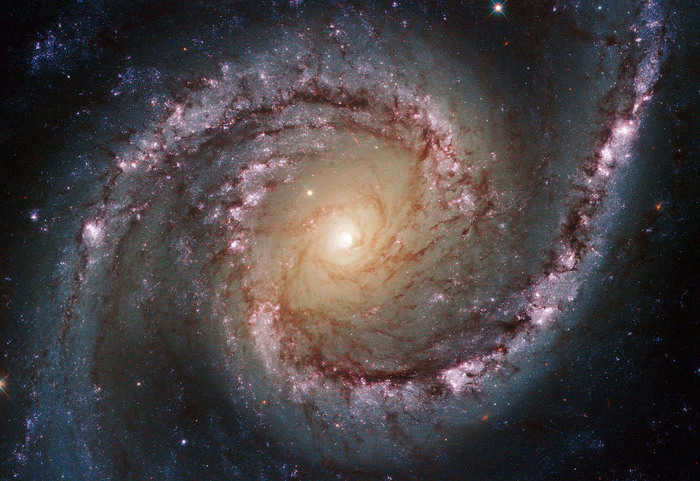

Located 2500 light-years away from Earth, IRAS 14568-6304 is a youthful star. The Circinus molecular cloud, a dusky expanse teeming with gas, dust, and fledgling stars, harbors a staggering 250,000 solar masses.

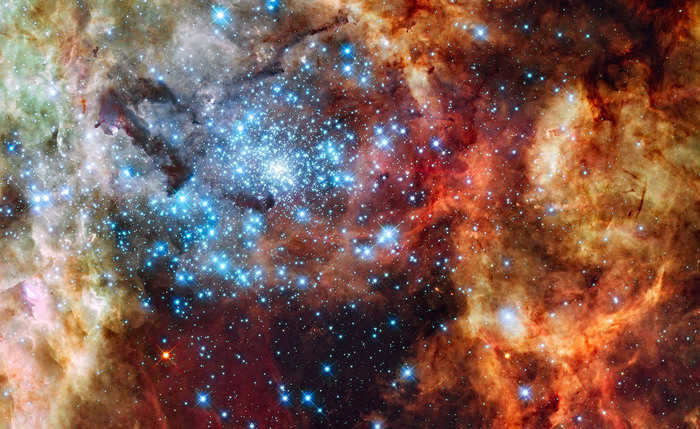
A collection of dazzling blue stars enveloped in radiant, luminous clouds forms the R136 star cluster, which serves as a celestial nursery. Situated in the heart of the Tarantula Nebula, this cluster is a sight to behold.
Comprised of youthful stars, including giants and supergiants, the R136 cluster boasts an estimated age of approximately 2 million years.

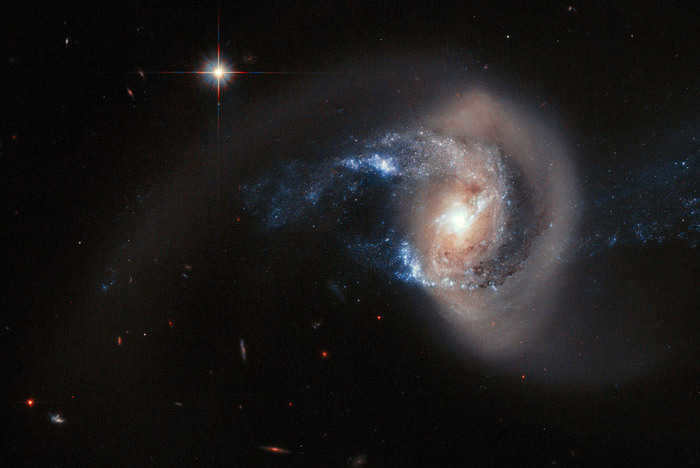
The constellation Pisces is home to the stunning spiral galaxy NGC 7714. This celestial beauty can be found approximately 100 million light years away from our planet Earth.

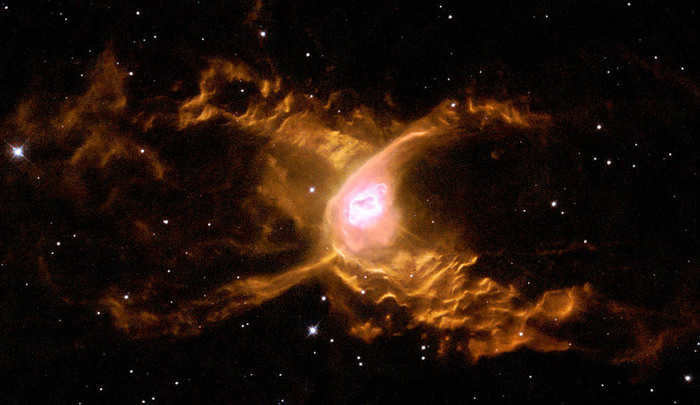
The Red Spider Nebula, also known as NGC 6537, has been captured in an image taken by the Hubble orbiting telescope. This breathtaking image reveals a unique wave-like structure that can be found in the constellation Sagittarius, approximately 3,000 light-years away from Earth. A planetary nebula is a fascinating astronomical phenomenon comprised of an ionized gas shell and a white dwarf star at its center. These nebulae are formed when red giants and supergiants shed their outer layers during the final stages of their stellar evolution, with masses that can reach up to 1.4 times that of our Sun.

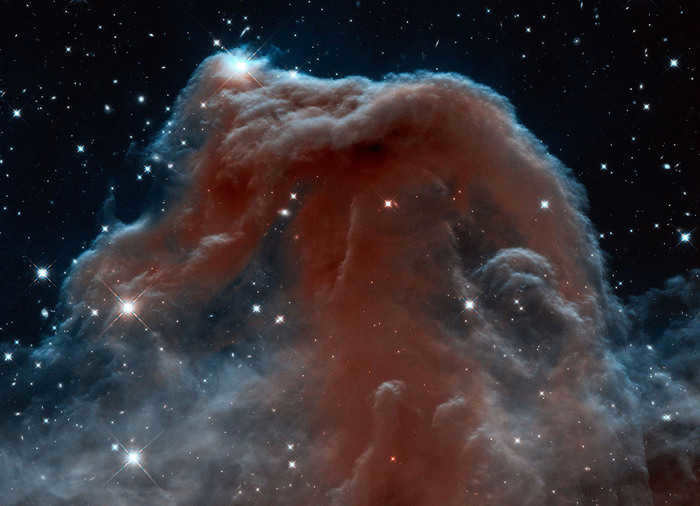
The Horsehead Nebula, located in the Orion constellation, is a prominent dark nebula that is widely recognized. Its distinctive shape resembles that of a horse’s head and stands out against a backdrop of glowing red. This red glow is a result of the ionization process caused by the radiation emitted from the closest bright star in Orion, known as ζ Orionis.

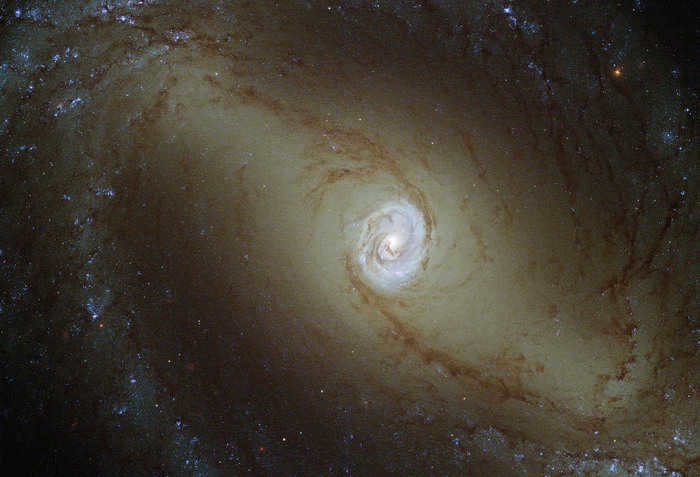
The Hubble Space Telescope captured a remarkable photograph of the closest spiral galaxy, NGC 1433, situated in the constellation Clock. Situated 32 million light-years from Earth, this galaxy is known for its high level of activity.

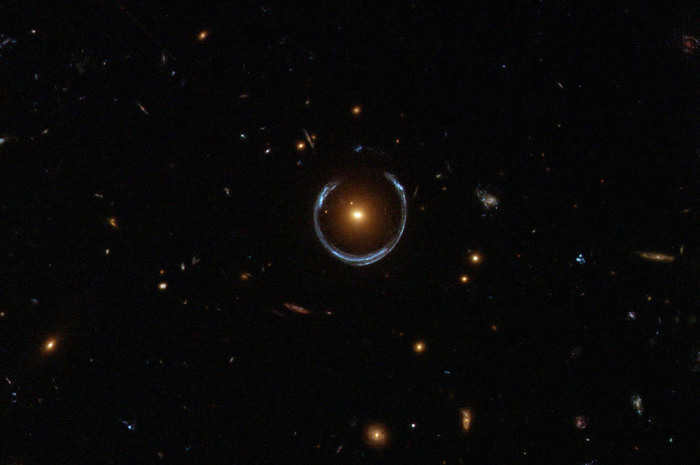
An uncommon cosmic event, the Einstein’s ring is a result of the phenomenon where the gravitational force of a massive object causes the bending of electromagnetic radiation as it travels towards Earth from a more distant entity.
According to Einstein’s theory of general relativity, the gravity exerted by large cosmic objects like galaxies distorts the surrounding space and alters the path of light rays. This leads to the formation of a distorted image of another galaxy, which serves as the source of the light. The galaxy responsible for bending space is referred to as a gravitational lens.

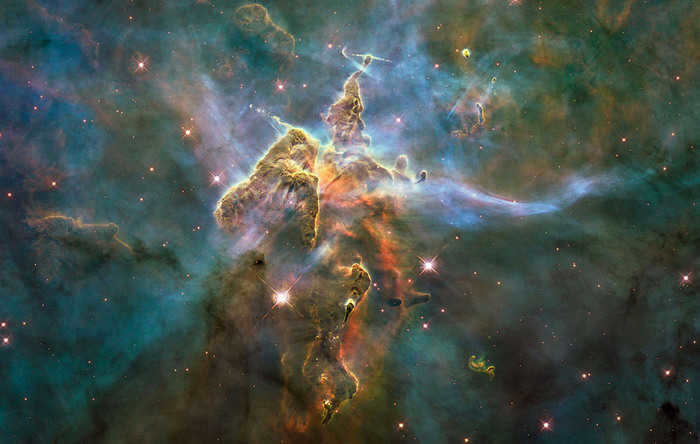
The NGC 3372 nebula, located in the constellation Kiel, is a remarkable celestial formation. This expansive and luminous nebula contains numerous star clusters scattered throughout its vast expanse.

Located in the constellation of Kita, Abell 370 is an extraordinary cluster of galaxies that resides approximately 4 billion light-years from us. At its core, this cluster is composed of numerous galaxies, totaling in the hundreds. Remarkably, Abell 370 holds the title for being the most remote cluster known to us. These captivating galaxies, which are positioned around 5 billion light-years away, continue to astound astronomers with their mesmerizing presence.

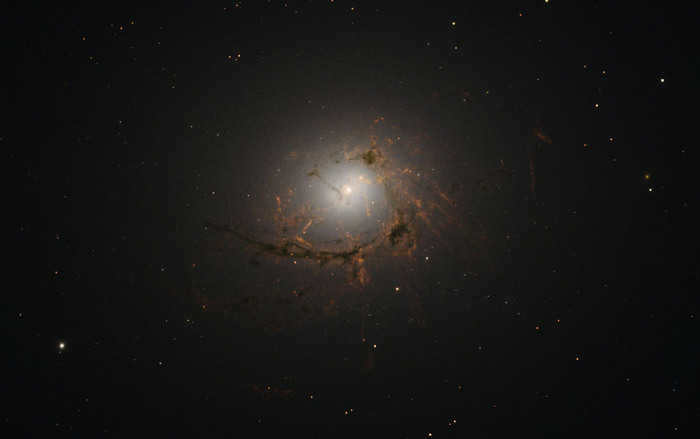
The Centaurus constellation contains the stunning galaxy NGC 4696, which is situated approximately 145 million light-years away from our planet. This galaxy holds the title of being the most luminous one in the Centauri cluster. Additionally, NGC 4696 is encompassed by numerous dwarf elliptical galaxies.

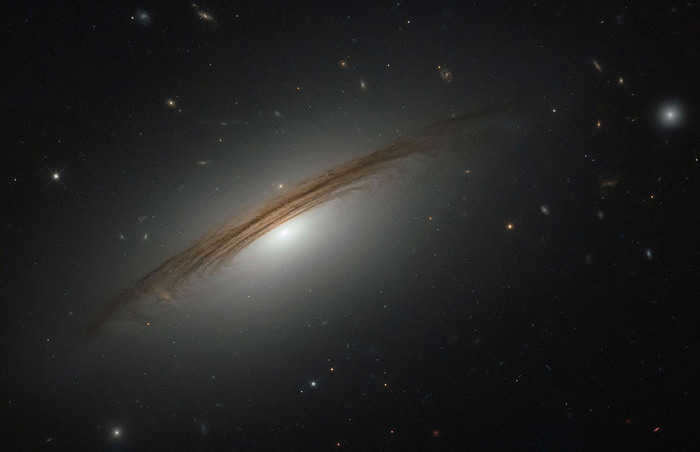
UGC 12591, located in the Perseus-Pisces galaxy cluster, has caught the attention of astronomers due to its unique shape. Unlike typical galaxies, it does not fall into the categories of lenticular or spiral, displaying characteristics of both.
What sets UGC 12591 apart is not only its unusual shape, but also its significant mass. Scientists have determined that its mass is approximately four times greater than that of our Milky Way.
In addition, this galaxy with a distinctive shape is also swiftly changing its position in space, while simultaneously rotating at an unusually high speed around its axis. The reasons behind this rapid rotation of UGC 12591 are still unknown to scientists.

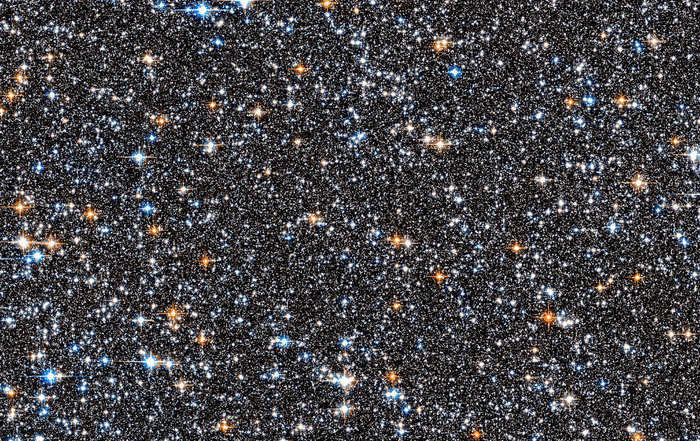
Can you believe the number of stars in this place! It’s the very heart of our Milky Way, situated a staggering 26,000 light years from us.

The PN M2-9 nebula, also known as the Minkowski Nebula 2-9, displays a distinct petal-like structure. This unique shape is believed to be a result of the movement of two stars in orbit around each other. The presence of a white dwarf in the system causes the larger star’s expanding envelope to take on the appearance of wings or petals, rather than expanding uniformly in a spherical manner.
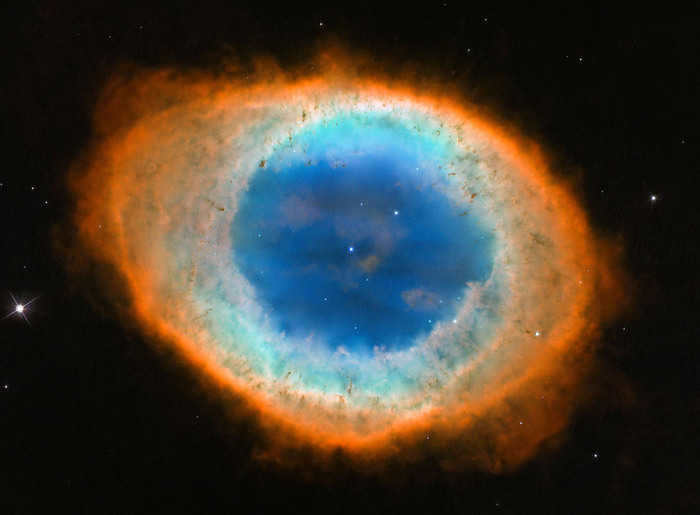
The planetary nebula known as the Ring can be found in the Lyra constellation. It is widely recognized as one of the most famous and well-documented examples of planetary nebulae. The Ring Nebula exhibits a ring-like structure that surrounds a central star. The nebula has a radius of approximately one-third of a light-year. By assuming that the nebula has been steadily expanding at a rate of 19 km/s, scientists estimate its age to be somewhere between 6000 and 8000 years.
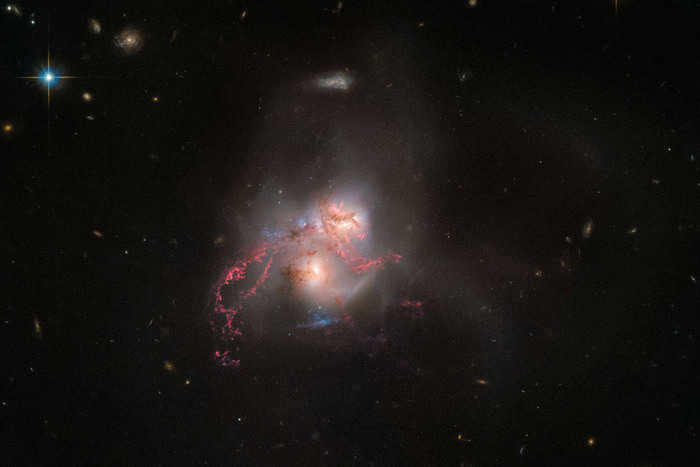
The constellation Big Dipper houses the stunning Galaxy NGC 5256.

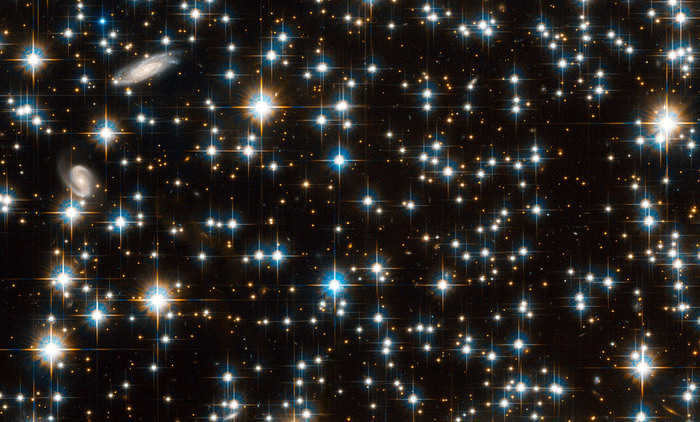
6791, a scattered cluster located in the Lyra constellation, contains a fascinating mix of stars. Notably, within the cluster, there exists a collection of white dwarfs that span a wide range of ages. Some of these white dwarfs have been shining for an impressive 6 billion years, while others have reached the 4 billion-year mark. These age discrepancies are particularly intriguing, as they deviate from the typical age of 8 billion years that is observed for the cluster as a whole.
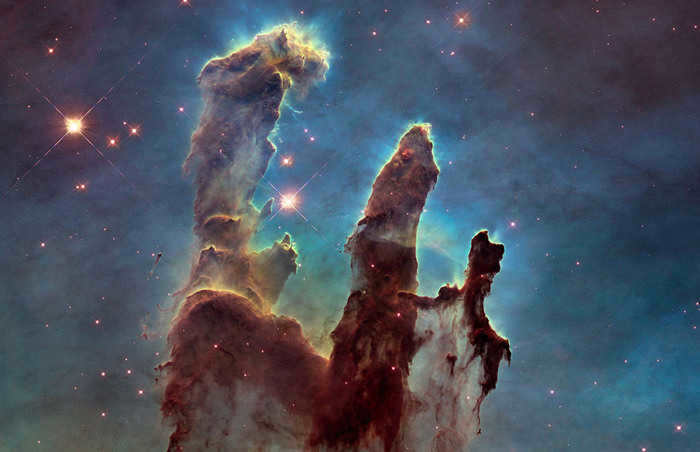


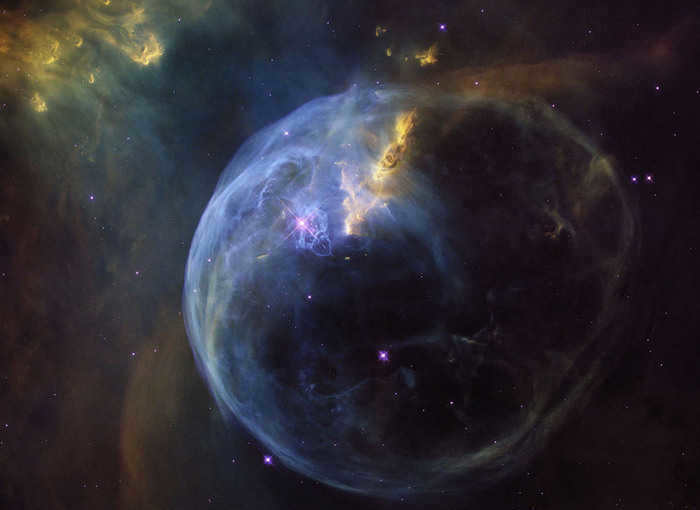
The Bubble Nebula, located in the constellation Cassiopeia, was created by the powerful winds emitted by a massive, hot star. Situated within a vast molecular cloud that spans a distance of 7,100 to 11,000 light-years from our Sun, this nebula is a truly breathtaking sight.

14.9K posts 45.3K subscribers
Guidelines for the Community
What regulations can exist in this space, other than the regulations established by the peekaboo itself 🙂
Given that we are discussing nebulae – I would like to present the forthcoming advancement in Space Engine, specifically the shader for new nebulae, which will not only be created using pre-made designs – but also generated at random for the uncharted universe:








After the collision of at least four separate small clusters of galaxies that occurred over a period of 350 million years, it becomes a bit uncomfortable. It all happened at the same time. It took millions of years.
I long for the day when I can witness the moment when I can leave the Earth, board a spaceship, set a course, and enter a state of suspended animation only to wake up near my desired destination. Then I can explore the celestial object, transmit the collected data back to the base, and start the process all over again, selecting a more vibrant and picturesque planet as my next destination ;)))
The Hubble telescope is an incredibly valuable tool, even if it’s mainly used for creating stunning desktop wallpapers.


Orion
Located 80 km from Minsk, the constellation Orion was captured using a Nikon d80 and Nikkor 50mm 1.8 lens.

Andromeda Galaxy
I made my first attempt to capture the Andromeda Galaxy through a telescope, but unfortunately, it didn’t go as planned. During my 30-second exposure, a mysterious dark cloud appeared and ruined the shot. Frustrated, I decided to switch to my 50mm lens with a tripod, and to my surprise, the results were much better. However, I am still eager to learn how to properly capture astrophotography through a telescope. I have a Celestron 70lt az, which is a relatively affordable option. If anyone has any advice or tips, I would greatly appreciate it!

The most alluring properties in our solar system
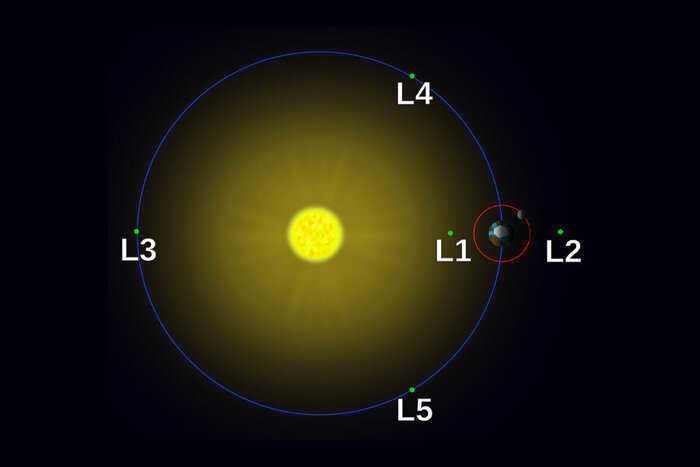
All heavenly bodies exert a gravitational pull on one another, with nearby objects being particularly affected. In such systems, the combined influence of other forces determines the shape of the orbits of the “participants of motion.” At certain points known as Lagrangian points, these forces are perfectly balanced. As a result, if an object with a relatively small mass is placed there, it will remain at a fixed distance from the bodies that create these stable islands. These zones are often referred to as cosmic parking lots, because once something enters them, the need to expend energy to stay there practically disappears. In essence, they are the perfect location for any man-made object intended for a prolonged stay in space.
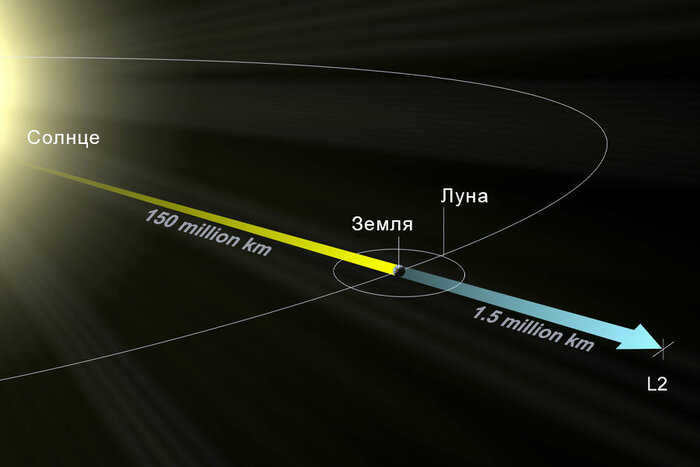
The issue of what can be placed in a specific Lagrangian point is quite fascinating in this context. Let’s focus on the ones created by the gravitational interaction between the Sun and the Earth. L1 is situated approximately 1.5 million kilometers from our planet, positioned between these two celestial bodies. Thanks to the unobstructed view of the star, it serves as an ideal spot for observing the Sun.
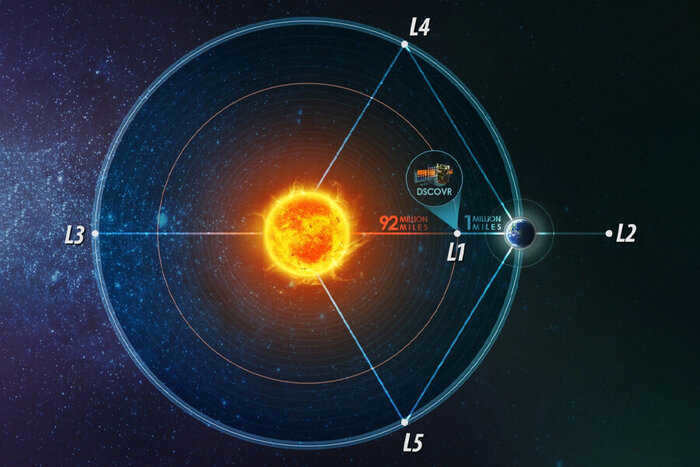
The Deep Space Climate Observatory is a spacecraft from the United States that is used to observe the Sun and Earth. It is situated at Lagrangian point 1.
On the opposite side of the Earth, at the same distance, is L2. This location is safely shielded from sunlight and offers unique opportunities for studying space. In 2022, the James Webb telescope, which astronomers have been eagerly anticipating for two decades, began its operations from this point.
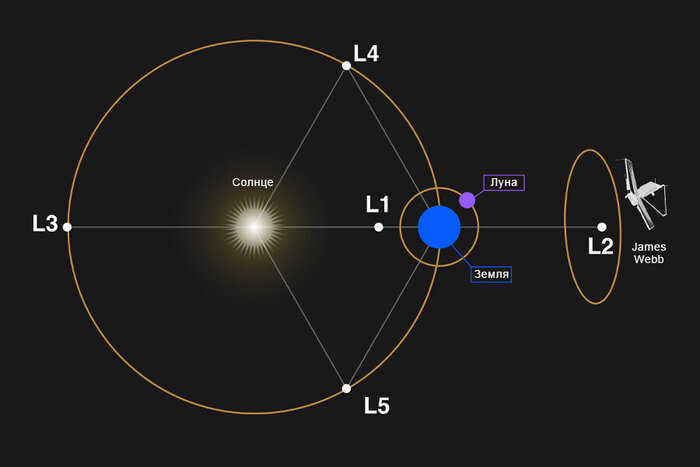
L3, located in the opposite side of the Earth’s orbit from the Sun, is an enigmatic and secretive place. It holds the unique distinction of being the only point in the vast expanse of the universe that cannot be observed from the surface of any planet, even in theory. This peculiar characteristic has made it a popular subject for science fiction writers, although scientists themselves have not found much practical use for it.
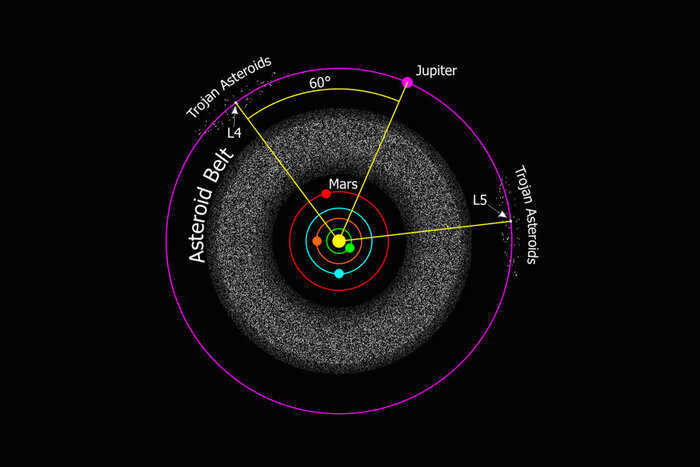
Every Lagrangian point within the solar system possesses its own unique characteristics. Some of these points could serve as a source for gathering construction materials, envisioning them as drifting asteroids. Other points could function as refueling stations, providing fuel for spacecraft voyaging into the vastness of space. It’s even conceivable that human colonies could be established and “suspended” at these locations. Naturally, this is a prospect that belongs to the distant future, one that we may not live to witness given the current state of affairs on Earth. Nevertheless, it’s always good to harbor dreams, isn’t it?
Thank you for your kind attention! If you enjoyed this article, you can show your support by giving it a “thumbs up” or subscribing to this channel. We would also like to take this opportunity to let you know that we have our very own Telegram channel where we regularly share fascinating posts about space and astronomy.
We deeply value every single one of our readers. If you would like to provide us with financial support (by using the button provided below), your name or nickname will be included at the conclusion of our upcoming publication. This gesture is our humble way of expressing our gratitude for your generosity and encouragement!

For centuries, the enigmatic allure of the night sky has captivated humanity. As optical technology has advanced, we have been able to unlock some of its secrets. Today, stargazing has become a popular pastime, offering both leisure and a means for scientific exploration. Beginners in this field often wonder what they can expect to see through a telescope. Even with semi-professional equipment, one can observe the moon’s surface, planets, galaxies, star clusters, nebulae, and comets.

Various Kinds of Optical Devices
If you want to have a pleasant experience while observing the beautiful night sky, it is important to make a purchase of a telescope. In our store’s inventory, you will find a wide range of options suitable for both professional astronomers and beginners. The equipment is categorized based on the type of device:
When making a selection, it is crucial to consider this specification. The quality of the image greatly depends on the diameter of the lens. This characteristic is also referred to as aperture, and it is the most significant aspect to consider for any telescope. Depending on its value, you will be able to view more or fewer celestial bodies, and distinguish even the tiniest details of their surfaces and structures. Additionally, it is worth noting that the higher the aperture, the more expensive the equipment will be.
- For children and beginners, it is recommended to use a telescope with an aperture of 50-80 mm;
- Amateurs should consider using a telescope with an aperture of at least 90 mm;
- Professional astronomers usually use equipment with an aperture over 150 mm.
The answer to the question of what can be observed through a telescope depends on the type of equipment used. The best price-quality ratio is offered by Levenhuk products. They have a wide range of models to choose from, suitable for different budgets.
What to observe with a beginner’s telescope
If you have a telescope with a 50 mm aperture, you can use it to view the surface of the Moon. This will allow you to see its topography and the largest craters. Additionally, you can also observe other planets in the Solar System and bright objects from the Messier catalog.
Telescopes with a 70-80 mm aperture provide a more detailed view of other planets. With such a telescope, you will be able to clearly see the rings of Saturn and the Great Red Spot on Jupiter.
Star clusters are another fascinating astronomical object that can be observed using a beginner’s telescope. They appear as clusters of bright and dim multicolored dots. This is a great opportunity to practice using star charts to locate objects. As you progress, you will also be able to see nebulae. These are clusters of dust and interstellar gas that form large spots of various shapes and sizes.
Of course, if you are just starting to explore the vastness of the night sky, you can employ a technique with low-power instruments. This method enables you to observe numerous celestial objects.

What can be observed through telescopes with different apertures
Thanks to modern technology, we are able to observe the planets of our solar system and their moons.
- Moon. With a hundredfold magnification, we can see the surface of the Moon in great detail, including craters, seas, mountains, and crevices. The Moon is visible every night, except during the new moon phase, as long as the weather is clear.
- Venus. While not the most visually striking object, Venus’ surface cannot be seen due to its dense atmosphere. However, we can track its phases of motion, which are similar to those of the Moon.
- Mars. It is fascinating to observe the planet during certain rotation cycles. When Mars is closest to Earth, dark spots resembling seas can be seen on its surface.
- Saturn. The rings of Saturn are perhaps the most breathtaking sight when observed through a telescope with an aperture of 90 mm or larger. Even smaller telescopes can reveal this characteristic phenomenon, while higher magnification allows for observing the gaps between the rings, cloud belts, and the planet’s satellites.
- Jupiter. One of Jupiter’s distinctive features is its cloud belts, with the number visible depending on the capabilities of the telescope used. Additionally, the planet’s satellites can be observed, including Callisto, Europa, Io, and Ganymede. These satellites can be detected by the shadows they cast on Jupiter’s disk as they pass in front of it.
When it comes to deciding what to observe through a telescope, one cannot overlook the fascinating world of double stars. These celestial phenomena occur when one star orbits around another. Double stars can come in the form of a pair or even clusters of multiple stars. What makes them particularly intriguing is that they emit radiation in different ranges, causing them to appear in various colors such as red, blue, and yellow.
An intriguing subject for investigation would be galaxies – conglomerates of billions of stars. When observed at low magnification, they appear as tiny dots, but with more advanced techniques, one can scrutinize their intricate geometries and spiral arms. The galaxy that is nearest to our own is the Andromeda Nebula. Other more remote nebulae, such as Orion, Dumbbell, and the Ring in the constellation Lyra, can only be observed with equipment that has a diameter of at least 200 mm. Due to their great distance from us and their low luminosity, they can only be seen in areas with minimal light pollution. Seasoned astronomers recommend venturing away from urban environments in order to reduce ambient illumination and enhance the visual experience.
Pleiades, which consist of globular and dispersed star clusters, are clearly visible in the nighttime sky. Typically lacking a fixed shape or a prominent center, they appear as randomly arranged circular spots.
One way to explore the possibilities of what can be observed through a 130 mm telescope is to study recurring astronomical events. Comets, for example, appear as small glowing patches with a distinct trail known as a tail. These bright celestial bodies, which often pass relatively close to Earth, are typically announced in advance through various media outlets. Additionally, an astronomical events calendar can provide information on the timing of their flights. With the help of high-quality optical instruments, it is possible to regularly observe comets in the nighttime sky.
How to begin stargazing
The view through the telescope will depend on various factors such as the atmospheric conditions, the expertise of the observer, and the type of equipment used. A refractor telescope is ideal for studying the moon and double stars as it produces a clear, bright, and well-defined image. If you prefer a more portable option, consider using a mirror-lens model. These models have the added advantage of minimizing image distortion. They are particularly useful if you plan on photographing celestial objects.

When purchasing a telescope, regardless of its make and model, the consumer is immediately intrigued by the potential sights it can offer. Naturally, establishing a personal observatory at home can be quite challenging, thus it is advisable to visit designated locations for optimal stargazing experiences. However, even having a telescope at home can provide a captivating adventure, as even models designed for children can leave a lasting impression.
What is visible through amateur telescopes?
When we think of space, our imaginations often conjure up grandiose images that are far beyond what can actually be seen through even the most powerful telescopes. It’s like comparing an illustration in an encyclopedia of the human body’s structure to an ultrasound image of specific organs. While there is a significant difference in the level of detail between the two, one offers a visual representation while the other provides a real albeit slightly blurry image.
Even a small telescope with decent optics can provide a glimpse of the Moon’s surface.
Some skeptics may argue that binoculars will enable you to observe the craters on the Moon. However, even when using high-quality binoculars, the Moon will only occupy a small portion of the field of view. It will be challenging to distinguish individual craters. On the other hand, if you use a seven-centimeter refractor with a magnification of 100 times, you will see the Moon filling the entire frame. Not only will the craters be visible, but also the details such as embankments, central hills, cracks, and mountain ranges. It’s important to note that this level of observation can be achieved with a 70mm refractor.
Now, let’s explore what else can be observed using a home telescope for amateur astronomers.
- Observing Planetary Disks. Even a small telescope with a magnification of 90x or 60x will reveal the distinctive shield and equatorial bands of Jupiter. However, viewing planets in general can be a disappointment for those who have preconceived notions about what they will see. Instead of detailed images, you will typically see tiny, pea-sized dots representing the planets. However, with a telescope that has a lens diameter of 10 cm or more, it is possible to observe the Great Red Spot, a massive vortex in Jupiter’s atmosphere.
Planets also have satellites, and observing them can be particularly fascinating. For instance, the Galilean satellites of Jupiter can be observed as they pass in front of or behind the planet’s disk, creating interesting shadow effects.
If the device has a diameter of more than 10 cm, you can observe the Cassius slit, which is the name given to the division in the rings.
- Mars. When viewed through the instrument, Mars will appear as a red dot with a white cap. During the moment of opposition, when Mars is closest to Earth, it is possible to see the seas on Mars as dark spots.
- Mercury and Venus. These two planets will also appear as dots to the observer, but their phases can be observed. In the telescope, they will resemble small moons, transitioning from an incomplete disk to a crescent shape.
- Uranus and Neptune. Uranus will appear as a very small star with a faint disk, while Neptune will be seen as a faint star.
- Star clusters. Scattered clusters are groups of stars that form a stunning and awe-inspiring sight against a backdrop of other stars. These clusters create a beautiful and breathtaking view. In contrast, globular star clusters are not as visually striking as scattered clusters, appearing more like simple spots.
- Nebulae. To observe these celestial objects, a dark sky is required, ideally free from light pollution. Attempting to view nebulae from an urban environment is unlikely to yield positive results. Even if they are visible, they will appear as faded grayish spots without much detail.
- Galaxies. Viewing galaxies can be challenging with small telescopes. It may be difficult to recognize these white spots with faint visible glow as actual galaxies.
The recommended size for an amateur telescope is 90-130 mm in diameter. However, if you plan to observe celestial objects from an urban area, it is advisable to opt for a larger telescope, such as 150 mm, 200 mm, or even 250 mm. Although these larger telescopes may not provide the same level of image quality as smaller ones, they can greatly enhance the observation experience when taken outside the city and properly installed.
What should be taken into account when choosing children’s telescopes?
When purchasing a children’s telescope, it is not necessary to focus solely on the magnification factor. It may sound strange, but the truth is that this characteristic is not the most important one for a telescope. Even with a lower magnification, children can still enjoy observing the cosmos. However, the diameter of the main mirror should be taken into consideration. For instance, if it is only 30 mm, it might not offer much, but with 60 mm, the studies become more intriguing.
What features should be considered in a regular children’s telescope:
- The moon (children are fascinated by its rough surface);
- The satellites of Jupiter;
- The phases of Venus;
- The Orion Nebula;
- Stars with a magnitude limit of 11.5;
- Large globular star clusters.
The planets in our solar system will appear like tiny peas, and the stars as tiny dots, only much brighter. Naturally, children might be a bit let down by this option, as they might be expecting a cartoon-like experience. However, it’s important to remind them that the great explorers, such as Galileo Galilei, didn’t have access to such advanced technology. Nevertheless, it didn’t deter them from making groundbreaking discoveries. Therefore, being able to gaze at the starry sky through a children’s telescope is still a wonderful opportunity for a modern child.
By the way, it’s also worth not dismissing the chance to observe objects on Earth. However, for this, special wraparound prisms will come in handy. These prisms have the ability to reflect the image (similar to what telescopes provide) to make it appear in its usual, straight orientation.
The telescope, with a diameter of 50-80 mm, is a great option for children aged 8 and younger, as well as for beginners of any age who are interested in observing space. With a 70 mm diameter telescope, even adult beginners can enjoy viewing space images. You’ll be able to see craters on the Moon and the cloud belts of Jupiter. It’s highly recommended to purchase a stable tripod to ensure steady and clear images. Additionally, it’s important to consider the location for observing. While children may be impatient, it’s essential to explain that for optimal image quality, it’s best to go outside of the city. The time of observation, atmospheric conditions, and telescope settings all play a crucial role in the overall experience.
What is visible through the most advanced telescopes?
To enhance their experience, individuals visit planetariums. Naturally, many desire to interact with the grand telescopes – colossal modern devices that enable glimpses into not only the present state of the Universe, but also its past (as reconstructed from compiled data). However, this privilege is reserved for a select few, while a trip to the planetarium is accessible to all.
The Moon is typically the first celestial body observers seek, and this remains true when using powerful telescopes. Its extraordinary topography can indeed be observed, although Neil Armstrong’s footprints remain invisible, unfortunately. Jokes aside, lunar craters and mountains also prove intriguing. Moreover, some amateur astronomers are even capable of detecting flashes on the lunar surface, for which there is currently no definitive explanation.
Despite the assistance of advanced technology, the following objects can be observed:
- Gas nebulae. Although it may be challenging to observe without special filters, the sight is truly breathtaking if you have them.
- Man-made satellites orbiting Earth. This is an extraordinary experience. You can even spot the International Space Station (ISS) and capture it in a photograph. However, it is important to have a good understanding of celestial navigation and utilize specialized software for calculating coordinates.
Speaking separately, it’s important to mention the Sun. There are still inexperienced enthusiasts of space exploration who dream of finding a telescope with 300x magnification to observe all the major celestial bodies, including the Sun. However, the Sun can only be safely viewed with special filters. It is dangerous for people to attempt using homemade contraptions such as films, floppy disks, or even smoked glass. Only a professional solar filter can facilitate this exploration; otherwise, the first glimpse of the Sun could be the last.
Looking at the Sun is not only dangerous through a telescope. Even in a finder, one should not gaze at this celestial body without a filter. With a filter, you can observe the sunspots on it.





