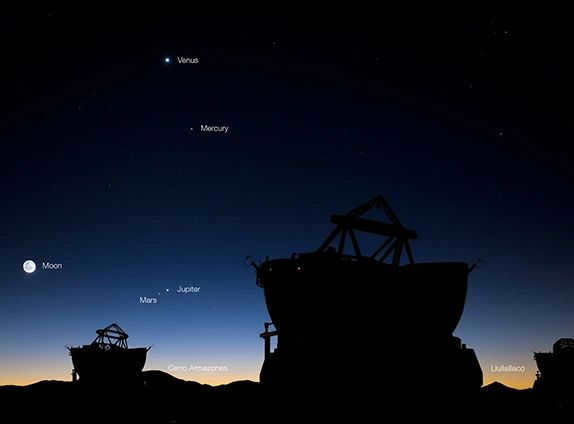
Imagine the scene: it’s late at night, everyone is asleep, and you decide to make yourself a cup of tea. You open the balcony doors, set up your telescope, and gaze at the moon’s craters and try to spot Saturn’s rings. It’s a peaceful and serene moment, one that captivates the imagination. And you’re not alone in this sentiment – telescope sellers have noticed a surge in demand for their products as options for entertainment become limited. But what kind of telescope is best for beginners? What can you expect to see through it? And why is the view likely to be different from the polished photos on Instagram?
Photo by Andrei Shokhan, photoshop.ru
It’s wiser to invest in a telescope rather than a Playstation.
Natalia Polyakova, a resident of Minsk, received a telescope for her 20th birthday, and she considers it to be one of the most valuable gifts she has ever received, she confidently states:

Natalia Polyakova
– When the package arrived, it caused quite a stir among my family members. It would have been easier for them to understand if I had asked for a gold necklace for my anniversary, but instead, I requested this intriguing device. My telescope is quite basic, but I am already considering ordering a slightly more advanced model that can be connected to a computer. This way, I can capture and magnify images of the mesmerizing night sky.
The telescope has found its place at our country house and is always in high demand during summer evenings. To aid in our celestial exploration, we have also hung a large map of the starry sky nearby.
For those who have doubts about whether the expensive equipment will collect dust in the closet, Natalia is here to convince you otherwise:
“It’s an amazing device. In my opinion, investing money in a telescope is much more worthwhile than, let’s say, buying a Playstation.”
You won’t be able to see another galaxy from your balcony

Nikita Obukhovich
An increase in demand for telescopes has been observed over the past two months, according to Nikita Obukhovich, the owner of Telescop.by, an online store specializing in optical equipment.
– Telescopes are most commonly purchased as gifts, with wives giving them to their husbands and parents giving them to their children. However, there are also cases where grown-up sons and daughters buy telescopes for their fathers, who have always dreamed of owning such a device but couldn’t afford it.
When it comes to purchasing a telescope, the most important factor to consider is the diameter of the tube. According to Nikita, the larger the diameter, the better the quality of the image:
– For children aged seven or eight, a telescope with a 50 mm diameter is appropriate. A 60 mm option is suitable for schoolchildren, while a 70 mm telescope is a classic choice for beginners. With a 70 mm telescope, you can observe craters and mountain ranges on the Moon, as well as the rings of Saturn and cloud belts on Jupiter. For those who are interested in viewing nebulae and galaxies, a telescope with a diameter of 114 mm or more is recommended. However, there is a caveat: if you can observe the Moon from your balcony, the city lights will hinder your ability to see other galaxies. In this case, it is necessary to travel outside the city for at least 50 kilometers.
The second important feature to consider is the tripod.
– It is important to ensure maximum stability. Sometimes it may appear that the “pipe” is large, but everything is loose and wobbly, resulting in a blurry picture. Additionally, make sure to pay attention to the package. Typically, a telescope comes with a lens and two eyepieces. It would be wise to also purchase a lunar filter as the Earth’s satellite is very bright, and without a filter, a beginner astronomer may experience discomfort in their eyes.
Nikita also emphasizes that observing the night sky is incredibly fascinating:
– It is also a great excuse to escape from the daily routine and indulge in some dreaming.

Andrei Shohan
There is a person named Andrei Shohan who is an amateur astronomer with 11 years of experience. He is also the administrator of the largest public forum in our country dedicated to astronomical observations. If he notices an increase in interest in this topic, he does not attribute it to the coronavirus pandemic and people being forced to stay at home:
– The optimal time for observing objects in the distant cosmos is during the middle of spring. This is because the nights are too short in summer and it is physically challenging to spend many hours outdoors in winter. Interestingly, the middle of spring is also when the traditional Messier marathon takes place. During this event, amateur astronomers attempt to locate and study as many objects as possible from the catalog compiled by French astronomer Charles Messier. In the 18th century, Messier created a list of 110 enigmatic objects, which were later discovered to be bright nebulae, galaxies, and star clusters.
Andrei’s involvement in the world of astronomy began in 2009 when he joined the astroclub “hv” at the Minsk planetarium. This organization is the largest association of amateur astronomers in the country.
– Describing a typical Belarusian astronomer is a challenging task. Our club consists of individuals from various professions, including doctors-surgeons, economists, and IT specialists. Furthermore, the age range within the club is vast, spanning from 20 to the deep 70s. The core of our organization consists of approximately 30-50 individuals, with an additional 100-200 couch astronomers who are primarily interested in admiring images of the starry sky rather than actively participating in the astronomical process. It’s worth mentioning that all my colleagues are incredibly supportive of beginners. Therefore, if you’re unsure about whether you need a telescope, I encourage you to ask an experienced astronomer to accompany you during observations. Only through firsthand experience can you truly determine if it’s the right fit for you.
Interestingly enough, according to Andrei, the verdict of “it’s not” happens much more frequently.
– Numerous newcomers who are captivated by vibrant space photos on Instagram often assume that they can simply purchase a telescope, set it up, and witness similar sights to those depicted in the pictures. However, they are often disappointed when the distant galaxy merely appears as a faint gray spot. To truly appreciate and comprehend what one is observing in space, a certain level of knowledge and experience is required. For instance, when setting up a telescope in a park and inviting others to gaze at Jupiter, most individuals only see a white sphere. Only those who possess the necessary understanding will be able to identify Galilean satellites, equatorial bands, and small vortices within the planet’s atmosphere.
Andrei himself has encountered numerous awe-inspiring events, but one of the most memorable moments was witnessing the final docking of an American shuttle to the International Space Station in 2011.
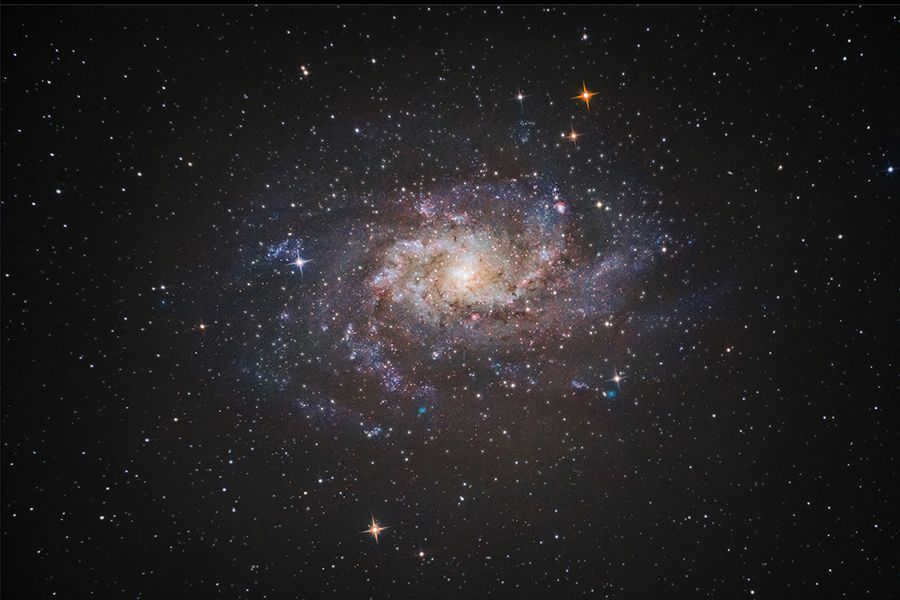

Andrei Shohan has a talent for not only observing celestial bodies, but also capturing their beauty through photography. One notable example is the Triangle Galaxy, which he skillfully photographed alongside Ruslan Zavadich.
Photo credit: Andrei Shohan and Ruslan Zavadich
– The telescope provided such clarity that even the intricate shape of the galaxy’s wings was visible. What other fascinating sights can be observed now? Personally, I find it intriguing to witness the occasional procession of lights moving from west to east. These lights are actually SpaceX’s Starlink satellites, which are soon to provide high-speed wireless Internet access to people all over the world. It’s not uncommon for those unfamiliar with this phenomenon to mistake it for a UFO.
Has Andrei ever had any personal encounters with unidentified objects?
– About six years ago, I witnessed a cluster of tiny stars in the night sky, – the astronomer reminisces with a grin. – I was puzzled for quite some time, trying to figure out what it could possibly be, until I discovered that they were actually LED lights attached to balloons – they were flying. I firmly believe that even the most seemingly inexplicable occurrences can always be explained logically.
Reprinting of the entire text and photos is strictly prohibited. Partial quoting is allowed with a hyperlink.
With my extensive experience in amateur-level telescope observations during nighttime, I aim to shed some light on what one can actually observe through a telescope priced under 100,000 rubles, which can be conveniently transported by car (i.e., not stationary).
Numerous individuals have observed the photographs captured by telescopes, and even those taken by the Hubble telescope. As a result, they often feel compelled to purchase a telescope of their own. However, once they begin exploring the celestial wonders, they are often left astounded by what they encounter.

It is a fact that our eyes do not have the ability to capture enough light to produce a vibrant and detailed image through a telescope (especially in low-light conditions where we see a dull black and white image), but a camera sensor can!
When looking through a regular telescope, most of what you observe will appear dull and obscured. To help you understand this better, let me provide you with some examples!

The photo shows the Crescent Nebula (NGC 6888 or Crescent Nebula). On the left is a photo taken with a camera, and on the right is how you would see this object through the telescope: 
It is important to note that telescopes of this kind can be quite heavy and come with a price tag starting at 50,000 rubles.

Shall we proceed? There are small galaxies located in the Virgo constellation (M86 and M84).
On the right side, you can see what is observable through the aforementioned powerful telescope.

Located in the constellation Triangle, the impressive M33 galaxy is a sight to behold through a 70mm telescope.
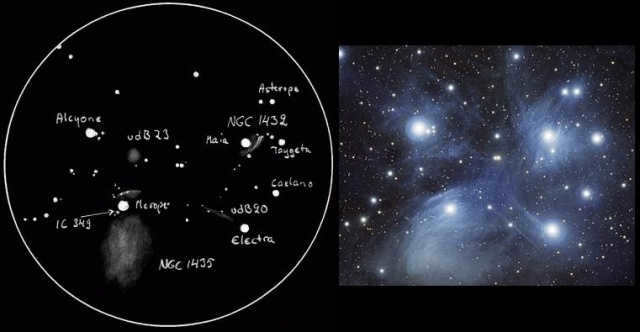
The Pleiades can be observed through a telescope as a group of luminous stars, however, the image reveals a distinct dust cloud.

Here we have a globular cluster located in the Sagittarius constellation (M22). The image on the left showcases the cluster, while the image on the right displays what can be observed through a telescope.
Furthermore, let’s categorize the various objects that can be observed through telescopes of different sizes.
Below is a list of what can be seen using telescopes of different diameters:
Albireo, Mizar, and other double stars with a separation greater than 2" can be observed.
Faint stars with a magnitude of up to 11.5m are visible.
Sunspots can be observed, but only with an aperture filter.
The different phases of Venus are visible.
Craters on the Moon with a diameter of 8 km can be observed.
During the Great Confrontation, it is possible to see the polar caps and seas on Mars.
On Jupiter, the belts are visible, and under ideal conditions, the Great Red Spot (GRS) and four satellites of Jupiter can be observed.
Saturn’s rings are visible, and with perfect seeing conditions, Cassini’s slit and the pink belt on Saturn’s disk can be seen.
Uranus and Neptune appear as stars.
Large globular clusters, such as M13, and scattered clusters can be observed.
Almost all objects in the Messier catalog can be observed, although without much detail.
The refractor telescope has an aperture range of 80-90 mm, while the reflector telescope has an aperture range of 100-120 mm. The catadioptric telescope, on the other hand, has an aperture range of 90-125 mm.
Double stars with a separation of 1.5″ or greater, faint stars up to magnitude 12.
Sunspot structure, granulation, and flare fields (only visible with an aperture filter).
Phases of Mercury.
Lunar craters approximately 5 km in diameter.
Polar caps and seas on Mars during oppositions.
Multiple additional belts on Jupiter and the BKP. Shadows cast by Jupiter’s satellites on the planet’s surface.
Cassini’s division in Saturn’s rings and 4-5 satellites.
Uranus and Neptune appear as small disks with no discernible features.
Several dozen globular clusters, with brighter ones showing signs of disintegration at the edges.
Many planetary and diffuse nebulae, as well as all objects in the Messier catalog.
The brightest objects from the NGC catalog (some details can be distinguished in the brightest and largest objects, but galaxies mostly appear as nebulous patches without details).
Refractor telescopes ranging from 100mm to 130mm, as well as reflector or catadioptric telescopes ranging from 130mm to 150mm.
These telescopes are capable of observing double stars with a separation of 1″ or more, as well as faint stars up to a magnitude of 13.
They can also reveal details of lunar mountains and craters that are 3-4 km in size.
If you use a blue filter, you may be able to see spots in the clouds of Venus.
During oppositions, these telescopes can capture numerous details on Mars.
You can also observe detailed belts on Jupiter and cloud belts on Saturn.
Additionally, these telescopes are excellent for observing faint asteroids and comets.
Furthermore, they provide the opportunity to view hundreds of star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies. The brightest galaxies may even show traces of spiral structure, such as M33 and M51.
Lastly, these telescopes offer a wide range of objects to explore in the NGC catalog, many of which have interesting details to observe.
There are double stars that have a separation of less than 1″, and there are faint stars that have a magnitude of up to 14.
On the moon, there are formations that are approximately 2 km in size.
Mars experiences clouds and dust storms.
Saturn has 6-7 satellites, and if you look closely, you may be able to see the disk of Titan.
When Saturn’s rings are fully open, you can observe spokes within them.
The Galilean satellites appear as small disks when observed.
With the use of advanced optics, the level of detail in the image is no longer limited by atmospheric conditions.
Some globular clusters can be observed with such clarity that individual stars can be seen all the way to the center.
Even when observing from areas with city lights, it is possible to see the intricate structure of many nebulae and galaxies.
Refractor with a diameter of 200 mm or greater, reflector or catadioptric with a diameter of 250 mm or greater.
Under optimal conditions, this telescope can observe double stars with a separation of up to 0.5″, stars down to magnitude 15 and fainter. It can also capture details of moon formations that are less than 1.5 km in size. Additionally, it can reveal small clouds and structures on Mars, and occasionally even Phobos and Deimos. Furthermore, it can provide a wealth of detail in Jupiter’s atmosphere, including the ability to observe Enke’s fission in Saturn’s rings and Titan’s disk. It can also observe Neptune’s satellite Triton and even Pluto as a faint star. However, it should be noted that the level of detail captured in the images is heavily influenced by the atmospheric conditions. This powerful telescope is capable of revealing thousands of galaxies, star clusters, and nebulae. It can also observe virtually all the objects in the NGC catalog, many of which display details that are not visible in smaller telescopes. Moreover, the brightest nebulae will show subtle colors when observed through this telescope.
However, this should not discourage you from pursuing an interest in astronomy. In the following paragraphs, I will elaborate on the reasons why you should consider purchasing a telescope.
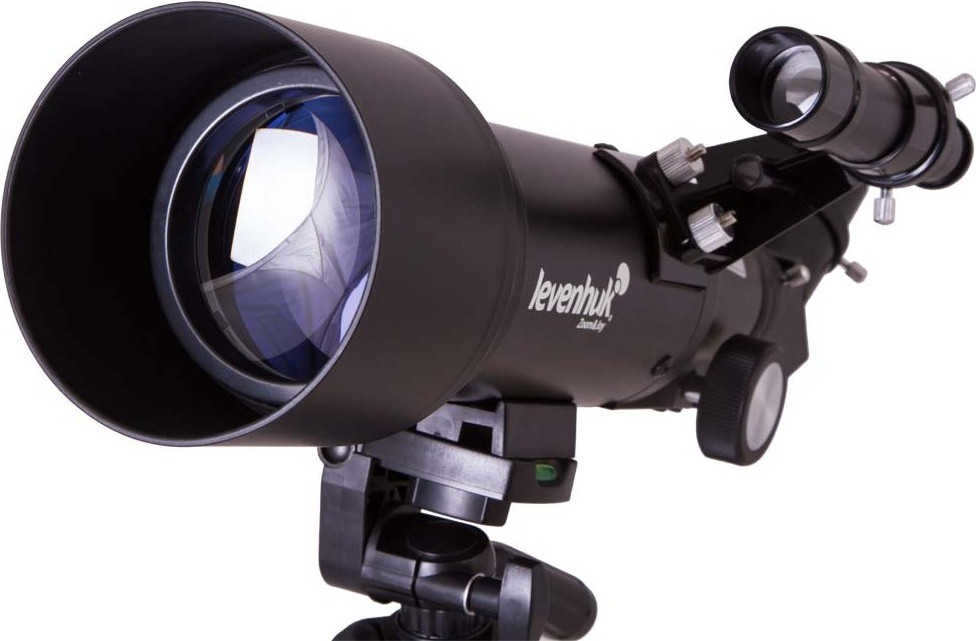
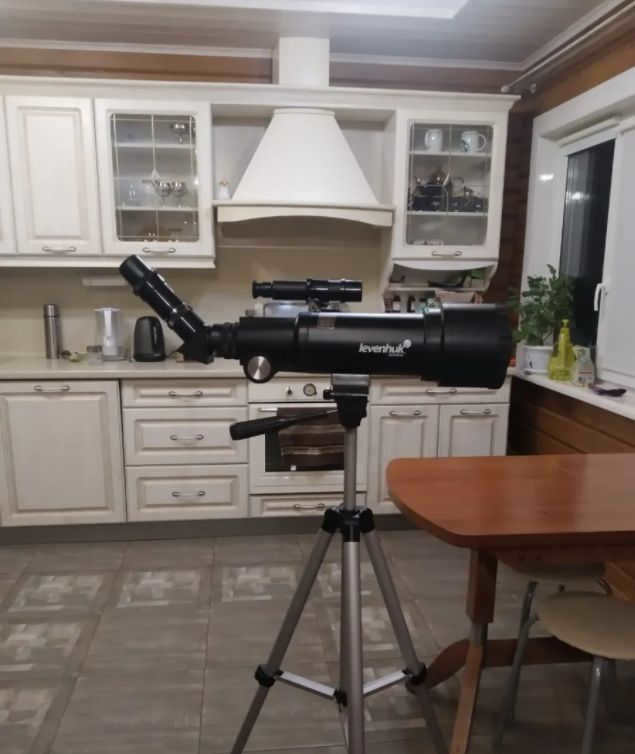
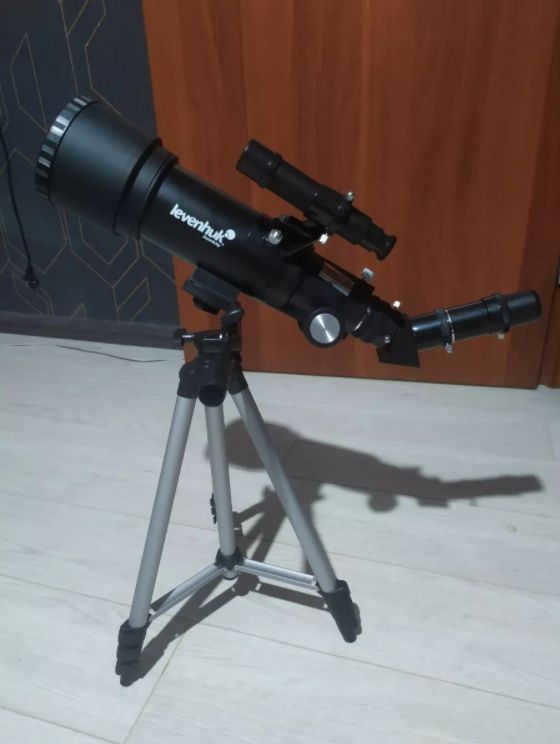
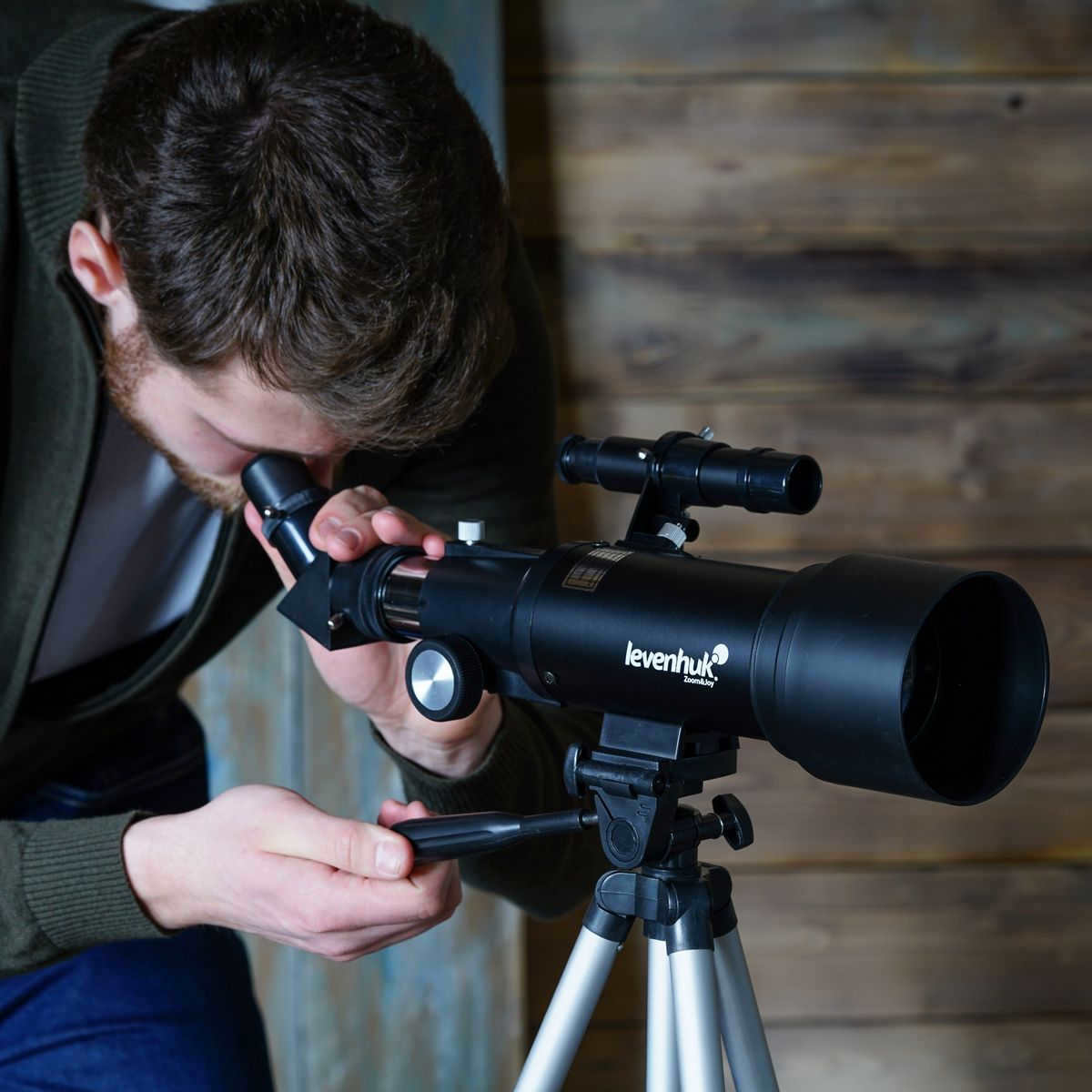
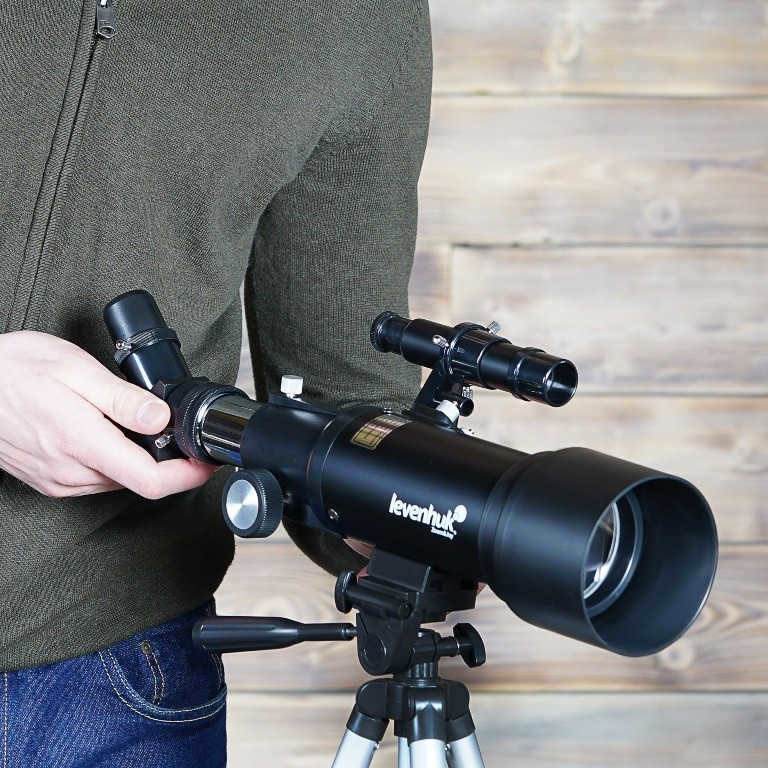
The Levenhuk Skyline Travel 70 is a telescope that appeals to a broad range of individuals.

This telescope is perfect for novice stargazers, kids, and individuals with more advanced knowledge in astronomy.

The refractor telescope is designed to be as small and portable as possible. It features a lightweight metal tube and a highly reliable construction.
Readers of our blog can enjoy a special offer of a 5% discount on our entire range of telescopes. Simply use the promo code: BLOG. Explore our collection of telescopes now!
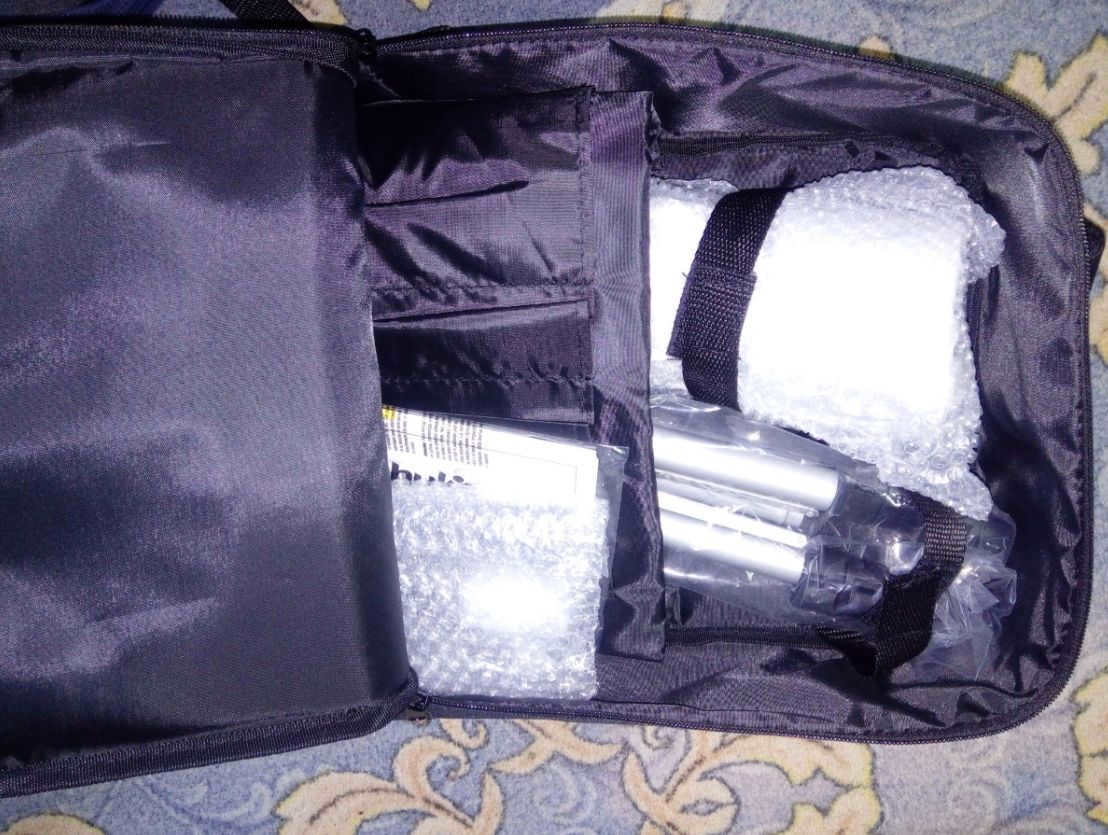
This telescope is conveniently compact and can easily fit into a dedicated backpack for transportation, which is included with the purchase. With this feature, you can take the telescope with you on trips out of town.

All lenses come with a multilayer coated finish, ensuring the image is of high quality and free from any distortions.

Telescope Gear
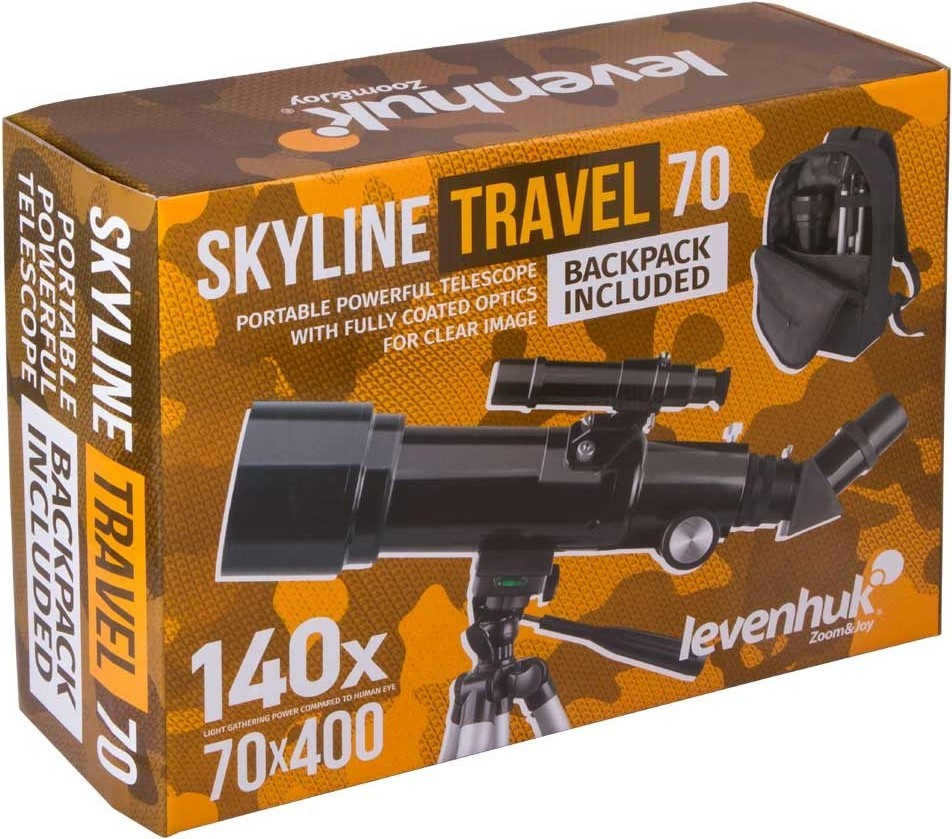
The telescope arrives in a vibrant cardboard package.

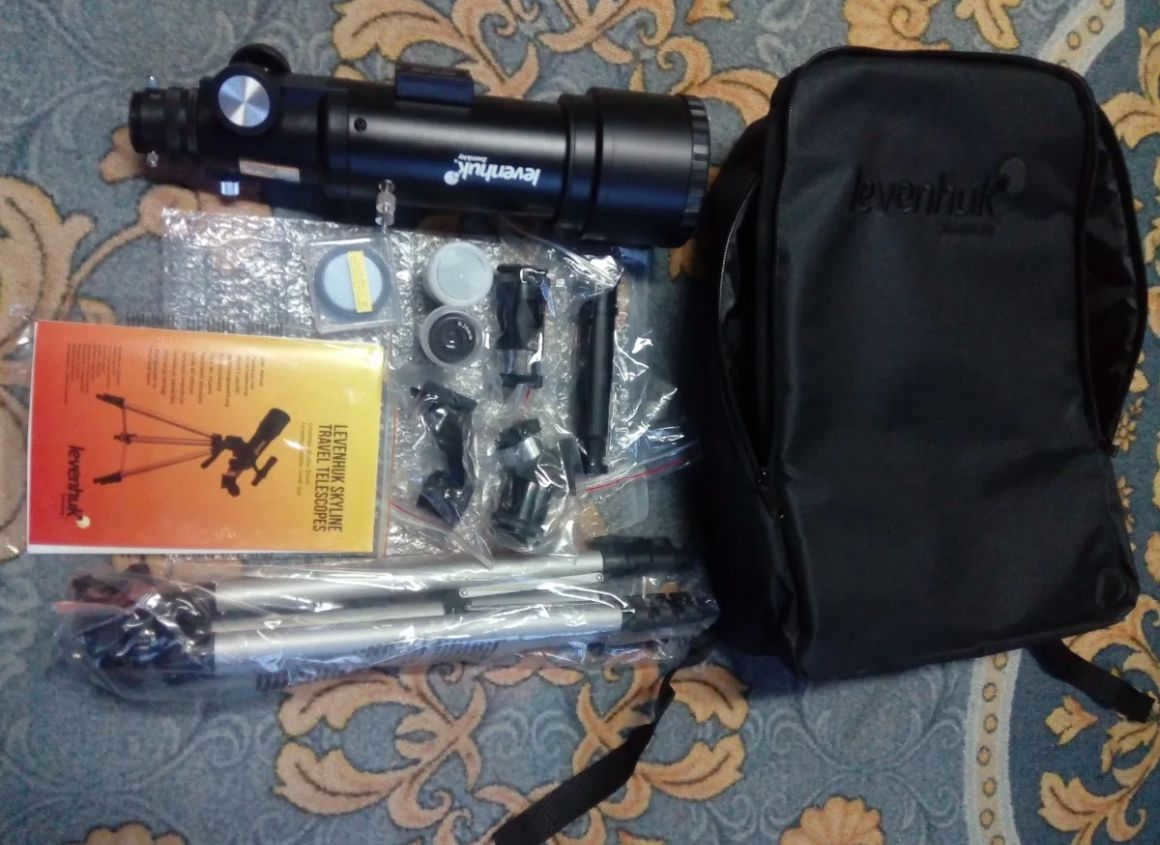
Within this telescope, you will discover a comprehensive collection of tools and resources to gaze upon the celestial bodies and explore the wonders of our universe.

There is no need to purchase any additional items for your initial use – you can start using the telescope immediately upon unboxing.






Characteristics
The Travel 70 is a device that comes with a spacious lens and a wide range of functionalities.


| Lens diameter | 7 cm |
| Focal length | 40 cm |
| Maximum usable magnification | 140x |
| Maximum magnification with included lenses | 120x |
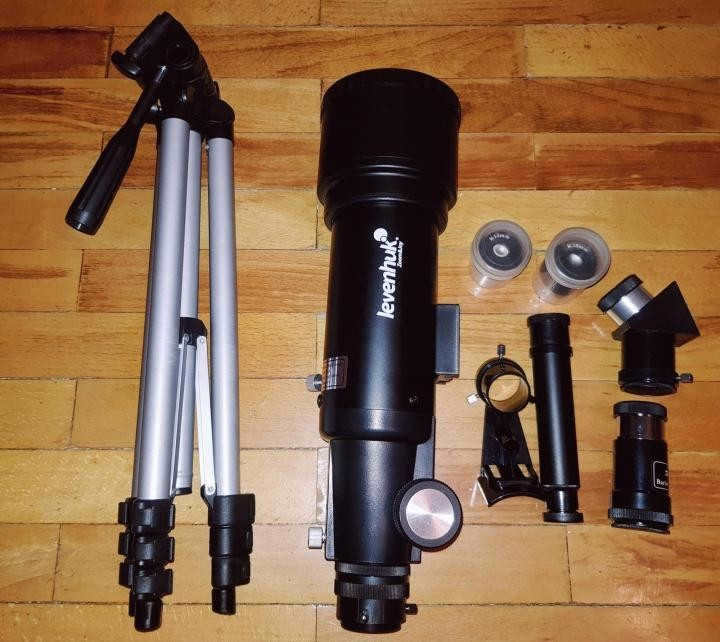
To enhance the user experience, the set comes with:
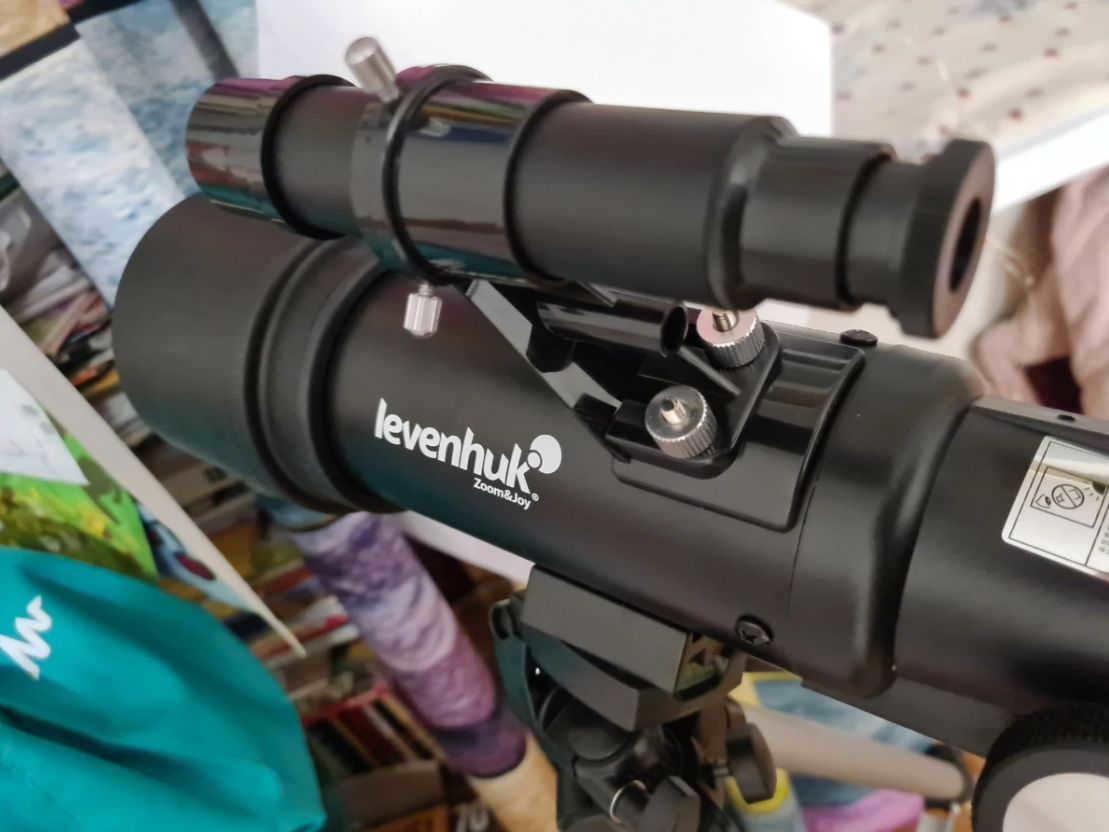
- An optical finder that facilitates locating objects in the sky;
- A diagonal mirror that provides a non-inverted image.

The package contains two Kelner eyepieces with focal lengths of 10 and 20 mm, providing magnifications of 40x and 20x, respectively. Additionally, it includes a Barlow lens that triples the magnification of each eyepiece.

Consequently, the highest possible magnification achievable with the included optics of the telescope is 120x, while the effective magnification is 140x.

The typical diameter for mounting is 1.25 inches. This size enables the utilization of eyepieces with varying focal lengths in order to achieve the desired level of magnification.

Operating the Telescope
The telescope is equipped with an azimuth mount, making it incredibly user-friendly and straightforward to operate. This mount allows for effortless movement of the tube in any direction and enables users to easily fixate on their desired celestial objects.
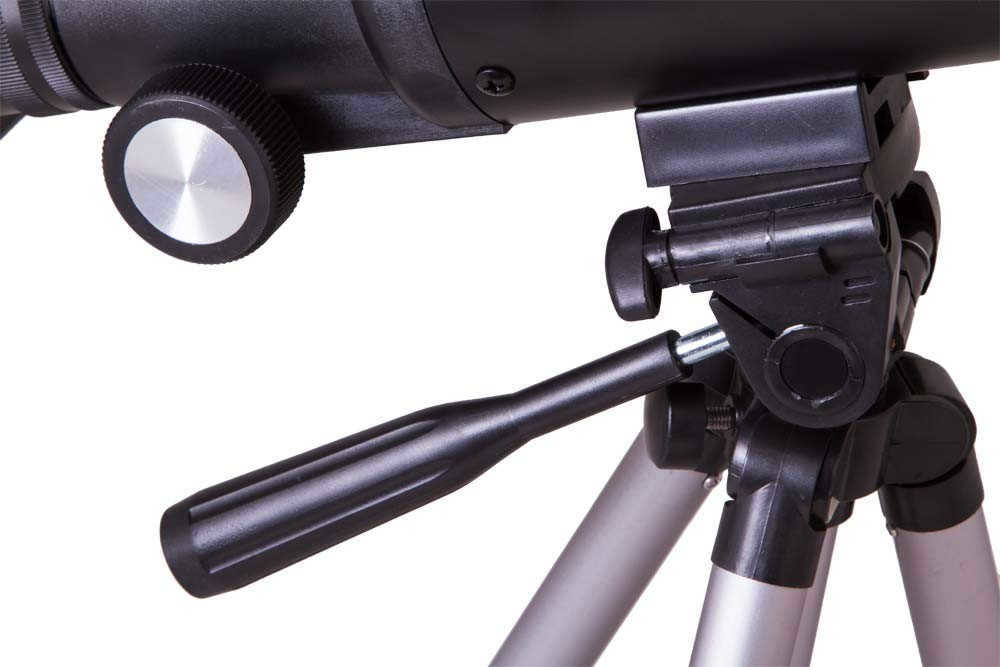

One can also modify the telescope’s azimuth if needed. The fine motion control knob provides effortless guidance of celestial objects in the night sky. Even a child would have no trouble with this.

The optical finder is designed to assist in promptly locating the desired object for observation.
Prior to usage, it is necessary to perform the following adjustments:
1. Identify a remote object that is at least 500 meters away from your current position.
2. Direct the telescope towards the chosen object, ensuring that it is roughly centered within the eyepiece. 3.

3. Adjust the optical finder by manipulating three screws.
4. Confirm that the object is centered both in the eyepiece and in the crosshairs of the finder eyepiece.
The telescope finder eyepiece offers a wider field of view compared to the telescope itself, although it provides lower magnification.

Now, in order to quickly align the telescope with the object under examination, simply locate the object within the optical finder’s eyepiece.
Readers of our blog are eligible for a 5% discount on all products.
Use the promo code BLOG to claim your discount. Browse our selection of telescopes
Once you locate the object within the optical tube’s eyepiece, you will be able to observe it in a magnified image.

What to look out for
Skyline Travel 70 is an excellent tool for exploring the solar system and observing various planets.

Key Characteristics of the Telescope
The size of a telescope’s lens diameter is the most crucial factor. The larger the diameter, the ability to see faint stars and distinguish finer details increases. It also enables the separation of closely located double stars. Another important aspect is the layout of the telescope, especially the presence and size of a center-shielding secondary mirror. In refractor telescopes with an objective lens, there is no central shielding, which results in enhanced contrast and detail. However, this advantage is primarily seen in long-focus refractor telescopes and apochromats. Short-focus refractor-achromats, on the other hand, are prone to chromatic aberration, which negates the benefits of a refractor. These telescopes are typically used at lower and medium magnifications.
One of the key accomplishments of contemporary technology in amateur telescopes is the introduction of computerized automatic pointing systems. Telescopes equipped with these systems can swiftly direct the observer’s attention to celestial objects with just a few button presses. These systems are commonly referred to as auto-guiding systems, and they have truly revolutionized traditional conceptions of amateur stargazing.

The distinction in the visibility of stars between a low-cost and a professional telescope
The higher the cost of the telescope, the better the visibility
It is recommended to invest in a telescope with a good margin, as this will allow for a more enjoyable stargazing experience, without only being able to see a vague outline of the star.
When purchasing a telescope, keep in mind that the magnitude of the celestial body mentioned in the documentation is rounded down to integer values.
It is preferable for the telescope to have a maximum resolution that can capture stars with a higher magnitude than your target star. The higher the resolution, the more dim stars you will be able to observe, resulting in a better view of your star.
Which is Better: Observing a Star with a Telescope or Satellite Photography?
There’s nothing quite like the experience of seeing a star with your own eyes! However, when it comes to planning a nighttime adventure in nature, some preparation is key.
So, if you’ve made the decision to give the gift of a star, you have plenty of time to purchase observation equipment before the next celebration rolls around!
However, please be aware that even with advanced telescopes, you will not be able to observe the same clear and stunning astronomical landscapes that you see on our website or in the photos of your star. Our images are captured using various wavelengths, including radio waves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, gamma rays, and terahertz radiation. These wavelengths allow us to reveal hidden details that are not visible to the naked eye and require long exposure times, ranging from a few minutes to several hours, from telescopes positioned in orbit around the Earth. This is why the view from the ground appears vastly different!
Now is the perfect time to select your gift set of papers and have the opportunity to purchase a professional photograph of your star!


Today is the day when you have the opportunity to witness and experience the awe-inspiring beauty of a star that is named after you. You can now acquire a meticulously captured photograph of your very own star! Additionally, feel free to reach out to us via the chat feature.

BUY THIS PHOTO NOW
If you purchase a photo at the time of star registration, we will select a star for you that is situated in a scenic location in outer space, likely near a galaxy or nebula. You will receive a star that will serve as the focal point of the photo, and the recipient will immediately recognize and appreciate the magnificence of the gift you have given them!
Example photo acquired during registration

BUY PHOTO LATER
It is worth considering that if you wish to purchase a photo at a later time and do not order it immediately upon registration, the star will be selected randomly. It is possible that instead of an awe-inspiring picture of the universe, the photo will only capture a tiny dot in the vast black sky.
Here is an example of a photo purchased after registration
You have the option to use the installment plan “I don’t cut corners on my favorites”.
P.S. If your star has been registered for a while and you would like to confirm whether it is situated in a scenic environment before ordering a photo, please reach out to us via chat and we will clarify this for you.
Stars with a magnitude of up to 1
Observation equipment: A bright star that can be seen with the naked eye in the city center.
Objects: Star clusters – Pleiades, h/χ Perseus; galaxies – Andromeda Nebula and Orion Nebula; Planets – ☿ Mercury, ♀ Venus, ♂ Mars, ♃ Jupiter, and ♄ Saturn.
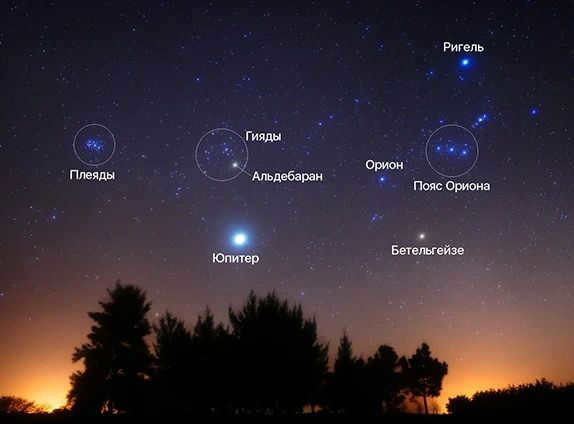

Stars with a brightness of up to 2 magnitudes
Equipment for observation: A prominent celestial body that can be seen without the aid of a telescope, located in the heart of an urban area.
Topics of interest: Clusters of stars – Pleiades and h/χ Perseus; galaxies – Andromeda Nebula and Orion Nebula; planets – ☿ Mercury, ♀ Venus, ♂ Mars, ♃ Mars, ♃ Jupiter, and ♄ Saturn.
Stars with a magnitude of up to 3
Equipment used for observation: The Bright Star, which can be seen with the naked eye from the city center.
Objects observed: Star clusters such as the Pleiades and h/χ Perseus; galaxies like the Andromeda Nebula and Orion Nebula; Planets including ☿ Mercury, ♀ Venus, ♂ Mars, ♃ Jupiter, and ♄ Saturn.
A photograph of your star, priced at 1980 ₽, is available from 1980 ₽

Stars with a magnitude of up to 4
Equipment needed for observation: A star that is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye even in an urban area.
Things to observe: Clusters of stars such as the Pleiades and h/χ Perseus; galaxies like the Andromeda Nebula and Orion Nebula; Planets such as ☿ Mercury, ♀ Venus, ♂ Mars, ♃ Jupiter, and ♄ Saturn.
A photograph of your star, taken in 1980, is available for 1980 ₽
Stars with a magnitude of up to 5
Observation equipment: The Bright Star, which can be seen with the naked eye in suburban areas.
Objects to observe: Clusters of stars – Pleiades, h/χ Perseus; galaxies – Andromeda Nebula and Orion Nebula; Planets – ☿ Mercury, ♀ Venus, ♂ Mars, ♃ Jupiter, and ♄ Saturn.
A photograph of your star, from 1980 ₽


Stars with a magnitude of up to 6
Observation equipment: The star is visible to the naked eye in areas without backlighting, away from urban areas.
The average person can see stars with a magnitude of up to 6.5, while those with acute vision can see stars with a magnitude of up to 8.
Subjects: Star clusters – Pleiades, h/χ Perseus; galaxies – Andromeda Nebula and Orion Nebula; planets – ☿ Mercury, ♀ Venus, ♂ Mars, ♃ Jupiter, and ♄ Saturn.
A photograph of your star is available for 1980 ₽
Stars with a magnitude of 7 or lower
Topic: Objects with a magnitude of 7 or lower.
Tools: Naked eyes or smartphone camera, theater binoculars or camera.
Important: Avoid looking directly at the Sun! Doing so can result in permanent harm to your vision.

Stars with a magnitude of up to 8
Topic: Anything with a magnitude of up to 8.
Tools: High-quality handheld binoculars – specifically models of the 12×42 variety. These binoculars offer a magnification of 12x, which is the maximum magnification you can manage if you are holding them up without a tripod. If you want to avoid the need for a tripod, these binoculars are the best option.
Stars with a magnitude of 9 or lower
Target for observation: Anything with a magnitude of 9 or lower.
Tools: Army binoculars mounted on a tripod. Specifically, models of the 20×50 variety. These binoculars offer a magnification of 20x. It goes without saying that the more advanced the equipment, the clearer the view, and consequently, the easier it will be to observe the star.


Stars with brightness up to the 10th magnitude
The objects that can be observed include anything with a brightness level up to the 10th magnitude.
For this observation, you will need a telescope mounted on a tripod. There are various models available with a magnification of at least 45x and a lens diameter of at least ⌀ 60 mm.
Stars with brightness up to the 11th magnitude
The objects that can be observed include anything with a brightness level up to the 11th magnitude. Additionally, double stars with a separation greater than 2″ such as Albireo and Mizar, as well as large globular clusters like M13 and scattered star clusters, can be observed.
To observe these objects, you will need an optical telescope with specific specifications. A refractor with a diameter of ⌀ 60-70 mm or a reflector with a diameter of ⌀ 70-80 mm would be suitable. The magnification range should be between 25x and 125x.
The cost of the equipment varies. You can find options starting from 10,000 ₽ without auto-targeting or starting from 25,000 ₽ with auto-targeting. Availability can be checked through the chat. Additionally, you can get a photo of your star for 1980 ₽.

Stars visible up to the 12th magnitude
Observation Subject: Anything that falls within the range of up to the 12th magnitude, in addition to: Double stars with a separation of 1.5″ or greater. There are numerous globular clusters, with the brighter ones appearing to disintegrate into stardust at the edges. Several planetary and diffuse nebulae can also be observed. However, galaxies mostly appear as nebulous specks without any discernible detail.
Required Specifications: Optical telescopes with the following specifications are recommended: Refractor with a diameter of 80-90mm, Reflector with a diameter of 100-120mm, and Catadioptric (mirror-lens) with a diameter of 90-125mm. Magnification ranges from 15 to 250x.
Cost of equipment:
Starting from 20,000 ₽ without auto-targeting.
Starting from 35,000 ₽ with auto-guidance.
Please inquire about availability through the chat.
Photo of your star, priced at 1980 ₽.
Stars visible up to the 13th magnitude
Topic: Celestial objects that can be observed up to the 13th magnitude, including: Binary stars with a separation of 1″ or greater. Numerous faint asteroids and comets. Countless star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies (with the brightest galaxies exhibiting hints of spiral structure such as M33 and M51).
Desired specifications: Optics Telescope: Refractor with a diameter of 100-130 mm, Reflector with a diameter of 150 mm, Catadioptric (mirror-lens) with a diameter of 130-150 mm. Magnification ranging from 30 to 300x.
Price
Equipment: Starting from 70,000 ₽ without automatic targeting
Starting from 100,000 ₽ with auto-guidance
Check availability via chat
Photo of your star, starting from 1980 ₽

Stars visible up to the 14th magnitude
Observation Subject: Anything with a magnitude of 14 or less, including: Double stars with a separation of less than 1″. Some globular clusters can be resolved into individual stars, even near the center. The structure of many nebulae and galaxies can be observed in detail when outside of areas with city lights.
Required specifications: Optical telescopes: Refractor with a diameter of 150-180 mm, Reflector with a diameter of 200 mm, Catadioptric (mirror-lens) with a diameter of 175-225 mm. Magnification range from 50x to 400x.
Cost:
Equipment: starting from 120,000 ₽ without auto-targeting
Starting from 180,000 ₽ with auto-guidance
Check availability through chat
Photo of your star: starting from 1980 ₽
Stars with a magnitude of up to 15
Storing in an apartment is impossible. It is easier to observe the star using online planet telescopes.
Focus: Any celestial object with a magnitude of up to 15, including double stars with a separation of up to 0.5″ under optimal conditions. The level of detail in the images depends on the atmospheric conditions. Numerous galaxies, star clusters, and nebulae can be observed. The brightest nebulae exhibit subtle colors.
Required specifications: Optical telescopes: Refractor with a diameter of 200 mm or more, Reflector with a diameter of 250 mm or more, Catadioptric (mirror-lens) with a diameter of 250 mm or more.
Cost of equipment: Starting from 150,000 ₽ without auto-targeting, from 200,000 ₽ with auto-guidance. Please check availability via chat. Photo of your star can be obtained for 1980 ₽.

Stars visible up to the 16th magnitude
Storing stars in an apartment is impossible. It is much easier to observe a star through online telescopes or order a photo of it.
The subject of observation can include stars up to the 16th magnitude, and even more depending on the capabilities of the telescope.
The cost of equipment starts from 10,000,000 ₽ with auto pointing. Additionally, you can purchase a photo of your chosen star for 1980 ₽.
P.S. Please note that the reference materials provided below are the minimum ideal requirements and are not guaranteed to be applicable to every individual’s visual ability, observing conditions, or the specific model of observing equipment they may be using. It is recommended to consult with the manufacturer of your observing equipment to determine the star magnitude and observing conditions that are compatible with your chosen model. Additionally, it is advisable to request specific data on the stellar magnitude of the star you wish to observe in order to compare it with the capabilities of your equipment. For more information, please read our disclaimer. It is important to note that any information provided regarding the availability and cost of telescopes does not constitute a legally binding offer under the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.

Astroscope
Astroscope supervision package commencing at $50 encompasses an independent telescope (COAST) and the Physics Innovations Explorer (PIRATE) automated telescope, situated in Tenerife.
The website is presented in the English language.
Visit Astrscope.org
iTelescope
On iTelescope.net, you can take advantage of the unique opportunity to control and capture images with a selection of 18 telescopes across 4 different observatories. With plans starting from just $90 per month, such as the Plan-90, you can shoot your starry subjects with ease. The website is conveniently available in English, making it accessible to a wide range of users. Experience the wonder of the cosmos by visiting iTelescope.net today!
Light Buckets
Light Buckets offers you the chance to operate and capture stunning images using their impressive collection of five telescopes. Although the site is known to be occasionally overwhelmed with traffic, the experience is well worth it. The cost for telescope control time is approximately $130 per hour, providing you with ample opportunity to explore the night sky. Accessible in English, Light Buckets invites you to visit their website at Lightbuckets.com and embark on an unforgettable astronomical journey.
There are 15 telescopes available that can assist you in locating a star in either hemisphere. To access these telescopes, you will need to create an account, which costs $300. Additionally, there is a separate fee of $10 per minute for controlling the telescope.
The website is in English.
Visit Slooh.com for more information.
WHEN WILL YOUR STAR BE VISIBLE IN THE SKY?
If you are planning a holiday and wish to see your star, but are unsure of the specific time it will be visible in the sky, we can help!
With our expert knowledge in astronomy, we can easily determine which constellations will be visible over your chosen city during your celebration.
We can also provide you with the time window in which you will be able to spot your named star in the sky.
Contact us via chat, as we are always ready to assist you!

*Trade-in – Swap your current star name registration for a new one in exchange for payment.
Do you have a star named after you, but you want something different?
Trade it in for a star that catches your interest!
We will apply the registration fee to the new star!
Reserve your new celestial body and include a note with your order indicating the number of the previously issued certificate for offsetting funds.
Donor authorization is required
If the star name registration was gifted to you without the donor’s consent, we are unable to make changes – neither to the star’s name nor to any text on the certificate. Changing the owner’s name for the star is only possible if it is changed on the passport. For any changes, we will personally reach out to the donor!
EXCHANGE YOUR CURRENT STAR NAME REGISTRATIONS FOR A COMPLETE FAMILY STAR SYSTEM
*Trade-in – Exchange an existing star name registration against payment for a new one.
If you or any of your family members have already registered star names on the ROSASTRONOMY.RF website and now wish to purchase a complete star system for your entire family, we are prepared to cancel the previous registrations for those individuals whose star names will be included in the new system. The corresponding amounts will be credited towards the registration of the family star system.
In this way, your entire family will receive a single address in the Universe, within a cluster of interconnected stars, without incurring any financial losses!
Authorization from the original registrant is required.
If you have received the gift of a star name registration, we cannot make any changes to the name of the star or the wish text on the certificate without the permission of the giver. This applies to both the name of the star and its inclusion in the star system. The only way to change the owner’s name on the star is by updating it in the passport. We will take care of contacting the giver for any necessary changes!
If you would like to book a star system for your family, please let us know the certificate numbers in the order note so we can apply the funds accordingly.
To view the cost of the star system, you can click on this link.

 “Mom,” “Dad,” “Me,”
“Mom,” “Dad,” “Me,”
or simply “myself.”
Regarded as one of the most breathtaking planets in our solar system, the colossal Saturn, along with its rings, leaves a mesmerizing and utterly astonishing impact. Once you catch a glimpse of this planet through a telescope, you will inevitably be captivated by its charm forever! However, obtaining a high-quality telescope, selecting the appropriate time, and knowing what and where to observe are indispensable prerequisites.
The optimal moment for observing the planet is during the opposition phases. These occurrences take place each year, albeit with a 14-day discrepancy. For instance, if the opposition fell on July 9 in 2019, it will be on July 20 in 2020. It is during this period that the rings are fully unveiled, and the planet’s visible radiance intensifies.

At this time, Saturn can be observed in the southwestern part of the night sky. If your telescope is equipped with an automatic guidance system, it will be easy to locate. Simply input the desired program and the telescope will automatically locate the object.
What kind of telescope can I use to observe Saturn?
- Binoculars can be used by the most attentive astronomy enthusiasts to observe the planet and its rings.
- With an amateur telescope of 60 to 70 millimeters, you can see Saturn in general, although without specific details. However, the Cassini gap can still be observed.
- With a telescope that has a lens of 100-125 millimeters, you can already observe the cloud belts of the planet, which have different colors.
- For more in-depth studies, it is recommended to use a telescope with a lens of 200 millimeters or more. With such an instrument, you can clearly see the belts and zones in the form of colored bands, as well as the fascinating details of the rings’ structure.
Additional accessories
If you want to fully experience the beauty of Saturn, consider purchasing a set of color filters. These filters are designed to enhance the contrast of specific features, allowing you to see more details.
- Dark yellow and orange filters are ideal for highlighting the belts and zones in Saturn’s atmosphere.
- By using a yellow filter, you can observe the green and reddish hues of the planet.
- The green filter is particularly useful when observing the polar regions, individual zones, and belts on Saturn.
- If you’re interested in observing the rings of Saturn in more detail, a blue filter is recommended. For more powerful telescopes, a blue and violet-blue filter can provide even better results.
The surface of Saturn is primarily composed of gases, resulting in the ability to only observe its atmosphere. However, the details of this atmosphere may not be as easily visible compared to Jupiter. This is primarily due to Saturn’s greater distance from Earth and its surrounding dense fog, which is composed of gas vapor.
Exploration of belts and zones
When observing Saturn through a telescope for the first time, it is likely that only the planet’s outline will be visible. However, with careful attention and closer examination, one can begin to notice distinct bands of dark and light colors. These bands are known as belts and zones, with a total of 16 of them present.
The equatorial zone is an incredibly fascinating area. It is known for the frequent occurrence of high-speed storms in its atmosphere. These storms appear as brilliant white spots on the planet’s surface. This remarkable phenomenon can be attributed to the release of heat from the planet’s interior, which rises along with ammonia. As the warm air interacts with the cold air, ice crystal clouds are formed in the atmosphere, emitting the luminous light that is visible from our vantage point on Earth.
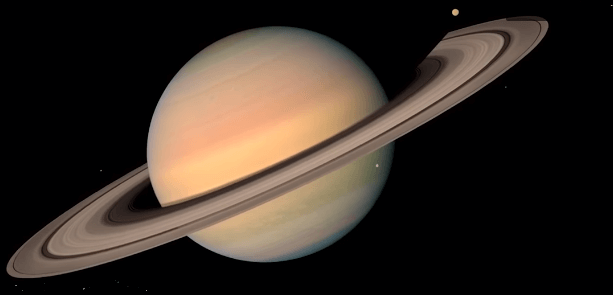

Observing Saturn’s belts and zones
Astronomers have taken a keen interest in Saturn due to its distinctive rings, often referred to as the crown jewel of our solar system. When observing Saturn’s rings through a telescope, one can observe three distinct parts – the outer part, which has a metallic color, the middle part, which is lighter, and the inner part, which appears quite dark. There are numerous gaps between these parts, with two particularly notable ones for observation – the Cassini Gap, located in the center, and the Enke Fission, situated at the outer edge.

During the entire 29 and a half year orbital period, the rings of Saturn are invisible to Earth observers on two occasions. This rare phenomenon occurs after 13.75 and 15.75 years, when instead of the rings, faint stripes are visible through the telescope. The next occurrence of this disappearance is anticipated to take place only in 2024-2025.

Observing Saturn’s Satellites
Currently, there have been 62 satellites discovered orbiting Saturn, but only eight of them can be observed from telescopes on Earth. These eight satellites are Mimas, Enceladus, Tefia, Dione, Rhea, Titan, Hyperion, and Japet. Among them, Titan is the largest and brightest, visible through powerful binoculars. In fact, Titan is even larger than Mercury. If you have a powerful telescope, you may even be able to observe the shadow of Titan as it passes across Saturn’s disk.
One particularly remarkable satellite is Japet, which has the ability to change its color. This is due to one side being covered in ice, while the other side consists of ice mixed with carbon.






