Light and color
Stars do not twinkle themselves. This is the impression received by an observer on Earth when they perceive the light of a star after it has passed through the atmosphere. This is a necessary condition for twinkling. If a very distant star is observed from space, it will not twinkle.
Astronauts who observed stars from the Moon, where there is no atmosphere, saw a sky filled with stars that shone with a steady, unwavering light. However, here on Earth, covered with a thick “blanket” of atmosphere, the rays of starlight, before reaching the surface, refract in different directions multiple times.
At what point do stars start to twinkle?
The twinkling of stars occurs when the light from a star transitions from a region of high atmospheric density to one of lower density. But why does this happen? The air molecules around us are in constant motion, never stationary. Warm air rises while cold air sinks. This movement causes the refraction of light to vary depending on the temperature. Thus, when light passes from a lower density layer of air to a higher density one, it causes the starlight to flicker.
When it happens, the outlines of stars blur and their images appear larger. The intensity of the stars’ radiation, or their brightness, fluctuates. Sometimes the star is highly visible, while other times it becomes dim. And then it becomes clear again. These variations in light intensity are scientifically referred to as scintillation. However, we commonly refer to it as “twinkling.”
Not all stars twinkle
Take planets, for instance, they emit a steady glow from the reflected sunlight and do not display the characteristic flickering seen in stars. Venus and Mars may appear as large, radiant stars in the night sky, but they are distinct from actual stars in that they do not twinkle. What is the reason behind this phenomenon?

When the planets come closer to Earth, they appear as small disks instead of tiny dots. The light that reflects off the different parts of the disks undergoes refraction, but in varying ways. Some parts of the disk reflect bright light, while others reflect dimmer light. As time passes, these bright and dim spots interchange. However, the overall intensity of radiation from the entire surface of the disk remains constant. Consequently, the planet’s disk emits a steady and uninterrupted glow.
How can you differentiate between a star and a planet?
The distinction between a star and a planet lies in the characteristics of their radiation. Stars tend to twinkle, while planets do not exhibit this twinkling effect. This particular attribute can be a useful method for distinguishing between the two celestial bodies. However, in cases where there is significant atmospheric disturbance, such as during a hurricane, planets may start to flicker as well. It is important to note that our sun is classified as a star, but it is much closer to Earth compared to the stars visible at night. Therefore, the sun appears as more than just a small dot in the sky.

The Sun appears to us as a vast, uniformly radiant sphere. If it were situated trillions of kilometers away from our planet, it would blend in with the multitude of other stars and exhibit the same twinkling effect. The twinkling of a star possesses a captivating beauty that can ignite the poetic imagination. However, for astronomers, it presents a formidable challenge. Even on nights with exceptionally clear skies, the atmosphere experiences significant air mass movements, known as disturbances, which greatly hinder the observation and photography of celestial bodies.
Optimal conditions for astronomical observations include nights with clear skies and a tranquil atmosphere free from disruptions. When the atmosphere surrounding the telescope is undisturbed, astronomers are able to observe celestial objects with excellent visibility and minimal flickering. As technology has advanced, high-powered telescopes have been launched into orbit, allowing scientists to observe the serene panorama of the cosmos and gaze upon the stars as they emit their eternal, tranquil brilliance.
Interesting video about the phenomenon of star twinkling
If you happen to come across any errors, kindly select the specific text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Stars, which are located light years away from Earth, appear as tiny dots when observed from our planet’s surface. As we gaze at the night sky, we can witness a captivating flickering effect of stars, displaying various colors such as blue, white, red, and yellowish. At times, this enchanting twinkling phenomenon even involves a change in hues.
What is the phenomenon of starlight?
Essentially, the captivating flickering of stars is merely an optical illusion. These celestial titans are composed of a blend of gases and have amorphous shapes. Deep within these stars, ongoing thermonuclear reactions occur, causing the gases to heat up and emit light.

The stars emit light with such intensity that their beams can traverse vast cosmic distances. Consequently, we are able to observe these remote entities of the Universe.
The characteristics of the phenomena taking place within stars are such that the radiance they emit is consistent and constant. To confirm this, one need only gaze upon the Sun. The star of our solar system in the nocturnal heavens, naturally, does not flicker.
What is the cause of optical illusion?
What is the reason behind our perception of twinkling stars? Interestingly, this phenomenon can only be observed from the Earth’s surface. The color of starlight can vary depending on the temperature of the gases that make up the stars. The hotter the star, the cooler the light it emits. This means that less heated stars appear red, while highly heated stars appear blue or white.
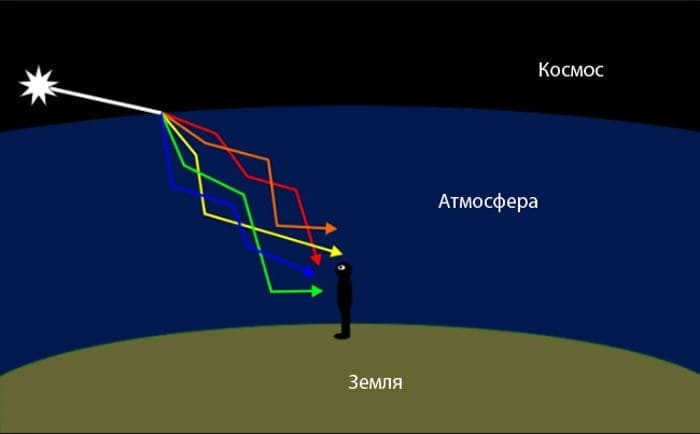
However, the flickering effect is actually caused by the structure of Earth’s atmosphere, which acts like a curved lens. The combination of gases that surround our planet, sustaining life for plants, animals, and humans, has a highly diverse composition.
Simultaneously, the Earth’s atmosphere is in a constant state of dynamic activity. The varying temperatures and pressures cause the different layers of the planet’s gas mixture to move at different speeds in relation to one another. Additionally, the Earth’s atmosphere frequently experiences the occurrence of both large and small vortices.
Consequently, the mobile composition of gases within the atmosphere scatters, refracts, and separates the light that passes through it into various spectra. Essentially, the Earth’s atmosphere functions as a curved lens, with its curvature periodically changing.
Why don’t the Sun and planets twinkle?
Upon closer inspection of the night sky, one may notice that certain objects do not twinkle. In addition to the Sun, the light emitted by the planets also remains constant. What causes this phenomenon?
Although the light reflected by the planets, similar to sunlight, undergoes scattering and refraction in the atmosphere, the planets appear larger to the naked eye because they are much closer to Earth, despite their smaller size compared to the stars.
The Phenomenon of Blinking and its Impact on Astronomical Observations
The mesmerizing blinking of stars has captivated humans for centuries, evoking a sense of wonder and awe. However, for astronomers, this enchanting optical illusion poses a significant challenge to their observation of the night sky. While the Earth’s atmosphere plays a vital role in sustaining life and shielding us from the perils of space, it also presents obstacles to scientific endeavors.
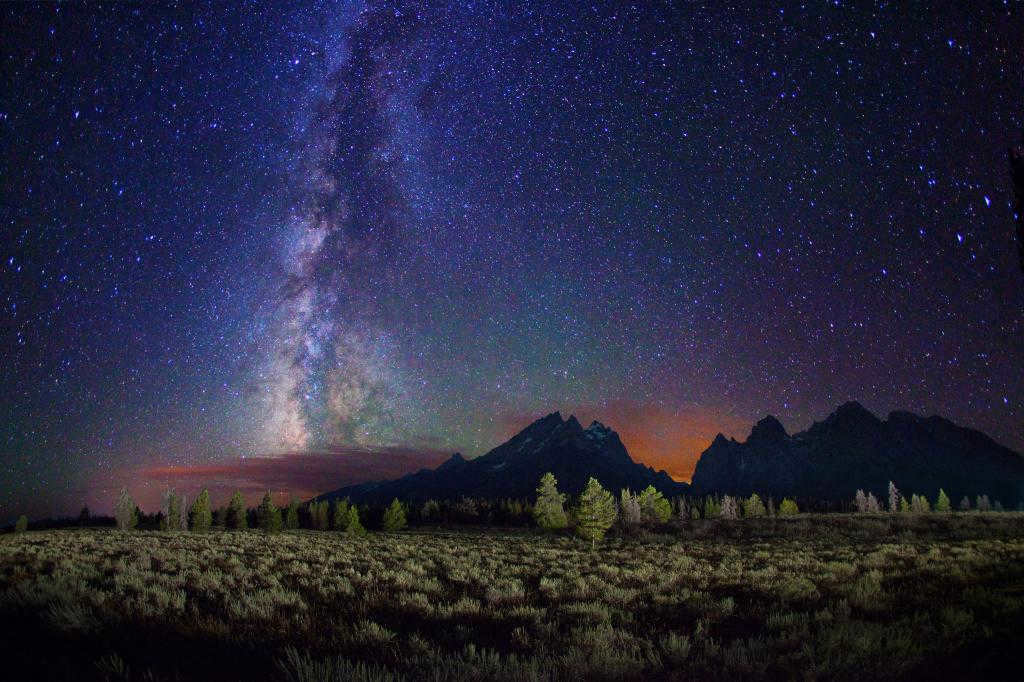

In order to overcome the interference caused by the flickering effect when observing stars, astronomers must either utilize costly telescopes with specialized designs, or gather data from multiple telescopes simultaneously. The Hubble Space Telescope, for instance, was able to capture its clearest images by employing special technologies that eliminate the blinking of stars.
The night sky adorned with stars always elicits unique emotions, often reducing the significance of earthly matters. It prompts individuals to recognize their insignificance in the vast Universe and embrace their role as a small part of something much larger than just planet Earth.

Have you ever wondered why stars twinkle? This question has undoubtedly crossed the minds of many. It is a mesmerizing sight, especially after a rainfall, when the stars glisten with an array of colors like a rainbow. Often, people struggle to provide a satisfactory answer to such an apparently simple question.
A straightforward response to a straightforward inquiry
The phenomenon of star twinkling is directly attributed to variations in the air. As a result of the Earth’s atmosphere being non-uniform, air masses move at different velocities, leading to the development of distinct currents and flows with varying temperature properties, density, and other characteristics. Consequently, starlight passing through the atmosphere can be refracted in numerous ways, giving rise to the enigmatic twinkle we observe.
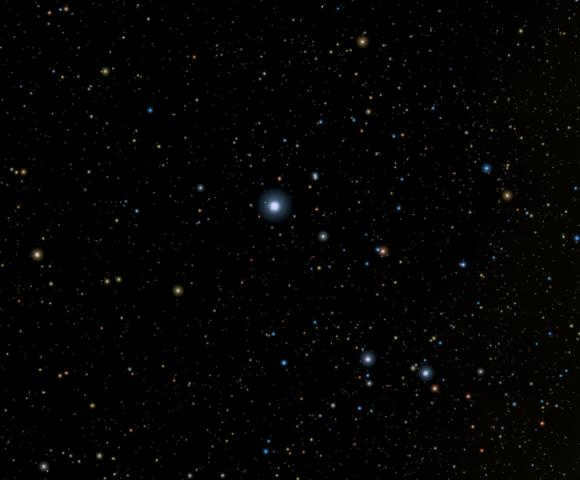

A shimmering celestial body
A celestial body shimmering in the vast expanse of the sky resembles the illuminations of a bustling metropolis when observed from afar. Moreover, if the atmosphere contains a high level of moisture, the radiance will alter its path and refract, creating a mesmerizing display of iridescent hues. The explanation for the phenomenon of stars twinkling is surprisingly uncomplicated. When a star nears the horizon, the refraction becomes even more pronounced due to the denser air, resulting in a distinct twinkle.
Stars and planets have a wide range of physical characteristics that set them apart, so it’s no surprise that they emit light differently. Even on a clear night with countless twinkling stars, the light from the planets in our solar system is distinct. Their light is constant and steady, similar to the Moon or the Sun, without any flickering. This can be observed without the need for an ultra-precise microscope.
Why does this phenomenon occur? Taking into consideration the atmospheric refraction that affects both starlight and planet light, it can be concluded that stars flicker on a point-by-point basis, just like planets do. However, due to the abundance of these points on a planet, an illusion of uniform light is created. It all comes down to the quantity of points of light.
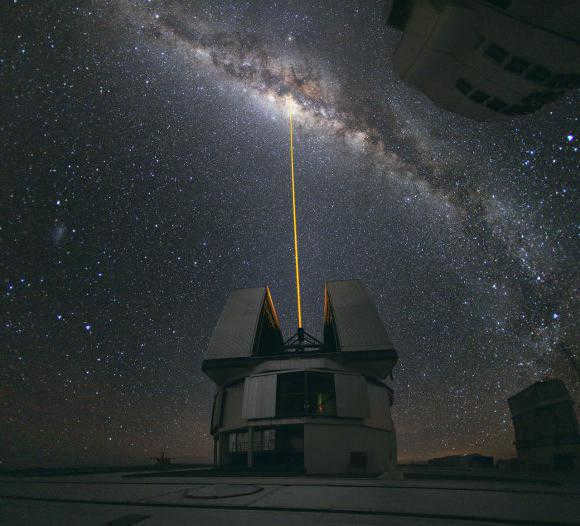

Stars of various kinds
When observing the stars without any magnification, they may all appear similar, differing only in their brightness. However, this assumption is quite far from reality. Upon closer inspection, one can actually distinguish stars based on their colors. This characteristic mainly pertains to the largest and brightest stars. For instance, Arcturus and Aldebaran display an orange hue, whereas Betelgeuse and Antares exhibit a red coloration. Sirius and Vega, on the other hand, shine with a white brilliance, while Spica and Regulus possess a white hue with a hint of blue. Furthermore, there are even yellow giants like Capella and Alpha Centauri.
Astronomers link the color of stars to a specific characteristic called temperature. Stars with surface temperatures up to 4 thousand degrees are classified as relatively cold and appear red, while the hottest stars are referred to as blue-white and can reach an astonishing temperature of 10-30 thousand degrees Celsius! With these temperature measurements, it becomes evident why stars appear to twinkle so brightly.

The phenomenon of stars twinkling has long puzzled astronomers. The question of why stars appear to twinkle is a complex one, with different interpretations depending on perspective. If we consider the twinkling as a result of atmospheric refraction, then it can be described as twinkling. However, in reality, stars do not actually twinkle themselves. It is the Earth-bound viewer who perceives them as twinkling due to atmospheric interference. If viewed from space, the stars would appear bright and steady, without any flickering. Astronauts have reported that the stars shine consistently, only appearing to twinkle to those observing from Earth.
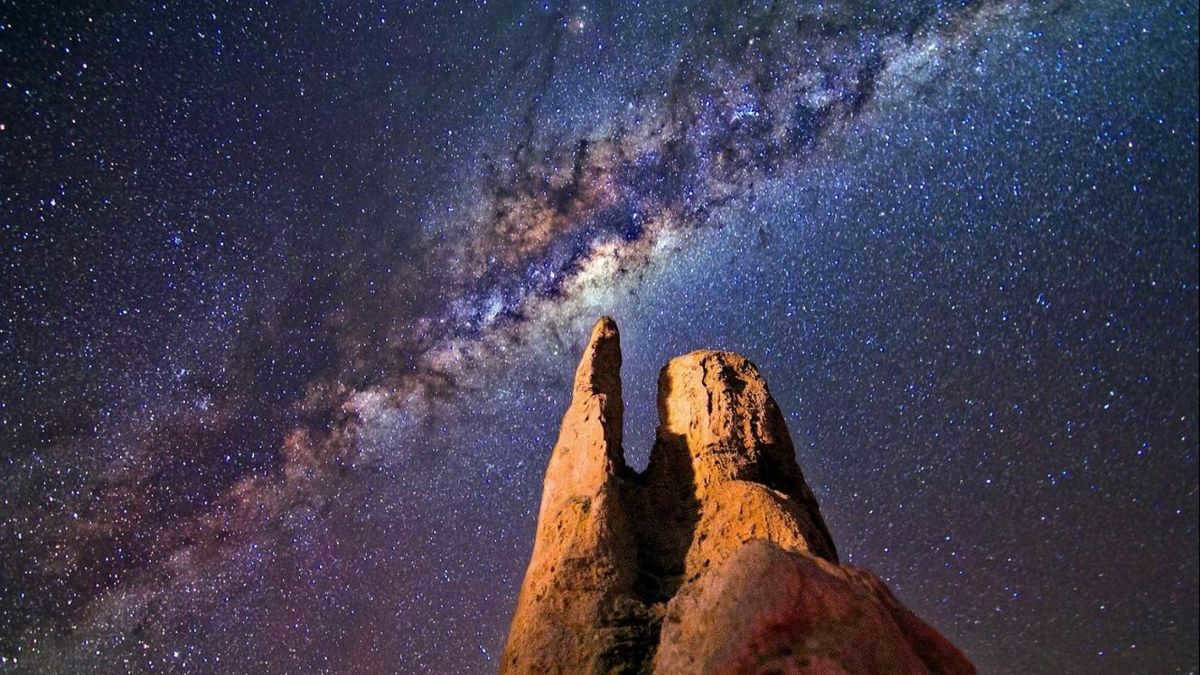


When you gaze at the sky on a clear night in a secluded area, you may observe the stars twinkling.
But what is the scientific explanation for this peculiar behavior of the stars? What is it about stars that causes them to twinkle?
Stars do not actually twinkle.
The straightforward answer to the query of why stars twinkle is that they do not actually twinkle. The twinkling effect we perceive has nothing to do with the stars themselves. Instead, it is a result of how we perceive them from our vantage point on Earth.
Since the stars are located so far away, we perceive them as minuscule points of light in the nocturnal sky.
“On a clear night, starlight traverses an extensive distance before reaching our eyes,” explained Ryan French, a physicist at University College London in the U.K. The closest star to us, Proxima Centauri, is over 4 light-years away from Earth.
Similar articles:
During its journey to our eyes, the light emitted by distant stars interacts with Earth’s atmosphere, resulting in the twinkling effect.
“As this point of light enters the atmosphere, it passes through varying layers of air, which is the main cause of the twinkling phenomenon,” explained French.
Therefore, the fluctuating atmosphere of Earth is responsible for the twinkling of stars. However, in the vacuum of space, far above the atmosphere, stars do not twinkle at all. This is one of the reasons why the Hubble Space Telescope was launched into orbit: it allows for clearer and undistorted images of space by avoiding atmospheric turbulence.
Reasons for Variation in Twinkling of Stars
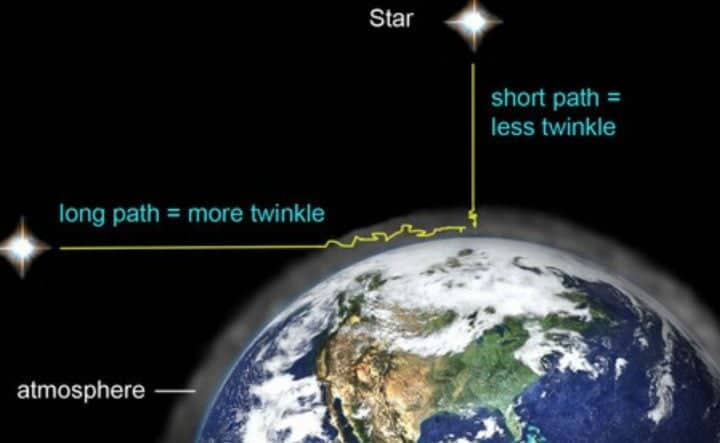
The amount of twinkling experienced by stars can be influenced by several factors. One such factor is the star’s position in our line of sight.
“Stars tend to twinkle more if their light has to pass through a greater amount of atmospheric layers before reaching our eyes,” explained French. “As a result, stars near the horizon appear to twinkle more.”
Weather conditions also play a role. Nights with higher humidity levels lead to denser air, causing stars to twinkle more intensively.
These factors are taken into consideration by astronomers when selecting optimal locations for the world’s largest and most advanced telescopes. Observatories are typically constructed in elevated and arid regions to minimize the amount of atmospheric interference between the telescope and the star.
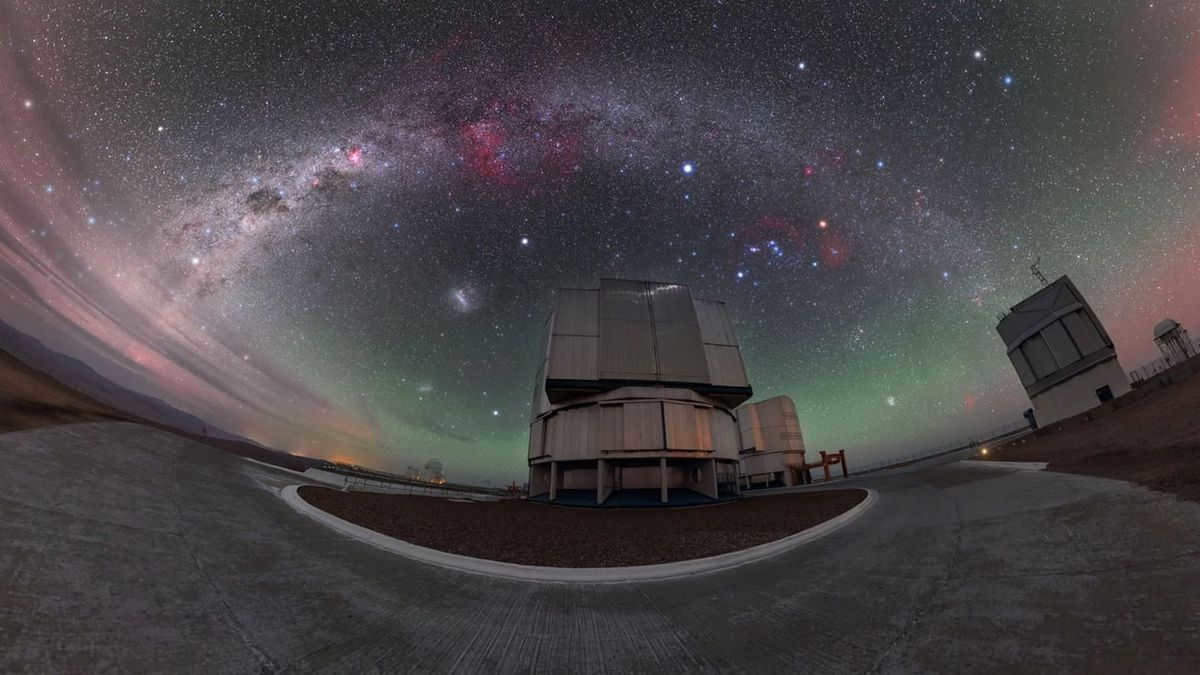

Optimal locations for observing the night sky include the arid Atacama Desert in Chile, as well as the volcanic peaks found in Hawaii and the Canary Islands of Spain. These areas are prime examples of places with what astronomers refer to as “favorable visibility.”
Upon gazing at the celestial expanse, one may also take notice of certain stars that undergo a change in hue as they twinkle. An iconic example of this phenomenon is Sirius, the most brilliant star visible in the Earth’s nocturnal dome.
“The starlight is slightly refracted and bent by the atmosphere, which can result in a variation of color,” explained French. “This effect is particularly pronounced with stars of greater luminosity.”
Additionally, you may also observe certain “stars” that do not exhibit any twinkling at all. This is due to the fact that they are, in fact, planets.
“Planets differ from stars in that they are not mere points of light in the sky, but rather have a certain width as they are much closer to us,” French explained.
In simpler terms, planets are too large in the night sky for Earth’s atmosphere to cause them to twinkle.
However, when observing planets or even the moon through a telescope, you may still notice a flickering effect. This is because the light you see must pass through the atmosphere before reaching your eyes.
Hello, I am the creator and manager of the UniverseTodayRu webpage. My passion lies in the fields of astronomy, physics, and mathematics. In the year 2010, I completed my studies at the Faculty of Physics and Mathematics at Pushkin BrSU. For my observations and photography, I utilize the Sky-Watcher BK 909EQ2 telescope and the Canon EOS 1100D camera. During my leisure time, you can often find me gazing at the stars, pondering the mysteries of the universe. Apart from the realm of exact sciences, I also hold a keen interest in all things related to software and information technology.

On our website, you can discover a plethora of captivating and fascinating narratives, as well as a wealth of knowledge and elucidations about the world. We offer a wide range of useful and engrossing information spanning various domains such as science, sports, nature, animals, and much more.
Indulge in reading and don’t forget to share with your friends!
In this particular article, we will delve into the question of WHY DO STARS TWINKLE
The stars themselves do not exhibit twinkling.
This optical phenomenon is perceived by Earth-bound observers due to the starlight passing through the atmosphere. Twinkling is a consequence of this atmospheric interaction. Interestingly, if you were to observe a star from space, even one situated at a great distance, it would not exhibit any twinkling.

When astronauts looked up at the sky from the Moon, they saw stars twinkling with a steady and constant glow. However, back on Earth, the stars appear to twinkle because of our atmosphere. The thick blanket of air refracts the starlight in various directions before it reaches the ground.
What causes stars to twinkle and when does it happen?
The phenomenon of star twinkling occurs when the light from a star transitions from a region of the atmosphere with high density to a region with lower density.
So why exactly do stars twinkle? The reason lies in the constant movement of the air masses surrounding us, as they are always in motion relative to each other.
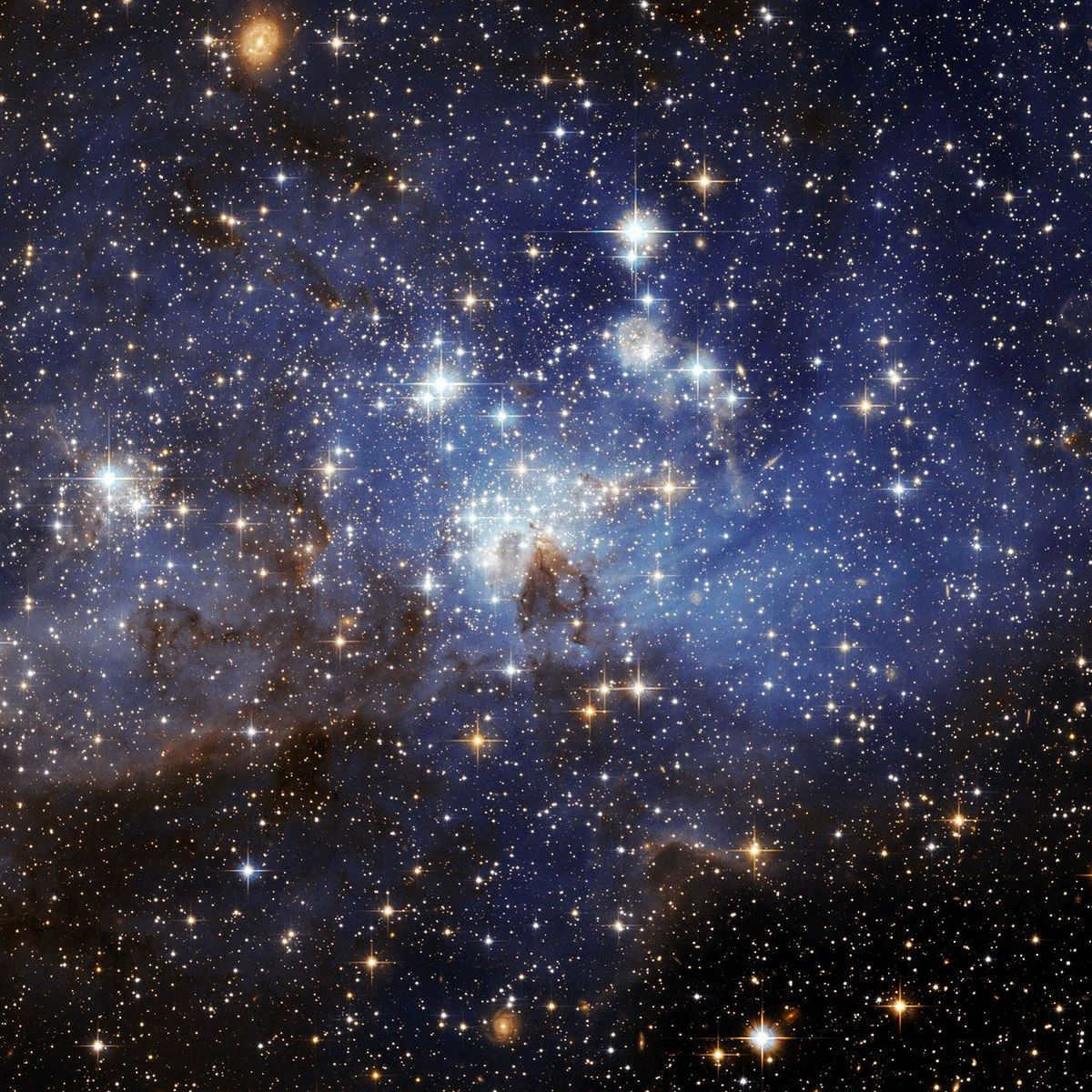

The twinkling of stars is caused by the movement of air in the atmosphere. As warm air rises and cold air falls, the density of the air changes, which leads to variations in how light is refracted.
When light travels from a region of lower air density to a region of higher air density, it can cause the light to flicker.
As a result of this flickering, the outlines of the stars become blurred and their images appear larger. Additionally, the brightness of the stars fluctuates, with some moments of intense radiation and others of dimness. This variation in light intensity is scientifically known as scintillation, but we commonly refer to it as “twinkling.”
Planets, such as the Earth, shine with the light of the sun that is reflected off their surfaces and do not flicker like stars do.
When we look up at the night sky, we can see Venus and Mars shining brightly, but they don’t twinkle like the stars. This is because these planets are much closer to Earth compared to the distant stars. As a result, we see them as larger objects with defined shapes, rather than as tiny points of light.

When light interacts with different areas of the disks, it undergoes the same refraction process but is refracted in a unique manner. Some parts of the disk reflect bright light, while others reflect dimmer light.
These reflections continuously change positions, resulting in a constant average intensity of radiation across the entire surface of the disk.
As a result, the disk of a planet emits a steady, non-flickering light.
What are the distinguishing characteristics between stars and planets?
Stars and planets can be differentiated based on their radiation patterns. Stars have a tendency to twinkle, whereas planets do not. This is generally a reliable way to distinguish between the two. However, it’s worth noting that if there is a high level of atmospheric disturbance, like during a hurricane, planets may appear to flicker as well.

The star that we see at night twinkle because they are located very far away from Earth. However, our sun is also a star, but it is much closer to us. Unlike the stars we see at night, the sun is not just a dot in the sky.
When we look at the sun, we see a large, evenly shining disk. This is because the sun is relatively close to us. If the sun were trillions of kilometers away from Earth, it would appear as a small dot among many other stars and twinkle just like them.

The sparkling of a star is a sight of beauty and can ignite the imagination of a poet. However, for astronomers, it presents a significant challenge. Even under clear skies, there are turbulent air masses in the atmosphere known as disturbances, which greatly hinder the observation and photography of stars.
The optimal time for conducting astronomical observations is during clear nights when the atmosphere is calm and undisturbed.
During moments when the atmosphere above the telescope remains tranquil, astronomers are able to observe with clear visibility and minimal twinkling. With advancements in space exploration, powerful telescopes have been launched into orbit, allowing scientists to observe the true serenity of the cosmos, gazing upon the stars as they radiate with a peaceful eternal glow.
The Moscow Planetarium offers a unique experience to explore the vastness of the Universe. Whether you are a professional astronomer or simply a curious amateur, there is something for everyone here. With the guidance of our knowledgeable staff, you can embark on a cosmic journey that will leave you with unforgettable memories. Time seems to stand still as you delve into the mysteries of the cosmos and feel the allure of the unknown.
Your journey begins at the Urania Museum, where the rich history of astronomy unfolds before your eyes. From ancient times to the present day, you can witness the evolution of this fascinating science. Marvel at the replica of the first telescope, make a wish as you touch a large meteorite, and capture a photo with the Moon or Mars as your backdrop.
From the museum to the Great Star Hall, you can experience a breathtaking journey through the celestial wonders. Witness the mesmerizing dance of celestial fireflies, explore the intricate constellations, and marvel at the dazzling flight of comets. Embark on a virtual spaceship and traverse the vastness of the Solar System, visiting each planet in all its majestic glory. Discover hidden corners of the universe that can only be seen through the lens of a professional telescope. This extraordinary adventure promises to captivate your imagination far beyond what any movie, even “Star Wars”, can offer.
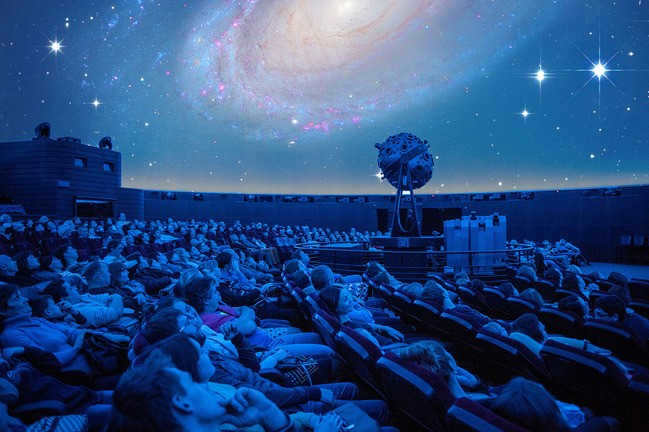

Moreover, there’s more to discover: once you complete your interstellar voyage, you will find yourself in the Sky Park, which is designed to resemble ancient observatories. Within this space, you will encounter Stonehenge, the Indian winged staircase known as Samrat Yantra, the pyramid of Cheops, and have the opportunity to measure your steps along the Moscow meridian.  If you aspire to become a true space explorer, to unravel the secrets of the universe and explore the vastness of the galaxy, you must pay a visit to the Interactive Museum “Lunarium”. This place is a marvelous kaleidoscope of captivating experiments and a genuine wonderland for the imaginative mind. You can launch your very own rocket, listen to radio signals from outer space, transmit a message to extraterrestrial civilizations, and even create a loyal companion – an alien. And only here will everyone experience the thrill of being a genuine hero, saving the planet from a meteorite collision.
If you aspire to become a true space explorer, to unravel the secrets of the universe and explore the vastness of the galaxy, you must pay a visit to the Interactive Museum “Lunarium”. This place is a marvelous kaleidoscope of captivating experiments and a genuine wonderland for the imaginative mind. You can launch your very own rocket, listen to radio signals from outer space, transmit a message to extraterrestrial civilizations, and even create a loyal companion – an alien. And only here will everyone experience the thrill of being a genuine hero, saving the planet from a meteorite collision. 
To conclude your stellar journey, you can immerse yourself in the 4D movie theater. The sensations are indescribable: a state-of-the-art stereo projection system, dynamic seats, and special effects. After uncovering all the mysteries of life in the Universe, you will embark on a voyage to comprehend the wonders of the Cosmos.