Stars are the primary celestial bodies in the universe. The existence of biological life heavily relies on the light and heat emitted by stars. Each individual star possesses unique characteristics and occupies a specific position within a hierarchy.
Understanding Stars in Space
A star is a celestial entity where thermonuclear reactions occur deep within its core. However, not all objects have the potential to become stars. To qualify as a star, an object must have a minimum mass of 0.08 times that of our Sun (1.9885⋅1030 kg). It must also consist of approximately 70% hydrogen and 28% helium in its gas composition. This gas mixture must reach a critical temperature threshold, which is required to trigger a hydrogen reaction. This reaction ultimately converts hydrogen into helium through a series of interlinked reactions.

Measurement of Distance
Estimating physical characteristics of space objects is impossible without knowledge of their distance. The concept of stellar parallax, which was pioneered by Tycho Brahe, provides a mathematically complex method for determining distance. From 1833 to 1838, various scientists, including the Russian astronomer V. Ya. Struve, used this method to measure the distance to Alpha Centauri, Vega, and 61 Swan.
The Earth’s atmosphere significantly hampers space observation. When using a ground-based telescope to calculate distance, there can be an error of up to 50%. However, the introduction of satellites has revolutionized the situation. The astrometric method now accurately determines the distance to space bodies.
Derived from the concept of parallax, a unit called a parsec (PARallax+SEKunda) was created to specifically measure the distance to faraway stars. It is equivalent to 206265 astronomical units. A parsec is the distance that light travels in 3.2616 years. Various units of measurement are utilized, including kiloparsecs, megaparsecs, and gigaparsecs.
It is important to keep in mind the speed of light. When observing an object from Earth, we see it as it appeared at a certain point in time, which is determined by its distance in light-years.
Groups of Stars in the Sky
A constellation is a traditional assemblage of stars that can be seen in the visible part of the sky.
For ease of navigation and classification, the sky has been divided into sections.
In reality, the celestial bodies within a constellation are often located far apart from each other.
Constellations visible in the Northern Hemisphere cannot be observed from the Southern Hemisphere, and vice versa. However, on clear moonless nights with favorable weather conditions, certain equatorial constellations like Sagittarius can be glimpsed just above the horizon. Additionally, the winter and summer skies present unique constellations due to the tilt of the Earth’s axis.
The 88 constellations have names that are partly derived from ancient myths, such as Andromeda, Cassiopeia, Perseus, and Swan, among others. Christianity has also contributed more recent names, such as Veronica’s Hair. In the Southern Hemisphere, scientists have assigned names to the constellations.
The stars within a constellation are identified using Greek letters, which are arranged in order of brightness, following the order of the letters in the alphabet:
- Α α – alpha;
- Β β – beta (vita);
- Γ γ – gamma;
- Δ δ – delta;
- and so on.
In previous times, stars were employed for divination purposes, but now they serve as a means to discover novel exoplanets. Sergei Popov, an astrophysicist, shared with RBC Trends the existing knowledge about our primary celestial body and the vast amount of additional information that scientists still need to acquire about it.
Astronomy has always had a keen interest in stars, as they are relatively easy to observe. However, in recent times, stars have taken on a new role as a tool for studying other celestial bodies. For instance, scientists can identify new exoplanets by studying the unusual changes in a star’s speed or brightness.
Furthermore, stars are crucial in the study of galaxies, including our own, as they provide a record of its formation. By analyzing various parameters of numerous stars, scientists can create a map of the galaxy and gain insights into its history. This information is also vital in understanding the formation of other types of galaxies, which in turn helps in comprehending the evolution of the Universe.
The Gaia optical-band space telescope was sent into orbit in late 2013. Originally planned to operate for five years, until 2019, it has exceeded expectations and continues to function. There are discussions underway to potentially extend its mission until 2025. This remarkable satellite enables scientists to accurately determine the precise coordinates, velocities, and additional physical attributes of over a billion stars.
Composition of Stars
A star is comprised of a mass of gas that undergoes thermonuclear reactions at its core. These reactions are responsible for the star’s ability to emit a powerful and sustained light.
About 99% of a star’s mass consists of hydrogen and helium, with the remaining percentage comprised of other essential elements that provide valuable information about the star’s age and formation.
Interestingly, all elements heavier than hydrogen and helium were already synthesized during the lifetimes of the earliest stars. Some of these elements were expelled into space, including a significant portion of elements heavier than iron that originated from supernovae. The collision of two neutron stars also leads to major events and the ejection of heavy elements.
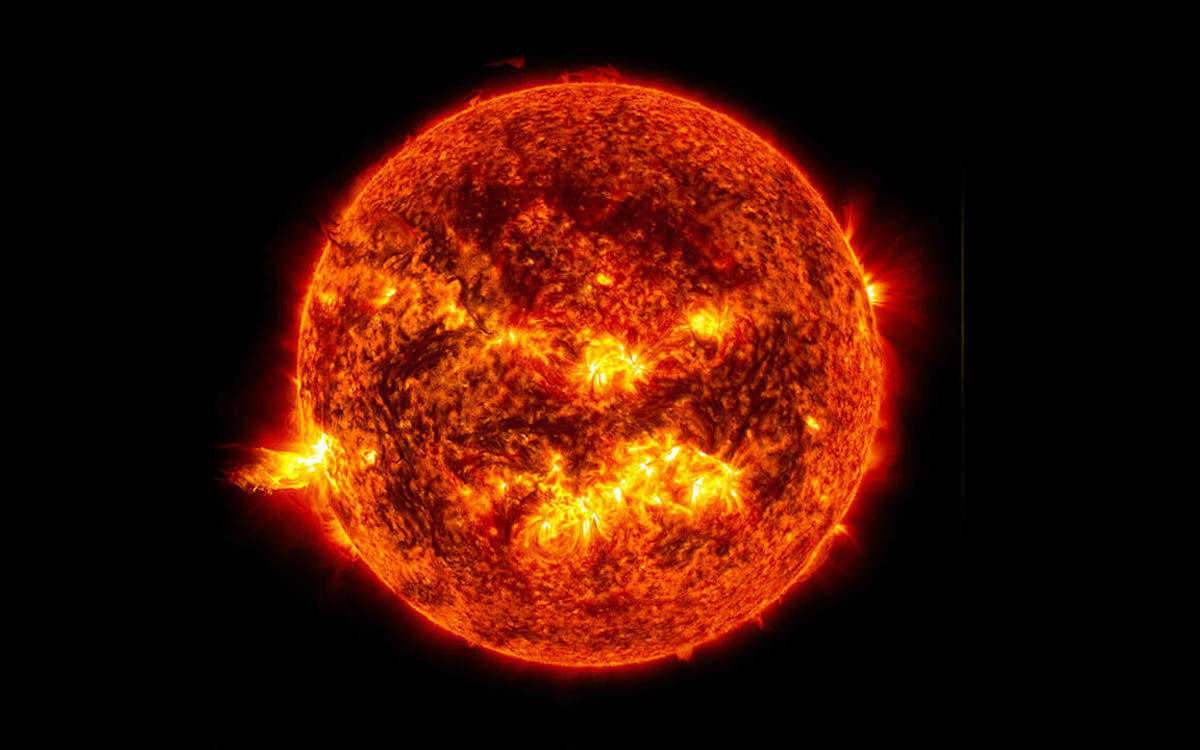
Understanding the Sun and the Origin of its Flares
The Sun, undoubtedly, holds the utmost significance for humanity as it serves as our primary star. The study of the Sun carries immediate practical importance for us. Several decades ago, humanity was unprepared for the immense power of solar flares, exemplified by the blackout in Quebec in 1989, which resulted from a solar storm.
Although solar flares do not pose a threat of Earth’s destruction as depicted in the movie “The Omen,” they can lead to severe technical disasters. These powerful energy releases disrupt the Earth’s magnetic field, giving rise to currents in conductive systems that can cause damage. Consequently, efforts are being made to prevent their impact on power lines, gas, and oil pipelines.
However, safeguarding communication satellites poses a greater challenge. Other astronomical instruments are also vulnerable to solar activity, which is why satellite launches are sometimes scheduled during periods of low solar activity.
Another major obstacle for a manned mission to Mars is the risk of encountering a coronal ejection, which is a massive cloud of plasma ejected by the Sun during solar flares. This issue could potentially be addressed by providing additional protection for the spacecraft and crew, or by planning the mission during periods of minimal solar activity.
The positive news is that powerful solar flares do not occur suddenly. The Sun operates on an eleven-year activity cycle, and if there is a foreseeable risk to humanity from a solar outbreak, astronomers can predict it decades in advance through astronomical observations.
Children are often taught that in five or six or seven billion years, the Sun will transform into a red giant and then a white dwarf, causing life on Earth to become impossible. However, this statement is not entirely accurate as the planet will actually become uninhabitable much earlier.
The intensity of solar radiation is gradually rising over the course of hundreds of millions of years. This gradual increase in the Sun’s influence is causing Earth’s climate to become warmer. If the composition of Earth’s atmosphere remains relatively constant, life on the planet will come to an end within a billion years due to the escalating solar luminosity. Fortunately, considering that very few individuals have plans that extend out that far into the future, the inevitable prospect can be set aside for now.
Thanks to the development of new satellites and ground-based telescopes, including neutrino telescopes, it may be possible in the near future to gain a deep understanding of the physics of the Sun. This knowledge is crucial for various reasons, one of which is predicting the Earth’s climate evolution.
Exploring the Sun’s secrets
Through in-depth studies using neutrino detectors, we now have concrete evidence that thermonuclear reactions take place at the core of stars. These detectors are able to capture particles emitted from the Sun’s interior within minutes of their formation. Despite traveling at nearly the speed of light, it still takes over eight minutes for these particles to reach Earth from the Sun’s core. Nevertheless, we have made significant progress in detecting neutrinos from all the major thermonuclear reactions.
If neutrino detectors have enabled us to peer deep into the core of the Sun, helioseismology allows us to gain insight into the dynamics occurring between the core and the surface of the star.
Close to the surface of the Sun, acoustic waves are generated, propagating inward, reflecting off the interior, and then traveling outward. The visible surface of the Sun experiences vibrations and “breathes” as various waves interact, causing different oscillations even within the same area. While these oscillations are not directly detected as sound, they can be observed through changes in light, thanks to the Doppler effect. Through interpretation and modeling, the resulting image provides valuable information about the speed of sound within the Sun’s interior, as well as fluctuations in temperature and pressure.
Scientists utilize the knowledge they acquire about the Sun to examine other celestial bodies. Remote stars may possess varying masses, chemical compositions, magnetic fields, or rotational velocities, but their fundamental structure remains consistent. Consequently, without delving into the depths of distant stars, we can confidently assert that they are arranged in a similar manner to the Sun.
Stars. What could be more enticing and enigmatic for a typical upstanding individual? Especially if he resides in the countryside. And has the opportunity on a clear moonless night, after completing the morning chores, standing in the doorway of a hay-scented stable with a full pail of warm milk, to gaze upon with unending awe several thousand stars shimmering out there, in the unfathomably distant realms of the Galaxy….
Humanity has revered the night sky for countless millennia. Any, even the harshest and cruelest appearing member of mankind sometimes, covertly from everyone else, gazes upward at night. And contemplates the extraordinary splendor and uncharted marvels that the cosmos possesses…
Regrettably, the starry sky is gradually becoming less accessible to us, particularly in large cities. The cause for this is light pollution, which hinders our ability to perceive the true beauty of the night sky, just as our ancient predecessors once did.
However, when we direct our gaze towards the night sky away from urban areas, we can still witness a vast multitude of stars. What’s intriguing is that these stars appear somewhat distinct even when observed without any visual aids! Evidently, the distances to these celestial objects can range from immense to moderate. Nevertheless, size also plays a significant role. So, how immense can the most colossal stars actually become? Today, let’s explore what modern astronomy has revealed so far.
Today, we will discuss the largest stars ever discovered by astronomers in the vastness of space. Sadly, these stars cannot be observed with the unaided eye, which is rather unfortunate.
The various celestial bodies in the vast expanse of space
The nearest celestial body to our planet is undoubtedly the Sun. Incidentally, it falls into a rather unique category of celestial bodies. In the Milky Way galaxy, there are less than 5% of celestial bodies similar to it. Approximately 80% of the celestial bodies in the galaxy are significantly colder and less massive compared to our Sun. These celestial bodies are commonly referred to as red dwarfs.
There are actually several factors that contribute to the different appearances of celestial bodies. These factors include temperature, mass, distance from Earth, and size, as mentioned earlier.
Consider the red dwarf star Proxima Centauri, which is part of the Alpha Centauri system. It holds the distinction of being the star nearest to us, at a mere distance of 4.2 light years from Earth. Proxima Centauri has a mass that is only 12% of the Sun’s mass and its luminosity is a mere 0.17% of our star’s luminosity. Consequently, it is imperceptible to the unaided eye.
Let’s recall a few details about the star Canopus. It is an extremely luminous star in the night sky of the southern hemisphere. In fact, it is the second brightest star after Sirius among all the stars in the sky, regardless of the hemisphere. Canopus is located 73 times farther away from us compared to Proxima Centauri, with a distance of 310 light years. However, due to its classification as a yellow-white supergiant, Canopus shines more than 10,000 times brighter than the Sun! Additionally, this celestial object is 8 times more massive than our own star.
These numbers are undoubtedly impressive, but they pale in comparison to the colossal giants that exist somewhere in the vastness of space. There are stars out there that are so massive, bright, and magnanimous that the Sun and Canopus appear as minuscule particles of sand in comparison to them…
So, let’s move on to specific illustrations. And to make it clear, as a reference for a particular conditional unit (S), let’s consider our Sun. Its fundamental characteristics are as follows:
UY Shield
This colossal star was discovered in the mid-19th century by German astronomers. And it’s actually quite challenging to gauge the magnitude of this enormous star. But let’s attempt it.
Imagine that the Earth is a tiny 2-centimeter sphere. On that scale, Jupiter would be 21 centimeters. The Sun would be 210 centimeters in diameter. Meanwhile, the UY Shield would be approximately 3.8 kilometers across! And this star can contain up to 5 billion objects like our Sun!
However, the enormous size of this colossal entity is not its sole source of renown. UY Shield also holds the distinction of being one of the most luminous celestial bodies ever observed by astronomers. Its proximity to Earth is estimated to be approximately 9,500 light years, and it emits a staggering amount of energy, surpassing that of our own Sun by several hundred thousand times!
Despite the considerable amount of time dedicated to the study of UY Shield by astronomers, this celestial giant remains shrouded in mystery. Scientists are still grappling with the task of determining its precise mass, age, and other critical characteristics, as well as its ultimate fate. The most probable outcome is a breathtaking hypernova explosion, surpassing the brilliance of a typical supernova event by a factor of 100. This cataclysmic event will offer a brief window during which UY Shield will be visible to the unaided eye.
VY of the Big Dog
Details about this massive object were initially recorded in the star registry of French astronomer Joseph Jerome de Lalande back in 1801. Until the detection of UY Shield, it held the distinction of being the most enormous star ever observed. Situated approximately 3,900 light-years from Earth, VY Big Dog and UY Shield share many similarities, including their size. Interestingly, astronomers are still engaged in a debate regarding which of these two stars is truly larger, mainly due to the substantial margin of error in determining the volume of UY Shield. Given the nature of such celestial bodies and their considerable distance from us, obtaining completely accurate measurements of their characteristics remains an exceedingly challenging task.
As per certain calculations, Big Dog VY loses mass equivalent to thirty times the mass of Earth annually. This rapid dissipation of material dispersed in the vicinity of the star has resulted in a significant decline in the brightness of Big Dog VY over the last few centuries. This phenomenon can be attributed to the formation of gas clouds that gradually obstruct the star’s emitted light.
Stevenson 2-18: The Largest Star in the Cosmos
Contrary to popular belief, Shields’ UY is not the largest star in the universe. In fact, it pales in comparison to the immense size of Stevenson 2-18. Discovered by American astronomer Charles B. Stevenson in 1990, this celestial object currently holds the title for the largest known star in terms of size and volume. Located approximately 19,000 light years away, Stevenson 2-18 is a true giant. To put it into perspective, if the star were to replace the Sun, its photosphere would extend all the way to the orbit of Saturn!
Imagine if you could travel at the speed of light. It would take you a staggering 9 hours to orbit the entire surface of Stevenson 2-18. In comparison, circling the Sun at the same speed would only take a mere 15 seconds!
Inside the colossal Stevenson 2-18, there are an astonishing 10 billion stars similar in size to the Sun. This is twice the number found within the UY Shield!

I’m craving for more!
Is it possible for there to be even more colossal stars out there in the vastness of space? That’s a truly thought-provoking question.
Based on the principles of stellar evolution, there exists a theoretical boundary that constrains the maximum size a star can attain. Scientists have meticulously calculated that the radius of such an astronomical entity should not surpass 1500 times the radius of our Sun. However, intriguingly, current estimates of the dimensions of the Stevenson 2-18 star indicate that it significantly exceeds this limit! It could be that our measurements are grossly inaccurate or, alternatively, it might be necessary for us to expand this upper limit in order to align theoretical predictions with observational data…..
The revelation concerning the Stevenson 2-18 celestial body strongly suggests the undeniable necessity of all these suppositions and hypotheses regarding the evolution of stars. Moreover, it is highly likely that these theories will be enhanced and refined in the future. Consequently, it is plausible that within the vast obscurity of the cosmos, colossal entities exist that surpass our wildest imaginations…
The celestial expanse captivates the attention of every romantic soul: it is an infinite abyss, shrouded in enigma… What lies within the depths of the universe? We comprehend that the distant planets and stars are beyond our reach, and yet we persist in fantasizing about the day when scientists will construct a spacecraft capable of traversing much greater distances… Naturally, by that time, numerous transformations will have occurred, but for now, we can find contentment in the current offerings available to us.
In today’s world, the Earth is illuminated by artificial lights, making it nearly impossible for urban dwellers to experience the awe-inspiring beauty of the Milky Way. The only way to truly witness its magnificence is to escape the city and venture into more rural areas, preferably during the months of June to August. During this time, the Northern Hemisphere experiences summer, while the Southern Hemisphere enters its winter season. If you truly want to witness the breathtaking beauty of the Milky Way, make sure to head to the outback!
However, while waiting for the perfect opportunity to admire the distant stars, why not take a closer look at what’s right in front of us? In this collection of stunning space photographs, let’s explore the names and brief information about some of the most beautiful stars in our universe.
10. Hakruks
Hakruks is a unique and innovative company that specializes in creating personalized solutions for businesses. With a team of highly skilled professionals, Hakruks offers a wide range of services including web development, digital marketing, and branding.
One of the key strengths of Hakruks is their ability to understand the specific needs and goals of each client. They take the time to listen and learn about the business, its target audience, and its unique selling proposition. This allows them to develop customized strategies and solutions that are tailored to meet the client’s objectives.
In addition to their technical expertise, Hakruks also places a strong emphasis on creativity and design. They believe that a visually appealing and user-friendly website is essential for attracting and retaining customers. By combining cutting-edge technology with innovative design concepts, Hakruks is able to create websites that not only look great but also deliver exceptional user experiences.
Another area where Hakruks excels is digital marketing. They understand the importance of online visibility and work closely with clients to develop effective marketing campaigns. From search engine optimization to social media advertising, Hakruks has the knowledge and experience to help businesses reach their target audience and drive traffic to their website.
Overall, Hakruks is a top choice for businesses looking to enhance their online presence and achieve their goals. With their personalized approach, technical expertise, and creative design solutions, Hakruks is able to deliver exceptional results for their clients.

The star called Gakrooks emits a brilliant light that captures the attention of many observers. It holds the position as the 24th brightest star, captivating the hearts of all romantics. Just like the Southern Cross constellation, its representation is utilized by various countries in the Southern Hemisphere. This celestial object is actually a binary star system, composed of two components that are separated by a distance of 400 light-years.
Upon gazing at Gacrux, it may appear as a solitary star, but in reality, it consists of Gacrux-A and Gacrux-B. Unfortunately, this particular star cannot be observed from Russia. However, if you possess a telescope in the Southern Hemisphere, you have the opportunity to witness its splendor. Countries such as Brazil, Australia, New Zealand, and others are fortunate enough to have access to this mesmerizing celestial spectacle.
9. Antares
can be paraphrased as:
9. Antares
can be rephrased as:
9. Antares
can be restated as:
9. Antares
can be rewritten as:
9. Antares
can be expressed as:
9. Antares
can be articulated as:

People living in the Northern Hemisphere have the opportunity to admire the stunning and dazzling star Antares during the late spring to early fall period. To locate it in the sky, one must navigate through the constellation of Scorpius, which is located in the place of the conventional head. Astronomers have given this star various names such as Satevis and Selkite, but the most popular name is Antares.
This star is a prominent component of the Scorpius constellation and serves as its brightest object. Its name is derived from its color. Since ancient times, people have been captivated by its red hue and luminous glow. Situated 600 light years away from our planet, this star shines much brighter and is larger compared to the Sun.

Pollux is renowned as the second brightest star in the night sky. Its luminosity sets it apart, ranking it as the 17th brightest star overall. This celestial body acquired its name as a tribute to the Dioscurus twins. For those who delve into ancient Greek literature, it can be found that Polydevk and Castor were twins and the offspring of Leda and Zeus.
Surpassing the brilliance of the Sun, Pollux resides within the constellation Gemini. It lies a mere 40 light years away from Earth. According to astronomical calculations, the star’s helium reserves are projected to deplete in approximately 100,000,000 years, transforming beta Gemini into a white dwarf. Additionally, this star is accompanied by an exoplanet, which was relatively recently discovered in 2006.
7. Rigel
Rigel, also known as Beta Orionis, is a bright blue supergiant star located in the constellation Orion. It is one of the most luminous and massive stars in our galaxy. Rigel has a radius about 70 times that of the Sun and shines with an apparent magnitude of 0.12, making it the seventh brightest star in the night sky. Its distance from Earth is approximately 860 light-years. Rigel is a young star, estimated to be only 10 million years old, and it is evolving rapidly. It is expected to explode as a supernova in the future, which will likely be visible from Earth. The name Rigel comes from the Arabic term “rijl jauzah al-yusra,” which means “the left leg of the giant.”

Close to our solar system, there exists a brilliant celestial body known as Rigel. This star emits an immense amount of light, shining 85,000 times brighter than our Sun. It is truly difficult to fathom such a level of luminosity. Rigel’s radiance is exceptionally strong and it can be found in the constellation of Orion. Similar to radiant lamps, Rigel illuminates the neighboring nebulae.
This colossal star is not alone, but rather consists of three individual stars: A, B, and C. Together, they emit a dazzling blue-white light. Locating Rigel is not a challenging task, as it is situated within the constellation of Orion. The three stars are positioned adjacent to one another. By looking down from the top star of Orion’s belt and shifting your gaze to the side, you will be able to spot this brilliant celestial body.
6. Capella
Capella is a star system located in the constellation Auriga. It is one of the brightest stars in the night sky and can be easily seen with the naked eye. Capella is actually a binary star system, meaning it is composed of two stars that orbit around a common center of mass. The two stars, Capella A and Capella B, are both giant stars that are nearing the end of their lives. Capella A is the brighter of the two stars and is classified as a yellow giant, while Capella B is a red giant. The two stars are relatively close to Earth, with Capella A being about 42 light years away and Capella B being about 48 light years away. The binary nature of Capella makes it an interesting object for astronomers to study, as it provides valuable insights into the evolution and dynamics of binary star systems.

Capella, a star that is 41 light-years away from Earth, is known for its vibrant yellow color and is considered one of the most luminous stars in the Ascendant constellation. Although it may appear as a single star to the naked eye, Capella is actually a binary system consisting of four components. The best time to observe Capella is during the winter months, although it can also be seen in the fall.
To locate Capella, one can use the Big Dipper as a guide. By mentally drawing a line through the stars Dubhe and Megrez, it is possible to navigate towards Capella. This star ranks as the 6th brightest in the night sky. Astronomers predict that Capella will eventually reach the end of its life cycle, although in human terms, this event is expected to occur relatively soon.
5. Fomalhaut
Fomalhaut is a bright star located in the constellation Piscis Austrinus. It is one of the brightest stars in the night sky and can easily be seen with the naked eye. Fomalhaut is also known as Alpha Piscis Austrini and is the brightest star in its constellation.
Fomalhaut is a young star, estimated to be only about 100 to 300 million years old. It is about 25 light-years away from Earth and has a mass about twice that of the Sun. The star is surrounded by a large debris disk, which is believed to be similar to the Kuiper Belt in our own solar system.
The debris disk around Fomalhaut was first discovered in 1983 and has been studied extensively since then. It is thought to be the result of collisions between small objects, such as asteroids and comets, in the star’s planetary system. The debris disk is also home to a planet, known as Fomalhaut b, which was directly imaged in 2008.
Fomalhaut b is a gas giant, similar in size to Jupiter, and is located about 115 astronomical units from its host star. It orbits Fomalhaut in a highly elliptical orbit, taking about 2,000 years to complete one orbit. The planet is still a mystery, as its origins and composition are not well understood.
In addition to Fomalhaut b, there is evidence of other planets or planetesimals within the debris disk. These objects have not been directly imaged, but their presence is inferred from changes in the structure of the disk over time.
Fomalhaut has been the subject of much scientific interest and speculation, as it provides a unique opportunity to study the early stages of planetary system formation. It is also a target of ongoing research in the search for extraterrestrial life, as the debris disk may provide clues about the presence of other habitable planets.
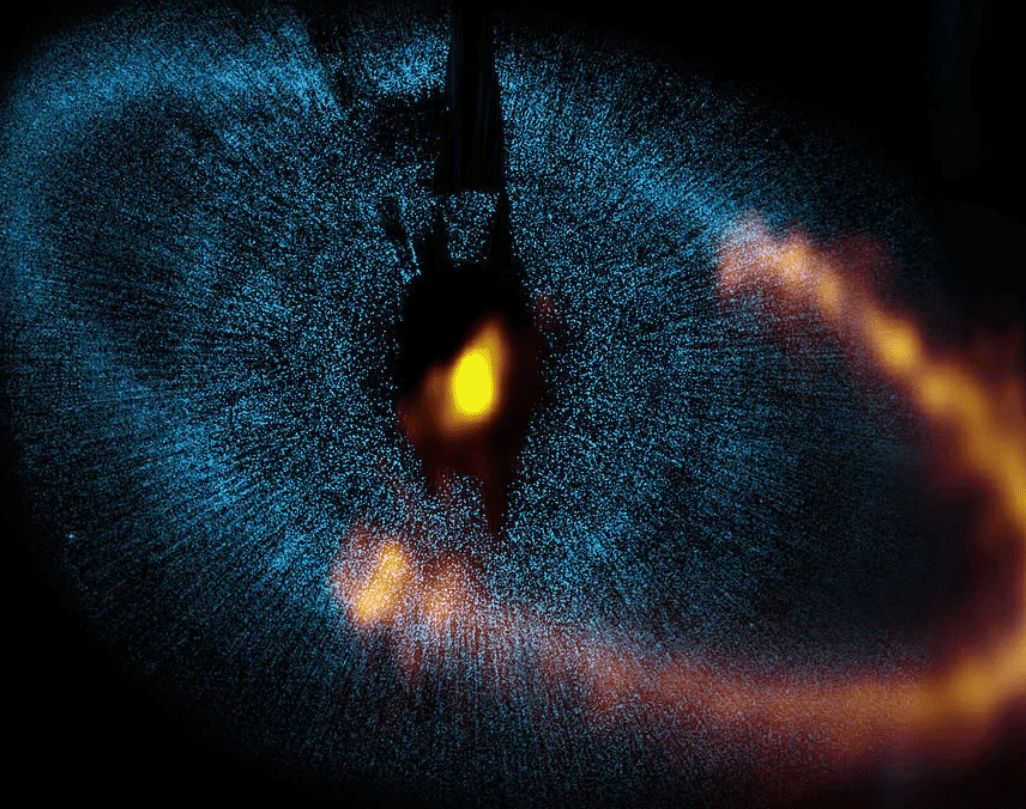
The constellation of South Pisces contains a star that shines brighter than any other. This star is known as Fomalgaut. Fomalgaut, which means “mouth of the whale” in Arabic, is ranked as the 18th brightest star and was first discovered by the Persians, Arabs, and Chinese. This star is both fascinating and relatively young. In Russia, it can be seen in the southern regions.
Fomalgaut has always captured the attention of astronomers and has been shrouded in mystery. Despite its youth, it shines with a luminosity 16 times greater than the Sun. This star possesses a powerful transformative energy, serving as a reminder that nothing in this world is permanent. Fomalgaut is located relatively close to Earth, at a distance of 25 light years, making it easily observable with astronomical instruments.
4. Hadar.
->
4. Hadar.
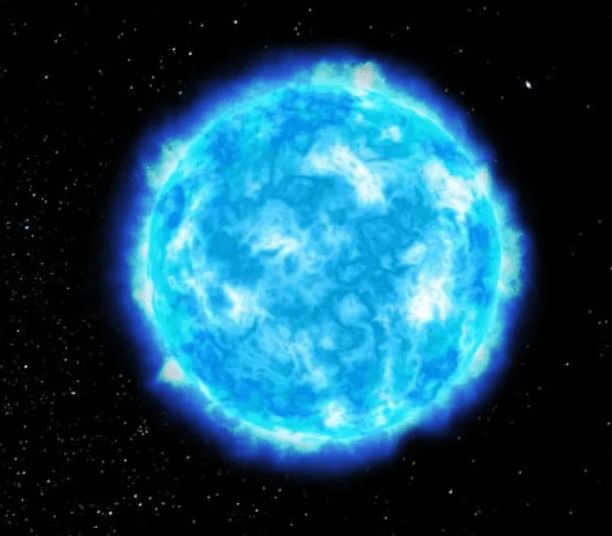

Hadar, known as the Bright Blue Star, is prominently displayed on the flag of Australia. It is the second most brilliant star in the Centauri constellation and is located 530 light years away from our planet. Hadar holds the 11th position on the list of the brightest stars. Upon closer observation, it becomes apparent that Hadar is actually a trio of stars.
Astronauts have predicted that the two stars within Hadar will eventually undergo a supernova explosion. Unfortunately, this star cannot be seen from Russia, except for those residing in southern latitudes. Hadar possesses a bluish hue and a luminosity measurement of 0.61. The name “Hadar” is believed to signify “low,” possibly referencing its appearance low above the horizon.
3. Adara
Adara is a unique and innovative company that offers a wide range of products and services. With a focus on technology and customer satisfaction, Adara has quickly become a leader in the industry.
One of the key features of Adara is its commitment to quality. The company works tirelessly to ensure that every product and service they offer meets the highest standards. This dedication to excellence has earned Adara a reputation for reliability and trustworthiness.
Another aspect that sets Adara apart is its emphasis on innovation. The company is constantly seeking new and improved ways to serve its customers. From cutting-edge technology to creative marketing strategies, Adara is always looking for ways to stay ahead of the competition.
Additionally, Adara takes pride in its customer service. The company understands that every customer is unique, and strives to provide personalized solutions to meet their individual needs. Whether it’s troubleshooting a technical issue or providing expert advice, Adara is always there to support its customers.
In conclusion, Adara is a company that stands out in the industry. With its commitment to quality, innovation, and customer service, Adara is a trusted name that customers can rely on.
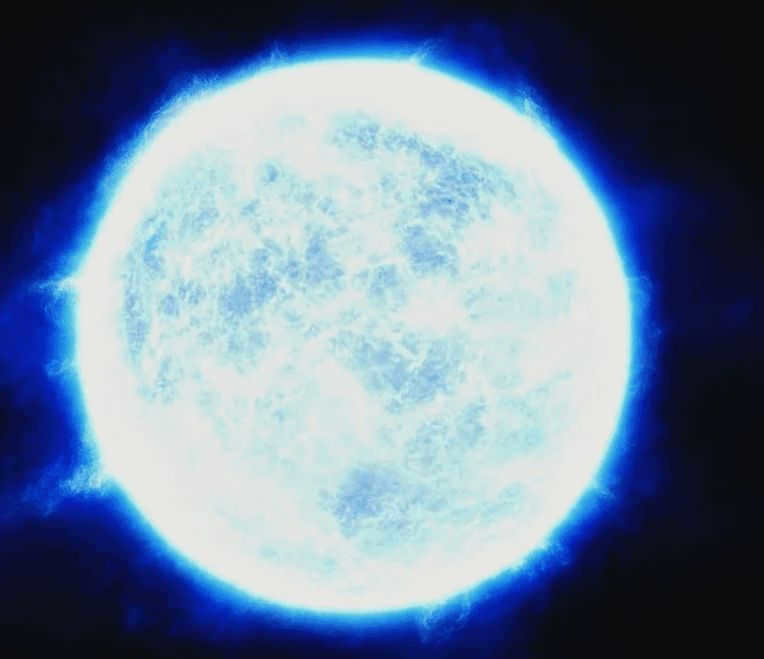

Adara is known as the brightest and most stunning celestial body in the Big Dog constellation. It can be easily spotted in the night sky due to its radiance, which surpasses all other stars except for Sirius. Adara is surrounded by other luminous stars like Rigel, Procyon, and others. Its distance from Earth is estimated to be approximately 430 light years.
With a luminosity 20,000 times greater than that of the Sun, Adara captivates observers from our planet with its brilliance. It is not just a single star, but rather a binary system, with its companion being Adara B. Currently, it can be observed in the central regions of Russia. The star emits an exceptionally bright light, leaving viewers in awe of its magnificence.
2. Spica
Spica is a binary star system located in the constellation Virgo. It is one of the brightest stars in the night sky and is easily visible to the naked eye. The name “Spica” comes from the Latin word for “ear of wheat” and refers to the star’s position in the constellation, which represents a maiden holding a sheaf of wheat. Spica is actually a close binary system, with two stars orbiting each other every 4 days. The primary star is a blue giant, while the secondary star is a white dwarf. This remarkable system has been studied extensively by astronomers and has provided important insights into the evolution of binary star systems.
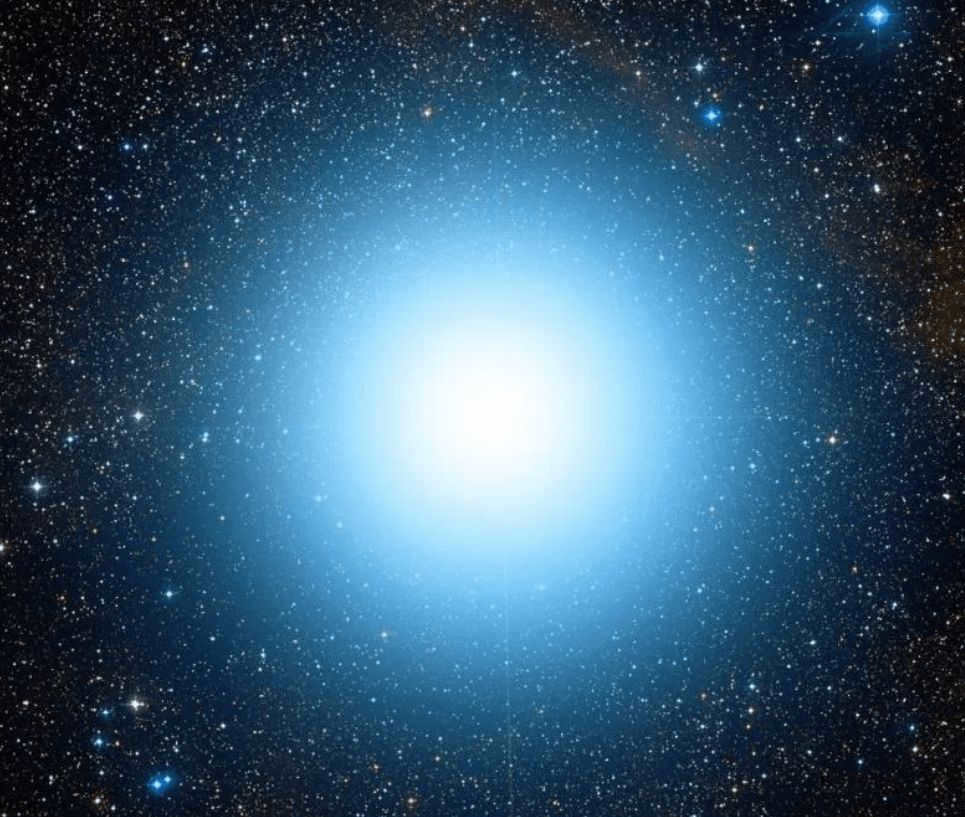

There are numerous astonishing stars that can be seen in the sky, and one of them is Spica. This particular star is situated within the constellation Virgo, and its image was utilized for the Brazilian flag. Along with Spica, the Virgo constellation comprises a multitude of other brilliant stars (at least 190). However, Spica shines more brightly than the rest, which makes it truly remarkable.
Ranking 16th in terms of brightness in the nighttime sky, this star is estimated to shine 12100 times brighter than the Sun. Although it is positioned 262 light years away from Earth, it is still visible and not difficult to locate. It is closely associated with the Big Dipper constellation. For a clearer view, one must venture away from urban areas where there is no light pollution.
1. Procyon
Procyon, also known as Alpha Canis Minoris, is the brightest star in the constellation Canis Minor. It is located approximately 11.4 light-years away from Earth and is one of the closest stars to our solar system.
Procyon is a binary star system, consisting of two stars that orbit around a common center of mass. The primary star, Procyon A, is a yellow-white main sequence star, similar in size and temperature to our Sun. The secondary star, Procyon B, is a white dwarf, which is the remains of a star that has exhausted its nuclear fuel.
Procyon is easily visible in the night sky and can be found by following the line formed by the stars in Orion’s belt to the left. It is one of the few stars that can be seen from both the northern and southern hemispheres.
The name Procyon is derived from the Greek word “prokyon,” which means “before the dog.” This is because Procyon rises before the “dog star” Sirius, which is the brightest star in the constellation Canis Major. In ancient times, the rising of Procyon and Sirius marked the beginning of the hot and humid days of summer.
Procyon has been studied extensively by astronomers and has provided valuable insights into stellar evolution and the properties of binary star systems. Its close proximity to Earth makes it an ideal target for scientific research and has allowed for detailed observations and measurements.
In addition to its scientific significance, Procyon has also played a role in human culture and mythology. It has been mentioned in various ancient texts and is often associated with the themes of brightness and illumination.
Overall, Procyon is a fascinating star that continues to captivate astronomers and stargazers alike. Its unique characteristics and close proximity to Earth make it an important object of study and a beautiful sight to behold in the night sky.






