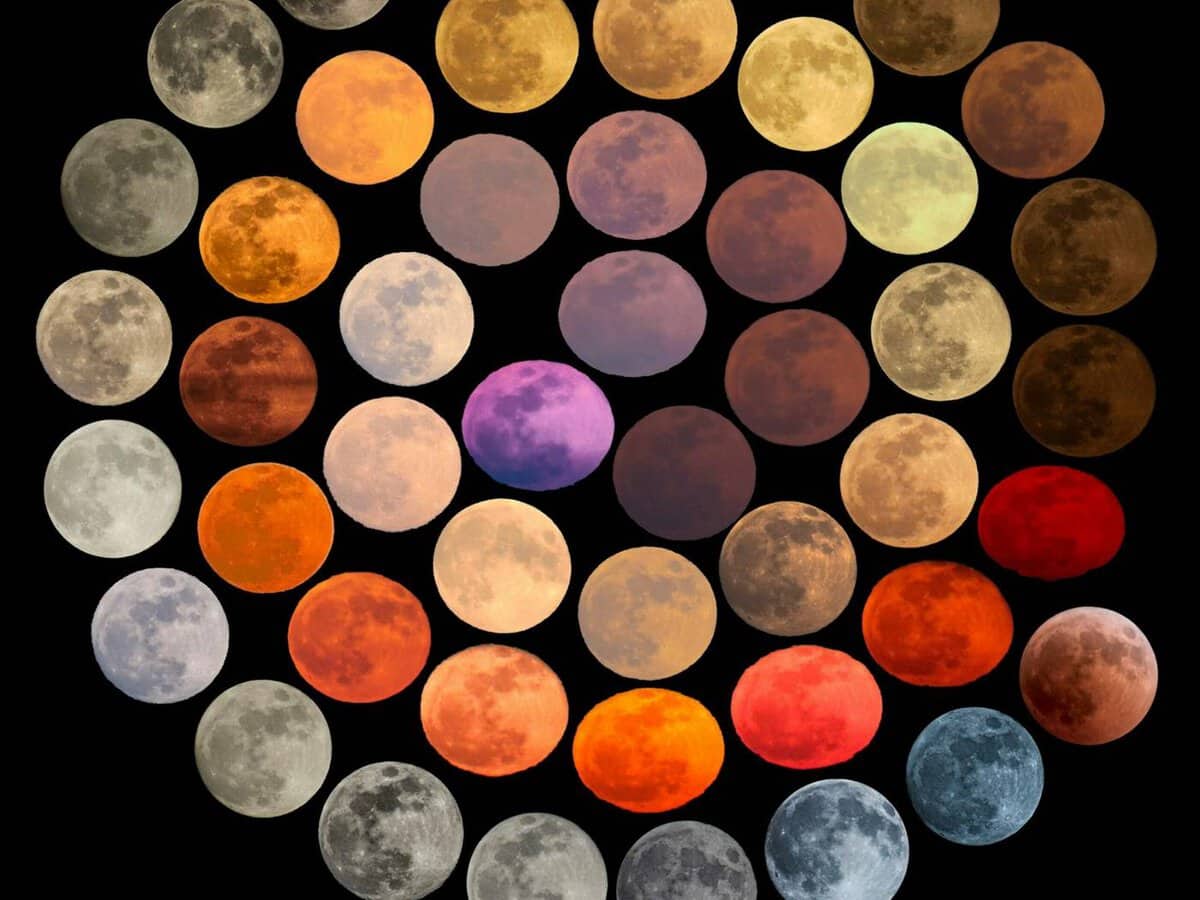
It may seem like a peculiar inquiry – the hue of the Moon. It is a common observation that it appears yellow, and upon closer inspection through a telescope, one may notice various shades of gray, with areas of varying darkness and brightness. This is also corroborated by photographs… However, the matter is not as straightforward as it appears. When examining natural color images of the Moon, distinct brown tones become evident.
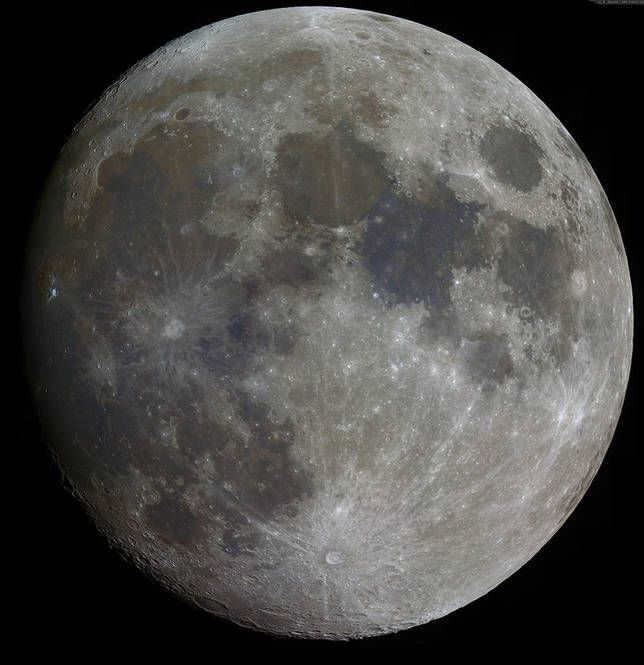

An amateur photograph of the Moon has been captured using various light filters and subsequently processed. Notably, there are distinct regions visible on the Moon that deviate from the typical gray color.
Interestingly, this observation has led to a theory suggesting that the American Moon landing was fabricated, and all the accompanying photographs were staged. Supposedly, the background was deliberately altered to appear uniformly gray, whereas in reality, it exhibits a more brown hue. This alleged oversight has sparked controversy and debate…
What is the true color of the Moon?
Our celestial body, the Moon, has undergone extensive research over the past few decades. We now have a better understanding of its geological history, which includes volcanic activity and the presence of lava rivers that transformed into seas. Additionally, the Moon has endured countless asteroid impacts, resulting in the formation of massive craters and the ejection of millions of tons of rock from its depths.
Through the analysis of data gathered from numerous satellites, modern geologic maps reveal that the Moon’s composition is highly diverse. As a result, its surface exhibits a non-uniform gray color. Similar to the Earth, the wide range of rocks on the Moon creates various shades across its surface.
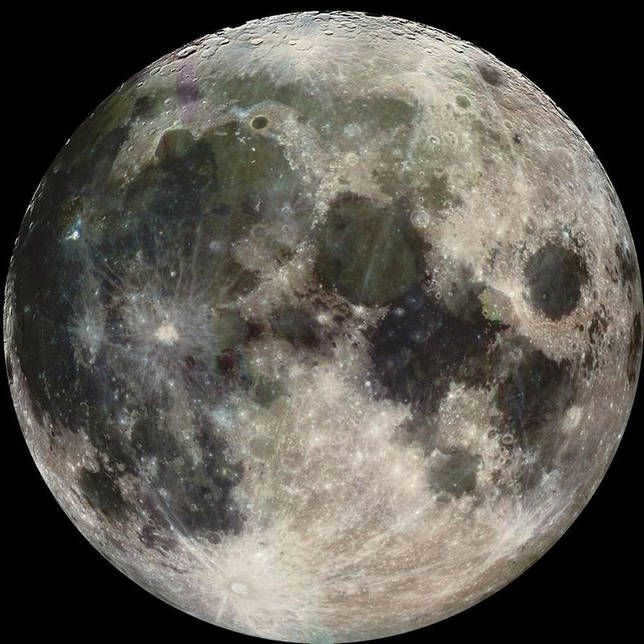

Amateur astronomers have the ability to create and successfully capture such images of the Moon. To achieve this, they utilize filters and capture photos using red, blue, and green colors. By combining and processing these images on a computer, the true colors of the Moon can be revealed. However, to the naked eye, the Moon appears differently.
The existence of a wide range of colors and rock formations on the Moon has been confirmed through samples brought back by the Soviet probe “Luna-16” and American astronauts. These missions have delivered hundreds of kilograms of lunar rock, showcasing its incredibly diverse composition. Among these samples, there are rocks that appear gray, brown, and even blue.
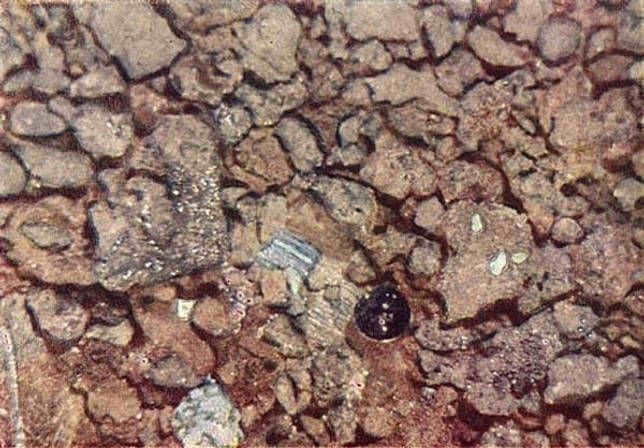

There are various hues of lunar rock samples that have been transported to Earth.
The magnitude of the satellite

When people look at the Moon, they may perceive it as either big or small because of an optical illusion. There are three different theories that explain this phenomenon. When the Moon is low on the horizon, it appears much larger than when it is directly overhead. This is because our eyes perceive the sky as a flattened dome, making objects appear larger than they actually are.
One theory, known as the theory of relative size, suggests that the presence of other objects in our field of vision can affect how we perceive the size of the Moon. When the Moon is compared to nearby buildings or trees, it may appear larger than if it were directly overhead.
When it comes to human vision, light-colored objects against a dark background always appear larger in size. This phenomenon is known as “irradiation” and is not limited to just the Earth’s satellite. For instance, on a chessboard, white squares tend to look bigger than black squares.
Signs and Superstitions
There are numerous folk beliefs linked to the crimson moon. In ancient times, it was believed that the presence of such a lunar phase predicted severe frosts and heavy rainfall. If the color changed during the spring season, it indicated significant temperature fluctuations between night and day.

In the Bible, the simultaneous occurrence of a blood moon and a solar eclipse predicted the onset of the Day of Judgment. In the Middle Ages, the crimson moon was associated with the invasion of dark forces and witches. Nowadays, various rituals are performed, as the magical effect is heightened during this period. In Africa, tribesmen were prohibited from gazing at the bloody month due to the belief that it would bring misfortune to the entire tribe.
Astrologers claim that when the fireball emerges on Earth, earthquakes and other catastrophes escalate. It is advised to refrain from long-distance travel, making important decisions, and postponing surgeries during this period. Statistics indicate a rise in the number of car accidents and increased irritability among individuals.
It is also advisable not to:
- Keep windows open at night;
- Experience the serenity of sleeping beneath the gentle glow of the Moon;
- Take a leisurely stroll in the evening as the sun sets;
- Indulge in the pleasure of enjoying alcoholic beverages.

However, the Maya civilization interpreted the occurrence of a fully red-colored moon as a positive omen. Within their calendar, this event was known as the “Ninth Glyph Tsolkin” and symbolized purification. It was widely believed that individuals born on this day possessed unparalleled strength and intelligence, with their destiny predetermined.
What is the reason behind the Moon’s unchanging face?
The Moon has always been a fascinating object of observation, captivating people with its beauty and being the second source of light in the sky. Its “Seas” and “Oceans” have inspired songs and poetry, making it an object of artistic admiration. However, the Moon is a peculiar satellite that distinguishes itself from others.
A peculiar neighbor.
The Moon stands out among the satellites orbiting other planets due to its unique characteristics. It is relatively large, sharing a similar composition to our planet, and exhibits unusual behavior.
This enigma has sparked numerous rumors and speculations. There have been theories suggesting the existence of an undiscovered civilization residing on the moon, beyond the lunar horizon. Some even proposed that aliens have established a clandestine base there. There was even a far-fetched notion that escaped Nazis sought refuge on the moon after World War II. However, this seems highly unlikely.
The most outlandish assumption was that the moon itself is actually an extraterrestrial spacecraft. Though its appearance is rather peculiar, one might wonder if the aliens have a deficiency in skilled designers. Nevertheless, the mystery persisted.
All is becoming clear.
The discovery of the hidden face of the Moon was unveiled in 1959, when the Soviet Luna- spacecraft orbited the satellite and captured images of it. As expected, there were no extraterrestrial beings, no mythical cities, not even remnants of Nazi activity. Instead, the photographs revealed the familiar lunar landscape: mountains, craters, and solidified lava.
Subsequent missions by the USSR and other nations confirmed these findings. However, this raised a pressing question: why does the Moon consistently present only one side to us, especially when there is nothing to conceal on the other side? This mystery prompted the scientific community to embark on a quest for answers.
Interestingly, there are tidal phenomena occurring on the Moon.
The most scientifically logical explanation for the phenomenon is the influence of gravity. The gravitational force exerted by the Earth on the Moon causes a tidal effect, not in the oceans as on Earth, but within the rocky interior of the Moon. As the Moon rotates, this tidal effect creates a “wave” that propagates through its interior.
As the tidal wave moves through the Moon’s interior, it causes rocks to rub against each other, generating heat and dissipating energy. This process ultimately leads to a slowdown in the Moon’s rotation. The friction between the rocks consumes energy, resulting in a decrease in the Moon’s rotation speed.
However, this explanation only accounts for the decrease in rotation speed and does not fully explain the complete halt of the Moon’s rotation. To address this gap in the theory, a new and intriguing hypothesis has emerged, although it has yet to be confirmed.
The hypothesis that has been given the name “moon-nut” suggests that during the cooling process of the Earth’s molten satellite, an uneven cooling occurred. The upper layers of the satellite cooled first, releasing heat into space. Once these layers solidified, a rigid crust formed, with liquid magma still present underneath.
Following this, the inner part of the satellite began to cool and solidify. As this happened, it naturally contracted in size and released volcanic gases. As a result, the core shrank and separated from the outer crust.
It transformed into a type of nut, featuring both a hard outer shell and a inner kernel. This inner core shifted laterally, causing a shift in the center of gravity. Consequently, the Moon began to strive for the same position, akin to Vanky Vstanky. While this theory has yet to be substantiated, there is ample reason to believe that there are indeed voids within the satellite.
Therefore, gravity, tides, and the Moon’s inhomogeneity caused it to constantly present one side to us. We consistently marvel at the visible side, pondering what secrets our beloved neighbor conceals on its unseen face. Or perhaps it is indeed inhabited by extraterrestrials. Who can say for certain?
Even though scientists don’t attribute any mystical meaning to this phenomenon, statistics indicate that when the color of the Earth’s satellite alters:
- there is an increase in the number of road accidents (especially during nighttime),
- some individuals experience heightened levels of anger and irritability,
- the mentally ill and unstable tend to deteriorate.
This is because the Earth’s magnetic field fluctuates depending on the moon’s position, which is evident from the existence of ocean tides. Given that the human body is comprised of 80% water, it too is subject to the unseen cosmic forces.
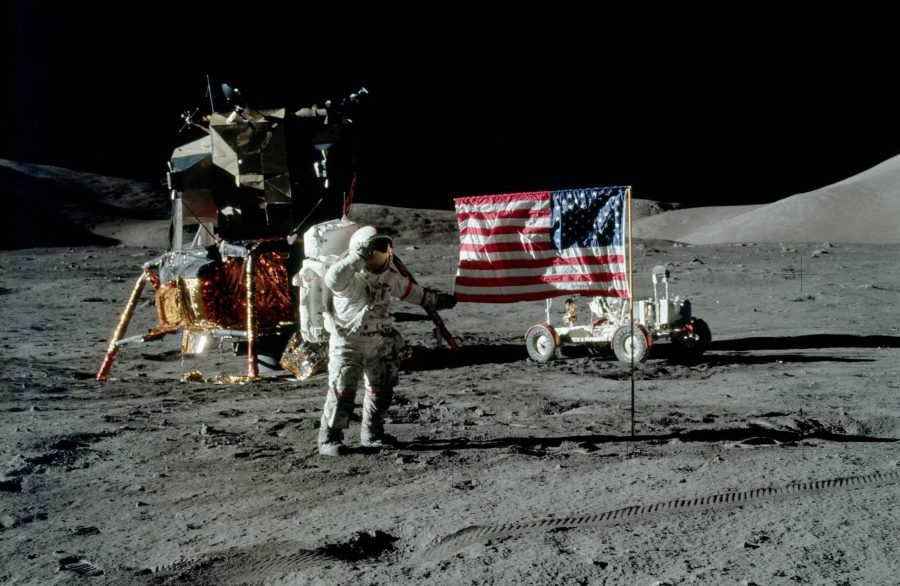
American Conspiracy Theories and the Moon Landing
The images captured by American astronauts during the moon landing have been subject to numerous rumors and speculations. Critics have accused the astronauts of faking the pictures due to the gray background depicted in them.
However, it is important to note that the Americans did bring back samples of rocks in various colors from the moon.
Furthermore, there is a photograph that shows the moon appearing yellow. This effect is a result of the lunar surface being reflected in the spacesuit worn by one of the American astronauts. It is worth mentioning that the surface of the spacesuit, which covers the astronaut’s face, is not a simple mirror but rather coated with a film of gold. As a result, the color is distorted.
The true colors of the lunar surface are visible in images where the dust has been cleared away. In these images, we can see shades that are perceptible to the human eye, such as reddish, bluish, and brown hues.
Sometimes, the term “super moon” is mistakenly used to describe a phenomenon that is unrelated to the moon’s current distance from the Earth. The reality is that when the Moon is low on the horizon, it always appears larger. This optical illusion is known as the Moon illusion or lunar illusion.
Scientists are still debating whether the Moon appears bigger or closer. The main question of why this happens remains unanswered. According to mathematical calculations, the Moon’s angular diameter should be slightly smaller at the horizon compared to the zenith. There are several theories, all of which are related to how our brain perceives visual information. Some suggest that the presence of earthly objects at the horizon makes the Moon appear larger in comparison. Others argue that the brain perceives the celestial sphere as asymmetrical, causing this phenomenon. Another theory proposes that the way our eyes read the visual information differs between the horizon and the zenith.
What is the origin of the term “blue moon”?
The concept of a “blue moon” does exist, although the Moon itself does not appear blue in color. Rather, it is simply a metaphorical expression. In recent times, numerous English terms and phrases have made their way into the Russian language, including “blue moon” and “super moon”. These names may sound beautiful, but many people are unsure of their meaning.
Typically, the Moon appears yellow when the sky is clear and it is high above the horizon. As it gets closer to the horizon, the color can shift to orange or even reddish due to light refraction in the atmosphere. However, the Moon is rarely ever blue, except in certain exceptional cases, which we will explore further.
The phrase “blue Moon” in English is roughly equivalent to “after the rain on Thursday” in Russian. It doesn’t refer to the color of our moon, but rather to a specific astronomical event that occurs occasionally. To put it simply:
A Blue Moon is the second full moon within a single month.
That’s why January 31, 2018 was considered a Blue Moon, as it was the second full moon in that month – the first one occurred on January 2.
How often does a blue moon occur?
A blue moon is a rare occurrence due to the almost perfect alignment of the lunar cycle, which lasts 29.5 days, with the number of days in a month. In order for a blue moon to happen, the full moon must fall on the 1st or 2nd day of the month, excluding February. In such cases, a second full moon can occur on the 30th or 31st day, earning the name “blue moon”. This unique alignment happens only once every few years.
However, there are exceptions to this rarity. The ancient Greek astronomer Meton discovered a phenomenon called the metonic cycle 2450 years ago. This cycle, which lasts 19 years, can lead to more frequent occurrences of blue moons.
This cycle consists of 235 lunar cycles and 228 calendar months. Since there are more full moons (235) than months, there will be instances during this period where there are two full moons in one month, specifically 7 times (235-228=7). Therefore, over the course of 19 years, there will be 7 occurrences of two full moons in one month, known as blue moons.
However, there is an exception to this. If it turns out that there is no full moon in February during the 19-year cycle – which can happen because February is shorter than the 29.5-day lunar cycle – then the next month will have two full moons, resulting in a blue moon. This can occur if the full moon falls on January 31, in which case there will be no full moon in the entire month of February, but two full moons in March – one at the beginning and one at the end of the month.
Typically, a blue Moon occurs once every two years. However, in 2018, we experienced a rare event where this phenomenon happened twice – in January and in March. And at the end of March, we will have the opportunity to witness the occurrence of a blue moon once again. After that, we will have to wait for another two years. The schedule for the next 19 years of blue moons is as follows:
- March 31, 2018.
- October 31, 2020.
- August 31, 2023.
- May 31, 2026.
- December 31, 2028.
- September 30, 2031.
- July 31, 2034.
- January 31, 2037.
Every 19 years, the cycle repeats itself, so in 2037 we will once again have two blue moons – in January and in March, just like in 2018.
When does a “blue moon” appear blue?
Occasionally, there are instances where you can witness a blue moon, meaning it is actually colored blue instead of its usual yellow or red hue in the sky. However, this occurrence is quite rare and typically happens when the moon shines through clouds or dust. For instance, during the eruption of the Krakatoa volcano in the 19th century, volcanic dust enveloped the entire planet, resulting in a blue-colored moon that could be seen for two consecutive years.
Another situation arises at the conclusion of a lunar eclipse, when the moon’s edge enters the shadow zone cast by the Earth’s upper ozone layer. The unique property of ozone is that it absorbs the red portion of the spectrum and reflects the blue, causing the moon’s edge to appear blue in this case. However, this ozone layer is very thin and cannot completely envelop the moon’s disk.

The Moon can appear blue during an eclipse due to its blue edge.
So now you have learned about the phenomenon of a blue Moon and the conditions under which it can actually appear blue. Enjoy your observations!

Light and color
When observing the Moon from space (no need to strain your imagination – there are photos of the Moon taken by astronauts), we can witness a luminous gray sphere, brilliantly illuminated by the Sun.
In contrast, the Sun appears dazzlingly white amidst the darkness of the cosmic void.

When observing the Moon from our planet, its appearance alters as it moves across the sky. As the Moon emerges from below the horizon, it presents itself as a radiant orange sphere. This transformation is due to the Earth’s rotation on its axis. As the Moon ascends higher into the sky, its vibrant orange hue gradually diminishes. The color transitions from orange to yellow, eventually settling into a pale white-yellow shade. When the Moon reaches its zenith directly above the viewer, it adopts an almost ethereal light gray color.
The hue of the Sun
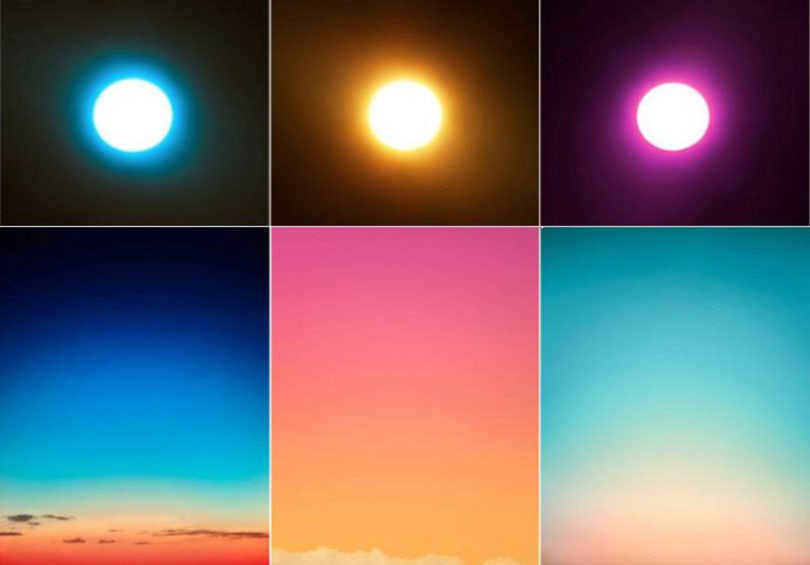

A similar phenomenon occurs with the Sun. When it is noon, the Sun appears to have a yellowish white hue. However, during sunrise and sunset, the Sun takes on shades of red, orange, or pink.
It is important to note that the actual colors of the Moon and the Sun do not change. The reason for the perceived color change is due to the Earth’s atmosphere. When we observe the Moon or the Sun through the atmosphere, it is like peering through a veil. The light from these celestial bodies must travel through the Earth’s atmosphere before reaching our eyes, and this journey alters the light’s spectral composition.
The presence of nitrogen, oxygen, and other gases in the air, as well as the particles of dust, smoke, and other pollutants in the atmosphere, cause a shift towards the red end of the visible light spectrum.
When smoke, dust, and other particles are present in the air, they cause a shift in the spectrum of visible light towards the red side. But how does this shift occur? The sun emits white light, and moonlight is simply a reflection of sunlight, so it too appears white. However, we know that sunlight actually contains all the colors of the rainbow. Therefore, as white sunlight travels towards Earth at a speed of 300,000 kilometers per second, it carries with it the entire rainbow spectrum. But once the light reaches Earth’s atmosphere, something magical happens. Some of the sun’s rays manage to reach the Earth’s surface without colliding with atmospheric gas molecules, preserving their pure white color.
During extensive wildfires, when plumes of smoke ascend into the atmosphere for extended periods of time, the ascending Moon takes on a crimson hue and dawns can possess an unsettling beauty. However, the majority of the rays are unable to evade this interaction. When they do, the light becomes dispersed. The majority of the light in the blue segment of the color spectrum becomes scattered. What ultimately reaches our visual perception are the rays of the remaining warmer colors. This is the reason why we perceive the Sun as being more yellow than its true nature.
The natural color of the Sun


When the Sun is directly overhead, it appears closest to its natural color. This is because the sunlight has to pass through a thinner layer of atmospheric air, resulting in less scattering of light. However, when the Sun is near the horizon, its rays have to travel through a longer path in the denser lower layers of the atmosphere before they reach our eyes.
During this journey, the sunlight encounters a large number of gas molecules and is heavily scattered. As a result, the color of the Sun changes dramatically when it rises or sets. The gas molecules in the atmosphere, as well as the particles suspended in it, scatter and absorb the blue rays of the spectrum. This is why the Sun appears as a vibrant orange ball during sunrise and sunset.
An intriguing video on the Sun’s color
If you come across any inaccuracies, kindly select the text and hit Ctrl+Enter.
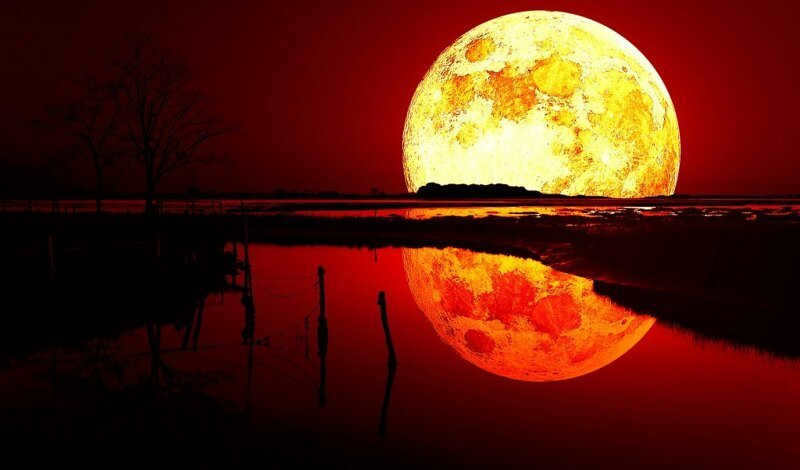

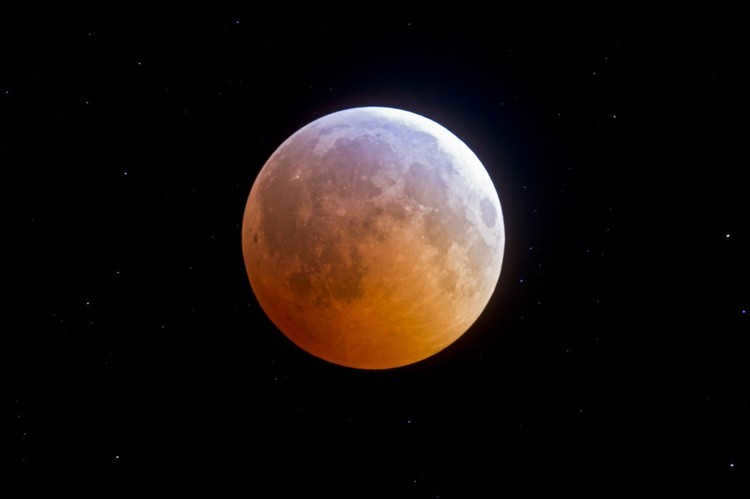
“And when the night luminary turns crimson, resembling the hue of blood, the celestial vault of the Earth shall part, and the progeny of chaos and darkness shall emerge into its luminosity, adorned with a visage so horrific that humanity has never beheld before!” Such could be a summary of a pre-apocalyptic book or film featuring a red moon. However, this, of course, belongs to the realm of fiction. In reality, there are several fascinating and genuine explanations for the moon appearing purple.”
The primary cause of the alteration in the Moon’s color


It is common knowledge that the Moon itself does not emit light, but rather reflects sunlight. The sunlight consists of various wavelengths, with each color having its own unique characteristics. The shortest wavelengths are violet and blue. When these wavelengths reach the Earth’s atmosphere, they scatter and give the Moon a mystical blue hue on clear nights. On the other hand, longer wavelengths pass through the Earth’s atmosphere with less scattering, resulting in the Moon having an extraordinary purple color when they hit its surface.
Location in relation to the horizon and presence of atmospheric pollution: alternate factors behind the reddening of the Moon

The Moon can also appear red due to its position in the sky. When it is close to the horizon during morning dawn or just before sunset, it takes on a scarlet hue to the human eye. A similar phenomenon can be observed during sunset and sunrise. When these celestial bodies are low in the sky, light must travel long distances and encounter various obstacles in the dense gas envelope of our planet. This scattering of light causes humans to perceive only the red part of the light spectrum.
During intense fires or volcanic eruptions, the Earth’s satellite often takes on a reddish color. This phenomenon can be attributed to significant atmospheric pollution. The presence of airborne particles such as soot, carbon monoxide, and other pollutants obstruct the path of light, particularly short waves. As a result, only long waves, such as red and orange, are able to reach our eyes. Interestingly, there are certain areas where the Moon is consistently observed with a red hue. In these cases, the cause can be traced back to industrial activities that contribute to the pollution of the surrounding atmosphere.
The reddening of the moon attributed to the occurrence of an eclipse
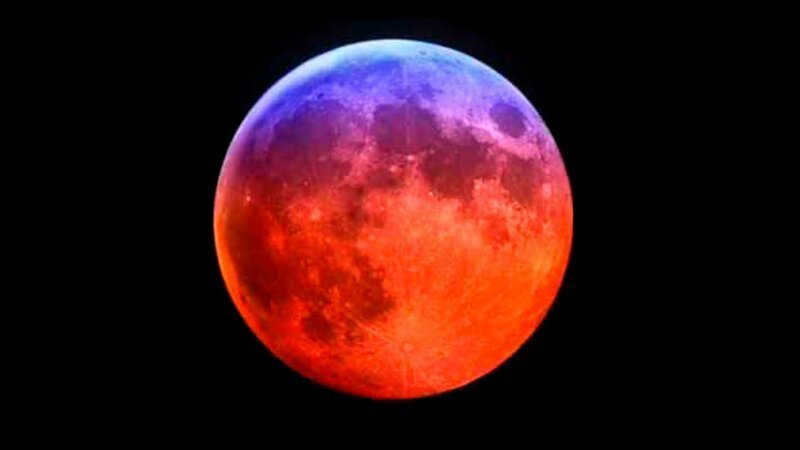

The night luminary takes on a bloody hue during an eclipse, a phenomenon that has fascinated mankind since the early days of astronomy. Each time it occurs, it has sparked panic and awe in society. Eclipses are not a frequent occurrence, as the Moon must fully enter the Earth’s shadow cone for one to happen. Even then, the Moon is still bathed in a tangential glow from the Sun’s rays, which pass through the atmosphere and scatter. Only the red-orange part of the spectrum manages to reach the Moon’s surface.
The Earth’s satellite sometimes appears exceptionally large: What causes the Moon to appear frighteningly huge?


- One reason for the moon sometimes appearing larger than it actually is has to do with the specific structure of the human visual system. This is known as the irradiation phenomenon, which is an optical effect that causes brightly illuminated surfaces to appear larger than their true size.
- The lunar illusion theory, developed in the 1960s by I. Rock and L. Kaufman, offers another explanation. According to this theory, the human brain has an inherent perception that the shape of the sky is imperfect. As a result, objects on the horizon appear larger than those directly overhead. The brain unconsciously adjusts for this perceived distance, leading to the perception of an enlarged moon.
When inquiring about the hue of the moon, a youngster might assert that it appears yellow. This is the impression we receive from our vantage point on Earth, as well as the depiction favored by artists. However, grown-ups tend to perceive the moon as gray. This conclusion is based on telescope images that can be readily accessed online.
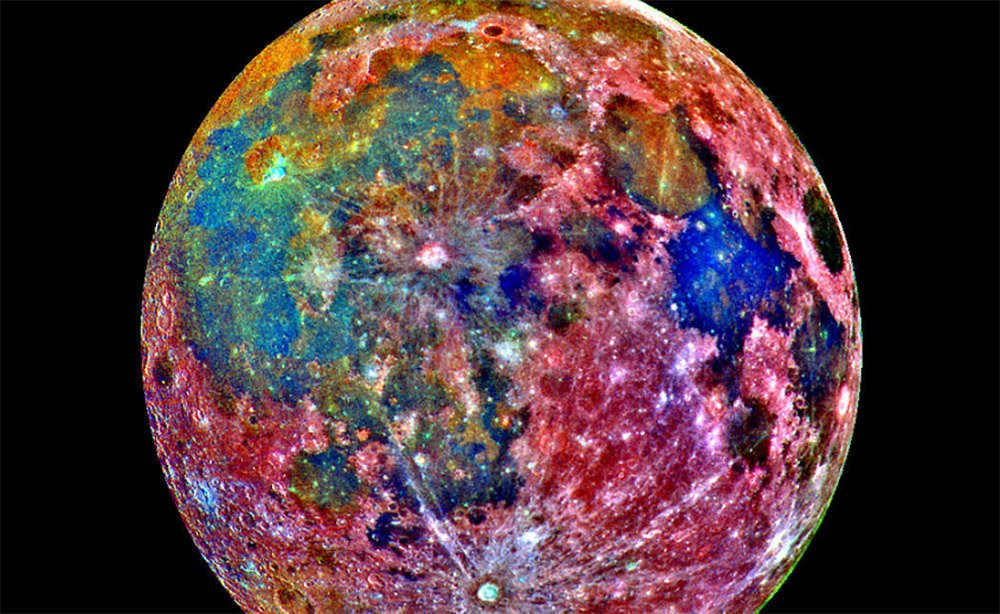
Why are both the initial and subsequent responses incorrect?
Vibrantly hued moon
The moon, Earth’s closest satellite, remains shrouded in numerous enigmas. There exist depictions of the moon emanating a full spectrum of colors akin to a rainbow. However, terrestrial beings will never witness this phenomenon firsthand, as these images are computer-generated based on radio waves. They do, however, allow us to discern which side of the moon experiences greater warmth and which side is comparatively weaker, reminiscent of Earth’s diurnal cycle.
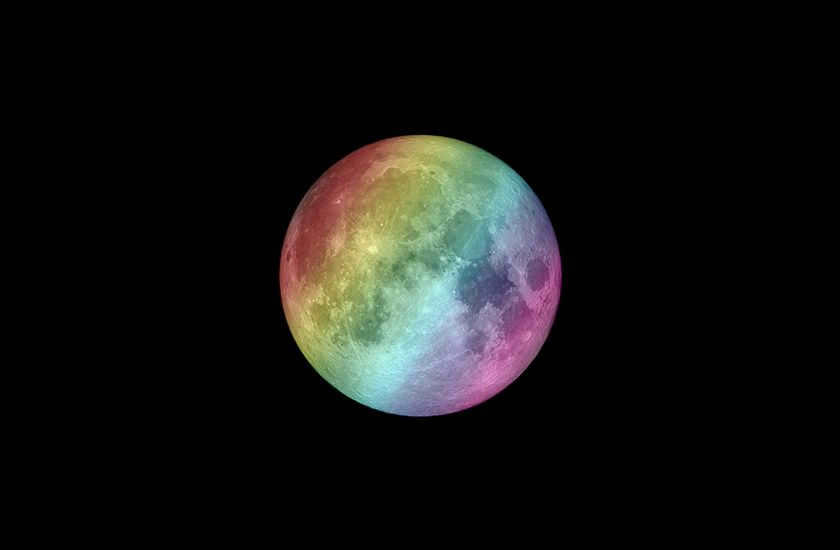

However, it is important to note that the Moon does not actually have a gray color, contrary to what many pictures might suggest, including those captured during the Apollo missions. The surface of the Moon is merely coated with a layer of dust known as regolith. Research has demonstrated that this dust is composed of tiny fragments of meteorites. Similar to Mars, which is covered in reddish dust and is often referred to as the “red” planet, the Moon appears gray to the naked eye.
Moon Anomalies
Indeed, the lunar pictures appear peculiar. The shadows cast on the lunar surface are sharp and the Moon’s surface seems to emit a glow. Additionally, the colors observed here appear distinct from those on Earth. This distinction became evident when American astronauts installed a gnomon instrument on the Moon’s surface. This instrument serves as a color indicator and is actually colored – it is easily visible in the museum where it is currently housed. However, in the lunar image captured by the astronauts, the gnomon appears almost colorless.
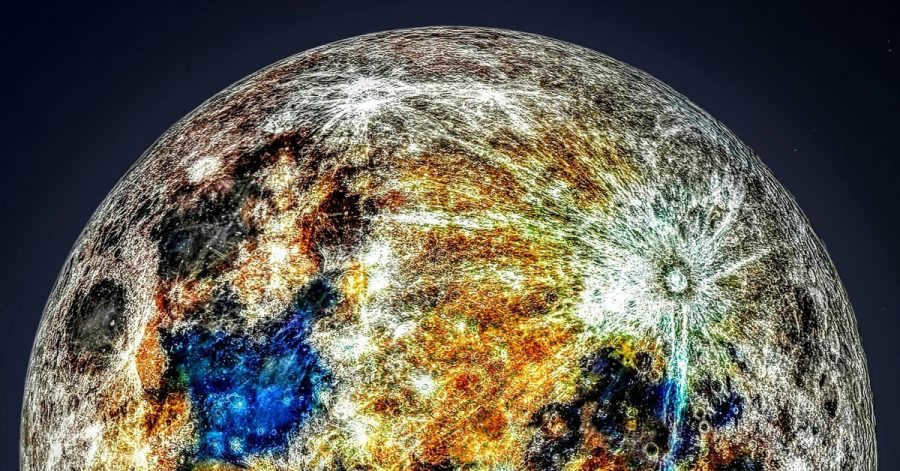

The true colors of lunar rock are not visible to the naked eye due to the presence of dust, regolith, and a sparse atmosphere. The moon’s low gravity allows dust to easily be dispersed, making it difficult to observe the actual colors. However, the rock samples that have been brought back to Earth reveal that the moon possesses a range of hues, including brownish, blue, and even blood red.
There has been a lot of speculation and rumors surrounding the photographs taken by the American astronauts during the moon landing. Some people have accused the astronauts of faking the pictures simply because the background appears to be gray.
However, it is important to note that the Americans did in fact bring back samples of rocks in various colors.






