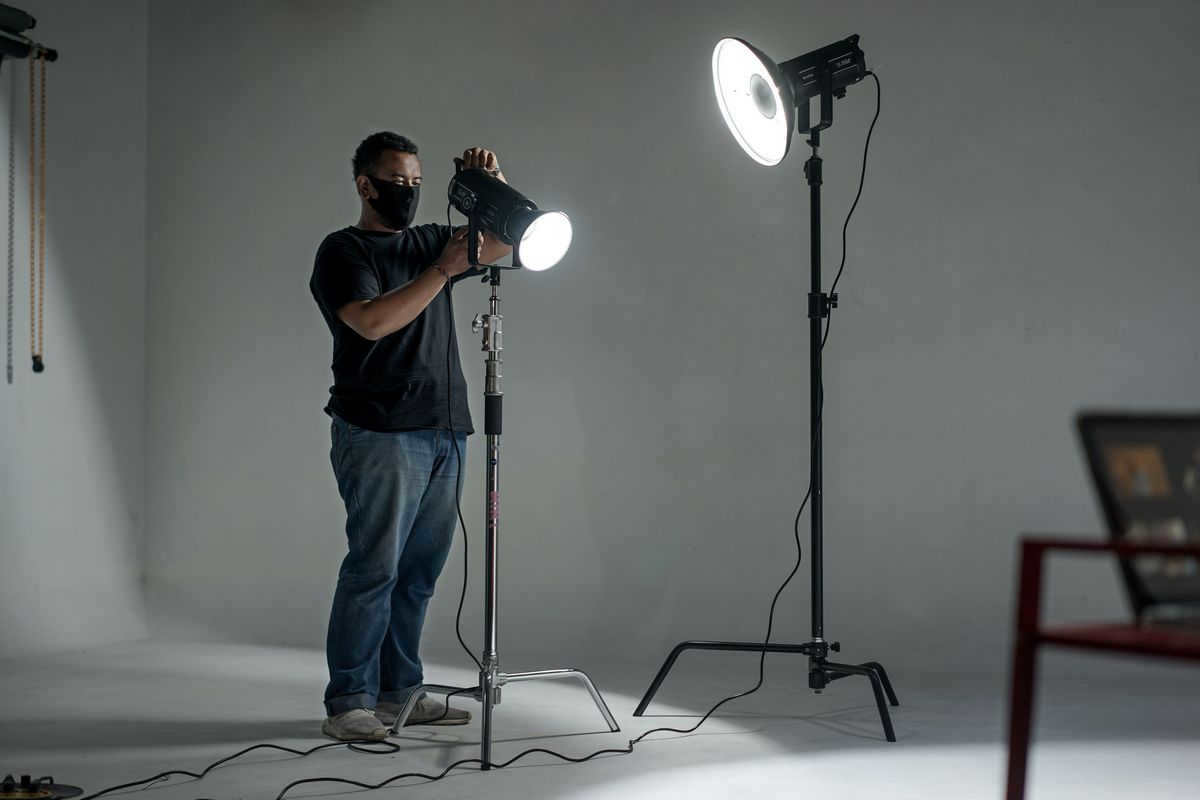
A reflector is a compact accessory designed for studio flashes that produces a focused, directional light with pronounced shadows, resulting in a three-dimensional and high-contrast photograph. Reflectors are commonly used in portrait and subject photography, and are frequently employed in fashion shoots.
In this article, we will discuss the various types of reflectors, methods for modifying them, and the different scenarios in which they can be beneficial.

A reflector is a fundamental accessory used in every photography studio / Source: unsplash.com
Understanding Reflectors
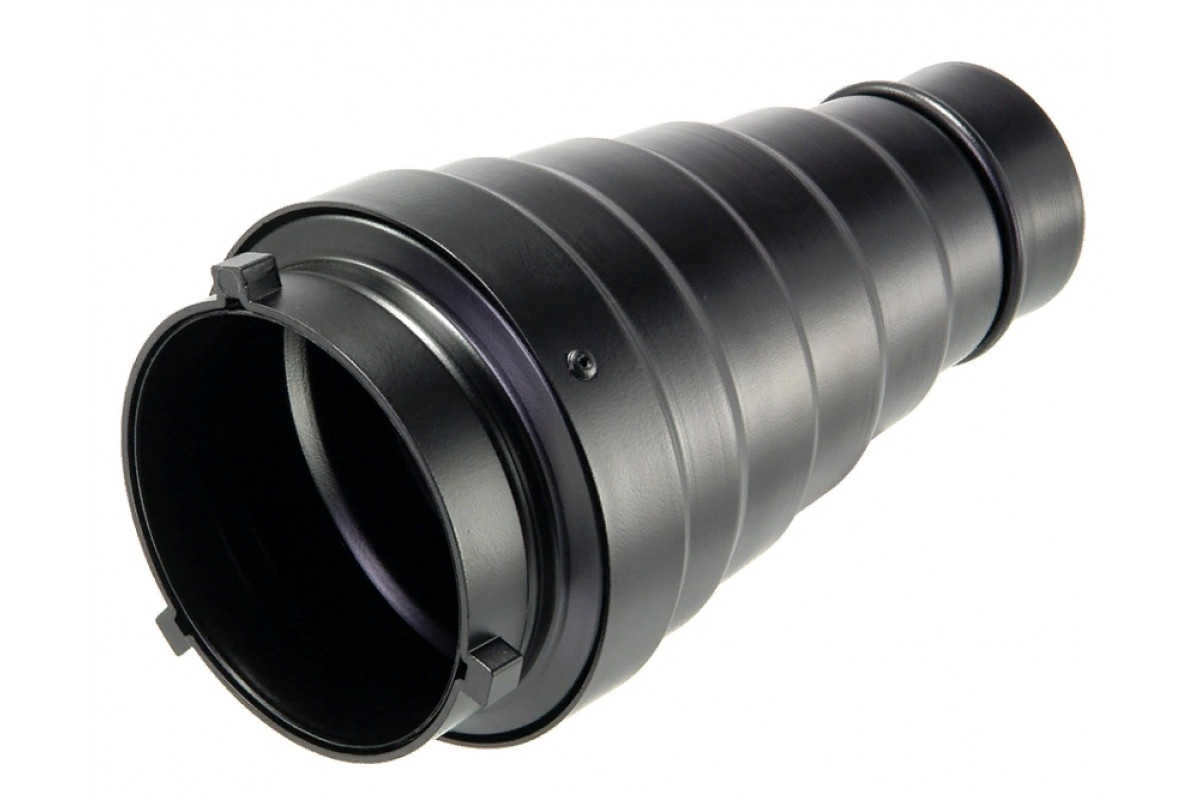
A reflector is a small attachment made of a durable material that is placed on a monobloc and encircles the monobloc’s bowl. Typically, it is no longer than a few tens of centimeters. With its shape and material, the inner surface of the reflector directs the flash’s light onto the subject in a focused beam, rather than scattering it in all directions.
The reflector produces a harsh light. This is evident in deep, well-defined shadows, a strong contrast between dark and light areas in the photograph, and vibrant, distinct highlights. Moreover, hard light effectively showcases the texture of skin, clothing, and objects.
Reflectors are utilized for various purposes:
– to capture dramatic and profound psychological portraits;
– for bold and stylized fashion shoots;
– in male portraiture to accentuate strength and brutality;
– in women’s portraits to convey energy and create a vibrant and captivating image;
– in product photography, particularly when highlighting the material of the product is essential.
Various Types of Reflectors
There are different types of reflectors for photography, each varying in shape and color of the inner surface. These variations allow photographers to use them for various purposes. Below, we discuss the different types of reflectors and explain why each one is necessary.
One type of reflector is a solid nozzle, measuring around 20 to 40 centimeters in length. It has a bowl-like shape that tapers towards the bottom. The narrower base of the nozzle is where the mount is located, allowing it to be attached to the flash.
The inner surface of this reflector is coated with silver. This silver coating helps to enhance the reflection of light from the walls of the nozzle, allowing the photographer to direct the light in the desired direction.
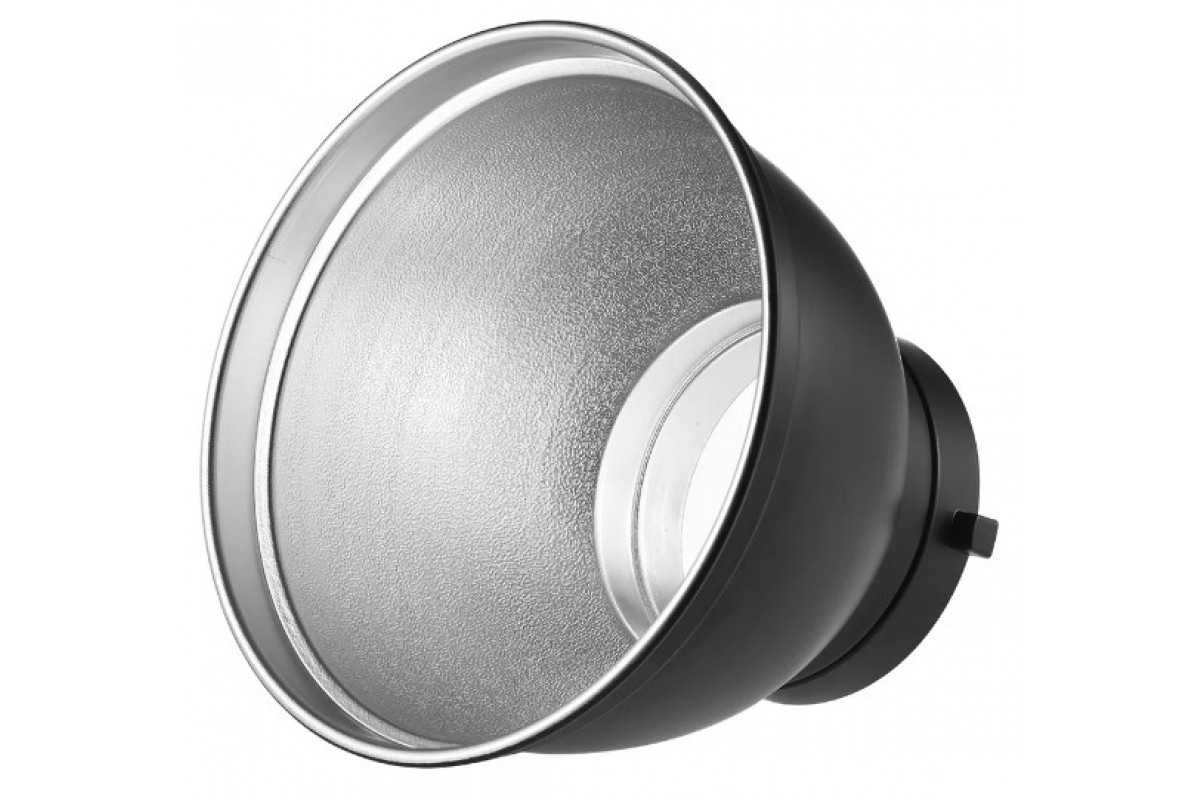

These types of reflectors are aimed at both the subject (person or object) and the background in order to provide illumination or, when combined with a color filter, to add color to it in a different shade / Source: fotosklad.ru
It is a broad reflector that extends smoothly from the mount to the sides of the tube, featuring a sharp angled cut. Its unique shape ensures that the reflector only illuminates the background area, with the light being blocked from reaching the model or entering the camera.
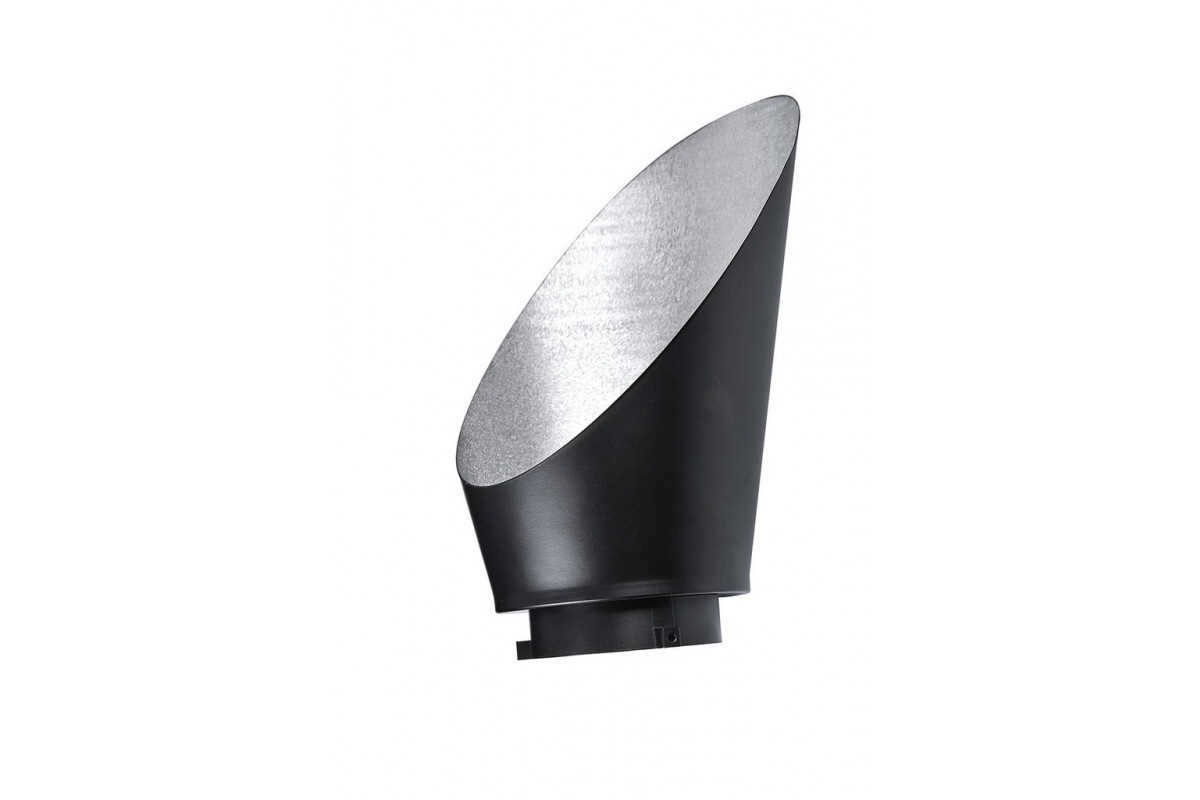

The unique design of the nozzle ensures a consistent illumination pattern – unlike a standard reflector, which creates a brighter light on the side facing the light source and gradually diminishes as you move away from it / Source: fotosklad.ru
Background reflectors are typically coated with either white or silver. The former is less commonly used and is known to produce a slightly weaker light output, as it reflects light slightly less effectively than silver. However, it does not alter the color temperature. Similar to standard reflectors, a gold-coated background reflector imparts a warmer light, while a silver-coated one creates a cooler light. A white-coated reflector maintains a neutral light.
The light emitted by the flash bulb is concentrated and directed in a narrow beam due to the conical shape of the flash diffuser. This is achieved by tapering the cone, causing the flash pulse to pass through a small aperture. As a result, the output is a focused and directional beam of light.

Light tubes are employed for the purpose of emphasizing the illumination. For instance, they can be utilized to bring attention to the backdrop or to draw out a specific element within a intricate arrangement, thereby highlighting a distinct object in the surrounding environment / Source: fotosklad.ru
Cone-shaped reflectors find application in the realms of portraiture, still life, and innovative experimental photography, frequently serving to accentuate the significance conveyed in motion pictures.
Customize Your Reflectors with Modifier Accessories
Enhance your photography experience by modifying any reflector to tailor it to your unique ideas and preferences. Discover the range of accessories available for reflectors and understand how they can diversify your shots.
One such accessory is a reflector attachment that fits on top of a classic reflector. It consists of a frame with four movable panels, also known as curtains.
By adjusting these curtains, photographers can:
- Direct the light more precisely.
- Control and block unwanted light from reaching the camera, background, or floor.
- Alter the shape of the light spot from round to oval, enabling the creation of unique patterns in the background.
- Another popular modifier accessory is the honeycomb.
A honeycomb is a circular metal grid that resembles the shape of a honeycomb. Its purpose is to provide rigidity and directionality to light by allowing it to pass through its small holes.
It is important to note that the size of the honeycomb mesh plays a role in determining the characteristics of the light. A smaller honeycomb mesh leads to a stiffer and more directional light, while a larger honeycomb mesh results in softer light.


By using modifiers for nozzles, you can enhance the capabilities of the light source / Source: unsplash.com
Honeycombs can be attached to both classic and cone reflectors. Reflectors are often sold as a set with honeycombs.
Colored light filters are translucent films that change the color of light, alter its color temperature, and can also reduce the intensity of the light beam.
Light filters can be attached to the reflector using clothespins or tape. There are also various light filters that consist of a square frame with a fixed colored film. In this case, the light filter is inserted into a special groove on the reflector.
Color light filters are used in all types of shoots where you need to:
- Introduce a colored backlight – a slim border outlining the silhouette of an individual;
- Apply one or more colors to the entire scene;
- Adjust the lighting to be cooler or warmer;
- Dim the light output when less than the minimum flash power is required.
All Russian language dictionaries: Explanatory Dictionary, Synonyms Dictionary, Antonyms Dictionary, Encyclopedic Dictionary, Academic Dictionary, Nouns Dictionary, Proverbs, Russian Slang Dictionary, Orthographic Dictionary, Accents Dictionary, Pronunciation and Stress Difficulties, Word Forms, Synonyms, Thesaurus of Russian Business Vocabulary, Morpheme-Orphographic Dictionary, Etymology, Etymological Dictionary, Grammatical Dictionary, Ideography, Proverbs and Sayings, Etymological Dictionary of the Russian Language.
Dear visitor, the website is currently undergoing development and relies solely on advertising revenue. We kindly ask you to consider disabling your ad blocker.
Explanatory Dictionary
1. A concave polished surface that reflects light or heat rays.
2. A device positioned near an antenna that emits or reflects radio waves in a specific direction.
Ushakov’s Dictionary
REFLECTOR, reflector, man. (derived from the Latin word reflecto – reflecting).
1. An optical device used for observing celestial objects, a telescope equipped with a reflective concave mirror (astronomy).
2. A device that reflects light using a curved mirror, redirecting the rays in a specific direction. A lamp with a reflector. Different types of reflectors are employed in the production of movies.
Ozhegov’s Dictionary
1. A device used for observing distant objects, consisting of a concave mirror or a system of mirrors.
2. A device that reflects light, typically consisting of a concave polished surface. It is used in lamps and other light sources.
adj. reflective, -aya, -oe.
Dahl’s Dictionary
REFLECTOR – a male noun of Latin origin. It refers to a mirror with a recessed shape that is used for reflecting light rays and increasing the amount of light passing through it. Reflectors are commonly used in lanterns, lamps, beacon lights, and other devices that require the reflection of light rays.
Mirror telescope, – on the contrary, has an objective made of glass. Reflection is a feminine noun that refers to the bouncing back of light rays. Reflex is a masculine noun that refers to vivid reflected light.
Dictionary of Nouns
An object shaped like a curved, polished, or mirrored surface that reflects radiation.
A reflector attached to a leg projected a focused beam of light onto a glass table filled with instruments and glasses (Bulg.).
A variety of telescope that utilizes a concave mirror or a series of mirrors.
A compact reflector telescope was positioned next to the window.
Encyclopedic Dictionary
REFLECTOR -a; m. [from Latin reflectere – to turn back, reflect].
1. A device that reflects rays emitted from a light source. It is used to cover the lamp. // Informal. A light source that has a reflector. The stage is illuminated with reflectors. Work is done under the light of reflectors.
2. A heating device that consists of an electric lamp or heating element and a reflector. The reflector is turned on to heat up a room.
3. A type of telescope that uses a main concave mirror along with auxiliary convex and flat mirrors to obtain images of celestial bodies.
◁ Reflective, -aya, -oe. Reflective lamp. Reflective mirror.
Reflector (derived from the Latin word “reflecto” meaning “turning back” or “reflecting”) is a device that consists of one or more mirrors and is capable of providing nearly complete reflection of electromagnetic waves (such as light) or sound waves that fall upon it. The reflecting surface of a reflector is designed to be mirror-like, with a roughness that is equal to or less than the wavelength of the waves. In order to concentrate the reflected waves, the surface of the reflector should be concave in shape, such as spherical or paraboloidal. Reflectors are widely used in various fields including acoustics, astronomy, radio engineering (for antennas), and even in our everyday lives.
Furthermore, in the field of astronomy, a reflector telescope is a type of telescope that utilizes a main concave mirror and auxiliary mirrors to create images of celestial objects such as stars, planets, and even the Sun. The largest reflector telescope in the world boasts a main mirror with a diameter of 6 meters.
A reflector is a device that is made up of one or more mirrors and is able to reflect electromagnetic waves or sound waves that come into contact with it. The surface of the reflector is mirror-like and should be concave in order to concentrate the reflected waves. Reflectors are commonly used in acoustics, astronomy, radio engineering, and in everyday life.
In astronomy, a reflecting telescope is used to create images of celestial bodies such as stars, planets, and the Sun. This type of telescope uses a main concave mirror as well as auxiliary convex or flat mirrors. The largest reflector in the world, located in Russia, has a main mirror diameter of 6 meters.
Large Encyclopedic Dictionary
A reflector is a device that consists of one or more mirrors and is capable of reflecting electromagnetic (such as light) or sound waves. The surface of the reflector is mirror-like and its roughness is comparable to the wavelength of the waves it reflects. In order to concentrate the reflected waves, the surface of the reflector is often concave, such as spherical or paraboloidal. Reflectors find applications in various fields including acoustics, astronomy, radio engineering (for antennas), and everyday life.
In the context of astronomy, a reflector refers to a type of telescope that uses a main concave mirror and auxiliary convex or flat mirrors to create images of celestial objects such as stars, planets, and the Sun. The largest reflector in the world, which is located in Russia, has a main mirror with a diameter of 6 meters.
Academic Dictionary
1. An object that redirects the rays emitted from a source of light.
Nadezhda Nikolayevna Garshin placed a reflector on the lamp and positioned her unfinished painting on the easel, illuminating it.
[Nyura] rushed to the electrical store and insisted on purchasing new headlights. The old ones had a faulty reflector.
2. A device used for heating that consists of an electric lamp and a reflector.
3. A type of telescope that captures images of celestial bodies using a primary concave mirror and additional convex and flat mirrors.
[Derived from the Latin word “reflectere” – to reflect].
Dictionary of Orthography
Emphasis Lexicon
illuminator, -a; pl. illuminators, -ov.
Pronunciation and stress challenges
illuminatorIlluminator, pl. illuminators, gen. illuminatorov, and in professional discourse illuminatorov, illuminatorov.
Word variations for the term illuminator
illuminator, illuminators, illuminator, illuminator, illuminators, illuminator, illuminators, illuminator, illuminators, illuminator, illuminator, illuminator, illuminatorah
Synonyms for the word reflector
Some possible synonyms for the word “reflector” include oblique light, telescope, and mirror.
Thesaurus of Russian business vocabulary
Morphemic and orthographic dictionary
Grammatical Dictionary
The word “reflector” can also be defined as “a device that reflects light or sound in a specific direction” (reflector m 1a [prof. m 1c①]).
Dictionary of Russian Language Gallicisms
REFLECTEUR (a, m.) is a French word meaning “reflector,” derived from the Latin word “reflectere” which means “to turn back.”
1. A concave mirror is used as a reflector. BAS-1. Hanging on the wall is a tin candlestick with a reflector, commonly referred to as a “front lamp” in Moscow for some reason. Leskov Nekuda. // 12-4 359. Auntie and Gildegarde carried a small pocket flashlight with a reflector (for examining the throat), a vial containing liquid, and a notebook in their pockets as they left. 1892. Leskov Yudol. // 12-11 191. In the people’s room, in front of a small dressing table placed near a lamp with a tin reflector removed from the wall, Sasha was styling her thick, shiny hair in a fashionable hairdo. 1898. O. A. Shapir Avdotya’s daughters. // Only an hour 105. She hurried from the tin shop to the electrical shop and insisted on getting new headlights. The old ones had a useless reflector. 1950. Rybakov Drivers. // R. 4-3 133. obsolete? Searchlight. Throughout the evening and night from Saturday to Sunday, air squads (escadrilles) with powerful reflectors were constantly being transported. This somewhat operatic performance by the air squadron did not completely reassure the Parisians. Contemporary. 1915 10 330. Those who did not experience the Revolution cannot imagine its grand solemn beauty. Red banners, the honor guard of Kronstadt sailors, reflectors from the Peter and Paul Fortress, illuminating the path from the Finland Station to Kseshinskaya’s house, armored cars. Krupskaya Vosp. 282. transfer. For him, Theophan’s head (Peter I) was the ultimate reflector of his transformative aspirations. Kartashev 2 342. I am not an active participant: I am a reflective one. I was never the driving force in anything; I was merely a reflector, and often a pointer as well. Vyazemsky Star. zap. kn. // PSS 10 290. This governing body may simply reflect the characteristics of the citizens, faithfully expressing their ability to govern, and serving as a more convenient form for complex public administrations. RM 1898 6 140.
3. An optical instrument that produces an image using a concave mirror for reflection. BAS-1.
4. A device that emits radio waves in a specific direction, located near the antenna. SIS 1985. – Lex. SAS 1847: refle/ctor.
Dictionary of Foreign Words
REFLECTOR (novo lat., from lat. reflectere – to deflect, bend backward). A reflector; a concave mirror used to reflect and amplify light; a projectile designed to reflect heat.
Scanwords for the term “reflector”
– An instance of a metal mirror utilized for the purpose of reflecting heat rays.
– A configuration of wires situated in proximity to an antenna.
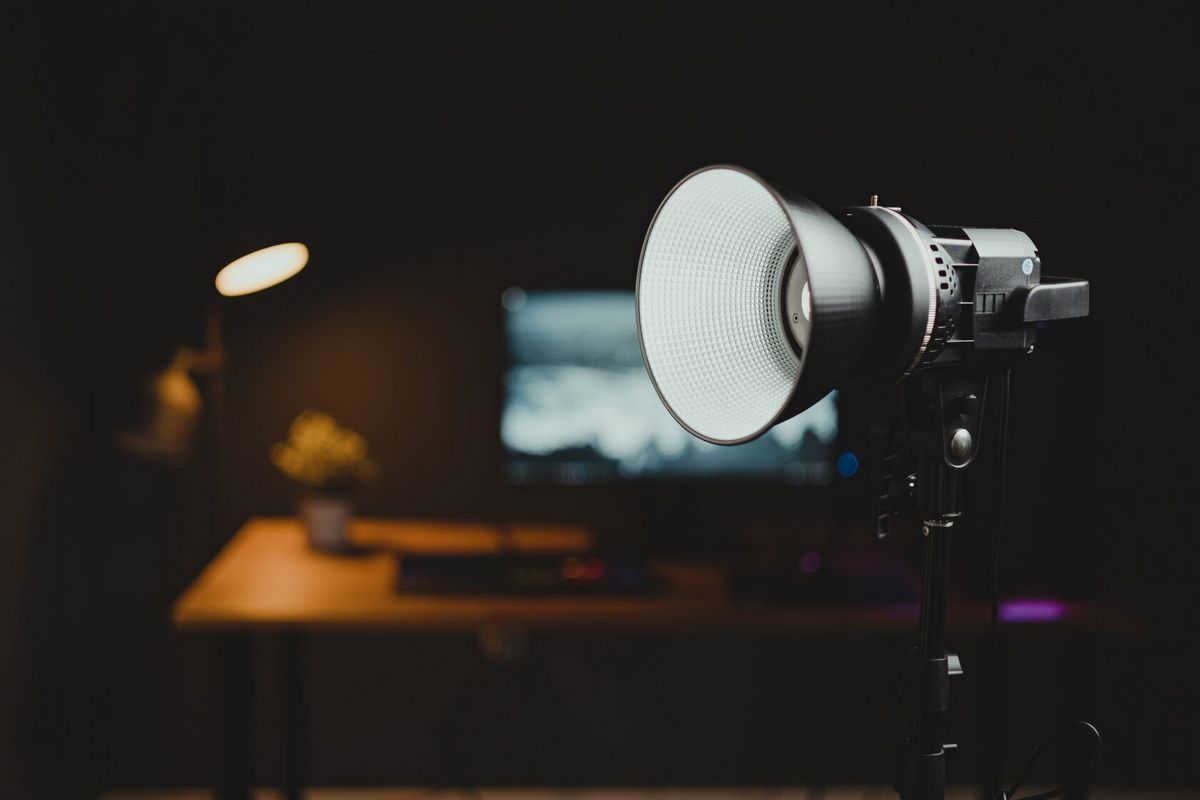

A reflector, also known as a shooting reflector, is a versatile tool utilized in the field of photography and video production in order to manipulate the lighting of various objects. This tool proves beneficial for both professionals in the industry and individuals engaged in amateur photography.
What exactly is a reflector?
A reflector essentially consists of a transparent or mirrored surface that has the capability to redirect incoming light. This surface can be constructed from a range of materials such as paper, plastic, or even aluminum. Additionally, the size and shape of the reflector can be customized to suit specific requirements and applications.
A reflector has the ability to alter the path of light that is directed towards an object, thereby enhancing the contrast and shadows present. Furthermore, it can serve to provide supplementary illumination and reflect natural light when used indoors.
The applications for reflectors are vast and diverse, encompassing various scenarios including portraiture, product photography, and landscape photography, among others. When employed in portrait photography, a reflector can contribute to the creation of softer lighting, the elimination of shadows, and the illumination of the subject’s visage. In the realm of landscape photography, it can be utilized to provide extra illumination to subjects situated in the foreground.
Tips for selecting a reflector
When it comes to choosing a reflector, there are several factors to consider, including size, shape, and material. These elements play a crucial role in determining the quality of lighting you can achieve. If you’re shooting portraits, it’s recommended to opt for a larger and softer reflector as it helps to create a more diffused and even lighting effect. On the other hand, when shooting product photography, a smaller and harder reflector can be a better choice as it produces a sharper contrast, highlighting the product details.
What is the proper way to utilize a reflector?
To maximize the benefits of a reflector, it is important to carefully position and angle it. The reflector should be positioned on the opposite side of the light source in order to bounce light onto the subject. The angle of the reflector can also impact the lighting of the subject. A reflector used for photography is a valuable tool that can contribute to optimal shooting conditions.
Both professional and amateur photographers can benefit from using a reflector. When selecting a reflector, factors such as size, shape, and material should be taken into consideration, as well as the specific shooting scenario. Additionally, the position and angle of the reflector should be adjusted to achieve the best possible lighting for the subject. Don’t be afraid to experiment with reflectors to create different effects and discover the ideal shooting conditions.
My adventures in photography, articles on camera gear and optics
One of the most essential and widely used tools in studio photography is the reflector. The elegant term “reflector” literally means a device that reflects. Its main purpose is to bounce and manipulate light.

The characteristics of the light emitted when a reflector is used are determined by various factors: – the reflector’s geometric shape and dimensions;
– the properties of its surface;
– the positioning of the lamp;
– the distance between the reflector and the object being illuminated. to content ↑
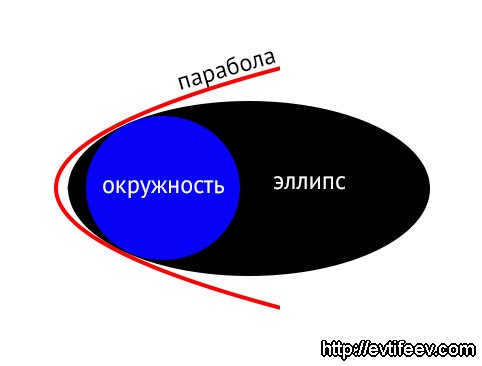
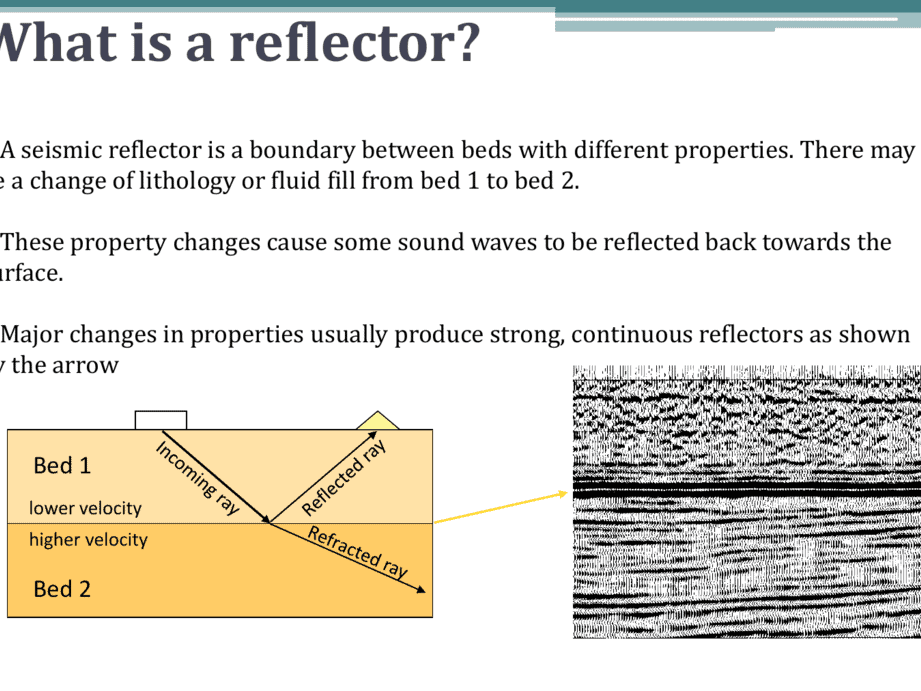
A quick and concise lesson on geometry
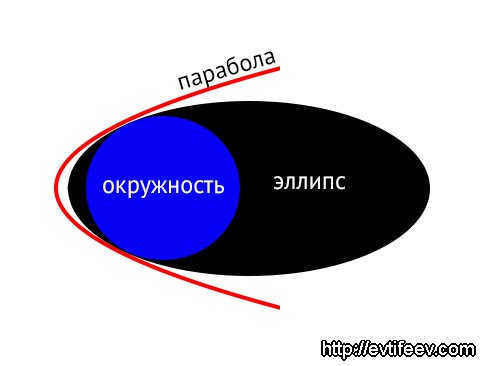
A sphere can be thought of as a three-dimensional circle. It is the surface created by a circle when it is rotated around a central axis. When a parabola is rotated, it forms an elliptic paraboloid. A circle can be seen as a specific type of ellipse. All of these shapes are considered conic sections. to content ↑
Reflecting with a spherical surface
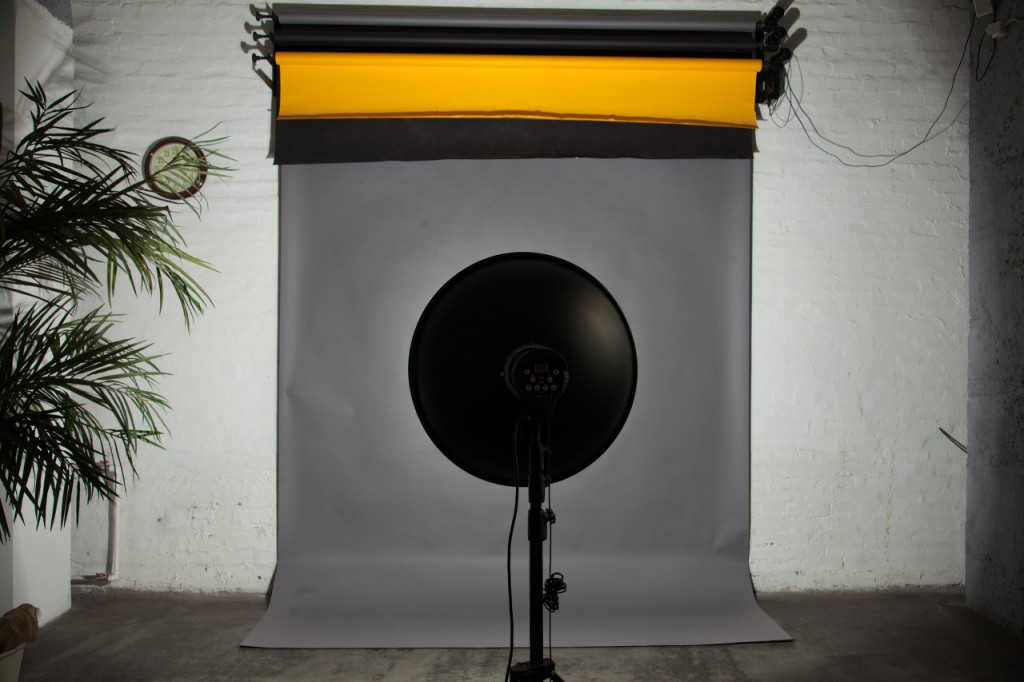
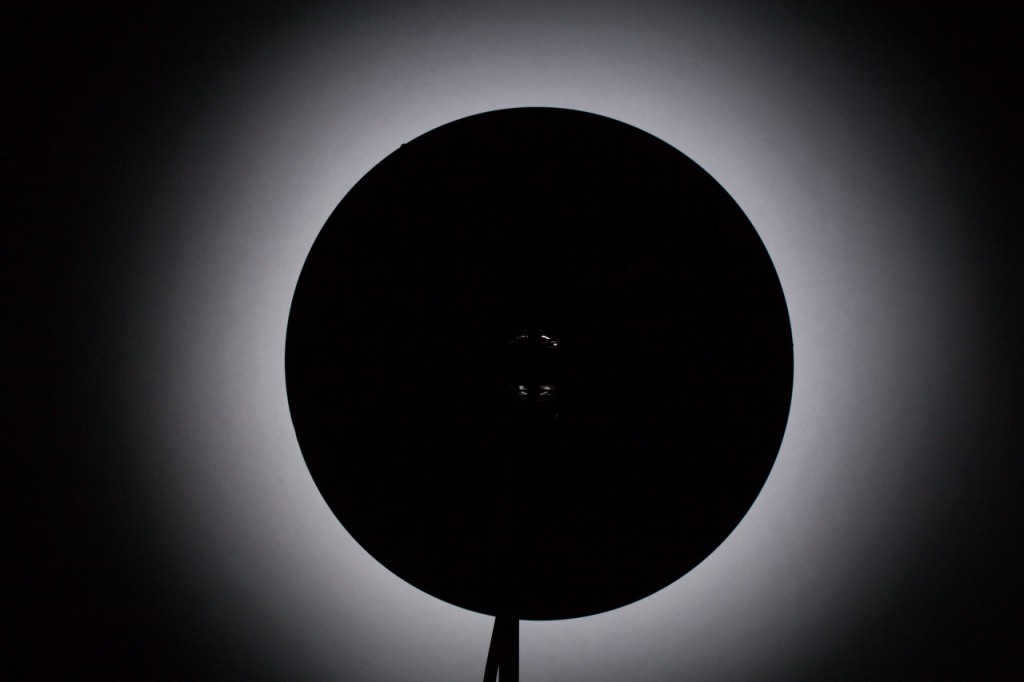
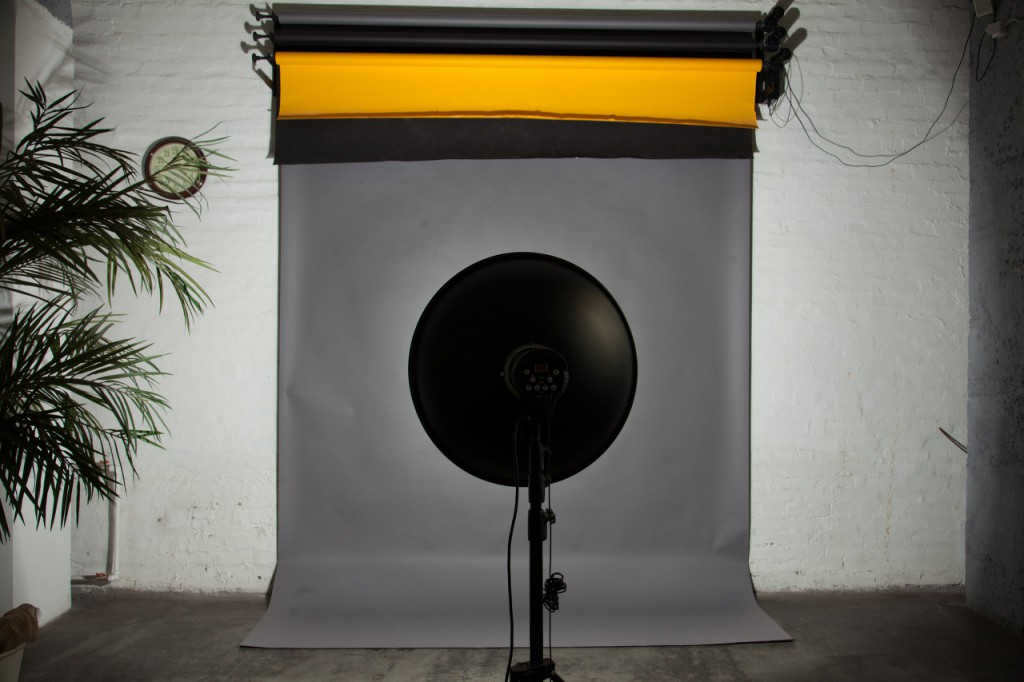
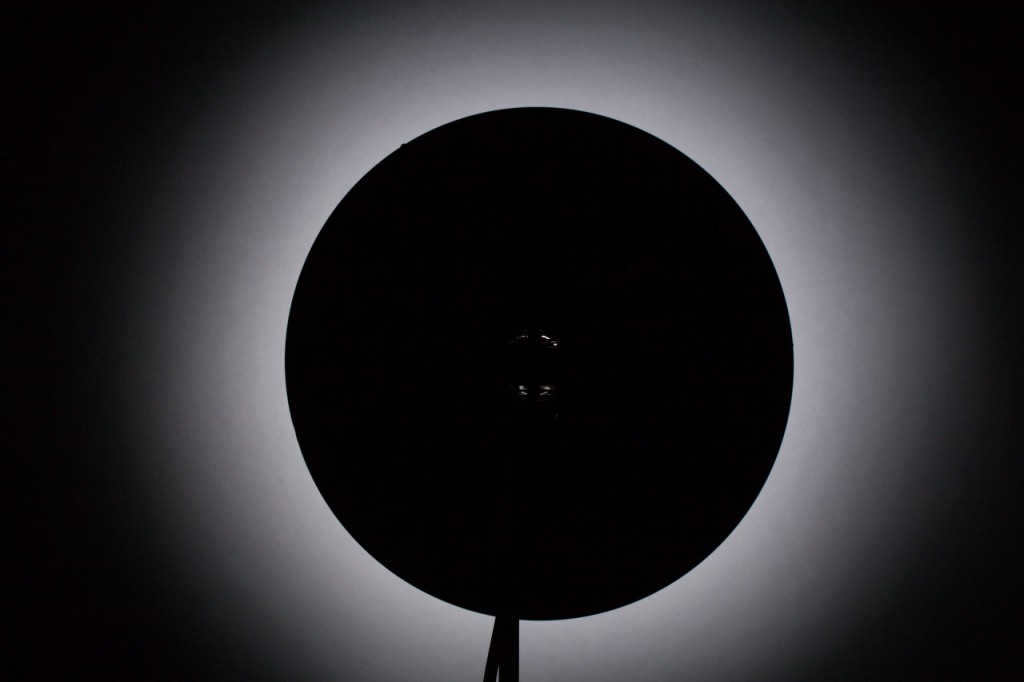
A reflector in the shape of a sphere with a lamp positioned in the center.
By positioning the flash lamp in the center, the light is redirected back towards the lamp. This results in a 40% increase in light output. However, due to the wide dispersion of the beams, this type of reflector is not particularly suitable for studio photography. Instead, a reflector with the lamp positioned at the focal point is more commonly used.
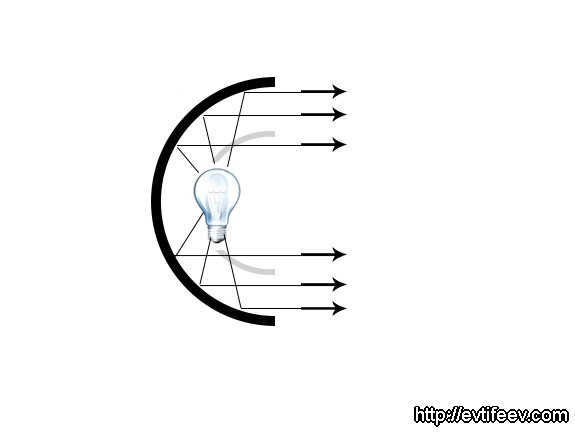
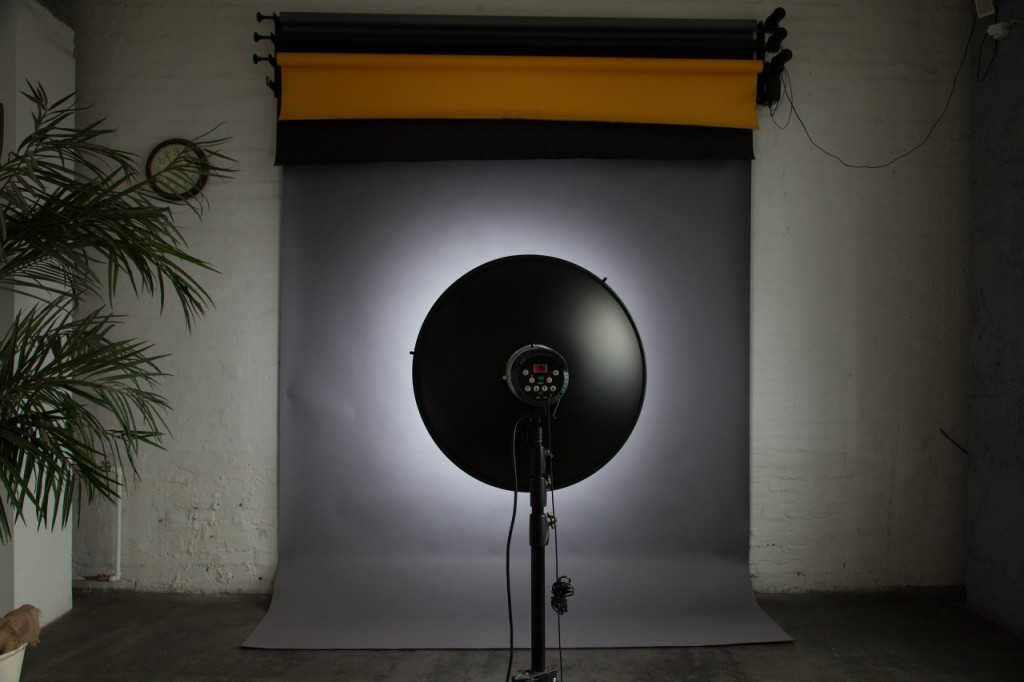
A spherical reflector is a reflector that has a focus point located on a sphere with a radius equal to half the radius of the reflector. When using this type of reflector, parallel rays are produced at the output, resulting in uniform lighting. This type of reflector is commonly used in flashlights along with a Fresnel lens. One well-known spherical reflector is the beauty dish, which is often used in portrait photography. It’s important to note that the focus point of the lamp in a specific beauty dish may vary, as there are numerous manufacturers who produce beauty dishes in different shapes, sizes, and positions. To determine the focus point of your beauty dish, you can refer to the principle of a spherical reflector.
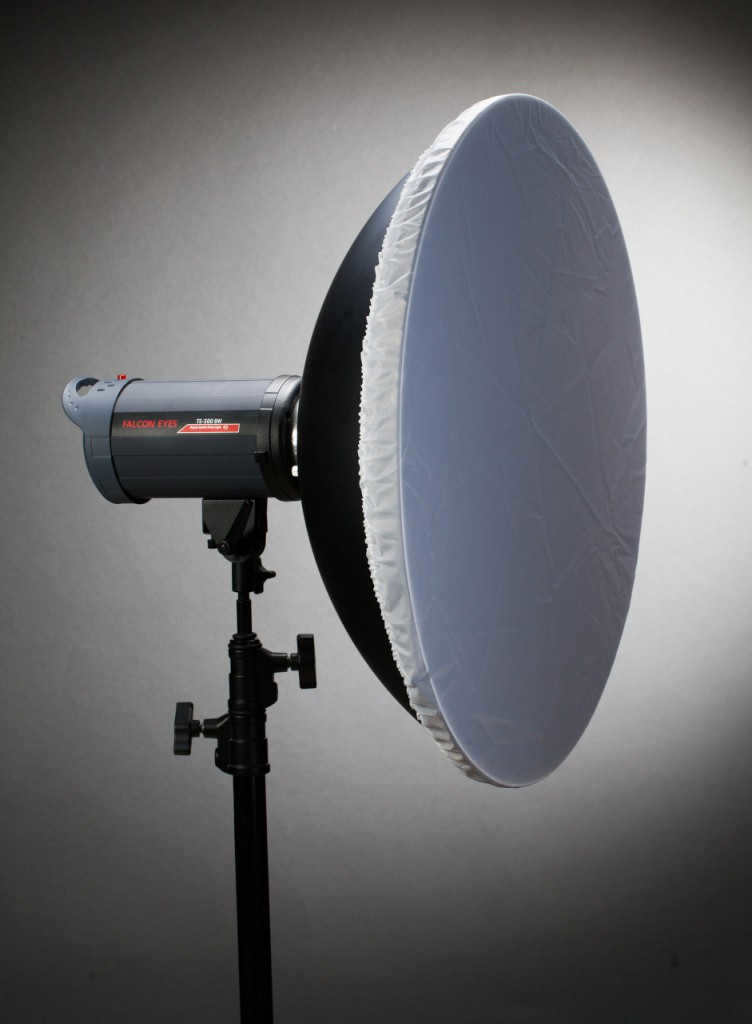

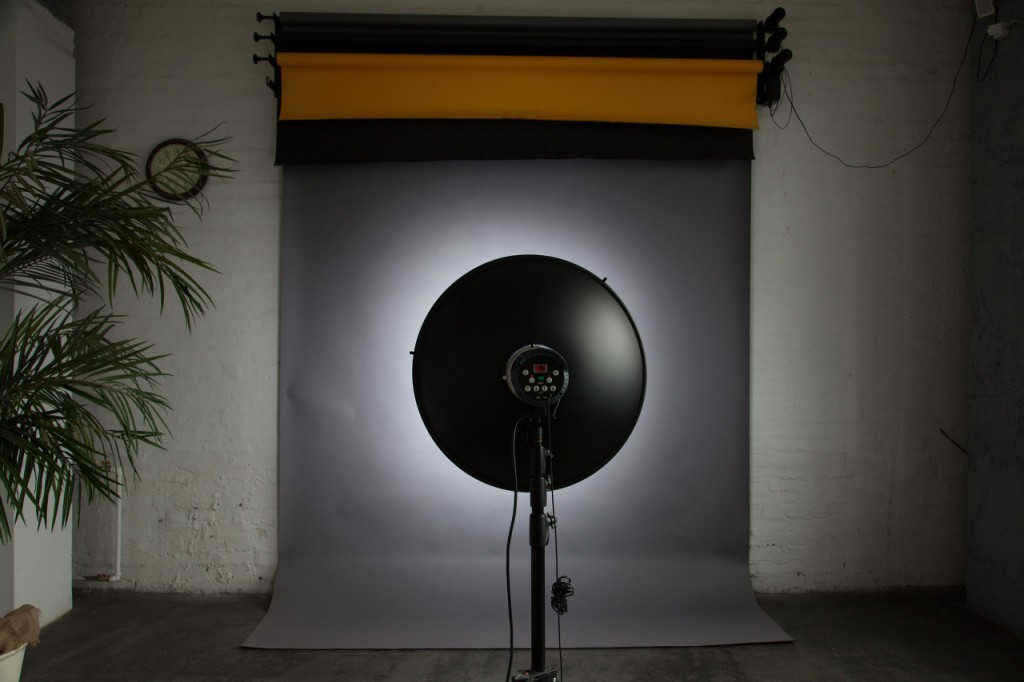
A portrait dish equipped with a honeycomb grid and a fabric diffuser
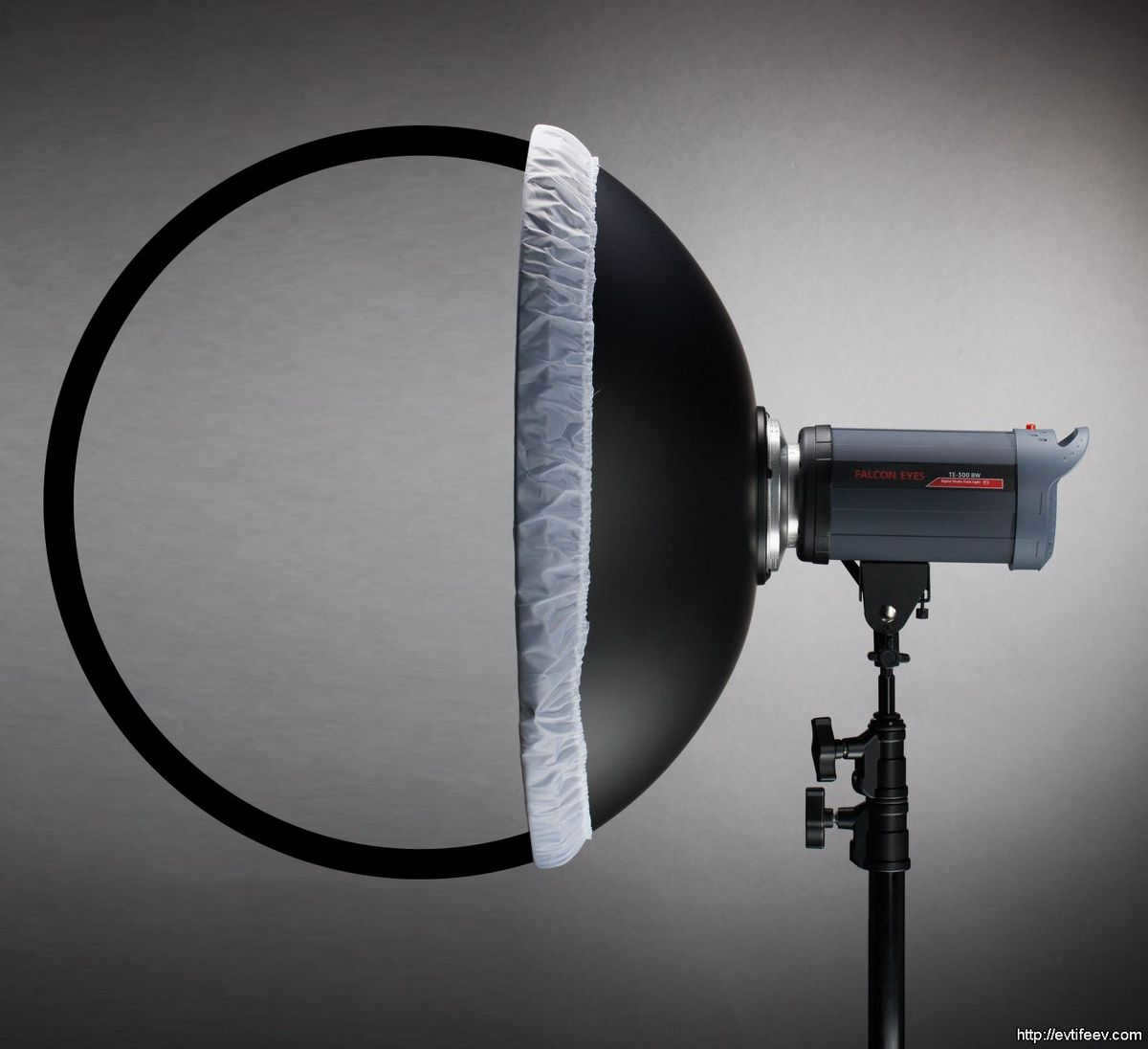

A spherical shaped portrait plate seen from the side.
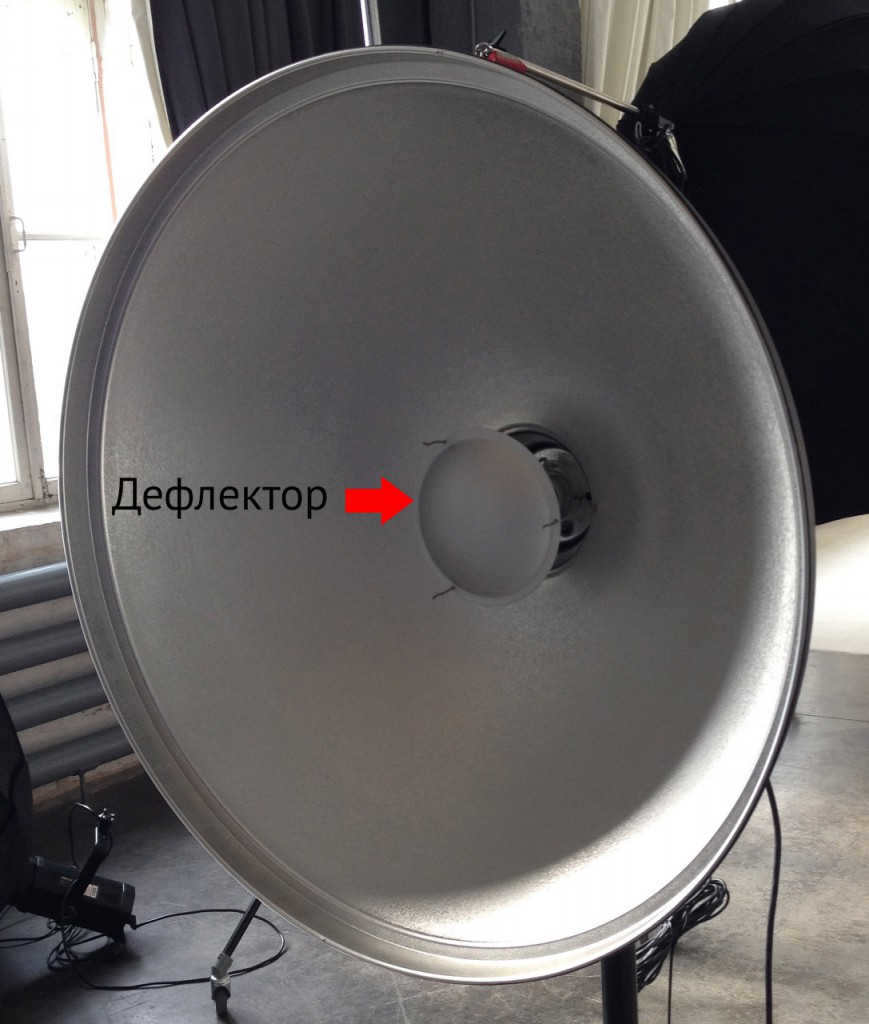

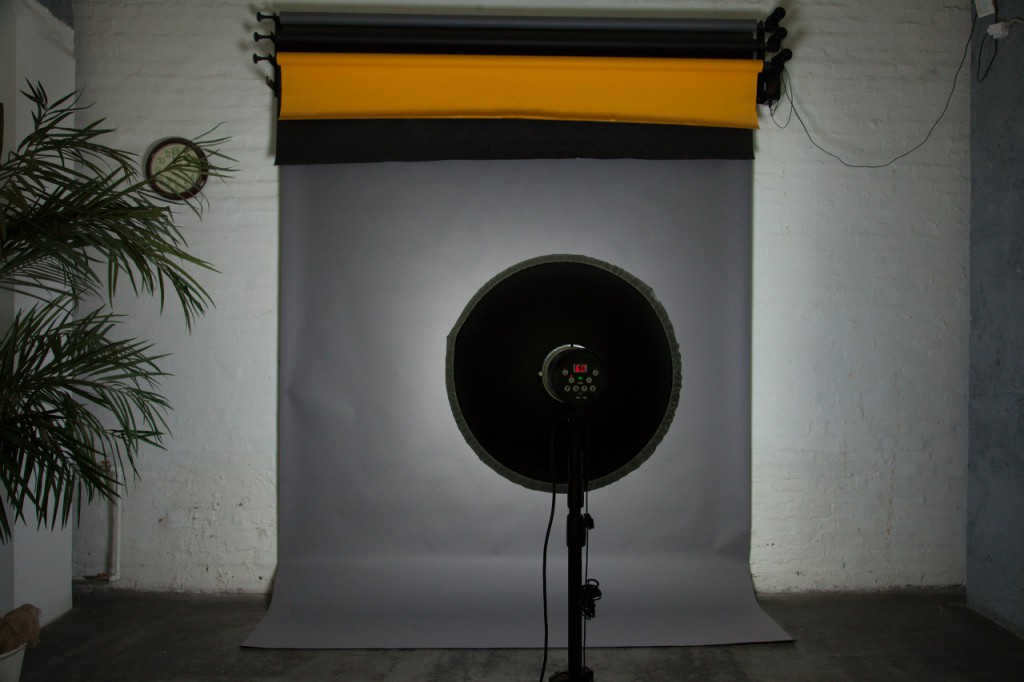
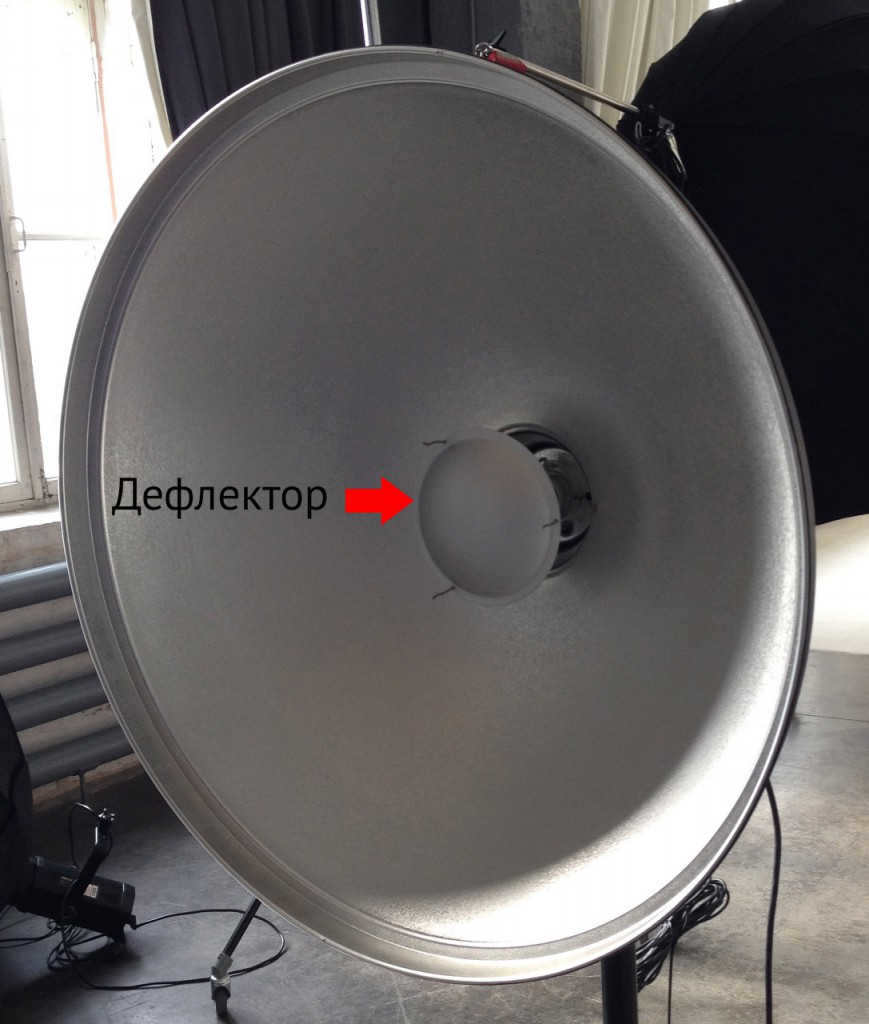
The deflector in the center is visible in the portrait dish that lacks a honeycomb.
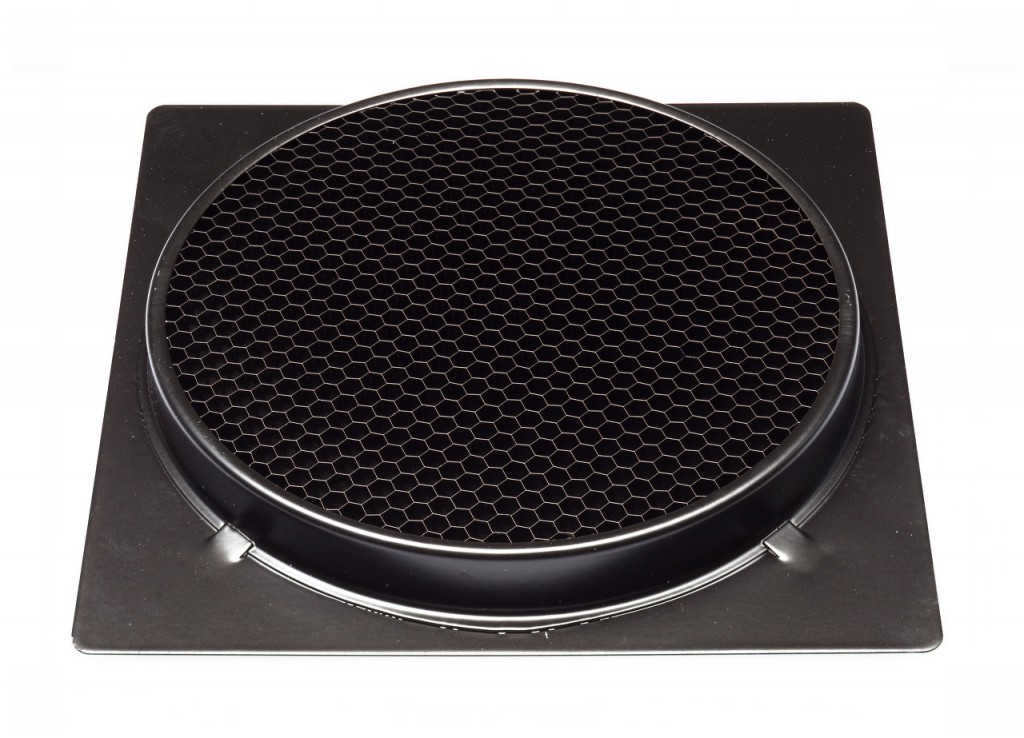

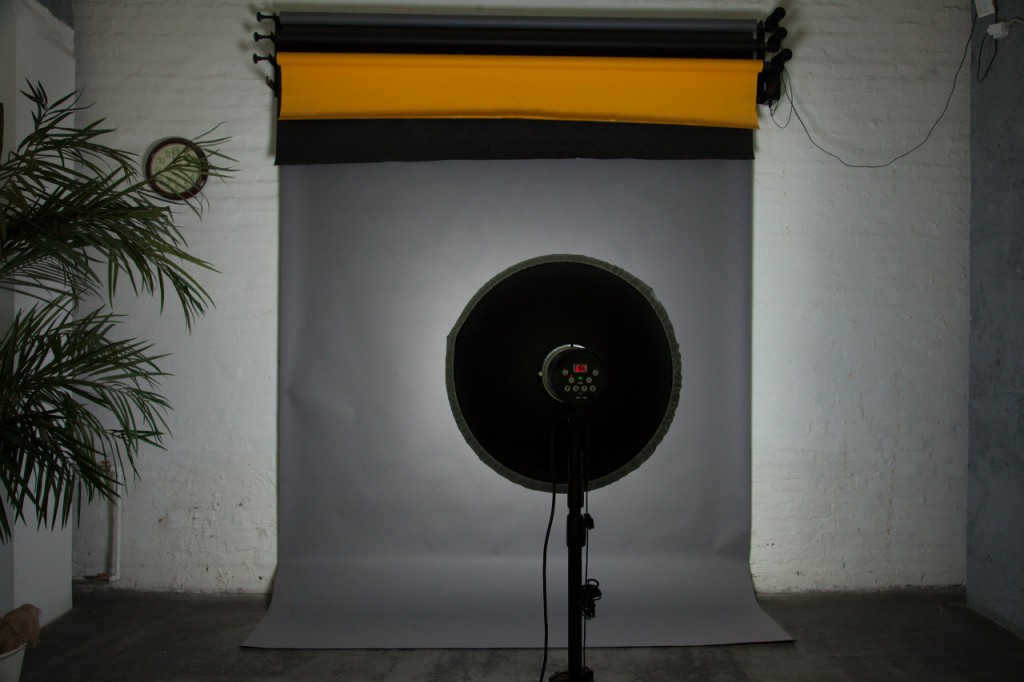
Honeycomb grids are used with reflectors to control the direction and spread of light. While these honeycombs are designed for standard reflectors, they can also be used with portrait dishes, with the only difference being the attachment method.
A portrait dish is unique among reflectors due to its larger size and the inclusion of a deflector at the center. This deflector reflects a portion of the light back onto the main reflector, ensuring an even distribution of light across the entire subject.

portrait plate lacking honeycomb

A plate with a honeycomb pattern is depicted in the portrait.

In the world of studio lighting, reflectors are an essential tool. They can be used to control and manipulate light, helping photographers achieve the desired look and feel in their images. Reflectors come in various shapes and sizes, but one popular option is a portrait plate with a honeycomb and fabric diffuser. This combination allows for precise control over the direction and intensity of the light, resulting in beautifully lit portraits. Whether you’re a professional photographer or just starting out, reflectors are a must-have in your lighting kit.

An image of a person with a decorative plate that represents their personality


Creating a portrait with the help of a portrait plate

Utilizing a honeycomb-equipped portrait plate within the confines of a studio

Glare caused by a portrait plate
A similar concept is applied in Flood light fixtures, although they are a more intricate apparatus in which the bulb is typically adjustable in relation to the reflector.
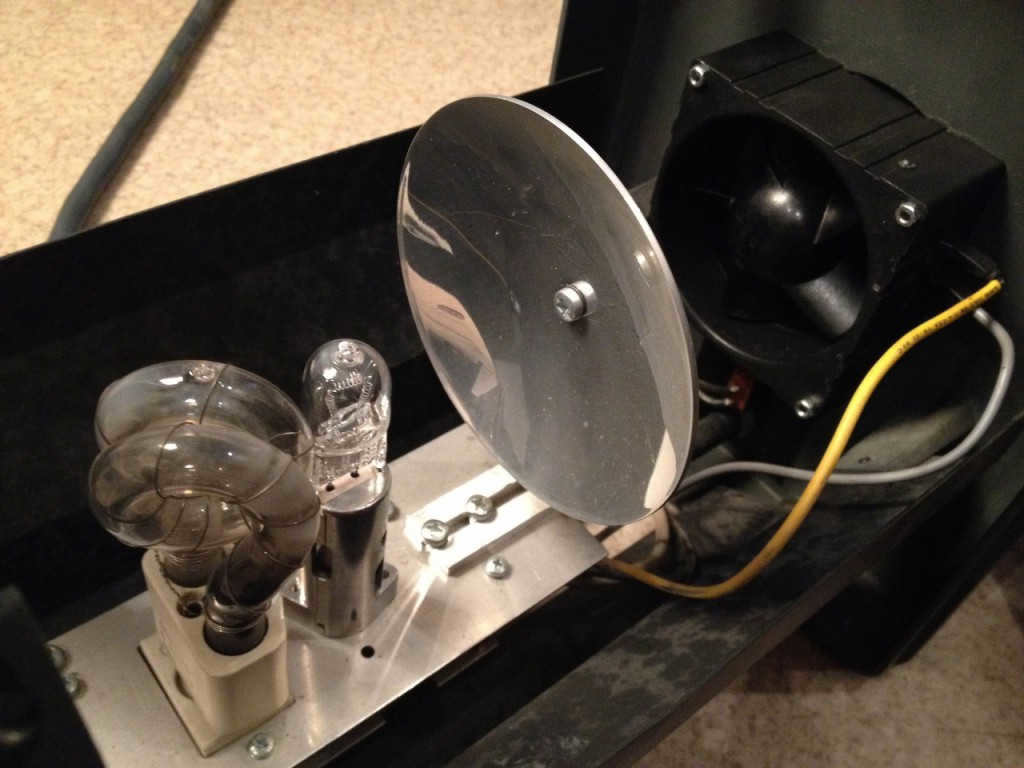

The Pulsospot is an optical device that concentrates the light into a specific spot. It is equipped with movable rails, allowing for easy adjustment of the distance between the lamp and the reflector.
In other words, the light is focused into a spot and then further collected by a Fresnel lens. In spot devices, the light is additionally gathered with a special lens after it passes through the reflector.
You can find more information about the use of sources with Fresnel lens here. Additionally, you can learn about sources with Fresnel lens here. An example of a spherical reflector is a photo umbrella, which is attached to the flash with its own rod and provides a soft but less controlled light.
The photo umbrella serves as a compact and affordable solution. Additionally, it offers the flexibility to be easily repositioned in relation to the flash. Depending on the desired effect, the inner surface of the umbrella can be silver, gold, or matte white. Silver surfaces provide a harsher light, while matte white surfaces produce a softer light.
It is worth noting that there are also “on the light” umbrellas, which function as diffusers rather than reflectors. However, this article focuses specifically on reflector umbrellas.
I will provide further information on photo umbrellas once I have conducted test shots.
Parabolic Reflector
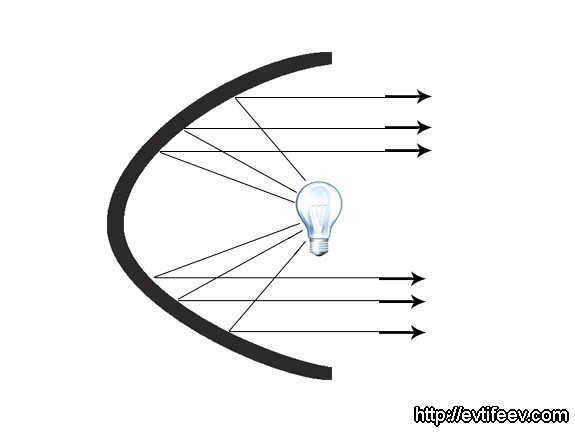
The parabolic reflector is capable of gathering and redirecting rays in a parallel manner, provided that the light source is positioned at the focal point of the reflector.
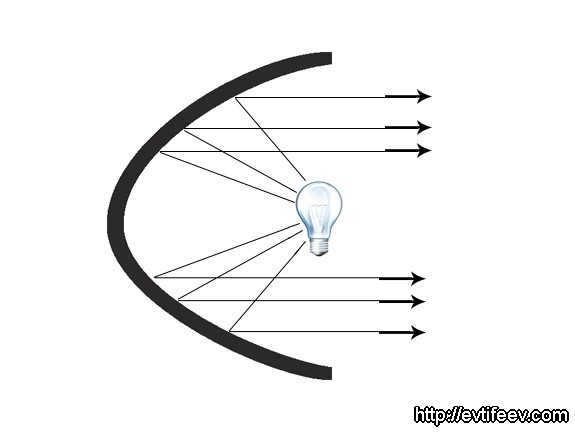
parabolic reflector with a lamp focused
If the lamp is moved closer to the reflector’s focus, the rays will spread out, and if it is moved away from the focus point, the rays will come together.
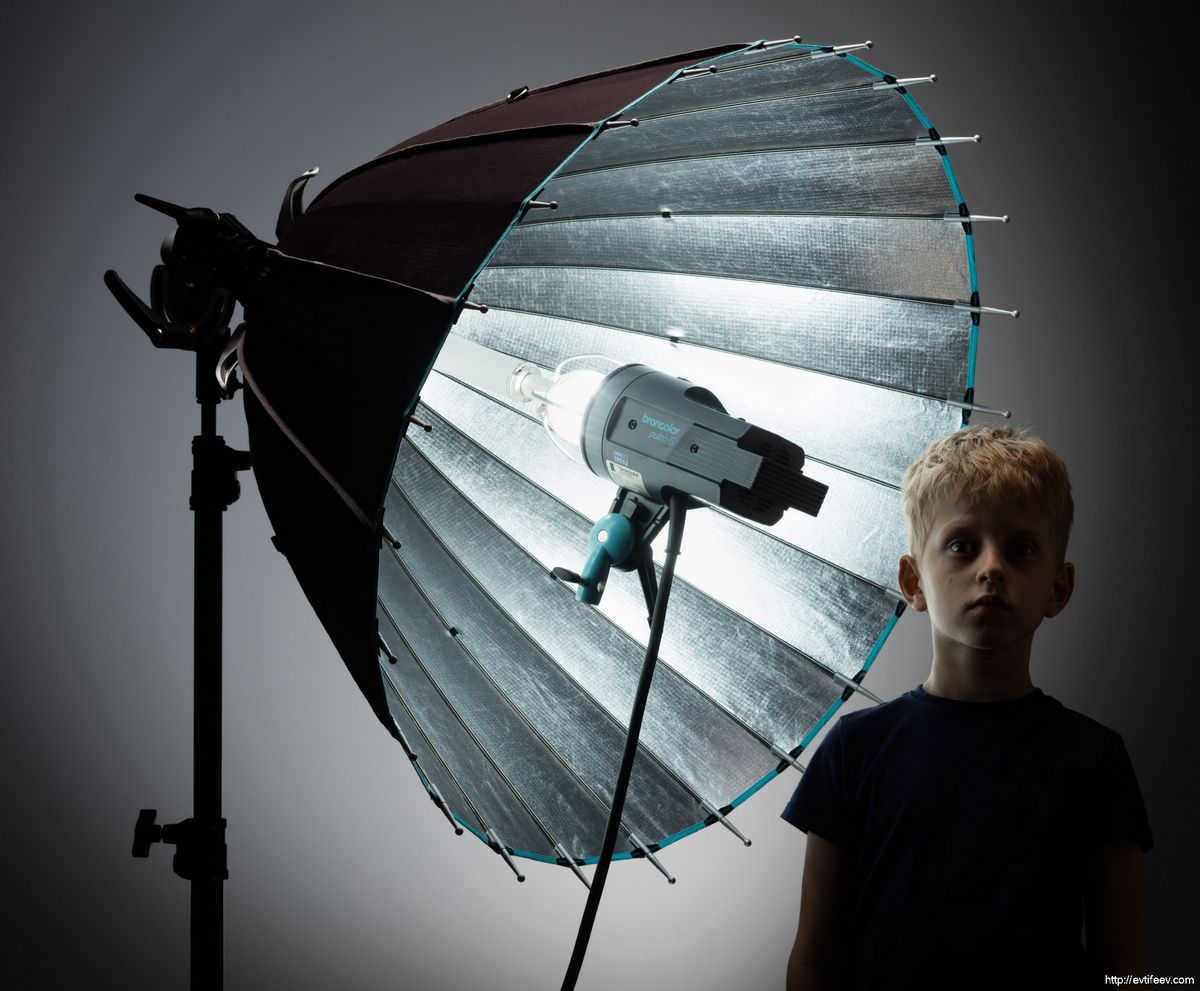
Instances of utilizing a parabolic reflector in studio equipment. Now, let’s talk about the most impressive reflector. Not because of its features (each tool has a different purpose), but because of its size! Some photographers primarily use PARA to astonish their clients and demonstrate that they have a professional studio.
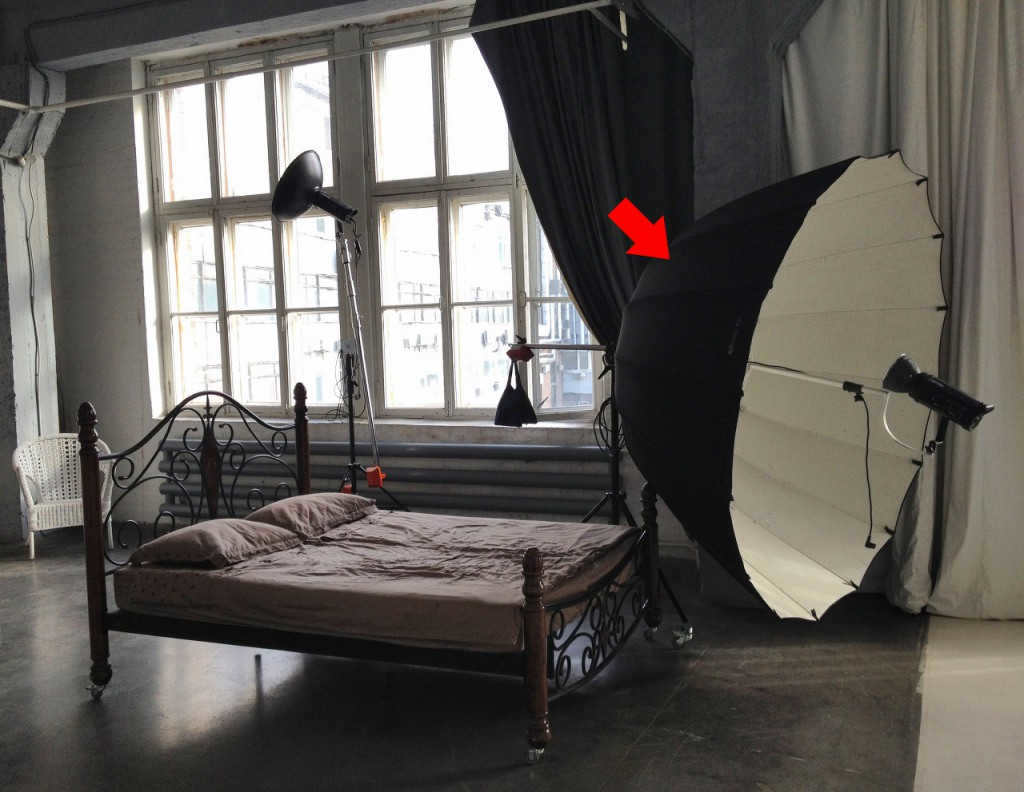

A parabolic reflector, commonly referred to as PARA, finds wide applications in location shoots, particularly in the western regions. It is extensively used in nature shoots due to its foldable nature, which allows for compact transportation in cars despite its large size. One of its key advantages is the soft light it produces, while also allowing the photographer to stand directly between the PARA and the model without altering the light and shadow pattern significantly. Although the photographer may partially block some light by standing in the path, the size of the PARA compensates for this effect. PARAs are available in various manufacturers, ranging from reasonably priced options to highly expensive and coveted ones.
Elliptical reflector
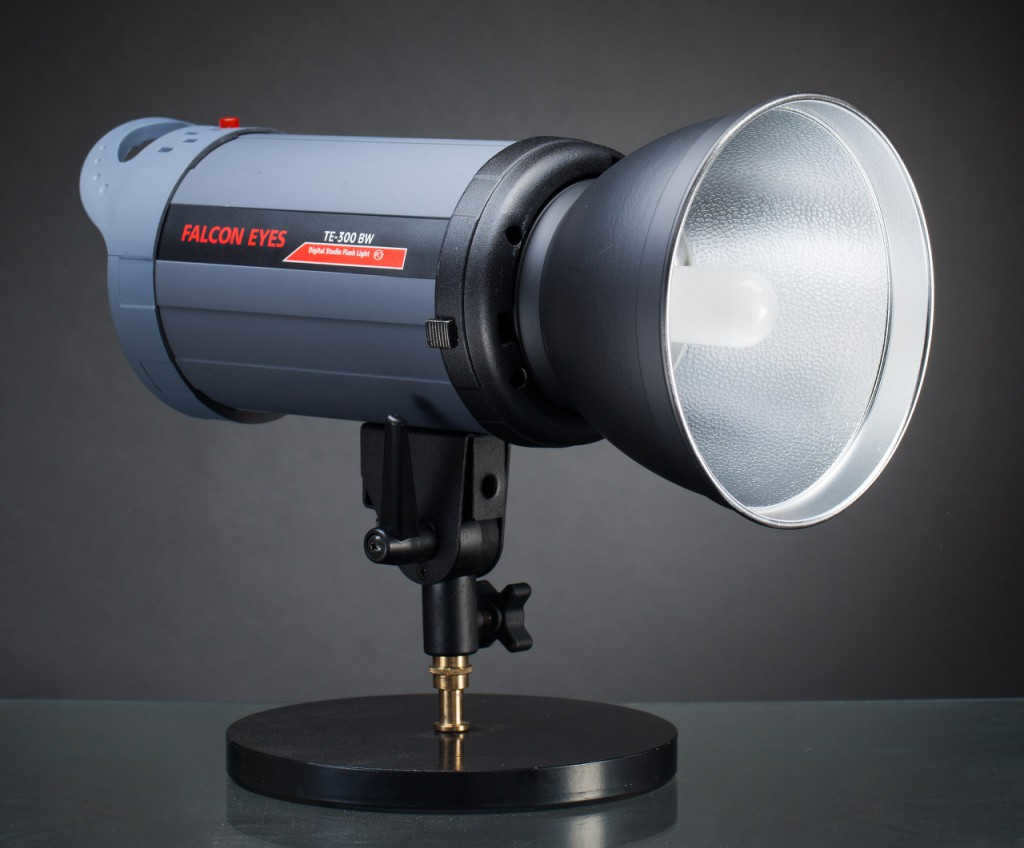
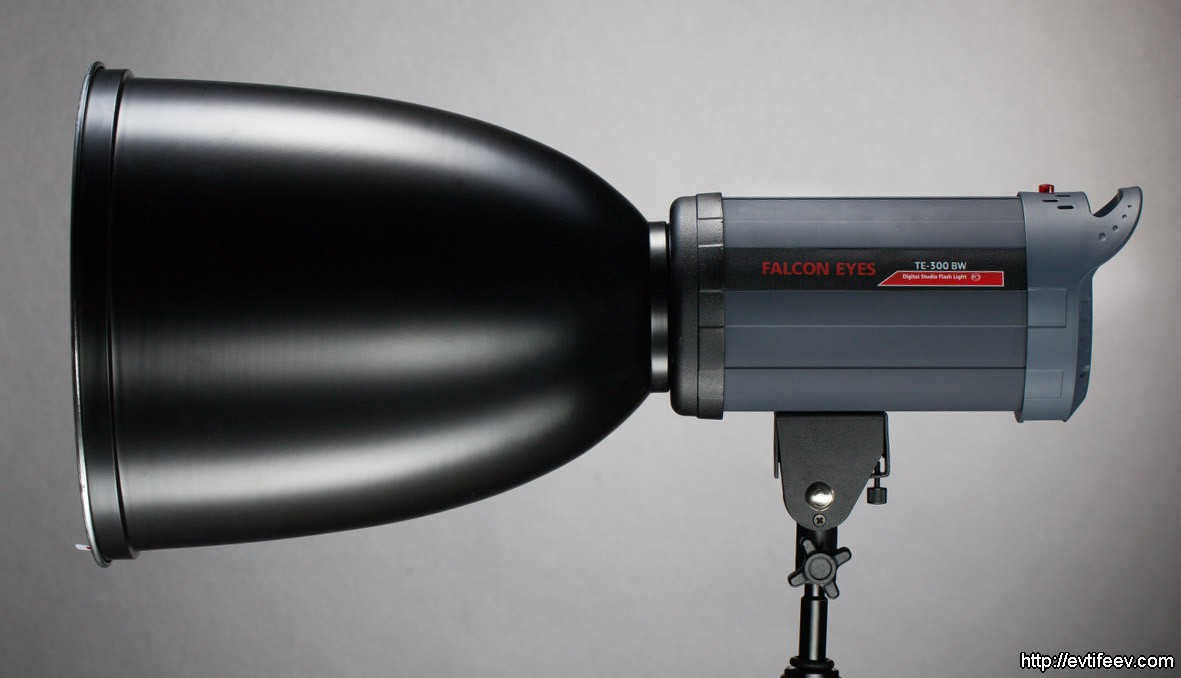
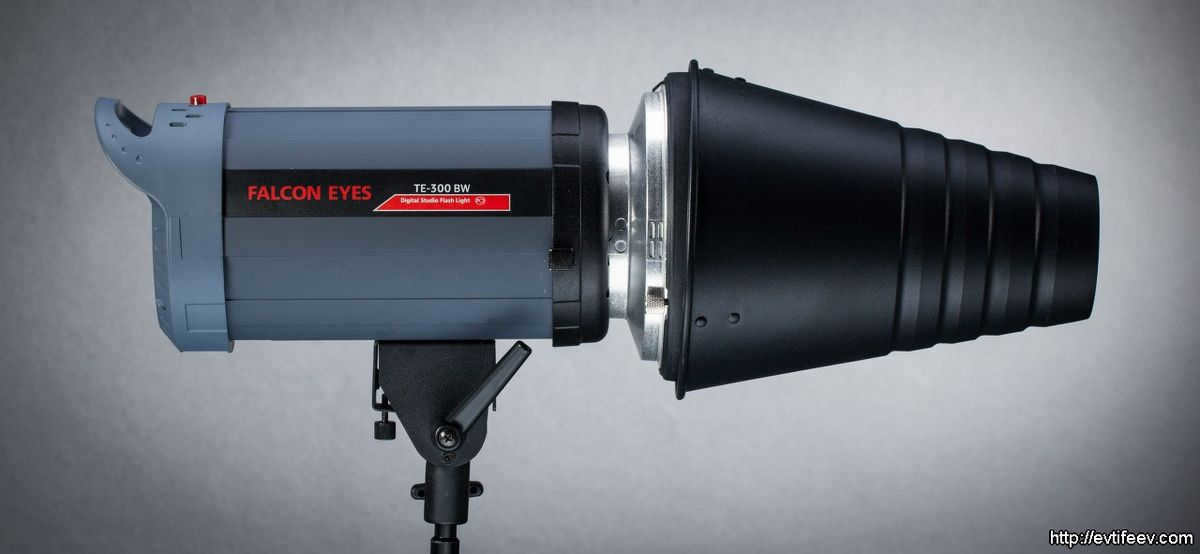
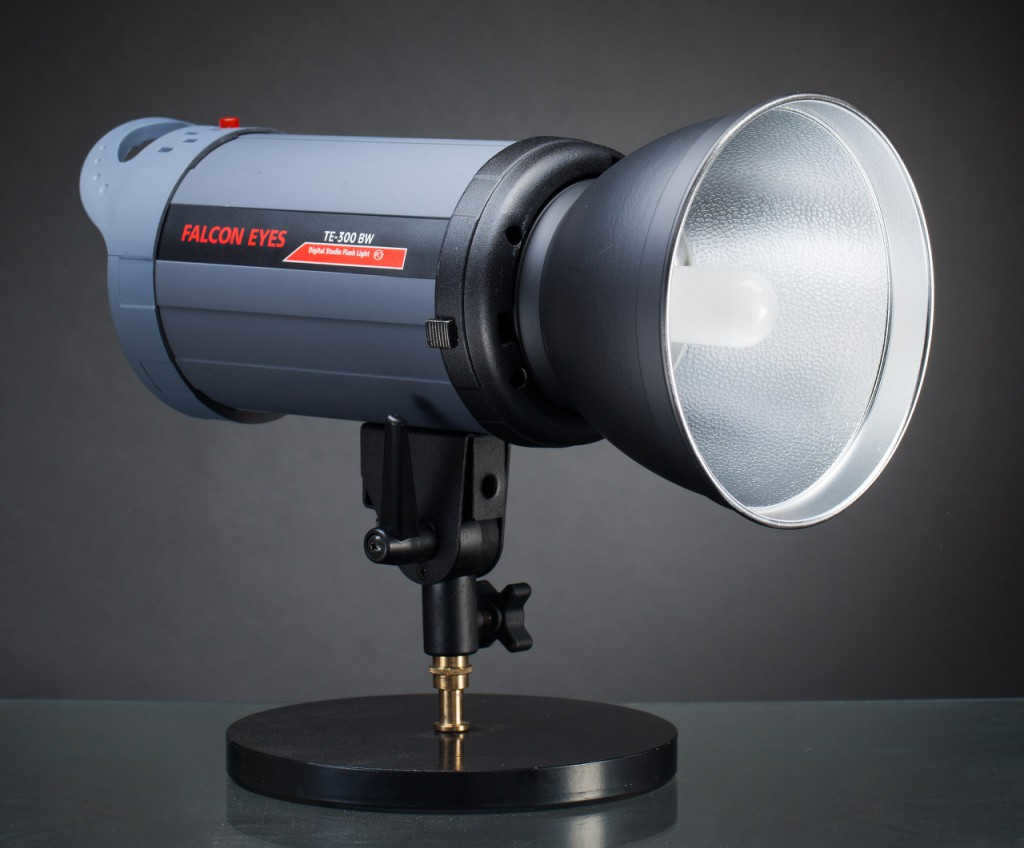
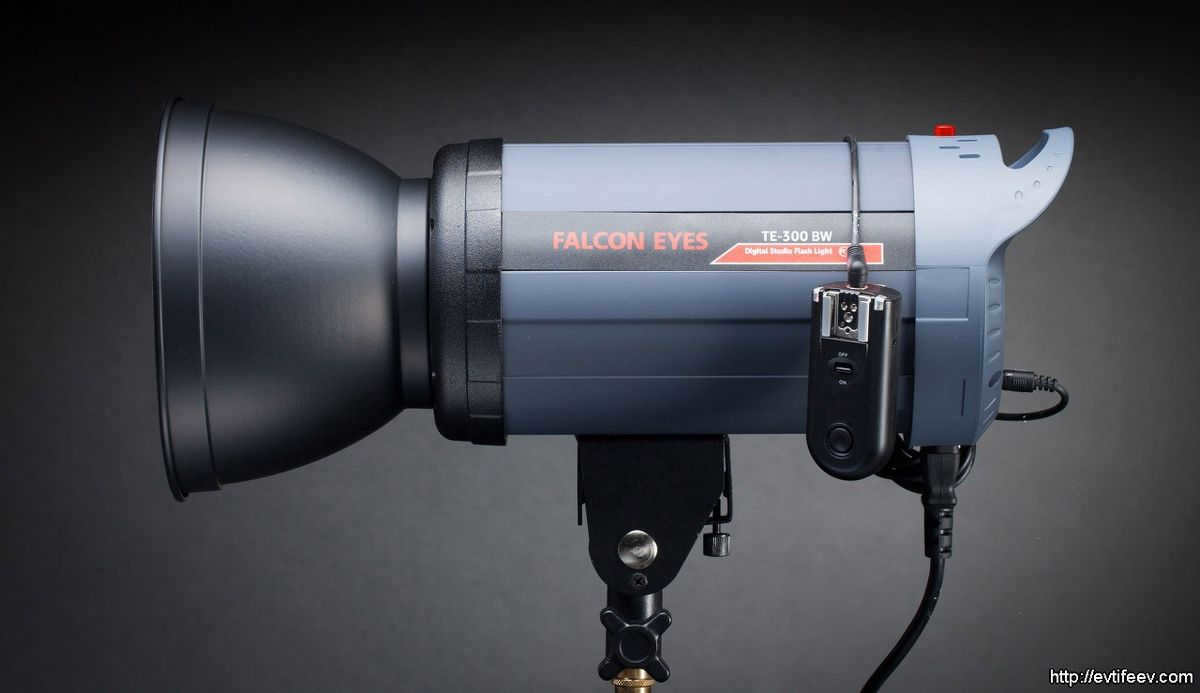
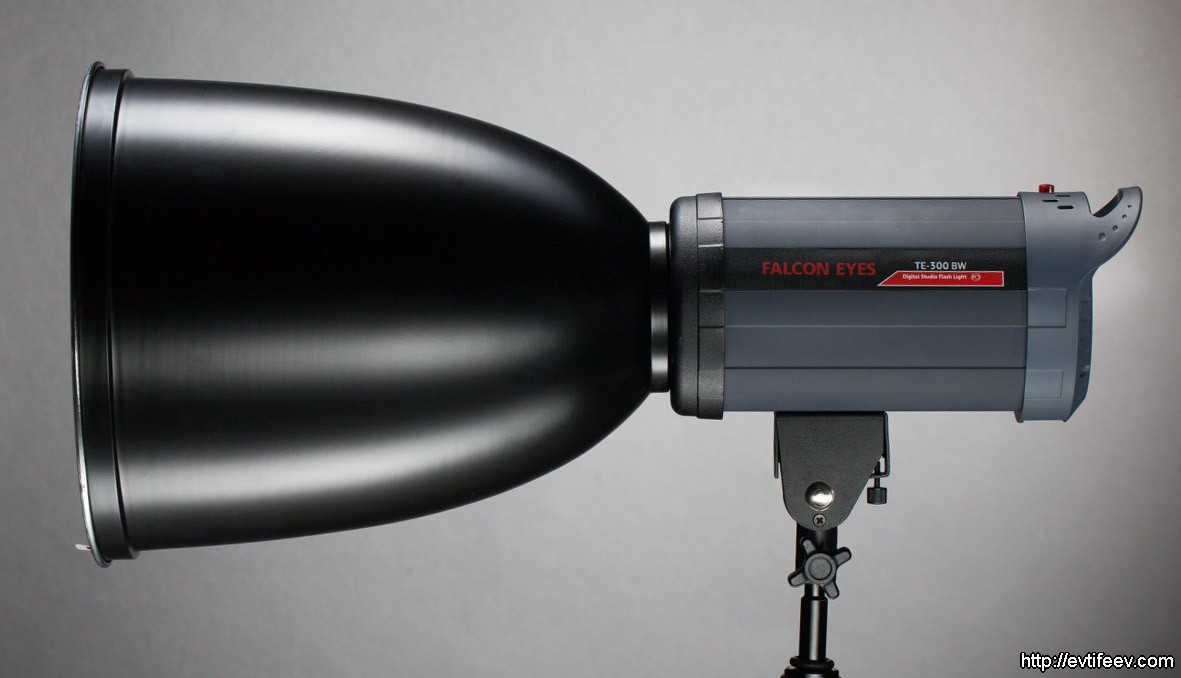
The image on the left depicts a typical 7-inch reflector manufactured by Falcon Eyes. Every studio equipment producer has their own unique diameter and design for a standard reflector. However, this particular reflector is commonly found among the assortment of elliptical reflectors offered by a specific photographic manufacturer.

A monoblock equipped with a conventional elliptical reflector
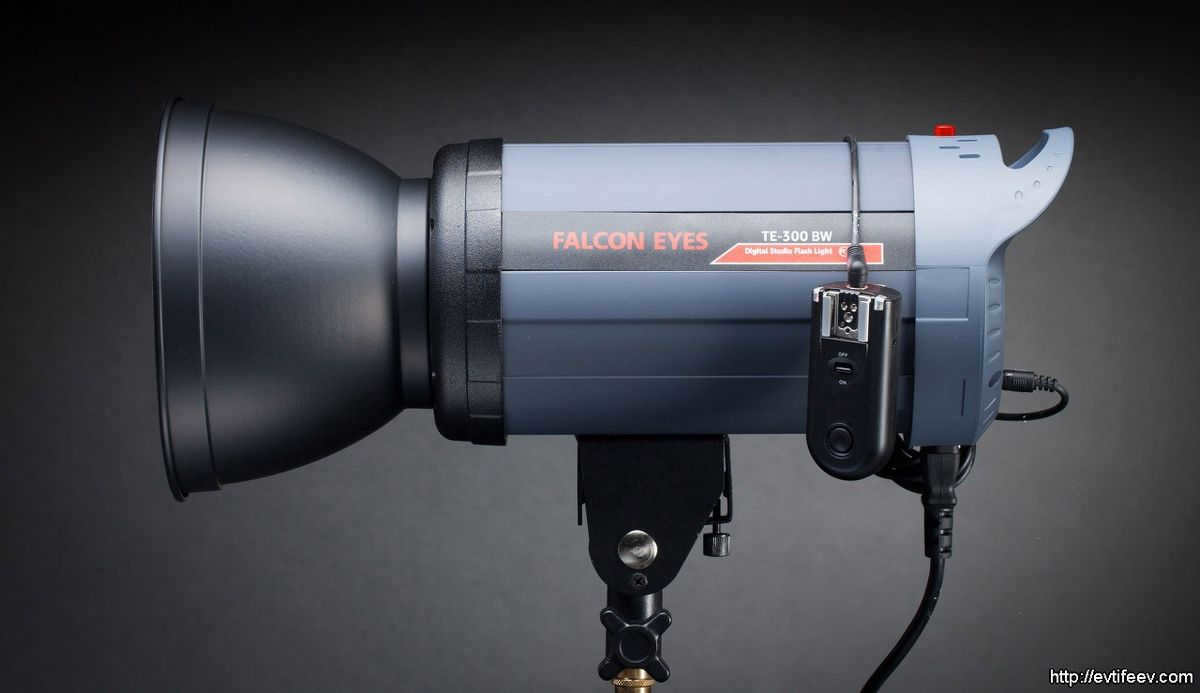

The shape of the reflector is standard.
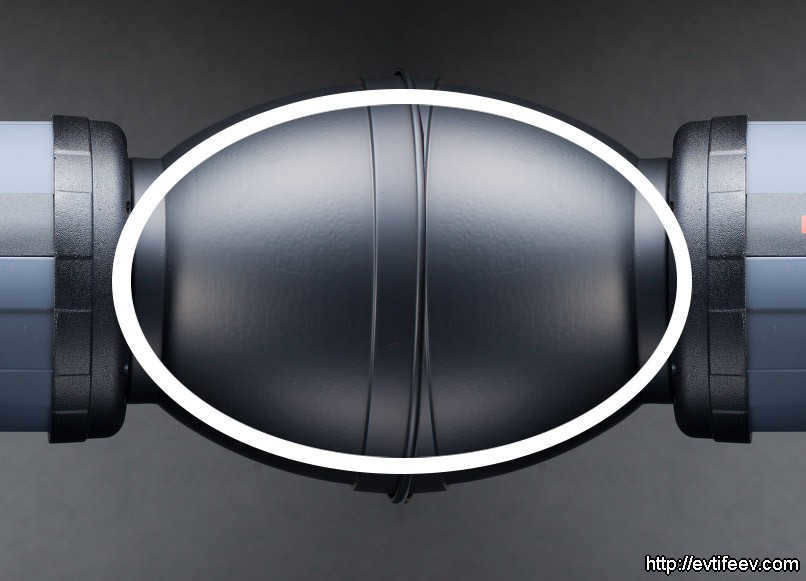

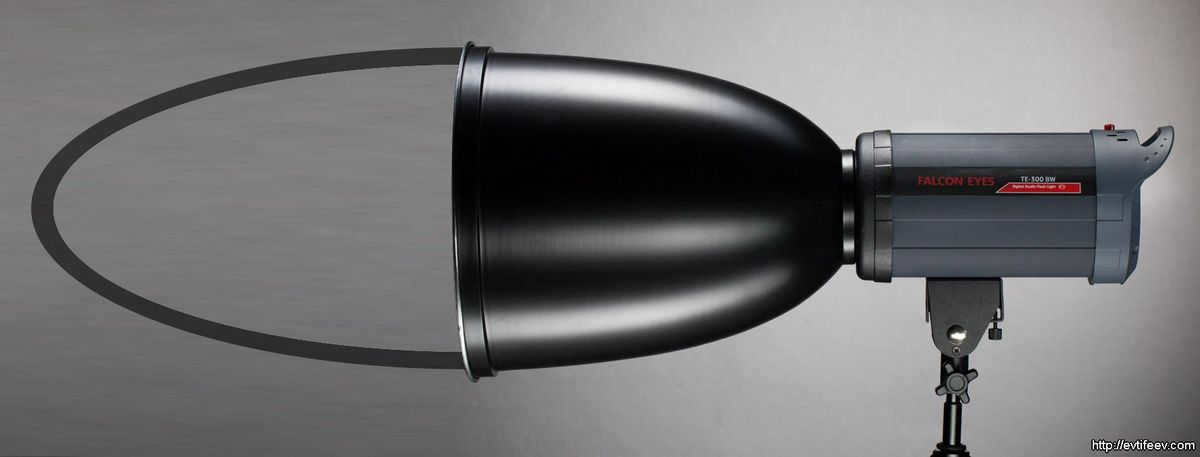
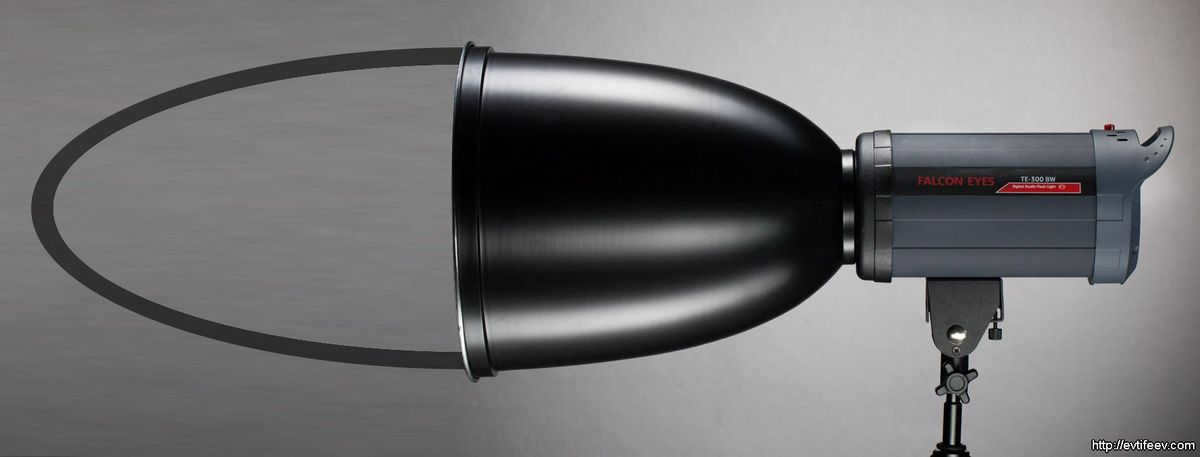
When you place one reflector on top of another and overlay an ellipse shape on top, you create an elliptical reflector.
Elliptical reflectors have the advantage of being highly effective in producing a bright spot of light. However, the resulting spot is non-uniform, with its circumference depending on the focal point. This is because the rays of light converge, rather than being parallel like in spherical and parabolic reflectors.
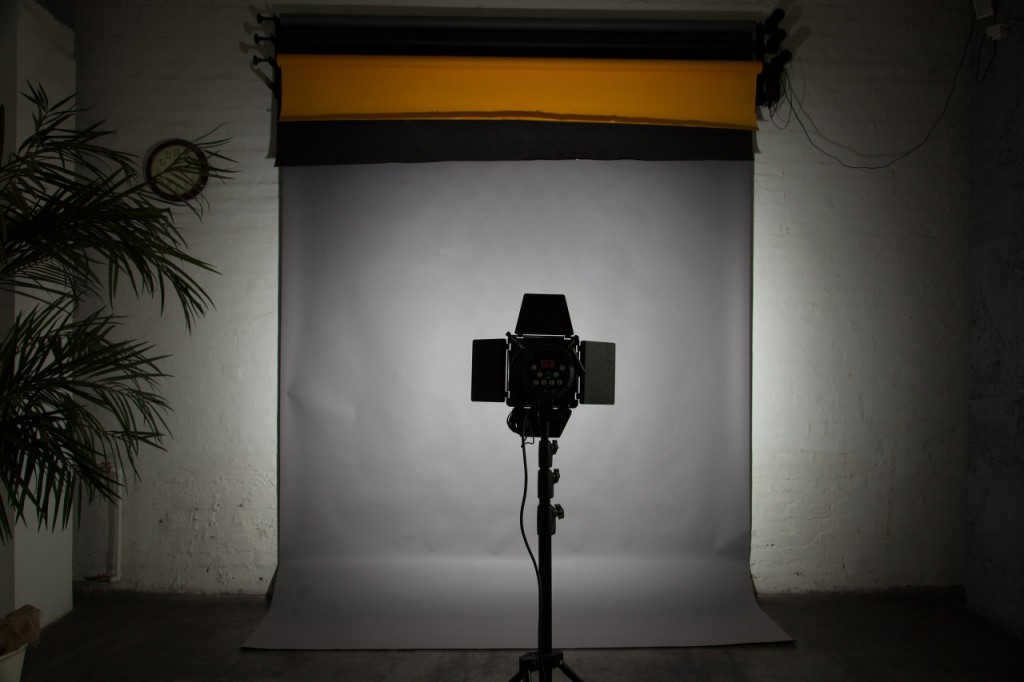

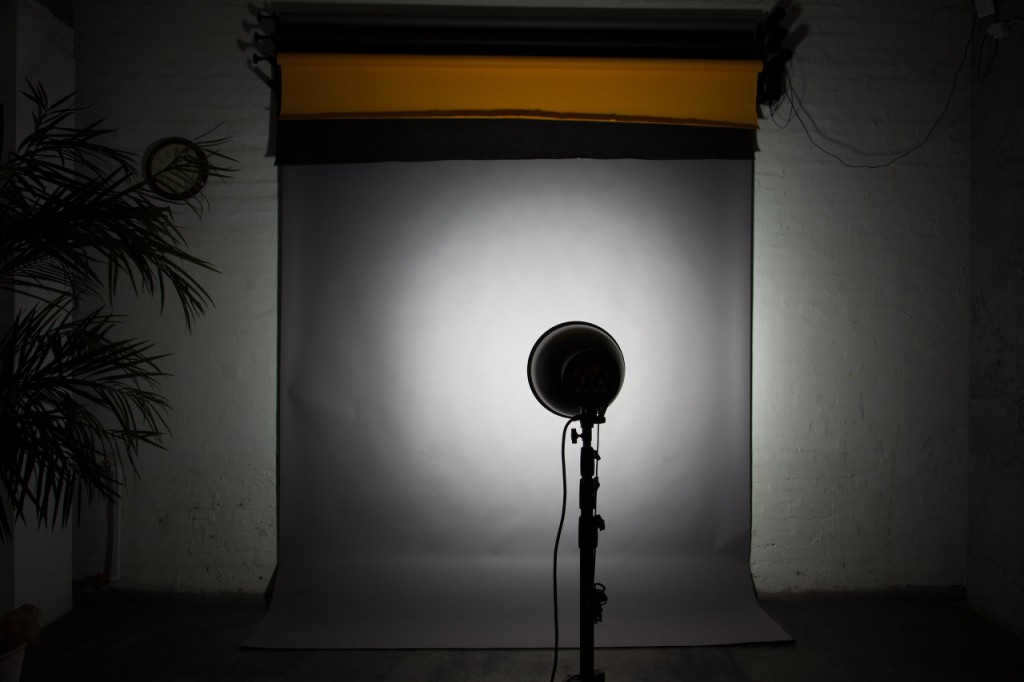
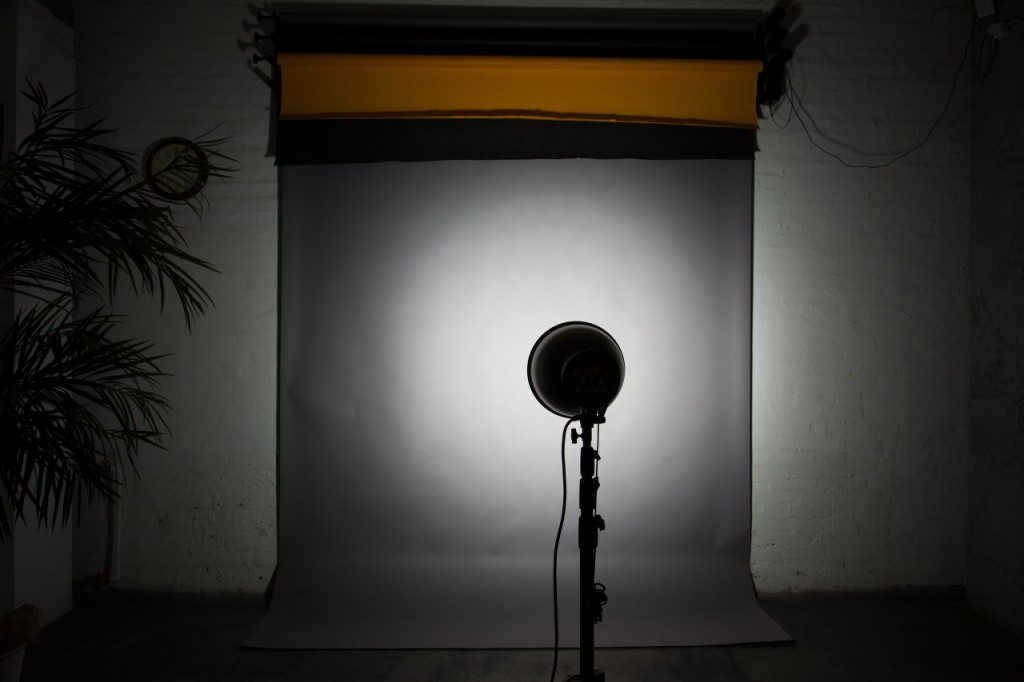
A reflector without a honeycomb and placed at a distance of 2.5m from the background.
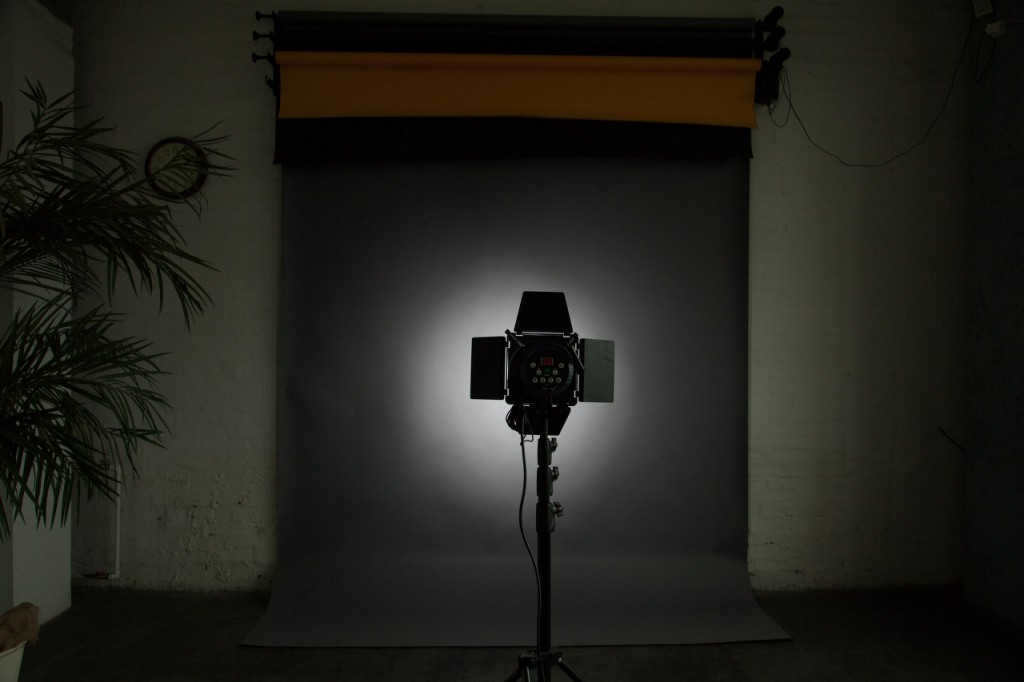

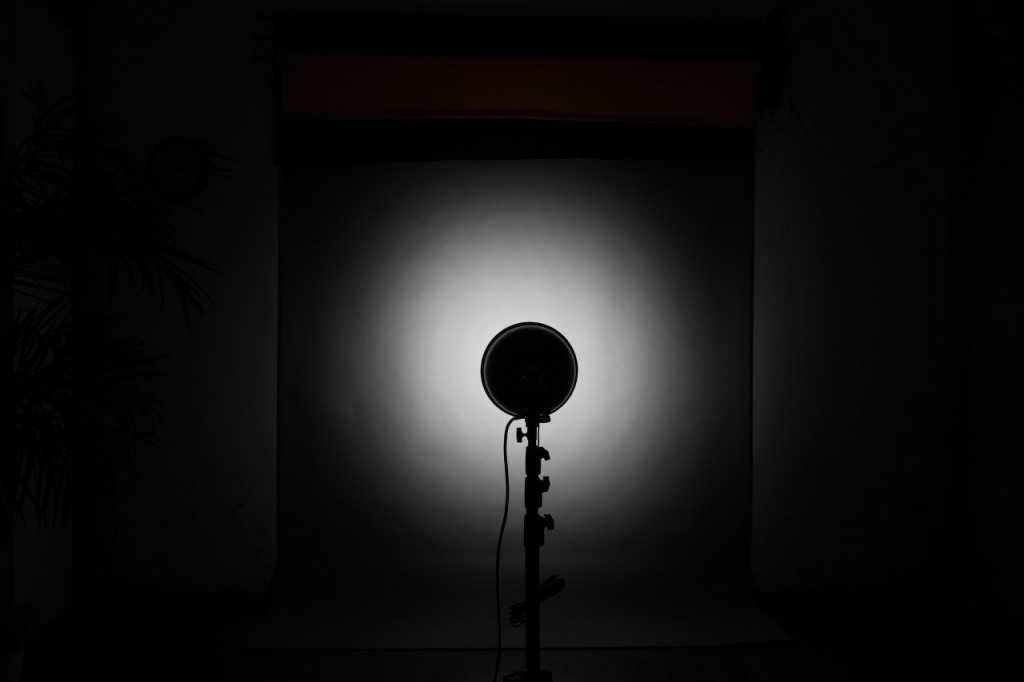
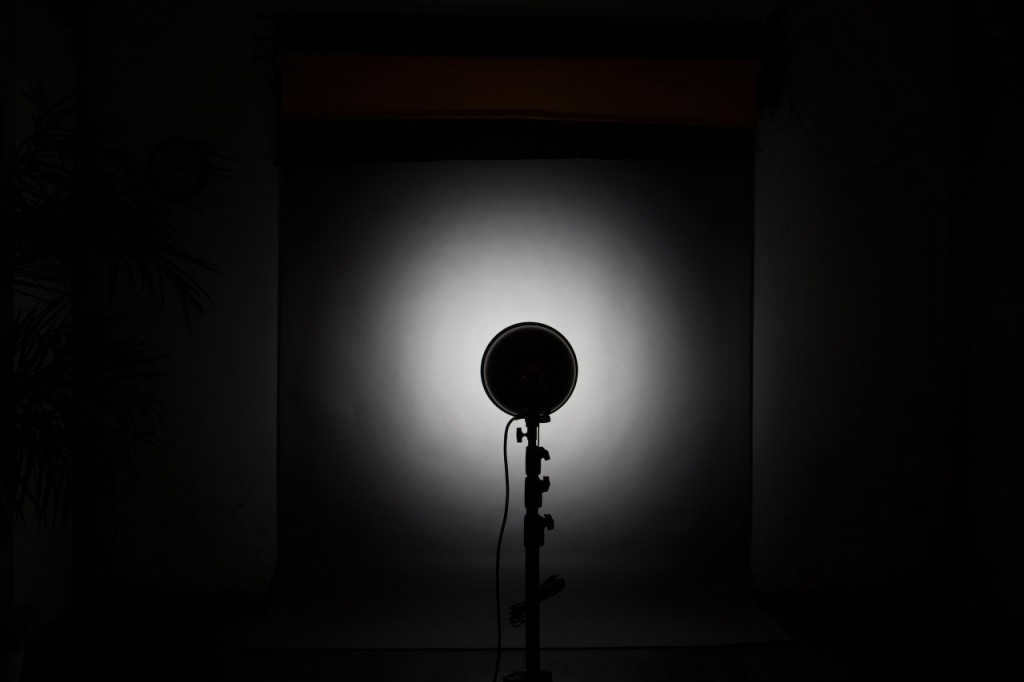
standard reflector with honeycomb, distance to the background 2.5m
The size of the light spot is greatly diminished. A demonstration of how elliptical reflectors function. [raw2]
[/raw2] It should be noted that the lamp only moves in high-end flashes. This demonstration is provided to illustrate the principle of operation: “What happens if.” The elliptical reflector is considered one of the most intriguing and desirable reflectors, and it can be found in any photography studio.

A regular elliptical reflector positioned towards the back-right to illuminate the hair.

What is a large elliptical reflector?

The shape of the reflector is a large ellipse.
By varying the diameter and depth of the reflector, we can achieve different sizes of spots and varying levels of lighting intensity (elliptical reflectors provide a fairly intense light). A deeper reflector will result in a smaller spot, while a larger diameter will create softer shadows.

A large reflector with no honeycomb, positioned 2.5m away from the background.

A honeycomb is attached to a large elliptical reflector.


Here is an instance of employing a regular reflector in the field of photography focused on subjects.
In order to capture this image, we utilized two regular reflectors and two sections of milk acrylic as diffusers. To read more, scroll up.
Distinctive Varieties of Reflectors
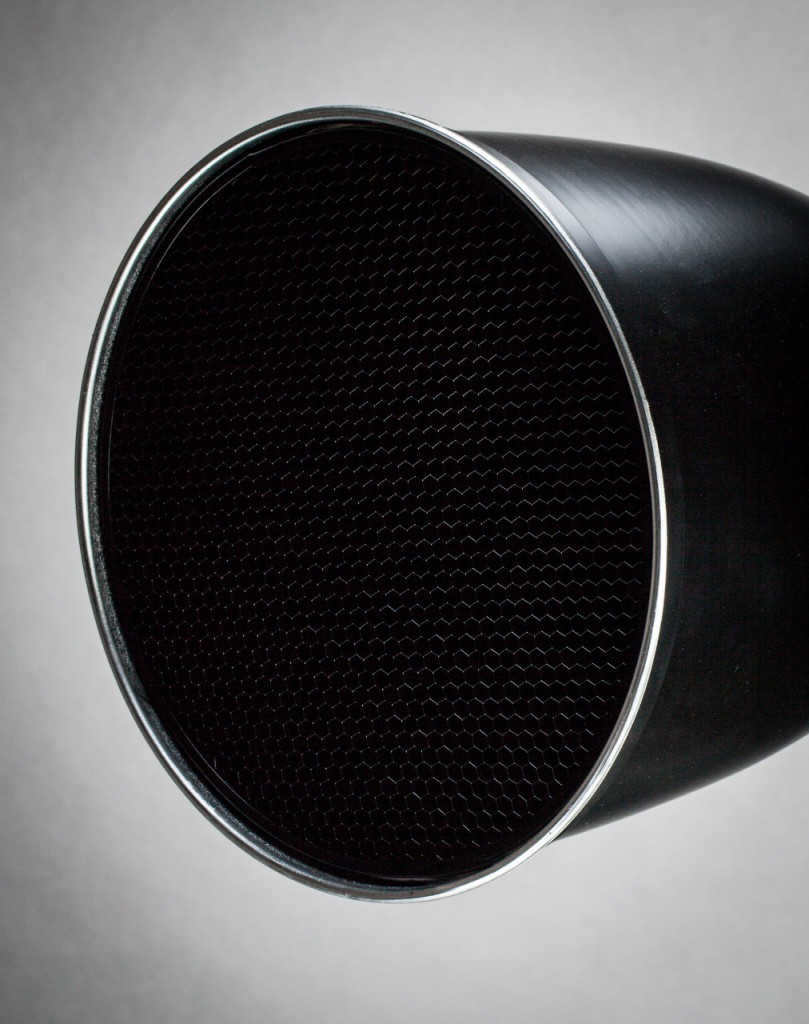
Additionally, there exist unique kinds of reflectors that are employed for particular purposes. One example is the Cone, also known as the Snoot.

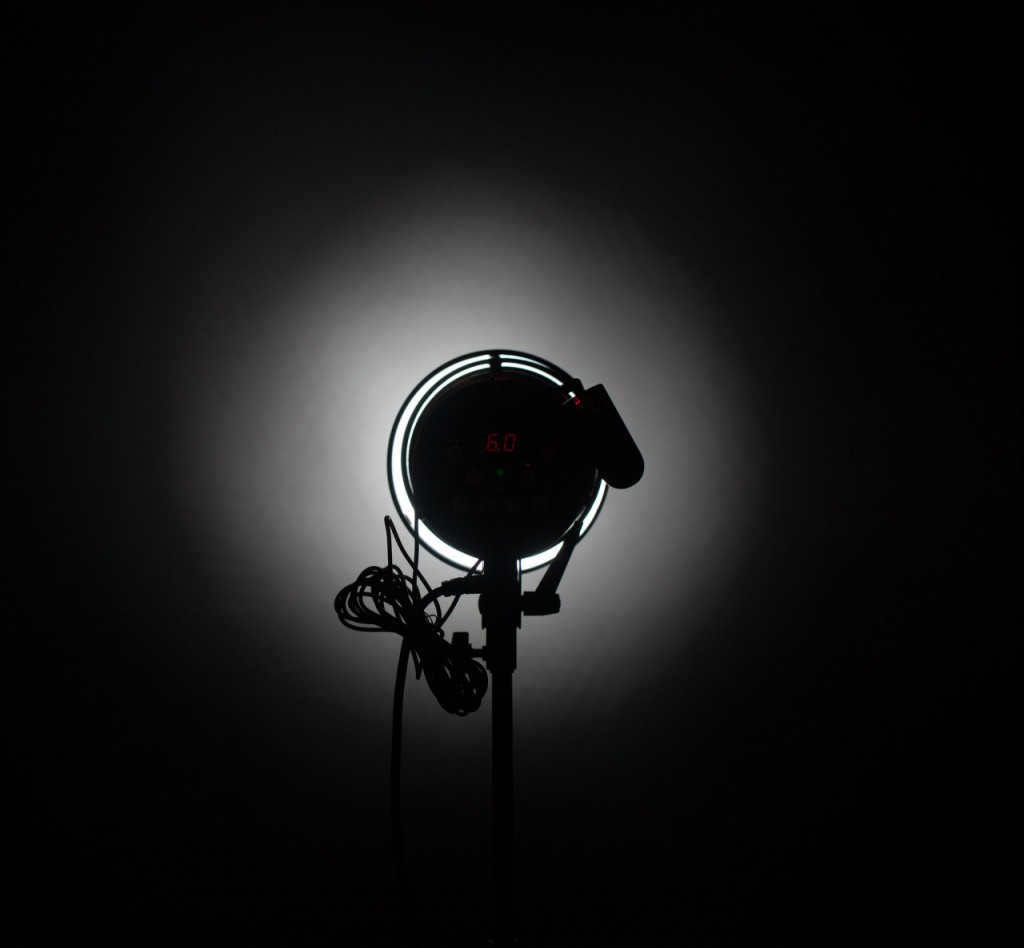
Introducing the Falcon Eyes DPSA-CST BW cone nozzle.
The conical reflector serves the purpose of effectively restricting the area of light coverage, thanks to its unique conical shape and depth. However, it is important to note that the Snoot significantly reduces the intensity of the light output.
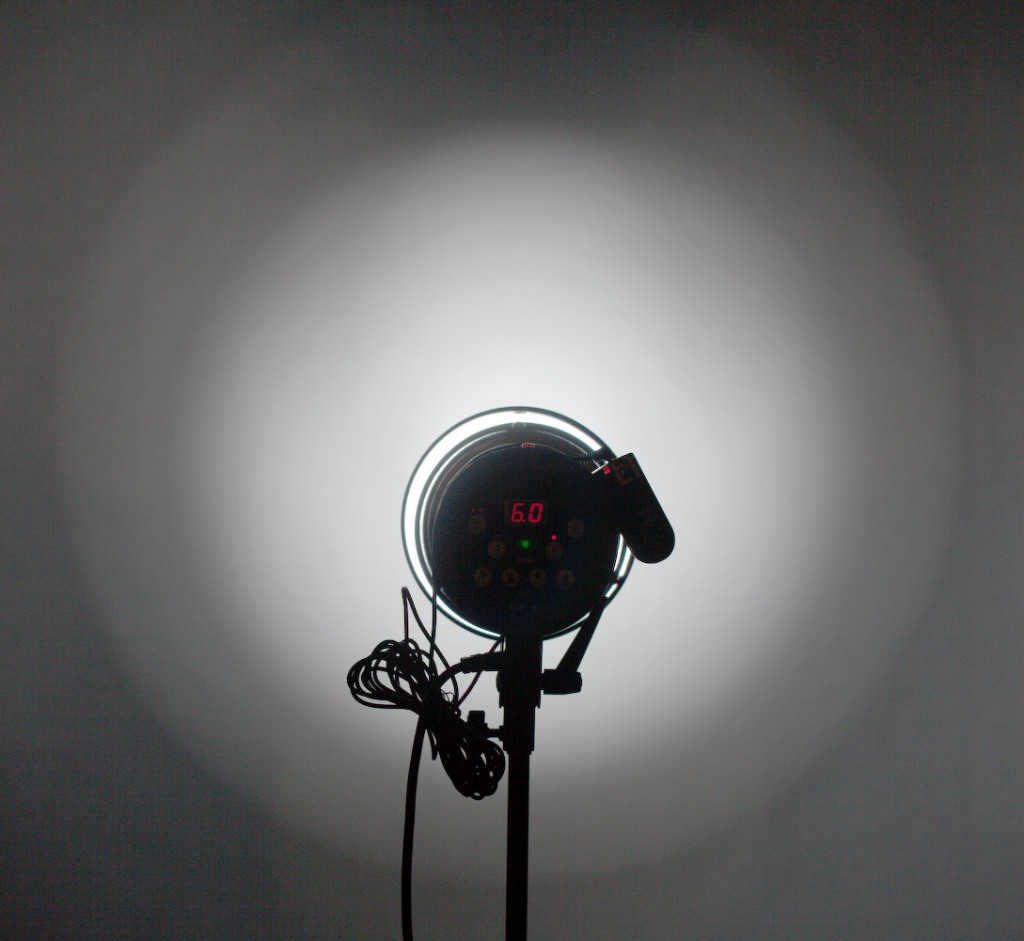

The light spot’s character from the snoot is being described here. It is observed to have a bright and evenly distributed center, with a secondary and less intense ring surrounding it. Honeycombs are commonly used with snoots and other reflectors.
These honeycombs are attached to the front part of the snoot and serve to narrow the light beam, resulting in a more precise and focused spot.
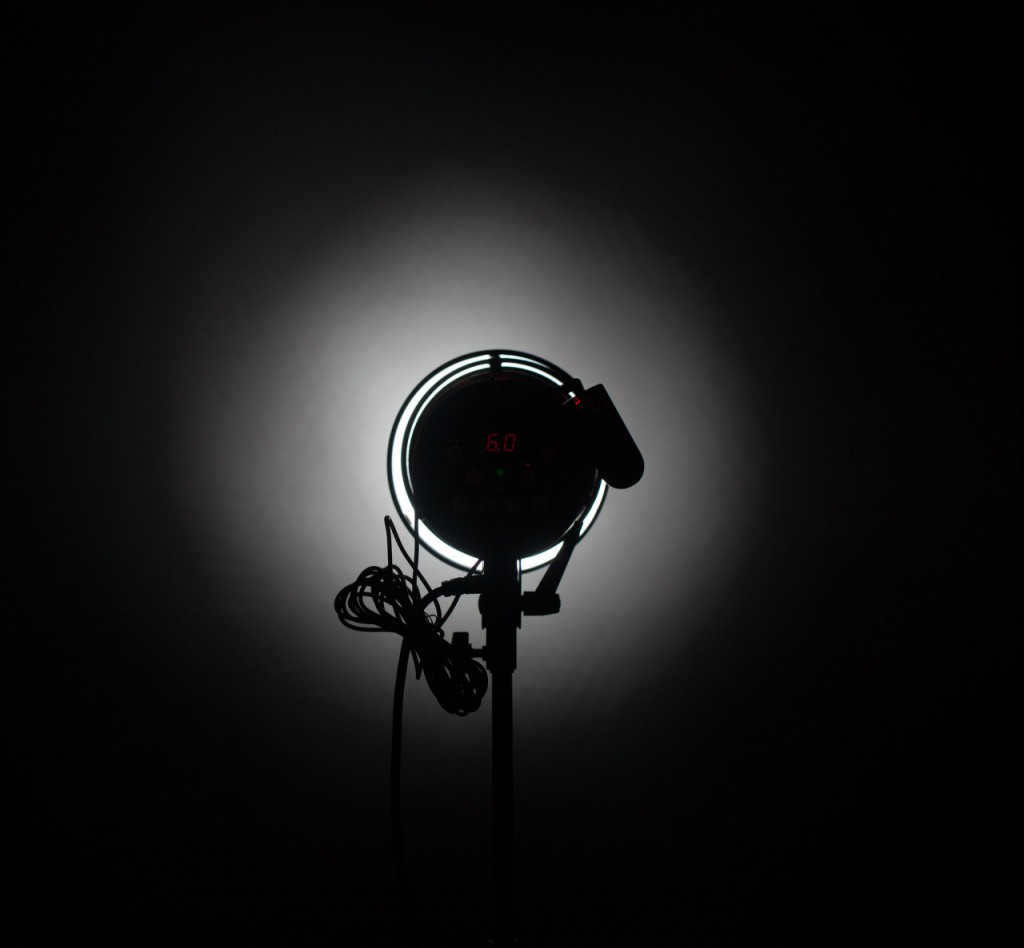

The outcome of the Snoot’s performance when combined with delicate mesh honeycombs.
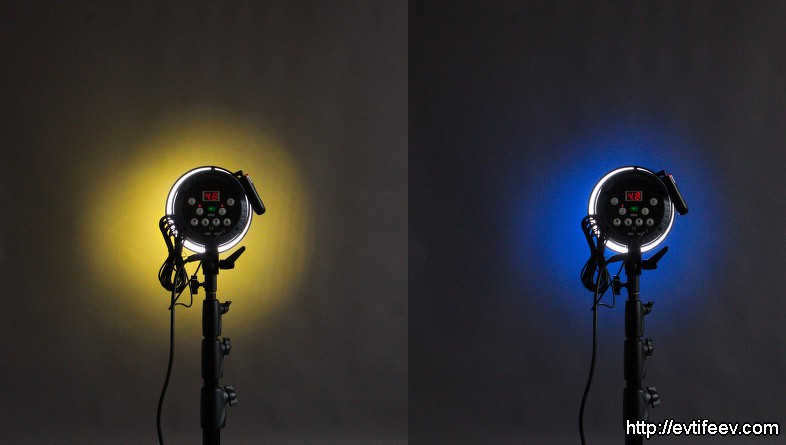

Another option is to place a folium filter in a circular shape underneath the honeycomb, resulting in a colored focal point.

Scope of Use The use of the Background Nozzle is specifically designed for illuminating the background. Its unique shape allows for a softer illumination of the background compared to a standard elliptical reflector. Here are some examples where the Background Nozzle can be used:

Although the background is slightly uneven, I wasn’t able to capture a picture that is flawlessly beautiful. However, the main point is still evident. The background nozzle effectively disperses the light, resulting in a more uniform light flux distribution. to content ↑
In this article, I have only covered a few varieties of reflectors. It is evident that if we delve into the wide-ranging concept of “reflector,” we could discuss various types of reflectors at length. In future articles, we will continue to explore different varieties of reflectors. You have now learned about the fundamental studio reflectors, their operational principles, and their traditional applications. The potential uses of reflectors are truly limitless, depending on your creativity and the capabilities of a specific reflector. update
When you visit a photo studio, I suggest using colloquial terms for reflectors. For instance, if you require a large parabolic reflector, it is commonly referred to as a “PARA” (short for “Para,” meaning large umbrella).
If you need a small elliptical reflector, it is typically called a “standard reflector” or a “pot”.
A beauty dish is simply referred to as a beauty dish, or sometimes as a “beauty plate” :).
There are also softboxes, stripboxes, octoboxes, and so on, which will be covered in future articles since they are not just reflectors, but separate accessories.I would appreciate your comments and seeing examples of your work with different reflectors. Look forward to an upcoming article on studio accessories! Stay tuned 🙂 Let the girl go. Let her float.
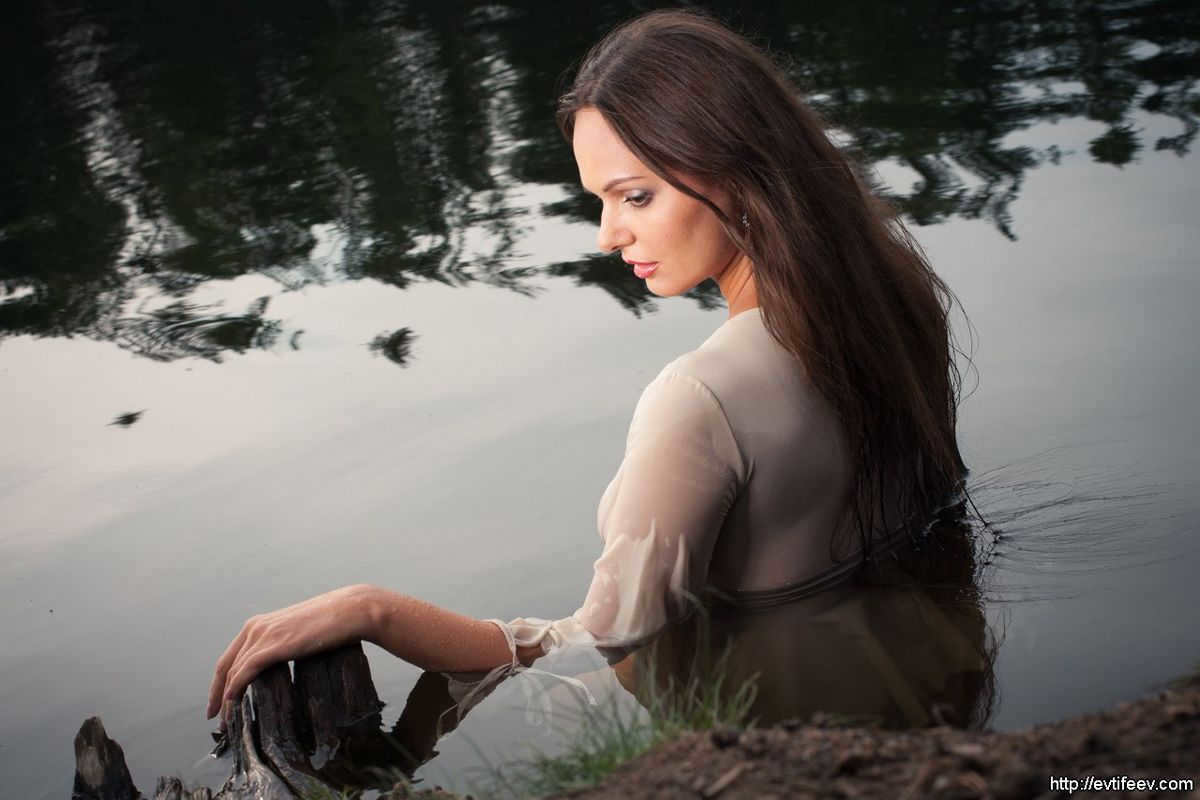

A photograph was taken using a portrait plate on a cloudy day.
This post was published in the categories of portrait, Photography Tests, photography, photography, nature photography, photography equipment. It discussed the use of snoots, reflectors, portrait plates, reflectors, light spots, snoots, honeycombs, standard reflectors, and studio lights. It also mentioned the use of foliar filters by Dmitry Yevtifeev. Make sure to bookmark this page for future reference. Don’t forget to share this article on Kontakontakte, Facebook, Google+, etc. and give it a 5-star rating if you enjoyed it!
Please rate the article
If you are interested in watching my videos, don’t forget to subscribe to my channel!   Take a look at my Instagram account to see what I am currently working on.
 Take a look at my Instagram account to see what I am currently working on.
 You can also find me on Vkontakte and Facebook. Subscribe to the RSS feed for updates.
Recommend my content to others.

Are you interested in getting the most recent updates on
photography-related content?
- – evaluations of lenses and cameras
- – articles about the evolution of photography equipment
- – undisclosed photography techniques
- – advanced photoshop editing techniques
Add a comment Cancel reply
8 thoughts on “Studio light, lesson 1: reflectors”
Am I correct in understanding that the reason “vapor” is important is because of its low power loss? The seller of Prograf mentions a “different light.” My studio is not very large, and the fixtures are quite powerful (500 J). I’m concerned that the size of the grandbox 1.2m might be a hindrance and not provide any advantage compared to the “octa” of the same size. (There is an issue with pre-order, so a decision needs to be made).
Instead of using the photo titled “the result of the snoot action”, I believe it would be more appropriate and accurate to use the photo that showcases the “character of the light spot from the snoot” immediately after describing the nozzle. As for the photo demonstrating the “result of the snoot work with fine-mesh honeycombs”, it can be included as the second photo.
Hello Igor, why do you find it misleading? This photo accurately represents the end result. Additionally, the photo depicting the “character of the light spot from the snoot” is essentially the same, but has been enhanced to highlight the varying levels of illumination it provides. When using fine-mesh honeycombs, the light spot becomes smaller (although I don’t have one on hand, unfortunately), and the honeycomb structure becomes visible if the snoot is positioned next to the background.
My explorations in the realm of photography, write-ups on photographic gear and optics
One of the easiest and most frequently used tools in studio photography is a reflector. This marvelous device is aptly named as it reflects light, fulfilling its purpose to perfection.

The characteristics of the light emission when utilizing a reflector rely on: – its geometric configuration and dimensions;
– its surface characteristics;
– the placement of the lamp;
– the distance to the illuminated object. to content ↑
Here’s a quick lesson on geometry:
A sphere can be thought of as a three-dimensional circle. The surface of the sphere is called the sphere itself. If you were to rotate a parabola, it would become an elliptic paraboloid. It’s worth noting that a circle is actually a specific type of ellipse. All of these shapes are known as conic sections. Back to content ↑
Using a Spherical Reflector
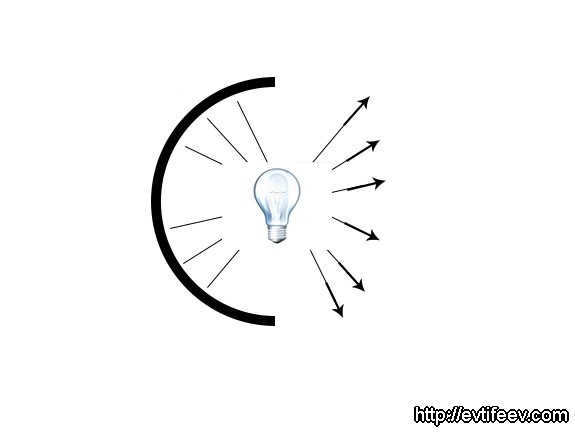
A spherical reflector is used in this studio lighting setup, with the lamp positioned in the center. Placing the flash lamp at the center allows the light to be reflected back into the lamp, resulting in an increase in light output of approximately 40%. However, due to the wide spread of the rays, this type of reflector is not the most convenient choice for studio photography. Another option is to position the lamp at the focal point of the reflector.
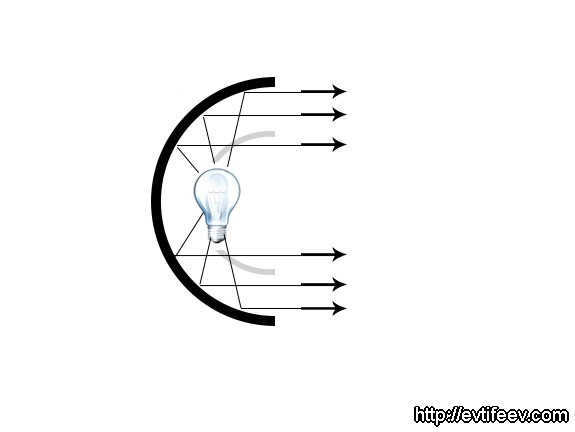
A spherical reflector refers to a reflector where the focus point is located on a sphere that has a radius equal to half of the reflector’s radius. This design allows for parallel rays to be emitted, resulting in uniform lighting. Flashlights often incorporate this type of reflector along with a Fresnel lens. One popular and widely used example of a spherical reflector is the portrait dish, also known as the beauty dish.
It is important to note that the focus of the lamp in your specific portrait dish may not be guaranteed. There are numerous manufacturers producing portrait dish lamps with different shapes, sizes, and positions. To determine the focus of your own lamp, you can apply the principle mentioned above.
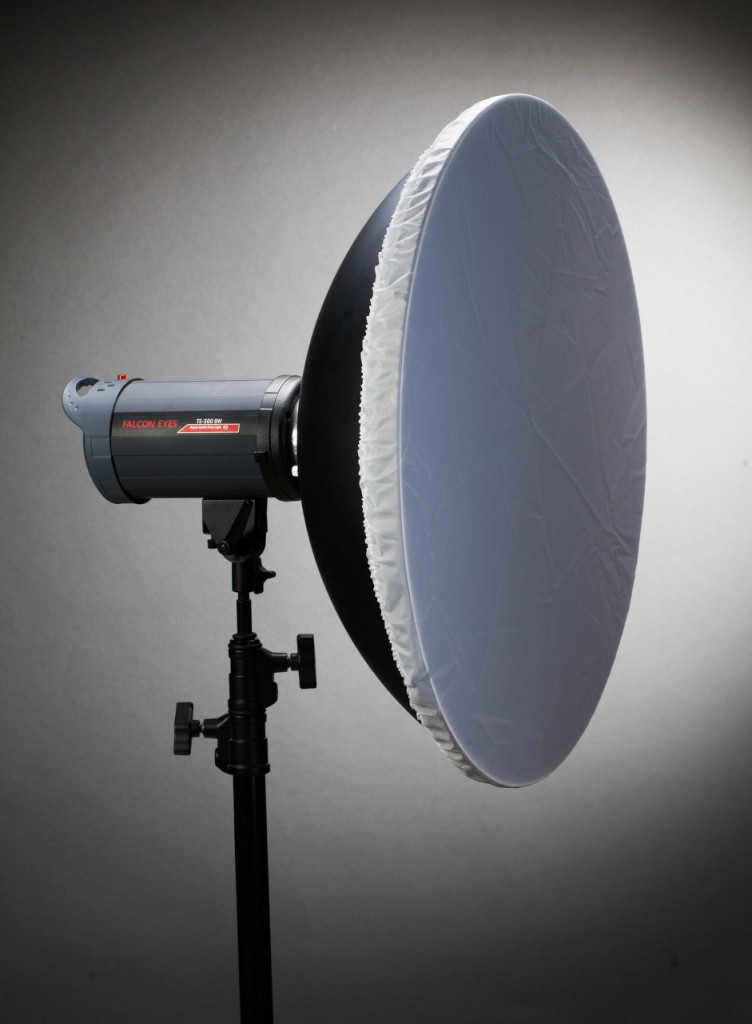

A reflector is an essential tool in studio photography. It helps control and manipulate light to achieve the desired effect. This particular reflector is equipped with a honeycomb and fabric diffuser, making it ideal for portrait photography. The honeycomb helps to focus and direct the light, while the fabric diffuser softens and diffuses it for a more flattering and even lighting. Whether you’re a professional photographer or just starting out, a reflector like this can greatly enhance your photography skills and produce stunning results.

The spherical shape of the portrait plate can be observed from the side.

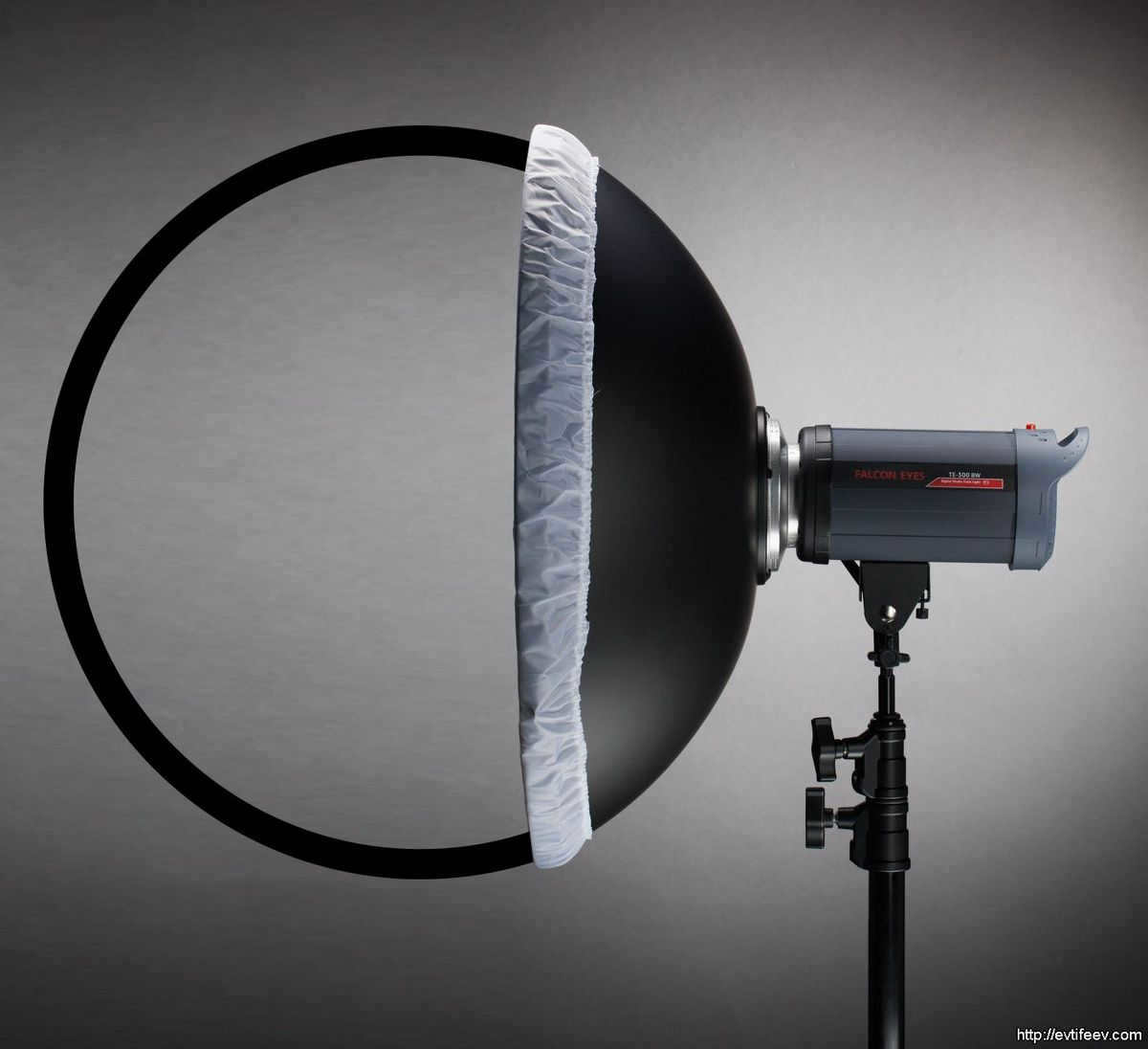
There is a dish without a honeycomb in the portrait – the central deflector is visible.
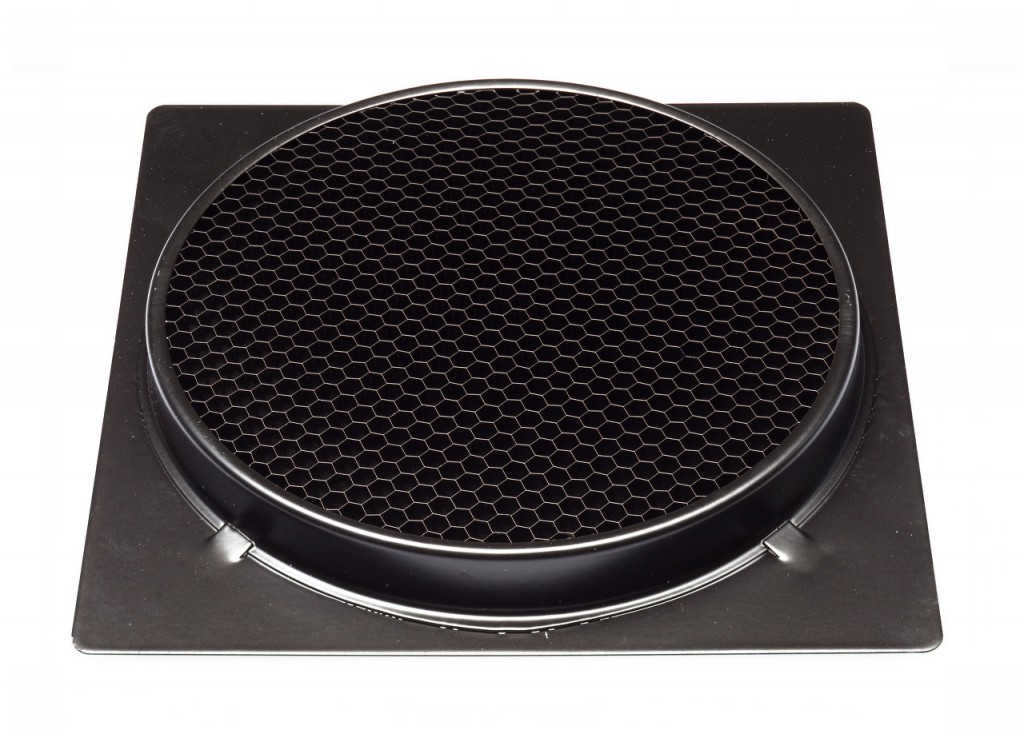

The honeycomb serves as an attachment for the standard reflector, while the honeycomb for the portrait dish functions in the same way but differs in its fixing mechanism.
The portrait dish distinguishes itself from other reflectors in two ways: its larger size and the presence of a deflector in the center. The deflector redirects some of the light to the center of the dish, ensuring even illumination across the entire light spot.

honeycomb-free portrait plate

This is a portrait plate featuring a honeycomb design.

A portrait plate equipped with a honeycomb and fabric diffuser.

pattern of illuminating a portrait plate


Use a portrait plate to create a unique portrait.

Working in the studio, I utilized a portrait plate adorned with a delicate honeycomb pattern.

Glare caused by a portrait plate
Floodlight sources employ a similar concept, although they are a significantly more intricate apparatus in which the lamp can typically be adjusted in relation to the reflector.
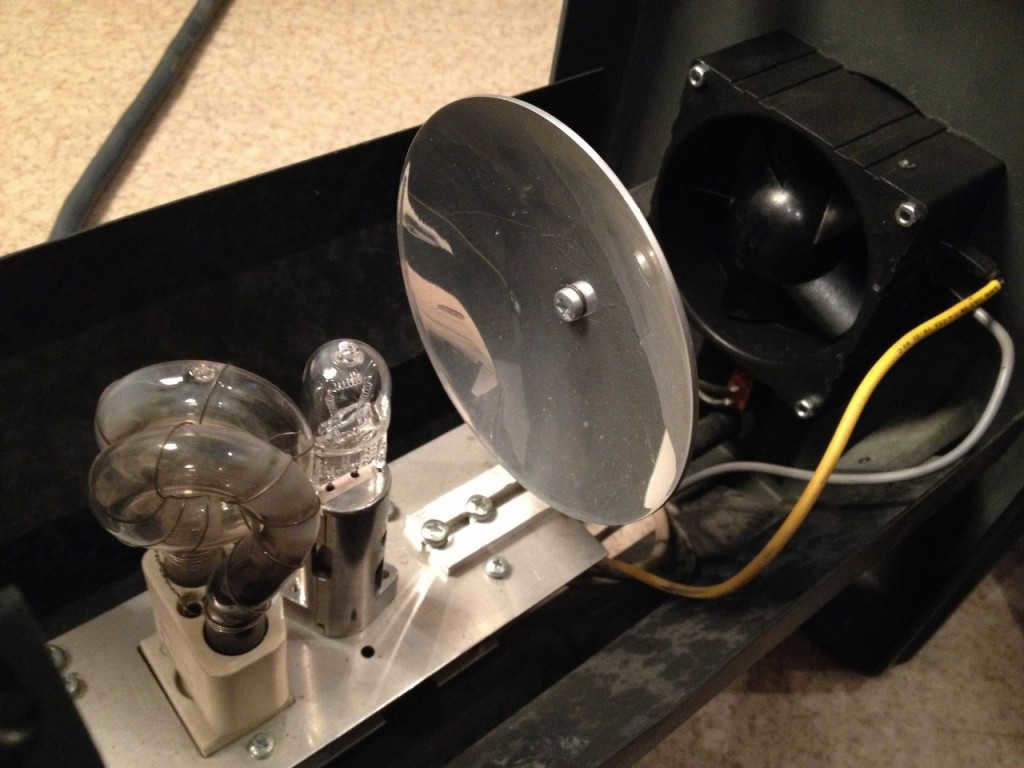

The Pulsospot is an optical device that directs and focuses light into a concentrated spot. This lamp is equipped with movable rails, allowing it to be easily adjusted and brought closer to the reflector.
Essentially, the Pulsospot concentrates the light into a spot and then collects it with the help of a Fresnel lens. In spotlights, the light is further collected after the reflector using a specialized lens.
You can learn more about the application of light sources with Fresnel lenses here. Additionally, there is another resource available that provides information on light sources with Fresnel lenses. Another example of a spherical reflector is a photo umbrella, which is attached to a flash using its own rod and produces a soft, yet less controlled light.
The photo umbrella is utilized due to its compact size and affordability. Additionally, the photo umbrella possesses the capability to adjust its position in relation to the flash. The interior surface of the umbrella can be silver, gold, or matte white. Silver surfaces produce a harsher light, while matte white surfaces produce a softer light.
There are also “on the light” umbrellas, which differ from the reflectors discussed in this article as they are diffusers. However, I will not delve into that topic here.
I will provide further information on photo umbrellas once I have conducted test shots.
Parabolic reflector
In the event that the light source is positioned at the focal point of the reflector, this form of reflector is also capable of gathering rays and guiding them in a parallel direction.
A parabolic reflector with a lamp positioned at its focus
When the lamp is moved closer to the reflector from the focus, the rays will spread out, and if it is moved farther away from the focus point, the rays will come together.

Elliptical Reflector
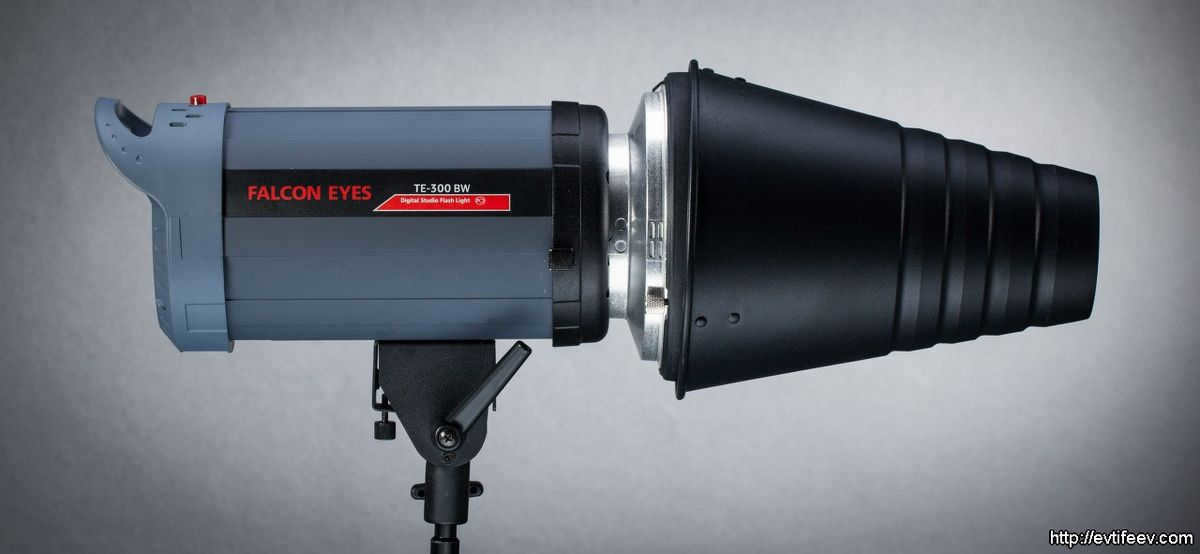
The image on the left displays a conventional 7″ reflector manufactured by Falcon Eyes. Each studio equipment producer offers a unique diameter and configuration for their standard reflector. However, typically, the reflector shown in the photograph represents the average elliptical reflector from that specific photo equipment manufacturer’s collection.

A monoblock equipped with a conventional elliptical reflector

typical form of a reflector
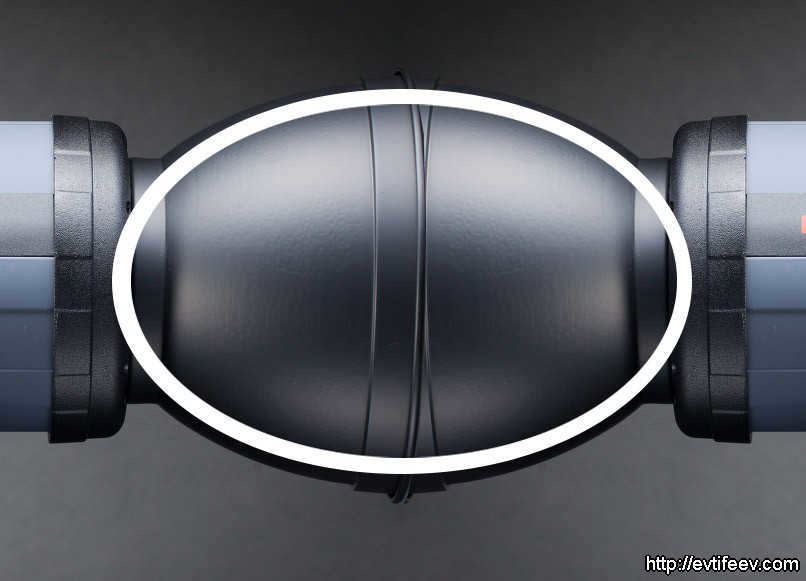

The shape of an ellipse can be achieved by placing one reflector on top of another and overlapping them.
One advantage of using elliptical reflectors is that they are highly effective in creating a bright focal point of light. However, the brightness of the spot may vary depending on the location of the focus, as the rays are convergent rather than parallel, as seen in spherical and parabolic reflectors.
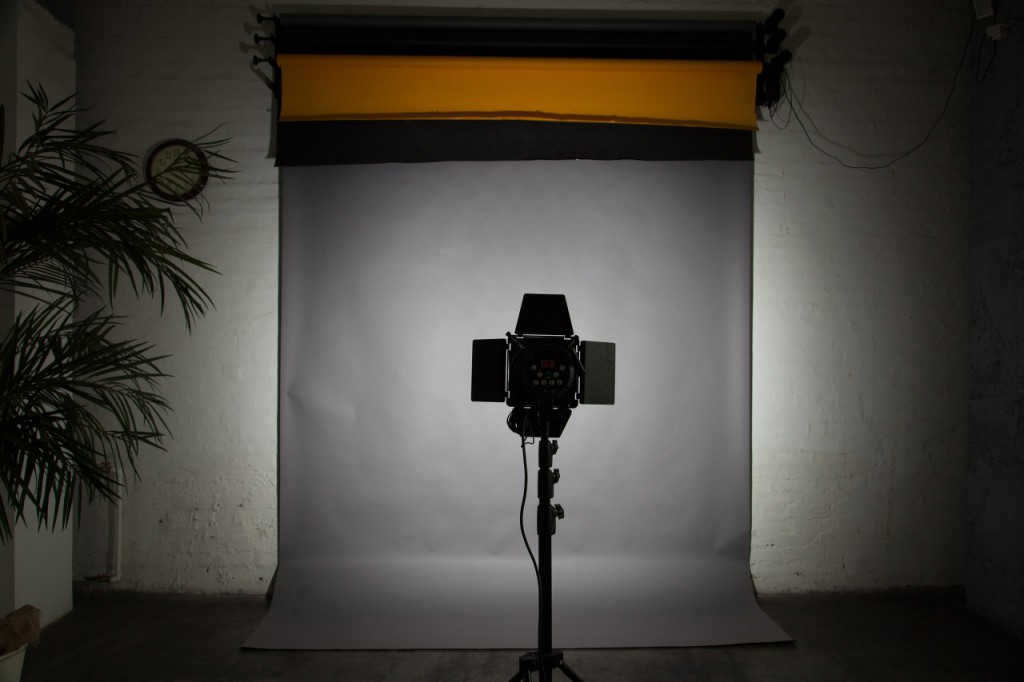

A standard reflector is being used without a honeycomb. The distance from the reflector to the background is 2.5m.
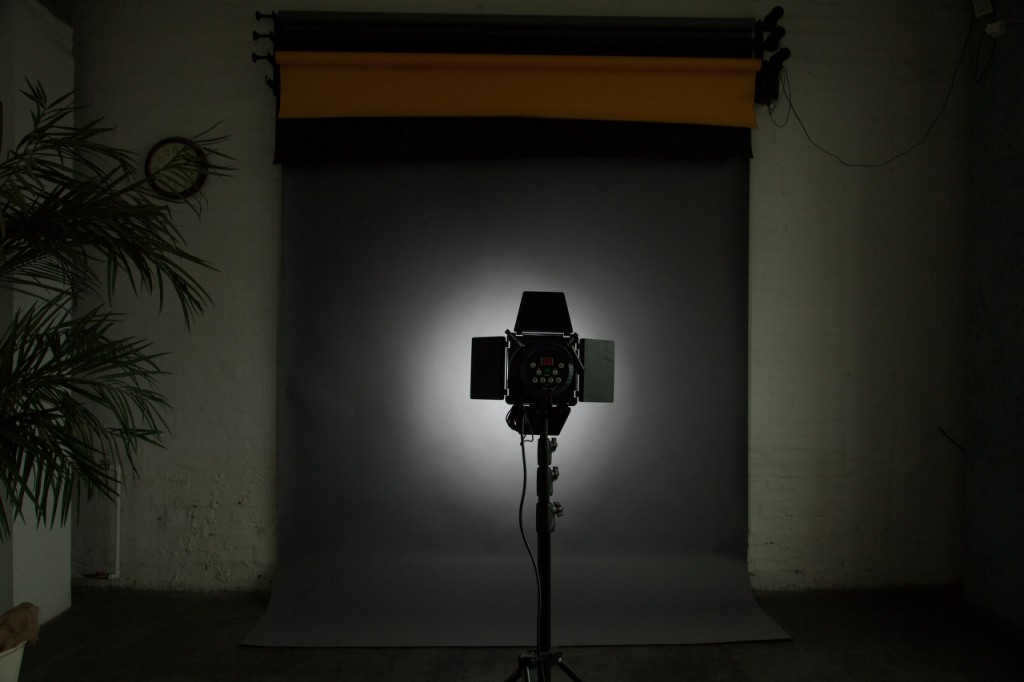

A standard reflector with a honeycomb is used, with a distance of 2.5m to the background. The result is a significantly reduced light spot.
Here is a demonstration on how elliptical reflectors work:
[raw2][/raw2]How elliptical reflectors work – demo.[raw2][/raw2]
Please note that the lamp only moves in very expensive flashes. This demonstration is provided to help understand the principle of operation, “What happens if.” The elliptical reflector is one of the most interesting and sought-after reflectors, commonly found in any photography studio.

The hair is illuminated by a conventional elliptical reflector positioned behind and to the right.

What is a large elliptical reflector?

The shape of an elliptical reflector is what makes it unique. By varying the diameter and depth of the reflector, we can achieve different sizes of light spots and varying degrees of light intensity. Elliptical reflectors, in particular, emit a more rigid light. Additionally, the depth of the reflector affects the size of the light spot, while the diameter determines the softness of the resulting shadows.

A big reflector with no honeycomb, placed at a distance of 2.5m from the background.

A honeycomb-equipped, elliptical reflector of considerable size.


Here is an example of utilizing a typical reflector in the field of subject photography
In order to capture this photograph, we employed two standard reflectors along with two milk acrylic pieces as diffusers. to content ↑
Distinct Varieties of Reflectors
Additionally, there are specialized types of reflectors that are employed for specific purposes. One such type is the Cone, also known as the Snoot.

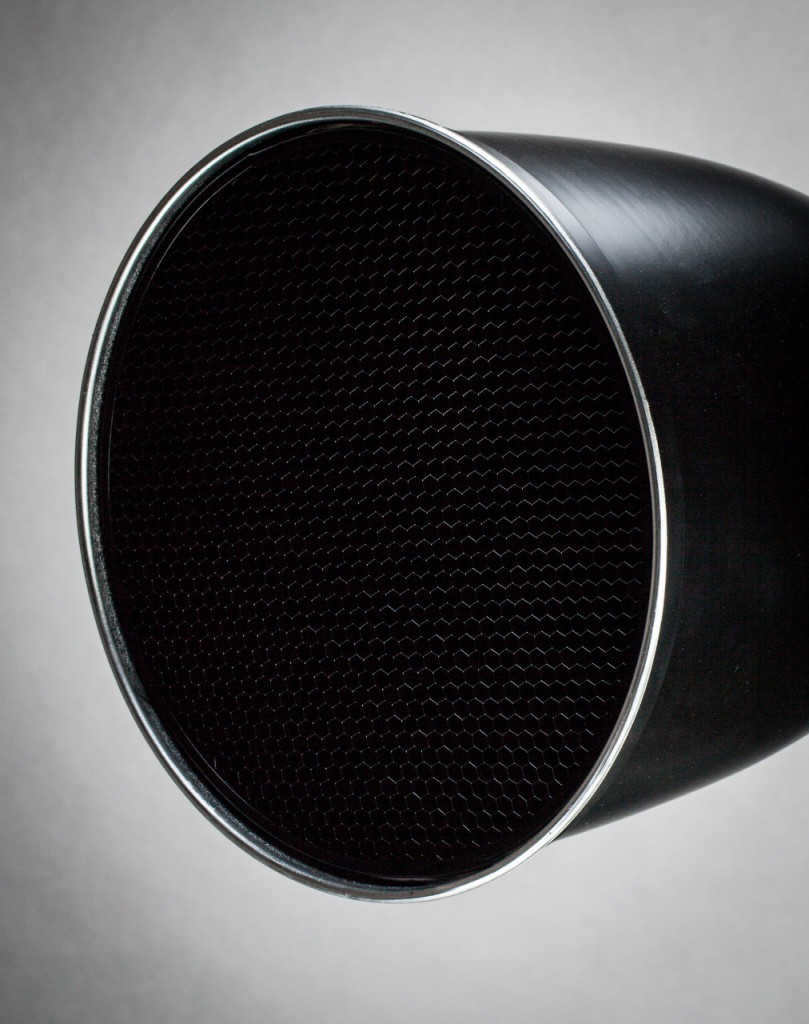
The Falcon Eyes DPSA-CST BW cone reflector is a type of reflector that is specifically designed to limit the light spot. Its conical shape and depth allow for strong light restriction. However, it is important to note that the use of a conical reflector like the Snoot can result in a significant reduction in light output.

The light spot’s characteristics can be altered by using a snoot.
When using a snoot, the center of the light spot is bright and relatively even, with a secondary, dimmer ring surrounding it. Honeycombs are often used with snoots, as well as with other reflectors.
These honeycombs are attached to the front of the snoot and help narrow the light beam, creating a more defined spot.

The outcome of the Snoot’s performance with delicate mesh honeycombs.
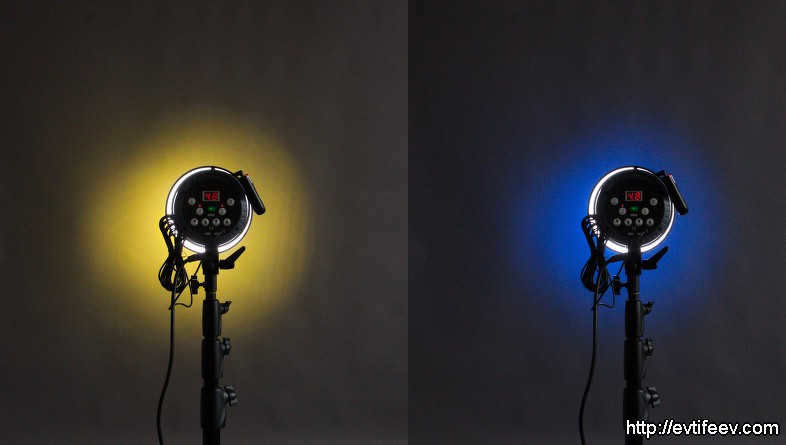

Another option is to place a folium filter in the shape of a circle underneath the honeycomb grid to create a colored spotlight effect.

Application Range The purpose of the Background Nozzle, as implied by its name, is to provide illumination for the background. Its unique design allows for a softer lighting effect on the background compared to a regular elliptical reflector. Here are a few examples of its use.

I didn’t capture a flawless image (the background is slightly uneven), but the main idea is evident. The background reflector disperses the light beam more evenly. to top ↑
In this article I have only covered a few types of reflectors. It is evident that if we consider the broad concept of a “reflector”, we could write about various types of reflectors for a significant amount of time. In future articles, we will continue to explore different types of reflectors. You have now learned about the fundamental studio reflectors, their operational principles, and classic uses. The range of applications is truly only limited by your imagination and the capabilities of the specific reflector. update
When visiting the photo studio, I recommend using colloquial names for reflectors. For instance, if you require a large-sized parabolic reflector, it is referred to as PARA (“Para”, large umbrella).
If you need a small elliptical reflector, it is called a “standard reflector” or “pot”.
A portrait reflector is simply called a Beauty Dish (“beauty plate” 🙂 ).
There are also softboxes, stripboxes, octoboxes, and so on, which will be discussed in future articles since they are not just reflectors but separate devices. I would love to hear your comments and see examples of your work with different reflectors. A new article on studio accessories will be coming soon! Stay connected.) We’ll release the girl. Let her swim.
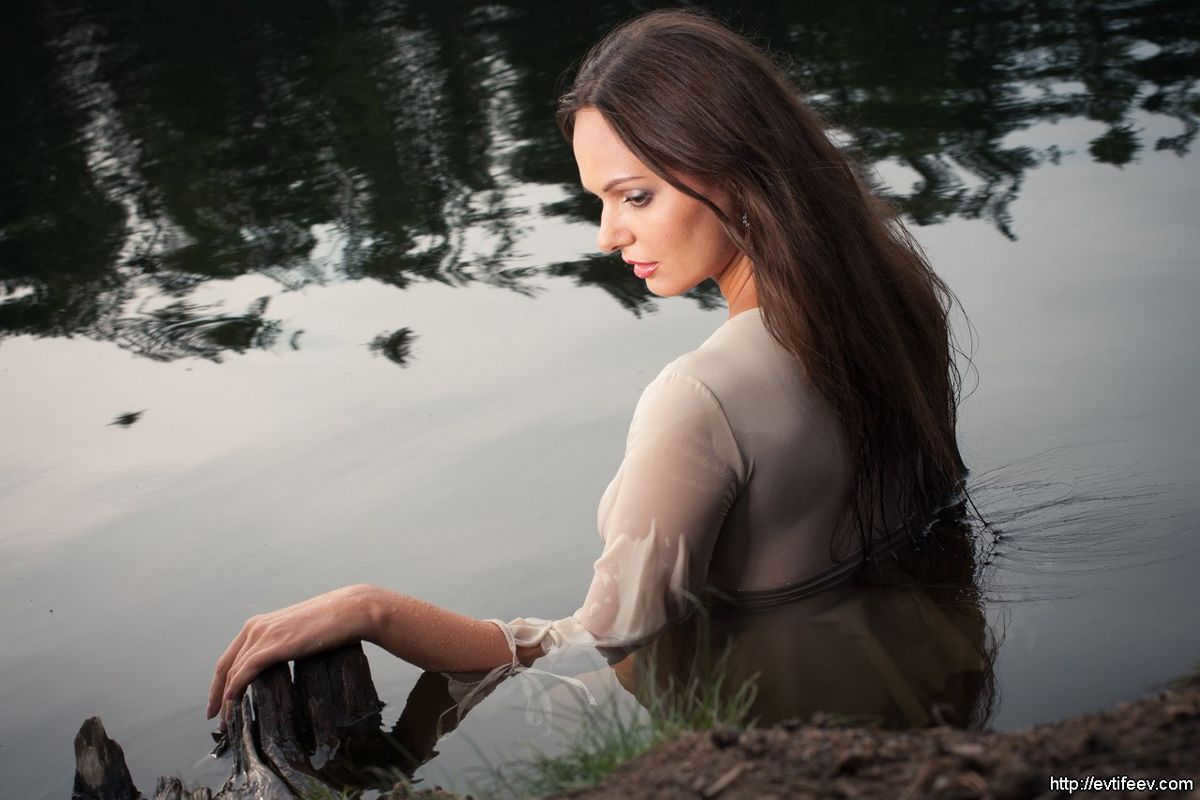

A photo was taken using a reflector to enhance the lighting in cloudy weather.
This post was published in the categories of portrait, Photography Tests, photography, nature photography, and photography equipment. It discusses various tools such as snoot, reflector, portrait plate, light spot, honeycomb, standard reflector, studio light, and foliar filters. The author, Dmitry Yevtifeev, encourages readers to add a permanent link to their bookmarks and share the article on social media platforms like Kontakontakte, Facebook, Google+, etc. The author also requests readers to rate the article with 5 stars if they enjoyed it.
Please rate the article.
If you want to check out my videos, be sure to follow my channel   Here’s my Instagram, where you can see what I’m currently working on.
 Here’s my Instagram, where you can see what I’m currently working on.
 You can find me on Facebook – I post important updates about my articles there.
 I’m also on Vkontakte, although I’m not very active there.
 Don’t forget to subscribe to my RSS feed for recommendations.

Are you interested in getting complimentary, current
articles about photography?
- tests of lenses and cameras
- articles about the evolution of photographic equipment
- confidential photography techniques
- professional ways of editing in photoshop