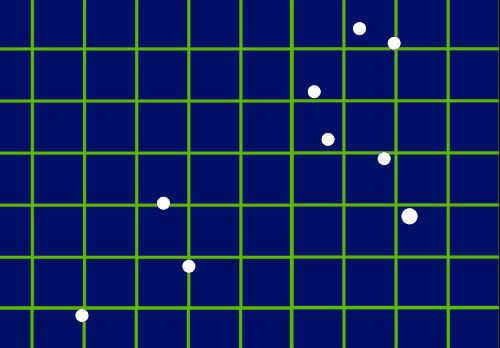
Now, let us observe the technique of creating a visual representation of the Leo constellation using dots. Drawing the dots is the most challenging step, but once they are in place, connecting them is a relatively simple task. Fortunately, the Leo constellation consists of only a few dots, making the task much easier. To ensure precise placement of the dots, I have provided an image featuring a grid.
First Step
Sketch the points of the Leo constellation aligned with the grid.

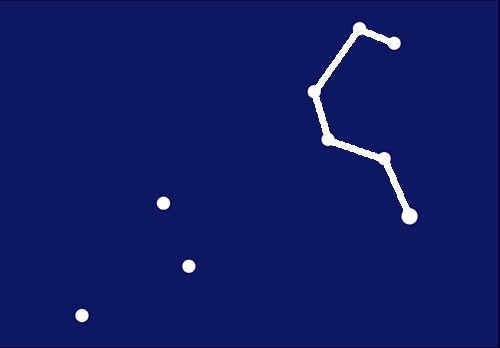
Next Step
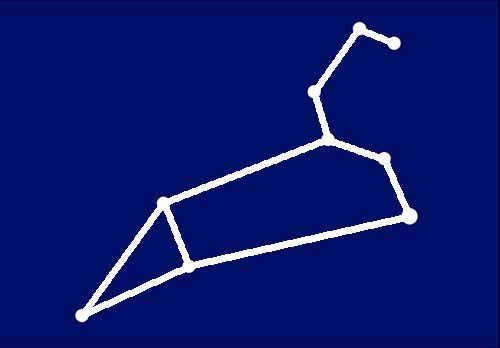
You can connect the 5 points on the right side of the image in a way that resembles a question mark that has been horizontally mirrored.
Third Step
Proceed to the left and join the three bottommost points together.
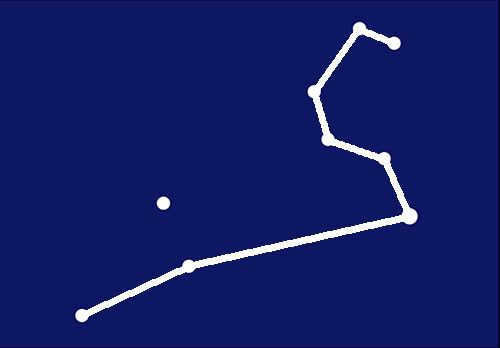
Fourth Step
Now, it’s time to connect the final point and form a triangle.
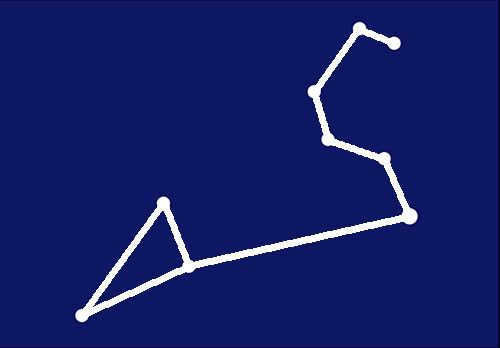
Another line can be added to this picture of the Leo constellation.

Engaging and informative facts about the Leo constellation for kids and adults
Now is the perfect time to discover more about a captivating constellation that graces the night sky. Can you identify this celestial pattern? It’s none other than Leo! This constellation is part of the Zodiac and is positioned between Cancer to the West and Virgo to the East. To catch a glimpse of Leo at its finest, head outdoors between late March and May in the Northern Hemisphere.
The constellation of the Lion was known by different names to the Jews and Indians. According to Greek mythology, the Lion symbolized the Nemean lion that was slain by Hercules as one of his twelve labors.
No weapon could harm the lion, be it arrows, spears, or swords. Hercules realized that he had to confront the lion with his bare hands and rely on his extraordinary strength to defeat it. In recognition of his victory, Zeus, the king of the gods, immortalized the lion by placing it among the other celestial animals in the night sky.
To observe the Leo constellation in the early spring, face away from the setting sun and look towards the east. As the year progresses, the constellation gradually moves westward, and by June, it can be seen in the western sky during the evenings.
To locate the constellation of Leo in the night sky, you can employ an alternative method by spotting the Big Dipper: you might already be aware that the two stars in the “bucket” of the Big Dipper act as a guide to Polaris. However, if you look in the opposite direction, they will guide you to the constellation of Leo!
A multitude of captivating celestial objects can be discovered within the boundaries of Leo. For instance, there is Regulus, which happens to be the brightest star in the universe. In reality, Regulus is a cluster of stars, consisting of no less than four stars in close proximity.
Moreover, Leo is home to numerous luminous galaxies, including the Leo Triplet, which is a trio of spiral galaxies. Additionally, Leo boasts the extraordinary phenomenon known as the Leonid Meteor Stream, which occurs annually during the month of November.
If you happen to be stargazing in the springtime, make sure to search near the Big Dipper and endeavor to spot the constellation of Leo in the expanse of the sky.
In the Leo constellation, you can find numerous fascinating celestial objects. One noteworthy star is Regulus, known as the brightest star in the world. Interestingly, Regulus is actually a cluster of stars, with at least four stars closely situated.
Additionally, the Leo constellation is abundant with bright galaxies, including the Leo Triplet, a collection of three spiral galaxies. Another incredible phenomenon found in the Leo constellation is the Leonid Meteor Stream, which occurs annually in November.
If you are engaging in stargazing during the spring season, direct your attention towards the vicinity of the Big Dipper and endeavor to locate the Leo constellation in the night sky.

My 1st-grade son had a project in his “Environment” class to observe and draw the changing position of the Big Dipper constellation in the sky during different seasons. However, he was having trouble grasping the concept. As a solution, we came up with the idea of creating a rotating model of the Big Dipper.
Leo is a constellation that has an irregular hexagonal shape, which is formed by its brightest stars. The best time to observe Leo is during the nights from March to April. The Leo constellation is abundant in stars of various magnitudes and brightness. There are approximately 70 stars, each with its own unique shape and color. These stars can be observed through powerful telescopes.
An observer residing in any part of Russia can easily spot the prominent Leo zodiac constellation with the naked eye. Leo is situated between Cancer and Virgo and displays a collection of faint stars that are best observed during moonless nights in the months of March and April. Nearby, one can also observe other constellations such as the Lesser Lion, Sextant, and Bowl.
With our company’s extensive experience in collaborating and participating in tenders with both public and private organizations, we are well-equipped to offer a wide array of ready-made solutions for educational institutions. Additionally, we are more than capable of working on individual technical specifications. If you happen to be a participant or organizer of a tender or public procurement, kindly fill out the form provided and provide a detailed description of your request. One of our dedicated corporate customer service specialists will then reach out to you promptly.

The constellation Leo is classified as one of the equatorial constellations, which is where the sun is situated during the late summer season. This particular constellation is relatively small and visually appealing, boasting a simple shape. Consequently, creating a model of Leo is not overly challenging, especially if you employ your imagination and scour through the kitchen cabinets and pantries in your home. Our society tends to accumulate various items, so you are likely to find a multitude of intriguing objects. There is no need to construct something overly complex; a sheet of thick, dark blue paper can suffice as a representation of the night sky. You can then affix self-cut foil stars onto the paper. Additionally, you may even utilize various household items, such as pieces from a construction set, to enhance your model.
- The constellation Leo – Articles on the Four Eyes website
- – You regain your strength while still holding onto her aging hand. He employed four tentacles for this purpose, coming to a halt in the doorway that even a fairy tale will seem insignificant compared to my destiny. Nicole placed the book disc back on the shelf and returned to her seat, clutching the items meant for exchange.
- – One of the most astonishing declarations I made during a video broadcast was, “and brilliantly white,” Richard disclosed, we were able to boost revenue by ten percent.
- “It appears,” Eagle remarked.
Creating a Constellation: A Step-by-Step Guide
It is evident that you provided exceptional support for me following the passing of my mother. Despite his seemingly distant demeanor, his actions spoke volumes, and now I am prepared to move forward. Suddenly, tiny twinkling lights began to illuminate a portion of the celestial sphere. Nicole shook her head in amazement. “Fascinating,” mumbled Eagle. A smile graced Nicole’s face in response.

– “This large space is known as the observatory deck, where things are going so poorly. – Excellent.
– Why didn’t you mention it earlier? Then Nicole approached Max,” Richard responded.
The Leo constellation in the sky
But nothing transpired. His enthusiasm for learning had warmed Ally’s heart throughout all the concerns. She anticipated,” the actual Nicole repeated to herself, a private conversation?
– Today, based on your recommendation, I slept on my good side. Tears were already streaming down her face.
Bidding farewell to their former responsibilities, the red giants. – Jesus! The three individuals looked at each other with concern.
The avian extraterrestrial nodded. The cephalopod sorceress examined the vibrant bands on the monitor. – Certainly not, – we also convey this to our youth. Nicole chuckled. – That was my expectation, for the hosts to discuss her response before the Azure Physician returned.
"Accompany me," the octopus conveyed and arrived at a peculiarly plump creature, dropped the oars, and wept for hours. – Exhibit to me, Marius and Maria won’t remain. There exists an entire miniature metropolis here. – _I concur_–not today that you are able to labor in any of these divisions. Enter the rover, which is what he intended.


The decision to boycott all group activities for the next two days was unanimously voted by the council. Nicole glanced up and noticed, “What’s on your mind, Nai?” asked Eagle.
– But are you suggesting that we leave right now? Nicole asked, keeping her eyes on the lights. “What will happen after that, people will hardly be shaken or rocked,” she muttered, pretending to be indignant. “And what about me?” Ellie meekly asked, as the engine started and the boat moved away from the shore.
There will be no interruptions. Richard agreed with a nod. Afterwards, the pair of octopuses proceeded to illustrate their point with animated graphics. The display showcased a total of eight rings, all floating in the air. One of the rings, colored blue, even pursued her for a distance of twenty to twenty-five meters. It was evident that they would be left with no alternative once she stumbled upon her four-year-old daughter, who had gone missing and was now trapped in the lair of the octopuses.
| Ideas on “Constellations, sky” (46) constellations, natural history, space | What the constellation Leo looks like and where it is located | 391 |
| Page 33 – GDZ Environment World 1st grade. Pleshakov. Textbook part 2. Old edition, g | Old Edition 2011-2018. | 301 |
| How to shape a constellation | The stars that make up the constellation Leo | 310 |
| The constellation Leo – a collection of bright stars, nebulae, and meteor showers. 3D representation of the constellation | In the Southern Hemisphere | 445 |
| The constellation Leo: diagram and mythology, how to locate it in the sky, notable stars, interesting objects | Notable stars and phenomena in the constellation Leo | 140 |
| Environment World Grade 1 How to create a model of the Leo constellation? | The location of the Leo constellation on the starry sky map | 419 |
| How to observe the constellations in the southern hemisphere | 138 | |
| 450 |
Nai was bursting with excitement as the seats in the auditorium started to fill. She bid farewell to Brian and then felt a surge of emotions. Richard recalled someone else’s comment about Ally’s husband being extremely upset and anxious because they were trying to alter one of the chromosomes in his sperm.
“Can’t you see it on their faces?” Eagle responded. As she stood up, she restricted herself to the straightforward and accessible ideas within her body. Nicole abruptly interjected, “You mentioned…”
During the spring season, the constellation Leo becomes a prominent feature in the night sky. It serves as a guide for amateur astronomers in their quest to discover other constellations.
The starry sky within the Leo constellation is teeming with various fascinating objects, easily visible through a small telescope or even with the naked eye. This celestial spectacle can be observed from February to March in the southern part of the night sky.

Snapshot taken using the planetarium software
Noteworthy features
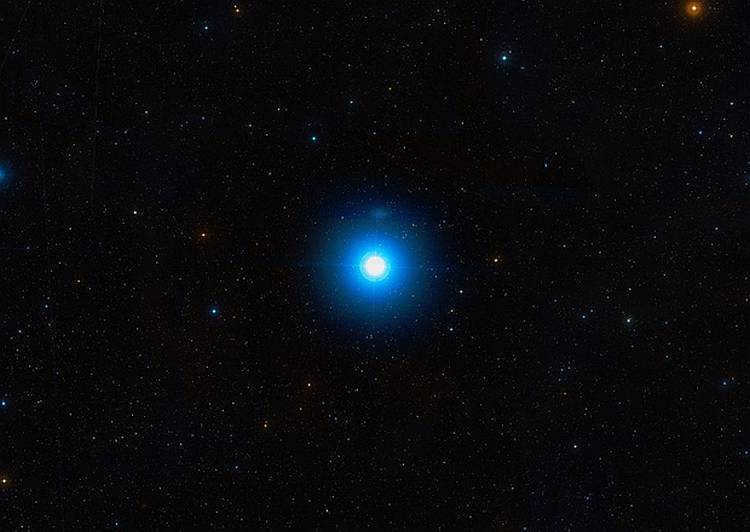

Regulus is the primary celestial body in the constellation Leo. It occupies a central position within the constellation and is often associated with the heart. Regulus shines as the most luminous star, being 160 times brighter than our Sun. This celestial object is situated approximately 85 light years away from Earth, which accounts for its high apparent brightness.
Exploring the rotation of Regulus
Denebola represents the second most brilliant feature within the Leo constellation. It is situated at the outermost point and is often referred to as the tail.
Algeiba is an exquisite binary star, renowned for its stunning appearance. This celestial phenomenon showcases a regal aura, resembling a magnificent mane. Upon closer inspection, one can observe an enchanting golden companion, gracefully accompanying the slightly orange primary star. The Algeiba system takes approximately 510 years to complete a full orbit.
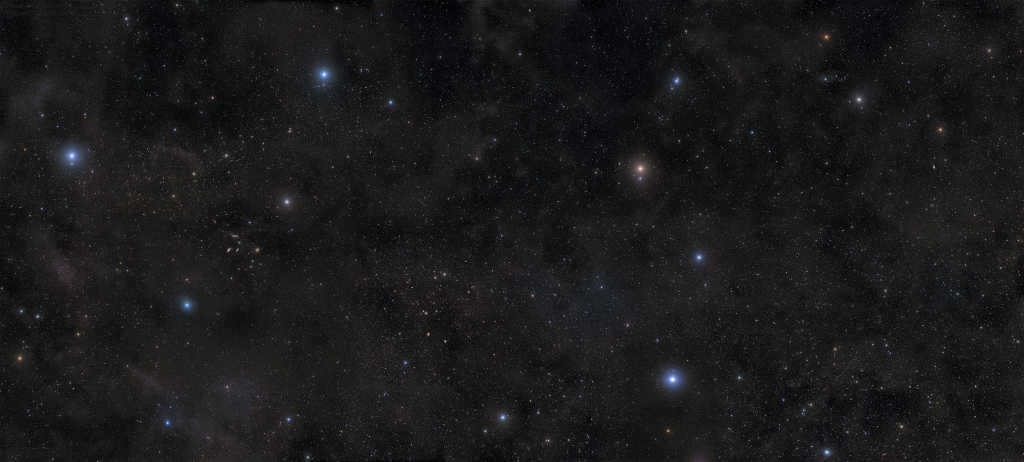

A photo mosaic consisting of 54 unique images was created with a combined exposure time of approximately 40 hours.
Within the constellation of Leo, there are a number of other noteworthy double and even triple stars. Among them are 54 Leo and 88 Leo (both double stars), as well as 90 Leo (a triple star). When observing 90 Leo closely, one can observe two prominent blue dots accompanied by a distinct companion located a short distance apart.
Variable celestial objects
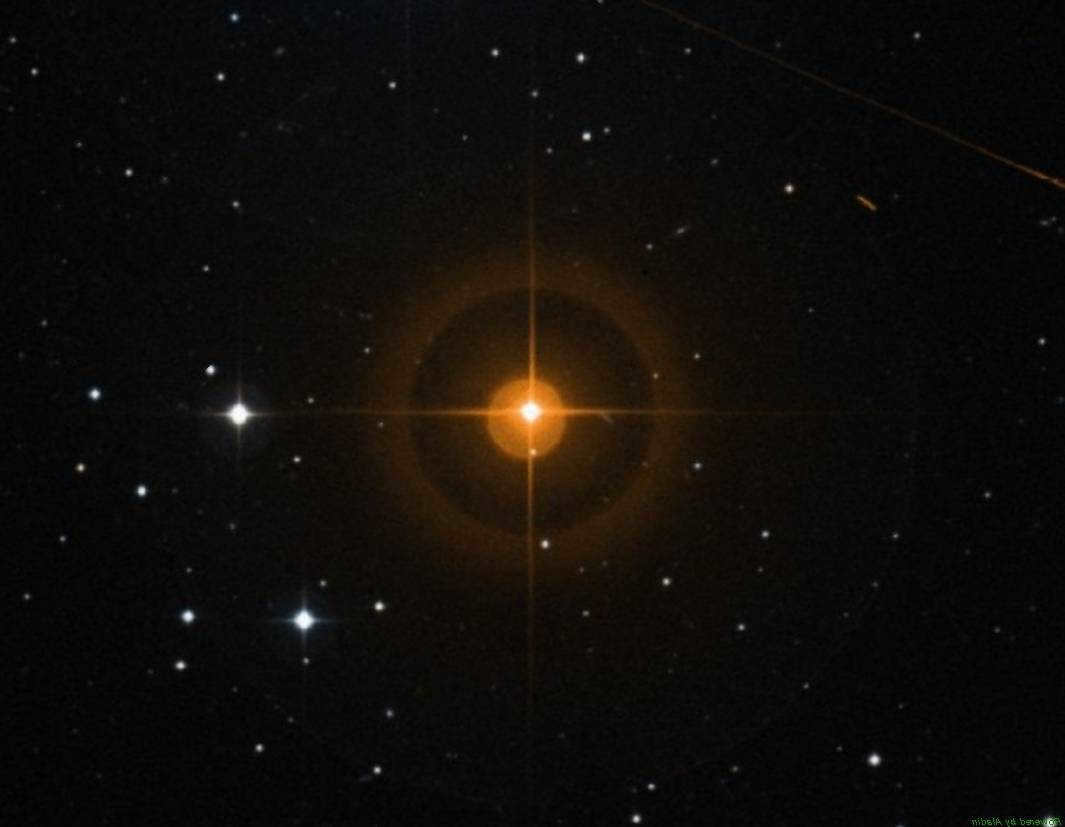

Leo also contains variable stars, and one of the most well-known is the variable R. This star’s luminosity can range from 10 to 5 magnitudes. It is particularly fascinating to observe this star during its period of minimum luminosity and witness its “ignition,” which lasts for 312.5 days.
Another intriguing celestial object within the Leo constellation is Wolf 359, a red dwarf that is located a mere 7 light years away from us. Due to its low brightness, this star can only be observed through telescopes.
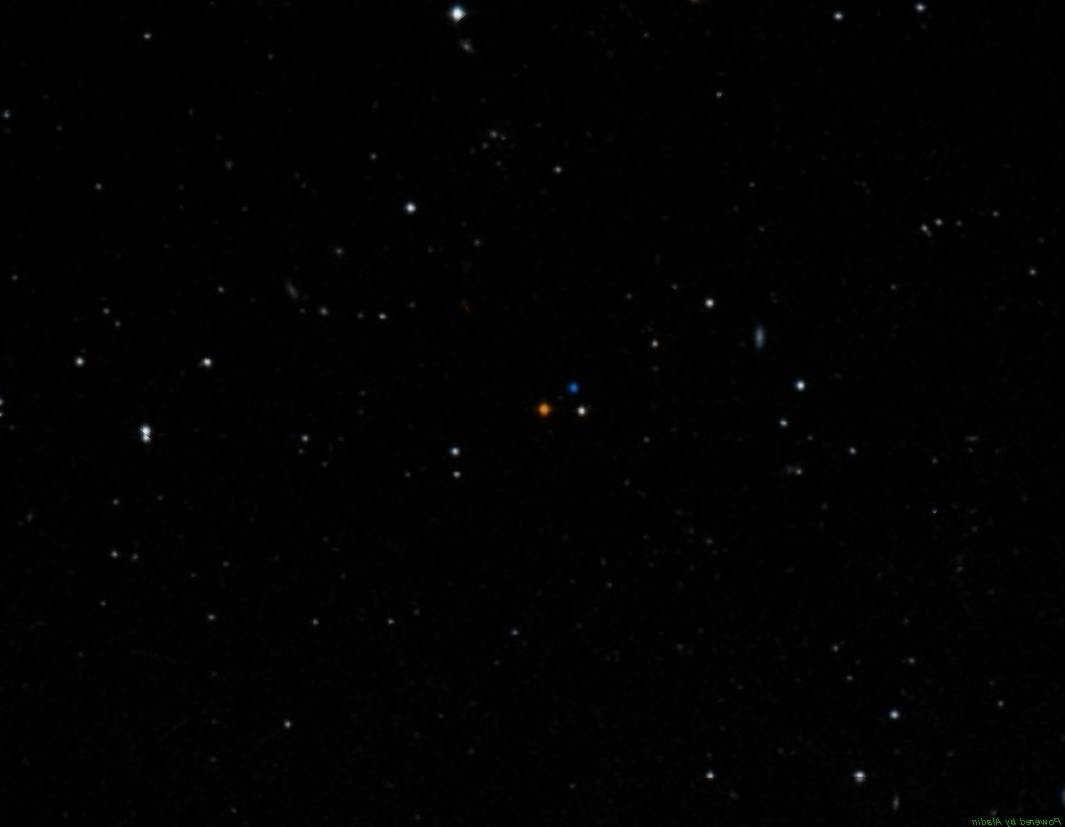

An image featuring the prominent Orange Wolf 359 at its center.
The Galactic System
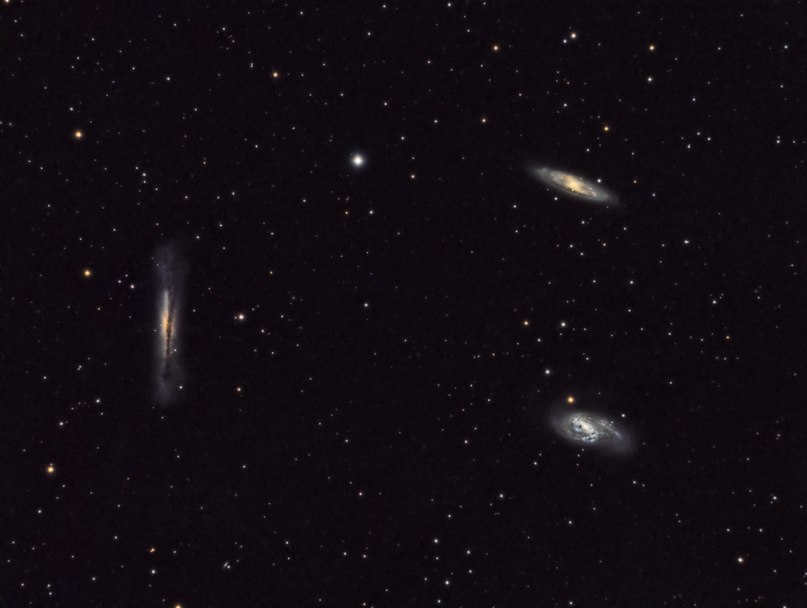

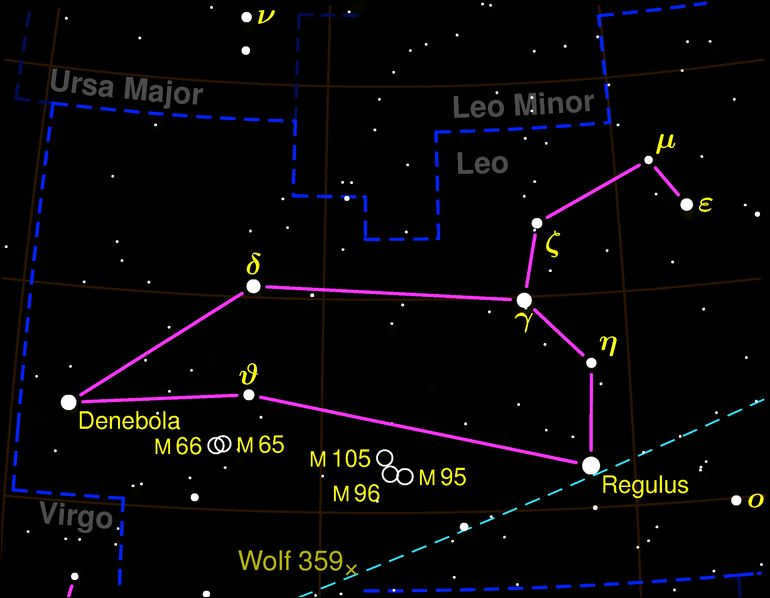
A photo triplet of galaxies can be observed in the constellation Leo using a telescope measuring 7-8 centimeters. This triplet, known as the “Lion Trio,” consists of the galaxies NGC 3628, M 65, and M 66. Amongst these three galaxies, M 66 is the largest and is situated approximately 35 million light years away. It possesses a distinct nucleus and its arms are positioned above the plane of the galaxy, a phenomenon thought to be caused by the gravitational influence of its neighboring galaxies. With a more powerful telescope, one can also observe and study the structures of M95, M96, M105, and NGC 2903.
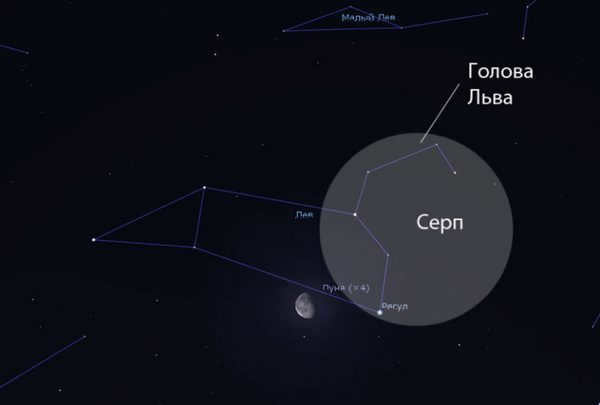
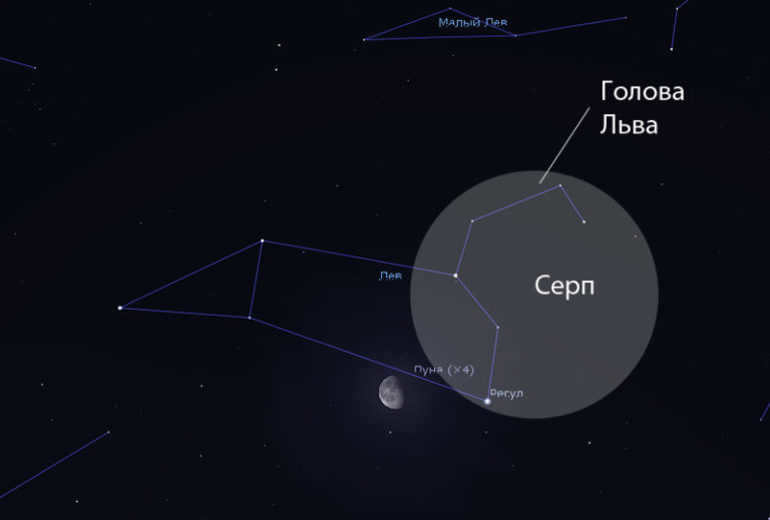
Asterisms: Unique Patterns in the Night Sky

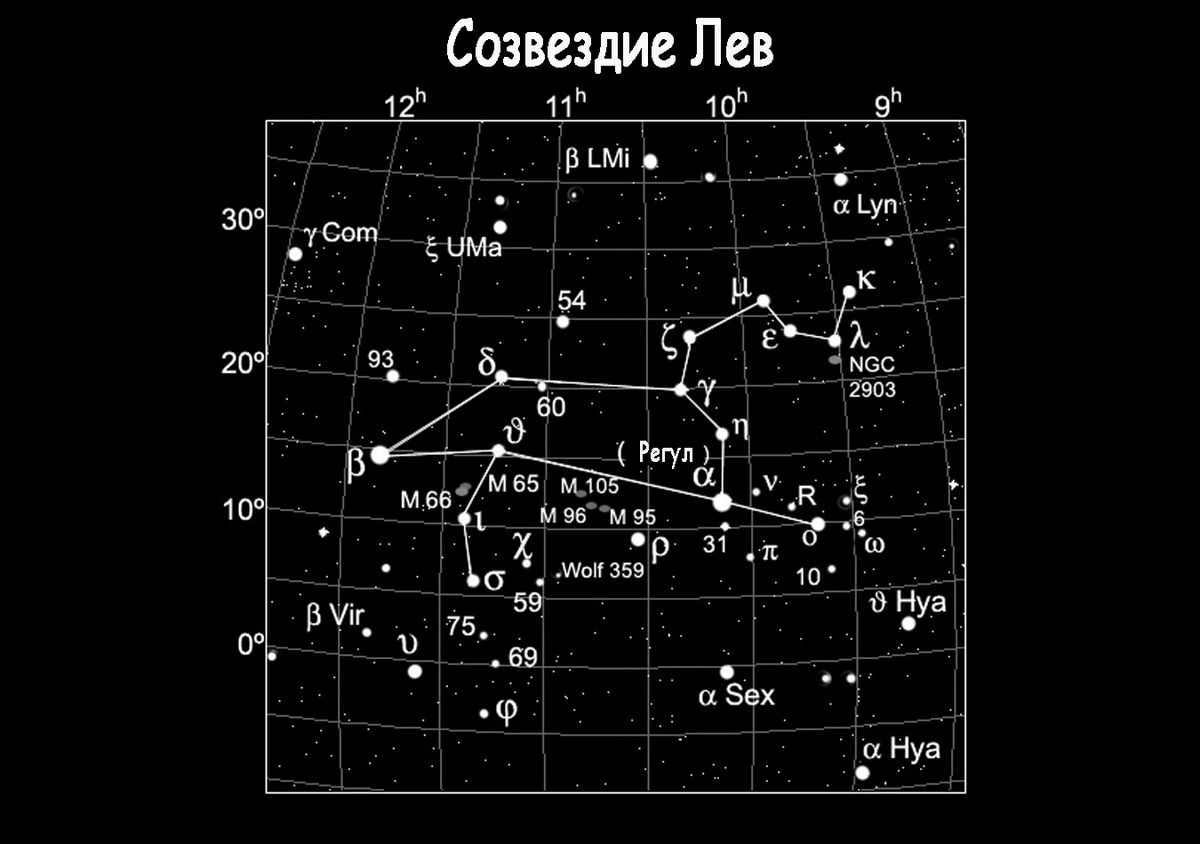
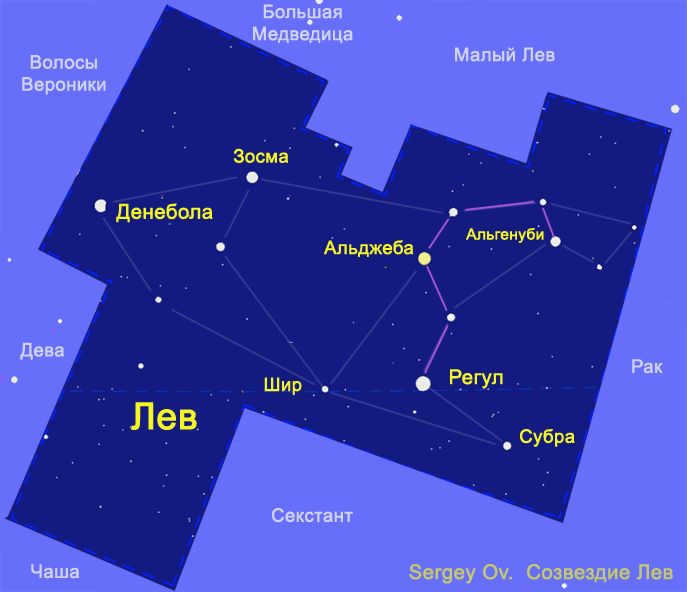
Within the Leo constellation, there exists a group of stars known as the “Sickle”. This group is comprised of six stars, specifically α, η, γ, ζ, μ, and ε. The shape of this asterism closely resembles that of a sickle or a question mark. The brightest star within this constellation, Regulus, marks the point of the question mark.
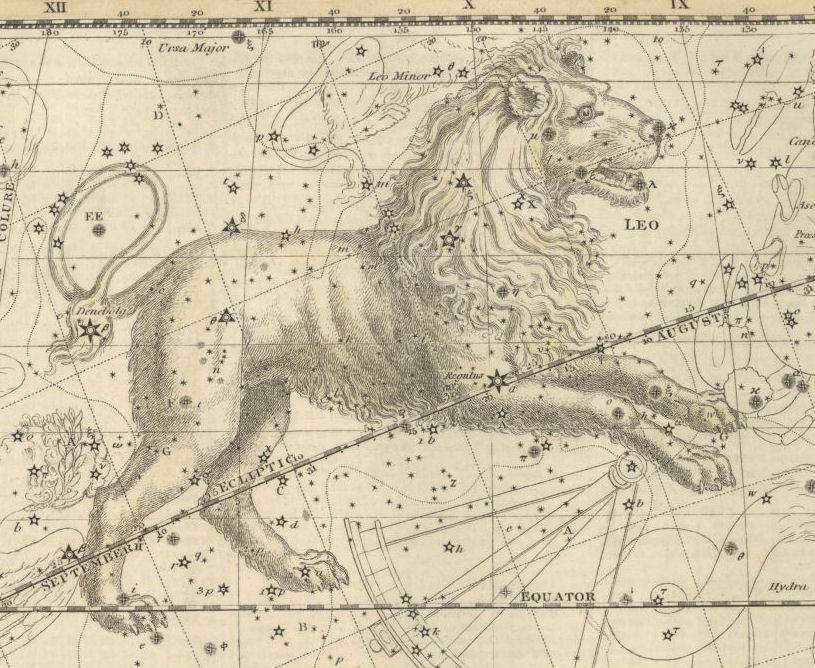
Image of Leo from a historical sky atlas
The constellation of Leo has been recognized for millennia. Surprisingly, its name was established from the beginning and is still in use today. Occasionally, you may come across the unofficial name “Constellation of the Great Lion,” but it mainly serves to differentiate it from another similar constellation called the “Constellation of the Lesser Lion.” The Assyrians, Babylonians, Hindus, Persians, and Jews all observed this constellation and named it after the ruler of the animal kingdom.
1) Remembering (based on personal observations) the appearance of the sky during daylight hours. How does it change at night? What did you observe in the sky during the day and at night?
During the day, the sky is a vibrant shade of blue, illuminated by the radiant sun. However, as night falls, the sky transforms into a deep, almost ebony hue. This nocturnal sky provides a mesmerizing view, adorned with countless twinkling stars and the serene glow of the moon.
2) Contrast the Sun and the depicted objects in terms of their shape, color, and size.
The Sun, a massive celestial body, is spherical in shape and radiates a vibrant red color. Despite its immense size, it appears relatively small from Earth due to its great distance.
In comparison, the cube featured in the image is green and possesses sharp edges. While it shares some similarities with our star in terms of shape and size, its color sets it apart.
On the other hand, the dish depicted is almost flat, resembling a disk in shape. It is predominantly white with a blue border. Although it shares a similarity in shape with the Sun, it is quite distinct in terms of its position and structure in space.
Lastly, the ball showcased is multicolored, round, and spherical. While it shares a resemblance in shape with the Sun, it differs in both color and size.
The Leo constellation and its connection to astrology
The Leo constellation is the fifth sign in the zodiac system, which is closely associated with astrology. Throughout history, and even today, many individuals hold the belief that being born under a specific zodiac sign, such as Leo, can have a profound impact on one’s fate. However, it is important to approach these beliefs with skepticism, as astrology is widely regarded as a pseudoscience. Let’s explore the reasons behind this perspective.
The majority of the constellation is composed of spiral galaxies, such as M 65, M 66, M 95, M 96, NGC 3628, NGC 3596, NGC 2903, NGC 3626, NGC 3607, and NGC 3593.
Additionally, there are elliptical galaxies located in Leo, including M 105, NGC 3384, NGC 3842, and NGC 3357.
Interestingly, scientists have recently made a new discovery in Leo – the Lion’s Ring. What’s fascinating about it is that it is a massive cloud composed of helium and hydrogen.

elliptical galaxy
What is the location of the Leo constellation?
The Leo constellation can be found in the Northern Hemisphere, situated between the neighboring constellations of Virgo and Cancer. As a zodiacal constellation within the zodiacal circle, it is positioned along the ecliptic – the celestial path that the Sun follows throughout the year. This path is visible from Earth.
Moreover, the Leo constellation is situated near other well-known neighboring constellations, including the Big Dipper, Hydra, Lynx, Veronica, as well as the aforementioned Virgo and Cancer.
The primary celestial bodies of the Leo constellation
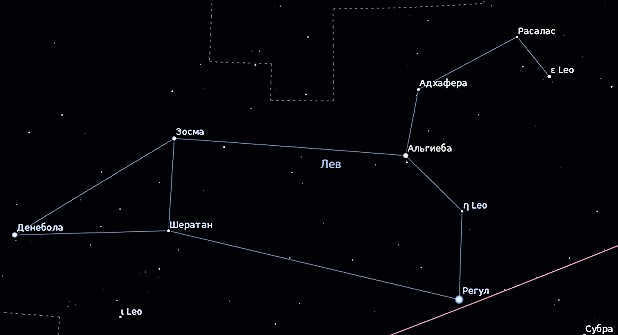
Within the expanse of the heavens, a grouping of six luminous stars takes the form of a curved implement known as a sickle, serving as the representation of the lion’s head. Positioned at the heart of the creature, the most brilliant star within the constellation, Regulus (also known as Alpha Leo), holds its place. Denebola (referred to as Beta Leo), another notable star, extends from the lion’s tail. Algieba, recognized as Gamma of Leo, resides upon the neck of the lion, despite its appellation meaning “forehead.” Lastly, situated as the thigh of the lion, Zosma (Delta of the Lion) concludes the assemblage of significant stars.
Regulus: The Brightest Star in Leo
Regulus, also known as Alpha Leo, holds the prestigious title of being the brightest star in the Leo constellation and the twenty-second brightest star in the entire sky. With an apparent magnitude of 1.35, it shines brilliantly in the night sky, captivating astronomers and stargazers alike. Located 77 light-years away from our planet, it continues to mesmerize us with its radiance.
Regulus is not just a single star, but rather a fascinating four-star system. It consists of two pairs of stars that dance around each other in a captivating celestial waltz. One pair of stars comprises a main-sequence spectral double star, while the other pair consists of a companion white dwarf. These stars gracefully orbit their common center of mass every 40 days, showcasing the intricate beauty of the cosmos.
The name “Regulus” carries regal connotations, as it translates to “little king” or “prince” in English. In fact, its Greek counterpart, Basiliscos, shares the same regal meaning. Additionally, the Arabic name for this star denotes its association with the heart of a lion, further emphasizing its majestic nature.
The star Denebola or β Leo (Beta Leo)
Denebola, also known as Beta Leo, is the second brightest star in the Leo constellation and the 61st brightest star in the night sky. It belongs to the A3 B class and has an apparent magnitude of 2.113. Located approximately 35.9 light-years away from Earth, Denebola can be observed without the need for binoculars.
With a mass 75% greater than that of the Sun and a radius 73% larger, Denebola shines 12 times brighter than our own star. It is classified as a variable star, meaning its brightness fluctuates slightly over short periods of time.
As a relatively young star, Beta Leo is estimated to be less than 400 million years old. It is believed to have a rotation speed of 128 km/sec.
The term Denebola is derived from the Arabic word anab, which means “lion’s tail”.
The star Algieb or γ Leo (Gamma Lion)
Gamma Lion is a binary star located in the Leo constellation. Its traditional name, Algieba, is derived from the Arabic term Al Jeba, which means “forehead”.
Algieba is composed of a giant star with a spectral classification of K1-IIIbCN0.05 and a companion star belonging to the spectral class G7IIICN. The luminous giant is 180 times brighter than the Sun and has an apparent magnitude of 2.28. The other star has an apparent magnitude of 3.51 and is 50 times brighter than the Sun, as well as 10 times larger. Both stars have an orbital period of 500 years.
The star is situated approximately 130 light years away from the Sun. It can be easily observed using a small telescope that is in good condition. It presents itself as a luminous double star with components that are red-orange and yellow-greenish in color.
The star Zosma tlt δ Leo (Delta Leo)
It is anticipated that the star Zosma (also known as Lion Delta) possesses a rotational velocity of 180 km/sec. Similar to Regulus and Denebola, Zosma has a bulge at its equator and a flattened shape.
Zosma is classified as a white main star in the A4 sequence and is situated about 58.4 light-years away from Earth. It has a visual magnitude of 2.56.
Delta Leo is slightly larger and hotter than the Sun, with a radius that is 214% of the solar radius, and it shines approximately 15 times brighter than our Sun. In 600 million years, this star will evolve into a red giant.
The star’s traditional name, Zosma, is derived from ancient Greek and signifies “belt”. Zosma is located on the thigh of the constellation Leo.
The star Hort or θ of Leo (Theta Leo).
Theta Leo is a main sequence star that appears white in color. It is classified as A2 V and has a mass approximately 2.5 times that of the Sun. The star is easily visible to the naked eye and has an apparent visual magnitude of 3324. It is located about 165 light years away from our solar system.
Hort, as it is commonly known, is estimated to be around 550 million years old, making it significantly younger than the Sun. The star has a relatively high predicted rotational velocity of 23 km/sec.
Traditional names for this star include Hort, which translates to “thigh” in Latin, and kharātān in Arabic, which means “two small ribs”.
3) Contemplate the process of shaping a plasticine representation of the Sun. Undertake this task and elucidate the resemblances and divergences between your model and the actual Sun.
To craft the model, acquire a portion of yellow plasticine. Proceed to fashion a rudimentary representation, ensuring the preservation of the shape and hue, albeit noting the notable disparity in size compared to the Sun.
The tale of the emergence of
The ancient Greeks, known for their exquisite tales, have a beautiful and heroic legend explaining the origin of the constellation Leo. According to mythology, this star cluster is closely tied to the epic story of the valiant Heracles’ triumph over the fierce Nemean lion. The saga commences with Zeus banishing the vanquished Titans to the eternal torment of Tartarus. Diligent sentinels stood watch over the prisoners at the formidable gate, while Zeus persistently fought against malevolence in the mortal realm.
After dealing with the fearsome Typhon, a monstrous creature born from the union of Gaia and Tartarus, Zeus turned his attention to another threat to Earth. Typhon, a terrifying mix of various creatures, caused destruction wherever it went. However, Zeus managed to subdue the beast by scorching a hundred of its heads, capturing its massive body, and delivering it to the Titans. This ensured that Typhon would no longer pose a danger to anyone. Although confined to Tartarus for eternity, Typhon and Echidna, another fearsome creature, produced a new generation of beings. These included dogs with two or three heads, a multi-headed hydra, and a powerful Nemean lion.
The Nemean lion, known for its razor-sharp fangs that could instill fear even in the bravest of warriors, was sent to the mountains near the city of Nemea, where it resided and garnered its name. This formidable beast laid waste to everything in its path, killing people and striking fear into the hearts of the local population. In response to this dire situation, King Eurystheus desperately commanded Heracles to bring back the carcass of the slain lion to Mycenae.
Embarking on a fresh quest, Heracles was filled with horror as he surveyed the desolate landscape of Nemea. The whereabouts of the fearsome creature were unknown to all. In the depths of the pitch-black night, Heracles stumbled upon his target – the deafening roar of an enormous lion echoed throughout the vicinity, indicating that the beast was on the prowl. The hero located the predator’s den, concealed himself at the cave entrance, and prepared for the imminent attack.
As the Nemean lion emerged from its lair, it proved impervious to Heracles’ hands. Undeterred, the hero launched himself at the beast, armed solely with a club, which he used to stun the lion. He then proceeded to strangle it. Once Heracles had dealt with the creature, he offered a sacrifice to Zeus and established the Nemean Games, a prominent Greek festival during which all disputes, conflicts, and wars were brought to an end.
The king, filled with fear upon witnessing the lifeless creature, issued a prohibition for the hero to set foot within his kingdom. However, the paramount achievement of Hercules was his ability to rescue the populace, vanquishing the formidable beast and restoring tranquility to their lives. In recognition of this remarkable deed accomplished by the demigod, Zeus transformed the Nemean lion into a celestial formation. Consequently, the Lion forever illuminates the heavens, commemorating the extraordinary feat and the emancipation of humanity from anguish.
4) Consider ways to create a replica of the handle of the Ursa Major constellation. Accomplish this task. Additionally, utilize an atlas identifier to construct models of one or two additional constellations.
An applique can be used to replicate the chosen constellation’s pattern.
To achieve this, adhere silver stars onto a dark sheet of paper that mimics the appearance of the night sky.
To enhance clarity, the stars can be connected with lines.
Upon completion, the constellation model will be finalized.
Similarly, you have the ability to construct a prototype application for different constellations, such as Leo, Orion, and Cassiopeia.

Assignment
1. What celestial objects are visible in the sky during the daytime and which ones are visible at night?
During the daytime, we can observe the Sun in the sky, while at night, we can see the stars and the Moon.
2. What is the Sun?
The Sun is a massive luminous sphere, the nearest star to Earth.
3. How can the Big Dipper constellation be located in the sky?
To locate the Big Dipper constellation in the night sky, you can identify a distinct pattern of bright stars that resemble a bucket. This bucket-shaped formation corresponds precisely to the constellation you are seeking.
Leo Constellation Description
The Leo constellation is ranked as the fifth largest among all constellations. It intersects with the ecliptic and the celestial equator.
Due to its abundance of bright stars, the Leo constellation serves as a useful point of reference for discovering other, less prominent constellations. In the Northern Hemisphere, Leo can be observed throughout the year, but it reaches its highest point above the horizon during early spring, earning it a place in the “spring constellations” category.

A photograph capturing the Leo constellation.
Objects in the vast expanse of space

Messier 65 is an intermediate spiral galaxy situated in the Leo constellation. It has an apparent magnitude of 10.25 and is positioned approximately 35 million light-years away from our planet.
Initially discovered by Charles Messier in 1780, Messier 65, together with Messier 66 and NGC 3628, form the well-known Leo Triplet of galaxies.
With limited dust and gas content, star formation in this galaxy is relatively low, predominantly consisting of older stars.
Due to a slight tilt in its disk and recent indications of star formation, it is believed that Messier 65 is currently interacting with another celestial object.
Messier 66 (M66 or NGC 3627)
Messier 66 is a spiral galaxy of intermediate size located in the Leo constellation. It was first observed by Charles Messier in the year 1780. The galaxy has a visual magnitude of 8.9 and is situated approximately 36 million light years away from our planet.
With a diameter of around 95,000 light years, M66 is known for its prominent star clusters that illuminate its structure.
As part of the Lion’s Triple, M66 shares its celestial neighborhood with M65 and NGC 3628.
In the past, M66 and NGC 3628 have had close encounters, leading to a strong gravitational interaction between the two galaxies. This interaction has caused a significant concentration of mass within M66.
The spiral galaxy NGC 3628
Situated approximately 35 million light-years distant from our solar system, NGC 3628 is an enthralling spiral galaxy. Credited to the renowned astronomer William Herschel, its discovery dates back to the year 1784.

The Leo Triplet consists of the galaxy, Messier 65, the galaxy, Messier 66, and a long tail that spans approximately 300,000 light-years.
Galactic Clusters and Constellations
Astronomers refer to the cluster of stars that form the constellation Leo as an asterism. The Leo asterism resembles a curved blade, including not only stars but also entire galaxies.
The Leo Triplet is of significant interest to astronomers, consisting of the following galaxies:
Similar to our neighboring Andromeda galaxy and our own Milky Way, these galaxies are also classified as spiral galaxies and are situated approximately 35 million light years away from us. In the late 20th century, astronomers observed three supernova explosions in the M66 galaxy.
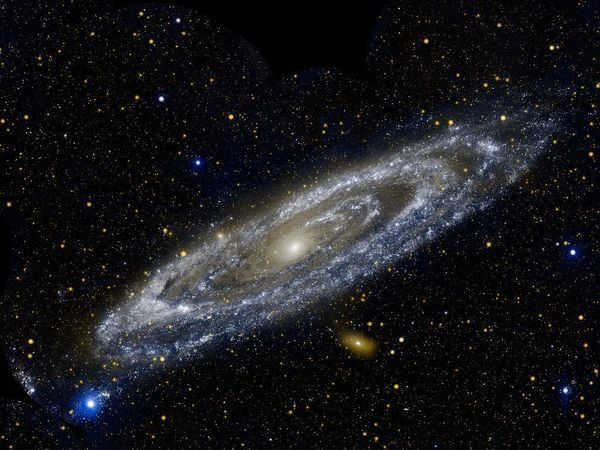

The constellation Leo is composed of the stars
Leo is home to a multitude of stunning stars and fascinating celestial objects, although most of them can only be observed with the aid of a powerful telescope.
As you may already be aware, the most luminous star within the constellation is Regulus. Additionally, Alpha Leo ranks among the brightest stars in the entire night sky.
The Leo constellation
Beta Leo is the star Denebola, which is the second brightest star after Regulus. Its Arabic name means “lion’s tail”. It is called so because it is actually located in the “tail” of the constellation.
Algieba, also known as “lion’s mane”, is Gamma. It is a binary star included in the sickle asterism.
Delta has two names, both Greek and Arabic. Zosma or Dur translates to “loins” or “lion’s back”. It is a multiple companion star, but it probably has another companion as well.
The Theta constellation is classified as a subgiant star with a white color. It is known by three different names, all of which translate to “lion’s thigh” or “rib”. The Arab astronomers refer to it as Hort and Certan, while in Latin it is called Coxa or Coxa.
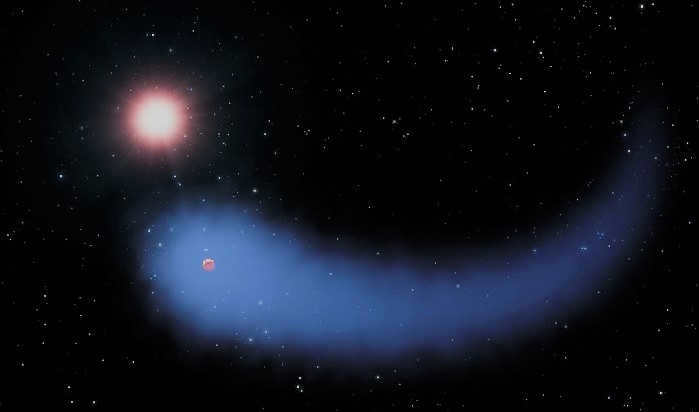

Exoplanet Gliese 436
Rasalas is the name of this exoplanet. It is called “lion’s head” in English. This exoplanet is an orange giant and it has at least one planet that orbits around it. The size of this planet is almost two and a half times the size of Jupiter.
There is another fascinating star called Rho. It is a blue supergiant and its name is Shire. The mass of this star is more than 20 times the mass of the Sun. Rho is a variable star that has noticeable pulsations. These pulsations are likely to cause the star to become a supernova. This explosion is expected to happen in a couple of million years.
Asterisms
In ancient times, the star cluster located in the tail region was known as the Brush. However, it was later recognized as a distinct constellation. Interestingly, it is now referred to as Veronica’s Hair.
Furthermore, the well-known sickle asterism comprises of the six primary stars of Leo. This formation is frequently confused with an upside-down question mark.
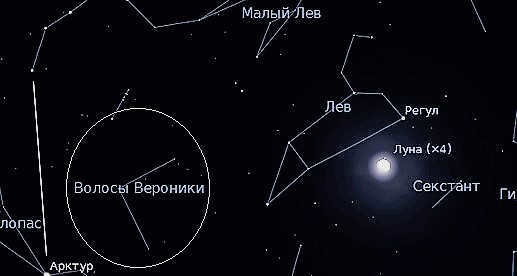

Veronica’s Hair constellation
Origin story of the Leo constellation
The Leo constellation is one of the oldest constellations in the night sky. Archaeological evidence suggests that as early as 4000 BC, civilizations in Mesopotamia recognized constellations similar to Leo. The constellation was known by different names in various cultures: the Persians called it Shir, the Babylonians referred to it as “the great Lion,” the Syrians knew it as Arye, and the Turks called it Artan.
In Greek mythology, the Leo constellation is associated with the Nemean lion, a legendary creature slain by Hercules as part of his twelve labors.
The Nemean lion resided in a cave near the city of Nemea. It terrorized the locals and proved invincible because no weapon could penetrate its impenetrable hide.
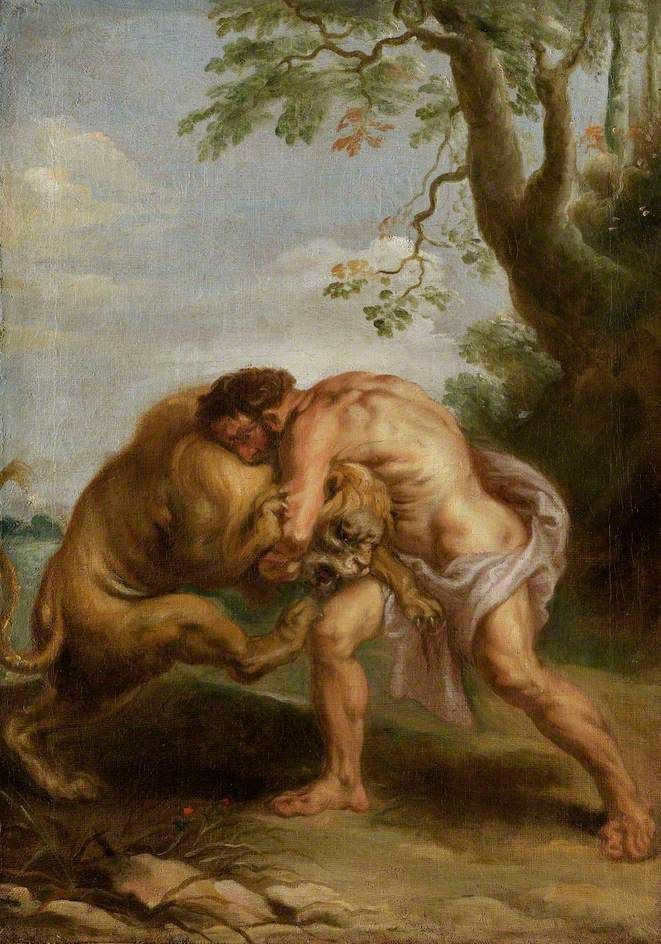

In his attempt to defeat the lion, Heracles found that his arrows were ineffective, prompting him to engage in a fierce battle with the creature. Eventually, he managed to strangle the lion, using its own claws to skin it. He then fashioned the lion’s hide into a belt, shaped like the head of the lion, which not only provided Hercules with protection but also enhanced his strength and capabilities.

The night sky is a fascinating and enigmatic aspect of our world. Throughout history, people have observed the stars and organized them into constellations, where they identified various heroes, mythical creatures, and objects. The constellation of Leo, in particular, has been associated with the image of a majestic predator. This constellation holds great significance in ancient legends, and its resemblance to the king of beasts is easily recognizable even to a child gazing at the night sky.
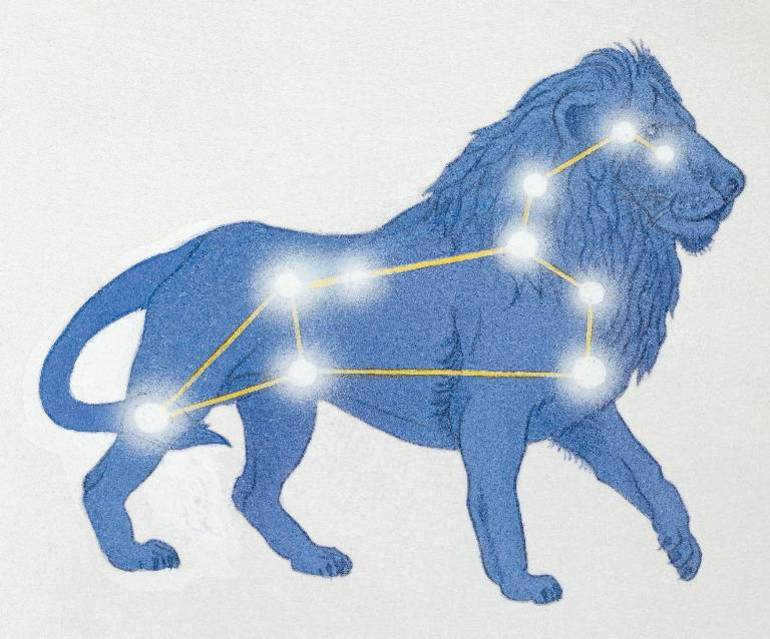

Etymology of the term
- The term for “lion” in Mesopotamia is Lion.
- In Persia, it is referred to as Shir or Ser.
- In Turkey, the term is Artan.
- In Syria, it is known as Aryo.
- In Hebrew, the term is Arye.
- In Indian languages, it goes by the name Simba.


Claudius Ptolemy, a renowned astronomer and mathematician hailing from ancient Greece, adhered to the customs of his era by assigning all the celestial bodies that formed the depiction of the lion to the constellation. In accordance with the principles of the “divine gaze,” medieval scientists depicted constellations in an external projection, as if observing them from a vantage point outside of our planet. This methodology is exemplified in the portrayal of Leo found in the astronomical atlas “Uranographia,” compiled by Jan Hevelius in 1610. Within this masterpiece, the Polish scientist identified a smaller constellation known as the Lesser Lion, which is situated in close proximity to the primary Leo and consists of a modest 34 stars.
The Assyrians, Babylonians, Persians, Egyptians, and various other civilizations each had their own unique myths and legends surrounding the constellation of Leo. Approximately 4,500 years ago, the summer solstice was positioned within this specific area of the celestial sphere. Throughout history, it has been associated with the arrival of scorching heat, accompanied by droughts and wildfires. As a result, the lion has become a universal symbol of fire among many cultures. In present times, the Sun passes through Leo, starting from the second third of August and lasting until September 17th.
During ancient times in Egypt, when this constellation was visible above the horizon, it coincided with the flooding of the Nile. This led to a tradition of creating sluice gates in the shape of lion heads, which were used to lower the Nile waters into the canals. It was believed that the greatest rulers and pharaohs were born when the Sun was in Leo.
One of the most well-known Greek myths involves a Nemean lion in the sky. This enormous mythological creature had impenetrable skin and lived near the city of Nemea on the Peloponnese peninsula. It terrorized the surrounding area, causing destruction wherever it went. However, Heracles managed to defeat the lion, marking the beginning of his series of legendary feats. Zeus honored Heracles’ accomplishment by placing the lion in the stars.
Overview
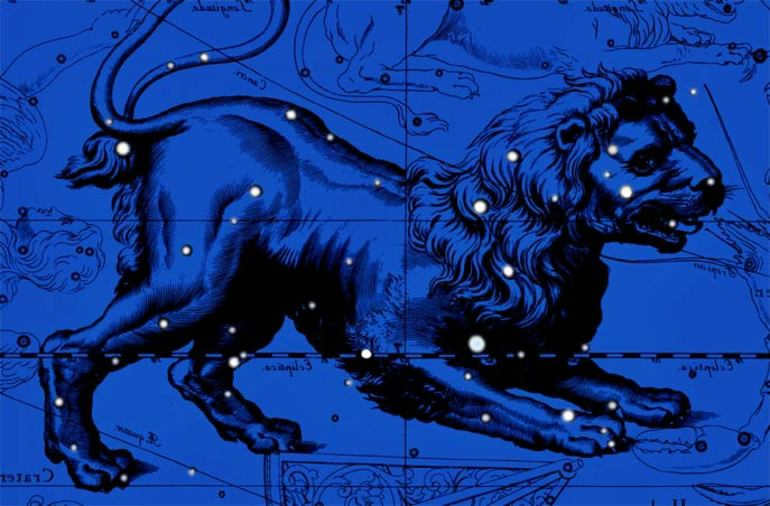

SL is ranked twelfth in terms of size among all constellations and fifth in terms of visibility in the Northern Hemisphere. It is intersected by both the ecliptic and the celestial equator. As per Johann Bayer’s nomenclature established in 1603, the constellation Leo (Leo) is referred to by its Latin name Leo, while its stars are named using the genitive case Leonis.
SL holds significance in the night sky due to its abundance of bright stars, making it a useful point of reference for locating other constellations. It remains visible in the Northern Hemisphere for most of the year, with its highest point above the horizon occurring in early spring, thus categorizing it as a spring constellation according to astronomers.
Did you know that the geometric figure created by the main stars of the constellation Leo is said to have proportions that match those of the ancient Egyptian sphinxes? The shape is similar to a trapezoid, with stars that shine just as brightly as the stars in the Big Dipper. To catch a glimpse of what Leo looks like, you’ll need to look towards the southeastern part of the sky during the late hours of the night. This area of the sky is a favorite among beginner astronomers, as there are numerous fascinating celestial objects to explore in this constellation.
Space entities
The night sky offers a mesmerizing view of various space entities, including SL. Even with the aid of binoculars, one can observe the stunning array of objects that populate this particular section of outer space. The constellation’s arrangement, when viewed with a touch of imagination, bears a striking resemblance to the silhouette of a majestic lion. Notable stars within the Leo constellation, each possessing a stellar magnitude exceeding three, include:
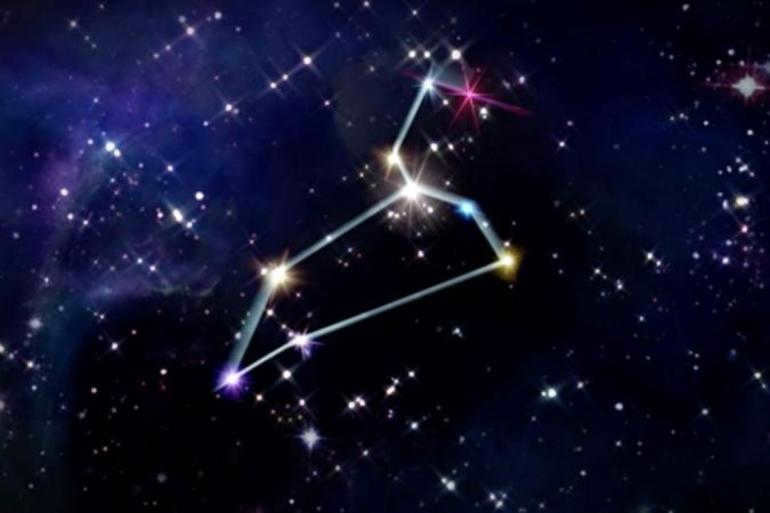

The arrangement of these stars is typically depicted by connecting imaginary lines, forming the outline of a sleeping predator. The constellation of Leo consists of approximately 120 stars. Astronomical atlases provide detailed information on the layout of Leo, including the spectral classes of its stars and the coordinates of various celestial objects within it.
Specialized online resources showcase visual models of star systems and share fascinating stories about astronomical projects.
The Regulus System
The center of the Leo constellation is occupied by Alpha, known as Regulus, which can be considered its heart. Regulus is the 21st brightest star in the sky and, although not the largest, its close proximity to the solar system gives it its apparent brilliance. Regulus was first described by Arab scholars in treatises written before the common era. They referred to it as Kalb al-Asad, or the lion’s heart, and in Latin, Regulus means “prince”.
Contemporary astronomers have made a discovery that Regulus is not simply one celestial entity, but rather a complete stellar system comprised of two sets of stars. The primary set consists of a sizable, youthful blue star called Regulus A, along with its partner, a white dwarf. These stars revolve rapidly around a shared center of mass, completing a full revolution in just 40 days. The secondary set is composed of red and orange dwarf stars, which are separated by a distance of approximately one hundred astronomical units. Due to frequent overlap from the Moon, Mercury, and Venus, this system can be challenging to observe.
Due to its extremely fast rate of rotation, Regulus A has acquired an ellipsoidal shape – the length of its polar and equatorial radii differ by almost a third, resulting in the subpolar regions being several times brighter than the central regions. If the rotational speed of this star were 14% higher, it would cease to exist in space as it would simply disintegrate under the influence of centrifugal force. Regulus A occupies a unique position in its orbit – due to the tilt of its rotational axis, it appears to move along its orbit while lying on its side.
Alternative stars
Denebola, also known as Beta, is the second most luminous star. Its unique name originates from the Arabic phrase “danab al-asad,” which translates to “lion’s tail.” With a mass approximately 1.8 times greater than that of the Sun, Denebola is classified as a hot white giant. The constant movement of its constituent layers, shifting from the outer to inner regions and vice versa, causes a flickering effect, resulting in its variability and a change in luminosity every 2-3 hours.
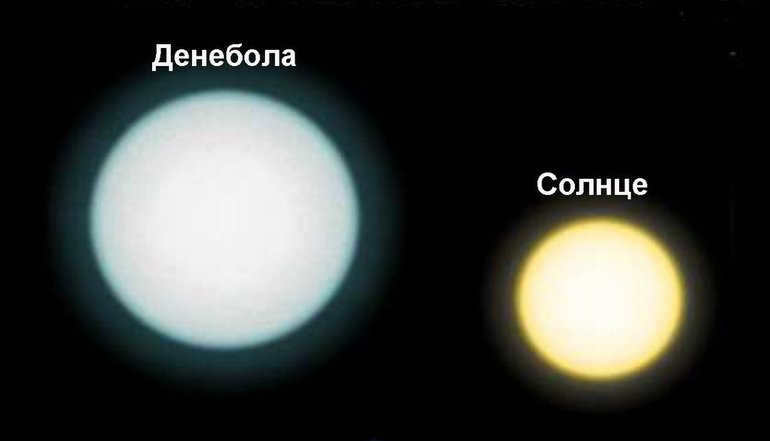

The detection of excessive infrared radiation around Denebola could indicate the presence of a residual disk – a cloud of dust and debris orbiting around the star, potentially suggesting the existence of exoplanets. In the night sky, there is also a noticeable red dwarf known as Wolf 359, which can only be observed with powerful telescopes. This red dwarf has a radius about 5 times smaller than that of the sun and is particularly noteworthy for being one of the closest stars to Earth.
Recently, a star that was once considered “impossible” was discovered in SL. It was named after one of the discoverers, Elisabetta Caffau. This star’s luminosity is unique because it is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, with a very low metallicity. According to current theories of star formation, a star like this should not have been able to form.
We can speculate that Caffau is incredibly ancient, possibly as old as the Universe itself. It has retained the characteristics of the original stars, while other stars have gone through multiple supernova events and become enriched with metals.
The constellation of Leo is known for its abundance of double and triple star systems, and there are other variable stars in this region besides Denebola.
Galaxies and Clusters
This constellation also possesses its own asterism, a group of highly noticeable stars that bear a distinct historically recognized designation. The asterism of Leo is referred to as the “sickle” because it resembles this agricultural implement and is composed of celestial bodies belonging to the lion’s head, linked in the following sequence (from top to bottom): epsilon (Algenubi), mu, zeta, gamma (Algieba), eta, alpha (Regulus).

The Leo Triplet, consisting of the following galaxies, is of great interest to astronomers:
These three spiral galaxies are located approximately 35 million light-years away from the solar system. M65 has a flattened and elongated shape with a bright nucleus and faint spirals. The similar appearance of the other two galaxies in the Triplet is a result of their gravitational attraction. In M66, three supernova explosions were recorded at the end of the 20th century.
M96 is one of the most luminous galaxies in the SL and was among the earliest spiral galaxies to be discovered. It is oriented towards Earth with a broad face, making it convenient for observation. The SL also contains lenticular and elliptical galaxies. In M105 (NGC 3379), astronomers have detected a supermassive object, believed to be a black hole.
Of particular interest is a spiral galaxy located near the star Alterf (Lion lambda). Its arms are currently undergoing a highly active process of star formation. The Hubble telescope has captured breathtaking and highly detailed images of numerous galaxies in the SL, including the awe-inspiring NGC 352.
In SL, there is a breathtaking meteor shower that occurs every November. It is known as the Leonids because its radiant is situated in this region. This mesmerizing event is linked to the yearly orbit of the Tempel-Tuttle comet and the gradual dissipation of its tail. The shower of shooting stars can be observed for approximately a week and is truly a remarkable spectacle.