The universe is a vast expanse, stretching across billions of light-years, and the majority of this space is empty. However, within this vastness, there are numerous colossal celestial bodies known as galaxies, each containing billions of stars. Among these galaxies is our very own Milky Way, which is quite sizable. But, when it comes to the largest galaxy in the universe, what do scientists know?
There are several galaxies that hold this impressive title, and each one is truly remarkable. Our Milky Way, while already immense and larger than many other galaxies, pales in comparison to these giants. With a staggering 200-400 billion stars, our galaxy is merely a dwarf in their presence.
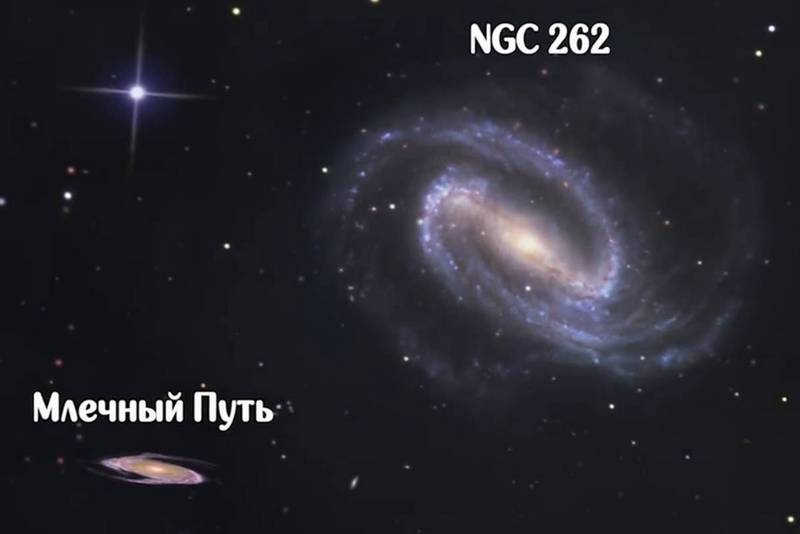
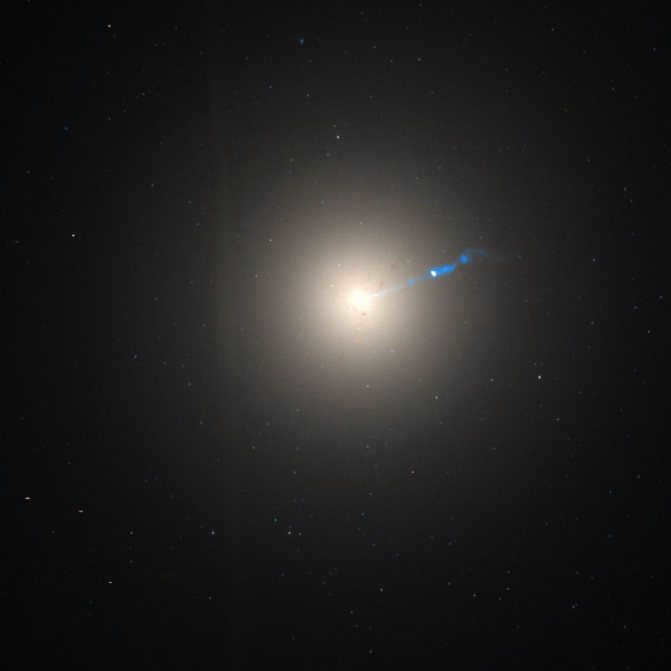
NGC 262 occupies the third position
This impressive spiral galaxy is situated in the Andromeda constellation and is oriented towards us in a flat manner. It is positioned approximately 200 million light years away, and it appears as a faint star in the sky with a magnitude of 13.1m, meaning that it can only be observed through a sufficiently powerful telescope with a large aperture.

NGC 262 is an incredibly massive galaxy, boasting a size that surpasses even our own Milky Way. The gas that surrounds NGC 262 alone is estimated to weigh 50 billion solar masses, enough to form countless stars similar to our Sun.
In terms of star count, NGC 262 reigns supreme with approximately 15 trillion stars. To put this into perspective, our Milky Way galaxy, which already contains a substantial 400 billion stars, pales in comparison as NGC 262 holds a staggering six times more.
As for its physical dimensions, NGC 262 spans a whopping 1,300,000 light-years, a staggering thirteen times larger than the cross section of our own galaxy. Truly, NGC 262 is a colossal entity, a true titan among giants.
Hercules-A ranks second
Situated in the constellation Hercules, the Hercules-A galaxy holds the position of number two. It is positioned at a distance that is ten times greater than NGC 262. The light emitted by this galaxy requires a staggering two billion years to reach our observation point.

The size of this gigantic entity is 1,500,000 light-years in diameter, surpassing the dimensions of its predecessor, and exceeding the size of our own galaxy by a factor of 15. Hercules-A boasts a weight that is 2,000 times greater than that of the Milky Way. Remarkably, the central black hole within this galactic behemoth possesses a mass of 2.5 billion solar masses!
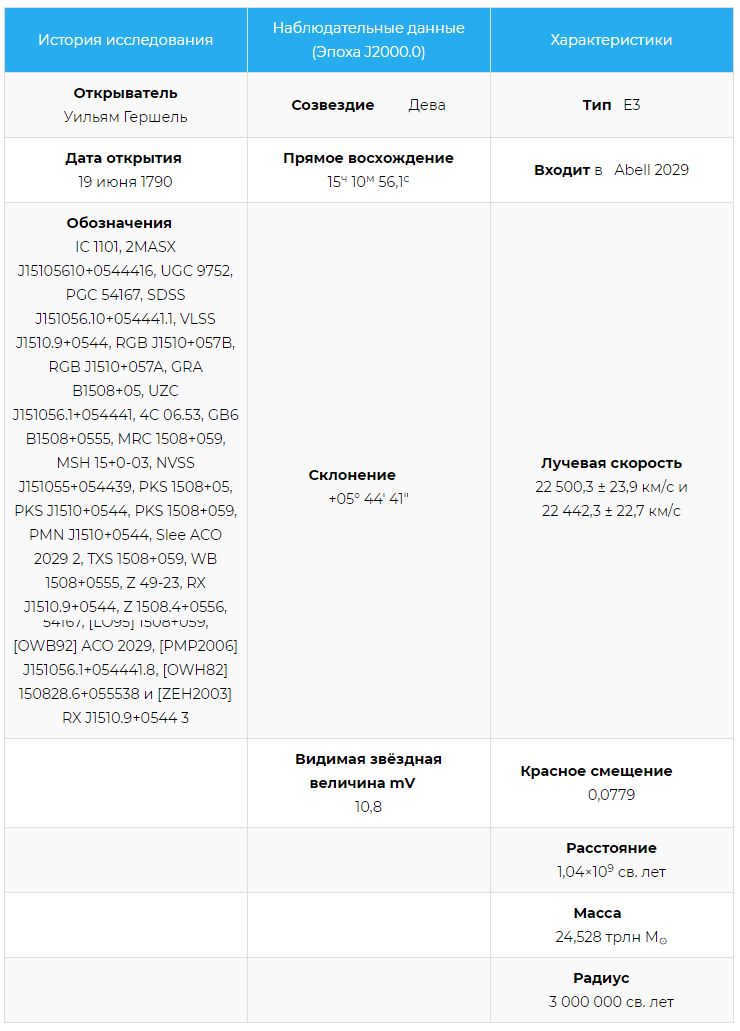
The discovery of this galaxy dates back to 1790 when it was first observed by William Herschel. Situated within the boundaries of the Virgo constellation, this galaxy resides in a vast cluster of galaxies, positioned approximately 1 billion light years away from our own. Categorized as an elliptical galaxy, it exhibits a brightness of 10.1m when viewed in the night sky.
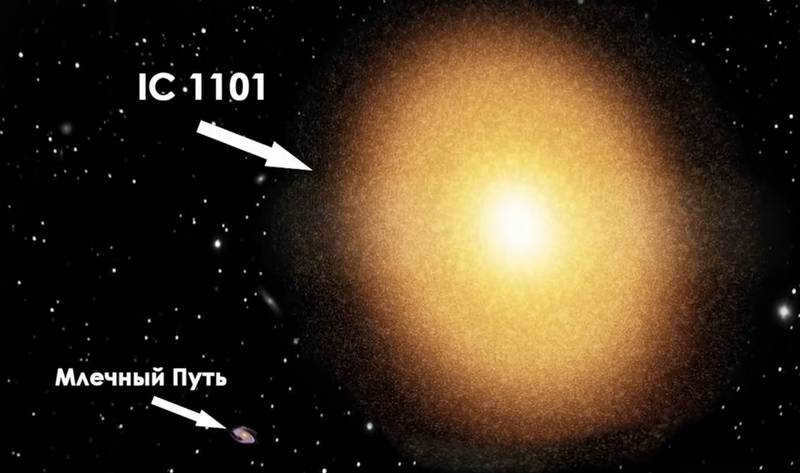
IC 1101 stands as the most massive galaxy in the entire Universe.
IC 1101, a behemoth in the cosmos, claims the title of the largest galaxy in the known Universe, surpassing all previous contenders. In terms of weight, it is 2,000 times heavier than our Milky Way, and its size dwarfs it by 60 times! Spanning from one end to the other would take a beam of light 6 million years. Remarkably, it is four times bigger than the previous Hercules-A galaxy, boasting an astounding 100 trillion stars.
This colossal galaxy formed through the merger of smaller galaxies, and it continues to consume nearby galaxies, expanding its colossal size.
IC 1101 is the biggest galaxy ever discovered in the entire Universe, and it is truly mind-boggling in terms of its sheer size.
The Universe that we inhabit is not something to be underestimated, as it is populated with an array of colossal entities. Planets, stars, galaxies, and clusters of galaxies – all of these can be so immense that in comparison, our solar system with its mere eight planets seems like a tiny speck in an expansive forest. “TechInsider” has compiled a list of the top five record-breaking celestial phenomena in various cosmic categories.

GQ Lupi b: The Biggest Exoplanet
Largest star: UY Scuti
When we think about the size of our Sun, we often consider it to be incredibly large. And in comparison to Earth, it is indeed massive, with a radius that is 109 times larger than Earth’s and spans 696,000 kilometers. However, if we were to multiply this size by 1,708, we would arrive at the radius of UY Scuti, a star located in the constellation of Shields, which is situated a distance of “only” 9,500 light-years away. What’s even more remarkable is that during its pulsation peak, which occurs approximately every 740 days, the radius of this celestial body can expand to a whopping 1,900 times the size of our Sun – truly a colossal entity.
When compared to the Sun, UY Scuti is approximately five billion times larger in volume. If UY Scuti were positioned at the center of our solar system, its outer edge would extend just past Jupiter’s orbit. The gas and dust emitted by UY Scuti would scatter even further, surpassing the orbit of Pluto and reaching a distance approximately 400 times greater than the distance between Earth and the Sun. UY Scuti is not only the largest star currently known, but it is also one of the most luminous and fastest-burning stars.
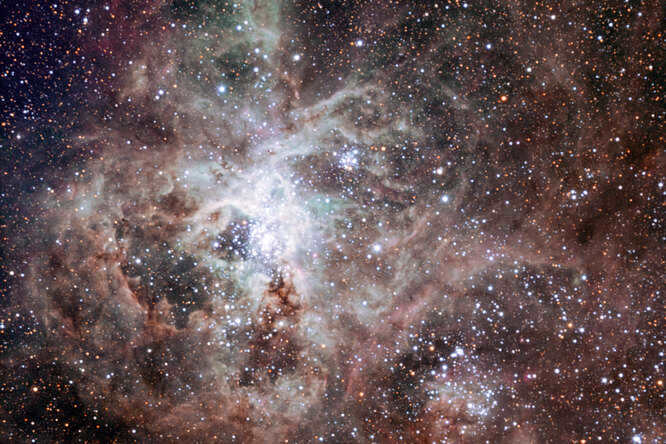
NGC 2070: The Largest Nebula in the Universe
The NGC 2070 nebula, also known as the Tarantula, holds the distinction of being the largest known nebula in the entire universe. It can be found within the Large Magellanic Cloud, which is a companion galaxy to our Milky Way, situated approximately 170,000 light-years away. The Tarantula nebula is a veritable breeding ground for celestial bodies, as within its vast expanse of gas and dust, countless young stars are born. Some of these stars eventually meet their explosive fate, resulting in supernovae that create awe-inspiring bubbles illuminated by X-rays. At the heart of this magnificent nebula lies a cosmic maternity home of sorts, known as the R136 star cluster. This cluster is home to a group of stars whose age is estimated to be around two million years old.
The most enormous galaxy: IC 1101
In terms of spiral galaxies, our Milky Way is not particularly impressive in terms of size: it spans 100,000 light-years from end to end, which is considered average. However, IC 1101 is a supergiant elliptical galaxy located at the heart of the Abell 2029 galaxy cluster. This extraordinary celestial entity stretches across an astonishing distance of six million light-years. Not only is IC 1101 60 times larger than the Milky Way, but it is also 2,000 times more massive. If IC 1101 were to take the place of our galaxy, it would engulf the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds, the Andromeda Nebula, and the Triangle Galaxy. The formation of IC 1101 can be attributed to the merging of galaxies that were the size of the Milky Way and the Andromeda Nebula.
While it’s impressive to think about the enormity of the biggest planets, stars, and galaxies, there is something even more mind-boggling out there. Allow me to introduce you to the Great Wall of Hercules – Northern Crown. This colossal flat formation is made up of galaxies that span over ten billion light-years, which is roughly 10% of the diameter of the entire universe. This astounding structure was first detected in November 2013 during observations of gamma ray bursts, and it’s believed that it could potentially house billions of galaxies.
TechInsider Online Edition
Founder of Fashion Press LLC: 119435, Moscow, Bolshoi Savvinsky per. 12, str. 6, floor 3, room II;
Address of the editorial office: 119435, Moscow, Bolshoi Savvinsky per. 12, p. 12, str. 6, floor 3, room II;
Chief Editor: Nikita Vasilenok
Email address of the editorial office: [email protected]
Phone number of the editorial office: +7 (495) 252-09-99
Label for the information product: 16+
The online edition is registered with the Federal Service for Supervision in the Sphere of Communications, Information Technologies and Mass Media, registration number and date of registration decision: series EL No. FS 77 – 84123 dated November 09, 2022.
© 2007 – 2023 "Fashion Press" Ltd.
The User, by publishing content on the Website, gives "Fashion Press" LLC the non-exclusive authority to utilize, duplicate, distribute, create modified versions, and also to present the materials and bring them to the attention of the public without any cost.
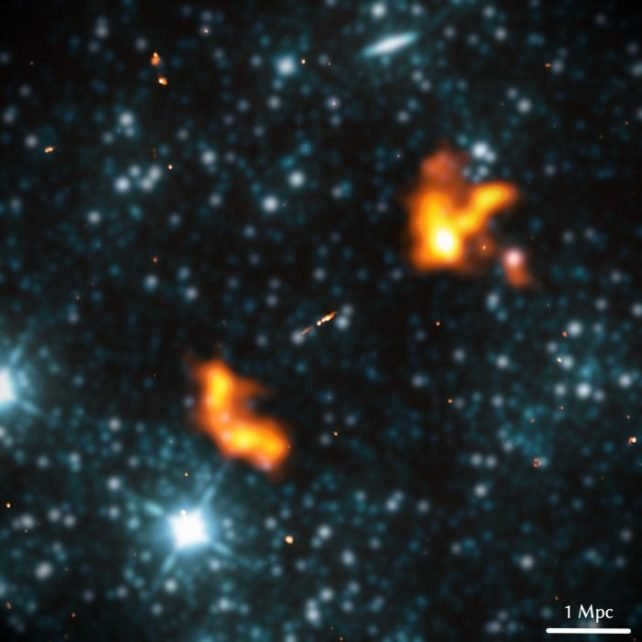

Earlier in the year, astronomers made a groundbreaking discovery – the largest known structure of galactic origin. It is called Alkionaeus, taking its name from a Greek mythological giant. Alkionaeus is a radio galaxy that spans an incredible five megaparsecs in space, equivalent to 16.3 million light-years.
Giant radio galaxies remain an enigma in the universe. They consist of a host galaxy, a cluster of stars revolving around a supermassive black hole at the galactic nucleus. Additionally, these galaxies feature colossal jets and lobes that extend from the center of the galaxy.
The interaction between these jets and lobes with the intergalactic medium generates radio emission by accelerating electrons, similar to a synchrotron.
Explore the Universe with an interactive map and journey through 200,000 galaxies
Not all of the matter from the accretion disk that spirals into an active black hole ends up being swallowed by the event horizon. A small portion of it is somehow directed towards the poles, where it is expelled into space as jets of ionized plasma traveling at speeds close to the speed of light.
These powerful outbursts can travel vast distances and eventually manifest as massive radio-emitting structures resembling petals. It’s not surprising that even our own Milky Way has these radio petals.
What remains a mystery is why some galaxies have these petals growing to enormous sizes spanning megaparsecs. These colossal formations, known as giant radio galaxies, offer clues as to what mechanisms are behind their extraordinary growth.
“If the parent galaxy possesses certain characteristics that significantly contribute to the growth of giant radio galaxies, it is highly likely that the largest giant radio galaxies are hosted by such parent galaxies. Similarly, if there are specific large-scale environments that promote the growth of giant radio galaxies, it is probable that these environments serve as hosts for the largest giant radio galaxies,” stated Martina Oei, a co-author of the study from the Leiden Observatory in the Netherlands.
The scientists conducted a thorough examination of various attributes in the data gathered by the Low-frequency ARray (LOFAR), which is an interferometric network encompassing approximately 20,000 radio antennas situated across 52 locations throughout Europe.
They meticulously reanalyzed the data utilizing an innovative data processing method, which involved eliminating compact radio sources that could potentially disrupt the detection of diffuse radio petals, as well as correcting for any optical distortions.
That’s how Alkionaeus was found. It’s a galaxy located in the Lynx constellation, approximately three billion light-years distant. Despite its immense magnitude, it is a relatively typical elliptical galaxy entwined within the fabric of the universe. It possesses a mass approximately 240 billion times greater than that of the Sun, housing a supermassive black hole at its core that is roughly 400 million times the mass of the Sun.
“Despite its size, Alkionay appears to be a rather ordinary galaxy in many aspects. The overall low-frequency luminosity density, stellar mass, and mass of the supermassive black hole are on the lower side, although they are similar to those of typical giant radio galaxies. This suggests that the growth of such giants does not necessarily require very massive galaxies or central black holes, and a high radio power may not be necessary either,” the researchers explained.
It is conceivable that Alcyoneus is located in a region of space with a lower density compared to the average, which could be contributing to its expansion. Alternatively, interactions with the cosmic web may be playing a role in the galaxy’s growth. Whatever the cause, scientists anticipate that this galaxy will continue to expand in the vastness of the universe.

Events
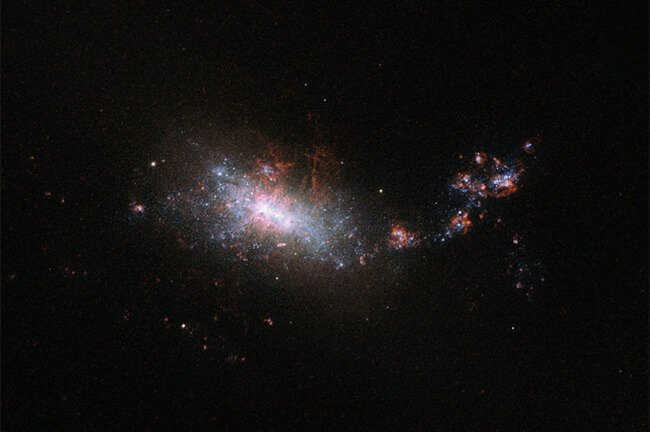
Astronomers have made an astounding discovery of a spiral galaxy of unprecedented size. Moreover, they assert that we are presently witnessing the genesis of an entirely new galaxy resulting from the collision of two galaxies.
This extraordinary spiral galaxy, known as NGC 6872, was observed by astronomers several decades ago and was believed to be one of the most massive stellar systems in the entire Universe.However, only recently has it been confirmed as the largest spiral galaxy ever documented by science.
Characteristics of NGC 6872, the Largest Galaxy
The galaxy NGC 6872 measures an impressive 522,000 light-years in width, which is five times wider than our own galaxy, the Milky Way. It is believed that this vast expanse was formed as a result of a recent collision with another galaxy, leading to the emergence of fresh stars in one of its arms. Over time, this process may eventually give rise to the formation of an entirely new galaxy.
These remarkable findings were made by a team of international scientists hailing from Brazil, Chile, and the United States. Utilizing NASA’s GALEX Space Telescope, these experts were able to study images and capture the ultraviolet light emitted by the youngest and hottest stars within NGC 6872.
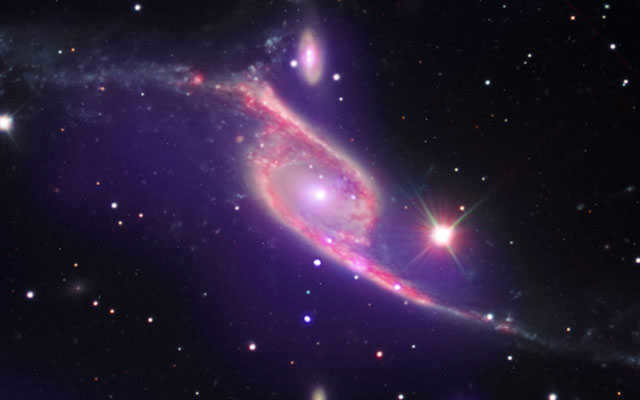

The magnificent view of Galaxy NGC 6872
The extraordinary size and appearance of NGC 6872 can be attributed to its interaction with a smaller galaxy, IC 4970, which is just a fraction of its mass, only one fiftieth. This unique pair is situated 212 million light-years away from Earth in the southern constellation known as Peacock.
Scientists theorize that large galaxies, including our very own, expand through the process of merging with other galaxies. This phenomenon occurs over billions of years, during which some galaxies assimilate smaller ones.
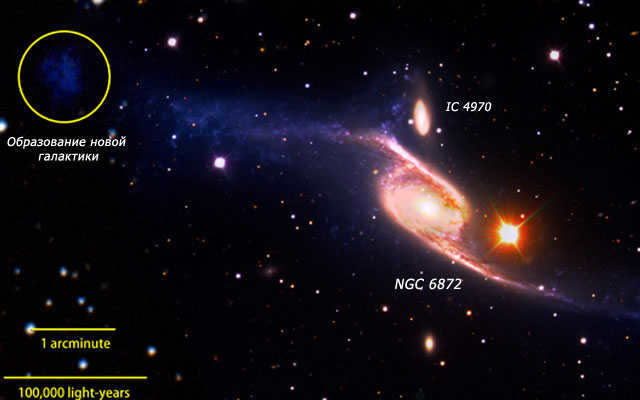
A fresh galaxy is formed by a cluster of young stars represented by the yellow circle.
Interestingly, the interaction between NGC 6872 and IC 4970 galaxies results in the formation of not just one large galaxy, but rather a small galaxy. The northeastern arm of NGC 6872 is particularly prominent in the image, with new stars being formed here, while at its other end (northwest) there is a fainter object that resembles a dwarf galaxy, according to the researchers.
Upon analyzing the energy distribution, the research team discovered that the two arms of NGC 6872 consist of stars of different ages. The youngest stars are located in the region of the northwestern arm, which coincides with the proposed new dwarf galaxy. As one moves closer to the center of NGC 6872, the stars gradually become older.
Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy is located at a distance of 2.52 million light-years from Earth.
Known for its stunning beauty, the Andromeda Galaxy is not only the closest galaxy to our own, but also one of the most captivating. It is visible on a clear night near the constellation Andromeda. Initially, it was thought to be the largest galaxy in its nearby galaxy group, but it was later discovered that the Milky Way is significantly more massive.
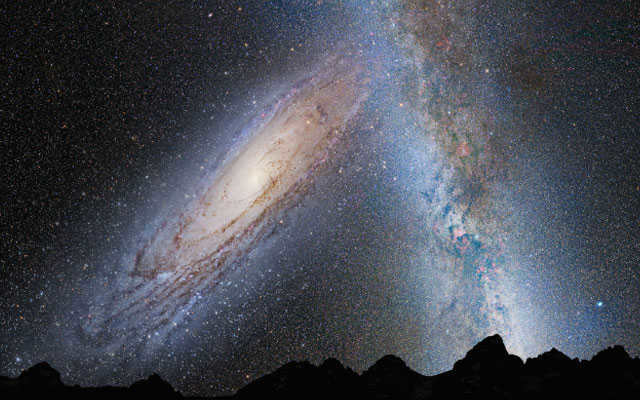

In approximately 3.75 billion years, the night sky will have a new look as the Andromeda galaxy gets closer to our Milky Way.
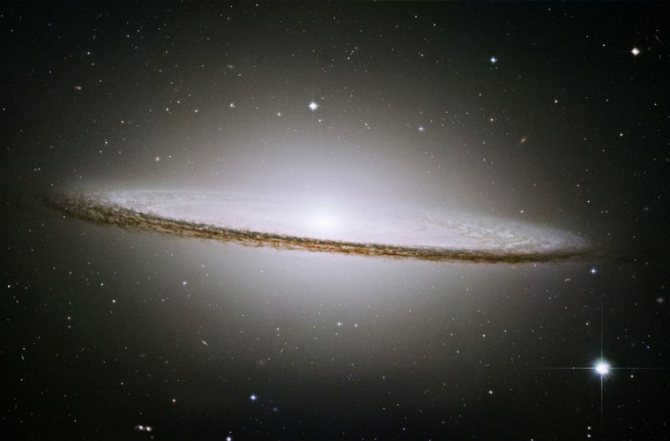
The Sombrero Galaxy.
Located about 28 million light years away from Earth
This spiral galaxy is found in the vicinity of the Virgo constellation.. It possesses a brilliant core, an exceptionally large central region, and a luminous, flat, ring-shaped dust band. The galaxy bears a resemblance to a sombrero hat. and that is why it has been given this name. At the core of this galaxy, there exists a massive black hole that intrigues astronomers greatly.
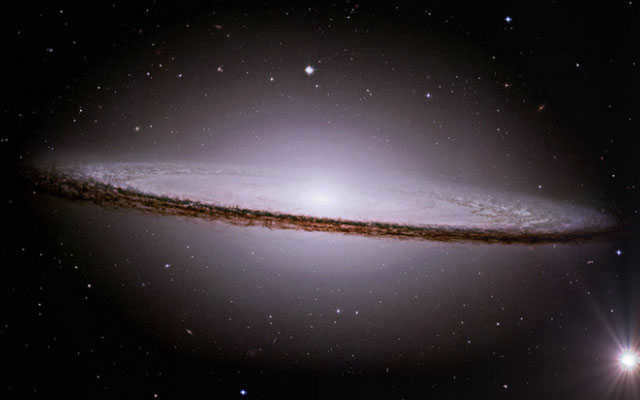

Even amateur telescopes can observe this particular galaxy.
A collection of galaxies – The Antennae galaxies.
Distance from Earth: 45 million light years
In the constellation of Corvus, an interesting group of galaxies is visible, creating awe-inspiring cosmic landscapes. This galaxy is currently experiencing a surge in star formation, meaning that stars are being created at a relatively rapid pace.
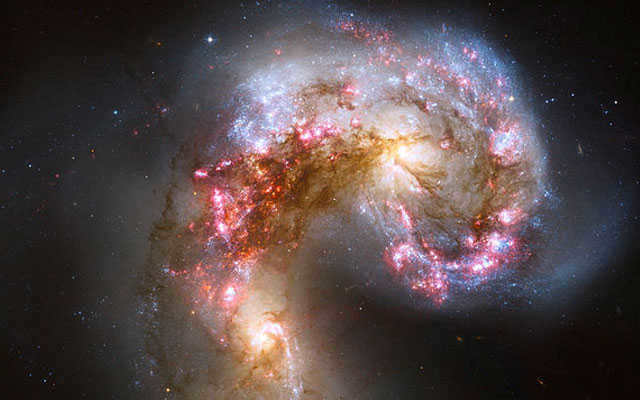

Astounding view of the Antennae galaxies
The Black Eye Galaxy in the constellation of Veronica’s Hair.
Distance from Earth: 17 million light years
The galaxy M 64, also known as the black eye, is incredibly unique due to its origin as a result of the merger of two galaxies spinning in opposite directions. It showcases a striking dark dust rim that contrasts with its luminous core.
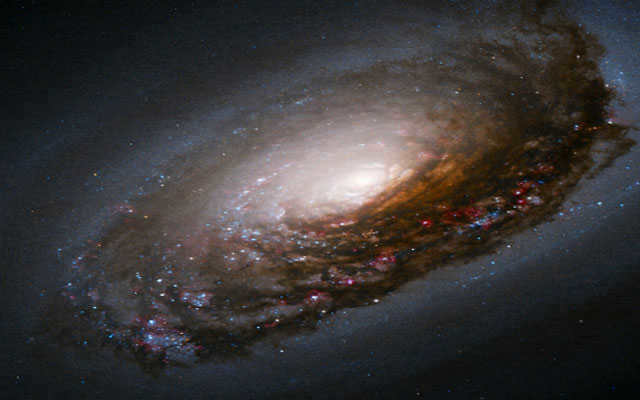

The Black Eye Galaxy is a favorite among amateur astronomers.
The impressive Whirlpool Galaxy.
Located 23 million light years away from Earth
Also referred to as Messier 51, this galaxy has earned the nickname Whirlpool due to its resemblance to a swirling vortex. Situated in the vicinity of the constellation Canes Venatici and accompanied by a smaller galaxy, NGC 5195, this galaxy is renowned as one of the most well-known spiral galaxies and can be easily observed using amateur telescopes.
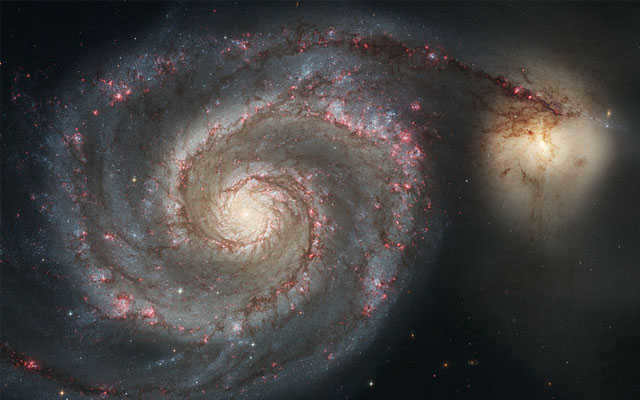

The Whirlpool galaxy, which is a companion, can be observed most effectively during the spring and summer months
The peculiar NGC 3314A galaxy located in the Hydra constellation
Distance from Earth: 117 and 140 million light-years away
These two galaxies, specifically NGC 3314A and B, are not colliding, but rather overlapping each other from our perspective.
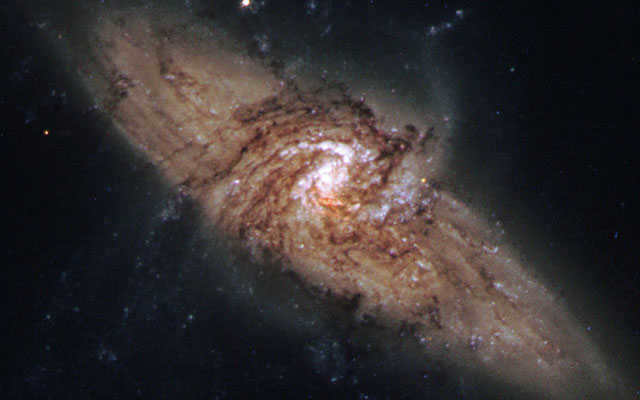

Intersecting galaxies
M 81 is a spiral galaxy situated in the Big Dipper constellation, also known as the Bode galaxy.
It is located at a distance of 11.7 million light-years from Earth.
Named after the German astronomer Johann Bode who discovered it, this galaxy is renowned for its breathtaking beauty. It is positioned within the Big Dipper constellation and can be easily observed. Apart from M81, there are 33 other galaxies present in this constellation.
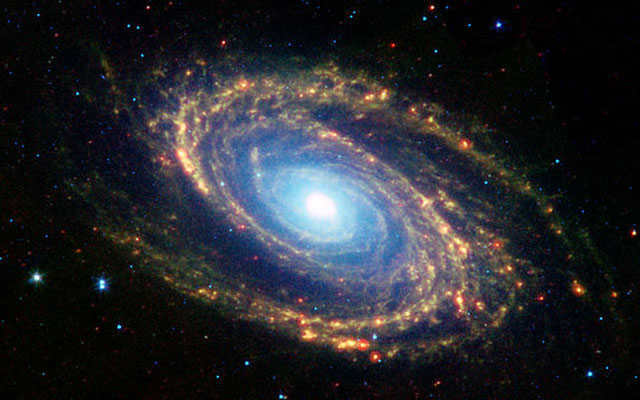

The Bode Galaxy showcases almost flawless spiral arms
The stunning ring galaxy known as Hög’s Object in the constellation of the Serpent.
Distance from Earth: 600 million light years
Named after the scientist who made its discovery in 1950, this ring-shaped galaxy possesses a unique structure and appearance. It stands as the first ring-shaped galaxy to be identified by the scientific community. The approximate diameter of its ring measures 100,000 light years.
The outer region of the ring is dominated by vibrant blue stars, while closer to the center lies a ring of reddish stars that are likely much older. Between these rings, there exists a darker ring. The exact formation of Hög’s Object remains a mystery to science, although several other similar objects have been documented.
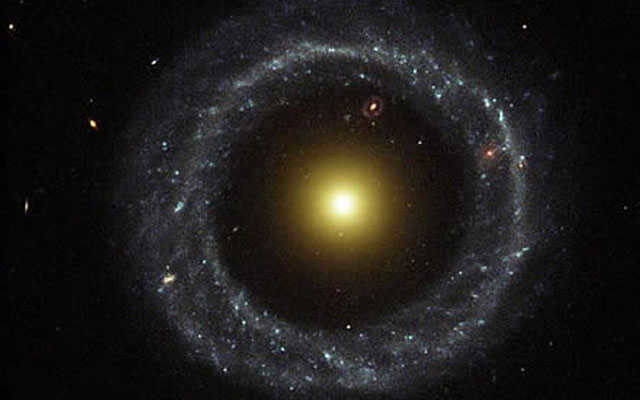

The Hubble Space Telescope captured an image of Hog’s Object in July 2001
Located in the constellation Big Dipper, The Cigar Galaxy
is situated 12 million light years away from Earth
The galaxy known as M 82, or The Cigar, is a satellite of another galaxy called M 81. What makes it special is the presence of a supermassive black hole at its center, accompanied by two smaller black holes in orbit. Additionally, this galaxy has a high rate of star formation. In fact, new stars are born at a rate 10 times faster than in our own Milky Way galaxy.
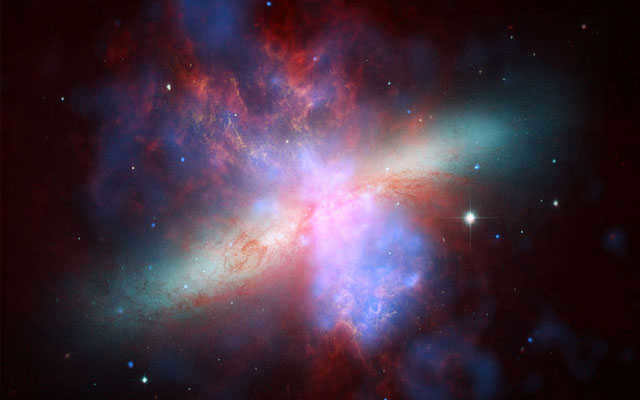

The breathtaking Cigar Galaxy.
Galaxy NGC 2787 in the Ursa Major constellation.
Distance from Earth: 24 million light years
The lenticular galaxy, known as NGC 2787, is a unique combination of elliptical and spiral galaxies. It stands out with its barely visible arms and a prominent bright nucleus at its center.
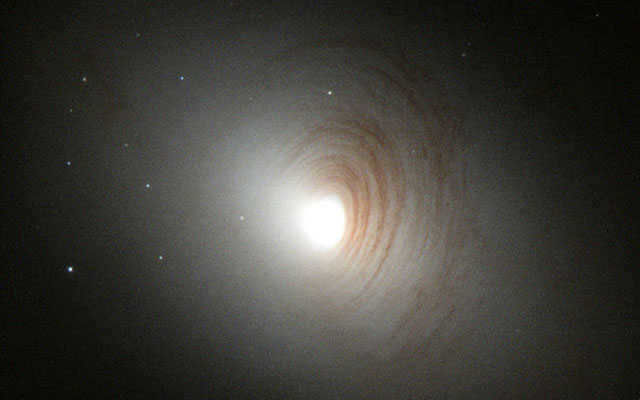

The Hubble Space Telescope captured a stunning image of Galaxy NGC 2787.
This image reveals a sight that has never been seen before. Additionally, experts believe that we are currently witnessing the extraordinary phenomenon of another galaxy being born.
Indeed, we are observing the birth of a new galaxy resulting from the collision of two existing galaxies.
Astonishingly, astronomers discovered a spiral galaxy named NGC 6872 many years ago, initially believing it to be
one of the largest star systems in the entire Universe.
However, recent research has unveiled that NGC 6872 is actually the largest known spiral galaxy in the field of science.
Characteristics of NGC 6872, the Largest Galaxy
The NGC 6872 galaxy spans a distance of 522 thousand light-years. It is equivalent to a width of 522,000 light-years.
It is worth noting that NGC 6872 is 5 times wider than our own galaxy, the Milky Way. This vastness may be attributed to a relatively recent collision with another galaxy, resulting in the emergence of newly formed stars within one of its arms. Over time, these stars could potentially lead to the formation of an entirely new galaxy.
These fascinating discoveries were made possible by the collaborative efforts of an international team of scientists from Brazil, Chile, and the United States. The team extensively studied images captured by NASA’s GALEX SPACE TELESCOPE, a highly advanced telescope capable of capturing the ultraviolet light emitted by the youngest and hottest stars. These images provide a stunning glimpse of the majestic NGC 6872 galaxy in all its splendor.
With a mass that is only
one fiftieth
of the mass of the enormous galaxy, this peculiar pair can be found 212 million light-years away from Earth in the
southern constellation of Peacock
.
Astronomers have the belief that the growth of large galaxies, including our own, occurs through the merging process with other galaxies.
. These processes can last for billions of years, during which time certain galaxies absorb other, smaller galaxies.
Within the yellow circle, there is a cluster of young stars that create a brand new galaxy.
An interesting fact is that the interaction between NGC 6872 and IC 4970 galaxies results in not one large galaxy, but instead one incredibly small galaxy.
The image clearly highlights the northeastern section of NGC 6872, where new stars are not actively forming. However, at the opposite end (northwest), there is a fainter object that bears a resemblance to a dwarf galaxy, according to the researchers.
Upon examining the energy distribution, the team of scientists discovered that the two arms of NGC 6872 consist of stars spanning various ages. Specifically, the youngest stars are concentrated in the northwest arm, which suggests the presence of a potential new dwarf galaxy. As one moves closer to the center of NGC 6872, the stars progressively age.
NGC 262 is the third galaxy in the list
This stunning spiral galaxy can be found in the constellation Andromeda and is positioned flat to our line of sight. It is located approximately 200 million light years away and appears as a faint star in the sky with a magnitude of 13.1m. Therefore, it can only be observed using a powerful telescope with a large aperture.

NGC 262 is an extraordinary galaxy due to its immense size. The gas enveloping it is equivalent to 50 billion solar masses, which could potentially form countless stars similar to our Sun.
This colossal galaxy houses approximately 15 trillion stars. In comparison, our Milky Way, which is already quite substantial, contains a maximum of 400 billion stars. Therefore, NGC 242 boasts six times more stars!
Spanning 1,300,000 light years, NGC 262 is a colossal entity that far surpasses the size of our own galaxy. In fact, its dimensions are thirteen times larger than the cross section of the Milky Way. It truly stands out as a mammoth galaxy among its peers.
Distance from Earth: 2.52 million light years.
This particular galaxy is the nearest galaxy to our own
and it is also one of the most stunning. It can be observed on a clear night close to the constellation Andromeda. Initially, it was thought that this galaxy was the largest in the closest cluster of galaxies, but it was later discovered that the Milky Way is significantly more massive.
This is approximately what the night sky will appear like in 3.75 billion years when the Andromeda galaxy approaches our Milky Way
IC 1101 is the most massive galaxy in the entire Universe.
William Herschel, a renowned astronomer, made the remarkable discovery of this colossal galaxy back in 1790. Situated in the constellation Virgo, within a vast cluster of galaxies, it is positioned at a mind-boggling distance of slightly over 1 billion light-years away from our planet. Characterized as an elliptical galaxy, IC 1101 radiates a luminosity of 10.1m, making it an awe-inspiring sight in the night sky.
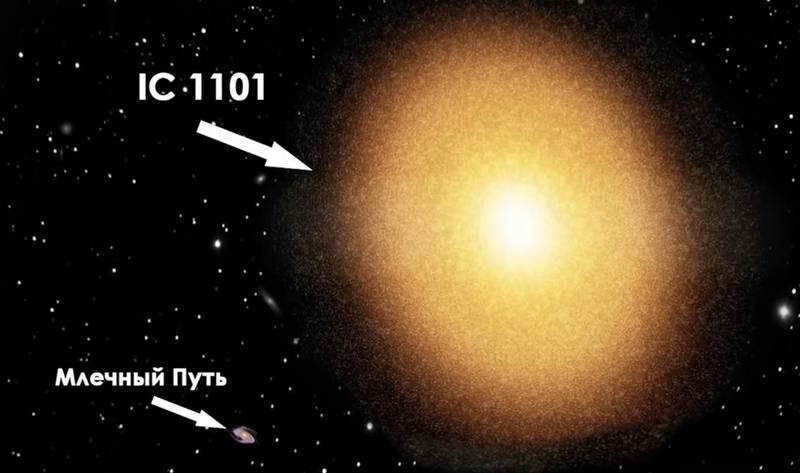
IC 1101, the biggest galaxy in the entire Universe, is truly a behemoth. It surpasses all other contenders, making it the largest galaxy in the visible part of the Universe. In fact, it is 2,000 times more massive than our Milky Way and a staggering 60 times larger! Spanning from one edge to the other would take a whopping 6 million years for a beam of light. To put it into perspective, this gargantuan galaxy is even four times bigger than the previous Hercules-A galaxy. With a mind-boggling 100 trillion stars, IC 1101 is a celestial titan.
This colossal galaxy was formed through the fusion of smaller galaxies, resulting in its current enormous size and mass. In fact, it is so immense that it is actively absorbing and assimilating other nearby galaxies, continuing to expand its already massive proportions.
IC 1101 holds the title of the largest known galaxy in the entire universe, and its sheer magnitude is simply incomprehensible.

Sombrero Galaxy
Distance from Earth: 28 million light years
This spiral galaxy is situated in the vicinity of the Virgo constellation
The Sombrero Galaxy boasts
a luminous core
and an incredibly vast central region along with a radiant, level, ring-like dust rim. The galaxy is reminiscent of
a sombrero hat.
hence its name. At the nucleus of this galaxy is
a colossal black hole
which holds great significance for astronomers.
Even amateur telescopes can capture a glimpse of this galaxy.
The biggest celestial body
Jupiter is the reigning champion as the largest celestial body in our solar system, boasting hundreds of Earth-sized planets within its vast boundaries. However, beyond the reaches of our visible universe, a true behemoth lies in wait.

A comparison of TRES-4B and Jupiter
Before 2011, Jupiter was considered the largest planet in the universe. It has been known since ancient times. It is located in our solar system, at a distance of about 484 million miles from the sun. Jupiter is a massive gas giant composed mostly of hydrogen and helium, with a mass over 300 times that of Earth. The temperature on Jupiter can reach up to -145 degrees Celsius, making it extremely cold compared to other planets. Despite its size and harsh conditions, Jupiter has been a subject of interest for scientists and astronomers due to its unique atmosphere and magnetic field.
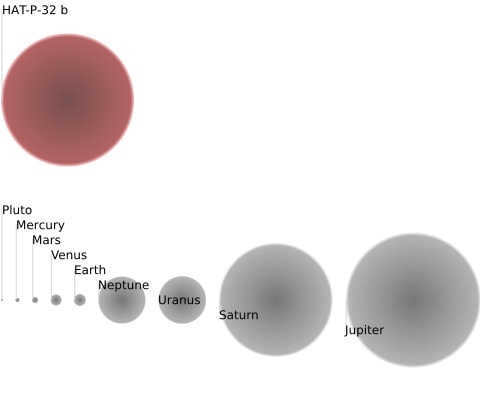
When it comes to comparing HAT-P-32b to planets in the solar system, there are some interesting facts to consider.
Presently, HAT-P-32b holds the title for being the largest planet in the Universe (within the area accessible for scientific research). The radius of HAT-P-32b measures 145,629 kilometers, which is equivalent to 2.037 times the radius of Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system. In terms of mass, this exoplanet weighs approximately 0.941 times that of Jupiter. It was first discovered in 2004, but it was officially designated as a planet on June 08, 2011. If you’re interested in learning more about the largest planets in the Universe, take a look at our article dedicated to this topic: the largest planets in the Universe.
When discussing exoplanets that potentially support life, one of the largest planets in existence is Gliese 581, which was discovered in 2007 at the La Silla Observatory in Chile, located 20,000 light-years away from Earth, through the use of Doppler shift.
Enormous Whirlpool Galaxy
Distance from Earth: 23 million light years
Also referred to as Messier 51
This particular galaxy has been given the name Whirlpool due to its striking resemblance to a swirling vortex. It can be found in close proximity to the constellation Hound Dog and is accompanied by a smaller galaxy, NGC 5195. The Whirlpool galaxy is among the most well-known spiral galaxies and can easily be observed using amateur telescopes.
The accompanying Whirlpool galaxy is best viewed during the spring and summer months.


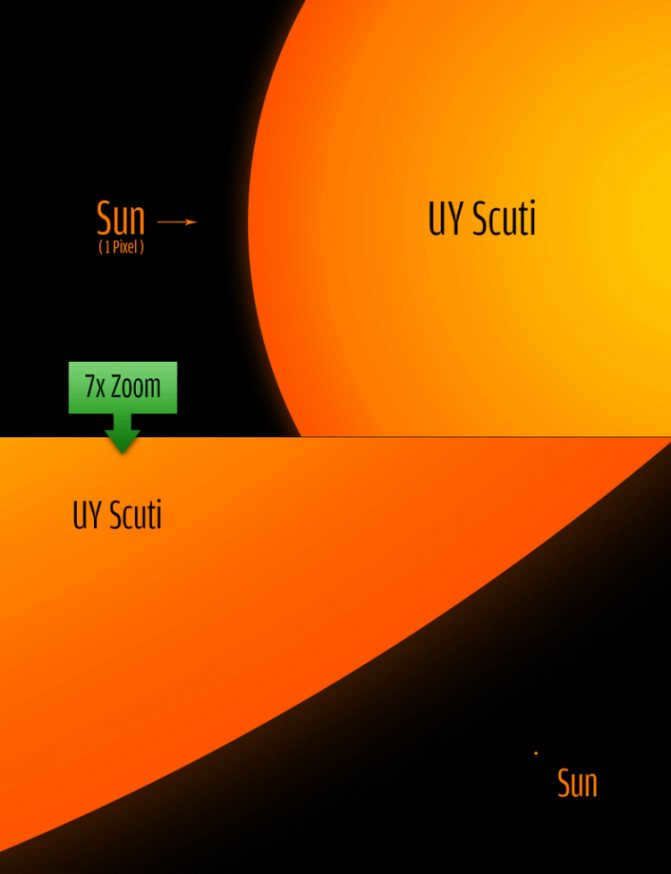
The Largest Star in the Universe: UY Scuti
0
View all images in the gallery
UY Scuti, a hypergiant star, holds the title for being the largest star in the known Universe. With a radius 1700 times that of the Sun, it surpasses any other star we have observed. If UY Scuti were located at the center of our Solar System, its immense size would extend beyond the orbit of Jupiter, and the gases and dust emitted from its surface would reach a distance 400 times greater than the distance from Earth to the Sun, extending even beyond the orbit of Pluto.
It is located about 600 million light years away from Earth
It was named after the scientist who discovered it back in 1950.
This particular galaxy has
a unique structure and appearance.
It was actually the first known galaxy with a ring shape. The ring itself has a diameter of approximately
100,000 light-years.
The outer part of the ring is mainly composed of bright blue stars
while the inner part contains a ring of reddish stars
which are believed to be much older. There is a darker ring located between these two rings. The exact formation process of
Hogg’s object
remains a mystery, although there are other similar objects that have been identified.
Hogg’s Object, captured by the Hubble Space Telescope in July 2001
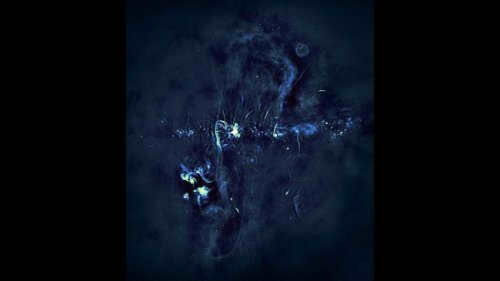
Fermi Bubbles: The Galactic Bubbles of Unprecedented Size
0
In 2010, a team of astronomers utilizing the Fermi Space Telescope made a groundbreaking discovery – they stumbled upon immense structures that originated from the depths of the Milky Way. These colossal cosmic formations, commonly referred to as “blobs,” can only be observed in specific wavelengths of light and span a staggering 25 thousand light years, equating to a quarter of the size of our own galaxy. The prevailing theory among scientists is that these expansive bubbles are the remnants of an exceptionally violent event, a monumental outburst of energy emitted by our central black hole, often referred to as its colossal “energy burp.”
The Cigar Galaxy in the constellation Big Dipper.
Located 12 million light years away from Earth
Galaxy M 82
Alternatively referred to as the
Cigar Galaxy
it is a satellite galaxy of M 81. It is famous for its supermassive black hole
which is accompanied by two smaller black holes in orbit
In addition, this galaxy has a high rate of star formation. At the core of the Cigar Galaxy, new stars are being born
10 times faster
than in our own Milky Way galaxy.
The astoundingly beautiful Cigar galaxy.


The most massive structures in the cosmos.
When we think of immense objects, our minds often turn to the ancient pyramids, the towering skyscrapers of Dubai, or the majestic Mount Everest. These awe-inspiring structures are undeniably massive, but in the grand scheme of the universe, they are mere specks in the vast expanse of space.
The most colossal asteroid
At present, the title of the largest asteroid in the universe belongs to Ceres. With a mass accounting for nearly a third of the entire asteroid belt and a diameter exceeding 1000 kilometers, Ceres is so enormous that it is sometimes classified as a “dwarf planet.”
The biggest planet
The most enormous planet in the universe is TrES-4, which was detected in 2006 and is situated in the Hercules constellation. TrES-4 orbits a star that is roughly 1400 light years away from our planet Earth.
TrES-4 itself is a massive sphere primarily composed of hydrogen. Its dimensions are 20 times greater than those of Earth. Researchers assert that the discovered planet’s diameter is nearly 2 times larger (1.7 to be precise) than Jupiter’s diameter, the largest planet in our solar system. The temperature on TrES-4 reaches about 1260 degrees Celsius.
Biggest black hole
When it comes to size, black holes are not particularly large. However, when considering their mass, these celestial objects are the largest in the entire universe. And the most massive black hole in space is a quasar, boasting a mass 17 billion times greater than that of the Sun. This colossal black hole resides at the very core of the NGC 1277 galaxy, an entity that surpasses the size of the entire solar system – its mass accounts for 14% of the total mass of the entire galaxy.
The largest galaxy
Known as “super galaxies,” these are conglomerates formed by the merging of several galaxies, and they are typically found in galactic “clusters” – clusters of galaxies. The largest of these “super galaxies” is IC1101, which is a staggering 60 times larger than the galaxy that houses our solar system. IC1101 stretches across a distance of 6 million light-years. In comparison, the Milky Way measures a mere 100,000 light-years across.
VY of the Big Dog is the largest known star and one of the most luminous stars in the celestial sphere. It is a red hypergiant situated in the constellation of Canis Major. The size of this star is approximately 1800-2200 times the size of our Sun, and its diameter reaches about 3 billion kilometers.
Astronomers have made a remarkable discovery of the most massive reservoirs of water ever encountered in the Cosmos. The colossal cloud, estimated to be around 12 billion years old, contains an astonishing 140 trillion times more water than the total volume of Earth’s oceans combined.
This gaseous water cloud envelops a supermassive black hole located 12 billion light-years away from our planet. This groundbreaking finding indicates that water has been abundant in the universe throughout its entire existence, as stated by the researchers.
The most extensive assemblage of galaxies
El Gordo is positioned at a distance of over 7 billion light-years from our planet, which means that what we are currently observing is merely an early phase of its existence. As per the analysis conducted by scientists on this galaxy cluster, it stands out as the largest and hottest cluster known at this distance, or even further.
The central galaxy situated within El Gordo emits an incredibly intense light and possesses a distinct blue luminescence. The researchers behind the study propose that this extraordinary galaxy is the outcome of a collision and subsequent merger between two galaxies.
By employing the Spitzer Space Telescope and optical images, researchers have estimated that approximately 1 percent of the cluster’s total mass consists of stars, while the remaining majority is composed of hot gas filling the interstellar space. This proportion of stars to gas mirrors that of other massive clusters.

In recent times, researchers have made an astounding discovery – the most immense frigid region in the cosmos (at least as far as the currently known universe is concerned). Situated in the southern region of the Eridanus constellation, this spot spans a staggering distance of 1.8 billion light years, leaving scientists astounded as they never fathomed that such a phenomenon could truly exist.
Despite being called a “void,” which means “emptiness” in English, this region of space is not completely empty. It actually contains approximately 30 percent fewer galaxy clusters compared to the surrounding space. Scientists believe that these voids make up as much as 50 percent of the volume of the universe and that this percentage will continue to increase due to the incredibly strong gravity that attracts all matter towards them. There are two aspects that make this particular void intriguing: its immense size and its connection to the enigmatic WMAP cold relic spot.

Back in 2006, scientists stumbled upon a peculiar cosmic “bubble” (or blob, as they prefer to call it), which was then crowned as the largest entity in the Universe. However, its reign was short-lived. Stretching across a whopping 200 million light-years, this bubble is essentially a colossal conglomerate of gas, dust, and galaxies.
What sets this bubble apart are its three “tentacles,” each housing galaxies that are four times denser than the average in the Universe. Within this bubble lies a cluster of galaxies and gas balls known as the Lyman-Alpha bubbles. These extraordinary formations are believed to have materialized roughly 2 billion years after the Big Bang and serve as authentic remnants from the early days of our universe.

For numerous years, experts have held the belief that our galaxy, the Milky Way, is being drawn through space at a velocity of 2.2 million kilometers per hour towards the Centauri constellation. Astronomers have put forward the hypothesis that this motion is brought about by the Great Attractor, an entity possessing a gravitational force of such magnitude that it can attract entire galaxies towards itself. However, determining the nature of this entity has proven to be a challenge for scientists, as it is situated beyond the region known as the “zone of avoidance” (ZOA). The ZOA is a portion of the sky adjacent to the Milky Way’s plane, where the density of interstellar dust is so great that the visibility of objects situated behind it is severely diminished.
When scientists decided to investigate further into the depths of space, they made a fascinating discovery. It turns out that the “great cosmic magnet” is actually much larger than anticipated. This immense object is known as the Shepley supercluster.
The Shepley supercluster is not your average cluster of galaxies; it is a supermassive one. Its size is so colossal, and its gravitational force so powerful, that even our own galaxy is subject to its pull. With over 8000 galaxies and a mass equivalent to over 10 million suns, this supercluster holds sway over every galaxy in our corner of the cosmos.
Enter the Laniakea supercluster
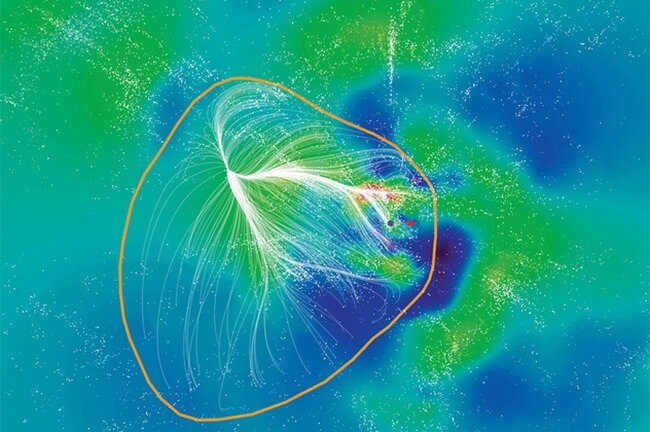
Clusters are typically formed by galaxies. These clusters are known as superclusters when they are densely packed together in specific regions of space. In the past, astronomers have used the physical location of these objects to map them in the Universe. However, a new method of mapping local space has recently been developed, which provides insights into previously unknown data in the field of astronomy.
The latest approach to mapping local space and the galaxies within it is primarily based on measuring the gravitational influence exerted by each object, rather than solely calculating its physical location.
The initial findings from the investigation into our neighboring galaxies using the novel research technique have already yielded results. Researchers have identified a fresh supercluster based on gravitational flux boundaries. The significance of this study lies in its ability to enhance our comprehension of our position within the cosmos. Formerly, it was believed that the Milky Way resided within the Virgo supercluster, but recent research indicates that this area is merely a part of the much larger Laniakea supercluster, one of the most expansive entities in the Universe. Spanning a distance of 520 million light-years, our location is situated somewhere within this vast supercluster.
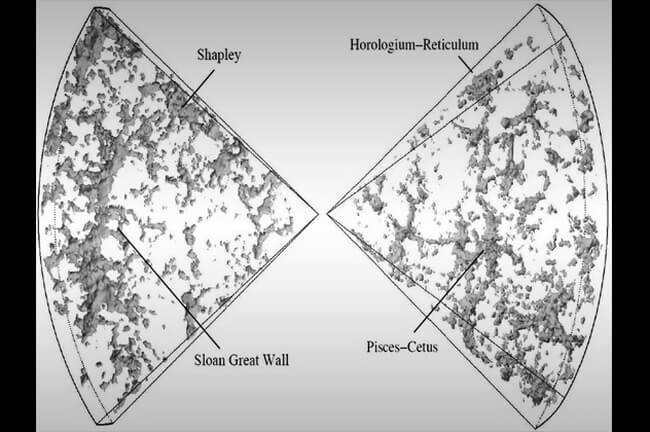
The discovery of Sloan’s Great Wall took place in 2003 during the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, a scientific project aimed at mapping countless galaxies in order to establish the presence of the largest objects in the Universe. Sloan’s Great Wall is an immense galactic filament consisting of numerous superclusters spread throughout the Universe, resembling the tentacles of an enormous octopus. With a length of 1.4 billion light-years, this “wall” was once regarded as the largest entity in the entire universe.
While the Great Wall of Sloan itself has received less attention compared to the superclusters it encompasses, some of these superclusters are noteworthy in their own right and deserve special recognition. For instance, one of them exhibits a core composed of galaxies that collectively resemble massive tendrils. Another supercluster displays an exceptionally high level of galaxy interactions, many of which are currently undergoing merging processes.
The Massive-LQG7 cluster of quasars.

Quasars, located at the center of galaxies, are celestial objects that emit high-energy radiation. These powerful emissions are believed to be generated by supermassive black holes that attract surrounding matter. The resultant radiation is approximately 1,000 times stronger than the collective energy output of all the stars in a galaxy. Currently, scientists have identified the Huge-LQG group of quasars as the third largest entity in the universe. This group consists of 73 quasars spanning a distance of 4 billion light-years. Researchers speculate that these massive quasar clusters, along with similar ones, play a significant role in the formation of the universe’s largest structures, such as the Great Wall of Sloan.
Giant gamma-ray ring

The Giant Galactic Gamma-ray Ring (Giant GRB Ring) is an astonishing object in the Universe, stretching over an impressive 5 billion light-years. Not only is it incredibly vast, but it also stands out due to its unique and peculiar shape. Scientists who have been studying gamma ray bursts, which are enormous releases of energy resulting from the demise of massive stars, have made an intriguing discovery. They have identified a series of nine bursts that originated from sources located at the same distance from Earth. These bursts have formed a magnificent ring in the sky, measuring 70 times the diameter of the full Moon.
The Great Wall of Hercules – Northern Corona

Astronomers have recently made a groundbreaking discovery during their gamma ray observation, finding the largest known object in the Universe. This colossal structure, named the Great Wall of Hercules-Northern Corona, stretches across an astonishing distance of 10 billion light-years. In fact, it is twice the size of the Giant Galactic Gamma-Ring. The reason why the brightest bursts of gamma rays come from larger stars, typically found in regions of space with higher matter content, is because these bursts are metaphorically seen as needles pricking into something much larger. Upon observing that a particular area in the Hercules and Northern Crown constellations was experiencing an unusually high frequency of gamma ray bursts, scientists concluded that there must be an astronomical object present. This object is believed to be a dense concentration of galactic clusters and other matter.
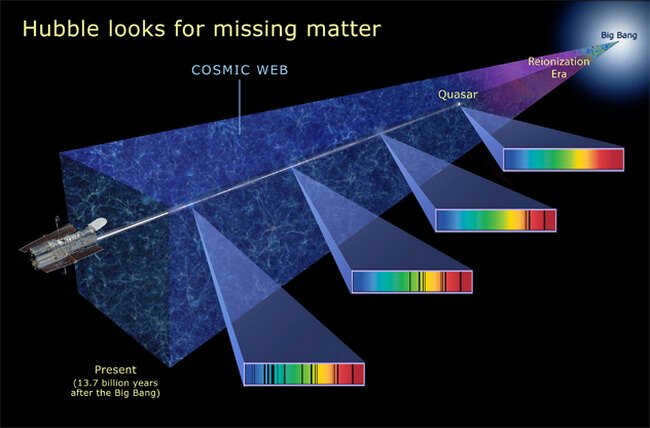
It is believed by scientists that the expansion of the universe is not a haphazard event. There exist theories that propose the existence of a colossal structure in which all the galaxies in the cosmos are intricately connected, forming filament-like structures that link dense regions together. These filaments are interspersed among less dense regions, creating a network that scientists have referred to as the Cosmic Web.
Scientists believe that the web was created during the early stages of the universe’s existence. This initial formation of the web was unstable and uneven, but it ultimately contributed to the development of everything we see in the Universe today. The “threads” of this web are thought to have played a crucial role in the Universe’s evolution, speeding up the process. Galaxies located within these filaments experience a much higher rate of star formation. Additionally, these filaments act as bridges for gravitational interactions between galaxies. Once formed within these filaments, galaxies move towards galactic clusters and eventually fade away over time.
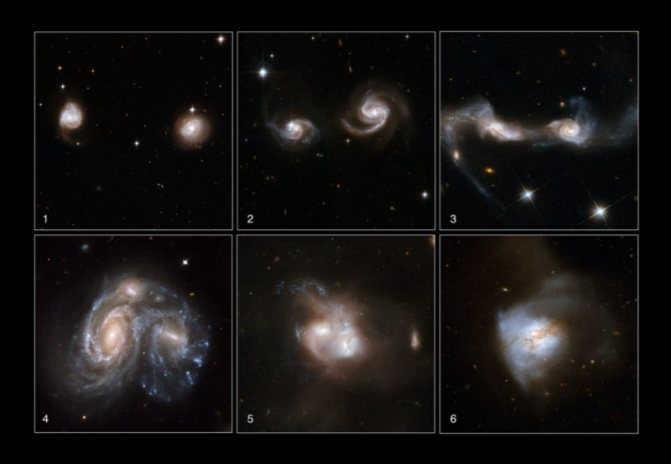
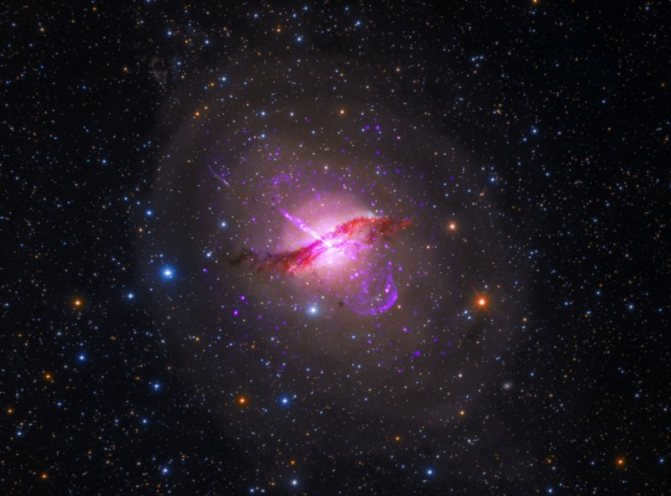
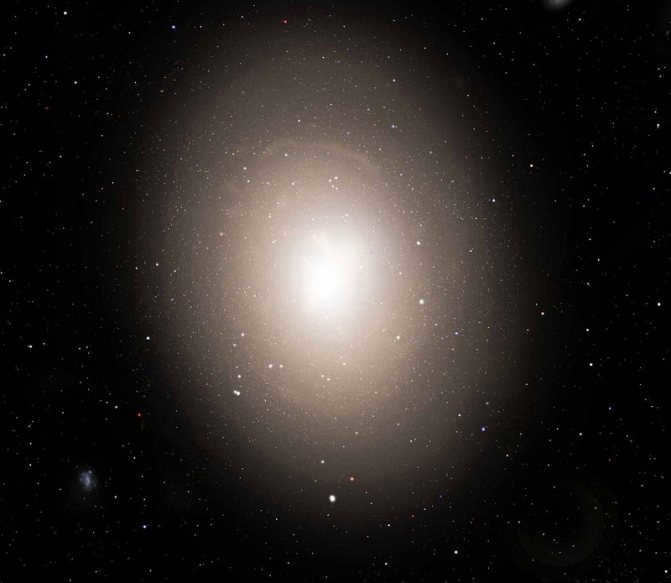










The biggest pulsar
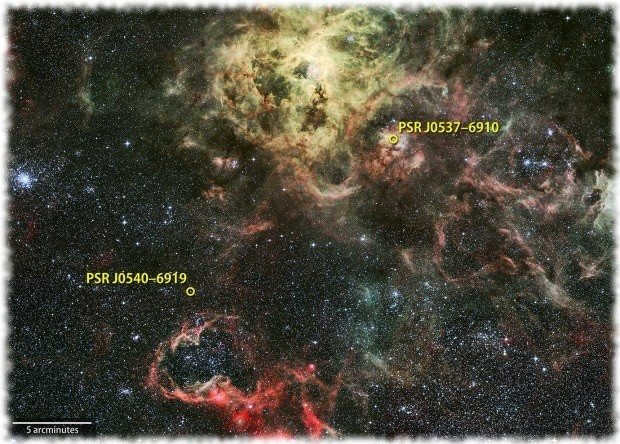

Scientists have made an incredible discovery in the Tarantula Nebula of the Large Magellanic Cloud. They have found the largest known pulsar, a pulsating star with an incredibly dense mass. This extraordinary finding was made using a state-of-the-art gamma-ray telescope located 165,000 light-years away from our own Milky Way galaxy.
The pulsar formed after a massive star exploded, leaving behind a dense core known as a neutron star. This neutron star has a diameter of just a few kilometers but has a mass equivalent to twenty times that of our Sun. What makes this pulsar even more remarkable is its gamma-ray emission, which is five times greater than the emission from the famous pulsar found in the Crab Nebula.
The pulsar spins at an astonishing rate of twenty revolutions per second, emitting the most powerful gamma rays ever observed. This groundbreaking discovery provides scientists with valuable insights into the nature of pulsars and the extreme conditions in which they exist.
The Shepley supergroup
The supergroup from Shepley is an exceptional musical ensemble that has gained a significant following in recent years.
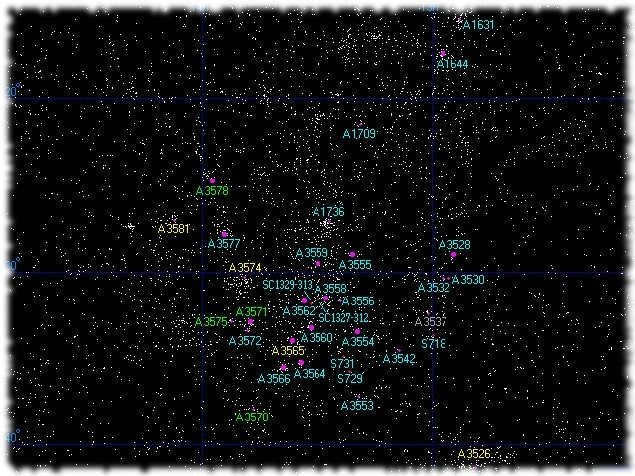
Shepley Supergroup Star Map
The Shepley Supergroup is an immense constellation of stars that was first observed in 1989. It boasts a remarkably high stellar density. In total, preliminary estimates suggest that the Shepley Supergroup contains a concentration of stars spanning over 500 million light-years. It is also home to the prominent galaxies A3560, A3558, and A3559. Altogether, approximately twenty-five galaxies are situated within the bounds of the Shepley Supergroup.





