The issue of determining the distance between the Moon and the Earth has been resolved for a long time. In ancient times, it was a matter of debate as science did not provide a clear answer. However, it is now known that the Moon is not larger than the Earth. This article provides valuable information on the parameters used for comparison. It covers topics such as the Moon’s rotation, as shown in the photo, its appearance from Earth, and other intriguing facts.

Comparing the Sizes of Earth and the Moon
Eratosthenes of Cyrenaica was the first person to provide a convincing explanation and accurate calculation of the Earth’s diameter. This groundbreaking discovery occurred in 240 B.C. Utilizing a scaphis, a bowl with a long needle, Eratosthenes determined the angle at which the Sun is positioned in the sky. By using this information, he was able to calculate the radius of the Earth.
Also, check out this article: The Truth About the Moon’s Color.

However, he made a slight mistake. Around that same period, Aristarchus of Samos, a Greek astronomer, mathematician, and philosopher, determined the distance between the Moon and the Earth, as well as the Sun, using the concept of similar triangles.

However, the response provided only addressed the proportional relationship. It is possible that these two scientists were in communication, and as a result, the sizes of the Moon and the Earth had already been determined.


Undoubtedly, these computations were well-known to the Egyptian scholar Hermes Trismegistus, who was believed to be a direct descendant of the surviving priests of Atlantis. Similarly, other scientists across different continents were also aware of these calculations. The Maya civilization and other ancient civilizations had made similar close calculations. However, this article focuses on the advancements in modern science and the knowledge we have today.


The Moon has a diameter of 3474 km, while the Earth has a diameter of 12742 km, making it 3.6 times smaller. When compared to other celestial bodies, the Moon is relatively small in size:
- The Moon’s length along the Equator is 10917 km;
- The Moon’s radius is 1737 km;
- The surface area of the Moon is 38 million square kilometers.

By comparing the dimensions to the latitudes of our country, we can make an estimation of the actual magnitude of the satellite. For instance, its diameter is equivalent to half the distance of the Moscow – Vladivostok federal highway.
Contrasting the sizes of the Earth and the Moon
The Moon’s size is 13.5 times smaller than that of the Earth. It is still difficult to determine how much larger the Earth’s landmass is compared to the Moon’s landmass. The Indian probe “Chandrayaan-1” has reported that some of the Moon’s water is distributed across lakes and flows from one to another. Recent data suggests that there is approximately 600 million tons of water in solid form. This is roughly equivalent to the water retention capacity of the Bureyskaya HPP during a flood or two-thirds of the volume of Lake Seliger. The land area of the Earth is 3.7 times greater than the combined lunar land area.


What is the size comparison between the Earth and the Moon? The Moon is 50 times smaller in volume than the Earth. In terms of total planetary parameter, it is only 2% of the Earth’s size. The Earth is naturally much larger than its satellite, with an 80-fold difference in mass. These statistics indicate a significant disparity in rock density that is not in favor of the Goddess Selene.

The Earth and the Moon have different sizes, and this is evident in the force of gravity. The Moon is smaller than the Earth, which means that the gravitational pull on the Moon is weaker. As a result, if a person weighs 70 kg on Earth, they would only weigh about 12 kg on the Moon. This difference in weight gives the person the ability to make long and high jumps on the Moon.
Aside from the fact that a weightlifter with a 200 kg barbell at 1200 kg would hardly emerge victorious. The slow process and muscle tension during the jerk would have undoubtedly played a significant role. It’s safe to say that it’s not as straightforward as it seems.
INFO: The concept of a hollow celestial body has its supporters, including those who extend this idea to our own planet, Earth.
Visualizing the Difference
Determining the distance between the Earth and the Moon is a straightforward task that astronomers have already accomplished. However, the significance of this calculation goes beyond mere numbers. It is a moment that inspires awe and wonder. Nowadays, there is a growing interest in calculating the journey to the Moon and exploring the possibility of space travel.
It appears that a consensus has been reached that it is more feasible to observe from a satellite. When measured in kilometers, the interval between the minimum convergence of apogee and the maximum distancing of perigee is calculated to be 363.104 – 406.696 km. This results in a discrepancy of 40.075 units, which is approximately equivalent to the circumference of the Earth’s equator.

Imagination can be stimulated in a more visual manner. Take, for instance, a comparison of familiar objects – a nickel and a pea. Alternatively, a tennis ball and a basketball. The ratio between them is 3.6, which is the same as the ratio between the Moon and the Earth.


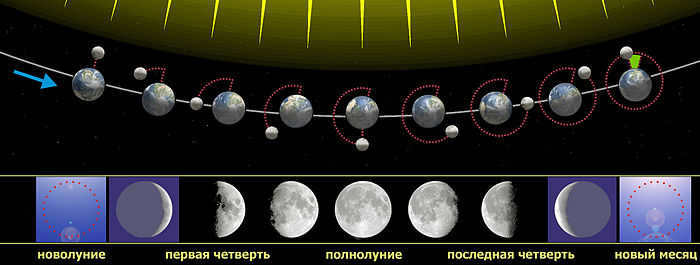
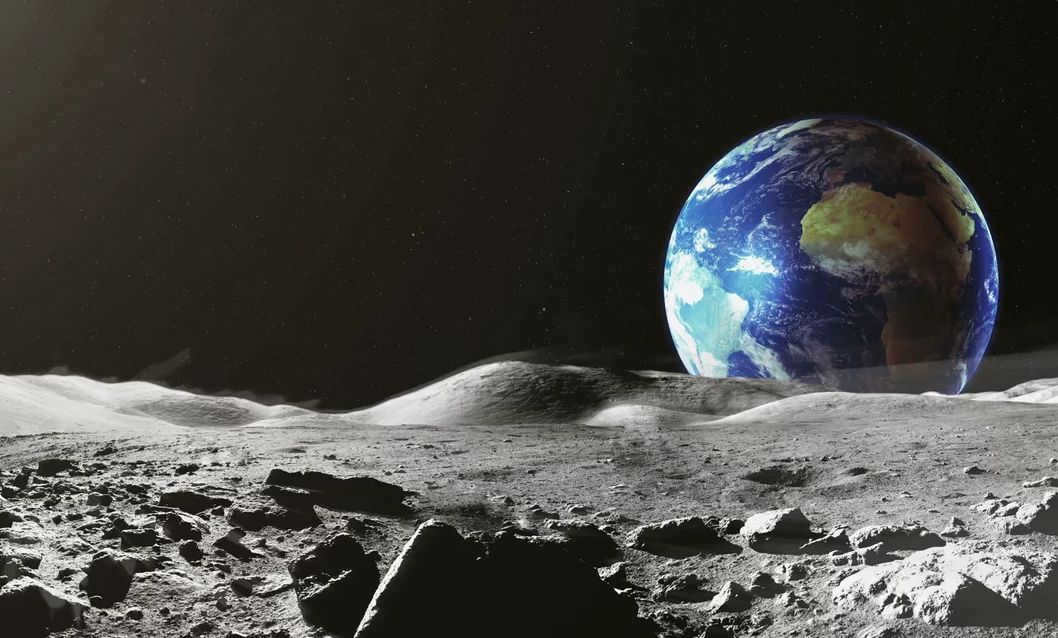
What does the Earth look like from the Moon?
It became possible to see what the Moon itself or the Earth looks like from its surface after receiving photos and videos from a satellite. These were captured by both astronauts and moonwalkers. Probes that were sent into the orbit of the closest space object to us also contributed to this.

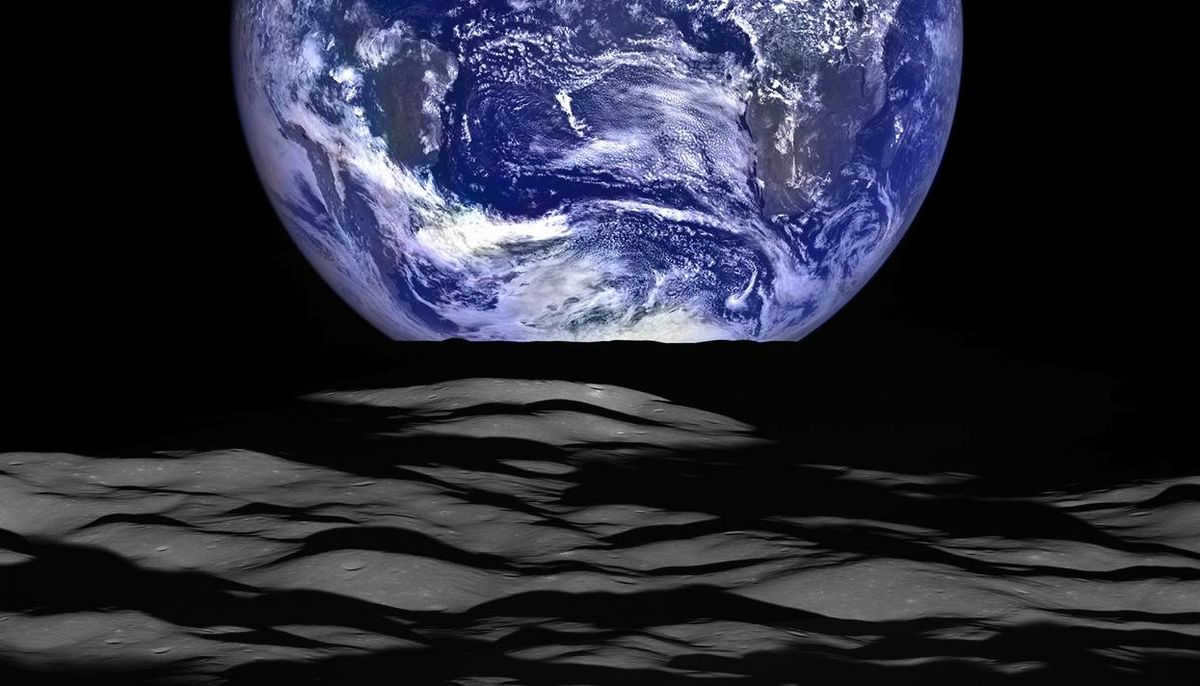
Earthrise photos are extremely precious. It’s not just because the Apollo 8 crew captured the most valuable picture in 1968.
It’s simply that these kinds of photos can only be taken from the moon during specific moments. This particular image is witnessed approximately once a month, yet its impact is truly awe-inspiring.


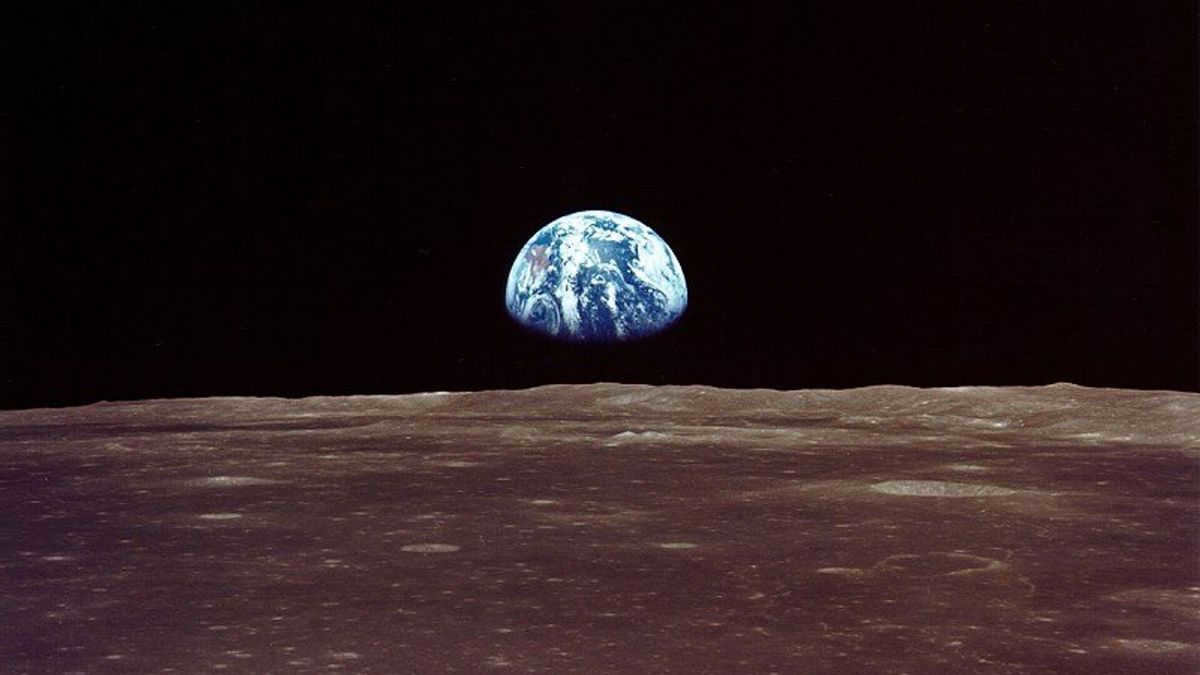
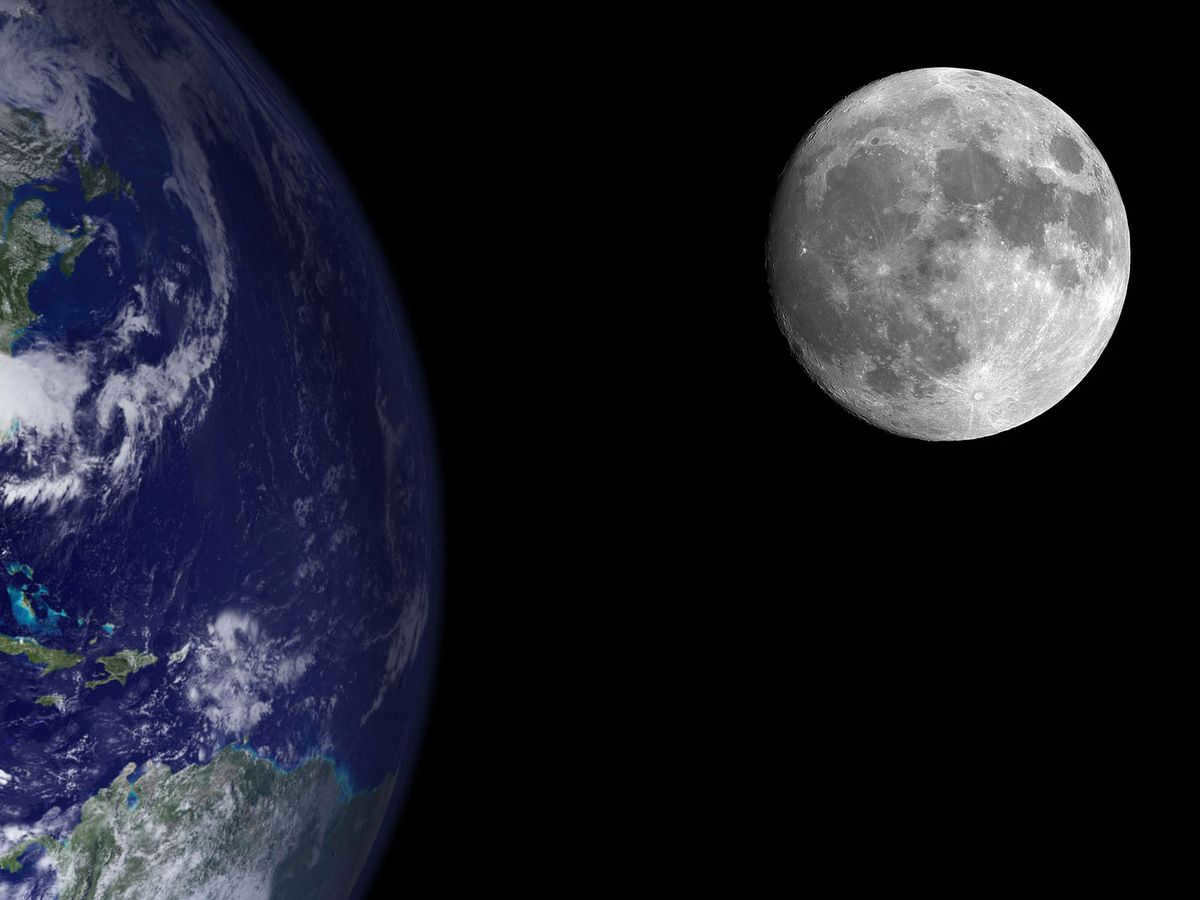
As mentioned, the Moon is smaller than the Earth, with the Earth being 13.5 times bigger than its satellite. This proportion is accurately depicted in the photo. Additionally, when viewed from the lunar surface, the Earth appears 43 times brighter than the Moon does from Earth.


Earthrise (video)
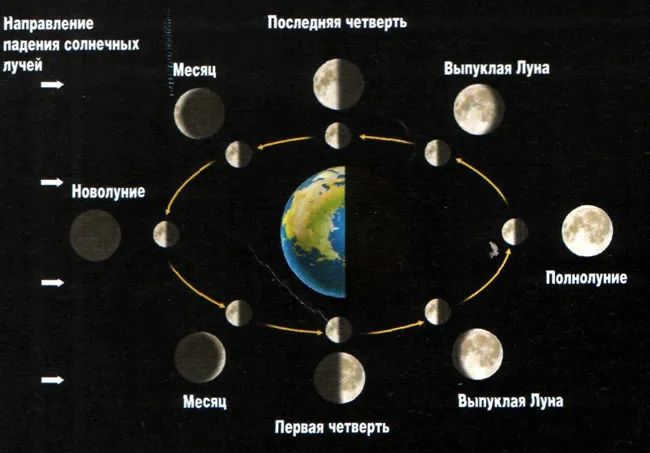
Does the moon spin around?
As stated by Efrem Pavlovich Levitan, an astronomer and writer of an 11th-grade astronomy textbook, the Moon and Earth used to be much closer to each other billions of years ago.
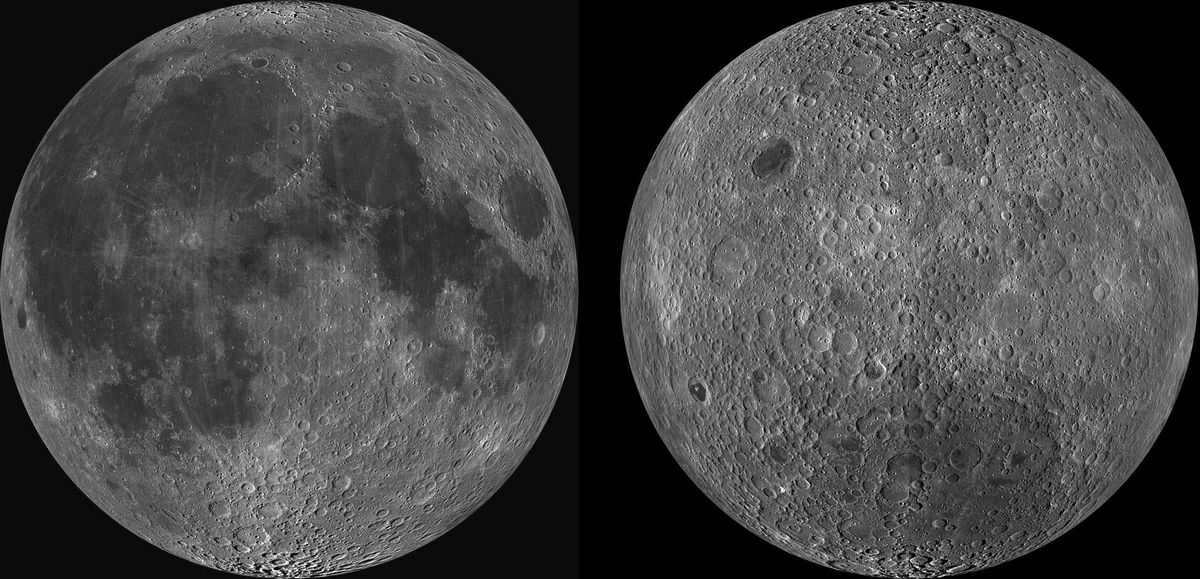

Currently, they are at a greater distance from each other, resulting in a longer orbital period of the Moon around the planet. During this stage of Earth’s development, the rotation period of the Moon is equivalent to its orbital period. This phenomenon embodies the core of the phenomenon.

Consequently, two statements arise:
- A solar day on the Moon lasts for 2 Earth weeks (synodic month).
- The dark side of the Moon, also known as the second lunar hemisphere, is not visible from Earth.
The question is open to debate, but the terminology is agreed upon. The definition of rotation is also subjective. However, it is always clarified that it will be referred to as “angular” in this context.


Various instances and hypotheses can prompt ideas. On the internet, there are discussions on theoretical astrophysics regarding spins and strings, violations of relativity principles, and more. It is intriguing to consider that even a plane unwound on a fishing line revolves around its axis.


However, based on certain principles, the situation is similar to that of a natural satellite: the side of the airplane that is hidden from the viewer is also not visible. Naturally, the airplane will not complete two rotations around its axis, as it is securely fixed. On the other hand, if the Moon were to do so, its entire surface would be visible.

Here’s another instance that illustrates the accepted theory. A pair of dancers spinning in a waltz remain motionless in relation to each other. However, the walls surrounding them shimmer like distant stars. Meanwhile, the dancers can come to a halt, and one of them can circle around the other without ever turning their back. It’s almost like a rotation on a different axis, although it is still acknowledged as such.

Is the Earth orbited by the moon? (video)
The moon is not the most well-known celestial body in our solar system. It is commonly known as a satellite of our planet, but what other information do we have about it? How big is it and what unique characteristics does it possess?
Understanding the Moon
The moon is a natural satellite that orbits around our planet. It is easily visible in the night sky and is one of the most prominent objects.
This cosmic object was created approximately 4.5 billion years ago when the young Earth collided with a Mars-sized object. This collision caused debris to break away from Earth, eventually combining to form the moon.
The moon plays a crucial role in life on Earth. One of its most noticeable effects is the creation of tides in our oceans. These tides are a result of the moon’s gravitational pull on our planet. These natural occurrences have a significant impact on marine ecosystems and other natural processes.
This cosmic entity is also the focus of scientific investigation and space exploration.
Exploratory expeditions to the moon have yielded valuable data regarding the genesis of our planet’s natural satellite, its geological makeup, mineral composition, and potential resources, rendering it a captivating candidate for forthcoming space exploration endeavors and potential utilization in space missions.

The comparison of the diameters of the planet and the satellite
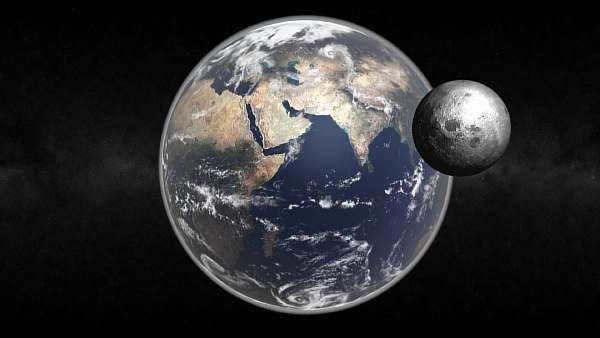
Which celestial body is larger – the Moon or the Earth? The Earth is significantly bigger than its companion. Our planet has a diameter of approximately 12,742 kilometers, while the diameter of the Moon is only around 3,474 kilometers.
An analysis of the sizes of the Earth and the Moon
Scientists have long ago provided an answer to the question – how many times is the Moon smaller than the Earth? The diameter of Earth’s satellite is 27% of the size of our planet. Therefore, the Moon’s size is approximately 4 times smaller.
In terms of mass, our planet is 81 times heavier than its satellite.

Differentiating the Earth from the Moon
Aside from the obvious disparity in size between the Earth and its celestial satellite, there exist other distinguishable dissimilarities:
The Earth boasts a significantly greater mass compared to its lunar companion. The mass of our home planet is approximately 5.97 x 10^24 kilograms, while the Moon’s mass is around 7.35 x 10^22 kilograms. Visual aids such as graphs or charts can be employed to effectively illustrate the disparities in mass between these two celestial bodies.
Gravity plays a significant role in distinguishing the Moon’s surface from that of Earth. Due to the Moon’s smaller mass, its gravitational pull is considerably weaker compared to our planet. This can be exemplified by observing how objects behave on both celestial bodies – for instance, jumps on the Moon would be much higher due to the diminished gravity.
Moreover, the physical compositions of Earth and its lunar companion differ as well. Our blue planet boasts vast oceans, continents, majestic mountains, and diverse natural formations, whereas the Moon showcases distinct deserts, mountains, and crater-filled surfaces. Visual aids such as photographs or images can effectively highlight these contrasting features.

Visualizing the Difference
To get a sense of the size difference between the Earth and the Moon, you can use pre-made models of both celestial bodies. Alternatively, you can compare a pea and a five-ruble coin, or two basketballs – one for basketball and one for tennis.
In both of these examples, the larger object is significantly bigger than the smaller one, just like our home planet is much larger than its companion.
How the Moon Offers a Unique View of Earth
When standing on the lunar surface, our home planet appears as a stunning, radiant sphere. Unlike the view from Earth, where the Moon appears as a small, gray satellite, from the Moon, Earth is a magnificent, immense disk set against the dark backdrop of space.
The most captivating aspect is the vibrant blue hue of our planet, which results from the reflection of sunlight off the vast oceans and atmosphere. This mesmerizing color dominates the view and creates a sense of awe and wonder.
The majority of Earth’s surface is covered by expansive oceans, which contribute to its shimmering appearance. Continents and clouds are also discernible, though they appear smaller and less prominent compared to the majestic oceans.
Does the Moon spin around its own axis?
The Moon, Earth’s natural satellite, does indeed rotate on its own axis. However, its rotation is very slow, nearly matching its orbital speed around our planet. This is why we always see the same side of the Moon facing us.
Video: Does the Moon orbit around the Earth?
If the Moon Didn’t Exist
If our planet lacked a natural satellite, it would have various effects on both the planet and its inhabitants:
- Tides: The moon plays a crucial role in creating tides on Earth. Its gravitational pull on the oceans causes water to rise and fall. Without this cosmic object, tides would be significantly weaker, potentially impacting the marine ecosystem and metabolic processes in the oceans.
- The moon also slows down the rotation of Earth. Without a natural companion, Earth would rotate faster, resulting in shorter days. This would likely have implications for the climate and distribution of temperature on the planet.
- Hydrocarbons. According to certain studies, the moon might have played a significant role in the creation of hydrocarbons. In the absence of this crucial celestial body, the conditions for the formation and distribution of these vital organic compounds could be altered.
- Earth’s axis stability. The moon aids in maintaining the stability of Earth’s rotational axis, ensuring a relatively consistent tilt in relation to its orbit around the Sun. Therefore, without the moon, the Earth’s axis would be more prone to significant fluctuations, potentially resulting in dramatic climate and seasonal variations.
- At night, the Earth’s satellite, through reflecting sunlight, acts as a natural source of light, particularly in remote and sparsely populated areas. If it were not present, nights would be significantly darker, potentially impacting the behavior of nocturnal animals and humans.
- The moon holds great cultural significance for humanity, as it is often associated with myths, legends, and rituals in many different cultures. Its absence could potentially disrupt the development of certain cultural traditions and religious beliefs.
- The moon also plays a vital role in space exploration, serving as a natural platform for missions and exploration. Without it, the development and testing of new technologies and strategies used in space missions could become more challenging.

Some fascinating details about the moon
- The moon rotates at a slow pace, matching its orbit around the Earth. As a result, it always presents the same face to us.
- If someone were to step foot on our planet’s natural satellite, their weight would be significantly reduced compared to Earth. The difference would be approximately six times less. This means that jumps on the moon’s surface can be much higher and cover greater distances compared to our own.
- The lunar valleys, mountains, and craters are the product of over 4 billion years of geological history. Craters are formed when the moon collides with meteorites and other celestial objects since it lacks an atmosphere to shield its surface.
- It is worth mentioning that the Moon does not have any natural satellites of its own, unlike our planet.
- Due to the absence of a dense atmosphere, the Moon is susceptible to meteorite impacts and other space objects. Consequently, its surface is dotted with numerous craters formed from collisions with celestial bodies of various sizes.
- The lack of atmosphere also results in a perpetually black sky above the Earth’s satellite, enhancing visibility of stars and other celestial objects.
- The exploration of the moon has also unveiled the existence of water in the soil and ice deposits in certain craters located at the poles of Earth’s satellite. It is currently believed that there is a small quantity of water in the form of ice within some craters on the lunar surface. This revelation makes the moon a potentially captivating object for future space missions and further exploration.
- On the moon’s surface, there are areas referred to as “seas” or “oceans” which appear dark and flat. These regions, however, do not contain actual bodies of water but are instead volcanic plains that were once filled with lava millions of years ago.
- The Moon has a significant impact on human life as it is involved in regulating various processes. One of its prominent effects is the creation of tides in the oceans, which occur due to the gravitational pull between the Moon and the Earth. These phenomena play a crucial role in the marine ecosystem and other natural processes.
Engaging video: Discover 43 fascinating facts about the Moon


Solar System
At any given time, the Moon is situated no closer than 361,000 kilometers and no farther than 403,000 kilometers away from Earth. The distance from the Moon to Earth fluctuates due to the Moon’s elliptical orbit around the Earth, rather than a perfect circle. Additionally, the Moon gradually moves away from the Earth at an average rate of 5 centimeters per year. Throughout the centuries, individuals have observed the Moon’s diminishing size. There may come a time when the Moon separates from the Earth and ventures into space, becoming an autonomous celestial body. However, this occurrence is not guaranteed. The equilibrium of gravitational forces ensures that the Moon remains firmly within Earth’s orbit.
What is the reason behind the Moon’s movement away from Earth?
Every object in motion has a natural tendency to continue moving in a straight line due to inertia. Similarly, an object moving in a circular path has a desire to break away from the circle and move tangentially to it. This desire to break away from the axis of rotation is known as centrifugal force. You may experience this force at a playground while riding a high-speed swing or when driving a car and making a sharp turn, feeling pressed against the door.
The term “centrifugal” means “moving away from the center.” The Moon also experiences this force, but it remains in its orbit due to the gravitational force exerted by the Earth. The Moon stays in orbit because the centrifugal force is counterbalanced by the force of Earth’s gravity. The closer a planet is to its satellite, the faster the satellite revolves around it.
Why is that so? Every object in motion has a certain amount of momentum. The momentum of a rotating object is determined by its mass, velocity, and distance from the axis of rotation. To calculate momentum, these three variables are multiplied together. Researchers have discovered that the momentum of an object remains constant. As a result, when an object gets closer to the axis of rotation, it will spin faster due to the law of conservation of momentum. This is because the mass in the equation cannot be altered arbitrarily.
What causes the moon to move backwards?
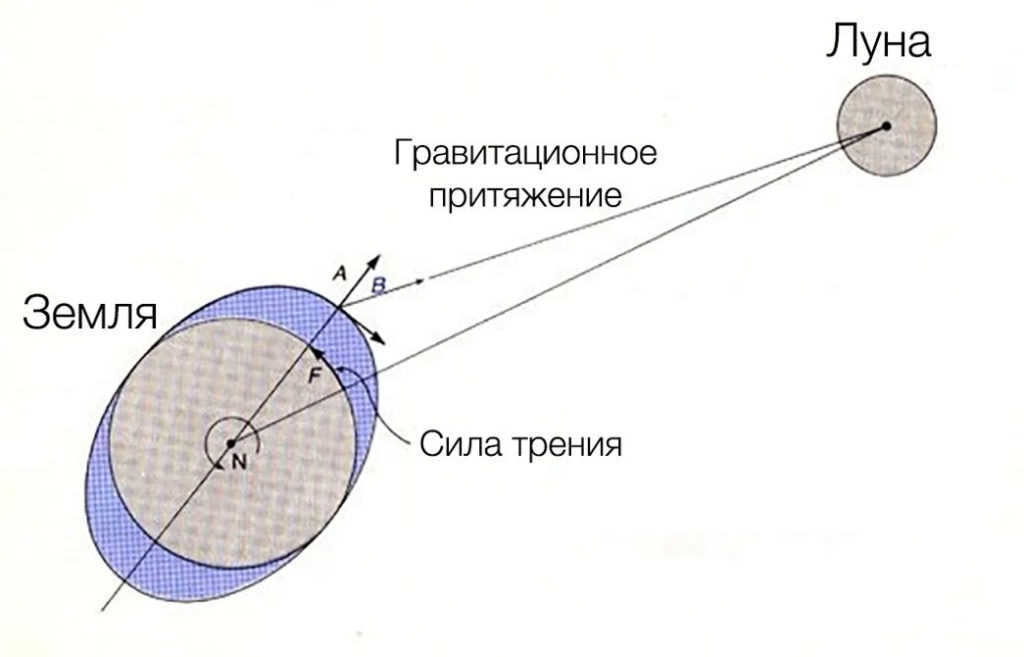
This principle, known as the principle of momentum preservation, states that the total momentum of a system remains constant unless acted upon by an external force. The Earth’s natural satellite, commonly known as the Moon, completes one full orbit around our planet in approximately 27 days. However, approximately 2.8 billion years in the past, a moon that was situated closer to Earth would complete its orbital journey in just 17 days. Clark Chapman, an esteemed astronomer affiliated with the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona, has suggested that at an even earlier point in time, the Moon was positioned even closer to Earth. Specifically, when the Moon initially formed approximately 4.6 billion years ago, its orbital period was a mere 7 days. If an observer had the opportunity to witness the Moon during that ancient era, they would have undoubtedly been awestruck by the immense size and captivating blood-red hue of the Moon as it ascended into the sky.
It is quite surprising that the movement of the oceans actually causes the Moon to move away from the Earth. This is how it works: the gravitational force of the Moon pulls on the water in the Earth’s oceans, attracting it towards the Moon. However, the Earth is not stationary – it rotates on its axis. As a result, when the ocean water surges towards the Moon, the rotation of the Earth pulls this mass of water away from the Moon.
The Moon is attracted by the gravitational force of the ocean water, but instead of pulling it directly towards itself, it exerts a slight forward force in the direction of the Earth’s rotation. This causes the Moon to receive an impulse that is not strictly aligned with the radius of its orbit, but tangential to it. As a result, the Moon’s orbit becomes longer over time. This lengthening of the lunar orbit is a gradual process that occurs month by month, causing the Moon to gradually move further away from the Earth. Although this process is slow and not easily noticeable, it has been occurring for millions of years and has had a significant impact on the Moon’s distance from our planet.
Perhaps in the future, the Moon will be distant enough from the Earth that the gravitational force of the Earth will weaken, allowing the Moon to embark on an independent orbit around the Sun. Nevertheless, experts are of the opinion that the Moon’s solitude is unlikely to pose a threat. This is because tides also affect the Earth. The shifting masses of ocean water exert a braking effect on the Earth’s rotation, causing the length of a day to increase by approximately half a minute every 100 years. (Billions of years ago, a day lasted no more than six hours.)
In the distant future, millions of years hence, the duration of the day and the period of one revolution of the Moon around the Earth will remain the same, but will extend well beyond twenty-four hours. As the Moon moves further away from the Earth, their rotations will become more synchronized, causing the ocean tides to align precisely with the Moon. At this point, the gravitational pull of the water will exert an attractive force on the Moon, causing it to halt its movement away from the Earth. This process will reverse once the tidal regions are positioned behind the Moon. The Moon’s orbit will begin to shrink, gradually bringing it closer to the Earth. It is possible that in the future, the colossal Moon will once again grace the sky.
Video: Measuring the Distance to the Moon
If you happen to come across any inaccuracies, kindly select the specific text and hit Ctrl+Enter to notify us.
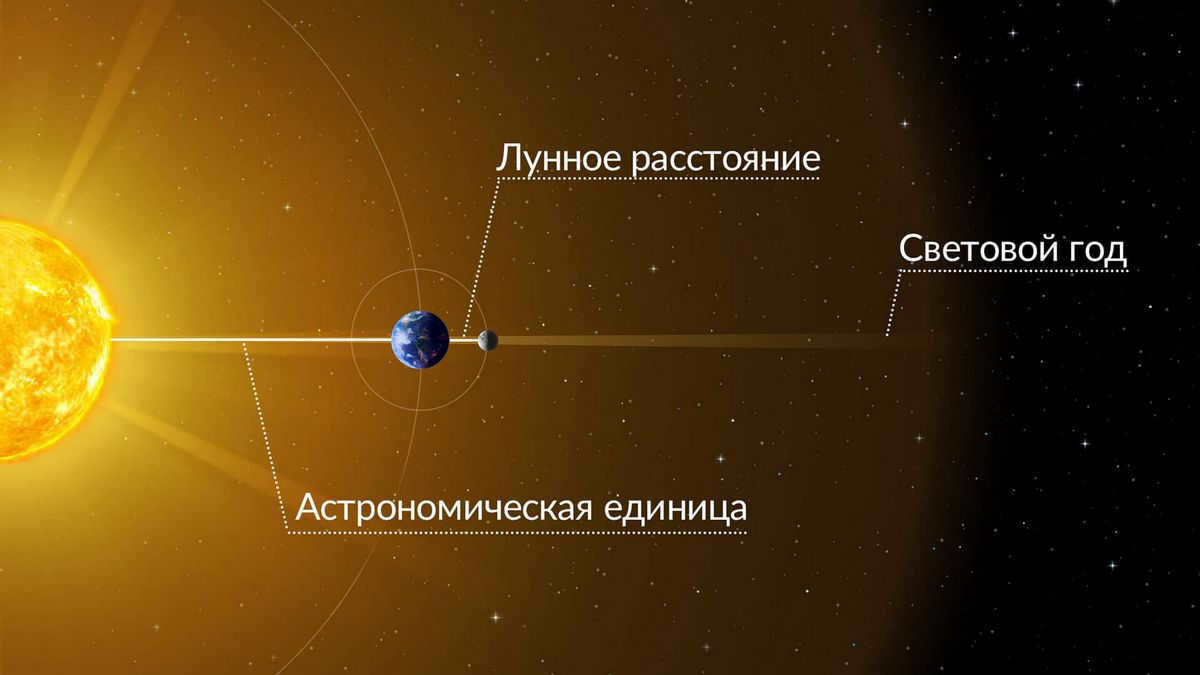
What is the measurement known as lunar distance? How are astronomical units utilized? What is the equivalent of one light year? In this article, we aim to provide straightforward responses to these inquiries.
Make sure to take a look at our infographic – within it, we have endeavored to effectively illustrate the utilization of space distance units.
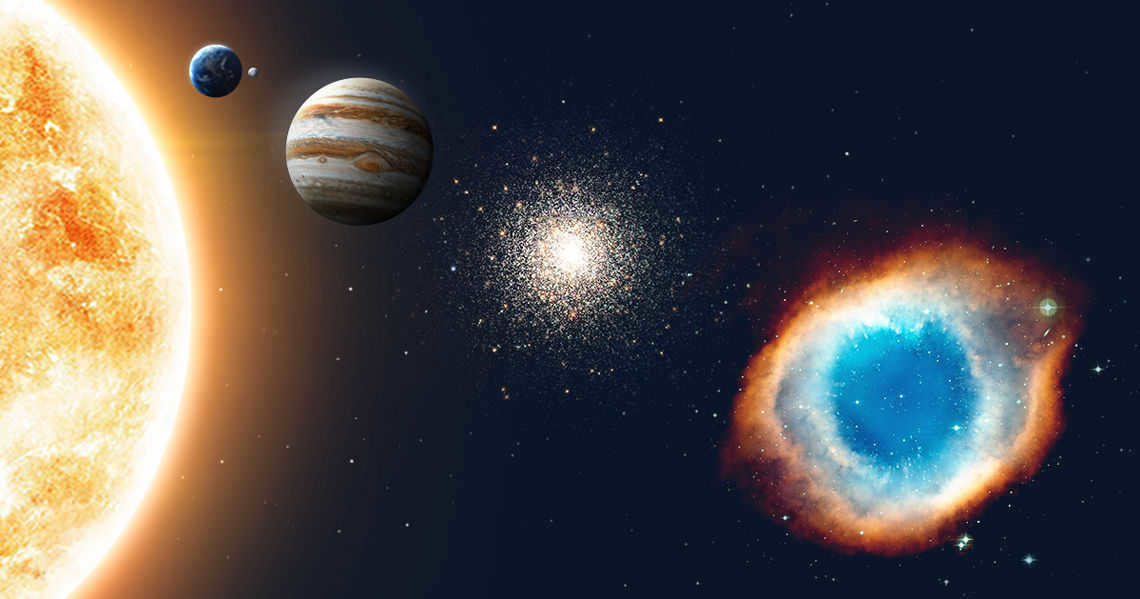

What is the comparison between lunar distance, astronomical unit, and light-year? Discover how astronomers utilize these concepts by reading our informative graphic.
What does lunar distance mean?
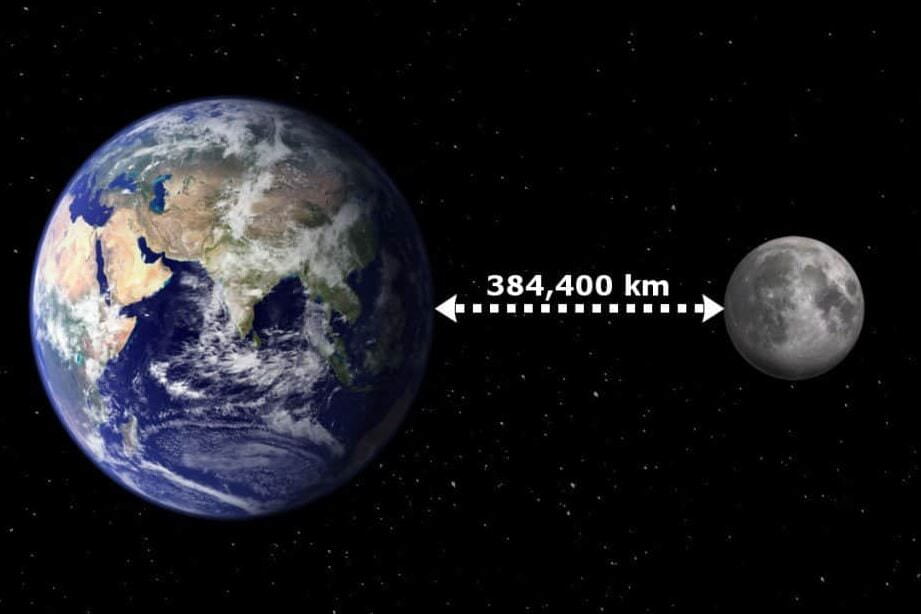
In the field of astronomy, lunar distance (abbreviated as LD) refers to the average span from the center of the Earth to the center of the Moon, which measures 384,400 kilometers. This distance is approximately equivalent to 30 Earth diameters.
Why is the average distance utilized? This is due to the fact that the Moon’s orbit is not perfectly circular, resulting in periodic changes in the distance from the Earth to the Moon. During perigee (the point in the lunar orbit closest to Earth), the Moon is, on average, approximately 363,228 kilometers away from us. Conversely, during apogee (the furthest point in the orbit from Earth), it is approximately 405,400 kilometers away.
Lunar distance is primarily utilized for measuring the distances to objects that are close to Earth – such as asteroids and comets. As an example, asteroid 2001 FO32, which came close to Earth in March 2021, was at a distance of five lunar distances from our planet.
What is an astronomical unit?
An astronomical unit (abbreviated a.u. or AU) is equivalent to the average distance between the Earth and the Sun, which is 150 million kilometers. Due to the elliptical orbit of the Earth around the Sun, the distance from our planet to the Sun varies by approximately 3% throughout the year. For this reason, astronomers use the average distance as a reference point.
Astronomical units are utilized for the purpose of measuring the distances between objects within the solar system and exoplanetary systems. As an example, Mars and Jupiter are situated 0.37 a.u. and 3.9 a.u. away from Earth, respectively, at the points in their orbits that are closest.
What does one light-year represent?
Despite its name, a light year (abbreviated sv. year or ly) is actually a unit of distance measurement, rather than time. One light-year is equivalent to the distance that light travels in a vacuum within 365 days – which equals 9.46 trillion kilometers.
Light years are employed to determine the distances to objects located outside of the solar system, such as other stars and galaxies. For instance, Proxima Centauri, the nearest star to our Sun, is situated 4.24 light-years away. The distance to our nearest large galaxy, the Andromeda Galaxy, is 2.5 million light-years away.
When it comes to professional astronomy, light-years are often preferred over parsecs (abbreviated pc or pc). One parsec is equivalent to 3.26 light-years.
Now that you have a better grasp of the distance measurement units for objects in space, we wish you clear skies and fruitful observations!

The typical measurement of the distance between the Earth and the Moon is usually done by calculating the distance between the centers of the two celestial bodies. This method is necessary because both the Moon and the Earth are constantly in motion. Due to the force of universal gravitation, the Moon, which is the Earth’s only satellite and the first satellite of the Solar System, continuously approaches and moves away from the Earth, following the traditional counting from the luminary. The distance between the Moon and the Earth in kilometers is not a fixed value, as it depends on the periods of motion, phases, and cycles of these celestial bodies, as well as their interactions.

Brief history of the problem
Attempts to determine the distance between the satellite and the planet have been made ever since humans realized that the Moon is not a hole in the solid sky that allows light to reach the planet at night. The commonly known figure of 384,400 kilometers (384,399 km to be precise) may be cited by authoritative sources as a number derived in relation to an astronomical unit.
However, the average distance is the value of the major semi-axis of the Moon’s orbit, which is 384,000 kilometers. And for the astronomical unit, it is defined as the distance from the Earth to the star that is the center and main driving force of the solar system.
The third celestial body of this solar system, the first one with an orbiting satellite, is located at a distance of 0.00257 astronomical units from its satellite. The latter is also the outcome of intricate computations, and it represents the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. The planet’s enigmatic satellite, which is nearest to the abode of humanity and perpetually present in the nocturnal firmament, has perpetually captivated human interest.
The moon was a mysterious and unfathomable enigma to the primitive consciousness.
Its capacity to traverse the sky and undergo transformations endowed it with mystique and enigma, thereby giving rise to numerous beliefs and superstitions. The advent of scientific inquiry, the relentless scrutiny of celestial motions, and the shadows cast upon the Earth engendered contemplation and calculation.
During ancient times in Greece, which was the center of modern European and world civilization, astronomers were constantly observing the movement of shadows and the celestial bodies, which were the brightest and most prominent in the sky above Earth. Other astronomers from different historical periods were also actively pursuing their studies:
- Aristarchus of Samos attempted to calculate the distance between the Moon and the Earth using a right triangle. However, he made a mistake that led to an error of nearly 29 times. This was primarily due to the Greeks lacking the means to make completely accurate astronomical observations.
- A hundred years later, Hipparchus of Nicaea achieved different outcomes by utilizing the radius of the globe as the measurement unit. He accurately calculated the distance between the Earth and the Moon, astounding even the most imaginative modern individuals. Only a truly exceptional scientist could use geometry, shadow observations, simple angular and optical instruments to calculate the distance with such minimal error (380-382 thousand kilometers).
- Currently, we are able to determine the remoteness by employing a laser beam. A reflector placed on the lunar surface by a space mission emits a beam of rays, some of which are then detected by a specialized device. The key factors in this method are the speed of light and the time it takes for the rays to travel the distance. Thanks to this precise method, measurements can now be made with minimal error.
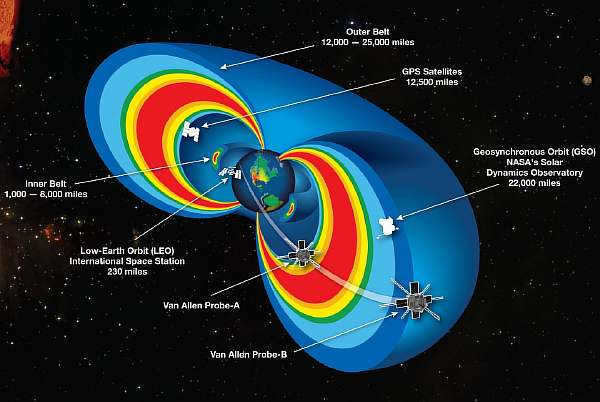
The calculation of distance in modern astronomy is based on a multitude of indicators – data acquired from the surface of our planet, radio signals and laser beams, spacecraft and telescopes, calculating machines and continuous observations.
The celestial scenery is in a constant state of flux due to the perpetual motion of the celestial bodies within it. The celestial object that is closest to our planet sometimes veers away and then returns on its elliptical orbit, resulting in variations in the distance, which can range from maximum to minimum values.
It is widely believed that our current understanding enables us to measure this distance with utmost precision, down to the nearest centimeter. However, search engine results may occasionally present different or conflicting figures. Furthermore, there are occasional claims that the exact measurements remain unknown.

Regarding the determination of distance and its various interpretations
Wikipedia is a widely-used platform to consult when in doubt about any piece of information. When asking for the distance between the Earth and the Moon, the response contains multiple figures, with an average of 384,467 kilometers.
The constant movement within the vastness of the Universe makes it impossible to provide a singular answer to the question of distance, thus necessitating knowledge of specific parameters. One must consider the Moon’s position in relation to the Earth’s surface and its movement based on its current phase.

Calculating the exact distance of the Moon from Earth in real time is an impossible task. This is due to the constant movement of the Moon, which means that the result will always be subject to noticeable changes.
However, by analyzing data obtained from long-term monitoring of the Moon, we can gain approximate knowledge about its distance from Earth. The Moon is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the only celestial body (besides Earth) that has been visited by humans.

Closest Point
The closest point of the lunar orbit to the third planet, known as the perigee, has an average distance of 363,000 km under various conditions. To simplify understanding, it is often rounded to 363,104 kilometers.
This value is of great significance in various beliefs, superstitions, and astrological predictions. However, it’s important to note that the actual distance can deviate significantly from the average, ranging from 356,400 kilometers to 370,400 kilometers – both of which are considerable distances by earthly standards. In recent times, the phases of the Moon and its proximity or remoteness from Earth have gained significant attention and importance among people.

The general public has grown accustomed to hearing astrologers’ predictions about the white moon (perigee) and black moon (apogee, or the farthest point from Earth), viewing alarming photographs, and learning the current location of Mars and the zodiac constellation associated with specific days of the month.
If you disregard mystical elements and popular superstitions, you can consider the forecasts’ results as reliable data. The cosmic balance does not negate the influence of the gravitational force, which causes not only the Earth to affect the Moon, but also allows the satellite to impact its primary celestial body. Additionally, the immense mass of the Solar System’s center enables it to maintain and rotate its planets and satellites, despite the considerable average distance of approximately 150 (149.6) million km.
All of this information is neatly summarized in the following table.
The distance between the centers of the Moon and the Earth is approximately 380 thousand km (384467 km), which can also be expressed as 0.00257 astronomical units (a. e.). This distance is roughly equivalent to 30 Earth diameters. The large semi-major axis of the Moon’s elliptical orbit, along which it moves closest to the Earth, is 384399 kilometers. It is worth noting that the concept of a stable Universe should not be assumed as a certainty.
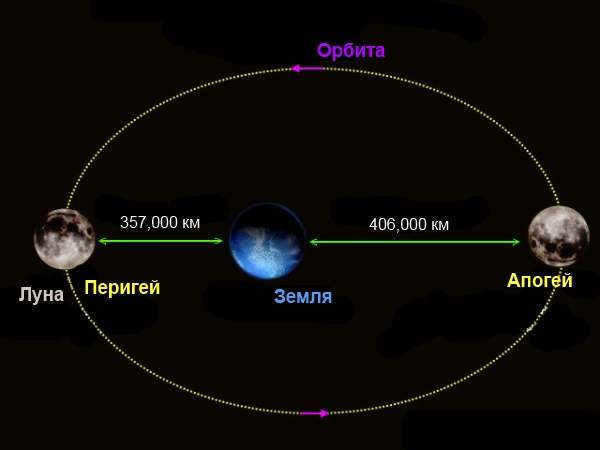
Due to various forces and influences, the universe is constantly evolving. One interesting change is the gradual movement of the Moon away from Earth. Every year, the Moon moves approximately 38 millimeters farther from our planet due to the gravitational-tidal acceleration. As a result, its orbit experiences variations, ranging from the closest point (perigee) to the farthest point (apogee).
Apogee
Apogee is the antithesis of perigee, which is the point in the lunar orbit closest to Earth. The term “apogee” originated from ancient Greek terminology and later became part of the scientific language of Latin. Instead of following a perfect circle during its complete revolution around the Earth, the moon’s orbit takes the shape of an ellipse.
Apsis refers to the two points along this elliptical path: the pericenter, which is the closest point to Earth, and the apocenter, which is the farthest point. The line connecting these apices can also vary. The minimum distance of apogee is 404,000 kilometers, while the maximum distance is 406,700 kilometers. It is estimated that during different stages of the moon’s rotations, it can be further away by over 25,000 kilometers.
The basis of modern methods for measuring distance is rooted in a variety of techniques, even dating back to ancient Greece, which have been visually documented and preserved to this day. The precision of Hipparchus’ calculations, made solely using angular measuring instruments, is truly remarkable. However, it is important to acknowledge the contribution of Eratosthenes, who accurately calculated the Earth’s circumference, providing Hipparchus with a crucial reference point.
Equally remarkable is the fact that the data obtained from Eratosthenes’ calculations regarding the planet’s diameter bring us incredibly close to the figures known today.
For more information on this topic, please watch the accompanying video.
Evolution of Distance Over Time
Complex calculations are the primary method for determining distances, which gradually become more overwhelming for the average person as time goes on.
The prevailing theory regarding the origin of the celestial body that was hurled into the Earth’s orbit approximately 4.5 billion years ago is the collision between Earth and another hypothetical planet.
When it first entered Earth’s orbit, the Moon was approximately 20 times larger than its current size and could be easily seen above the horizon. Some scientists speculate that it may have been at a seemingly absurd distance of about 15-20 thousand kilometers in today’s terms. By knowing the diameter, it is simple to calculate the radius.
The Moon is an incredibly fascinating celestial object that is influenced by not only the Earth, but also by the Sun and other elements of the solar system. Even without knowledge of its origin hypothesis, one can surmise its remarkable existence as the sole satellite of our planet and one of the largest in our solar system. However, analysis of lunar soil samples revealed an age of 4.1 billion years, which is significantly younger than the proposed date of the cosmic catastrophe.
Thanks to Newton’s groundbreaking discovery of the theory of universal gravitation, scientists finally had scientific explanations for the numerous questions that had puzzled them for years. One such question was why the predictions of solar eclipses made by renowned ancient researchers did not align with the actual occurrences of these celestial events. Halley proposed that the lengthening of Earth’s day was the cause of this discrepancy, and he attributed it to the gradual drift of the Moon. To validate this hypothesis of a natural satellite gradually escaping its orbit, it would be necessary to continually measure the distance between the Earth and the Moon.

Radar and laser detection have revealed that the annual separation is 3.8 cm, and by a peculiar coincidence, the distance between the planet and the satellite is 3.8 x 10 to the power of 5 km. It appears that determining the number of years it will take for the Moon to move away from Earth, or when it will become tidally locked to the satellite, is not a difficult task as long as one knows the simple calculation formulas.
However, accurately estimating this time is impossible, even with the knowledge that a year consists of 365 revolutions of the Earth around the Sun (although there are actually more, leading to calculation errors), and a day is precisely 36,300 seconds. Additionally, the speed of light is three hundred thousand kilometers per second.

The estimated timeframe for calculating the potential lunar departure is 616 billion years or beyond, thus it is not prudent to engage in conjecture about what might occur if… at this point. It is even challenging to ascertain a period during which there will be no solar eclipses because the moon will not reflect starlight (the rays of the sun).
While the seas, oceans, and other bodies of water continue to dutifully shift their volume under the gravitational pull of the moon, creating tides, it is uncertain how many more occurrences of this phenomenon will take place. However, it is certain that it will not happen for another billion years. Currently, the frictional force generated by these tides causes a slight increase in distance each year, but this increase will gradually become more pronounced over time due to the effects of friction. Ultimately, the speed can only be compared to the past, not the future.

Ways to Visualize Distance
One interesting aspect to consider is the future when human beings will embark on regular back-and-forth flights. When measuring distance in miles, the numbers may not be as overwhelming. However, when using meters, it becomes almost incomprehensible. For example, 365,400 or 375,000 miles would increase by a thousand. Even with knowledge of spacecraft speeds at that time, calculating the actual distance is no easy task.
This is because space travel would not be a simple straight line, but would need to take into account factors like gravity, parallax, and the latest technological advancements, which are largely unknown at this point.
In ongoing research, scientists are attempting to send a rocket to the Moon when the distance is at its minimum, not the average: 380,000 km.

The time it takes to travel to the Moon will not depend on the apogee or perigee, but rather on the portion of the path that needs to be covered in order to overcome Earth’s gravity. However, if we consider only days and hours, the quickest way to reach the Moon would be through light, which would take approximately 1.3 light seconds. Based on all of this, we can draw the following conclusions:
- Walking to the Moon would only take 9 years (unfortunately, Earth’s proportions don’t apply in weightlessness);
- If a car were to travel at a constant speed of 100 km/h, it would take around 160 days;
- Using a passenger airplane (with a speed of 800-810 km/h) would take approximately 3 weeks;
- The Apollo spacecraft took three days to reach the Moon in ’69;
- Future flights advertising on modern devices promises to cover the entire area in just a few hours and provide an opportunity to witness firsthand what is currently only known through photographs.
The duration of the parrot’s flight remains to be calculated, however, this requires knowledge of its species and average speed, such as to the 1020th galaxy in the constellation Kit. This is because any numerical value, be it a million or 237, when converted into a visual or physical representation, can only provide a metaphorical sense of the time it takes to traverse a certain number of kilometers.

For someone who is not well-versed in astronomy, it is sufficient to be aware that the approximate distance between the Earth and the Moon is around 390 thousand kilometers. It is not essential to know how this translates to miles, inches, or the flapping of a parrot’s wings. There are no immediate plans for mass excursions to explore the lunar surface or for the satellite to break free from its center of gravity. Nevertheless, the curious mind of mankind is increasingly pondering the possibilities of venturing into space, and there may come a day when space travel becomes commonplace.