While artificial intelligence has proven to be highly capable in various tasks, it can sometimes provide inaccurate answers. If you are unsatisfied with the response, consider asking the question in a more specific and detailed manner, providing precise parameters.
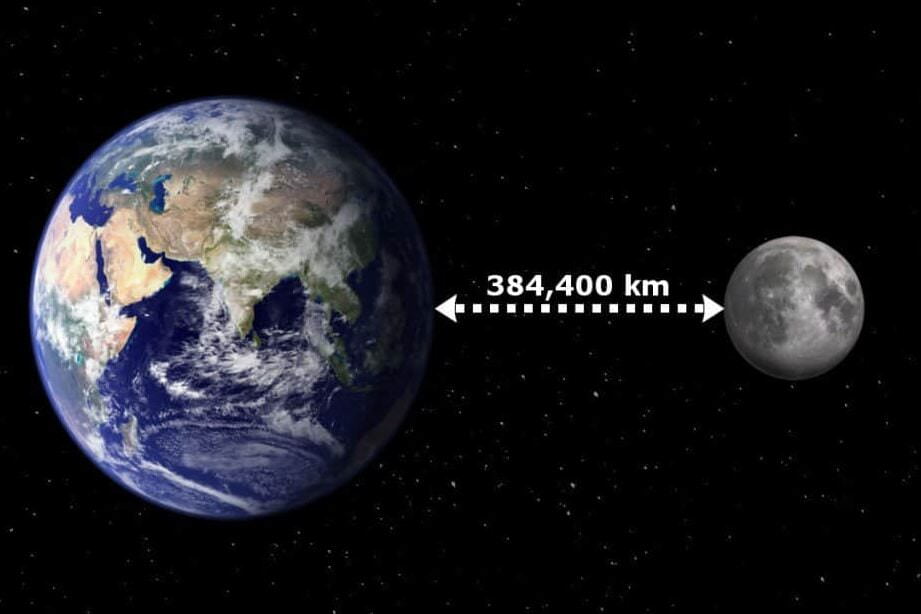
The average distance between the Earth and the Moon is approximately 384,400 kilometers. This measurement represents the typical distance between these two celestial bodies within the habitable solar system. However, it is important to note that the exact distance may vary slightly due to the Moon’s non-circular orbit and minor fluctuations. Throughout its orbit, the Moon can range from approximately 363,104 kilometers to 405,696 kilometers away from the Earth.
The Moon, Earth’s solitary natural satellite, is ranked as the fifth largest moon in the solar system based on its size. Its diameter measures approximately 3,474 kilometers, making it about 1/37th the size of Earth. However, when it comes to volume and mass, the Moon is significantly smaller than Earth. Its mass is only about 1/80th that of Earth.
The Moon exerts various effects on Earth. One of its primary impacts is through gravitational forces, which result in tides. Additionally, the Moon’s gravity influences the formation of mountains within Earth’s crust. Furthermore, the Moon plays a crucial role in shaping Earth’s climate. Its influence on Earth’s axis of rotation leads to seasonal changes throughout the year.
The Moon is a subject of scientific investigation as well. Its illumination provides us with the opportunity to observe the nocturnal sky and investigate celestial objects. The Moon missions, such as the Apollo program conducted by the United States, have amassed a substantial amount of information regarding its geology and composition. Additionally, there are intentions to dispatch humans to the Moon as part of the Artemis program, which aims to further explore Earth’s satellite and prepare for human missions to Mars.
All in all, the distance between the Earth and the Moon is roughly 384,400 kilometers, and it wields significant influence over our planet and its biological processes. The study of the Moon is indeed a worthy objective for scientists and space explorers.
You need to sign in to leave a comment.
Interact with the neural network by asking any question!
To ask a question to the neural network, you must be logged in to the website.
ChatGPT Artificial Intelligence in Russian: complete overview, features, and usage
(Resolved) What tasks do you want to tackle as a Test / QA Engineer? We’d like to understand the problems you can and want to solve….
(Resolved) Choose the hotel(s) that offer all-inclusive meals: Cosmos Moscow VDNH Hotel (Moscow) Marriott Grand Hotel (Moscow) Andron-O…
(Solved) Generate tables (output: file in CreateStructure.sql repository in the Tables branch)2.1 dbo.SKU (ID identity, Code, Name) 2.1.1 Restriction on unique…
(Resolved) Which types of tests are employed to identify memory leakage issues using the black box approach?…?
(Resolved) Looking for a great text about selling trendy, high-quality sneakers at an affordable price…
(Resolved) What societal attitudes and regulations impact you when it comes to instances of child neglect, physical, psychological, and sexual abuse…
(Resolved) The outcome of the conflict in Ukraine: Future predictions
(c) ChatGPT in English 2023. All rights reserved. If you come across any unauthorized content, please reach out to [email protected].
Do you have any questions for our neural network?
By selecting “Register” or “Sign in via Google,” you acknowledge and agree to the Terms of Service, consent to the processing of your personal data, and confirm that you are at least 18 years old.
Form for Reporting Illegal Content.
Contacting the Project Administration
Notification Regarding the Usage of Cookies
Our website, similar to the majority of others, employs cookies and other related technologies (such as pixel tags) in order to provide services that are tailored to your interests and requirements. Additionally, we utilize these technologies to collect statistical and marketing information for the purpose of analyzing and enhancing our services and websites.
By utilizing this website, you are granting your consent to the usage of cookies and other similar technologies in accordance with this notification.
If you do not wish to consent to the usage of this type of cookie, you must adjust the settings of your browser accordingly or refrain from using our website.
Please be aware that if you choose to block or delete cookies, we cannot guarantee that our website will function properly on your browser.
Cookies stored on our website do not contain any personally identifiable information.
What are cookies and other similar technologies?
A cookie is a small text file that is stored on your computer, smartphone, or other device when you visit websites.
Some pages you visit may also use pixel tags and web beacons, which are electronic images known as single-pixel (1×1) or blank GIF images, to collect information.
Cookies can be placed on your device by us (referred to as “first-party” cookies) or by other operators (referred to as “third-party” cookies).
There are two categories of cookies utilized on the website: ‘session cookies’ and ‘persistent cookies’. Session cookies are temporary cookies that are stored on your device until you exit the site. Persistent cookies, on the other hand, remain on your device for an extended period or until you manually remove them (the duration of a cookie’s presence on your device relies on the specific cookie’s lifespan and your browser preferences).
There are various types of cookies:
Essential cookies. These files are necessary to ensure the proper functioning of the website and to utilize its features. Disabling the use of these files will result in a decrease in website performance and the inability to use its components and services.
Performance, efficiency, and analytics cookies. These files allow us to analyze how visitors interact with the website, optimize its content, and measure the effectiveness of advertising campaigns by providing information about the number of visitors, duration of use, and any errors that occur.
Functional cookies remember users who have previously visited our website, their specific settings (such as language and region), and preferences, helping to personalize the website’s content.
Email Tracking. We may utilize technology to monitor whether you have opened, perused, or forwarded specific messages we send to your email. This is essential to enhance the usefulness of our communications for the user. If you prefer not to receive notifications, kindly unsubscribe using the “Unsubscribe” link found at the bottom of the relevant email newsletter.
Social Media Access Buttons. These buttons are employed to enable users to share a link to a page on social media or electronically bookmark a page. These buttons serve as links to social media websites operated by third parties, which may subsequently gather information about your online activity, including on our website. We encourage you to review the respective terms of use and privacy policies of these sites to comprehend how they utilize your data and how you can opt out of their data usage or have your data deleted.
External Web Services. Occasionally, we utilize external web services on this website. For instance, we may incorporate them to showcase specific components (such as images, videos, presentations, etc.) or to conduct surveys. Similar to social media share buttons, we are unable to prevent these sites or external domains from gathering data regarding your interactions with the site’s content.
What is the process for managing cookies?
By default, most internet browsers are programmed to automatically accept cookies.
However, you have the ability to modify your browser settings to either block cookies or receive notifications when cookies are being sent to your device (please consult your browser’s user guide for specific instructions). Keep in mind that disabling cookies may impact your browsing experience.
If you use multiple devices and/or browsers to access the internet, it is important to adjust the settings on each one accordingly.
Concluding Conditions
At our sole discretion, we reserve the right to modify this Notification periodically.
If you have any inquiries, please feel free to reach out to us via the provided contact information on our website.

– If we were to compare the sizes of the Moon, the Earth, and the Sun, we could line up a pea (representing the Moon), a five-ruble coin (representing the Earth), and a double door (representing the Sun).
– A complete lunar day lasts for 29 Earth days, while it takes the Moon 27 of our days to complete a full orbit around the Earth.
– The Moon does not have any natural satellites of its own.

– The absence of an atmosphere on the Moon means that our Earth is not shielded from the potential danger of meteorite impacts. As a result, the Moon’s surface is covered in numerous craters, both large and small, which were formed from countless collisions with celestial rocks of various sizes. – The lack of an atmosphere on the Moon leads to extremely cold temperatures during the night. This extreme cold means that any water present on the Moon would be frozen solid. The harsh conditions on the Moon make it impossible for any living organism to survive. If there ever was life on the Moon, it would have long since perished.
If the moon did not exist


It is possible that without it, life on the blue planet would never have emerged. The Moon is responsible for the changes in seasons. Without it, the temperature fluctuations would be so extreme that an African summer could easily be replaced by Arctic cold in the same region. Nights would be significantly darker than they are currently, especially when we observe a full lunar disc in the sky.
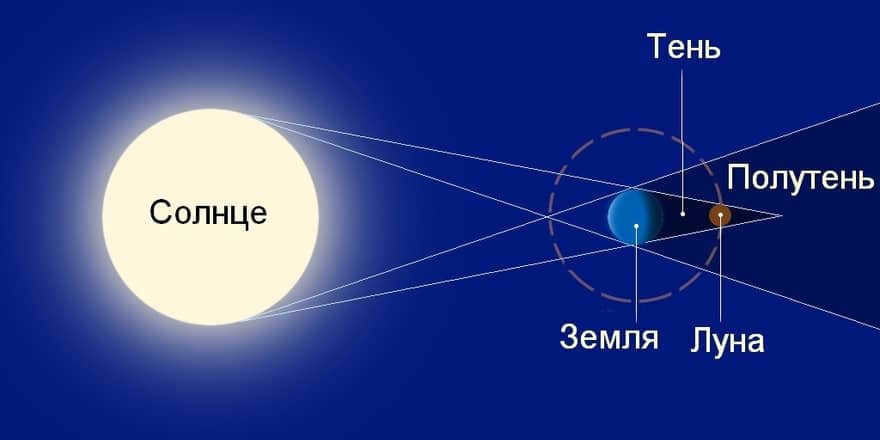
If it weren’t for the Moon, humans would not have the chance to marvel at the unique spectacle of a solar eclipse. This is because the Moon is perfectly positioned to completely block out the Sun when it aligns with the Earth.
The year on the planet would be significantly altered. The moon, in addition to influencing the tides, also slows down the rotation of our planet multiple times. Without it, a day would only last for eight hours. Consequently, the duration of a year would extend to approximately one thousand days.
Thus, the Moon’s influence extends beyond its visual appeal and romantic ambiance. Despite its considerable distance (requiring a three-day journey to reach it), the satellite has a profound impact on Earth. Without the Moon, the landscape of mountains and plains, as well as life forms, would be vastly different.

How to Reach the Moon
The average distance separating the Moon from Earth is 384,402 km. Let’s visualize this measurement in relation to Earth’s distances.
If one were to drive from Brisbane to Perth by car, they would need to cover a distance of 4,310 km, which would take approximately 46 hours. To cover a distance equivalent to the Earth-Moon distance, this journey would need to be repeated over 89 times. It would require five and a half months of non-stop driving, without accounting for traffic jams and potential accidents.
Fortunately, the Apollo 11 astronauts were not bound by Australian speed limits. In 1969, the Columbia command module reached lunar orbit in a mere three days and four hours.
Newest scientific findings
The Moon has been extensively studied, attracting the attention of scientists worldwide. Numerous countries have launched a multitude of satellites, totaling approximately a hundred, in order to conduct thorough research on this celestial body. The first satellite dedicated to lunar exploration was the Soviet spacecraft Luna-1, which successfully reached the Moon in 1959. This groundbreaking event marked the beginning of a new era in lunar exploration. The research complex deployed by Luna-1 was able to successfully land on the lunar surface, collect samples of soil, capture and transmit high-resolution images back to Earth, as well as make approximate calculations concerning the Moon’s mass. In addition to Luna-1, the Soviet Union also deployed two lunar rovers, each serving different purposes on the lunar surface. The first rover operated for an impressive period of almost 10 months, covering a distance of approximately 10 km. The second rover, on the other hand, functioned for about 4 months, covering a remarkable distance of 37 km during its mission.

What is the Visible Size of the Moon from Earth?
The visible size of the Moon from Earth is equivalent to 360 angular degrees, which is the full circumference of the celestial sphere. In other words, the Moon occupies approximately half of one degree (or 31 minutes) in terms of angular diameter. To put it into perspective, the width of the fingernail on your index finger, when observed from an outstretched hand, is roughly equivalent to one degree, or two moons.
It is a remarkable happenstance that the perceived dimensions of the Sun and the Moon are nearly identical for those living on Earth. This is due to the fact that the closest star is 400 times larger than its satellite. Not only is it 400 times larger, but it is also positioned 400 times further away. This fortuitous alignment allows Earth to be the only planet in the solar system where a total eclipse of the Sun can be observed.

What defines a planet?
Within the field of astronomy, there exists a distinct and specific definition for the term “planet.” It refers to a celestial body that orbits a star. In order to be classified as a planet, it must possess enough gravitational force to obtain a spherical shape, while lacking the necessary mass for thermonuclear fusion reactions. This prompts the question, “Is the moon considered a planet or a star?” As you and I have already deduced, the moon is not a star. The majority of planets are comprised of heavier elements, yet astronomers have also identified objects whose composition is predominantly composed of gases such as hydrogen, helium, and methane.
Every planet has undergone a process of formation from a liquid state. Over time, the heavier elements have accumulated in the core, resulting in its formation, while the lighter elements have remained on the surface.

What is the distance from the Earth to the Moon
The distance between the Earth and the Moon is not fixed and can vary. On average, the distance is approximately 384,400 kilometers, measuring from the centers of both celestial bodies. To put it in perspective, you could fit about 30 Earths within this space, and it takes light approximately 1.28 seconds to travel this distance.
Imagine if you could drive to the nearest celestial body at a speed of 95 kilometers per hour. Considering that the entire distance is equivalent to about 10 times the circumference of the Earth, the journey would take approximately the same amount of time as making 10 complete loops around the equator. In other words, it would take just under six months. The fastest recorded journey to the Moon so far was achieved by the New Horizons interplanetary spacecraft, which reached the Moon’s orbit a mere eight and a half hours after its launch on its way to Pluto.
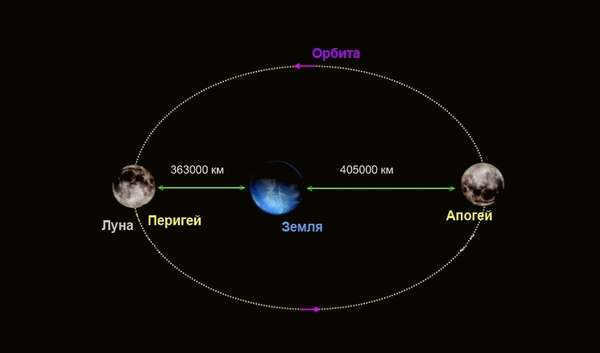
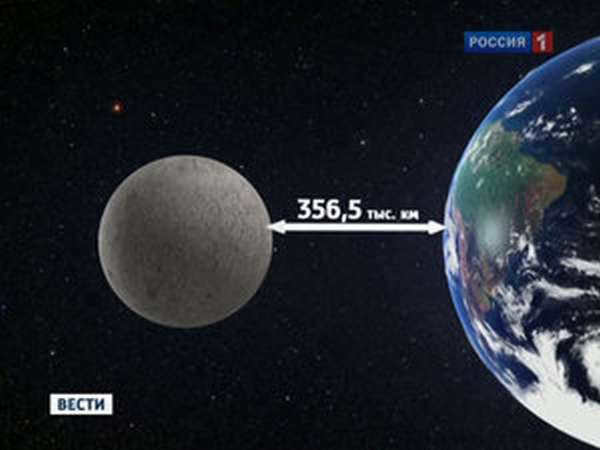
The Moon does not have a perfectly circular orbit, but rather an elliptical orbit with the Earth located inside it. At different points in its orbit, the Moon is closer or farther from the Earth. As it rotates around a common center of mass with the Earth, the Moon is either approaching or moving away from us. The closest distance between the Moon and Earth occurs when the Moon is at the point in its orbit called perigee. Conversely, the farthest distance occurs at the point known as apogee. The minimum distance between the two celestial bodies is 356,400 km, while the maximum distance is 406,700 km. Therefore, the distance between the Moon and Earth varies by a range of 28 to 32 Earth diameters.
In the 2nd century AD, Ptolemy was able to obtain the first relatively accurate estimates of the distance to our Earth’s “neighbor”. In today’s world, we have the luxury of using advanced reflective instruments on satellites to measure this distance with incredible precision, having only a few centimeters of error. The process involves directing a laser beam towards the Moon and observing the time it takes for the beam to return to Earth after being reflected. By knowing the speed of light and the duration it takes for the beam to reach the sensors, calculating the distance becomes a straightforward task.
What is the actual distance of the Moon from Earth?
Estimating the exact distance of the Moon from Earth is not as simple as it may appear. The Moon follows an elliptical path around our planet, causing its distance from us to constantly fluctuate. This variance can be as much as 50,000 km, which explains why the Moon’s size in the night sky appears to change. Moreover, the Moon’s orbit is influenced by various celestial bodies within our solar system. Furthermore, due to tidal forces, the Moon is gradually drifting away from Earth.

The Apollo mission provided us with a unique opportunity to thoroughly investigate the most up-to-date information. In 1969, American astronauts successfully placed a series of mirror reflectors on the surface of the Moon. These reflectors are still functional today and require no external power source. The reflector system is designed in such a way that it reflects laser beams sent from Earth back to the source.
By precisely calculating the time it takes for the laser beam to travel to the Moon and return, scientists have been able to accurately measure the distance between the Moon and Earth. The findings revealed that the Moon is gradually moving away from Earth at a rate of 38 mm per year, which translates to approximately 4 meters per century.
The brilliance of the celestial body
The luminosity of a celestial body is also worth taking into account. The reflectivity (i.e., the brightness visible to us from Earth) of the Moon is three times lower than that of our blue planet. This means that the illumination provided by the Moon is 41 times weaker when observed from space compared to Earth. This translates to a difference of four star magnitudes.
Our planet, Earth, is surrounded by a life-sustaining layer of atmosphere, beyond which lies the vast expanse of outer space. The Moon, one of Earth’s natural satellites, orbits the planet in an elliptical trajectory. As a result, the distance between Earth and the Moon varies.
In the 2nd century BC, Hipparchus of Nicaea, an astronomer from ancient Greece, conducted the initial measurement of the distance between the Earth and its satellite, which is equivalent to 30 Earth diameters. The renowned geographer and mathematician Eratosthenes determined the length of the Earth’s diameter.
Pay attention! The approximate length between the centers of the Earth and the Moon is around 384,000 km.
The measurement of the distance
Advanced techniques of measurement can determine the movement of the satellite and perform calculations with utmost accuracy. Laser locators employed for this purpose can precisely measure the distance to the Moon and other celestial bodies with an accuracy of approximately 2 cm.

The process of determining the distance between the earth and the moon involves utilizing a technique known as signal time measurement. To accomplish this, a specialized corner reflector is installed on the satellite by scientists.
A laser pulse is emitted from the surface of the Earth and is reflected off the satellite, eventually returning to an optical device after a specific period of time. The time it takes for the light beam to travel from the Earth to the Moon and back is then calculated, allowing experts to determine the necessary interval.
Planet-Satellite Interaction
If the planet were completely stationary, the satellite would orbit it in a consistent circular path, with slight variations in the distance between the Earth and the Moon. However, in reality, the planet itself is in constant motion as it orbits the Sun. This means that the satellite must constantly adjust its trajectory to keep pace with the planet and prevent falling behind.

The Earth is not the sole celestial object that influences the speed of movement of its neighboring moon. The Sun, a massive ball of fire, exerts a gravitational force several times stronger than that of the Earth.
As a result, the path traveled by the Moon to reach its destination appears as a complex spiral. The lunar trajectory experiences oscillations in its axis, causing the Moon to periodically approach and recede from the Earth. During these moments of intense rocking, the Moon moves far away from the Earth.
All of these factors contribute to an effect where the visible area of the Moon is not always the same.
The distance between the Earth and the Moon is approximately 384,403 kilometers, which is equivalent to 0.00257 astronomical units.
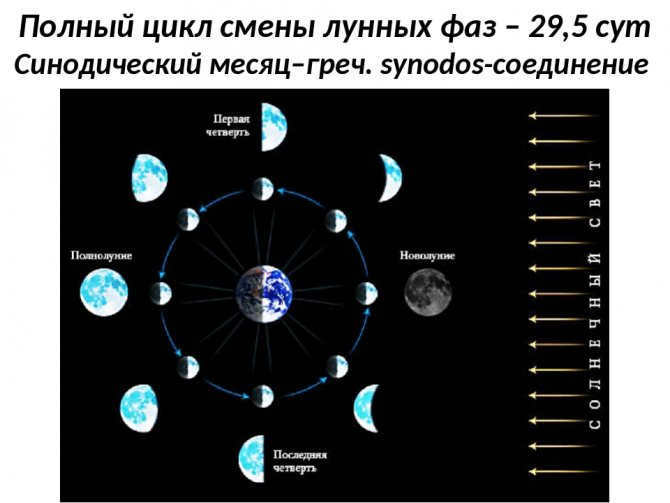
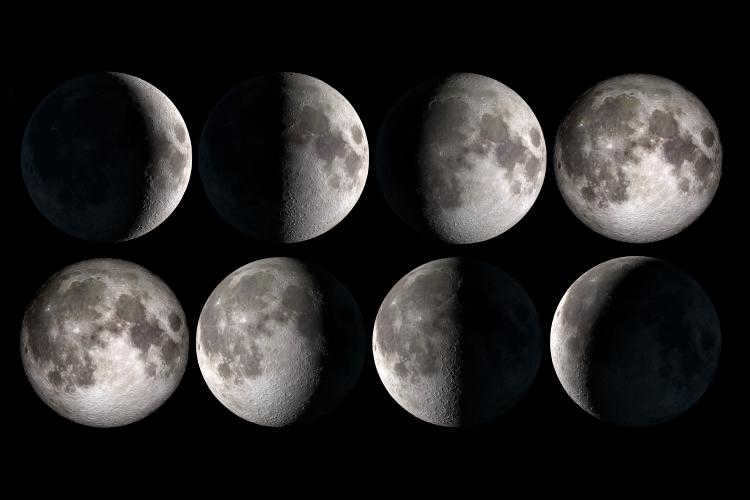
Isn’t it fascinating? Over the course of 4 weeks, the Moon completes a full orbit around the Earth. Throughout this journey, the Sun’s illumination causes the Moon to undergo changes in appearance every 28 Earth days.
Overview of the Moon

The Moon is the closest celestial body to Earth, and its surface is marked with craters caused by meteorite impacts. Some of these impacts were so powerful that they penetrated the lunar crust and reached the mantle layer.
These impacts created large cavities known as lunar seas, which appear as dark spots when viewed from Earth.
The Moon lacks the air and water necessary for life, and its soil has a different chemical and granular composition compared to Earth’s soil, resembling volcanic sand in appearance. Additionally, the atmosphere on the Moon is extremely thin.
As a result, the surface of the Moon experiences a significant variation in temperature, ranging from -173°C during the night to +127°C during the day. The region that is nearest to the Sun undergoes the most intense heating. Moreover, the sky on the Moon always appears black, irrespective of whether there is solar illumination or not.
Summary
Scientists predict that in the future, the Moon will come closer to Earth due to gravitational attraction. This proximity may result in the Moon being destroyed by tidal forces when it gets within 12,000 km of the Earth. The remnants of the Moon will then form a ring-like structure similar to Saturn and other gas giants in our Solar System, drifting in space.
The Moon is a celestial body made up of rocks and has a spherical shape. It does not have an atmosphere and shows no signs of life. As the Earth’s only natural satellite, it has a diameter that is approximately one-fourth the size of our planet. Even before the era of space exploration, people recognized that the Moon was full of enigmas and secrets.
- Motion
- The factors influencing the Moon’s motion
- The measurement of the distance between the Earth and the Moon
- Methods for determining the distance to the satellite
- The average distance to the Moon according to Wikipedia
- Final thoughts
It is among the largest natural satellites in the solar system, ranking alongside the planets’ moons. The soil density on this moon is relatively low, and scientists are still puzzled by the samples they have collected from its surface for detailed analysis. According to the theory of origin, it came into existence around 4.1 billion years ago.
Here’s an intriguing fact: Learn about the solar system, the planets in their order, and the fascinating history behind their names.
Motion
The average distance between the Earth and the Moon is 384,400 kilometers, which is approximately 60 times the radius of our planet. The Earth’s only satellite moves in an elliptical orbit, so its proximity to the planet and its apparent size to an observer can vary depending on its position. At its closest point, called perigee, the satellite is 363,104 kilometers away from the Earth. When it reaches its farthest point, known as apogee, the distance between the centers of the Earth and the Moon is 406,696 kilometers. This means that the difference in distance between perigee and apogee is 43,592 kilometers.
The Moon’s surface brightness changes as the satellite orbits closer to and farther away from the planet. Studies have shown that the satellite doesn’t generate its own light but instead reflects about seven percent of the sunlight scattered from the Sun. This characteristic is attributed to the presence of a regolith layer formed by meteorite impacts. The regolith consists of debris particles that vary in size, ranging from tiny microns to large pieces that can cover the surface for tens of meters.
Here’s an intriguing question: which planet is the farthest from the Sun?
Factors influencing the movement of the Moon
The Moon’s orbit is determined by the gravitational forces exerted on it by both the Earth and the Sun. However, the Sun has a significantly stronger gravitational pull on the Moon compared to our planet. Apart from the Sun’s influence, the Moon’s motion is influenced by various other factors:


- The duration of the sidereal month is 27 days, 7 hours, 43 minutes, and 11.51 seconds,
- The angle of inclination of the lunar orbit changes in relation to the Earth’s rotation around the Sun,
- The lunar orbit experiences changes at both perigee and apogee,
- The points where the planes of the Moon’s and the Sun’s orbits intersect are shifting,
- The perigee longitude increases with a period of 8.8 years,
- The dimensions of the orbit change at both apogee and perigee.
The motion of the Moon’s orbit can be likened to an unwinding spiral.
Here’s something fascinating: the captivating names of stars, their origin stories, and the names of constellations.
Measuring the Distance between the Earth and the Moon
The distance between the Earth and the Moon is not a fixed value. In the second century BC, the ancient scientist Hipparchus of Nicaea was able to calculate this distance. His calculations yielded a value equivalent to thirty Earth diameters, which is approximately 384,000 kilometers.
The diameter size could be measured by another ancient Greek mathematician and astronomer named Eratosthenes of Cyrenaica. He placed a pole in a vertical position near the library building and measured the length of the shadow it cast. He then calculated the smallest angle that the sun’s rays formed when they hit the pole, which turned out to be seven degrees. Using the knowledge that on the summer solstice in the city of Siena, the sun is at its highest point in the sky, and the distance from Siena to Alexandria is 5000 stadia, Eratosthenes deduced that 5000 stadia is equivalent to 7 degrees of the Earth’s meridian. The full meridian consists of 360 degrees, or approximately 250,000 stadia.
Here is an intriguing question: what are the consequences of the Earth’s axial rotation?
There are various techniques for calculating the Earth-Moon distance:
These measurements remain consistent, as the lunar disk fully covers the solar disk during a total solar eclipse. To calculate this, a regular wooden stick can be used. If you hold the stick at arm’s length, the ratio of its width to the distance between your eyes is the angular size of the Moon in radians. This value is equivalent to 0.0087. Converting radians to degrees gives approximately 0.5. With knowledge of the Earth’s radius and the Moon’s angular size, determining the distance to the Moon becomes simple. Through geometric calculations, a distance equal to 30 Earth diameters is determined.

A laser beam is emitted from Earth’s surface towards the reflectors placed on the Moon by astronauts over four decades ago. It travels at the well-known speed of light and upon reaching the reflector, it bounces back. The duration of this journey is approximately one second. Scientists meticulously record the precise time and utilize it to calculate the exact distance to our natural satellite. This measurement technique has been instrumental in ascertaining that the celestial body nearest to Earth gradually deviates its course from the planet by a few centimeters each year.
Average distance to the moon: wikipedia
The average distance between the closest point of the Moon’s orbit and the Earth is approximately 362,000 kilometers. On the other hand, the farthest point of the lunar orbit is located at a distance of about 405,000 kilometers.
Twice a year, during the new moon phase when the Moon approaches the node (the point where its orbit intersects the ecliptic), a solar eclipse occurs. During other times, the Moon’s motion is either below or above the Sun. Lunar eclipses, on the other hand, occur during full moons, and the Moon should also be near the node of its orbit.
Every 18 years and 224 days, a straight line connecting the nodes completes a rotation around our planet. Interestingly, the direction of this rotation is opposite to the course of the Moon.
Final Thoughts

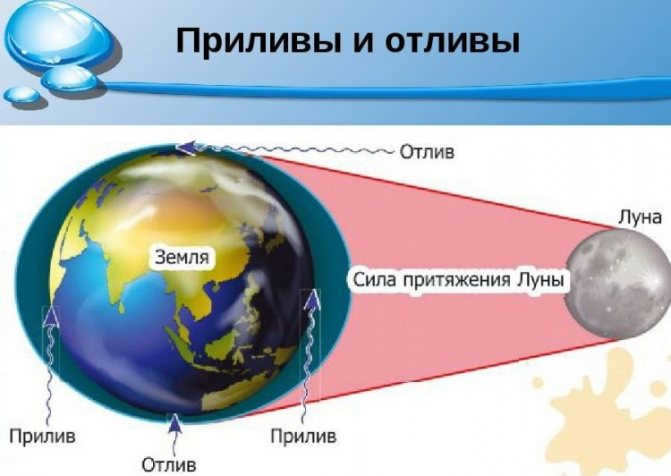
Over the course of a hundred years, the length of a day on Earth increases by a thousandth of a second. This occurrence is brought about by the gravitational forces of the closest celestial body to our planet. The Moon’s gravitational pull on the Earth’s oceans causes tides, which in turn slows down the rotation of the Earth.
The gravitational field also impacts the shape of the Moon. There is distortion on the side of the Moon that faces the Earth, although it is possible that this distortion is a result of the internal structure of the satellite.




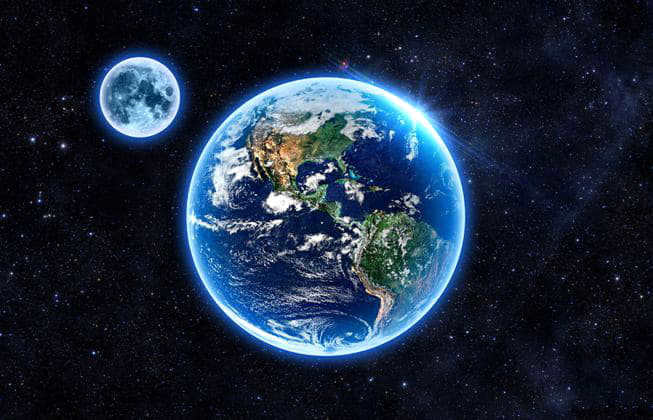
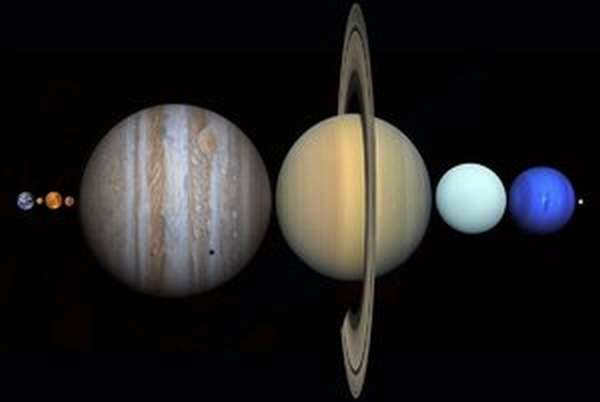
The Moon is one of the most prominent celestial objects that can be observed without the aid of a telescope, and it is also the nearest celestial body to Earth. Due to its close proximity, the Moon has captivated human fascination since ancient times, giving rise to various legends about its origin and the formation of its surface features. Of particular interest has been the age-old question of the Moon’s size in comparison to that of Earth. Thanks to advancements in space exploration, we now have accurate measurements of both the Moon and Earth’s sizes, as well as the distance between them.
The Moon, being a natural satellite of Earth, is indeed smaller in size. Credit: yandex.ru
Across the entire country
Spanning from one side of Australia to the other, the distance between the cities of Perth and Brisbane measures 3606 kilometers. This vast expanse represents the full length of the Australian continent. In a fascinating comparison, if we were to align Australia and the Moon, extending the lunar sphere to match its diameter, the lengths of the two would be nearly identical.
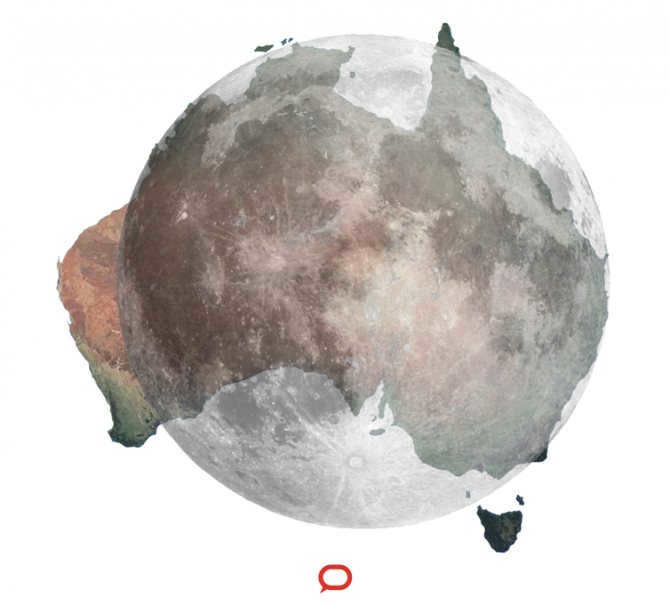


However, it is important to consider a more comprehensive perspective. Despite having a comparable extent to Australia, the Moon is significantly larger in size. With an area of about 37.94 million square kilometers, the Moon is nearly five times the size of Australia, which only has an area of approximately 7.69 million square kilometers.

A contentious matter
Nevertheless, in recent times, a group of scientists has been attempting to substantiate the claim that this celestial entity is indeed a planet. Their argument is predicated on the fact that, when compared to the other satellites in the entire solar system, the Moon holds a unique position. Firstly, the celestial body possesses a significantly greater mass in comparison to its counterparts. Furthermore, the Moon is situated at an extraordinarily vast distance from the Earth, making it unlikely to be captured by the Earth’s gravitational force. Moreover, this enigmatic celestial wonder revolves around our azure planet in a manner that deviates from the equatorial plane, a characteristic not commonly observed in genuine satellites.
The question of whether the Moon is a planet or a satellite is still open to many. It is possible that in the near future, astronomers will classify the Moon as an independent planet. However, in all current astronomy textbooks, it is referred to as a satellite.
What is the exact distance between the Earth and the Moon?
Calculating the precise distance between the Earth and the Moon turns out to be more complex than we might think. The Moon’s path around our planet is not a perfect circle, but rather an elliptical shape. This means that the distance between the Earth and the Moon is constantly changing, with a potential difference of up to 50,000 km. As a result, the apparent size of the Moon in our sky is also in constant flux. Furthermore, the Moon’s orbit is influenced by other celestial bodies in the solar system. Additionally, due to tidal forces, the Moon is gradually drifting away from the Earth over time.


The Apollo missions provided an opportunity to extensively study this information. In 1969, American astronauts visited the Moon and installed mirror reflectors on its surface. These reflectors, which operate without the need for energy, are still functioning today. The reflector system is designed to reflect a laser beam back to its source when it is sent from Earth.
By calculating the time it takes for the laser to travel to the Moon and back, scientists were able to accurately determine the distance to the Moon and track its distance from Earth. The findings revealed that the Moon is gradually moving away from Earth at a rate of 38 mm per year, which is equivalent to approximately 4 meters per century.
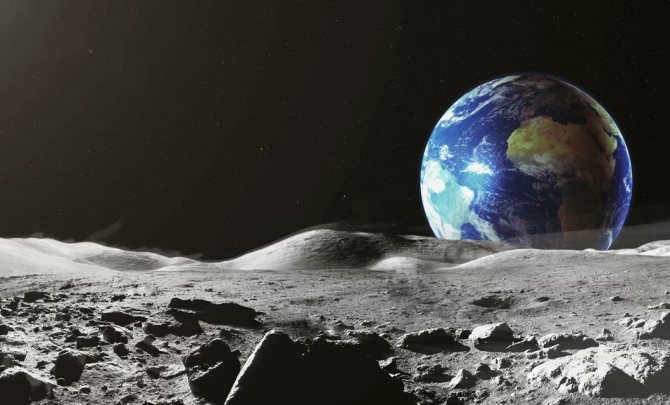
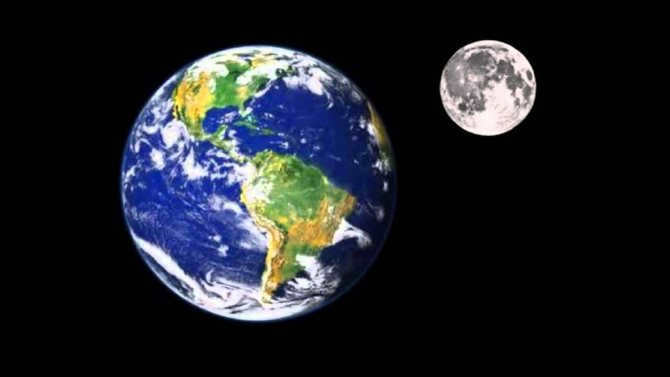



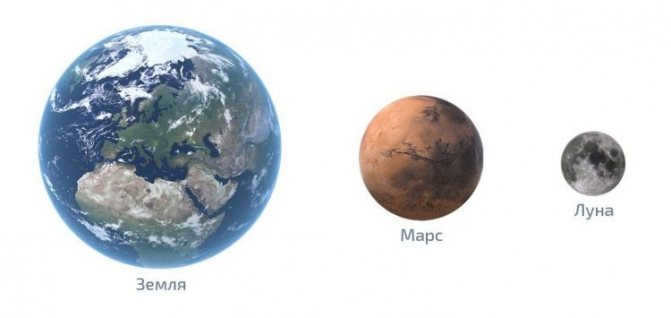

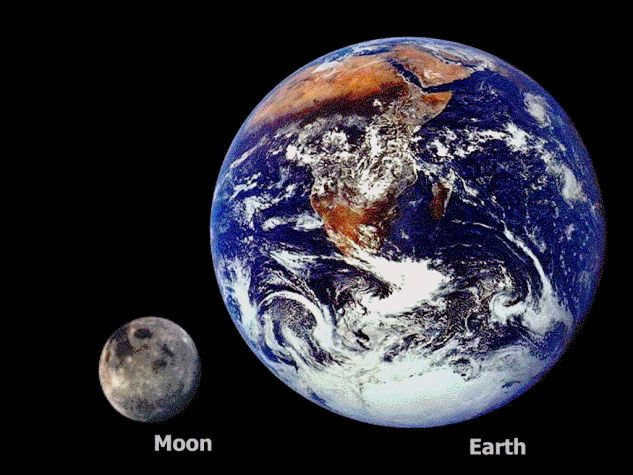
Scientists discovered a while back that the satellite is 6 times tinier than the celestial body. By observing the photo, one can determine the number of times the Earth is bigger than the Moon. Visual data is processed more effectively, after all. The magnitude of the Earth’s size compared to the Moon is astounding!
When observing the satellite from the Earth, it appears relatively tiny, measuring about 30 cm in diameter. However, when viewed from the horizon, its size becomes much more impressive.
The Moon has a radius of 1737.1 kilometers, whereas the average radius of our blue planet is 6371.0 km. Therefore, the satellite is approximately 3.667 times smaller than the Earth.
What is the ratio of the Earth’s area to the Moon’s area? The Moon has a surface area of 37.93 million square kilometers, while the Earth has a surface area of 510.1 million square kilometers. In other words, the Moon’s surface area is equivalent to the combined size of Russia, Canada, and China.
How many times is the Earth’s volume larger than the Moon’s volume? The Moon is nearly 50 times smaller than Earth in terms of volume, occupying only 2% of the total space.
The density of the satellite is 3.34 g/cm³. It is only 60% of the density of the Earth. The reason for this difference is that the Earth is bigger and has more pressure in its interior. In fact, the Earth’s interior has a huge core that contains 32% of its mass. On the other hand, the Moon’s core can only hold up to 5% of its mass, which is about 350 km in size.
How many times is the Earth larger than the Moon in terms of mass? It is 81 times. The mass of the satellite was being determined
Steps to Reach the Moon
The distance between the Moon and the Earth is approximately 384,402 kilometers. Let’s visualize this measurement in comparison to the Earth’s distance.
If we were to drive from Brisbane to Perth, the distance would be around 4,310 kilometers, taking approximately 46 hours. To cover a distance equal to the Earth-Moon distance, this journey would need to be repeated more than 89 times. It would take around five and a half months of non-stop driving, without considering traffic or accidents.


Luckily, the Apollo 11 astronauts were not restricted by the speed limits of Australia. In 1969, the Columbia command module successfully entered lunar orbit within a mere three days and four hours.

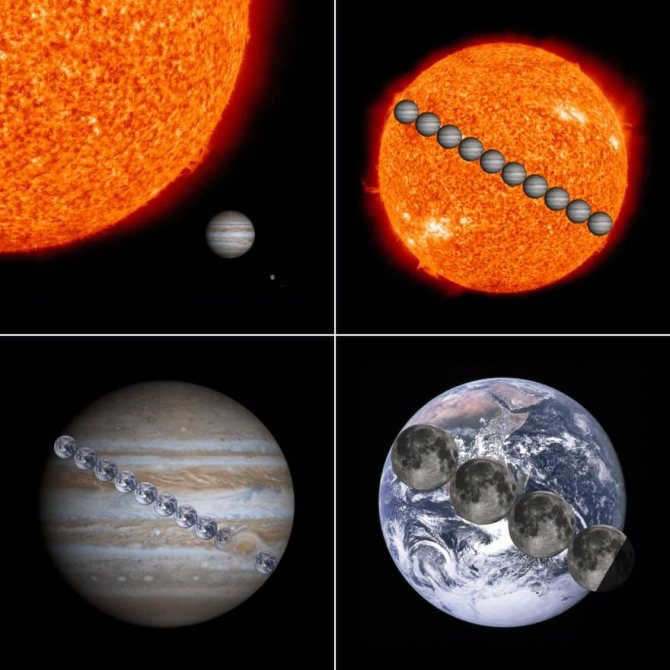
The Moon is a celestial body that has been accompanying Earth for centuries. While it does not emit light, it has the ability to reflect it. In our country, it is considered to be the Earth’s satellite, as we have previously established, and it is the closest satellite to the Sun. When it comes to brightness in our sky, the Moon is regarded as the second brightest object after the Sun. Humanity has always observed only one side of the Moon, as its rotation is synchronized with Earth’s rotation around its own axis. The Moon’s movement around our planet is irregular, sometimes moving away and sometimes approaching. Many astronomers have long been attempting to unravel the mysteries of its movement, but this process is incredibly complex and influenced by factors such as the planet’s flattening and even the Sun’s gravitational pull.

Solar eclipse
The Sun’s equatorial diameter is nearly 1.4 million kilometers, approximately 400 times larger than the Moon’s diameter. Interestingly, the distance between the Earth and the Sun (which is 149.6 million kilometers) is also about 400 times greater than the distance between the Earth and the Moon.
This is the reason why the Moon and the Sun appear to be the same size when observed from Earth. Consequently, when the Moon and the Sun align (as seen from Earth), a spectacular event occurs – a total solar eclipse.
Unfortunately, scientists have predicted that solar eclipses on Earth will eventually come to an end. Due to its gradually increasing distance, the Moon will eventually be too far away to completely block out the Sun. The majority of scientists believe that this will occur in approximately 600 million years.
Definition of a satellite
You and I have determined that the Moon is not classified as a planet or a star. What can we deduce about satellites? Satellites are objects that revolve around other celestial bodies along a specific trajectory. Their movement is influenced by the force of gravity. In this scenario, the orbit can either be dynamic or stable.
A celestial body can only become a satellite if it is captured by the gravitational field of its cosmic neighbor while traveling through space, or if it forms from the same gas-dust cloud that gave birth to the planet itself. Now, let’s discuss the nocturnal luminary. The Moon does revolve around our planet, but its origin story differs slightly. It is believed that over four billion years ago, the Earth, which was still in its protoplanet stage, collided with a similar body named Theia in outer space.

This collision took place tangentially, resulting in a significant amount of debris hitting Earth’s orbit, which supposedly later came together to form the Moon. Despite this origin story, astronomers maintain that the Moon is indeed a satellite of the Earth.
When the question arises: “Is the Moon a satellite or a planet?”, you can confidently answer that this celestial body is unequivocally a satellite of the Earth.
Moonwalkers
Despite advancements in space exploration, the Moon remains the sole celestial object that humans have set foot upon, an event that took place fifty years ago. Half a century has passed since the initial (and exclusive to one nation) moon landing, and only four out of the twelve individuals who ventured onto our planet’s satellite are presently alive.
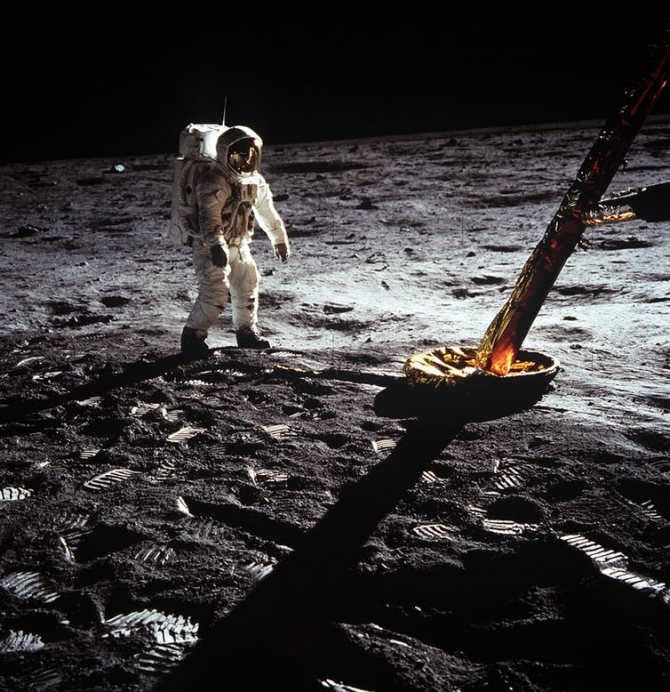

With the hope that in the near future, mankind will have the opportunity to once again set foot on the Moon, we can envision a future where a new generation is inspired to continue the exploration of our closest celestial companion.
In the field of astronomy, there exists a precise definition for this particular term. It refers to a celestial entity that revolves around a star. Such an entity must possess sufficient gravitational forces to assume a spherical shape, but its mass is insufficient for fusion reactions. Many individuals often inquire, “Is the moon considered a planet or a star?” We have already deduced that this celestial body is not classified as a star. The majority of planets are primarily composed of the densest elements. However, astronomers are aware of certain objects whose composition is predominantly composed of gases, such as hydrogen, helium, and methane.
Each individual planet has formed from a liquid state. Over time, the denser elements have concentrated towards the center, creating a core, while the lighter elements have remained on the surface.

The composition of the lunar surface
When we observe our enigmatic celestial body, it appears as a luminous, yellowish orb. At times, it may take on a nearly white or dark orange hue, but it always captivates with its exquisite beauty. These transformations are a result of our viewing the Moon through the Earth’s atmosphere, which contains countless suspended particles that can alter the spectrum of reflected light.
In reality, the surface of the Moon is quite different from its apparent yellow and silvery appearance. It is adorned with vast flat regions known as lunar seas, which are actually enormous craters formed by collisions with celestial objects and subsequently filled with lava. Additionally, there are elevated areas on the Moon that form a rugged, mountainous landscape.
Influence of the Moon on Earth processes
The Moon serves as a natural satellite for the Earth, exerting a significant impact on both the planet itself and its inhabitants. One of the most notable effects is the creation of tides. Due to the gravitational force of the Moon, the waters of the world’s oceans are attracted, resulting in the occurrence of low tide along the coastlines. Conversely, on the opposite side of the Earth, a high tide is formed as the water seems to be pushed in.
Furthermore, the lunar 28-day cycle is closely intertwined with human biorhythms. This is because the gravitational pull of our satellite influences various human organs and the circulatory system. Additionally, the human psyche experiences a certain level of pressure from the Moon, with the intensity of this influence varying depending on the lunar phase.
Astrological Connection between the Sun and the Moon

Based on astrological doctrine, the Sun and Moon exert a significant impact on an individual’s personality and fate. The Sun represents the element of Fire, governing all aspects of one’s consciousness. Conversely, the Moon draws its energy from the Water element and guides the subconscious mind. When combined, these celestial bodies can provide individuals with a deeper understanding of their life’s purpose, inspire philosophical contemplation, and foster spiritual growth.
This particular characteristic becomes most apparent when it occurs in Zodiac signs associated with the elements of Water or Fire. The Sun-Moon conjunction in the birth chart can not only provide insights into specific personality traits shared by an entire generation, but also offer predictions about their future destiny. This aspect offers valuable information about: individual characteristics, perspectives, internal responses to external influences, behavioral patterns, and reservoirs of internal energy.
New discoveries in lunar research
The Moon has been a subject of extensive scientific investigation, with numerous countries launching over a hundred satellites to explore its mysteries. The pioneering research satellite, Luna-1, was launched by the Soviet Union in 1959. This groundbreaking mission allowed for the first-ever descent to the lunar surface, enabling the collection of soil samples and the transmission of photographs back to Earth. It also provided valuable insights into the Moon’s mass. In addition to Luna-1, the Soviet Union successfully deployed two lunar rovers on the Moon’s surface. One of these rovers operated for an impressive duration of 10 months, covering a distance of 10 kilometers, while the other rover continued its exploration for 4 months, covering a remarkable 37 kilometers.

Different chapters found in alternative sources
What is the reason for the shorter lifespan of unmarried individuals?
What is the reason for the shorter lifespan of unmarried individuals? To begin with, it is not the case that every unmarried individual lives shorter lives compared to the average married person. This is not a common occurrence for individuals who are not in relationships and do not face difficulties in finding partners, so the explanation for the longer life expectancy of married individuals is more complex.