Astronomy is the specific discipline that investigates the Sun and other celestial bodies, including the planets within our solar system and their moons, exoplanets, asteroids, comets, meteoroids, interplanetary matter, interstellar matter, pulsars, black holes, nebulae, galaxies and their clusters, quasars, and much more.
Related topics
References in literature
Continuation of related topics
Observing and detecting exoplanets can be quite challenging due to their faint light compared to their parent star. The brightness of the parent star is significantly greater than that of the planet, making it difficult to directly observe and detect exoplanets. This presents a considerable difficulty in detecting such a faint light source.
This article focuses on the current understanding of the various stages of the universe’s development, starting from its formation to the present day. The understanding is based on several theories.
Radio astronomy is a branch of astronomy that focuses on the study of celestial objects through the analysis of their electromagnetic radiation within the radio wave spectrum, which spans from millimeter to kilometer wavelengths.
Astronomy, one of the oldest natural sciences, is concerned with the motion and characteristics of celestial bodies. In its early stages, it was closely intertwined with astrology. However, during the Renaissance in Europe, astronomy and astrology were definitively distinguished as separate disciplines. Other fields such as astrophysics and cosmology, which explore extraterrestrial objects, were previously considered part of astronomy but have since emerged as distinct scientific disciplines in the 20th century.
Lesson 1
Astronomy is the primary scientific field that explores the the makeup, movement, inception, and progression of celestial entities.
The term “astronomy” is derived from the Greek words astron (star) and nomos (law).
The aims of astronomy encompass: Studying the positions and motions of celestial bodies in space, determining their size and shape, and investigating the physical composition of celestial entities.
What is the definition of a galaxy?
A vast, solitary assemblage of stars held together by gravity.
What is the definition of the universe?
An immensely expansive expanse of space encompassing all celestial bodies within it.
How did the field of astronomy originate?
Out of practical human necessities: the necessity for spatial orientation.
What does astronomy focus on studying?
Astronomy studies various celestial objects such as galaxies, stars, planets, and planetary satellites.
One of the main activities in astronomy is the systematic and active observation of phenomena and processes occurring in the Universe.
Astronomical observations played a crucial role in the discovery of the chemical element helium.
An optical telescope is specifically designed to capture and visualize the light emitted by celestial bodies. It allows for a wider field of view, enhancing the visibility of these objects.
| Branch of astronomy | Summary |
| Applied astronomy | Calculations, directions, precise time, tools used in this procedure |
| Celestial mechanics | Investigates the principles of motion of heavenly bodies, masses, and forms |
| Comparative planetology | The exploration of the physics of the planets in the solar system |
| Astrophysics | The examination of stars, the phenomena happening on celestial bodies |
| Stellar astronomy | The study of the physical condition and processes of entities |
| Cosmology | Explores the overall principles of the structure and evolution of the Universe |
| Cosmogony | Examines the origin of celestial bodies |
Astronomy provides solutions to a multitude of challenges in the field of astronautics: it aids in the meticulous selection and precise calculation of artificial celestial body orbits; facilitates the determination of distances to celestial bodies; assists in identifying the most opportune time for interplanetary flights; and enables the exploration of matter as well as the study of the impact of solar energy on human beings.
What is the focus of the field of astronomy?
Astronomy, which traces its roots back to the Stone Age (VI-III millennia BC), is a discipline that explores the motion, structure, origin, and evolution of celestial bodies and their systems.
The study of astronomy holds significant historical importance due to its practical applications. These applications can be categorized into various groups:
Astrological concepts played a significant role in the early stages of astronomy, aligning with the mythological beliefs of ancient civilizations.
The progression of astronomical understanding
The Ancient World of Antiquity (BC). The study of Philosophy led to advancements in astronomy and the development of elements of mathematics, particularly geometry. This knowledge was present in various ancient civilizations including Ancient Egypt, Ancient Assyria, Ancient Maya, Ancient China, Sumerians, Babylonia, and Ancient Greece.
There were several scientists who made significant contributions to the field of astronomy, such as PHALES of Miletus (625-547, ancient Greece), Eudoxus of Cnidus (408-355, ancient Greece), ARISTOTEL (384-322, Macedonia, Dr. Greece), ARISTARCHUS of Samos (310-230, Alexandria, Egypt), ERATOSPHENE (276-194, Egypt), and Hipparchus of Rhodes (190-125, ancient Greece).
Archaeologists have discovered evidence that early humans possessed basic knowledge of astronomy as early as 20,000 years ago during the Stone Age.
The Second Pre-telescopic period (from our era up to 1610) was marked by a decline in science and astronomy. This period saw the collapse of the Roman Empire, frequent barbarian raids, and the rise of Christianity. However, there was also a rapid development of Arabian science during this time, which later contributed to the revival of science in Europe. It was during this period that the modern heliocentric system of the world structure was established.
Several scientists made significant contributions to the field of astronomy during this period. These include Claudius Ptolemy (87-165, Dr. Rome), Abu Reyhan Muhammad ibn Ahmed al-Biruni (973-1048, present-day Uzbekistan), Mirza Muhammad ibn Shahrukh ibn Timur (Taragai) ULUGBEK (1394-1449, present-day Uzbekistan), Nicholas Copernicus (1473-1543, Poland), and Tycho (Tige) Brahe (1546-1601, Denmark).
III Telescopic prior to the introduction of spectroscopy (1610-1814). Development of the telescope and its utilization for observations. The principles governing planetary motion. Unearthing of the planet Uranus. The initial hypotheses on the genesis of the solar system.
During this period, several scientists made significant contributions to the development of astronomy:
- Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) from Italy
- Johann Kepler (1571-1630) from Germany
- Jan Gavelius (1611-1687) from Poland
- Hans Christian Huygens (1629-1695) from the Netherlands
- Giovanni Dominico (Jean Domenic) Cassini (1625-1712) from Italy-France
- Isaac Newton (1643-1727) from England
- Edmund Halley (1656-1742) from England
- William Friedrich Herschel (1738-1822) from England
- Pierre Simon Laplace (1749-1827) from France
IVth Spectroscopy and photography. (1814-1900). Observations using spectroscopy. Initial calculations of stellar distances. Identification of the planet Neptune.
During this period, several scientists made significant contributions to the development of astronomy. These include Joseph von Fraunhofer (1787-1826, Germany), Vasily Yakovlevich (Friedrich Wilhelm Georg) STRUVE (1793-1864, Germany-Russia), George Biddell ERIE (ERIE, 1801-1892, England), Friedrich Wilhelm BESSEL (1784-1846, Germany), Johann Gottfried GALLE. (1812-1910, Germany), William HAGGINS (Huggins(1824-1910, England), Angelo SECCI (1818-1878, Italy), Fyodor Alexandrovich BREDIKHIN (1831-1904, Russia), and EDWARD CHARLES PICKERING (1846-1919, USA).
Astronomy
Astronomy is beneficial as it lifts us beyond our own selves; it is beneficial as it is grand; it is beneficial as it is exquisite. It is the discipline that reveals to us the insignificance of mankind in physical form and the magnitude of our spirit.
Henri Poincaré
What is the field of astronomy?
Astronomy is the scientific discipline that focuses on exploring the vastness of the universe, including its intricate movements, organization, and composition. Moreover, it encompasses the investigation of the origins and evolution of celestial entities and systems. In essence, astronomy delves into the realms of space, planets, and various celestial objects.
The principles of astronomy are firmly grounded in the meticulous observation and comprehensive analysis of the surrounding cosmos.

The Origins of Astronomy
Astronomy can be traced back to ancient Greece, where it first began to be studied by Pythagoras and Aristotle.
The word “astronomy” is believed to have originated from the ancient Greek words “astrom” meaning star and “nomos” meaning law. It can be translated as either “stellar law” or “law of the stars.”

Astronomy: Exploring the Mysteries of the Universe
The field of astronomy delves into the vastness of the cosmos, encompassing a wide range of celestial objects and phenomena. From ancient philosophers like Pythagoras and Aristotle to modern-day scientists, the study of astronomy has captivated our curiosity for centuries.
What Does Astronomy Study?
At its core, astronomy investigates the wonders of the universe. This includes the examination of stars, planets, meteors, and comets, as well as the exploration of galaxies, nebulae, and other celestial bodies that reside in the vast expanse of outer space.
In essence, astronomy is the study of space and all that it contains, offering us a glimpse into the mysteries of the cosmos. Through observation, research, and technological advancements, astronomers continue to unveil the secrets of the universe and expand our understanding of the world beyond our planet.
When did the field of science emerge?
Indeed, astronomy predates other scientific disciplines and is considered one of the oldest sciences. It is difficult to pinpoint an exact date for the emergence of astronomy, as it originated many centuries ago, around the 3rd to 2nd centuries BC. The study of the surrounding world became essential for our ancestors to ensure their survival, particularly in terms of navigation and agriculture. This knowledge also led to the development of timekeeping and was applied across various aspects of human life, from basic needs like food and clothing to expanding one’s knowledge and satisfying curiosity.
Ancient astronomy
It is widely accepted that the scientist Hipparchus is credited with being the pioneer of science. He was among the first to accurately calculate and describe the movements of the Sun and the Moon. Additionally, Hipparchus introduced a classification system for stars based on their brightness, which remains in use to this day.
Astronomy Objectives
Similar to other scientific disciplines, astronomy has its own set of goals and objectives.
Currently, there are three main tasks that are being pursued:
1) investigating the positions and movements of celestial bodies, as well as determining their shapes and sizes;
2) studying the structure and composition of celestial bodies;
3) researching the formation, evolution, and future of celestial bodies.
In the past, astronomy was more rooted in philosophical perspectives. However, with the advancements in technology, it has become a more precise and accurate science. Today, it is closely intertwined with mathematics, physics, chemistry, and biology. Philosophy also continues to play a significant role in the fundamentals of astronomy.

What is the primary objective of astronomy? It is highly likely that you have already discerned this.
The primary scientific discipline we have mentioned has the goal of examining and exploring the phenomena and objects of the cosmos. Naturally, this is done in order to comprehend the nature of the universe. To comprehend its structure and characteristics.
Humanity aspires to unravel its enigmas and secrets. Scientists endeavor to elucidate the origins of everything. Moreover, everyone longs to ascertain what lies ahead. To discover the truth and obtain an accurate depiction of the world.
Thanks to the field of astronomy, we have already acquired a vast amount of knowledge. Looking ahead, it is evident that there is still much more to discover and learn. The progression of science is constant and unyielding.
With that being said, we bid you farewell and hope to see you again soon!
Exploring the Depths of Astronomy
Take advantage of the unbeatable offers on Tinkoff products by visiting this link
When you choose to save your number, we will reward you with a generous 500 ₽ balance on your SIM card and an additional 1000 ₽. Don’t miss out on this incredible opportunity!
Order a SIM card through this link and receive 500 rubles directly into your account. It’s a fantastic deal!
Discover the finest deals on TINYKOFF products by visiting this link. You won’t be disappointed!
What is the field of astronomy?
The term “astronomy” originated from the contributions of Pythagoras and Hipparchus during the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC. In contemporary society, astronomy encompasses various branches of study.
Astronomy investigates the cosmos as a whole and its individual components, such as stars, comets, planets, constellations, galaxies, and more. Furthermore, astronomers dedicate their efforts to researching black holes, nebulae, and the celestial coordinate system.
There exists a strong correlation between astronomy and various other scientific disciplines. Mathematics, physics, chemistry, geography, biology, mechanics, and radio electronics are just a few examples of the many sciences that modern astronomers rely on. The knowledge acquired through the study of these subjects undoubtedly aids in the understanding and exploration of astronomy.
In order to conduct research in the field of astronomy, it is essential to possess a combination of mathematical and geographical knowledge. Additionally, a understanding of chemistry is necessary in order to determine the chemical composition of celestial bodies and explain the chemical processes that occur in outer space. Furthermore, a grasp of physics is indispensable in order to comprehend the physical processes that take place on stars and to study the shape of celestial bodies. Linguistics can assist in the study of the meaning and origin of constellation, star, and planet names. Radio electronics and mechanics are valuable in learning to utilize telescopes, understanding their structure, and conducting space research. Biology provides insight into the effects of sunlight on all living organisms on Earth. Finally, a study of history takes us back in time and aids in understanding the origins of celestial bodies, as well as introducing us to ancient astronomers.
The Scale of the Universe and its Dimensions
Scientific research has conclusively demonstrated that the universe possesses definite boundaries. Its vastness is measured in terms of light-years, with an estimated count of approximately 45.7 billion. To put this into perspective, if we were to equate one light year to 10 trillion kilometers, the magnitude of the universe becomes truly mind-boggling.
The Abundance of Celestial Bodies in the Universe
The universe is teeming with a myriad of celestial bodies, also known as cosmic entities. These entities encompass a wide range of sizes, ranging from the microscopic to the colossal. Examples of small cosmic bodies include meteorites, asteroids, and comets. As scientists continue to explore and analyze these celestial bodies, they have recently discovered the largest known entity in the universe: UY Scuti, a star with a radius 1700 times greater than that of our Sun.
Allow’s examine celestial objects more closely and identify their attributes.
Asteroids are formations of rock that constitute the asteroid belt. It is situated between the orbits of Jupiter and Mars. The shape of asteroids is irregular, with bodies ranging in diameter from 30 meters to several kilometers. To date, researchers have identified over 97,853,768 of these small cosmic bodies. Asteroids move in orbit around the Sun.
Comets consist of a compact nucleus. When they approach the Sun, the nucleus starts to heat up and the substances it is composed of begin to vaporize. This process leads to the formation of a gaseous envelope and subsequently a tail. As the comet moves away from the Sun, the tail and envelope dissipate. Occasionally, comets can be observed with the naked eye. The most recent comet visible in the night sky within the past 7 years was C/2020 F3 NEOWISE, which appeared in July 2020. Generally, scientists utilize telescopes to study these celestial objects.
Meteoroids are solid celestial bodies that are larger than atoms but smaller than asteroids. They can be both primary objects themselves or fragments of other space objects, including not only asteroids but also comets. Celestial bodies that enter Earth’s atmosphere are referred to as meteors. These can include fragments from comets or asteroids.
When meteorites fall, they create a mark – a crater. The largest crater known as Wilkes has a diameter of 500 kilometers.
Stars are celestial bodies that emit light and heat. They are enormous spheres of gas. The Sun is the closest star to Earth. On clear nights, a variety of stars can be observed in the sky. Our ancestors recognized the significance of these “glowing dots” as they aided in navigation through space and were often the subjects of myths and religious tales. Even in ancient times, people without any advanced technology could see various creatures depicted in the stars, leading them to identify constellations. Currently, there are a total of 88 constellations, with 12 of them being zodiacal.
Planets are large spherical objects that orbit the Sun on a specific axis and are not satellites of any other cosmic bodies. There are a total of 8 planets in our solar system:
Telescopes: terrestrial and space telescopes
A telescope is a specialized instrument used for observing celestial objects. Its main function is to gather as much light as possible from a celestial body and increase the viewing angle for studying that body. The amount of light captured by the telescope is directly proportional to the size of its lens. Therefore, a larger lens allows for the observation of smaller objects.
The scientist Galileo Galilei is credited with creating the first telescope in 1609, which was not significantly different from the telescopes already in existence at that time. However, Galilei’s device used more powerful lenses, allowing for a 20x increase in image size. This groundbreaking invention led to the first important discoveries in space and is currently housed in a museum in Florence.
While ground-based telescopes are capable of observing the Sun, planets, and satellites, they are unable to provide detailed studies of stars. Even the most powerful telescopes can only view stars as small, flickering dots.
Space telescopes located in orbit provide a more in-depth exploration of space and the Universe. These incredible instruments play a crucial role in studying the history of our cosmos. The inaugural space telescope was launched in August 1957, capturing a high-resolution photograph of the Sun from an altitude of 25 km.
Contemporary telescopes, whether situated in space or on the ground, are equipped with advanced computer programs. These programs transmit images to monitors, enabling us to view them in their true form without any distortion.
Where are the biggest optical telescopes situated?
Generally, telescopes are positioned in secluded areas far from the hustle and bustle of cities. Mountainous regions or vast deserts are ideal for this purpose. Some of the largest telescopes in the world are:
Russia’s most extensive telescope, the BTA (Big Telescope Alt-Azimuthal), is situated in the mountains at an elevation of 2070 meters in Karachay-Cherkessia. Its mirror has a diameter of 6 meters.
The initial astronomers were solely reliant on optical telescopes in order to investigate the vast expanse of space. As a result, their ability to study and explain the cosmos was limited to what their naked eye could perceive. Nevertheless, modern astronomy has experienced significant advancements due to the ability of scientists to conduct observations across a wide range of wavelengths. This newfound knowledge and technological progress have led to the emergence of entirely new fields within the discipline, including gamma-ray astronomy, radio astronomy, and X-ray astronomy.
Every object in space emits a series of undetectable waves, but they can be measured using specialized instruments. The importance of these measurements cannot be overstated. For instance, gamma or X-ray radiation, which reaches Earth from space, provides insight into the immense processes occurring in the furthest reaches of the Universe. Due to the vast distances involved, it is impossible for humans to visually study all cosmic objects. Our understanding of the cosmos is primarily based on the radiation emitted by celestial bodies. This radiation has allowed us to determine the distances between objects in the Universe, as well as their composition, age, size, and more.
The concept of “all-wave astronomy” refers to the practice of conducting modern observations of cosmic bodies across all known ranges of electromagnetic radiation.
Development of domestic cosmonautics: a brief history
The beginnings of domestic cosmonautics can be traced back to the mid-20th century. In 1946, the establishment of Experimental Design Bureau No. 1 marked the beginning of a mission to develop satellites, launch vehicles, and ballistic missiles. A decade later, the bureau successfully pioneered the design of the first carrier rocket, which ultimately launched the world’s first artificial satellite into orbit.
This monumental achievement in space exploration propelled the development of domestic cosmonautics to new heights. Shortly thereafter, another satellite was sent into space, this time with an extraordinary passenger on board – a dog named Laika.
Exploration of the Moon became possible with the launches of interplanetary stations, and as early as 1959, a spacecraft successfully landed on the surface of our planet’s satellite. During this mission, the Soviet Union captured images of the Moon’s far side, which enabled scientists to name nearly all of its major features.
The First Photograph of the Moon’s Far Side
A significant milestone in the advancement of domestic space travel occurred with the first manned spaceflight, which took place on April 12, 1961. Yuri Gagarin piloted the Vostok spacecraft during this historic event. In 1965, another breakthrough was achieved when a human ventured into outer space for the first time.
Until 1991, domestic space exploration continued to yield numerous discoveries and accomplishments:
The Inauguration of the Initial Man-Made Satellite of the Earth
October 4th, 1957 marked a historic moment for the global space industry. On this particular day, the first-ever man-made satellite was successfully launched into orbit. This significant milestone marked the beginning of space exploration and paved the way for groundbreaking advancements in both national and international space endeavors.
The Baikonur Cosmodrome, situated in Kazakhstan, served as the launch site for this momentous occasion. The R-7 launch vehicle was utilized for the mission. The satellite remained in outer space for a remarkable 92 days, completing a staggering 1440 orbits around the Earth. This unprecedented feat enabled scientists to conduct groundbreaking studies on the upper layers of the ionosphere. Additionally, invaluable data on the performance of equipment in space conditions was gathered and calculations were meticulously verified.
The maiden artificial satellite of the Earth
Modern astronautics has achieved a significant milestone in its advancement. Today, space is no longer seen as something incredibly distant, but rather as a tangible reality. The launch of modern spacecraft and journeys into outer space have become increasingly common occurrences in the Russian state, despite their high cost.
Space tourism is no longer a surprise, as individuals can now pay a certain fee to experience a trip on a spaceship. Furthermore, space exploration is conducted at a remarkably high level. Present-day scientists are actively working on the development of solar power plants and the advancement of technologies capable of influencing the Earth’s climate.
Since 2016, the Vostochny cosmodrome in the Amur region has been operational. This has provided Russia with the ability to launch spacecraft from its own territory, eliminating the need for dependence on other countries.
There are upcoming plans to send manned spacecraft to the Moon, unmanned spacecraft for space exploration, and to execute the Sea Launch program in the near future.
Russia’s main objective is to advance its domestic space industry, explore the potential of modern space technology, and establish a leading position in the global space industry.

Astronomy, the oldest scientific discipline, focuses on the exploration of the Metagalaxy; however, it still cannot definitively answer the query about the nature of the Universe. The concept of the Universe exists in two forms – philosophical and material. These two perspectives can be viewed as distinct entities or as interconnected. If we define the observable universe as the entirety of space, then a synonymous term would be cosmos.

Cosmology Definition and Significant Information
In the field of cosmology, the universe is defined as the observable region of the world. Another term used to refer to it is Metagalaxy. Behind this extensive definition lie numerous mysteries, as space research has been ongoing for a considerable amount of time and shows no signs of stopping in the foreseeable future.
Throughout scientific investigations, numerous facts about the universe have been uncovered, which possess a high level of certainty.

- Chemical composition. Outer space consists of about 75% hydrogen, along with helium, oxygen, carbon, and other less common impurities.
- The universe is continuously expanding, causing all objects to move away from each other. Because of this, the Metagalaxy does not have a clearly defined center, similar to an inflated balloon. Approximately 5 billion years ago, this expansion started to accelerate, leading scientists to propose various hypotheses about its future.
- The arrangement of galaxies in the Universe can be depicted as a cellular formation. However, due to continuous movement, the network gradually elongates.
- The most luminous entities in the observable region (quasars) exhibit repeated occurrence of the Lyman spectrum. Investigating this phenomenon has enabled the simulation of the Universe’s macroscopic organization.
Origin and evolution
There is a theory that suggests that in the distant past, stars, galaxies, and their clusters were not only located closer together but were also mixed and compressed into a single substance. However, this substance was extremely dense and hot, which eventually led to the general expansion of the universe.
Approximately 14 billion years have passed since then. During this time, several significant developments have occurred:
- The formation of gravitational interaction.
- The birth of the first fundamental particles.
- Matter becoming transparent to radiation.
- The formation of the nuclei of primary elements.
- stars, galaxies, planetary systems.
In this way, the Universe came into existence as humans understand it now. Its basic representation is as follows:
- 4.9% regular matter, which is recognizable on Earth.
- 26.8% mysterious matter, composed of massive particles. It does not emit any electromagnetic radiation, which makes it difficult to directly observe.
- 68.3% enigmatic energy, which triggers the expansion of space.

The structure created by these components covers an immense expanse. The actual size of the Universe has not been determined by modern scientific research. Many scientists argue that it is boundless. However, if we consider the distance to the farthest observable object from Earth as a hypothetical boundary, its magnitude would be 45.7 billion light years. This measurement is known as the Hubble radius. It does not indicate the end of the universe, but rather signifies that once this distance is surpassed, the object’s velocity of moving away from the observer exceeds the speed of light.
There is currently limited knowledge regarding the specific form of the Metagalaxy. According to recent data from the astronomical satellite Planck, it appears to have a flat shape. However, ongoing research suggests that there is still much to discover, and in the near future, new information may emerge that challenges our current understanding.
Structure inside

Despite the immense expanse, the composition of the cosmos appears to be relatively straightforward. It exhibits a consistent density and undergoes temporal transformations in accordance with precisely defined principles, thereby precluding an unequivocally constant state.
The cosmos is a complex entity, encompassing a myriad of diverse constituents that manifest in various configurations. Among its most prominent structures are galactic filaments, which, in conjunction with cosmic voids, form colossal “walls”.
The galaxies in the Universe are organized within these groups. They are presented in a vast quantity, approximately two trillion. Humanity inhabits the Milky Way, situated in a formation known as the Pisces-Keith superscope complex. Other stellar systems are exceedingly distant from this galaxy. However, a handful of them are visible to the unaided eye. These celestial bodies are identified by the following designations:
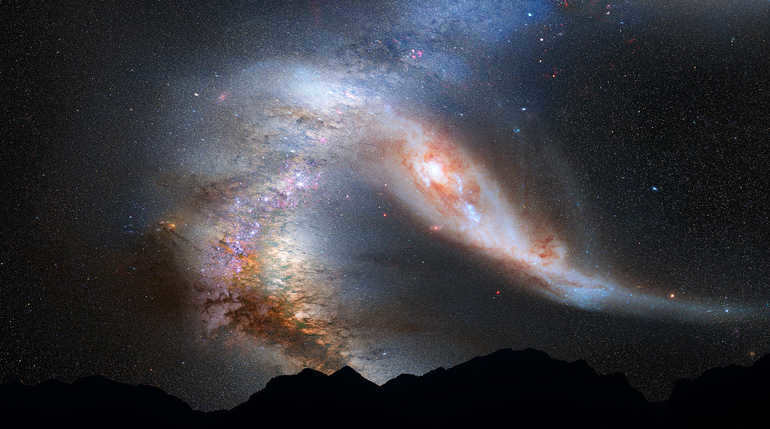

- The Milky Way’s closest neighbor, the Andromeda Nebula, contains a significantly larger number of stars. If you are in the northern hemisphere of the Earth, you can observe it in the sky.
- The Magellanic Clouds are two unique satellite galaxies of the Milky Way that can be seen in the southern hemisphere.
- Both the Triangle Galaxy and the Andromeda Nebula, which are visible in the northern hemisphere, are smaller in size and mass compared to the Milky Way.
Similar to the Milky Way, all of these galaxies belong to the spiral class. Additionally, there are elliptical and irregular galaxies present in the universe.
Approaches to studying
So, how did scientists gather all this fascinating knowledge about the secrets of the cosmos? Researchers employ multiple approaches to studying the universe simultaneously:

- Optical observations are conducted using a telescope, which is capable of collecting light. Light is one of the most valuable sources of information about cosmic processes, making it possible to study distant objects.
- Spectral analysis is another method that utilizes a telescope, but this time it is equipped with a spectrograph. The spectrograph breaks down the spectrum into its individual components, providing data on the object’s chemical composition, velocity, and even the temperature of its radiation sources.
- Cosmic radio emissions can be detected using a radio telescope. These emissions are transmitted by objects located in the farthest regions of the universe, as well as by ionized hot gas and neutral hydrogen in interstellar space. By analyzing the data obtained from the radio telescope, scientists can determine the distance and speed of celestial bodies.
- Astrophysics of neutrinos. This technique involves the detection of low-energy particles generated during thermonuclear reactions, which serve as the Sun’s energy source. By measuring the intensity of the neutrino flux, we can gain insights into the physical processes occurring within the star.
- Space-based astronomy. Distinguishing itself from other methods, this approach involves conducting observations and experiments in the interplanetary space. This eliminates atmospheric disturbances that can cause image instability in telescopes and allows for achieving diffraction-limited spatial resolution.
- There are various branches of astronomy that focus on different types of radiation, such as infrared, ultraviolet, X-ray, and gamma-ray. To observe these types of radiation, telescopes are installed on rockets and Earth satellites, as the planet’s atmosphere absorbs them and they cannot be detected on the surface. These telescopes are used to study a wide range of objects including dim cooled stars, exoplanets, molecular clouds, galaxy clusters, black holes, and more.
Maybe in the near future, alternative approaches to investigating the cosmos may emerge. Humanity will uncover something incredibly extraordinary about it, causing a complete paradigm shift in our understanding of the Universe.
However, it is challenging to conceive that humans will ever achieve complete exploration of the vast expanse of outer space. Within its immense domain, it appears that there will perpetually be space for enigma and intrigue.
Exploring the phenomenon: why do small black holes have the greatest impact on the curvature of space?

In 1979, J.-P. Luminet created a simulation that depicted the formation of a black hole and the accretion disk that surrounds it.
In November 1784, the English astronomer and priest John Michell proposed the concept of a celestial body so immense that even light would be unable to escape from it. Michell’s calculations indicated that such a body could possess a density similar to that of the Sun. He reasoned that these “dark stars” would form when a star’s diameter exceeded that of the Sun by 500 times and the escape velocity from its surface surpassed the speed of light in a vacuum. Michell further suggested that these supermassive, non-radiating entities could be detected through their gravitational influence on nearby visible bodies. Initially, scientists were optimistic about the idea of these invisible giants existing right before their eyes. However, their enthusiasm dwindled in the early 19th century with the discovery of light’s wave nature. The wave-particle duality of light raised questions about how gravity would impact fleeing light waves, casting doubt on the existence of these “dark stars.”
Introducing the new comet C/2023 P1 (Nishimura)
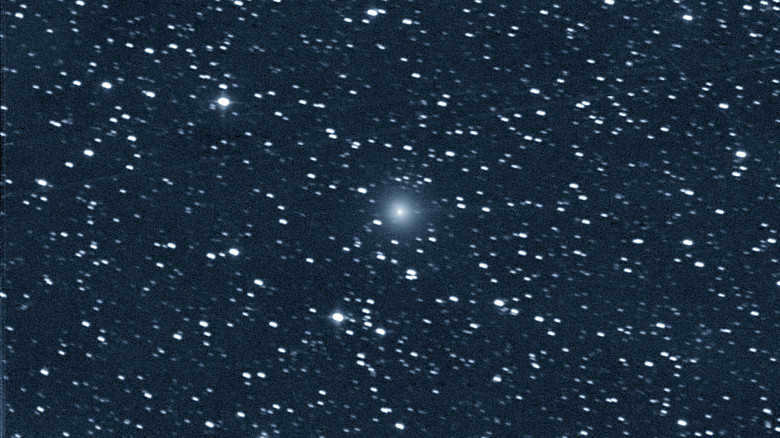

Comets are unexpected visitors. While the old ones, which we have long been familiar with, can sometimes be disappointing (which is not surprising, considering that they have had time to deplete and melt during repeated approaches to the Sun), newly discovered comets can often be bright and spectacular. However, this is not always the case.
Comet C/2023 P1 was spotted by Japanese astronomer Hideo Nishimura on the night of August 11-12, 2023. The comet was located in the constellation Gemini (and it still is). It can be said that the discovery of the comet was a stroke of luck, as finding a faint, hazy object (with a magnitude of 12) in the brightening pre-dawn sky is a remarkable stroke of luck and a testament to the highest level of professionalism.
Sundial in a horizontal position
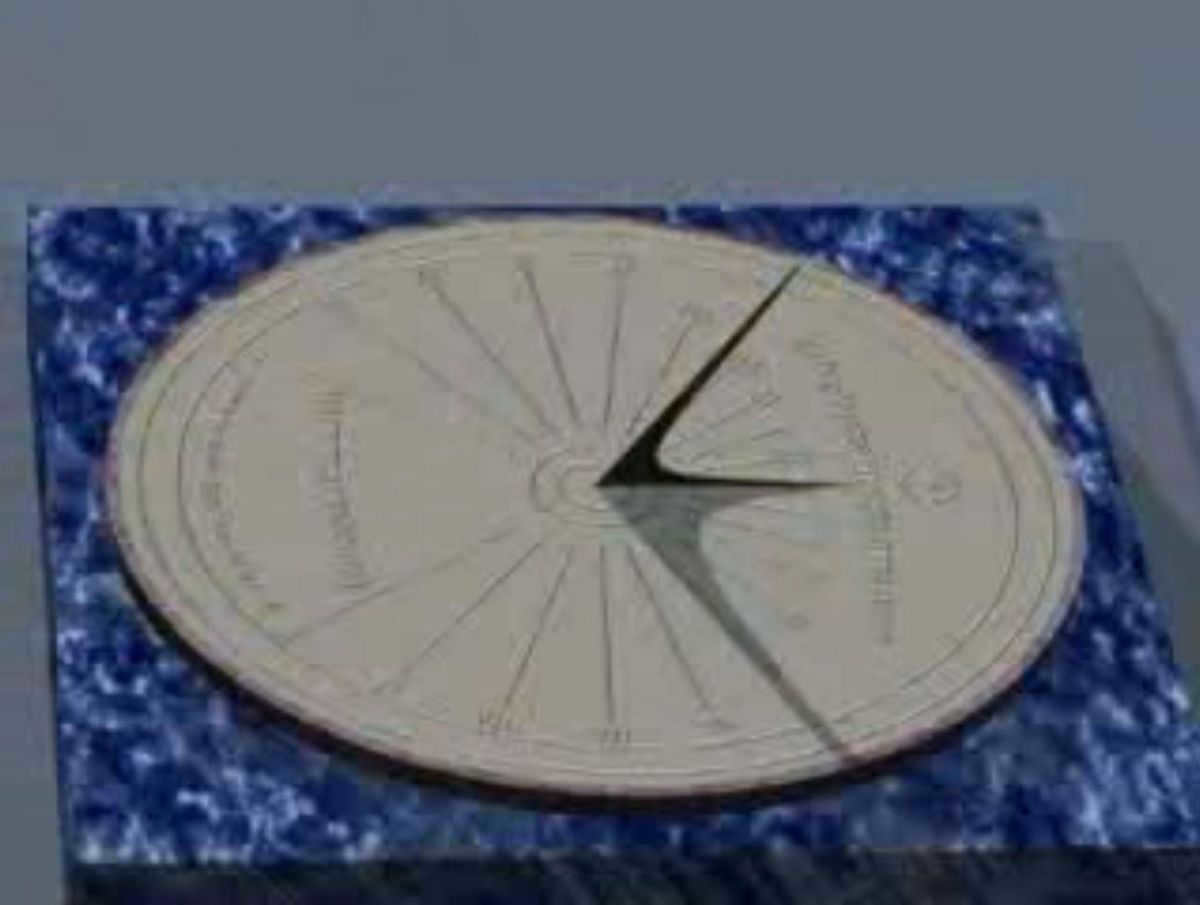

This article explains the process of labeling the face of a horizontal sundial for any given latitude and provides instructions for constructing the most basic horizontal sundial.
Voyager 2: issues and malfunctions of the spacecraft that NASA has been working to resolve since 2010. The mission is ongoing

Recently, there has been news about a significant malfunction of Voyager 2, a spacecraft that was launched into space over 45 years ago. Currently, it is situated at a distance of approximately 133 astronomical units from Earth. Consequently, rectifying errors and addressing issues is a challenging task. Nevertheless, NASA engineers are effectively managing the situation (at least for now).
Interestingly, the probe and its companion spacecraft continue their journey. Throughout the years, there have been a few failures, albeit not many. Let’s delve into the most noteworthy ones. The specifics are provided below.
Articles
A compilation of the latest science fiction updates we overlooked

A recent study has revealed a “gravitational anomaly” present in certain star systems that has the potential to challenge a fundamental concept of the universe. The anomaly is observed when wide double stars, which freely rotate, move in a manner that contradicts established models of gravity based on the theories of Isaac Newton and Albert Einstein. This groundbreaking discovery suggests the existence of an alternative physics theory that does not rely on the presence of mysterious and unidentified phenomena like dark matter to explain the observed cosmic phenomena.
The true color of the Sun: Explanation from an astrophysicist

If the statement “seeing is believing” holds true, it specifically applies when we perceive light with our eyes. This concept defines the act of seeing from a human perspective. However, for some reason, individuals tend to believe the highly questionable assertion that the Sun is genuinely a green-colored star.
If you have ever opened your eyes, observed the Sun, and noticed green-colored objects, you would personally attest that the Sun is not truly green. So, why do intelligent individuals convince themselves that the Sun possesses a blue-green hue?
Variable stars aid astronomers in the quest for alien life
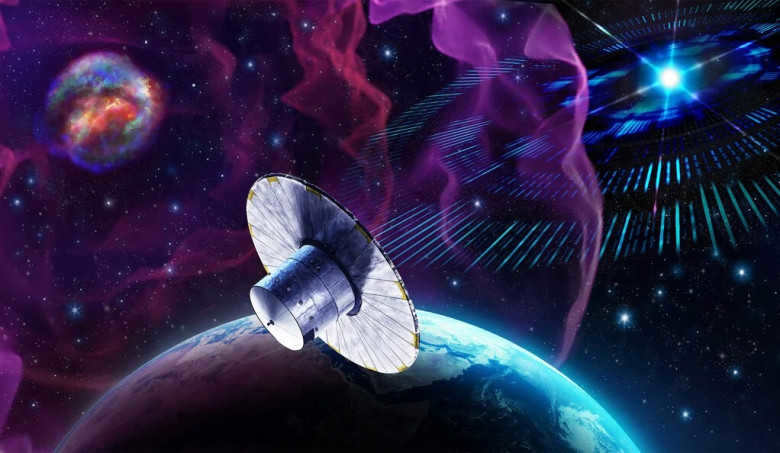

The Gaia Observatory, operated by the European Space Agency (ESA), has been stationed at the Lagrangian point L2, located between Earth and the Sun, for almost ten years. Its main objective is to gather extensive data on the positions, movements, and velocities of stars, exoplanets, and celestial bodies within the Milky Way and numerous neighboring galaxies. By the conclusion of its primary mission in 2025, Gaia will have meticulously analyzed approximately one billion astronomical entities, resulting in the creation of the most precise three-dimensional space catalog ever formulated.
ESA has released three sets of data from the Gaia mission so far, with the most recent one (DR3) being made available in June 2022. Alongside the significant advancements brought about by these data releases, researchers are discovering additional ways to utilize this astrometric data. In a recent investigation, a team of astronomers proposed the utilization of the Gaia Data Release 3 catalog of variable stars to aid in the quest for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI). By aligning the search for transmissions with noteworthy occurrences (such as the explosion of a supernova star), scientists can narrow down the search for extraterrestrial signals.
The Impact of Webb’s Images on Astronomy: Unveiling the Secrets of the Early Universe
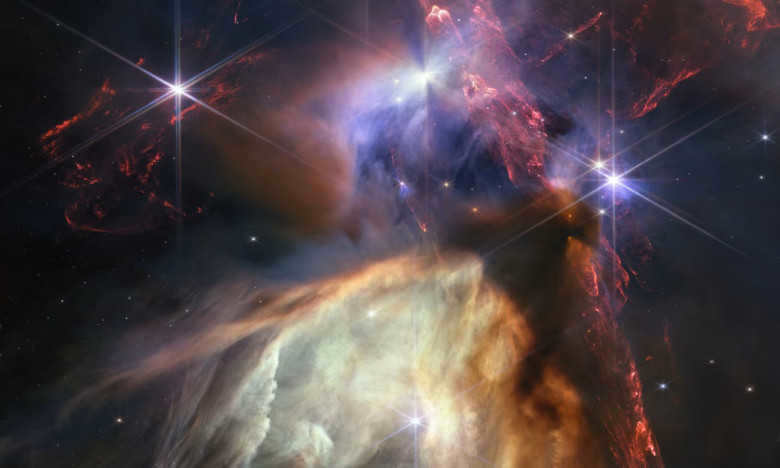

Last year, the James Webb Space Telescope was able to capture light emitted from a cluster of ancient galaxies, which had been traveling for more than 13 billion years. This is a remarkable discovery as it suggests that the universe was already undergoing star formation shortly after the big bang. Although the images captured by the telescope may not be visually striking, they provide valuable scientific insights into the early history of the cosmos.
However, the field of astronomy was left in awe. One of the items captured in the massive mirror of the telescope happens to be the most ancient galaxy ever discovered in the cosmos. This particular galaxy, which goes by the rather mundane title of JADES-GS-z13-0, emerged a mere 320 million years after the cataclysmic event known as the Big Bang, preceding the formation of our own planet. Despite its small size in comparison to the Milky Way, it was evident that this galaxy was generating new stars at a rate similar to our own celestial home.
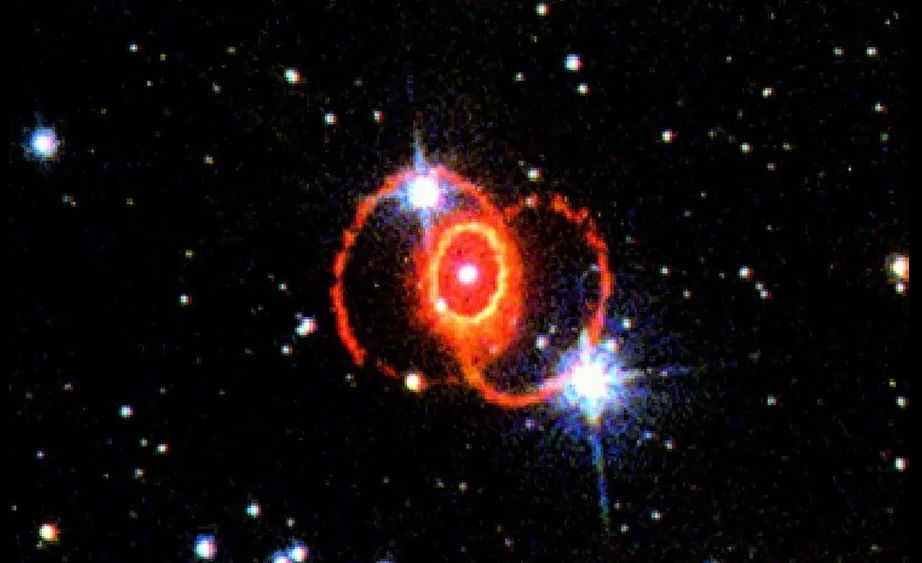
Describing the appearance of an astrophenix. Challenges in interpreting supernova SN1987A

A roundup of the science-pop news from this week that we haven’t covered
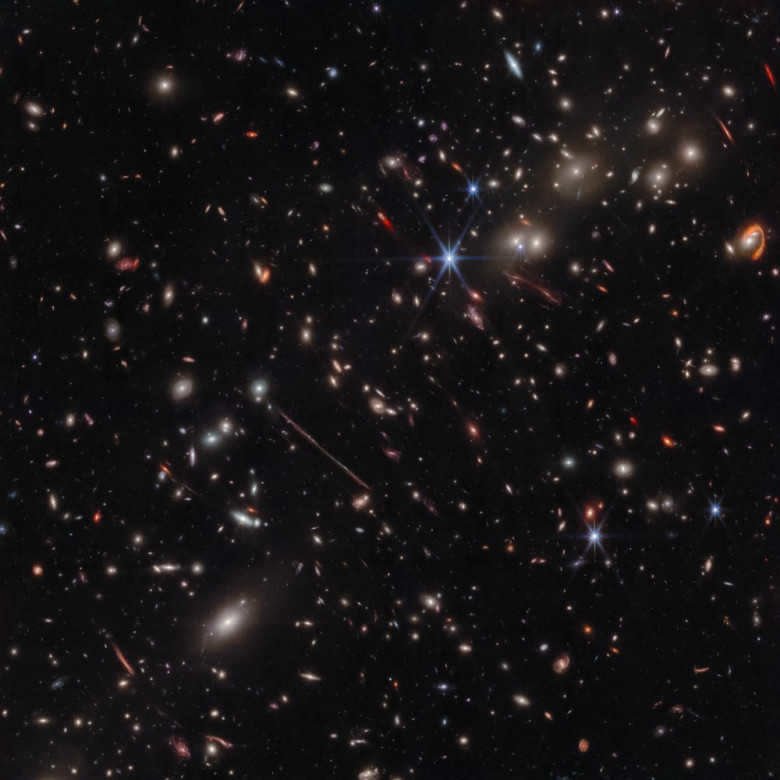

A recent discovery of the galaxy cluster called El Gordo has provided scientists with a unique opportunity to observe previously unseen celestial objects. Utilizing NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, an infrared image has captured a multitude of distorted galaxies, many of which were only hinted at in previous Hubble Space Telescope images.
El Gordo, aptly named “The Fat Man” in Spanish, is a cluster of hundreds of galaxies that existed approximately 6.2 billion years ago, making it comparable to a cosmic teenager. It currently holds the title of being the most massive cluster known to date, further adding to its significance in the scientific community.
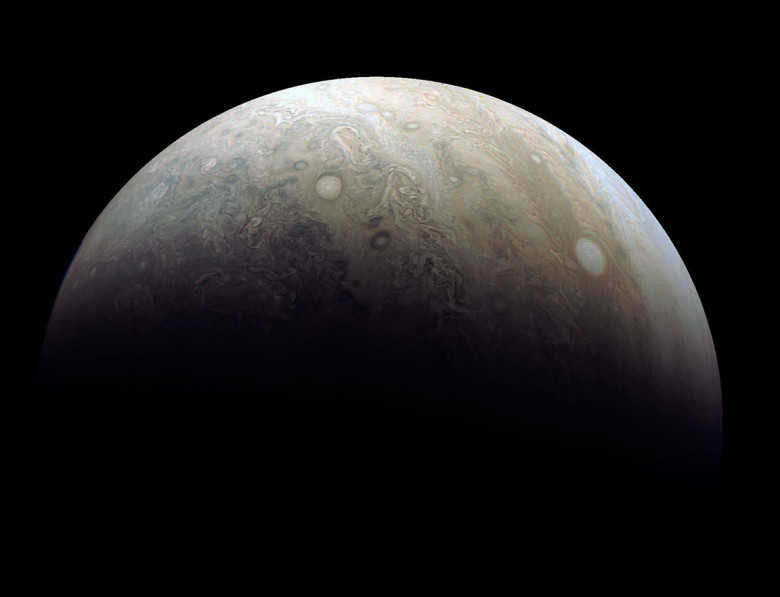
The tale of the gas giant: exploring the enigmatic atmosphere

The Earth’s first “potentially hazardous” asteroid has been detected by a groundbreaking algorithm
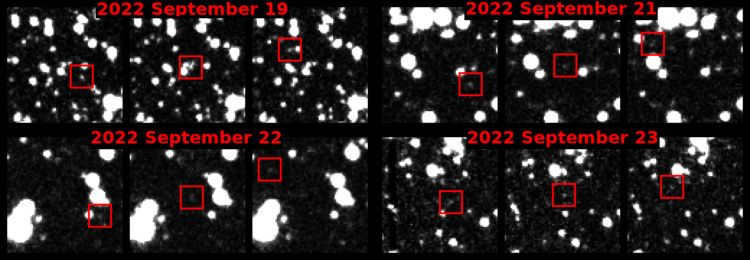
An algorithm for detecting asteroids has been developed to search for near-Earth asteroids as part of the Vera C. Rubin Observatory’s upcoming survey of the night sky. This algorithm has successfully identified the first asteroid that is considered “potentially hazardous” – a term used to describe space rocks that are in close proximity to Earth and are of interest to scientists. The asteroid, named 2022 SF289, has a diameter of approximately 200 meters and was discovered during a test run of the algorithm as part of the ATLAS study in Hawaii. It is important to note that 2022 SF289 does not pose a threat to Earth in the foreseeable future. This discovery validates the effectiveness of a next-generation algorithm called HelioLinc3D, which is able to identify near-Earth asteroids with fewer and more diverse observations compared to current methods.
“The detection of 2022 SF289 provides us with a feeling of assurance as it showcases the practicality of the software that Rubin will employ in its search for countless unknown asteroids that could pose a threat,” stated Ari Heinze, a scientist at Rubin and the primary creator of the HelioLinc3D software, who is also affiliated with the University of Washington.
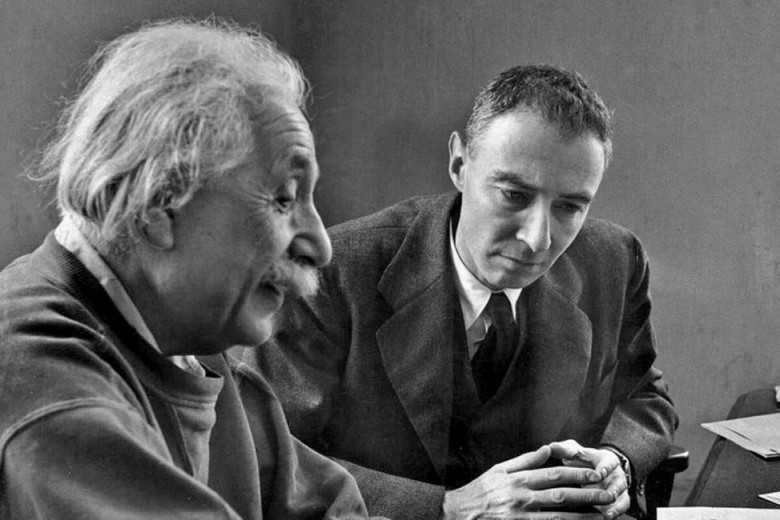

Oppenheimer gained fame as the head of the American atomic weapons program, but his contributions to the field of astrophysics are equally significant, particularly in regards to our understanding of black holes and how they are formed. This article offers unique scientific insights that are not covered in the Oppenheimer film.
The initial images were transmitted by the “Euclid” space telescope

On Monday, July 31, the first images from the Euclid telescope of the European Space Agency were transmitted to Earth. These mesmerizing images not only captivate our attention, but they also serve as confirmation that the space observatory’s instruments are functioning correctly.
The success of Euclid brings great joy, as its main objective is to map the unexplored regions of our universe by analyzing billions of galaxies that are located up to 10 billion light years away. In addition, the agency asserts that this ambitious map will be “three-dimensional” in nature, incorporating the element of time to showcase the evolution of these cosmic entities over time.
Why the universe will never be fully explained by the laws of physics

Understanding the immensity of the cosmos is a daunting task: our galaxy alone contains billions upon billions of stars, and there are trillions of galaxies scattered throughout the universe. However, what captivates cosmologists even more than the staggering numbers themselves is the mystery of how all these celestial bodies came into existence over the course of 13.8 billion years. This is the ultimate journey into the depths of time. Without planets, life as we know it cannot flourish, and without stars, planets cannot form. Galaxies are the homes of stars, and the existence of galaxies relies on the intricate structure of the Universe. The tale of our origins is inscribed across the heavens, and we are just beginning to decipher its message.
In the past, it appeared that the immense cosmos could be comprehended by a limited number of rigid physical principles. Newton demonstrated this concept by proving that the falling of apples from trees and the orbits of planets around the sun are both caused by the force of gravity. This revolutionary integration of terrestrial and celestial occurrences continues to be taught today: it is believed that all the countless molecules, atoms, and subatomic particles in the universe adhere to the same set of principles. The majority of evidence supports this belief, and as a result, furthering our comprehension of these principles will address any remaining inquiries regarding the history of the cosmos.
A compilation of the science-pop news from the past week that we haven’t covered
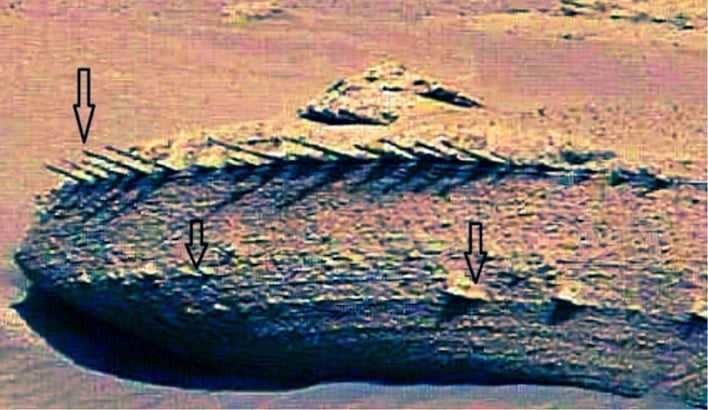

An imprint resembling the aftermath of a spaceship’s crash landing has been discovered on Mars
In a recent study, researchers do not dismiss the possibility that the horizontal protrusions captured in photographs by NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity might be linked to extraterrestrial spacecraft. The particular image in question was captured by Curiosity during its time in Gale Crater on Mars, utilizing the ChemCam camera, between sols 3786 and 3800.
Earlier this year in April, many people were left intrigued by Curiosity’s April Fool’s Day image. Some speculated that they were observing “the fossilized back of a Martian dragon,” while others believed they had stumbled upon the preserved remains of an ancient creature that once inhabited Mars. During an interview, NASA scientists stated that the peculiarly shaped rocks were most likely formed when “minerals were carried through cracks in the rock by liquid water.” However, a new study suggests that the idea of an extraterrestrial spacecraft leaving these markings cannot be entirely dismissed.

Throughout its long history, mankind has had a desire to comprehend the universe in which it exists, and it is through this yearning that scientific breakthroughs have been made and subsequently organized.
For instance, this is how mathematics, as a systematic discipline, came into being in ancient Greece, with Euclid, Pythagoras, and Eratosthenes as its founding figures. It is undeniable that mathematics has come a long way since then, but the theories proposed during that time laid the groundwork for the future advancement of science.

However, it was the laws and phenomena of physics that made revolutionary discoveries in astronomy possible. So, what is our current knowledge of the universe, and what books can expand our understanding on the topic?
“The Fascinating World of Astronomy” – Yakov Isidorovich Perelman
Yakov Isidorovich Perelman, a Soviet mathematician and physicist, is credited as the pioneer of the popular science genre in literature. This genre aims to explain intricate processes and phenomena in a straightforward and comprehensible manner, targeting a broad audience.
In his book, Yakov Perelman discusses the fundamental principles of astronomy. However, this piece of work distinguishes itself from typical school textbooks by not being a mere compilation of static facts and convoluted mathematical equations. Instead, it presents a lively and captivating narrative that sheds light on various scientific facets, elucidating them and providing a fresh perspective.
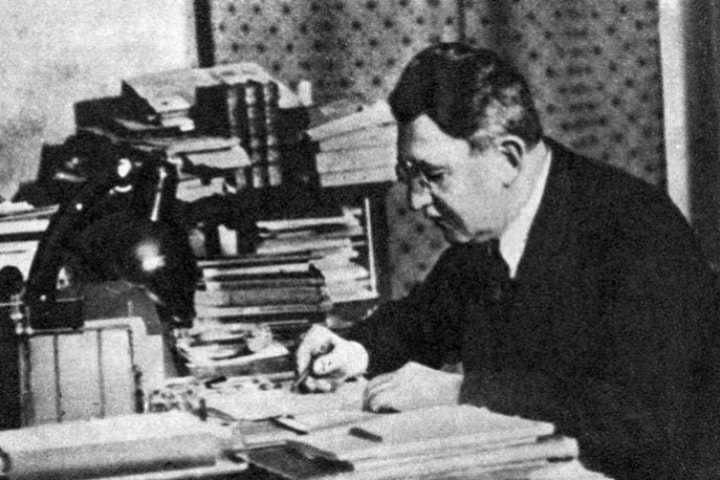


Yakov Isidorovich Perelman and his book “Entertaining Astronomy”
In the introduction of “Entertaining Astronomy”, Yakov Isidorovich Perelman stated:
“Astronomy is a delightful field of study: as the French scientist Arago once said, it does not require any embellishments. Its accomplishments are so captivating that there is no need to actively draw attention to them. However, the study of the celestial bodies is not solely comprised of astonishing discoveries and daring theories.
It is founded on the everyday occurrences that repeat themselves day after day. Individuals who are not avid stargazers are usually only vaguely acquainted with this mundane aspect of astronomy and show little interest in it, simply because it is difficult to focus on what is always right in front of their eyes.”
Yakov Isidorovich Perelman
The book is divided into five chapters:
“Cosmos” by Carl Sagan
If you have been longing to learn about astronomy but have hesitated, then “Cosmos” by Carl Sagan is the ideal book for you. This book is perfect for those who want to expand their horizons and discover the answers to intriguing questions such as why the Moon doesn’t fall into the Sun, how the Earth was weighed, and what mistakes Jules Verne made in his novels.
“Cosmos” is Carl Sagan’s most renowned work, captivating an audience of over 140 million people. In this book, Sagan explores the evolution of the universe over billions of years. He also delves into the progress of science and our civilization. Alongside astronomy, Sagan touches upon anthropology, biology, history, and shares his philosophical perspective on the world. Through a dialogue-like approach, he makes it easier for readers to comprehend the vast amount of information presented in the book.
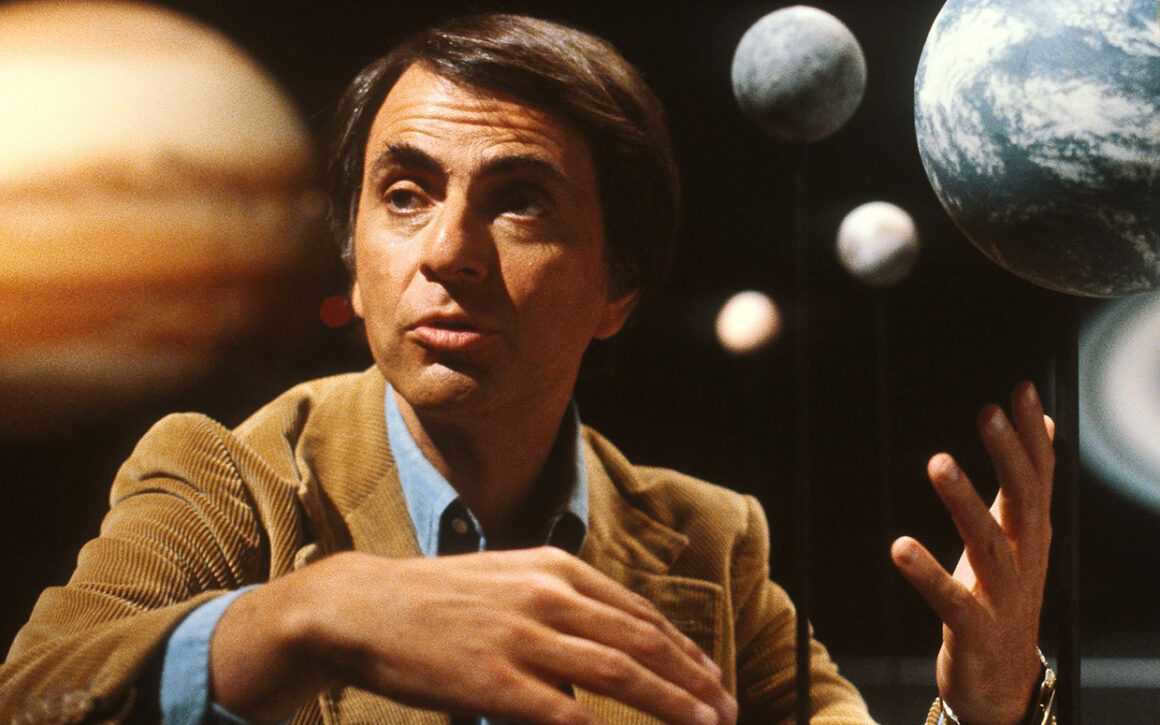


Carl Sagan and his book Cosmos
"Nowadays, we find ourselves at a critical juncture in the advancement of our society and possibly our species. Whichever path we decide to take, our fate is undeniably intertwined with science. This is precisely why it is imperative for us to comprehend the principles of science; it is ultimately a matter of survival. Furthermore, science is genuinely enjoyable. It is evolution’s way of making learning enjoyable – those who possess knowledge are more likely to thrive."
Carl Sagan
- Chapter I. Exploring the vast cosmic ocean
- Chapter III. Harmony of Worlds
- Chapter IV. Heaven and the underworld
- Chapter V. The Blues of the Red Planet
- Chapter VI. The adventures of travelers
- Chapter VII. The Ridge of Night
- Chapter VIII. Travels in space and time
- Chapter IX. The Life of the Stars
- Chapter X. The Edge of Eternity
- Chapter XI. The permanence of memory
- Chapter XII. Galactic Encyclopedia
- Chapter XIII. Who’s in charge of the earth?
These chapters are in sync with episodes of the TV series “Cosmos: A Personal Journey,” which is also part of this project. The film is a great addition to the book, so it’s definitely worth checking out.
“Astrophysics at the Speed of the Cosmos, or Unraveling the Enigmas of the Universe for the Time-Constrained” – Neil Degrasse Tyson
“Astrophysics at Warp Speed” serves as Neil Tyson’s introduction and is among the most renowned accessible science books in the realm of space sciences. Rather than relying on intricate jargon and convoluted equations, the author employs memorable comparisons to elucidate various phenomena.


Neil Degrasse Tyson and Donald Goldsmith collaborated on a book called “The Story of Everything: 14 billion years of cosmic evolution.”
"The mysteries of the universe are vast and incomprehensible to most people."
Neil Degrasse Tyson
In his book “Astrophysics at Space Speed, or The Great Mysteries of the Universe for Those Who Don’t Have Time for It,” Neil Degrasse Tyson explores topics such as dark energy, dark matter, and the big bang, providing readers with a concise introduction to the field of astrophysics.
“Parallel Worlds” – Michio Kaku
Michio Kaku delves into the intricacies of the universe, exploring higher dimensions and the destiny of the cosmos in his captivating book. Currently, the most pertinent model of the universe is examined, shedding light on the concept of parallel worlds and the significance of the multiverse. Demonstrating his expertise, Kaku skillfully addresses these inquiries throughout the four sections of his book, presenting the information in a clear and accessible manner for readers of all backgrounds.

Michio Kaku and his book “Parallel Worlds”
“With the influx of novel information that is currently being received, along with cutting-edge technology such as space satellites capable of scanning the sky, new gravitational detectors, and the near completion of new particle gas pedals the size of cities, physicists are filled with confidence that we are entering an era of great discovery in the field of cosmology. In essence, this is a flourishing period for physicists and all those who embark on the pursuit of understanding the origin and destiny of our universe,” expressed Michio Kaku in the foreword.
Michio Kaku
“The Story of Everything: 14 Billion Years of Cosmic Evolution” – Neil Degrasse Tyson and Donald Goldsmith
Neil Tyson presents another captivating book that delves into the intricacies of the universe’s evolution. This enlightening journey encompasses the momentous events such as the Big Bang and the subsequent expansion of the universe, leading up to the emergence of life on Earth and the ongoing quest for alternative life forms beyond our familiar realm of hydrocarbon-based life.
From the infinitesimal singularity that birthed our modern cosmos to the intricate systems like our own solar system that harbor humanity, Tyson intricately weaves together the threads of astronomy, anthropology, and biology. By embracing multiple disciplines, the authors aim to paint a comprehensive picture of the universe’s enigmatic wonders and answer the myriad of questions that lie within.


The book “The History of Everything. 14 billion years of cosmic evolution” and one of its authors – Donald Goldsmith
“100 Billion Suns. The Birth, Life, and Death of Stars” – Rudolf Kippenhan
It’s likely that you haven’t come across this publication before, even if you have an interest in the field of space science. Nevertheless, it was through this book that my fascination with astronomy, cosmology, and astrophysics first began.
This exploration of stars delves into the fundamental concepts of cosmology and astrophysics, which can be quite challenging to grasp and comprehend. Rudolf Kippenhahn adeptly explains these concepts in a manner that is accessible, drawing upon the experiments and studies conducted by other scientists as well as his own personal experiences. The book covers a wide range of topics including the significance of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, the evolutionary process of stars of varying spectral classes, the possibility of extraterrestrial life, and the efforts made to establish contact with beings from other worlds.


Rudolf Kippenhahn is renowned for his remarkable publication titled “100 Billion Suns: A Comprehensive Guide to the Birth, Life, and Death of Stars.”
Upon delving into the pages of this masterpiece, not only will you acquire a profound understanding of intricate concepts delivered in a lucid manner, but you will also become well-versed in scientific jargon.
“Is There Intelligent Life Beyond Earth?” – revised by Jim Al-Khalili
Presented here is a compilation of nineteen insightful chapters penned by a diverse group of esteemed scientists, each renowned in their respective fields. Contributors include Martin Rees, Ian Stewart, Seth Shostak, Nick Lane, and Adam Rutherford. Collectively, these chapters encapsulate the cutting-edge advancements and breakthroughs in the study of extraterrestrial life.


Jim Al-Khalili and his book "Are We Alone in the Universe?"
The inquiry into the presence of different life forms, civilizations, and habitable planets cannot be definitively answered through the lens of a single discipline. What is required is a holistic perspective, which is precisely what this publication offers – 19 concise essays, each presenting arguments pertaining to the issue from the standpoint of various scientific fields.
“Dr. Einstein’s Monsters. On black holes, big and small” – Chris Impey
Black holes are fascinating celestial objects that have captured the imagination of people for centuries. It is no surprise that they have been the subject of numerous films and books. Chris Impey, an expert in the field, has meticulously organized the existing knowledge about black holes, separating fact from fiction and debunking any unreliable information.


Chris Impey and his book "Dr. Einstein's Monsters. On Black Holes, Big and Small."
"Most people have a mistaken understanding of black holes. They are not celestial vacuum cleaners that devour everything in their vicinity. Black holes simply distort space and time near the event horizon."
Chris Impey
“The First Three Minutes” – Steven Weinberg
Despite its title, “The First Three Minutes” explores not only the initial moments of the universe but also delves into its evolution and offers predictions for the future. In fact, all the research and data presented in this book are rooted in the crucial “three minutes” that followed the Big Bang.
In his work, Steven Weinberg examines various models of the universe, speculates about what lies ahead, and sheds light on the captivating past. Humanity has made significant strides in understanding the enigma of the Big Bang, which remains one of the cosmos’ most perplexing phenomena. By unraveling this mystery, we can hope to find answers to many of the pressing questions in modern cosmology.


Steven Weinberg and his book The First Three Minutes.
"It is a common occurrence in the field of physics that we underestimate the significance of our theories. We often fail to recognize that the numbers and equations we manipulate on our desks have real-world implications."
Steven Weinberg
“The Theory of Everything” – Stephen Hawking
Stephen Hawking is most well-known for his book A Brief History of Time, which I highly recommend reading, dear readers. However, I would like to discuss another one of his works in this article – “The Theory of Everything”. This book is a monumental achievement by the scientist, consisting of seven lectures.
In “The Theory of Everything”, Stephen Hawking eloquently explains, with clever anecdotes and concrete examples, how our understanding of the universe has evolved over time, the various theories regarding the universe’s expansion, the enigma of black holes, the future prospects of our universe, the nature of time, and the contenders for the coveted title of the “theory of everything”.


Stephen Hawking and his masterpiece The Theory of Everything
"The discovery of the expansion of the cosmos is one of the most significant intellectual revolutions of the 20th century. It is astonishing that no one had conceived of it earlier when one becomes aware of it."
Stephen Hawking
This book is unquestionably deserving of your attention.
FAQ: Fascinating Books on the Topic of Space
The concept of the universe is an incredibly complex and expansive subject that lacks a precise definition. However, the origin of the term itself is quite intriguing. The word “universe” is derived from the ancient Greek word “οἰκουμένη,” which can be translated as “inhabited space.” According to current data, the majority of space, particularly the portion observable to us, appears to be devoid of any inhabitants, rendering this name somewhat outdated.
What we do know for certain is that space is vast, and the areas we have explored thus far seem to be composed of an almost ethereal substance. To truly comprehend the vastness of space, scientists must tackle another fundamental question: Does the universe possess an endpoint?
There exist two prevailing theories on this matter, both with their own sets of adherents within the scientific community:
Based on the available evidence, the prevailing hypothesis suggests that the universe is infinite.
The task of counting the stars is an insurmountable one, primarily due to the vast distances that separate us from many of the stars visible in the night sky. This means that the light emitted by these stars takes a significant amount of time to reach Earth. For instance, it takes approximately eight minutes for light from the Sun to reach us, and about four years for light from Proxima Centauri, the closest star to our solar system.
There could be extensive debate about the significance of these fields in relation to others. Allow me to reiterate Neil Degrasse Tyson’s words: “No matter who you are, engaging in the exploration of the origins of existence will provide a profound emotional boost, as if understanding humanity’s beginnings somehow enhances your ability to adapt to what lies ahead. Life and the cosmos impart the same lesson: comprehending your origins is just as crucial as envisioning your destination.”
We have a deep passion for science at ADME and we are confident that there are some mind-blowing facts about the cosmos that will leave you speechless. And as a special treat, we have a few exciting opportunities for those who have always dreamed of venturing into space as an astronaut and discovering the wonders of the universe.
Methuselah’s Star is one of the most ancient stars ever recorded
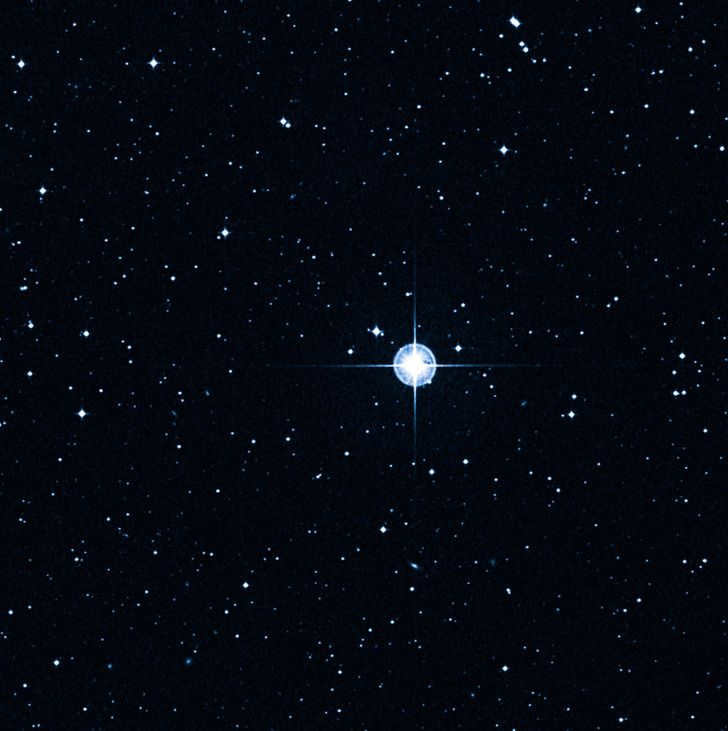

Methuselah’s Star, also known as HD 140283, was first discovered more than a century ago and quickly gained recognition. It is classified as a second-generation star, which means it formed several hundred million years after the Big Bang, making it one of the oldest stars in existence.
However, during its initial dating process, there was a mistake. Based on the available data, the star’s age was determined to be 14.46 billion years, which seemed impossible considering that the age of the universe was calculated to be 13.8 billion years at that time. This discrepancy remained an unsolved mystery for quite some time. Eventually, a new study was conducted, providing a revised age for Methuselah’s Star of 13.7 billion years.
Brown dwarfs are cool celestial bodies
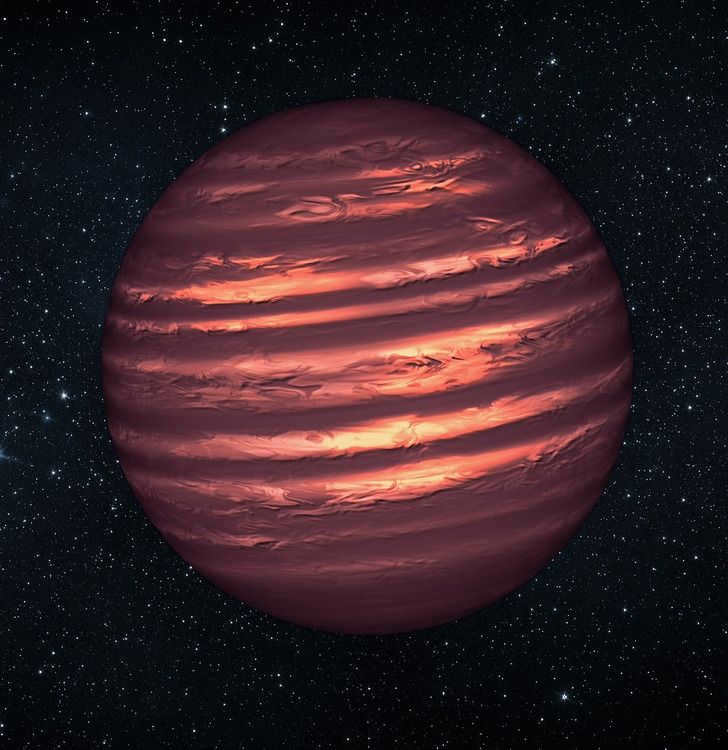

Previously, it was commonly believed that all stars are massive and fiery, but this is not always the case. Brown dwarfs are a unique type of star that does not conform to these typical characteristics. They have a similar size to Jupiter, which is relatively small for stars. Additionally, their temperatures are significantly lower. The coolest brown dwarfs can have temperatures as low as 27 degrees Celsius. °C. Due to their low temperature, these stars have a dark red appearance and gradually shrink and fade over time.

Venus and Earth share several similarities. They both formed approximately 4.6 billion years ago and have similar mass and size. Just like Earth, Venus experiences volcanic eruptions. While Venus has an atmosphere, it consists mostly of carbon dioxide, with the upper layers containing oxygen and nitrogen, essential for human respiration. It is highly probable that Venus once had its own oceans, but due to the planet’s extreme heat, the water evaporated entirely.
Space adaptation syndrome
refers to the collection of symptoms experienced by astronauts during their adaptation to the microgravity environment of space. The syndrome is characterized by a variety of physical and physiological changes that can affect the astronaut’s overall well-being. These symptoms may include nausea, dizziness, headaches, and general discomfort. It is believed that the lack of gravity in space disrupts the body’s normal functioning, leading to these symptoms. Researchers are continuously studying space adaptation syndrome in order to develop effective countermeasures and improve the overall health and comfort of astronauts during long-duration space missions.
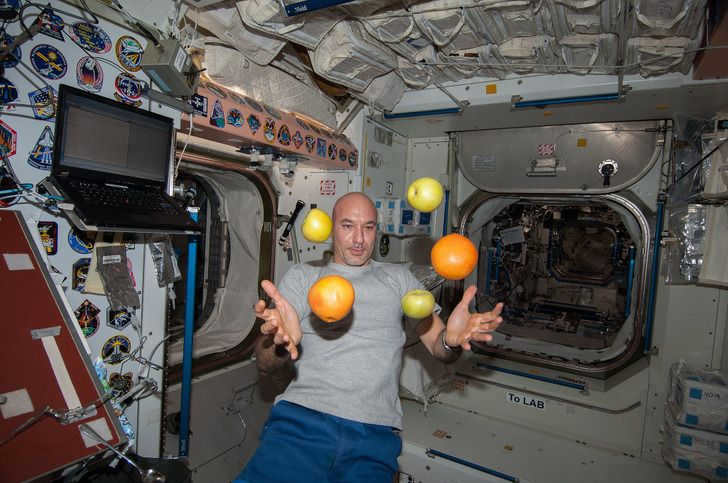

Humans do not feel very comfortable when they are in a state of weightlessness. Aside from the ability to float around the room and have objects hover right next to you, weightlessness comes with a number of negative effects. These effects include a decrease in appetite, headaches, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and spatial illusions.
One of the most extreme cases of a reaction to weightlessness occurred with astronaut Jake Garn during a flight in 1985. He felt so terrible that his colleagues jokingly invented a unit of measurement for the severity of the condition during the adaptation period to weightlessness – 1 garn. However, most astronauts typically experience discomfort no more than 0.1 garn on this scale.
A world bathed in the light of twin suns

A unique poster has been created by NASA’s Exoplanet Exploration Program, specifically the “Exoplanet Travel Office,” showcasing the fascinating exoplanet Kepler-16b. This extraordinary planet, also known as Tatooine, reminiscent of the iconic planet from the Star Wars movie series, offers a truly extraordinary vacation experience with its dual suns. On Kepler-16b, visitors can bask in the warm glow of not one, but two suns, creating an unforgettable spectacle where shadows are always accompanied. The scientific community has been captivated by this planet, leading to the creation of a dedicated poster by the Exoplanet Travel Office project of NASA’s Exoplanet Research Program.
A “vocalized” cosmos
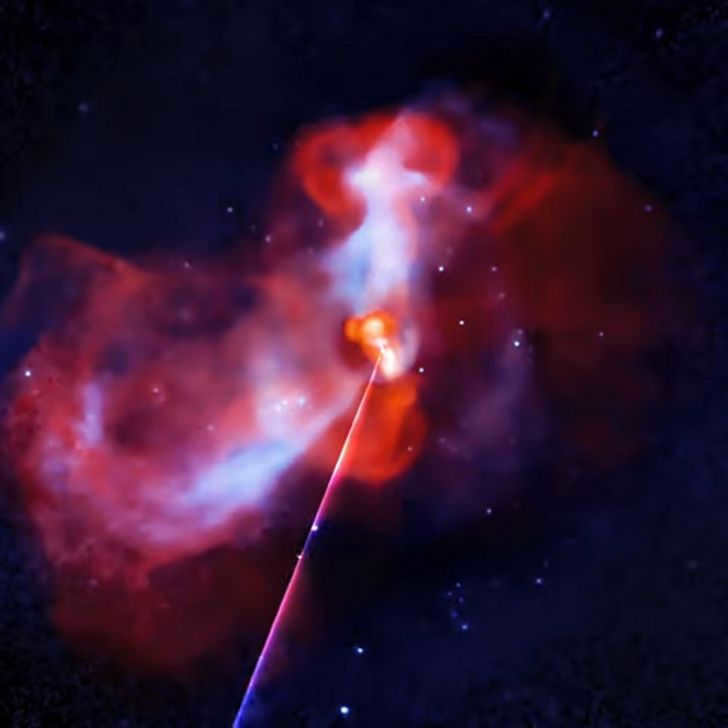

The study of the universe is a field that is mostly characterized by silence, with the information gathered by telescopes being presented through charts, graphs, and images. However, NASA’s X-ray Laboratory and the Explore the Universe program have come up with a unique project that aims to bring sound to the cosmos. This project involves converting data collected by telescopes into audible sounds.
In this project, the intensity of light is directly translated into the volume of sound. Objects that are located farther away from the center produce higher-pitched sounds, while individual stars create a more erratic and jerky sound. On the other hand, clusters of stars generate a more sustained and continuous sound.
Did Mars harbor any form of life?
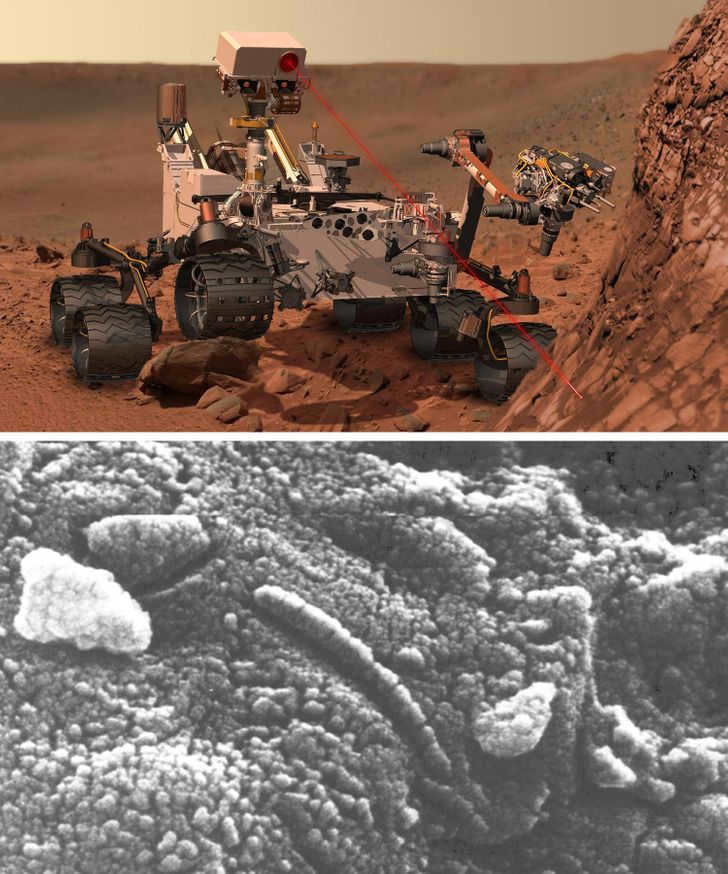

In 1996, a group of researchers conducted an examination of a meteorite from Mars. The news of their findings spread like wildfire after NASA scientists announced the discovery of preserved microstructures in the meteorite that bore a striking resemblance to fossilized bacteria.
Throughout its ten-year mission, the Curiosity Mars rover accomplished many feats, including the identification of stable carbon isotopes. This discovery led scientists to speculate that these isotopes may have originated from past life on Mars. While this is purely speculative, the study of Mars remains an active and ongoing endeavor, steadily expanding our knowledge of the enigmatic red planet.
An internet sensation has emerged featuring astronaut Thomas Marshburn, who recently returned from two space missions, discussing his awe-inspiring experiences. In the midst of his captivating story, Marshburn demonstrates the effects of weightlessness by casually releasing a glass into the air, where it remains suspended without any external support. This remarkable phenomenon is a direct result of the body adapting to the absence of gravity during space travel, allowing objects to effortlessly float in mid-air without the need for any additional assistance or grounding.
The celestial source of gold

During nuclear reactions occurring in stars, various chemical elements, including hydrogen, helium, carbon, neon, and up to iron in the periodic table, are synthesized. For a considerable period of time, the origin of elements heavier than iron, such as gold, remained enigmatic as they were not generated during the typical nuclear reactions within stars.
Previously, it was believed that all elements heavier than iron were produced through the merging of neutron stars. However, recent research indicates that supernova explosions also contribute to the formation of such chemical elements. Moreover, during this process, additional heavy elements are formed, although less frequently. Consequently, all gold, even the most ordinary ring or pair of earrings we wear, is created during large-scale cosmic events.
Presence of Water on the Moon
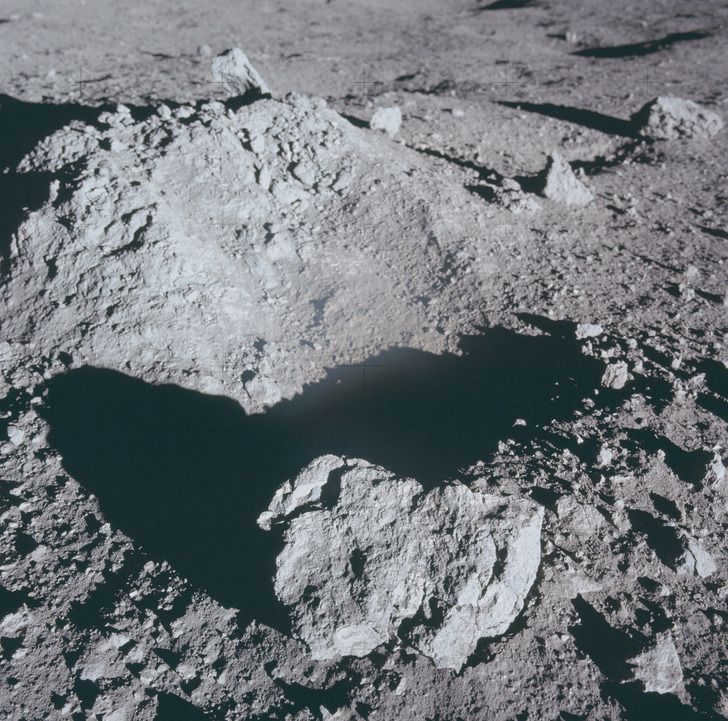

For a long time now, there has been speculation about the presence of water on the moon. However, recent research conducted by the Chinese Academy of Sciences has provided solid evidence to support this claim. Towards the end of 2020, samples of lunar soil were successfully delivered to Earth, and upon analysis, traces of water were discovered. It is important to note that the amount of water found is minuscule, comprising just a tiny fraction. As a result, scientists are now beginning to consider the possibility that the water may not have solely been brought by the solar wind, but rather, there could be an internal source of water within the moon itself.
Earthly Storms
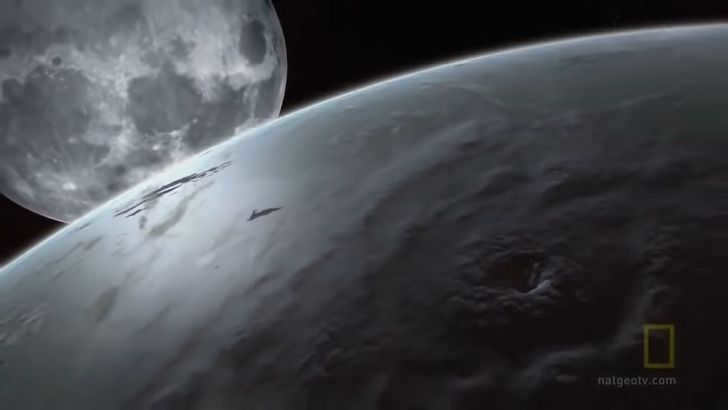

In the early stages of the solar system’s formation, the Earth and the Moon had a different appearance. Even their distance from each other was not the same as it is today. The Moon has been gradually moving away from the Earth at a rate of 3.8 centimeters per year. As a result, it is not surprising that in its early existence, the Moon was approximately 65,000 km away from the Earth, compared to its current distance of 384,400 km.
During that time, the entire planet was covered by a vast ocean. The close proximity of the Moon and the Earth’s rapid rotation (with a day lasting a little over 6 hours instead of our usual 24 hours) created immensely powerful storms and enormous waves. These storms persisted for thousands of years until the Moon had moved far enough away and the Earth’s rotation had slowed down.
A world where rain falls as glass
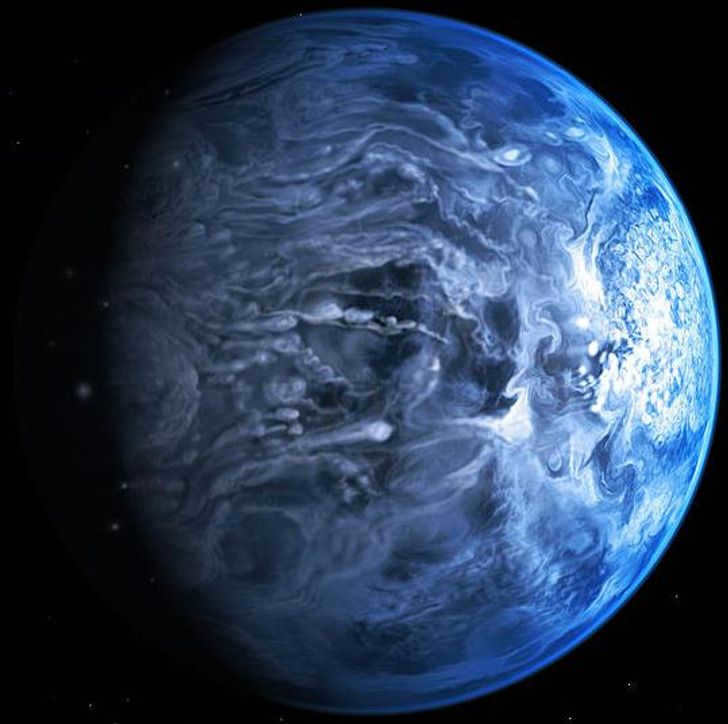

In the constellation of Foxy, there exists a celestial body that was discovered in the year 2005. This celestial body is of similar magnitude to our very own Jupiter and it is not too distant from our Earth, being situated at a distance of approximately 64.5 light years. (It is important to note that a light year represents the distance traveled by light within the span of one calendar year). This distance implies that if we had the privilege of observing it at close proximity, the images we would behold would be from almost 65 years ago. It is quite fascinating to learn that during the course of studying its atmospheric conditions, researchers have discovered an intriguing fact: this celestial body regularly experiences precipitation in the form of molten glass.
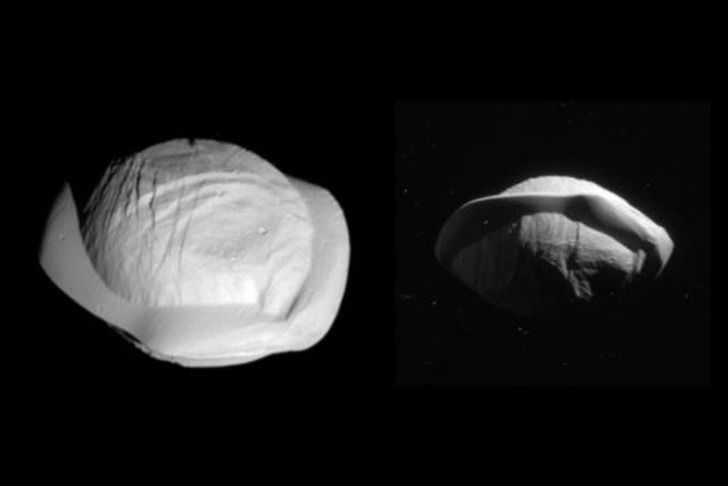
Saturn possesses numerous moons, but one of them stands out. Pan, which derives its name from a figure in Greek mythology, is an inner moon, implying that its orbit aligns with Saturn’s renowned rings. Due to its gravitational pull, this moon attracts dust particles and accumulates them on its surface. However, the settling of these particles is not uniform, resulting in Pan’s peculiar dumpling-like appearance.
Extra Benefit #1: an opportunity to visit Mars

If you’ve always dreamt of venturing into outer space, or at the very least leaving a trace of yourself out there, NASA has a project just for you: by signing up on their website, your name will be etched onto a microchip that will be sent to Mars on the next mission. As a token of your “participation” in this endeavor, you will receive a symbolic ticket. It’s worth mentioning that the author of this piece is among those who have decided to seize this opportunity.
Bonus #2: Explore the Cosmos from the Comfort of Your Computer






