In which galaxy is planet Earth located? What is the name of our galaxy? We reside on one of the entities within the Solar System – the Milky Way conglomerate. In various cultural interpretations, the designation of our galaxy may vary, but the concept of a “path” is consistently emphasized. The term “Milky” can be substituted with synonymous expressions. Initially, only the visible clusters – the spiral arms of the galactic structure – were referred to as such. Through ongoing research, astronomers have gained a wealth of knowledge about our celestial abode. How do we currently understand the Milky Way?
What exactly is a galaxy?
According to information from Wikipedia, a galaxy is an immense collection of stars, cosmic dust, and gas that are bound together by the force of gravity. At the core of this structure lies a colossal nucleus, serving as the central point around which all the components orbit. In many cases, this nucleus is believed to be a black hole.

Astronomers have the ability to observe approximately 100 billion galaxies in our vicinity using modern equipment. These galaxies have masses ranging from 10 7 to 10 12 solar masses.
Each galaxy typically consists of several components:
- The majority of the galaxy’s mass is made up of dark matter;
- Up to 30% of the total objects in a galaxy are interstellar dust and gas;
- The remaining 1% of the galaxy’s mass is composed of various elements such as stars, planets, black holes, asteroids, and neutron stars.
Galaxies are often found in groups ranging from a few tens to tens of thousands. Groups of hundreds are known as clusters, while those consisting of thousands are referred to as superclusters.
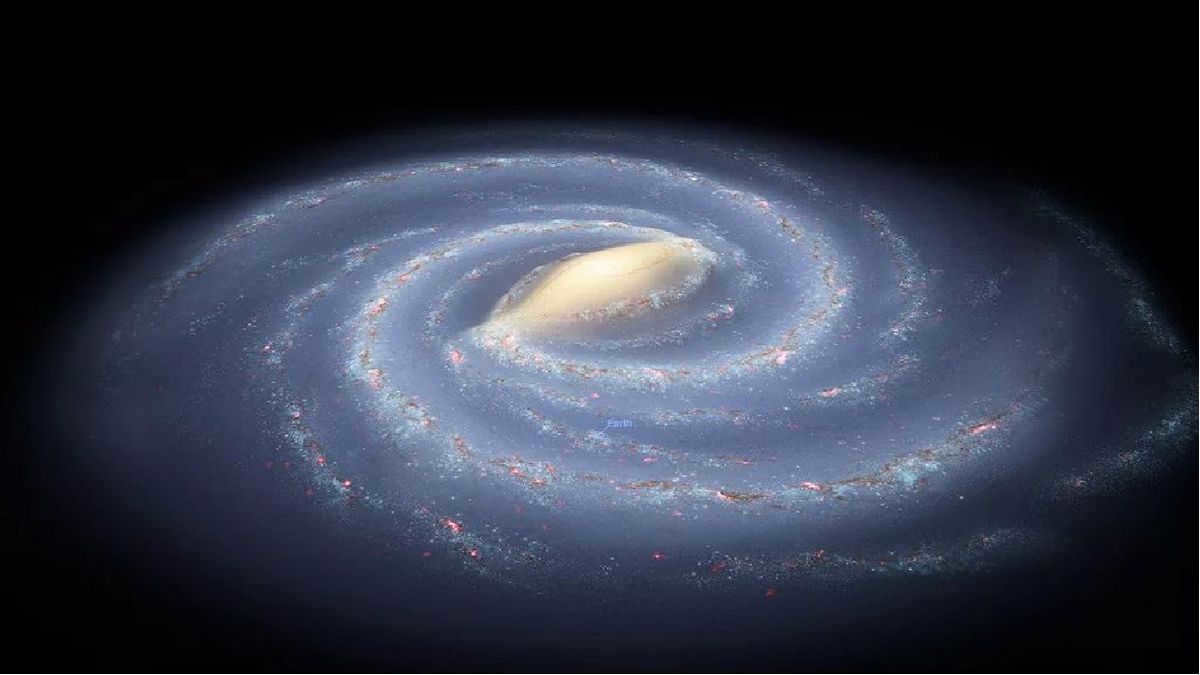
Milky Way Galaxy
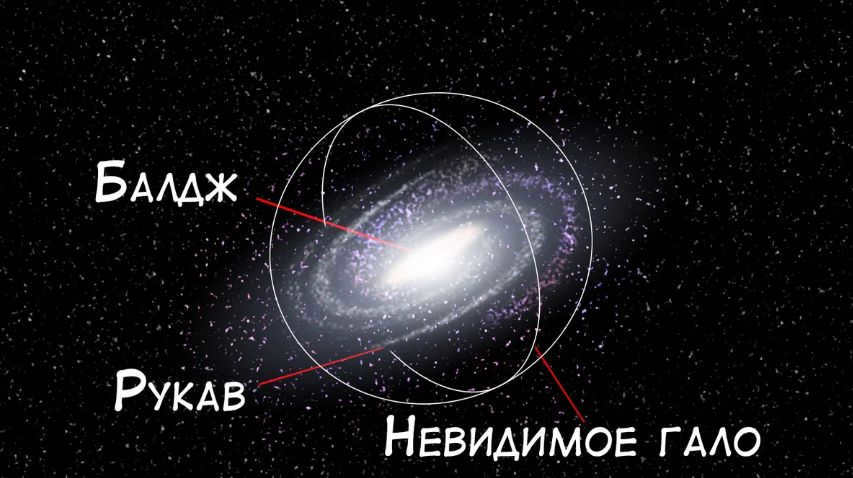
The Milky Way is a vast collection of dust, gas, and stars, including our very own Sun and Earth. Spanning billions of kilometers around our planet, this galaxy is classified as a spiral galaxy, resembling a massive spiral when viewed from above. At its center lies a bar-like structure known as the central bulge, which is adorned with a brilliant band of stars.

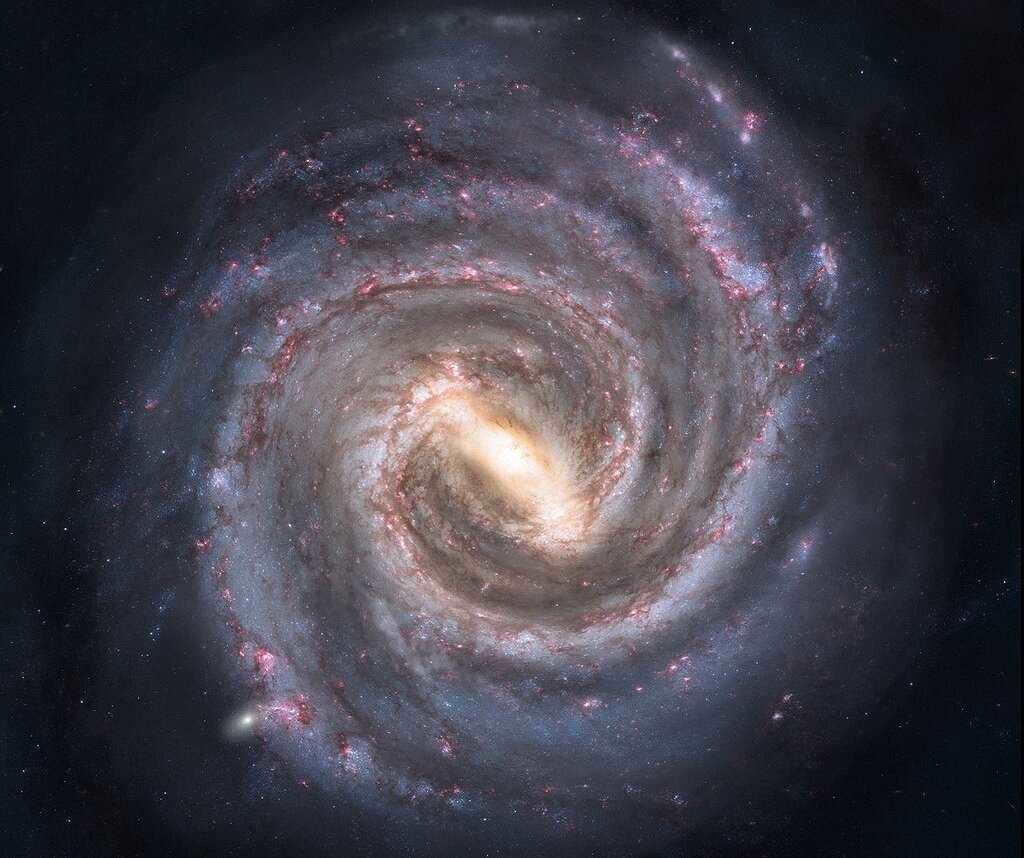
Previously, it was believed that all the spiral arms surrounding the nucleus of the galaxy were the same. However, recent images captured by a state-of-the-art infrared telescope have revealed distinct variations between these arms, dispelling this notion.
Formation of the Milky Way
The birth of our galaxy can be traced back approximately 14 billion years ago when two massive clusters of dust and gas collided due to the gravitational pull. This cosmic encounter gave rise to a spherical structure known as a “halo,” which eventually transformed into a compact disk.

Scientists struggle to determine the origins of the first galaxies. The composition of the Universe is not uniform, as it consists of galaxies and voids in between.
What exactly is the Milky Way? According to the European Space Agency, one hypothesis suggests that dark matter with a higher density than its surroundings emerged in the universe. This dark matter possessed the ability to gravitate, allowing it to attract other dark matter. As gravity increased, the process continued, resulting in the accumulation of clumps that eventually drew in normal matter. From this process, the first stars were formed.
Fascinating! The Milky Way still houses ancestral clusters today, known as globular clusters. Within these clusters, the oldest stars with an estimated age of 13 billion years can be found.
Approximately 12 billion years ago, the initial constituents of dark matter combined, resulting in the formation of the first dark matter elements. As a consequence of this merger, the proto-Milky Way emerged as an independent entity in the vastness of outer space. Possessing a formidable gravitational force, it incessantly drew in additional matter.
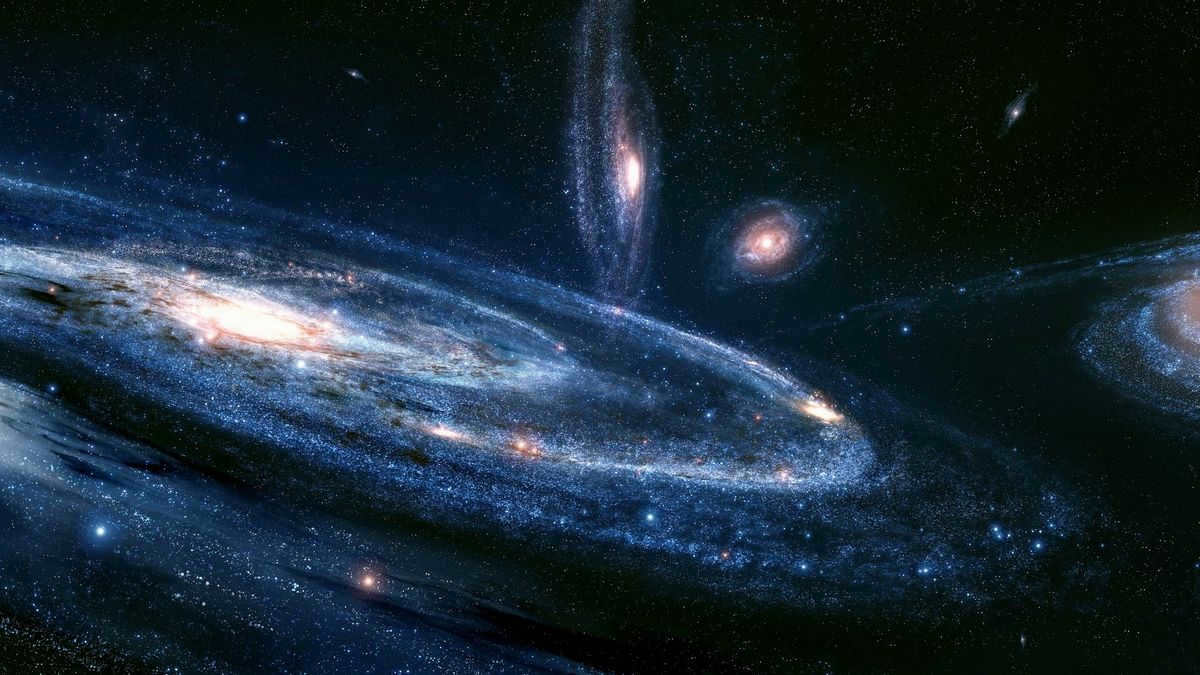

The gas cloud at the center became denser and collapsed, resulting in the formation of a narrow disk that exhibited rapid rotation. This gave rise to the creation of new stars, marking a period characterized by a prolific generation of stars.
Driven by the force of gravity, the Milky Way assimilated smaller galaxies, disassembling their clusters in the process. The remnants of these galaxies were transformed into smaller entities that were subsequently incorporated back into the original structure.
The classification, composition, and morphology of the Milky Way
Exploring the inquiry: what exactly constitutes the Milky Way, it is initially understood that it is a relatively youthful entity. It falls under the category of spiral galaxies with a central bulge, akin to approximately two-thirds of the star clusters observed.
The central bulge gradually diminishes over time.
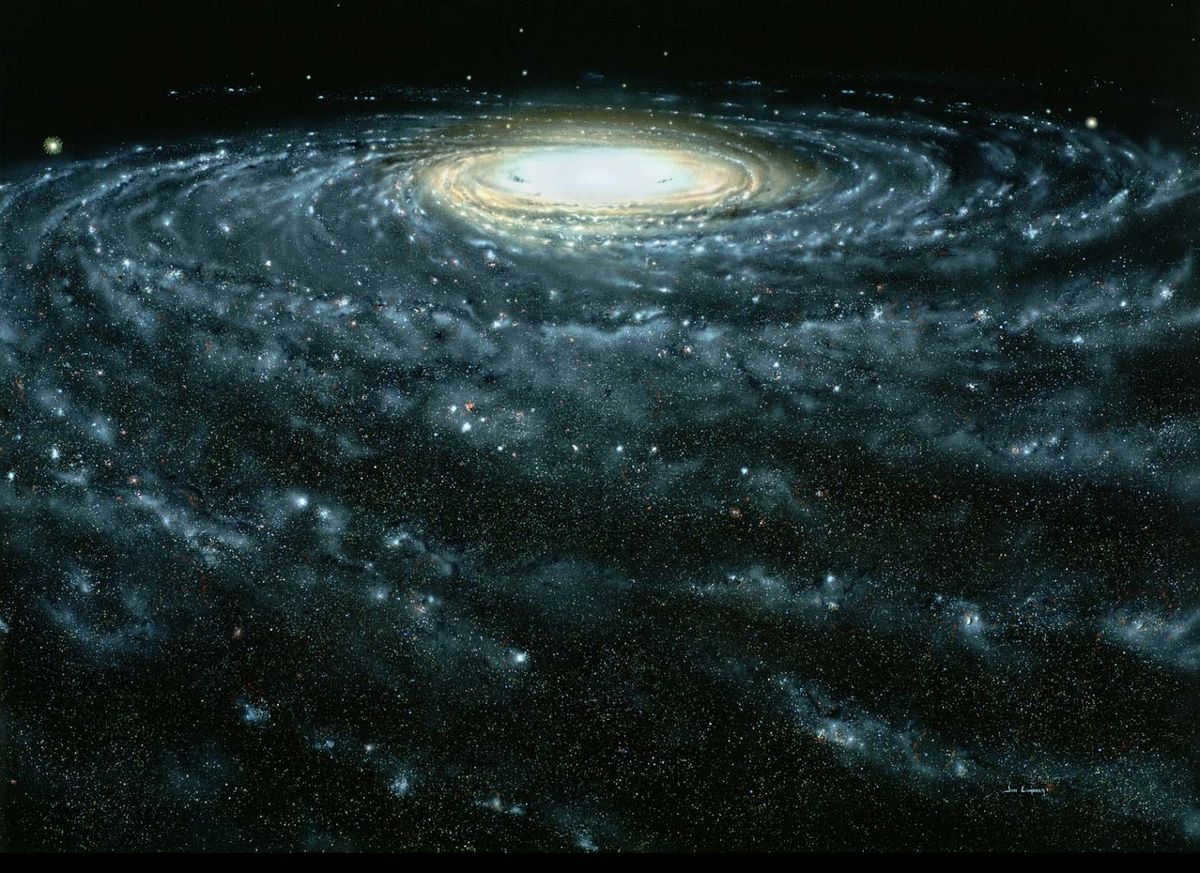

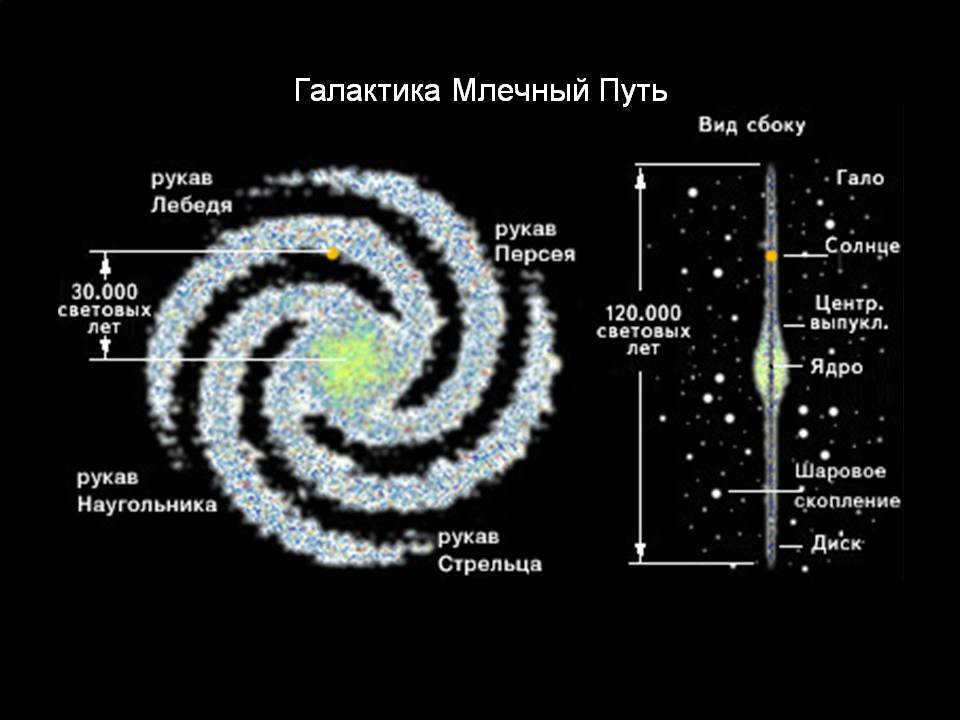
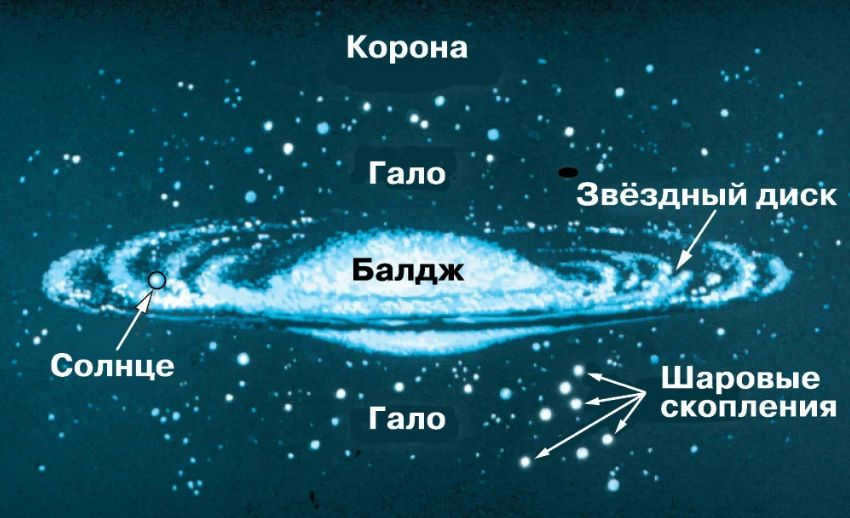
In our galaxy, there are different components that make up its structure:
- The central part, known as the nucleus, is where the mass of star clusters is concentrated. It is the active region of the galaxy and produces energy.
- Surrounding the nucleus is the bulge, which contains giant stars, old luminaries, and glowing gas clouds. It is the brightest part of the galaxy and rotates at a high speed. However, it is not visible to the naked eye due to the presence of sleeves that cover it.
- The lintel is like a bridge that connects the bulge to the arms of the galaxy. Astronomers often compare it to a riverbed.
- The sleeves are the arms of the galaxy and consist of the majority of the galaxy’s gas, dust, and young stars and clusters.
- The disk is a thin layer that collects a significant portion of the visible elements in the galaxy.
- The halo is the remaining space in the galaxy. Its exact size is still unknown.
- Globular clusters are star-enshrouded satellites that are held together by the force of gravity. They orbit around a central point.
The Milky Way can be observed as a dim luminosity in the nighttime sky. It is mostly composed of faintly glowing stars. The best time to see it is during the months of August and September.
What is the most common color of objects found within the Milky Way galaxy? Being relatively young in terms of cosmic age, it appears white with a slight pinkish hue.
Origin of the name of our galaxy
The name “Milky Way” is used to refer to our galaxy in Russia, as well as in many European and American countries. The name originated from ancient Greek mythology.

Legend has it that Zeus, the supreme god and father of Heracles, desired to bestow divine powers upon his son. To achieve this, he needed to intoxicate him with the milk of a goddess. One night, Zeus carried the baby to a slumbering Hera, but she disapproved of her husband’s plan. As she pushed the baby away, the milk splashed across the sky, forming a radiant circle. The ancient Greeks originally referred to this phenomenon as the “galaxias kyklos,” meaning “Milk Circle.” When the term was borrowed into Latin, “circle” was translated as “path.”
Over time, this concept spread worldwide thanks to the influence of the Church, Latin, and Ancient Greek. Today, the Milky Way is a well-known celestial phenomenon across all cultures.
The Milky Way’s Discovery: A Journey Through Time
As mankind’s understanding of the universe advanced, astronomers observed that celestial bodies in space were not static but in constant motion. The Moon orbited around the Earth, which itself revolved around the Sun. This prompted scientists to question if our Sun was just a part of a grander celestial dance. Their investigations yielded numerous breakthroughs and insights into the vastness of our galaxy.

- G. Galileo. A scientist known for constructing the inaugural telescope in the 17th century. He successfully demonstrated that the Milky Way consists of numerous stars.
- U. Herschel. During the 18th century, Herschel illustrated a diagram of the Milky Way: a stretched-out cloud with an irregular shape. He positioned the Sun in the center. This concept of the Universe’s structure was widely accepted by astronomers until the 20th century.
- Y. Kapteyn. In 1920, Kapteyn provided the most precise description of our galaxy, including an estimate of the number of stars within the Milky Way. Minor revisions have been made in recent times.
The primary features and measurements of the Milky Way
The Milky Way is a part of the Local Cluster, alongside various other celestial bodies. It has a diameter of approximately 100,000 light years and contains between 200 and 400 billion stars. Spanning 27,000 light years from the Sun, it rotates around its center at a speed of around 230 km/s. Its mass is 3 trillion times greater than that of the Sun, and it is estimated to be around 13.7 billion light years old.
Mass
The weight of the entire universe has been determined through calculations, based on the assumption of the minimum number of stars being 200 billion. It is believed that each star has a weight equal to that of the Sun, which accounts for 4% of the total galactic mass. In addition to the weight of stars, there is also the weight of gas, which exceeds the stellar weight by a factor of 3, and the presence of dark matter. As a result, the minimum mass of the Milky Way is estimated to be equivalent to 3 trillion Suns (6×10 39 ).
Luminosity
The brightness of the galaxy is estimated to be 20 billion times that of the Sun. This is equivalent to approximately 8×10 36 watts.
Size
Previously, the diameter of our galaxy was believed to be around 100,000 light years. However, in 2020, astronomers proposed that it is actually 1.9 million light years. This hypothesis has yet to be confirmed.
The Formation and Composition of the Milky Way Galaxy
According to calculations, it is estimated that the Milky Way galaxy contains approximately 200 billion stars, which are concentrated in a flattened disk structure. So, what exactly is included in this unique formation?
The Disk Structure
The diameter of the Milky Way’s disk is approximately 100,000 light-years. Its rotation rate is known to be unstable but significantly faster than the halo. In close proximity to the black hole, the speed is nearly zero, but as you move further away, it increases to around 240 km/s at a distance of 2,000 light-years. Beyond this threshold, the velocity can fluctuate within a specified range. The mass of the disk is estimated to be 150 billion times greater than that of the Sun.

In close proximity to the galactic disk, there exist young stars that have an age of no more than a few billion years. A significant number of these stars have high temperatures, making them part of the flat component. Along the galactic plane, one can find numerous gas clouds, ranging from small ones measuring about 1 parsec in diameter to giant ones that span thousands of light years.
Nucleus
The central part of the galaxy contains a bulge that is growing thicker and has a diameter of 8 thousand parsecs. The star clusters in this region have an elliptical shape. The nucleus is located in the constellation of Sagittarius, and it is 27.7 thousand light-years away from the Sun.
There is a widely accepted belief that the central black hole is approximately 4 million times larger than the Sun. Another similar mass, which is up to 10 thousand times heavier than the Sun, orbits around it. Additionally, there are smaller black holes nearby with a rotation period of about 100 years.
The gravitational force exerted by these objects causes nearby stars to have a unique orbital rotation. Astronomers have therefore come to the conclusion that all star clusters in this area rotate in close proximity to black holes.
This particular region of the Milky Way contains a large number of stars, with several thousand located within a radius of 1 to 3 parsecs. The rotational speed of these objects can reach up to 240 km/s.
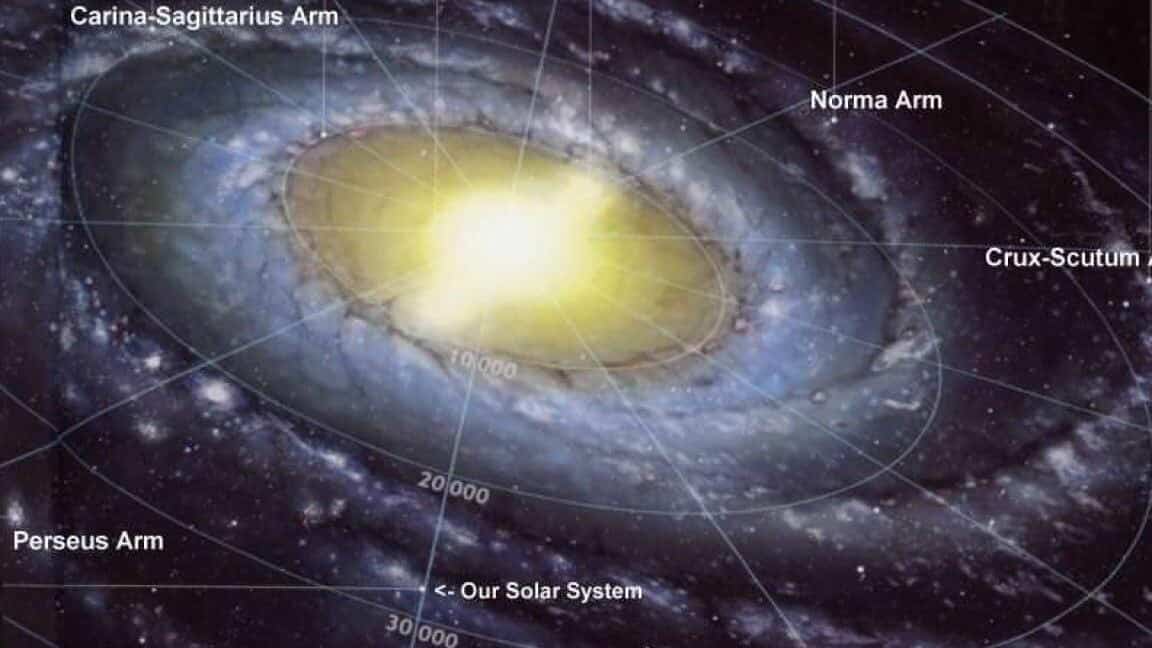
The Arms of the Galaxy
Positioned within the same plane as the disk in the corona, the galaxy features various arms, including Swan, Perseus, Orion, Sagittarius, and Centauri. Among these arms, the Sun is situated within the Orion arm. Moving at a velocity of approximately 230 kilometers per second, our star completes a full rotation around the galactic center once every 240 million years.
It is a spherical celestial structure. It extends over an area of 5 to 10 square light-years. The temperature is approximately 500,000 Kelvin. Comprised of aging, diminutive, faint stars and globular clusters (located up to 100,000 light-years away from the central region). The central region of the Milky Way disk aligns symmetrically with the center of the halo.
Clusters of stars can exist as a collective or as individual entities. These objects have been in existence for approximately 12 billion years. They move along an elongated orbit at a relatively slow pace, although some exhibit chaotic movement. Within this galaxy, there is no ongoing star formation. The majority of its mass is composed of dark matter.
The position of the Sun and Earth within the Milky Way galaxy
The distance from the Sun to the center of the Milky Way is approximately 27 thousand light-years. (35 thousand light-years from the junction). It is situated in the middle, between the two arms known as Sagittarius and Perseus. The distance from the Earth to this location is about 3 thousand light-years.
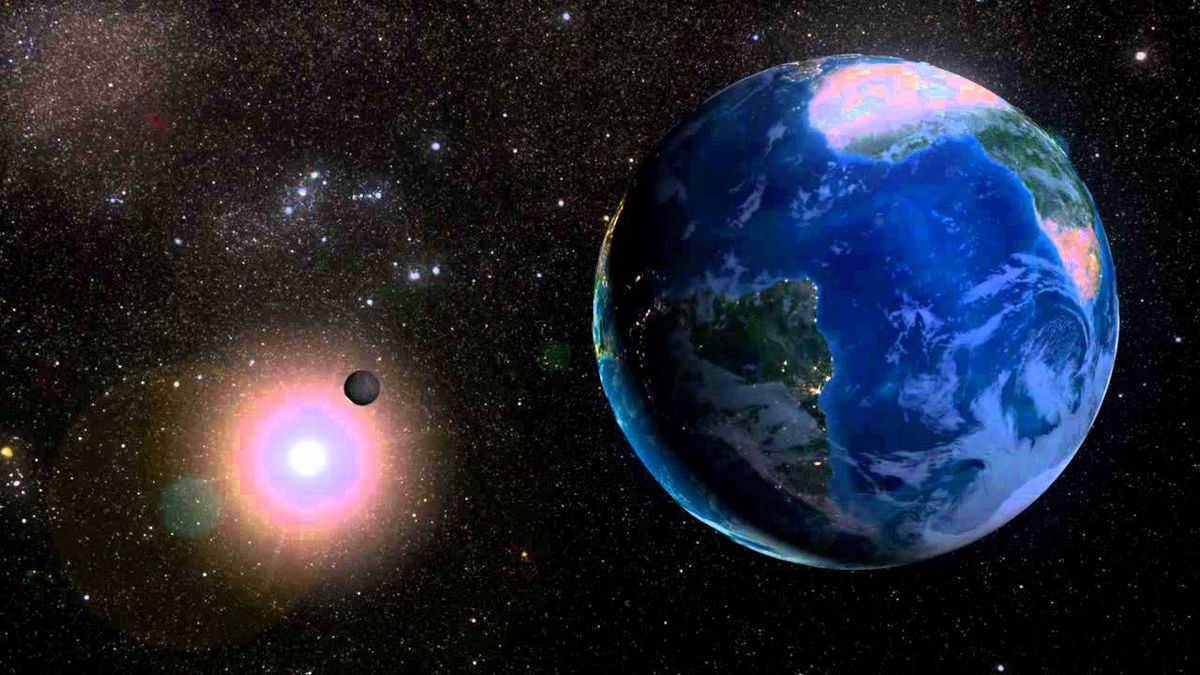

Our star, known as the Sun, resides in the central region where the rotation is in sync with the compression wave of the spiral arms. This synchronization is vital for the existence of life on our planet.
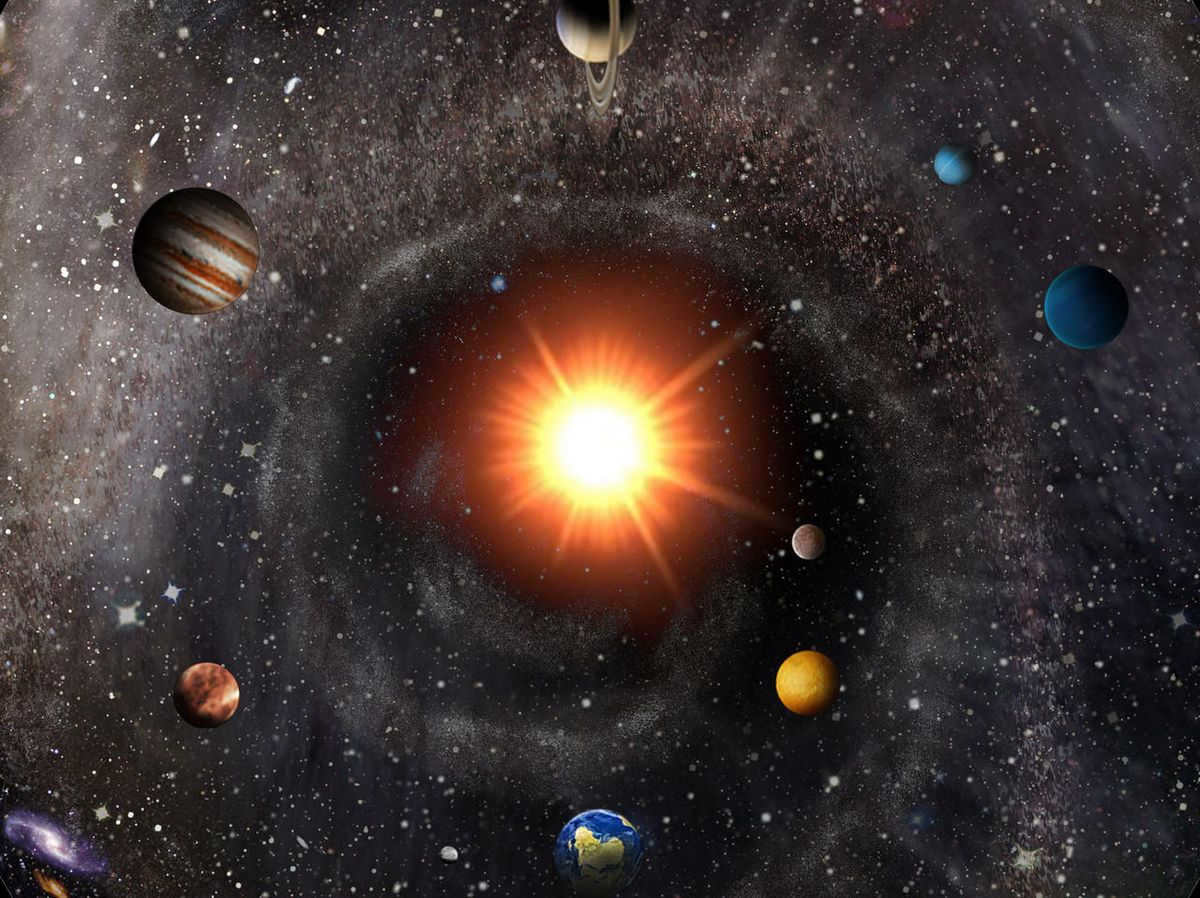
Based on the analysis, our solar system is situated within an interstellar cloud composed predominantly of hydrogen and a smaller component of helium. This cloud is positioned approximately 30 light years away. In turn, this cloud exists within the confines of the “local bubble”, a gas cloud with an elongated structure formed by remnants of supernovae. The “local bubble” spans a distance of 300 light-years. This positioning provides a sense of tranquility as it shields humanity from harmful radiation and potential collisions with erratically moving celestial bodies.
The Position of the Milky Way in the Universe
According to the most recent information, the Milky Way is situated within the Laniakea supercluster, which is the largest known structure in the universe. This supercluster consists of hundreds of galaxies that are interconnected.
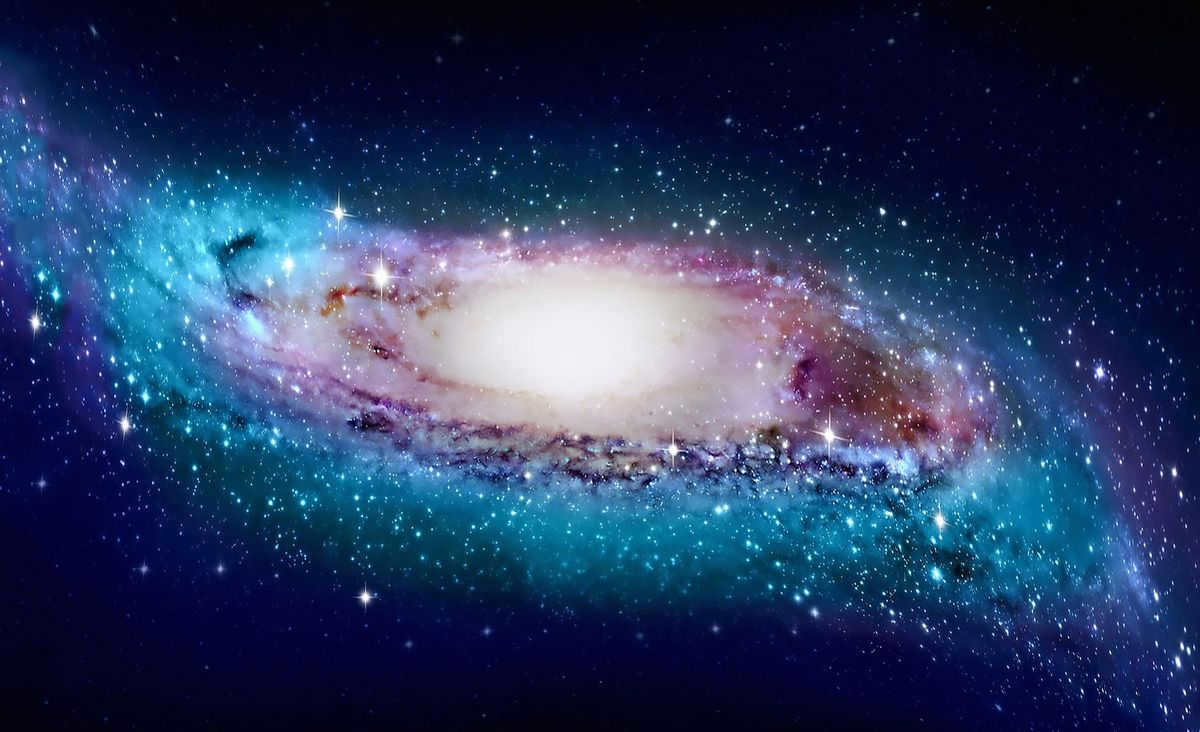

The galaxy that contains the Virgo supergroup, which includes the Local Group and the Great Attractor, is known as Laniakea. The Milky Way is a member of the Local Group. Laniakea itself is a part of the Pisces-Keith complex group.
It is worth noting that astronomers speculate that Laniakea is gradually pulling the galaxy towards its center.
Evolution and future predictions for the Galaxy made by astronomers
According to scientists, the Milky Way is estimated to be 100 million years younger than the Universe itself. During its rapid development, elements such as carbon and oxygen were formed, preventing stellar objects from burning out within a few million years. The disk of the Milky Way continues to build new stars by absorbing gas clouds from the halo. However, the availability of gas for new star formation is becoming limited, indicating that half of the galaxy’s lifespan has already passed.
A notable characteristic of the Milky Way is its ability to merge with smaller clusters. Presently, the galaxy is interacting with the Sagittarius constellation’s Magellanic clouds as they are drawn into its arms.
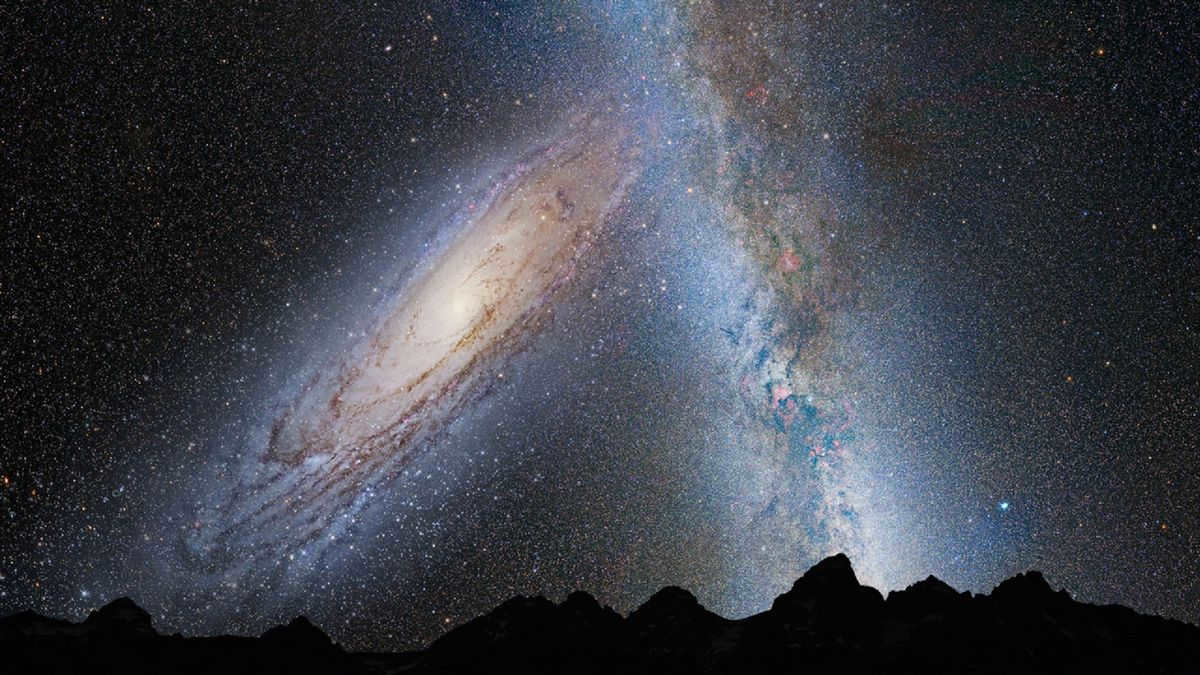

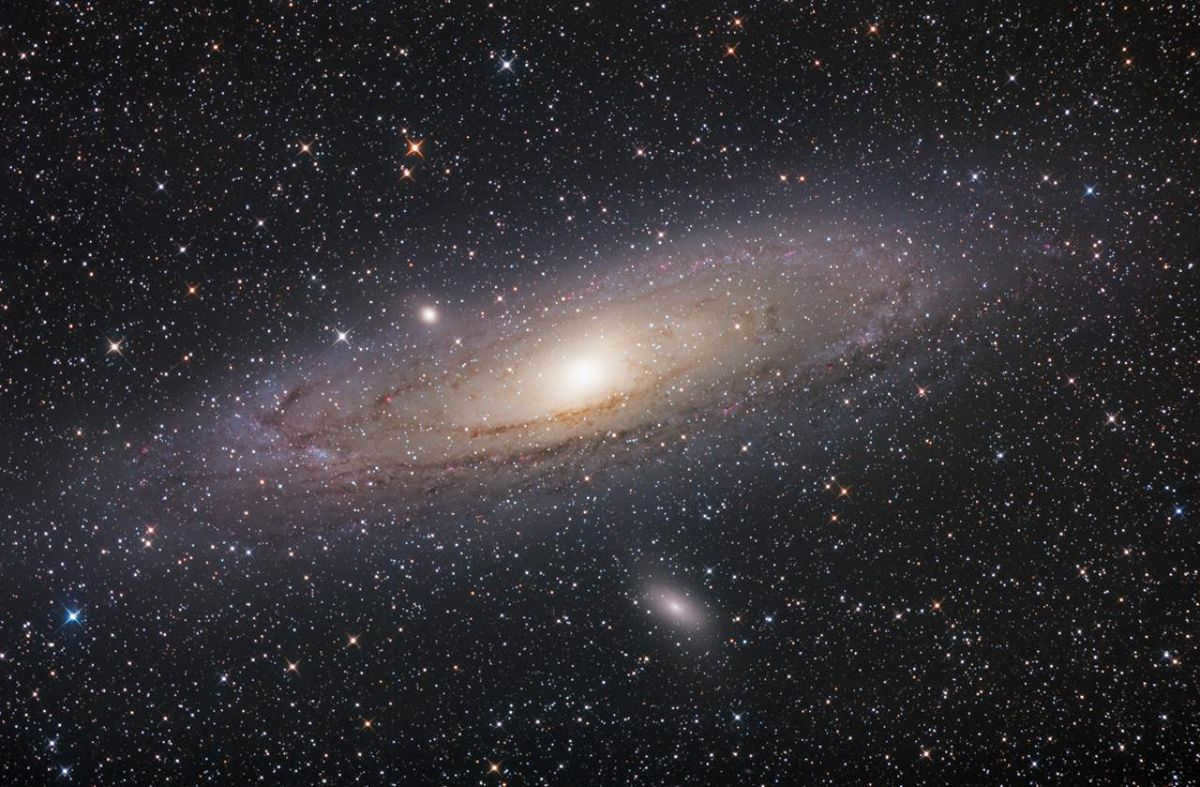
In the vastness of space, our Universe shares a border with a larger one known as Andromeda. Scientists predict that in billions of years, Andromeda will engulf the Milky Way, causing our galaxy to become a part of it rather than dissolving completely.
The Mythology and Various Names of Our Galaxy in Different Cultures
What is our galaxy called in different cultures? In the myths and legends of various societies, the evolution of the universe is depicted in diverse ways:
- In Armenia, there is a legend that tells of the deity Vahagn stealing hay from the Assyrian ancestors and fleeing to the heavens. As he ascends, straws from the stolen hay fall to the ground, creating a celestial path. In Armenian culture, our galaxy is referred to as “the road of straws.” Similar interpretations can be found among the Arabs, Jews, Persians, and Turks.
- In Hungary, it is believed that Atilla would descend from heaven to earth along the Milky Way if he felt threatened. It is said that the sparks seen are actually blows from the hooves of a horse.
- According to Greek mythology, there are multiple legends surrounding the Milky Way. One of them involves Hera’s milk, while another tells the story of Rhea, the mother of Zeus. Rhea was married to Cronus, who ate his children to prevent being overthrown by one of them. To protect her baby, Rhea dressed a stone in baby clothes and tricked Cronus into feeding it. The milk from Hera’s breast spilled over the stone, creating the Milky Way.
- In India, it is believed that the Milky Way is formed by a trail of milk left behind by a red cow as it moves across the sky in the evenings. The Rigveda mentions a sacred road known as Aryaman, while the Bhagavata-purana refers to the celestial dolphin’s belly as a part of the Milky Way.
- Japan. In Japan, they compare it to a river made of silver. During holidays, people release lanterns on rivers and streams, symbolizing stars and the souls of the departed.
- Slavs. This is known as the “God’s Road,” where souls journey to paradise, while the thunderer Perun rides in his chariot.
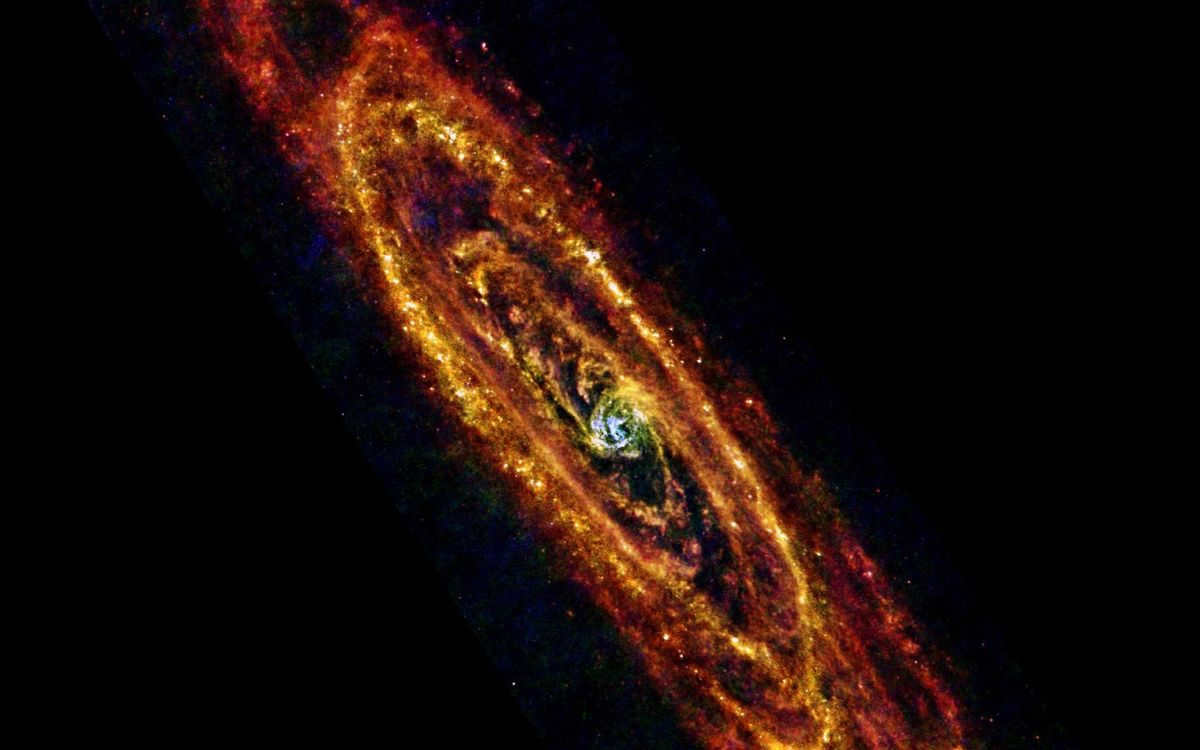

Aside from the mythological explanation, there exist alternate names for our galaxy. One such example is the Ukrainian term “Chumatsky shlyah”. The term “chumaks” was used to refer to traders. During their journeys, a group of stars in the sky became their guiding point of reference.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the estimated number of stars in the Milky Way galaxy?
The exact count is not known, but experts in astronomy suggest that there could be as many as 400 billion stars in the Milky Way galaxy.
How many planets are believed to exist in the Milky Way Galaxy?
Scientists speculate that there are at least 100 billion planets in the Milky Way Galaxy, and approximately 10 billion of them are similar to Earth in terms of their characteristics.

What is the name of the galaxy that contains it?
Referred to as the Sun exclusively in our solar system, there is only one. However, within the Milky Way, there are 3.2 thousand stars that comprise their own unique solar systems.
The stretch of constellations in our galaxy spans across 30 constellations. The brightest section, known as the galactic center, can be found within the Capricorn constellation.
The Largest Planet in the Milky Way
Jupiter, with a diameter of 139,820 km, holds the title of the largest planet in our solar system. It is situated between the planets Mars and Saturn.

TrES-4, which was discovered in 2006, is considered the largest planet in the Milky Way. This planet can be found in the constellation Hercules and has a diameter exceeding 257 thousand kilometers.
The nearest galaxy to the Milky Way
The Andromeda galaxy, located approximately 800 kiloparsecs away from our own galaxy, is the largest within the Local Group. It is classified as a type Sb spiral galaxy.
The Milky Way serves as our galactic residence. Despite extensive study by astronomers, this cosmic expanse still holds numerous mysteries. Advancements in technology continue to reveal more information about our existence and the future of our galaxy within the Universe.
Galaxy versus Universe
If someone were to claim that the distinction between a galaxy and the universe lies solely in their respective sizes, they would be correct. Have you ever pondered this? As humans, we often discuss our universe, but do we truly grasp the concept? The remarkable strides made by science in recent decades have allowed us to learn a great deal about our immediate surroundings (i.e., our terrestrial neighbors and relatives), yet our knowledge remains minuscule compared to the vastness of existence. The terms “universe” and “galaxy” are frequently used interchangeably, leading to confusion among many individuals. However, the reality is quite distinct. Let us delve deeper into this matter.
What is a Galaxy?
A galaxy is a vast collection of stars and dark matter that are held together by gravity. Galaxies vary in size, ranging from small ones with around ten million stars to massive ones that can contain up to a hundred trillion stars. Our Sun is just one of the stars in our galaxy, which is called the Milky Way. To put things into perspective, our solar system, consisting of our Sun and the other seven planets, is merely a small oasis within our galaxy, which in turn is like a minuscule speck in the vastness of the universe.
The galaxy in which our solar system is located is called the Milky Way. This particular galaxy is just one of numerous galaxies in the vast universe. To be exact, there are approximately 100 billion stars, some of which are significantly larger than our own Sun. In terms of galactic distances, the nearest star to our Sun is about 4 light years away, which is considered a relatively short distance. The Milky Way, with its 100 billion stars, is actually considered a small galaxy. In comparison, our neighboring galaxy, the Andromeda Galaxy, is much larger than the Milky Way. These galaxies can be categorized into three main types based on their appearance: elliptical, spiral, and irregular.
The image displayed below showcases luminous specks, which according to NASA, represent individual galaxies.

What is the Universe?
The universe is an expansive entity that surpasses our comprehension. It encompasses the collective entirety of numerous galaxies. In this context, it is accurate to acknowledge that our solar system, which holds such significance for our planet and ourselves, is merely a minuscule component within the immense expanse of the universe, extending far beyond the boundaries of our solar system and the Milky Way. Consequently, it becomes evident that the universe exceeds the cumulative size of all galaxies. It is estimated that there are approximately 200 billion galaxies within the observable universe. The observable Universe encompasses the section of the Universe that we are capable of observing from our vantage point on Earth.
Try to envision a million stars like this in our galaxy, and then contemplate the countless billions of galaxies that populate our Universe, and you will come to comprehend the immense scale of the Cosmos. Given the current array of instruments at our disposal and the extent of our knowledge, attempting to fathom the size of the Universe is an exercise in futility. It is conceivable that in the future, we may acquire the means to more accurately ascertain the dimensions of this vast and mysterious expanse.
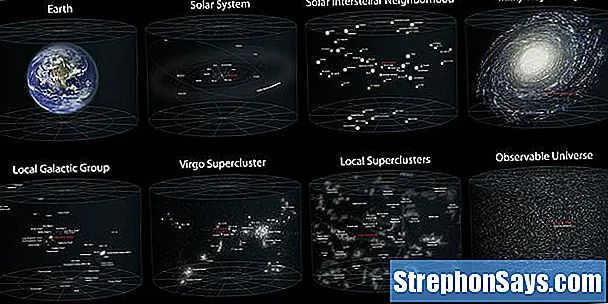
The composite spatial scales of the observable Universe
What sets apart the Galaxy from the Universe?
– The distinction between a galaxy and the universe lies solely in their respective sizes.
– Our solar system is a component of our galaxy, which harbors numerous stars including our Sun.
– There are billions of galaxies like ours scattered throughout the universe.
– The size of the universe remains unfathomable given the current knowledge and tools at our disposal.
– It is helpful to envision our galaxy, the Milky Way, as a mere particle within the vast expanse of the Universe.