
- History of astronomy
EXTEREGALACTIC ASTRONOMY is a field of study within astronomy that focuses on objects and phenomena that exist beyond our own galaxy. These objects primarily consist of distant star-gas systems, known as galaxies, which share similar characteristics to our own galaxy but are located at distances ranging from hundreds of thousands to billions of light-years away from Earth.
The most luminous galaxy that can be observed from our own is the
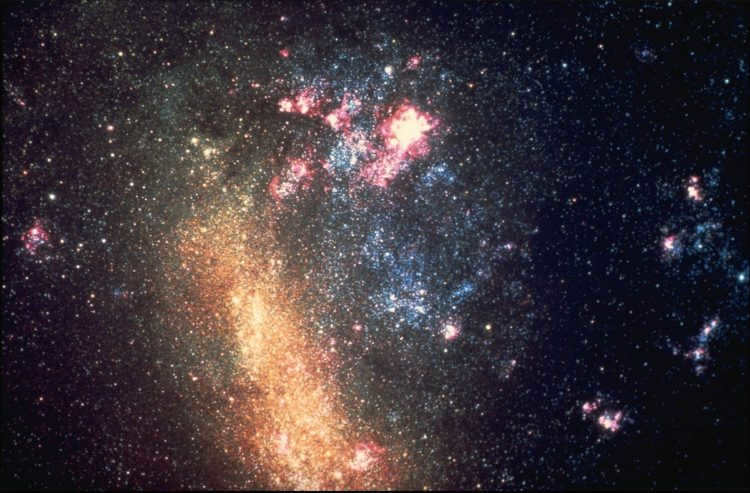

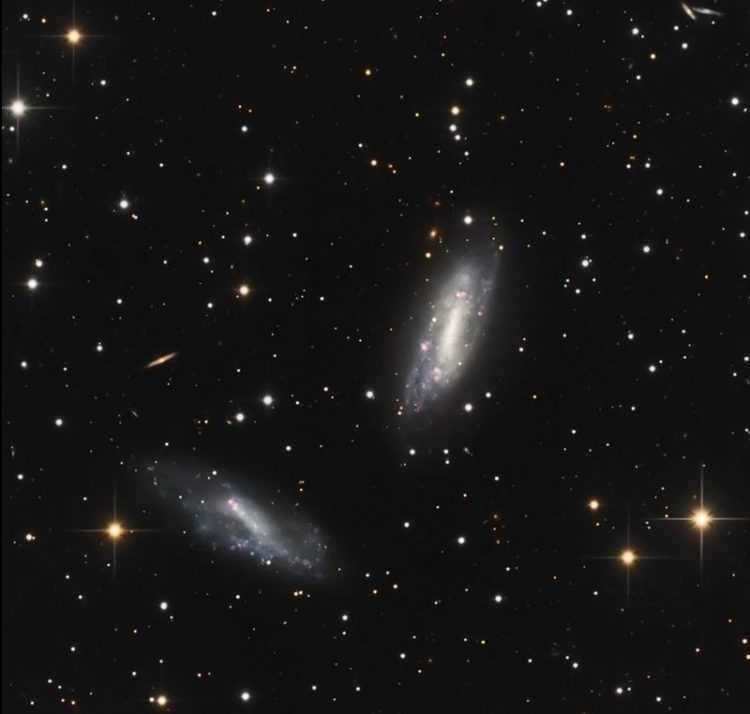
The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) is the most prominent galaxy that can be observed from our own galaxy, the Milky Way. It is primarily visible in the Southern Hemisphere of Earth. The LMC is one of the eleven dwarf galaxies currently orbiting our Galaxy and is the second farthest galaxy from us, following the Small Magellanic Cloud. The LMC is an irregular galaxy that consists of a region containing old red stars, clouds of younger blue stars, and a bright red star-forming region.
In 1987, the LMC became the host of SN1987A, the most luminous supernova of our era.

The Milky Way engulfs its galactic neighbor – one of the galaxies in the Sagittarius constellation (not to be mistaken with the zodiac sign Sagittarius).
The galaxy Sagittarius is our closest neighbor, but it was only discovered in 1994. It is situated 75,000 light-years away from the Sun and 50,000 light years from the center of our galaxy. The formation of the Sagittarius galaxy and its proximity to our Galaxy are still not fully understood.
The Sagittarius galaxy’s plane is nearly perpendicular to the Milky Way’s plane. Scientists speculate that due to the influence of the Milky Way, Sagittarius is gradually transforming into a sort of “cosmic spaghetti”. Our Galaxy devours all the planets that are distant from its center.
The Large Magellanic Cloud, located 170 thousand light-years away, is the nearest galaxy to us after the Milky Way.
Galaxies at the farthest reaches

X. Spinrad, an employee of the University of California at Berkeley, is a prominent astrophysicist who has dedicated his creative work to studying distant galaxies. He has made significant discoveries of ultra-distant galaxies. In 1975, Spinrad first identified a record-breaking galaxy in the northern direction of the Pleiades star cluster. This galaxy, known as ZS 123, is located a staggering 8 billion light years away from us. It is noteworthy for having the highest level of radio emission, surpassing other giant galaxies by a factor of 6.
During another series of observations in 1984, Spinrad made further discoveries of radio galaxies, including some of the most distant ones known to science.
The optical radiation from the radio galaxy ZS 256 travels a staggering distance of 10 billion light years to reach our solar system. 10 billion light years. Furthermore, this distance continues to increase as the galaxy moves away from us at a velocity of 200,000 km/s. Unlike its neighboring radio galaxies that have distinct elliptical shapes, ZS 256 presents an irregular and elongated configuration.
We have recently obtained a somewhat clear image of the next galaxy that breaks records in terms of distance. It is located a mind-boggling 12 billion light years away. 12 billion light years away.
Discoveries of such ultra-distant galaxies are not random occurrences. They are usually the result of years of dedicated work by multiple groups of astronomers. This is exemplified by the recent finding of yet another extremely distant galaxy with an apparent stellar magnitude of 20.19.
The farthest stars and celestial bodies

The Spitzer Space Telescope has captured the light emitted by the farthest stars in the universe, which began to shine approximately 200 million years after the formation of the universe.
The most remote observable “entity” in the Universe. – relic radiation that originated from the separation of matter and light into two “fractions” from the original matter of the universe just 1 million years after its inception.
The farthest blast

In 2009, an explosion of such magnitude was observed by NASA’s Swift orbiting observatory that it could be seen from the edge of the observable Universe. This explosion was located farther away than any known galaxies, quasars, or visible supernovae. With a redshift of 8.2, it holds the record for being the most distant gamma-ray burst ever detected.
Gamma-ray burst GRB 090423 occurred a mere 630 million years after the Big Bang in a Universe that was so young that astronomers had not yet theorized the existence of any objects capable of exploding at that time. The faint infrared afterglow of GRB 090423 was observed by ground-based telescopes within minutes of its discovery.
It is highly likely that this explosion of a star, known as a gamma-ray burst, occurred during the early stages of the universe and resulted in the formation of one of the earliest black holes.
The furthest gamma-ray burst ever recorded.
On September 4, 2005, a cosmic gamma-ray burst (GRB050904) took place in the Pisces constellation at a redshift of z=6.29. Simultaneously, observations with the 25-cm TAROT telescope revealed its brightness in the infrared range to be 14m.
NGC 1316 is the galaxy that experiences the greatest number of supernovae.

The American spacecraft Swift transmitted an exclusive image back to Earth, showcasing two supernovae stars that erupted in the NGC 1316 galaxy, five months apart.
NGC 1316, an enormous elliptical galaxy situated approximately 80 million light-years away from Earth, is believed to have commenced absorbing a neighboring spiral galaxy hundreds of millions of years ago.
In 1980 and 1981, astronomers observed two supernova explosions in the NGC 1316 galaxy. Recently, as reported by New Scientist, two more supernovae occurred in NGC 1316, with only a few months between their eruptions.
This brings the total number of supernovae stars that have exploded in the NGC 1316 galaxy to four over the course of 26 years, setting a new record in the history of space observations. Typically, a large galaxy experiences three supernova explosions per century.
In 2005, two supernovae (2005en and 2005eo) were detected in the UGC 4132 galaxy in the Gemini constellation on the exact same date (September 27)!
Most luminous gamma-ray burst in the visible spectrum
The astronomical event of a gamma-ray burst on January 23, 1999 (GRB990123) in the Volopassus constellation took place at a redshift of z=1.60. Simultaneously, its brightness in the optical range, as observed by the ROTSE-I camera equipped with a Canon 200mm/f1.8 lens, reached a magnitude of 9m.
The biggest aircraft

Astronomers have made an incredible discovery – they have spotted the longest known stream of plasma, extending over a distance of more than a million light-years.
Throughout the Universe, scientists have observed relativistic jets, which are massive streams of plasma that travel at incredible speeds. These jets have been detected from a variety of objects, including neutron stars.
However, the most powerful jets are observed coming from the active cores of galaxies. In these regions, enormous amounts of matter are constantly collapsing into supermassive black holes. Some of this matter gets twisted and accelerated, resulting in jets that can travel hundreds of thousands and even millions of light years away.
The farthest organics
Chemical compounds with the potential to be the foundation of alien life are being found in a galaxy located 250 million light-years away from our solar system.
Scientists made this groundbreaking discovery during the testing of a state-of-the-art sensor at the Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico. The telescope was directed towards the Arp 220, an ultraluminous infrared galaxy known for its turbulent nature and unique double nucleus.

Arecibo’s latest broadband spectrometer has the capability to identify chemical compounds by capturing radio waves that have passed through their clusters. In contrast to traditional instruments that allow for the scanning of space in search of specific atoms or molecules, this spectrometer can simultaneously cover bands that are 800 MHz wide. The results of its observations have surprised scientists greatly. It has detected the presence of methanimine and hydrogen cyanide. These two substances serve as precursors for amino acids, and from them, there is a direct path leading to the formation of the simplest amino acid, glycine.
Clip
If we wish to embark on a journey to the closest star, it would take us a little over four years to reach it, provided that our speed is equal to the speed of light, which is 300,000 kilometers per second. Is this an achievable feat?
23.07.19 22:11
text: Elena Tkachenko
photo: INNOV.RU
2056

Perhaps in the future, humanity will construct a rocket capable of achieving a velocity of at least 100,000 kilometers per second, equivalent to one-third the speed of light. With such technology, a round trip journey would take approximately 25 years, which is a reasonable timeframe. However, if one were to travel to the adjacent galaxy, the distance would span an astonishing 2.5 million light years. Thus, reaching that destination would be an unattainable goal. Furthermore, when it comes to the nearest black hole to Earth, there are certain intricacies and complexities to consider.
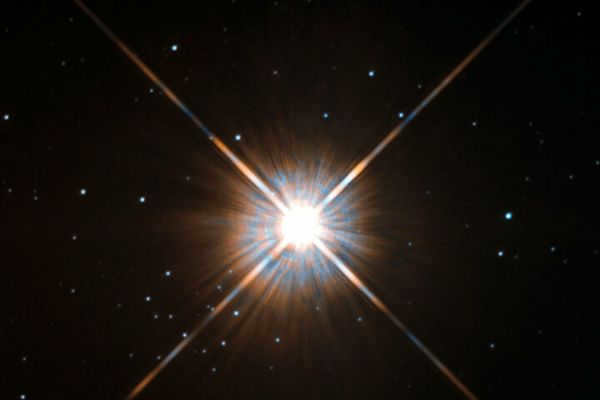
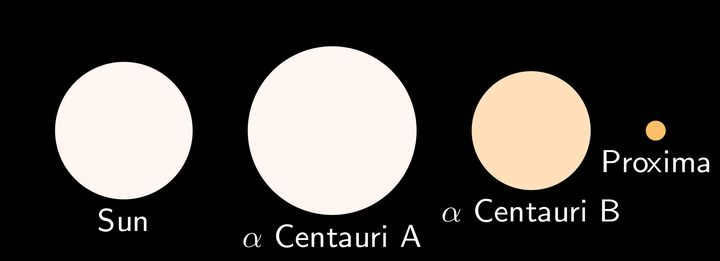
An “accessible” celestial body
This celestial body is known as Proxima Centauri, one of the trio of stars that make up the Alpha Centauri system. In comparison to our sun, Proxima Centauri is significantly smaller, with a diameter that is only one-seventh the size. Additionally, it weighs one-seventh as much. As a red dwarf, this celestial neighbor emits a dimmer and cooler light. However, when combined with its two neighboring stars, it creates a luminous spectacle in our night sky, ranking third in brightness after Sirius and Canopus.


Marhorr – own work
In both 2016 and 2019, two planets similar to our own were found in close proximity to this star. It’s conceivable that there may be some sort of life present there. Alpha Centauri cannot be seen in our hemisphere, it’s only visible to those in the Southern Hemisphere.
Author: Original MetaPost program by David Benbennick
Unreachable yet closest galaxy
This is Andromeda, and its distance is so immense that when we observe the galaxy in the sky, we are actually seeing its past that occurred millions of years ago, as the light takes an incredibly long time to reach us. However, it’s worth noting that there are galaxies even further away, and the “visible” past we observe is already billions of years old.
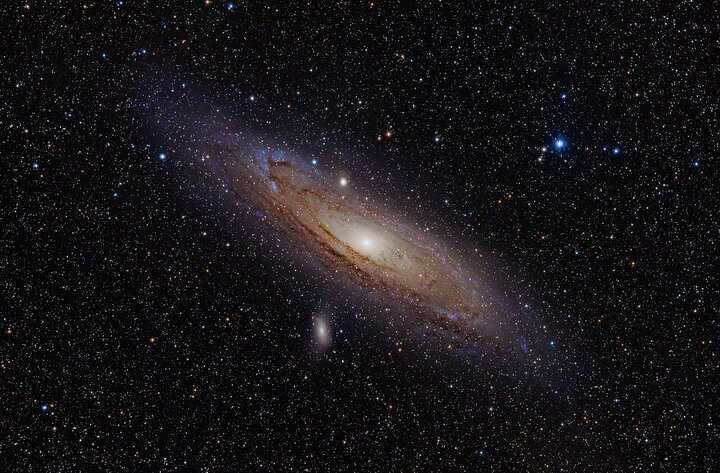

The Andromeda Galaxy, situated in the constellation Andromeda, is a spiral galaxy that is approximately 2.5 million light years away.
In this “neighboring” galaxy, there exists approximately 3-5 times more stars compared to our own galaxy, totaling around 1 trillion! The Andromeda Galaxy is a remarkable celestial object outside of our galaxy that can be observed with the naked eye, particularly its core. With the aid of binoculars or a telescope, the visibility of the Andromeda Galaxy is greatly enhanced, provided one knows where to direct their gaze.
The closest black hole
If we have a grasp of the terminology, then we have “black holes” (BHs) and “supermassive” ones (SMHs). The former are relatively “small”, representing the final stage of a star’s life that is 2-2.5 times heavier than the sun. However, the latter are immensely enormous, residing in the cores of galaxies. Just how immense? It’s difficult to fathom – at least 3-6 billion times heavier than our sun. In the core of our own galaxy, there exists such a supermassive black hole known as a BHD, positioned 26,000 light years away from Earth. The closest small black hole is situated 3,000 light-years away. Black holes themselves do not emit any detectable radiation, and they are identified through indirect indicators, typically neighboring celestial bodies such as stars that exhibit rapid movement around the massive invisible entity. If there are no “indirect indicators” present near a BH, it becomes undetectable by any other means. Hence, it is plausible that a black hole may be much closer to us than we currently surmise.
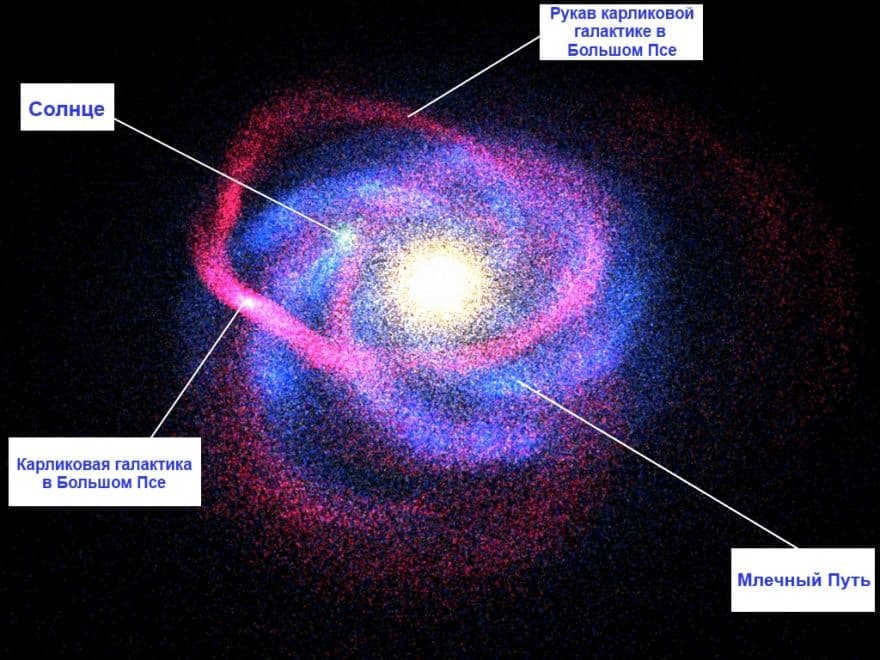
What is the closest galaxy to the Milky Way? The Spiral Andromeda, a dwarf galaxy in the Big Dog constellation, is the closest galaxy to the Milky Way. It is located at a distance that can be seen on the galaxy map, and there have been studies conducted with photos of this galaxy.
It is important to understand that the Milky Way is not the only galaxy of its kind. There are many others that are organized into specific groups. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group, which consists of 54 galaxies. Therefore, we are not alone in the universe.
While many people believe that the Andromeda galaxy is the closest to the Milky Way due to the ongoing collision and merger process between the two, scientifically speaking, it is the closest representative of the spiral galaxy type. The discovery of this dwarf galaxy is relatively recent, so it is time to update your knowledge.
What is the nearest galaxy?
The closest galaxy to the Milky Way is currently the dwarf galaxy in the Canis Major constellation. It is located 42,000 light-years from the center of our galaxy and 25,000 light-years away from our solar system.

Distinctive Features of the Nearest Galaxy to Us
It is widely believed that this galaxy harbors a staggering number of one billion stars, a significant portion of which have reached the red giant phase of their lifecycle. It assumes the shape of an elliptical structure, with a mesmerizing array of stars shimmering in the background. Additionally, it boasts a complex ring-like configuration known as the Unicorn Ring, which gracefully wraps around itself three times.
During an in-depth exploration of this celestial formation, researchers stumbled upon a dwarf galaxy residing in the Canis Major constellation. It is speculated that this dwarf galaxy was devoured by the aforementioned larger galaxy. Furthermore, the globular clusters located in close proximity to its core (NGC 1851, NGC 1904, NGC 2298, and NGC 2808) were once a part of the absorbed galaxy.
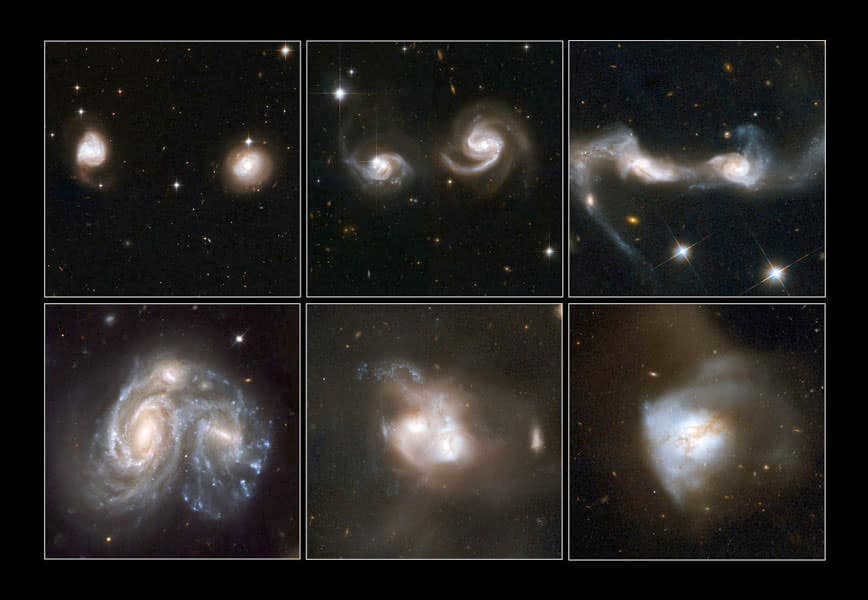

Astronomers have captured various instances of galactic mergers through the lens of the Hubble telescope
Unveiling the closest galaxy to our planet
Previously, it was believed that the closest galaxy to Earth was a Dwarf elliptical galaxy situated at a distance of 70,000 light years. However, there has been a recent discovery of a galaxy that is even closer, at a distance of 180,000 light years.
In 2003, the dwarf galaxy in the Big Dog constellation was revealed. Astronomers conducted a comprehensive survey of 70% of the sky using the All-Sky Survey and identified approximately 5,700 celestial sources emitting infrared light. Infrared light is particularly significant as it is not obstructed by gas and dust, allowing for the detection of numerous M-type giants in the Big Dog constellation. Some of these giants even formed faint arcs.
The discovery of the formation was made possible due to the abundance of M-type stars. These low-temperature red dwarfs, although not visible to the naked eye, can be observed in the infrared due to their lack of brightness.
This data supports the theory that galaxies can grow by assimilating smaller neighboring galaxies. Our Milky Way galaxy is a product of this process and continues to evolve. Since the stars from the former Dwarf Galaxy in the Big Dog now belong to our galaxy, one could argue that it is the closest galaxy to us.
The discovery of a dwarf galaxy in Sagittarius in 1994 was a significant milestone. Another nearby spiral galaxy, M31, is currently approaching us at an accelerating speed of 110 km/s. In approximately 4 billion years, it will eventually merge with our galaxy.
Now you are aware that the closest galaxy to the Milky Way is a small galaxy in the Canis Major constellation. However, what fate awaits it? Scientists hypothesize that it will eventually be dismantled by the gravitational force of the Milky Way. Notably, its main body has already undergone distortion and this process shows no signs of stopping. The accretion will culminate in a complete merger of the two objects, adding another billion stars to our galaxy’s already impressive count of 200-400 billion. Thus, the proximity of the nearest galaxy has wreaked havoc upon it.
What is the distance to the nearest galaxy? March 12th, 2013
For the first time ever, scientists have successfully measured the precise distance to the nearest galaxy. This dwarf galaxy is known as the Large Magellanic Cloud. the Large Magellanic Cloud. It is situated 163,000 light years away from us, or to be more exact, 49.97 kiloparsecs.
The Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy is drifting through the vastness of outer space, encircling our galaxy, the Milky Way, much like the Moon orbits the Earth.
Enormous clouds of gas surrounding the galaxy gradually disperse, giving rise to the birth of new stars that illuminate the interstellar expanse with their radiant light, creating stunning and vibrant cosmic vistas. These awe-inspiring landscapes have been captured by the renowned Hubble Space Telescope, affectionately known as “Hubble.”
Contained within the small expanse of the Large Magellanic Cloud is the Tarantula Nebula, which serves as the brightest stellar nursery in our celestial vicinity, bearing witness to the ongoing process of star formation.
Using a method called eclipsing double stars, scientists were able to make precise calculations by observing rare pairs of stars that are gravitationally bound together. When one star outshines the other, the overall brightness of the system decreases, allowing researchers to compare their brightness and determine their exact distances with remarkable accuracy.
Accurately determining the distances to celestial objects is crucial in understanding the size and age of our Universe. However, the question of exactly how big our Universe is remains unanswered by scientists.
Once astronomers achieve such precision in measuring distances in space, they will be able to study objects that are even farther away and ultimately determine the size of the Universe.
These enhanced capabilities will also enable them to more precisely measure the rate at which our universe is expanding and calculate the Hubble constant with greater accuracy. This constant is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American astronomer who demonstrated in 1929 that our universe has been steadily expanding since its inception.
The closest dwarf galaxy to us is the Large Magellanic Cloud, but our largest neighbor is the spiral galaxy Andromeda, which is approximately 2.52 million light years away.
Over time, the distance between our galaxy and Andromeda is gradually decreasing. They are moving towards each other at a speed of about 100-140 kilometers per second. Although they will eventually collide, this won’t happen for another 3-4 billion years.
It’s possible that this is what the night sky will look like to an Earth observer in a few billion years from now.
Due to their constant dynamics, the distances between galaxies can vary greatly at different stages of time.
The Extent of the Universe
The observable Universe boasts an astonishing diameter of billions, perhaps even tens of billions, of light years. Numerous celestial bodies that we can observe through telescopes have long vanished or appear drastically different due to the immense amount of time it takes for light to reach us.
This collection of illustrations serves to provide a general sense of the scale of our Universe.
The Solar System featuring its largest entities (planets and dwarf planets)
The Sun (located in the center) and its closest stars
The Milky Way Galaxy, showcasing the cluster of star systems that are nearest to our Solar System
A cluster of neighboring galaxies, which currently includes over 50 galaxies and continues to expand as we discover new ones
The Virgo Supergroup is a local collection of galaxies with a size of approximately 200 million light-years.
It is a group of supergroups of galaxies.
The Milky Way, which is a prime example of its galaxy type, is so incredibly massive that it would take light over 100,000 years to travel from one edge of the galaxy to the other, moving at a speed of 300,000 kilometers per second. The Earth and the Sun are situated around 30,000 light-years away from the center of the Milky Way. If we were to send a message to a hypothetical being living near the center of our galaxy, we wouldn’t receive a response until 60,000 years later. A message sent at an airplane’s speed of 600 miles or 1,000 kilometers per hour at the time of the Universe’s birth would only make it halfway to the center of the Milky Way by now, and the wait for a response would be a staggering 70 billion years.
There are galaxies that surpass the size of our own galaxy. The largest galaxies, which emit significant amounts of radio wave energy, like the well-known Centaurus A in the southern sky, have diameters that are one hundred times larger than the Milky Way. Conversely, the universe also contains numerous small galaxies. A typical example of a dwarf elliptical galaxy, found in the constellation Dragon, spans only about 10 thousand light-years. Despite their unassuming appearance, these galaxies are still incredibly massive. For instance, the dwarf galaxy in the Dragon constellation has a diameter that exceeds 160,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 kilometers.
To gain a visual understanding of the immense distances separating galaxies, let’s imagine shrinking them down to the size of an average person. In a typical region of the Universe, the “adult” galaxies would be, on average, 100 meters apart, with a few smaller “children” galaxies scattered in between. This would create a vast expanse resembling a baseball field, with plenty of empty space between the players. Only a handful of locations would exhibit tight clusters of galaxies. In our scaled-down model of the Universe, it would resemble a city sidewalk, lacking any resemblance to a crowded party or a packed subway car during rush hour. If we were to reduce the stars within a typical galaxy to the height of a human, the population density would be incredibly sparse: the nearest neighbor would reside a staggering 100,000 kilometers away, roughly a quarter of the distance separating Earth from the Moon.
It should be evident from these illustrations that the distribution of galaxies in the Universe is rather sparse and primarily consists of empty space. Even when accounting for the sparse gas that fills the gaps between stars, the overall density of matter remains incredibly low. The realm of galaxies is vast and predominantly void.
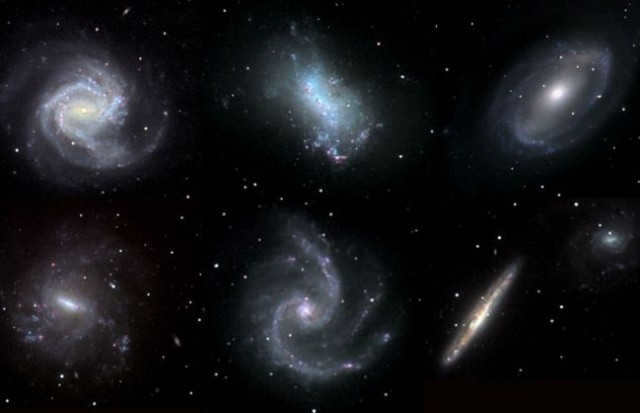
Galaxies within the Universe exhibit a great deal of diversity. Some possess a flat and circular shape, while others take the form of flattened spirals, and there are those that exhibit little to no discernible structure. Building upon the groundbreaking research of Edwin Hubble in the 1920s, astronomers classify galaxies into three primary categories based on their shape: elliptical (denoted as E), spiral (denoted as S), and irregular (denoted as Irr).
Astronomy is an incredibly captivating field of study that unveils the vastness and variety of the cosmos. Very few individuals could claim to have never gazed up at the scattered stars in the nighttime sky during their childhood. This spectacle is especially breathtaking during the summer months, when the stars appear close and radiantly luminous. Over the past few years, astronomers worldwide have displayed a particular fascination with Andromeda, the nearest galaxy to our own Milky Way. We were intrigued to investigate what specifically draws these scientists to Andromeda and whether it can be observed without the aid of telescopic lenses.
Andromeda: a concise description
The Andromeda Nebula galaxy, commonly referred to as Andromeda, is among the largest in the universe. It boasts a size that is approximately three to four times greater than our very own Milky Way, which houses the Solar System. Rough estimates suggest that it contains an astounding one trillion stars.
Andromeda is categorized as a spiral galaxy and can actually be observed in the night sky without the need for specialized optical equipment. However, it is important to note that the light emitted by this celestial cluster takes more than two and a half million years to reach our planet! Astronomers assert that what we perceive as the Andromeda Nebula today is actually a depiction of how it appeared two million years ago. Truly a remarkable phenomenon, wouldn’t you agree?
A History of Observations: The Andromeda Nebula
The Andromeda Nebula was initially observed by an astronomer hailing from Persia. In the year 946, he recorded it and described it as a hazy glow. Centuries later, a German astronomer meticulously observed the galaxy for an extended period using a telescope.
In the mid-1800s, astronomers discovered that the spectrum of Andromeda differed significantly from other known galaxies, leading them to theorize that it was comprised of numerous stars. This hypothesis was subsequently proven correct.
It wasn’t until the late 1800s that a photograph of the Andromeda galaxy was finally taken, revealing its spiral structure. Prior to this, it had been regarded simply as a vast section of the Milky Way.

Exploring the Galaxy’s Composition
Astronomers have recently conducted a thorough analysis of the composition of the Andromeda Nebula using state-of-the-art telescopes. Among the key findings, the Hubble telescope has revealed the presence of approximately four hundred young stars orbiting around the black hole. Surprisingly, these stars are estimated to be around two hundred million years old. This discovery has left scientists astounded, as it was previously believed that star formation was impossible in the vicinity of a black hole according to known laws of nature.
There are multiple satellite dwarf galaxies surrounding the Andromeda Nebula, and their presence could be attributed to absorption. This is particularly fascinating considering that scientists anticipate the imminent collision between the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy. However, this extraordinary occurrence will occur in the near future.
The Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way: Approaching Each Other
For a while now, scientists have been making predictions based on their observations of the movement of both star systems. It turns out that Andromeda, a galaxy, is constantly moving towards the Sun. In the early 1900s, an American astronomer was able to calculate the speed at which this movement is occurring. This value of three hundred kilometers per second is still widely used by astronomers worldwide in their observations and calculations.
Collision: what will occur?
With the unavoidable merging of the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies, astronomers are endeavoring to simulate the event in order to gain some insight into this phenomenon. Based on computational data, it is projected that following the merger, our solar system will be situated on the outskirts of the resulting galaxy, drifting approximately one hundred and sixty thousand light years away. This distance represents a significant shift from our current position in relation to the galactic center, as we will be moving away from it by a distance of twenty-six thousand light years.
The upcoming galaxy merger has been named Milky Meda, and scientists predict that it will undergo a rejuvenation process for at least 1.5 billion years. This cosmic event will lead to the formation of new stars, enhancing the brilliance and beauty of our galaxy. Furthermore, the merger will also result in a change of shape. Currently, the Andromeda Nebula is positioned at an angle to the Milky Way, but as the merger progresses, the combined system will transform into a more elliptical shape and expand in size, so to speak.
The future of humanity: can we survive the cosmic clash?
And what will be the fate of the human race? How will the merging of galaxies impact our planet? Surprisingly, scientists predict that there will be no direct consequences for us. The only changes we will witness are the emergence of new stars and constellations. The entire celestial map will transform as we find ourselves in an entirely unfamiliar and uncharted region of the galaxy.
Of course, a small fraction of astronomers do entertain the possibility of some negative outcomes. In this scenario, Earth could potentially collide with the Sun or another celestial body from the Andromeda galaxy.

Is there any possibility of finding planets in the Andromeda Nebula?
Scientists are continuously searching for planets in various galaxies, with the hope of discovering a planet similar to Earth within the vastness of the Milky Way. Up until now, over three hundred celestial bodies have been identified and studied, but they all belong to our own star system. In recent years, astronomers have directed their attention towards the Andromeda galaxy, questioning whether there are any planets present.
Thirteen years ago, a team of astronomers proposed a theory, using advanced techniques, that one of the stars within the Andromeda Nebula could potentially be hosting a planet. This hypothetical planet is estimated to have a mass six percent that of Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, and a mass three hundred times greater than that of Earth.

Preparing for a Sky Search for a Galaxy
As mentioned before, it is possible to spot a neighboring galaxy in the night sky even without the aid of a telescope. However, some basic knowledge of astronomy is required, such as being able to identify constellations.
In urban areas, the presence of light pollution makes it difficult to see certain star clusters. To get a clear view of the Andromeda Nebula, it is recommended to venture out to the countryside during late summer or find a city park with minimal street lighting. The best time to observe it is in October, although it is visible above the horizon from August through September as well.
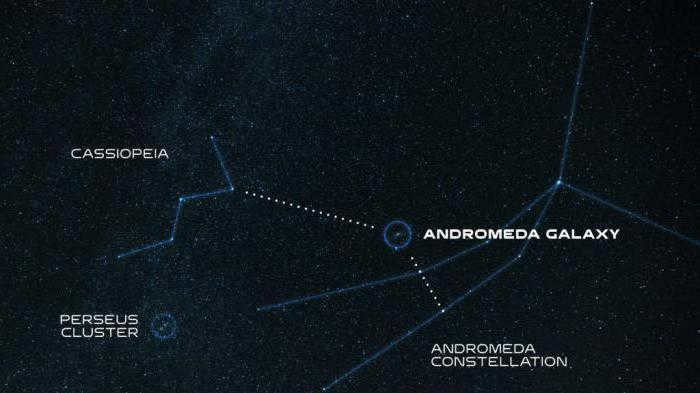
Searching for the Andromeda Nebula
Many aspiring astronomers have the desire to discover the true appearance of the Andromeda galaxy. This celestial body appears as a small, luminous spot in the sky, but it can be located with the help of the nearby bright stars.
In the autumn sky, locating the constellation Cassiopeia is the simplest method – it resembles the letter W, but is more elongated than its written form. This constellation is usually highly visible in the Northern Hemisphere and can be found in the eastern part of the sky. The Andromeda Nebula galaxy is positioned below Cassiopeia. To catch a glimpse of it, a few additional reference points must be identified.
Below Cassiopeia, there are three shining stars that form a line and have a red-orange color. The star in the middle, Mirac, is particularly useful for beginner astronomers as a reliable guide. If you trace a straight line upwards from Mirac, you will come across a small luminous patch that resembles a cloud. This luminosity is none other than the Andromeda Galaxy. What’s even more fascinating is that the light we observe from the galaxy was emitted long before humans even existed on Earth. It’s truly a remarkable fact, don’t you think?
Scientists have made progress in unraveling one of the universe’s main mysteries by studying the origins of galaxies, stars, and planets. They believe that the material from which celestial bodies and their clusters later formed was a result of the big bang, which occurred approximately 15-20 billion years ago (see “Science and Life” №).
In the constellation Lyra, there is a fascinating planetary gas nebula known as the Ring Nebula.
Another well-known nebula, the Crab Nebula, can be found in the constellation Taurus.
The Great Orion Nebula is also a notable celestial object.
In the constellation of Taurus, you can admire the Pleiades star cluster.
Our Galaxy has a close neighbor called the Andromeda Nebula.
The Small and Large Magellanic Clouds are galactic clusters of stars that accompany our Galaxy.
One of the largest spiral galaxies that can be observed from Earth through powerful telescopes.
Science and Life // Illustrations
Our galaxy, known as the Milky Way, is home to billions of stars, all orbiting its center. It’s not just the stars that are in motion in this vast galactic carousel. There are also nebulae, or clouds of gas and dust. Many of these nebulae are not visible to the naked eye, but become visible when observing the night sky with binoculars or a telescope. What types of celestial mist will we encounter? Perhaps distant clusters of stars that cannot be distinguished individually, or something entirely different?
Nowadays, astronomers possess knowledge about the nature of each nebula. It appears that they exhibit significant diversity. Some nebulae consist of gas and are illuminated by stars. Due to their spherical shape, they are referred to as planetary nebulae. Many of these nebulae were formed as a result of the evolution of massive stars that have reached old age. An example of a “nebular remnant” originating from a supernova (we will provide more information on this) is the Crab Nebula located in the Taurus constellation. This nebula, resembling a crab, is relatively young. It is known to have been born in the year 1054. Additionally, there are nebulae that are much older, with ages ranging from tens to hundreds of thousands of years.
Memorial nebulae could be named as planetary nebulae and the remnants of supernovae that once erupted. However, there are other types of nebulae where stars are not extinguished but rather born and grow. An example of such a nebula is the Great Orion Nebula, which can be observed in the constellation of Orion.
Clusters of stars are quite different from these nebulae. The Pleiades cluster, located in the constellation of Taurus, is easily visible to the naked eye. It is hard to imagine that it is not a gas cloud, but rather a collection of hundreds and thousands of stars. There are even more “rich” clusters that contain hundreds of thousands or even millions of stars! These clusters, known as globular star clusters, form a whole entourage of “balls” surrounding the Milky Way.
Although most of the star clusters and nebulae visible from Earth belong to our Galaxy, there are some very distant nebulae that are actually entire galaxies!
One of our most famous galactic neighbors is the Andromeda Nebula in the constellation Andromeda. When we look at it with the naked eye, it appears as a blurry nebula. However, when we observe it with large telescopes, the Andromeda Nebula reveals itself as a stunning galaxy. Through the telescope, we can see not only the multitude of stars that make up the galaxy, but also the spiral arms extending from its center. In terms of size, our neighbor is even bigger than the Milky Way, with a diameter of approximately 130 thousand light-years.
The photographs of the Andromeda Nebula clearly display not just the galaxy itself, but also some of its satellites. Of course, the satellites of the galaxy are distinct from, for instance, planets – the satellites of the Sun or the Moon – a satellite of the Earth. Galactic satellites are also galaxies, albeit “smaller”, composed of millions of stars.
Our galaxy possesses satellites. There are numerous of them, and two of them can be seen with the naked eye in the Southern Hemisphere sky of the Earth. Europeans first spotted them during Magellan’s circumnavigation of the globe. They initially mistook them for some form of clouds and labeled them the Large Magellanic Cloud and the Small Magellanic Cloud.
The satellites orbiting our Galaxy are situated in closer proximity to the Earth compared to the Andromeda Nebula. The journey of light from the Large Magellanic Cloud to reach us takes only about 170,000 years. Until recently, this particular galaxy was believed to be the nearest satellite of the Milky Way. However, astronomers have recently made discoveries of satellites that are even closer, although they are considerably smaller than the Magellanic Clouds and cannot be seen with the naked eye.
When examining the “portraits” of various galaxies, astronomers have come across galaxies that differ from the Milky Way in terms of their structure and shape. Such galaxies are numerous – they include both visually stunning galaxies and galaxies that lack a distinct shape, resembling, for instance, the Magellanic Clouds.
It hasn’t even been a century since astronomers made a remarkable revelation: distant galaxies are moving away from each other in various directions. To comprehend this phenomenon, you can conduct a simple experiment using a balloon.
Take a balloon and draw small circles or squiggles on it using ink, felt-tip pen, or paint to represent galaxies. As you begin to inflate the balloon, the drawn “galaxies” will gradually spread farther apart. This mirrors the behavior of galaxies in the universe.
Galaxies rush away from each other, serving as the birthplace, life, and final resting place of stars. Not only stars, but also planets, are found within galaxies. It is highly likely that there are numerous star systems in the Universe, resembling our solar system in some ways but also exhibiting unique characteristics. In fact, astronomers have recently discovered approximately 300 planets orbiting other stars.
The desire to explore other galaxies and travel through space has long captivated the human imagination. This aspiration has served as a source of inspiration for both our scientists and writers, and it continues to hold significance in the present day. The rapid advancements in space technology that have taken place in recent decades have brought us to the cusp of a new era in space exploration.
Despite the immense obstacles and technical complexities involved, there is a growing sense of optimism regarding the possibility of future intergalactic travel. Ongoing scientific advancements in areas such as spacecraft development, energy systems, and medicine have served to mitigate risks and make such journeys increasingly feasible. The exploration of other galaxies holds the potential to provide us with novel insights into the universe and offer solutions to fundamental questions surrounding the origins of life.
Undoubtedly, venturing to another galaxy is an immense undertaking. The expanses of space are vast, and it could take years, even centuries, to reach the nearest galaxy. However, if we persist and remain undeterred, perhaps we can overcome these challenges and achieve something truly extraordinary.
The Future of Inter-Galactic Travel
Contemplating the possibility of journeying to other galaxies often ignites the imagination and captivates the interest of many individuals. But how feasible is it to realize such voyages?
Currently, mankind’s technological capabilities are confined to exploring the nearest planets and moons to Earth. Nevertheless, with the advancement of science and technology, certain scientists maintain confidence that in the future, we will possess the means to embark on inter-galactic travel.
One of the most exciting concepts is to utilize the immense speed of light in outer space. If scientists were able to discover a way to surpass this limitation, the opportunities for intergalactic travel would become boundless.
An alternative proposal involves constructing space-time portals that would allow for instantaneous travel between different points within the galaxy. Although this technology remains purely speculative at present, there are some experts who believe it could eventually become a tangible reality.
Additionally, there have been suggestions for developing intergalactic spacecraft capable of traversing vast distances in outer space. These spacecraft would need to be outfitted with state-of-the-art technologies to ensure the safety and well-being of the crew during extended journeys.
Nevertheless, in spite of these concepts and presumptions, there is a substantial array of scientific and technical obstacles that must be resolved in the forthcoming period to actualize voyages to alternative galaxies. This necessitates not merely novel breakthroughs in physics and cosmology, but also considerable investments in scientific research.
Hence, the future of voyaging to alternative galaxies remains an extraordinary notion. However, with the progression of science and technology, we are drawing nearer and nearer to the prospect of realizing this aspiration. Conceivably, in mere a few decades, humanity will possess the capability to traverse the uncharted depths of the cosmos.
What opportunities does science provide us with?
Science provides us with a myriad of possibilities and opens up novel realms of knowledge and experiences. Across various scientific domains, we have the ability to make groundbreaking discoveries, solve intricate problems, and advance technologies that have the potential to revolutionize our lives.
Medicine and healthcare
Scientific research in the field of medicine enables us to devise innovative methods for diagnosing, treating, and preventing diseases. Through the application of scientific principles, we can combat perilous infectious ailments, fabricate vaccines, and develop novel medications. Scientific breakthroughs in genetics empower us to gain a deeper understanding of our DNA and create tailored treatments.
Technology and innovation
Energy and the environment
In the realm of energy and the environment, scientific advancements provide us with the potential to create new, cleaner, and more efficient sources of energy. By conducting research on solar, wind, nuclear, and other energy sources, we can decrease our dependency on fossil fuels and minimize our ecological impact.
Space exploration and extraterrestrial discovery
Science grants us the opportunity to explore outer space and other planets. Through studying their composition, atmosphere, and searching for signs of life, we can gain a deeper understanding of how these celestial bodies can be utilized for colonization or to address challenges on Earth. Such exploration can lead to groundbreaking discoveries and technological advancements that revolutionize our perception of the world and the potential for our own progress.
Science and the field of education
Education and society benefit greatly from the influence of science. By conducting scientific research, we can devise innovative teaching techniques, produce more impactful educational resources, and foster scientific literacy. Science molds our capacity for critical thinking, enabling us to scrutinize data and arrive at well-informed conclusions.
The myriad opportunities presented by science open up new horizons and enable us to thrive in various aspects of life. This instills in us a sense of optimism for a future where the potential of humanity knows no bounds.
Advancements in Space Technology

The development of space technology is a crucial aspect of scientific and technological advancement. Humanity constantly strives to find ways and opportunities to explore outer space and investigate other planets and galaxies.
Each year, the accomplishments in modern space technologies become increasingly remarkable. Novel satellites, interplanetary stations, and probes enable us to examine our solar system and unveil new possibilities for exploring far-off galaxies.
Space telescopes have a unique role in the advancement of space technology. Telescopes like Hubble and James Webb expand our knowledge of the Universe by enabling us to observe distant stars and galaxies. These telescopes are equipped with state-of-the-art optical and electronic systems that generate high-quality images and data on celestial objects.
As technology progresses, scientists and engineers are constantly striving to enhance rocket engines and propulsion systems. The development of more efficient and powerful engines opens up new opportunities for intergalactic travel. Some projects are already exploring the feasibility of constructing spacecraft using solar ion propulsion, which offers significantly greater speed and efficiency compared to traditional rocket engines.
Commercial applications are also being found for space technology. SpaceX and Blue Origin, for example, are actively working on the development and testing of new rockets and spacecraft in order to create cost-effective and reusable systems for space travel.
In general, the development of space technology is constantly advancing and changing. With each new discovery and advancement, we are able to learn more about space and lay the groundwork for future exploration of other galaxies.
Researching Black Holes
Black holes are an enigmatic and captivating phenomenon in the cosmos. Investigating these celestial objects holds immense importance for the fields of astronomy and physics. Black holes possess a gravitational force so powerful that it engulfs everything in its vicinity, including light.
Diverse methods and techniques are employed in the study of black holes:
- Radio Waves: By utilizing radio telescopes, black holes can be examined through their radio emissions. This aids in determining the existence and characteristics of a black hole.
- X-rays: Black holes have the capability to emit X-rays. Scientists can leverage X-ray telescopes to examine this radiation and gather valuable insights about the black hole.
- Scientists also use supercomputers to simulate artificial scenarios and conduct experiments in order to study black holes.
- Understanding the origin and evolution of black holes is one of the primary objectives of black hole research. Additionally, scientists are intrigued by the potential use of black holes for intergalactic travel in the future.
Astral travel: is it a mere fantasy or a genuine experience?
Astral travel is a phenomenon that sparks intense debate and controversy. Some individuals firmly believe that astral travel is a real and tangible experience that allows one to journey to alternate realms and dimensions, while others dismiss it as nothing more than a figment of the imagination.
What exactly is astral travel?
Astral travel refers to a state in which consciousness separates from the physical body and embarks on a voyage to the astral plane. The astral plane is considered a subtle existence that runs parallel to our physical world. Within the astral plane, one can encounter diverse entities, explore different locations, and acquire fresh knowledge and experiences.
Is there any empirical evidence to support astral travel?
It is challenging to provide evidence to confirm experiences with astral travel because this phenomenon occurs on the level of consciousness and perception. However, there are numerous testimonies from individuals who assert that they have visited other worlds and dimensions, encountered spirits, or experienced astral projection.
What is the purpose of engaging in astral travel?
Advocates of astral travel argue that it is a means of expanding one’s consciousness, acquiring new knowledge, and experiencing higher levels of reality. They believe that astral travel aids in understanding the profound mysteries of life and attaining spiritual enlightenment.
The primary methods of astral travel:
- Consciousness projection method: This technique involves consciously transcending the consciousness beyond the physical body.
- Dreaming technique: while sleeping, one can become aware of being in a dream and gain control over the dream, including astral travel.
- The practice of meditation: meditating helps to focus the mind and liberate consciousness from physical limitations.
Criticism and skepticism regarding astral travel:
Many members of the scientific community are skeptical of astral travel and regard it as mere fantasy and fiction. They highlight the lack of scientific evidence and explanations for many of the phenomena associated with astral travel.
Exploration within the realm of psychology

Interest in psychology research is increasing year by year. This is not only because of the advancement of the field itself, but also due to the growing recognition of the significance of psychological well-being in our lives. Numerous studies are being conducted to gain insights into various aspects of human psychology and behavior.
Some of the most fascinating studies in the realm of psychology encompass:
- The exploration of emotions and their impact. Scientists delve into diverse emotions and their effects on our well-being and decision-making. Understanding the emotions we experience in different situations and how they influence our behavior can enhance our self-awareness and empathy towards others.
- Research on Interpersonal Relationships. This field delves into various aspects of interpersonal relationships, including communication, interaction, and conflict. Scholars aim to create models and approaches that can enhance our understanding of and ability to cultivate healthy relationships with others.
- Investigation of Psychological Well-being. This realm focuses on the factors that influence our psychological and overall well-being. Researchers strive to comprehend the elements that contribute to happiness and success, as well as those that can generate feelings of distress.
Advancements in the field of neurobiology

The field of neurobiology focuses on studying the nervous system and its functions. Over the past few decades, numerous significant breakthroughs have been achieved in this realm, which have greatly contributed to our understanding of how the brain operates and how we perceive the world.
An essential finding in neurobiology involves the discovery of mirror neurons. These neurons become active both when we perform an action ourselves and when we observe others performing the same action. Extensive research has demonstrated that mirror neurons play a critical role in fostering empathy and comprehending the actions of others.
Another significant finding in the field of neurobiology is the potential for brain plasticity. Previously, it was believed that the brain reached its full development by the end of childhood. However, recent studies have demonstrated that the brain has the ability to change and adapt throughout an individual’s lifetime. This breakthrough opens up new possibilities for the development of treatments for diseases of the nervous system and the enhancement of cognitive function.
Another noteworthy breakthrough in neurobiology has been the identification of a connection between the nervous system and the immune system of the body. Researchers have discovered that certain neurotransmitters, which are typically involved in signaling within the nervous system, also play a role in regulating the immune system. This discovery deepens our understanding of the intricate relationship between physical and mental health in humans and may have implications for the development of novel treatments for a range of diseases.





