The well-known constellation known as Veronica’s Hair is situated in the northern celestial region. This particular region has gained popularity primarily because it is the location of the north pole of the Galaxy. There is a vast array of thousands of galaxies and clusters that can be observed within this area.
Covering an area of 386.5 square degrees, the constellation Veronica’s Hair is ranked as the 42nd largest constellation.
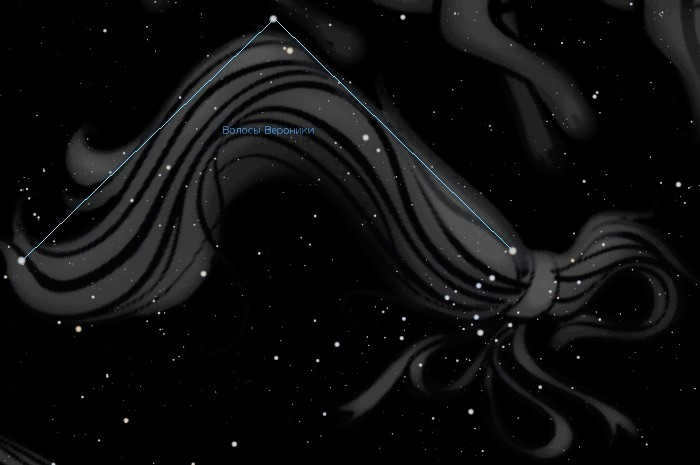

Legend of the star pattern
The star pattern known as Veronica’s Hair was once classified as an asterism. In ancient Greece, it was associated with the constellations Virgo, Volopassus, and Leo.
According to the myth, there was a king in Egypt who had a wife named Berenice. To show her gratitude for her husband’s military victory, she decided to make a sacrifice to the goddess Aphrodite.
Berenice cut off her own hair and placed it in the temple of the goddess. On the first night, the priest witnessed the appearance of new stars that resembled strands of a woman’s hair. This was seen as a sign that Aphrodite had accepted Berenice’s offering.
Interestingly, this asterism was known by different names. It was also referred to as the Hair of Ariadne and the Curl.
Which stars are part of the constellation Veronica’s Hair?
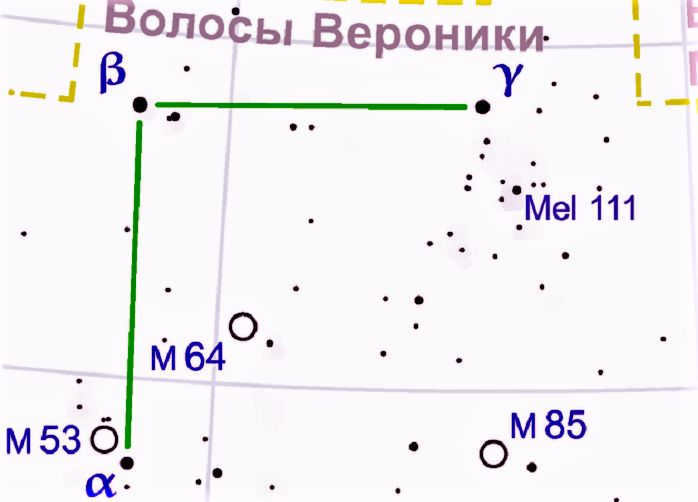
Alpha – Diadem is a binary system with a blue-white subgiant. Despite being the second brightest star in the constellation, it is known as the stone from Berenice’s crown.
The brightest star in the area is Beta, a yellow-white subgiant.
Gamma is classified as an orange giant of the K1II class.
FK Veronica’s Hair is a variable star and serves as the prototype for the FK Com class, characterized by large cold spots on their surface.
These are just a few examples, as there are a total of 64 stars in the constellation that can be seen with the naked eye. However, some of them may be challenging to observe.

Other celestial bodies
Interestingly, the constellation of Veronica’s Hair contains a variety of fascinating celestial bodies.
For instance, it is home to some well-known gravitationally connected systems:
- Messier 64, also referred to as the spiral galaxy The Black Eye. It is also known as the Black Eye galaxy, the Sleeping Beauty galaxy, and the Evil Eye. This galaxy is famous for its bright core and dark dust streak, which visually resemble an eye. Its easily detectable nature only adds to the intrigue for astronomers.
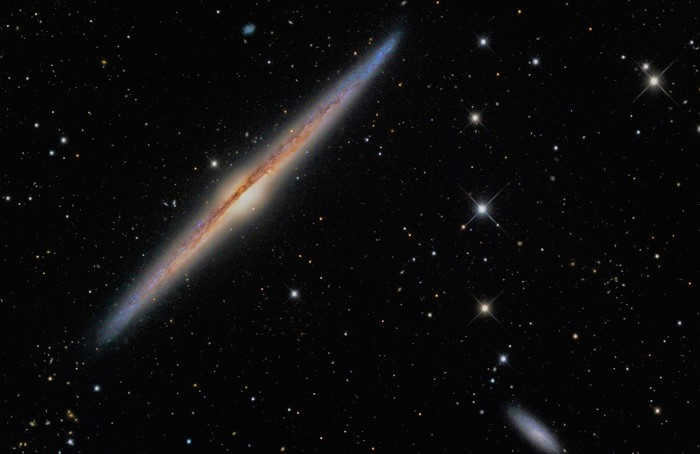
- NGC 4565, also known as the Needle Galaxy, is situated just above the North Pole of the galaxy. It is believed to be a spiral system with a distinctive convex center.
- The Veronica’s Hair galaxy cluster is a vast collection of stellar systems, comprising approximately 1000 galaxies, predominantly elliptical in shape and classified as SO type. The cluster’s abundance has facilitated extensive scientific research, which has played a crucial role in advancing our understanding of the universe. Furthermore, this cluster continues to receive significant attention from researchers.
- The star system formation known as the Virgo cluster is located in the northern part of the Virgo constellation. It consists of several spiral galaxies, including M 88, M 91, M 99, M 100, and one lenticular galaxy, M 85.
- Messier 98 is an intermediate spiral galaxy characterized by its elongated structure.
- NGC 4889 is a massive elliptical galaxy.



Furthermore, there is a distinguishable cluster known as Melotte 11, which is composed of 40 stars. Despite its relatively small size, it emits a significant amount of light.
Moreover, the area also encompasses globular clusters, including Messier 53 and NGC 4147. These clusters consist of a compact group of stars with a spherical shape.
Additionally, it is worth noting the presence of a meteor stream called Coma Berenicidae.
Veronica’s Hair is definitely a constellation worth observing. It deserves attention for several reasons, not least because it encompasses almost every characteristic of a significant landmark.

Observation
If you want to locate the constellation of Veronica’s Hair, you should search for it within the latitude range of +90 to -56 degrees.
Veronica’s Hair is classified as a spring constellation due to the most favorable observing conditions during this time. In the night sky, you can discern a faint shimmering region at least.

Veronica’s hair is a celestial entity located in the nocturnal expanse, prominently observable in the Northern Hemisphere of Earth. It encompasses a myriad of celestial bodies, including stars, galaxies, and clusters thereof. Covering an extensive expanse of approximately 386.5 square degrees in the celestial sphere, the constellation of Veronica’s Hair lacks any discernible distinguishing features that may be readily apparent to the unaided eye.
Searching the Skies
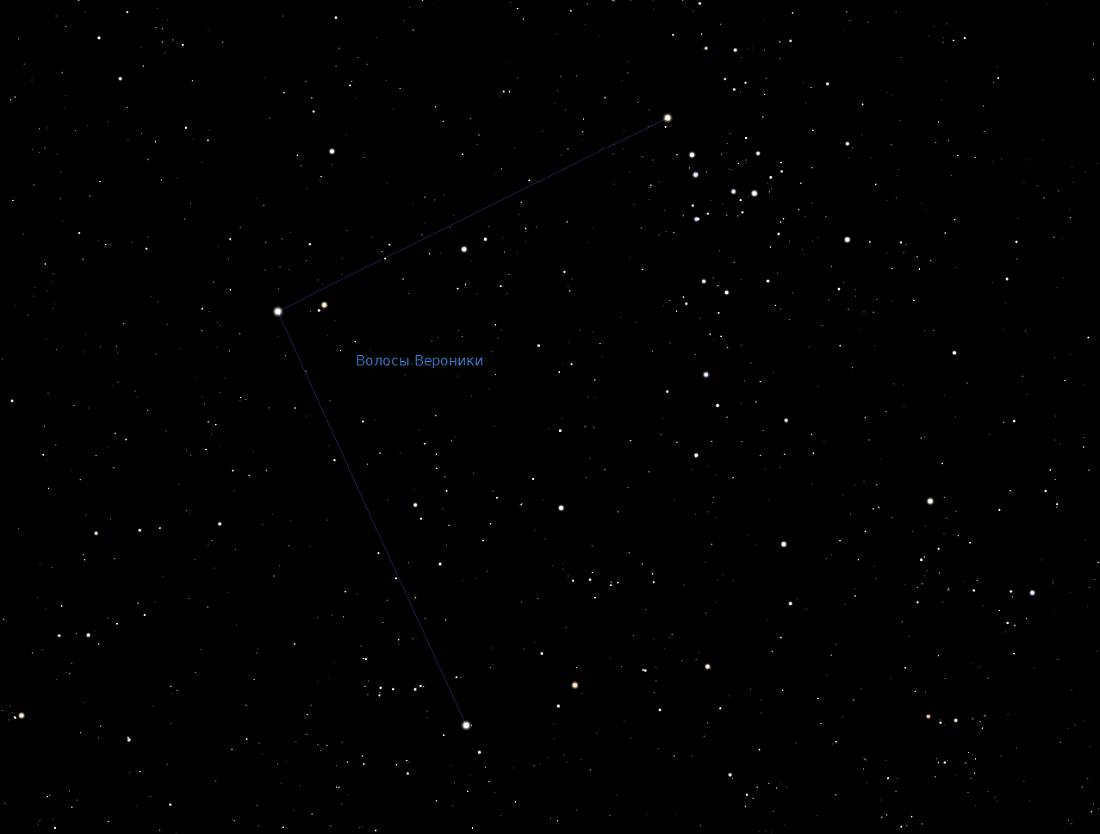

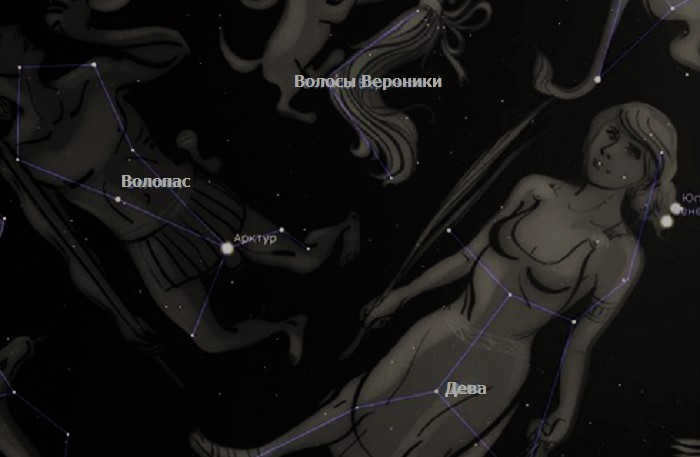
The constellation known as Veronica’s Hair is not easily visible in the night sky due to the absence of bright stars. However, it can be located with the help of neighboring constellations. To the east, it is bordered by Volopassus, while Leo borders it to the west. By connecting the bright stars Arcturus and Mufrid with an imaginary line, you can determine the direction to look for the Diadem. On the west side, you can use Denebola as a reference point. In terms of visibility, the constellation is best observed in March and April when it rises high above the horizon, making it visible throughout Russia.
Unique items
During a night without a moon, it is possible to observe up to 64 brilliant stars with the unaided eye in the constellation. Located within the constellation Veronica’s Hair is the northern celestial pole of our Milky Way galaxy, which has a direct entrance of 12h 51m and a declination of +27° 07′. Within this constellation, there are approximately 50 stars with a brightness exceeding the 6th magnitude. Among these stars, the most significant are Diadem and β Veronica’s Hair.
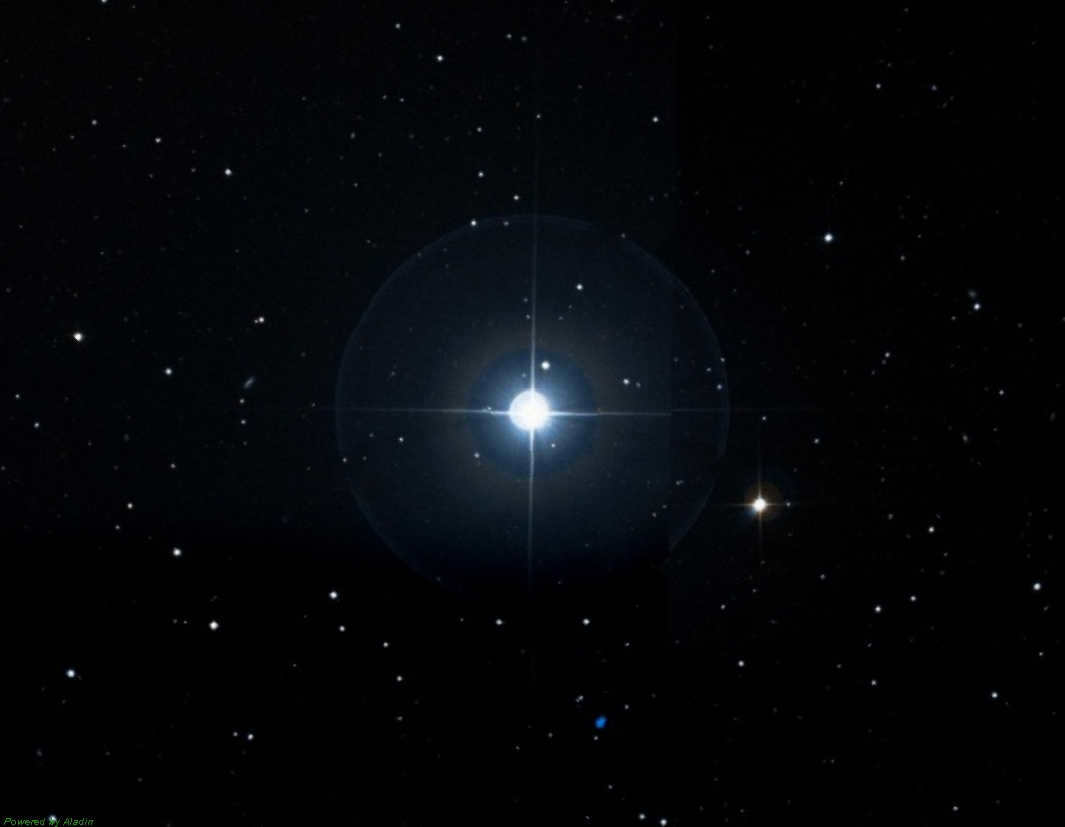

Diadema is the second most luminous entity within the constellation. It is also known as α Hair of Veronica. This binary star system possesses a magnitude of 4.32. The two components of this system are nearly indistinguishable in every aspect. Moreover, it is classified as an eclipsing variable star. Remarkably, it is the sole star in the entire constellation to possess its own distinctive appellation.
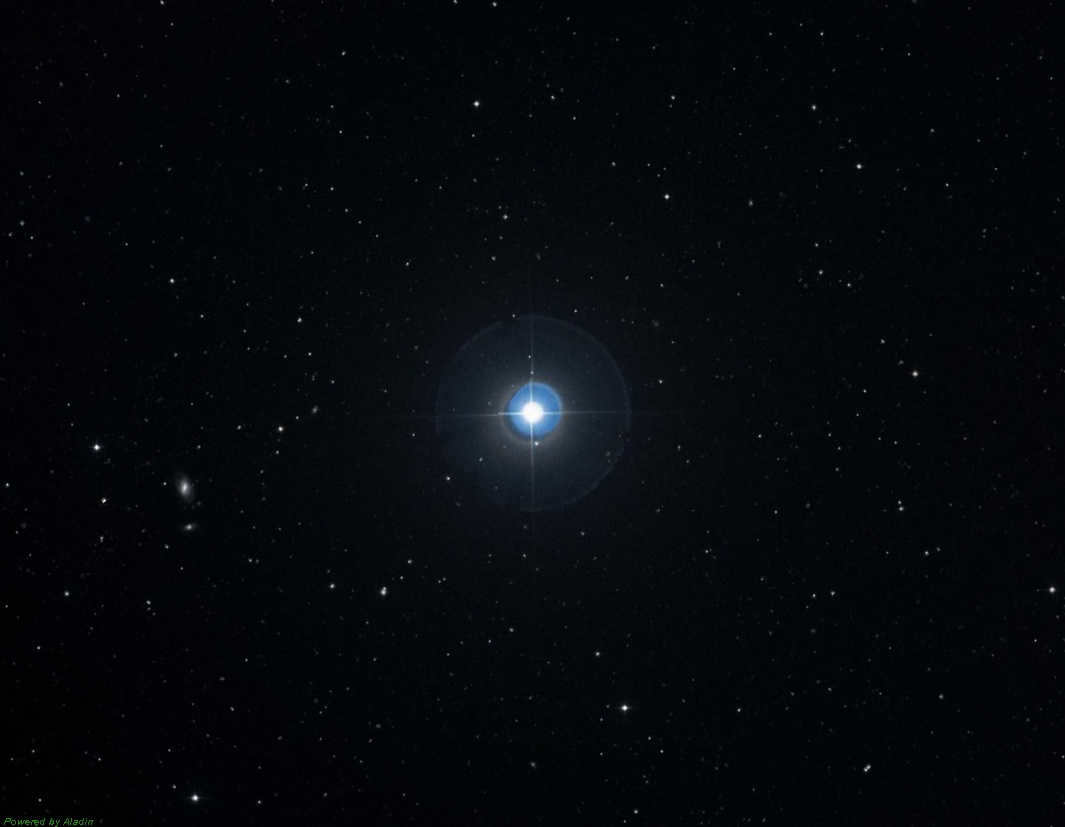

β Veronica’s Hair – provides us with a sneak peek of stars similar to our Sun. By observing it, we can get an idea of what it appears like from a distance of 27 light years. It possesses a stellar magnitude of 4.26.
Galaxies and Other Entities
Cluster of galaxies in Veronica’s Hair
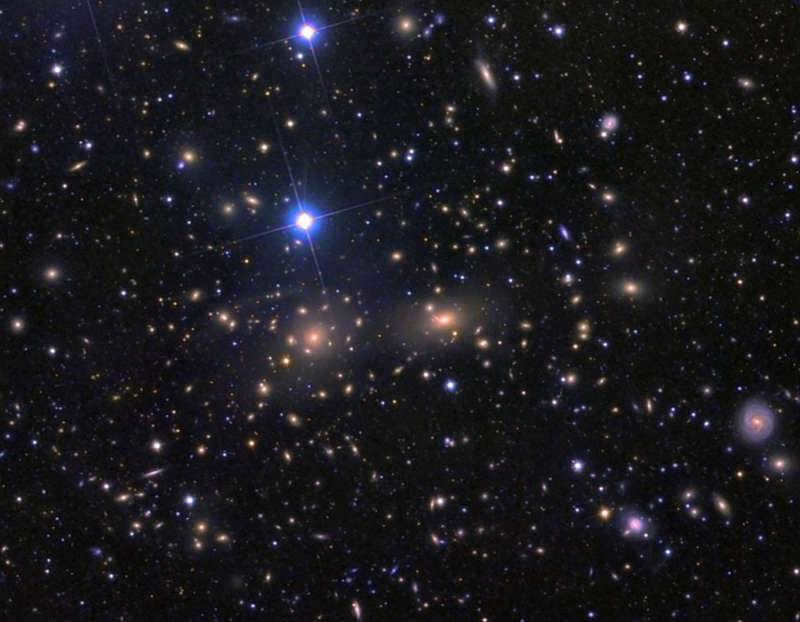

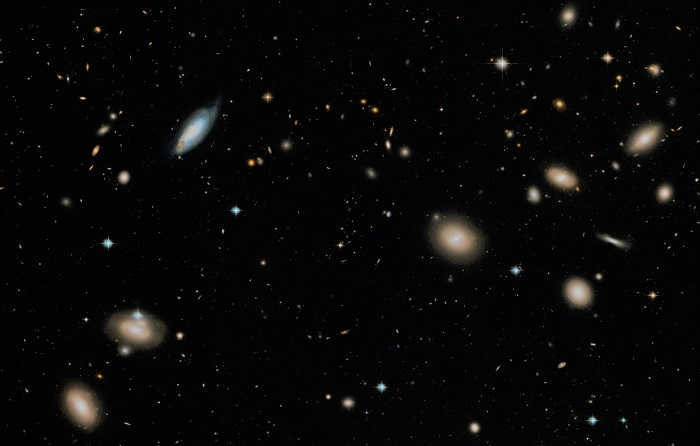
Coma galaxy cluster is the name given to a constellation that contains a remarkably bright and distant group of galaxies. It is situated approximately 370 million light years away. The cluster itself is known as Coma.
An overview of the Coma galaxy cluster, captured by the Hubble telescope

The galaxy M64, also known as the Black Eye galaxy, is distinguished by the presence of a massive dust cloud surrounding its core. This unique feature makes it a captivating sight when observed through a standard telescope.

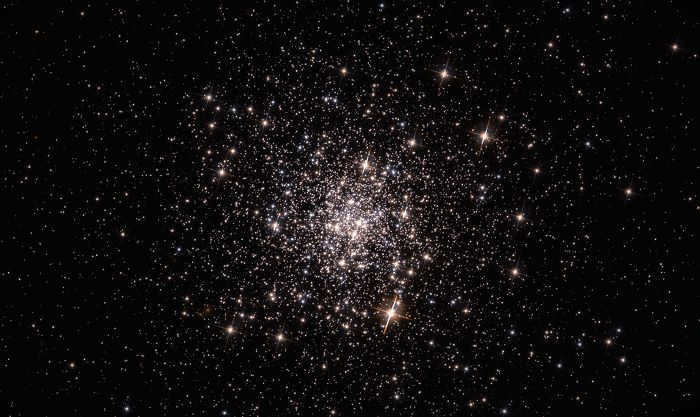
NGC 5053 Photo of a globular cluster
If you have a small telescope, it is simple to locate globular clusters in close proximity to us, such as M53 and NGC 5053, within the constellation.
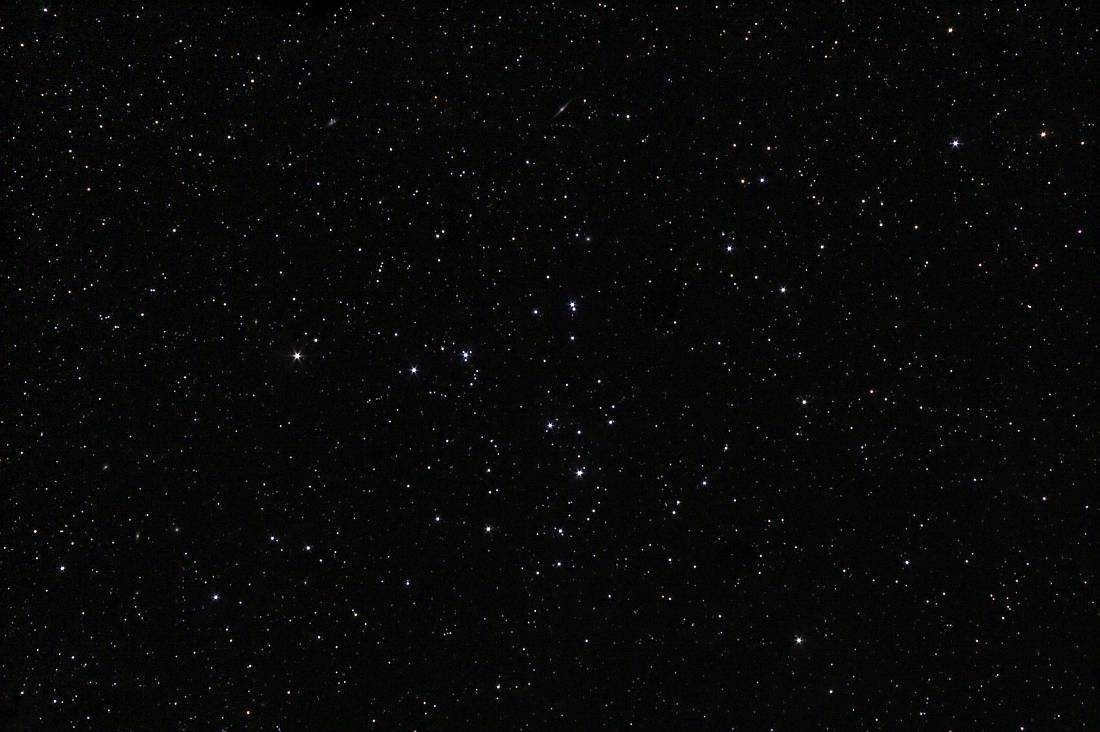

Image of the scattered cluster Mellot 111
Veronica’s Hair is the name given to a constellation that contains a well-known and expansive cluster of stars known as Mellot 111. This cluster is made up of a diffuse arrangement of stars with varying magnitudes, ranging from 5 to 10. Occupying a significant portion of space within Veronica’s Hair, the Melotte 111 cluster is estimated to be located approximately 270 light-years away from our position.
The Past
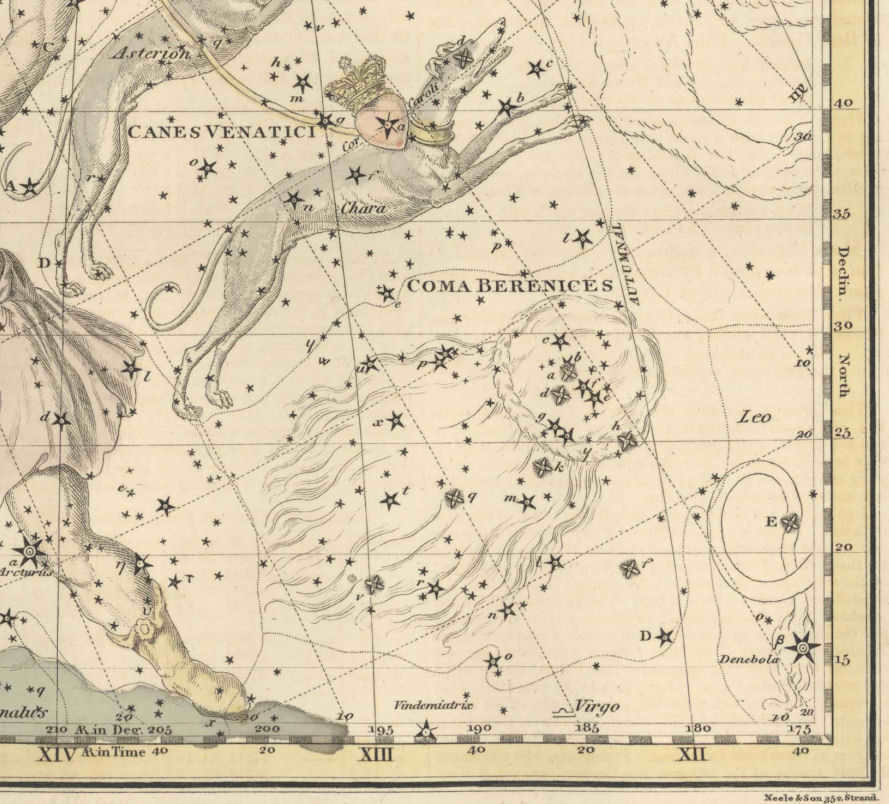

The constellation Veronica’s Hair is depicted in an ancient sky atlas.
Veronica’s Hair was not recognized as a separate constellation until the third century BC, prior to which it was a part of Leo. Claudius Ptolemy documented this in his writings. In ancient times, this constellation was known as an asterism. It derives its name from the wife of Egyptian Pharaoh Ptolemy III, who was called Berenike, meaning “bearing victory.”

As early as 1536, the celestial globe created by Vopel featured an image of the constellation known as Berenices Crinis, which translates to Veronica’s Hair. This constellation was officially included in Tycho Brahe’s catalog in 1602.
During that time, the constellation had various names like “Hair,” “Hair of Virgo,” “Strand of hair,” “Braids,” and eventually became known as “Hair.” Eventually, it acquired the modern Latin name “Coma Berenices” (known as “Hair of Veronica” or “Hair of Berenice” in Russian).
At times, Hair of Veronica is also referred to as Hair of Ariadne or Venus (Aphrodite).
Veronica’s Hair is a group of stars located in the northern hemisphere, covering an area of 386 square degrees. It is surrounded by the constellations of Volopassus, Hound Dog, Big Dipper, Leo, and Virgo. There are approximately 60 stars in Veronica’s Hair that can be seen without the use of a telescope. The best time to observe this constellation is during the months of April and May. However, due to the lack of bright stars, it can be challenging to locate in the night sky. It is recommended to use the neighboring constellations as a guide.
To locate Veronica’s Hair, you can draw an imaginary straight line connecting the bright stars Arcutur (Alpha Volopasa) and Mufrid (Eta Volopasa). This line will point you towards Diadema (Alpha Veronica), the brightest star in the constellation. Another reference point is Denebola (Alpha Leo), which marks the western boundary of Veronica’s Hair. The constellation is also home to a cluster of extragalactic nebulae.
Within Veronica’s Hair, there is a star cluster called Melotte 111. This cluster is located approximately 280 light years away from Earth and consists of 50 stars. The topmost star in the cluster is Gamma, which is slightly brighter than the others. Another notable feature of Veronica’s Hair is the Virgo cluster of galaxies, which partially overlaps with the constellation. Additionally, there is a massive cluster of galaxies located in Veronica’s Hair and Leo, approximately 290 million light years away.
With a small telescope, you can observe nearby globular star clusters such as M53 and NGC 5053. The Black Eye galaxy (M64) is also visible, with its distinctive dark dust cloud surrounding the nucleus. The brightest star in Veronica’s Hair is Beta, which has a magnitude of 4.0. This star closely resembles the Sun in terms of its characteristics and provides a glimpse of what our own star may look like from a distance of 27 light years.
Diadema (Alpha Veronica Hair) is the only star in the constellation that has its own name. It is a double star with a magnitude of 4.0 and is believed to be an eclipsing variable star. The components of Diadema are nearly equal in magnitude.
Veronica’s Hair is located at the north pole of the Galaxy, offering a view of thousands of galaxies and hundreds of galaxy clusters.
Celestial arrangement of the celestial stars of the constellation Veronica’s Hair:
The constellation Veronica’s Hair
Veronica’s Hair is a constellation situated in the northern hemisphere. Translated literally, it signifies “Berenice’s Hair” and was named in honor of Queen Berenice II of Egypt. Ptolemy believed it to be a star cluster within the Leo constellation (the tip of its tail). Only in the 16th century did it become recognized as a distinct constellation on Caspar Vopel’s Astronomical Globe. However, Tycho Brahe, who included it in his 1602 catalog, is still regarded as its discoverer.
Despite being relatively small, the constellation of Veronica’s Hair is home to numerous renowned celestial objects, such as the Black Eye Galaxy (Messier 64), Messier 98, Messier 99, Messier 100, the globular cluster Messier 53, the Needle Galaxy (NGC 4565), and the Veronica’s Hair Galaxy Cluster. Additionally, it encompasses the northern section of the Virgo cluster. An interesting fact about the constellation of Veronica’s Hair is that it includes the North Galactic Pole.
Facts, Location, and Map
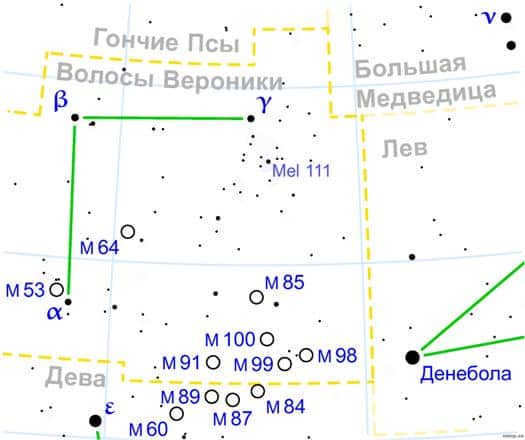
The constellation Veronica’s Hair is ranked 42nd in size, covering an area of 386 square degrees. It is situated in the third quadrant of the northern hemisphere (NQ3), and its latitude ranges from +90° to -70°. It shares borders with Leo, Virgo, the Big Dipper, the Hound Dogs, and the Wolf.
Within Veronica’s Hair, there are two stars known to have planets, as well as 8 Messier objects: M53 (NGC 5024), the Black Eye Galaxy (M64, NGC 4826), M85 (NGC 4382), M88 (NGC 4501), M91 (NGC 4548), M98 (NGC 4192), M99 (NGC 4254), and M100 (NGC 4321). The brightest star in this constellation is Beta Veronica’s Hair. Additionally, there is a meteor stream known as Coma Berenicesida.
Veronica’s Hair is part of a collection of constellations that includes Wolopassus, Giraffe, Dragon, Big Dipper, Little Dipper, Lynx, Little Lion, Northern Crown, and Hound Dogs. A star map provides a visual representation of the constellation, showcasing its prominent stars, celestial objects, and neighboring constellations.
The legend of the constellation known as Veronica’s Hair revolves around a historical figure, Queen Berenice II of Egypt. Queen Berenice was married to Ptolemy II, who was engaged in a conflict against the Seleucids following the murder of his sister in 243 BC, known as the Third Syrian War. Concerned for her husband’s safety, Queen Berenice made a vow to the goddess Aphrodite, offering to cut off her beautiful long locks if her husband survived.
Upon her husband’s safe return, Queen Berenice immediately fulfilled her promise and placed her hair in the temple of Aphrodite. However, the next day, her hair mysteriously disappeared, much to the king’s anger. An astronomer explained that Aphrodite was so enamored with Queen Berenice’s hair that she decided to elevate it to the heavens, forming the constellation we now know as Veronica’s Hair.
The main celestial bodies
Here is an introduction to the celestial bodies of the star group known as Veronica’s Hair, including detailed descriptions and characterizations.
Diadema (Alpha of Veronica’s Hair) is a binary star system composed of two stars belonging to the spectral class F5V. Their magnitudes are 5.05 and 5.08 respectively. This system is located 63 light-years away. The two stars appear to move in a straight line, almost to the point where they seem to oscillate, with a maximum separation of 0.7 arc seconds.
The diadem is the second brightest star in the constellation, with an apparent magnitude of 4.32. It represents the jewel in Queen Berenice’s crown. The term diadem is derived from the Greek word διάδημα (diádēma), meaning “stripe”.
Beta Veronica Hair is the most luminous celestial body in its constellation, despite being classified as a beta star, with a visual magnitude of 4.26. It is a main-sequence dwarf, located 29.78 light-years away. It bears a resemblance to the Sun, albeit slightly larger and brighter. Notably, there are no known planets in its orbit.
Gamma of Veronica’s Hair, on the other hand, is a colossal star categorized as a K1II spectral class giant. It boasts an apparent magnitude of 4,350 and is positioned 170 light years away.
FK Veronica’s Hair, another notable star in the constellation, is a variable star with an apparent magnitude that ranges from 8.14 to 8.33 over a span of 2.4 days. It serves as a prototype for FK Com class variable stars, which are characterized by having large cold spots on their rotating surfaces. Classified as a G5II star, it is situated 800 light years away.
Cosmic entities
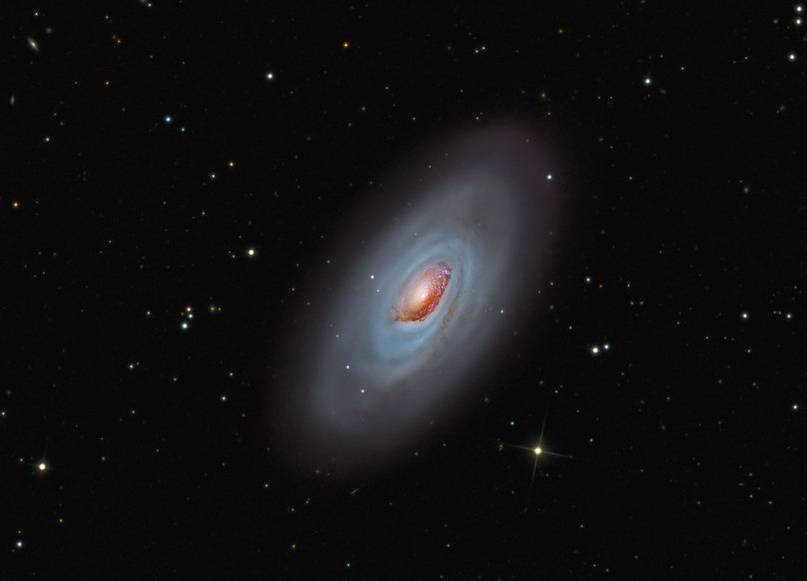
Messier 64, also known as the Black Eye Galaxy or NGC 4826, is a breathtaking spiral galaxy located approximately 24 million light-years away. With an apparent magnitude of 9.36, this celestial object is often referred to as the Sleeping Beauty Galaxy or the Evil Eye Galaxy.
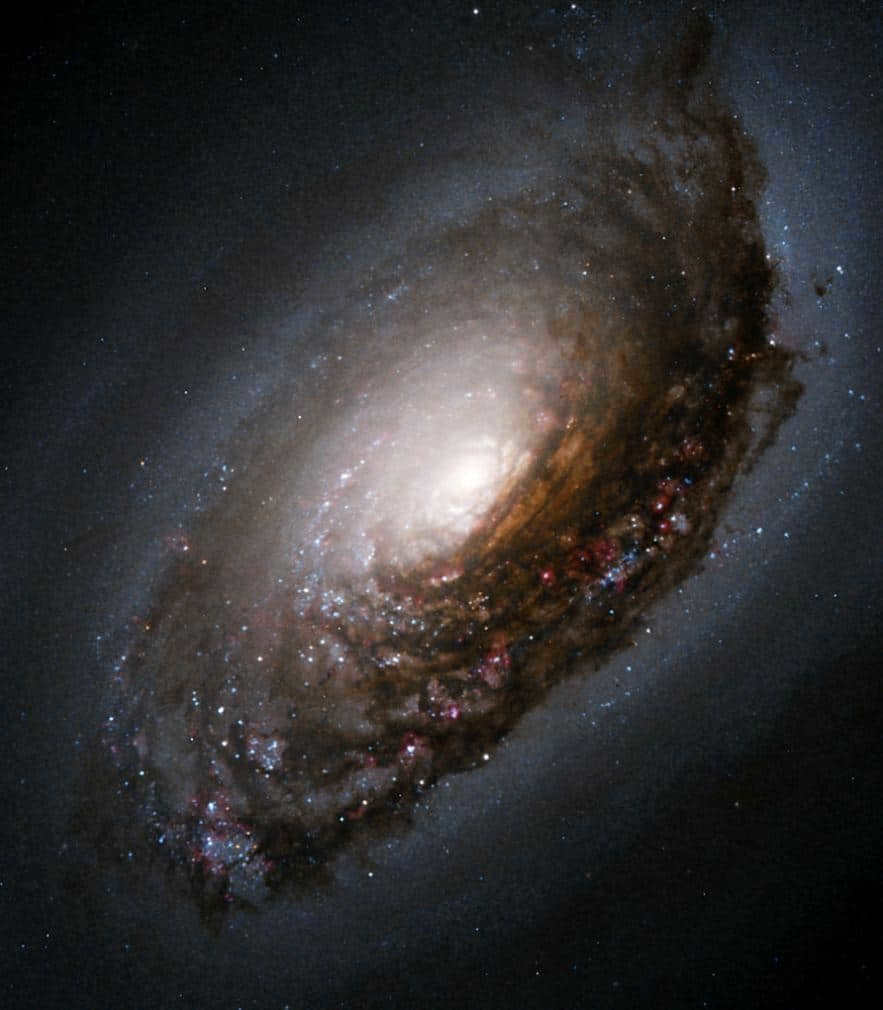

Located in the constellation of Veronica’s Hair, the galaxy known as M64 is a popular target for amateur astronomers due to its easy visibility even with a faint telescope. It stands out with its bright nucleus and a distinctive dark dusty streak that has earned it the nickname “Evil Eye.”
M64 is no ordinary galaxy, as it exhibits a unique characteristic where the gas in its outer regions rotates in the opposite direction compared to its inner regions. It is speculated that M64 may have absorbed a smaller satellite galaxy approximately one billion years ago.
NGC 4565, also known as the Needle Galaxy, is a well-known spiral galaxy that can be easily spotted in the night sky.
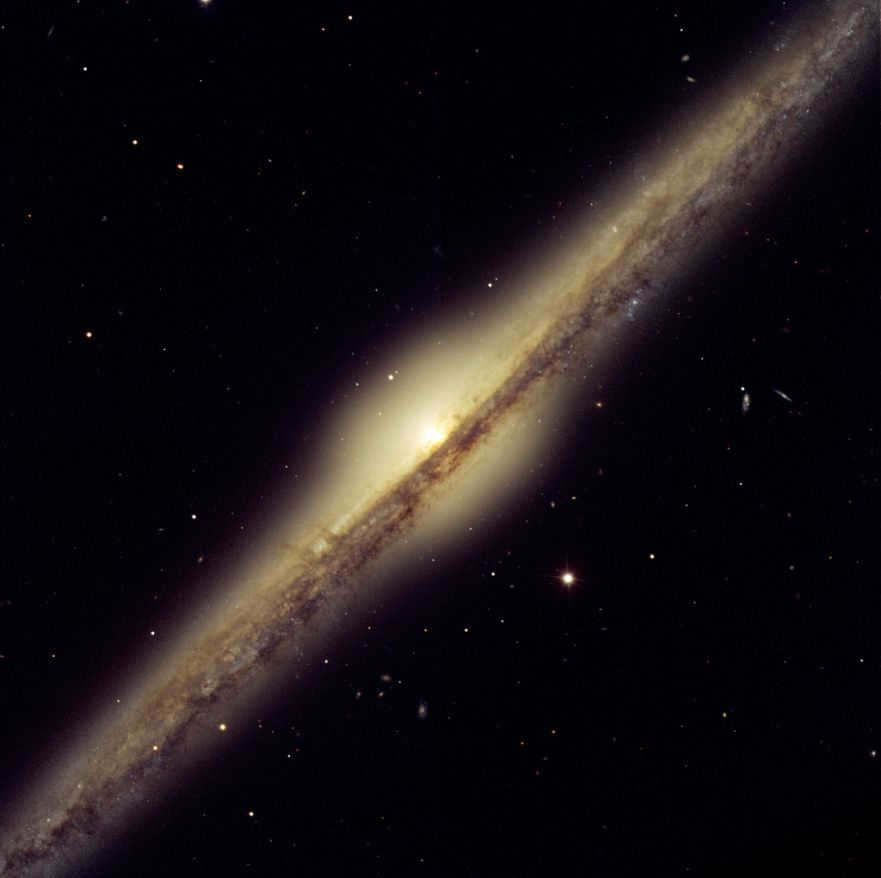

The constellation Veronica’s Hair is named after the Greek mythological figure Veronika, who was known for her long, flowing locks. This constellation was first discovered in 1785 by the astronomer William Herschel. It can be easily observed using a small telescope. Located just above the Galactic North Pole, it is positioned 1 degree east of the star 17 Veronica’s Hair. With a visual magnitude of 10.42 and a distance of 42.7 million light years, this constellation is a fascinating sight in the night sky.
Astronomers have determined that NGC 4565, which is part of the Veronica’s Hair constellation, is a spiral galaxy with a central bulge. Its unique shape has led scientists to believe that it has a junction. This galaxy stretches an impressive 16 angular minutes in length, making it a notable feature within the constellation.
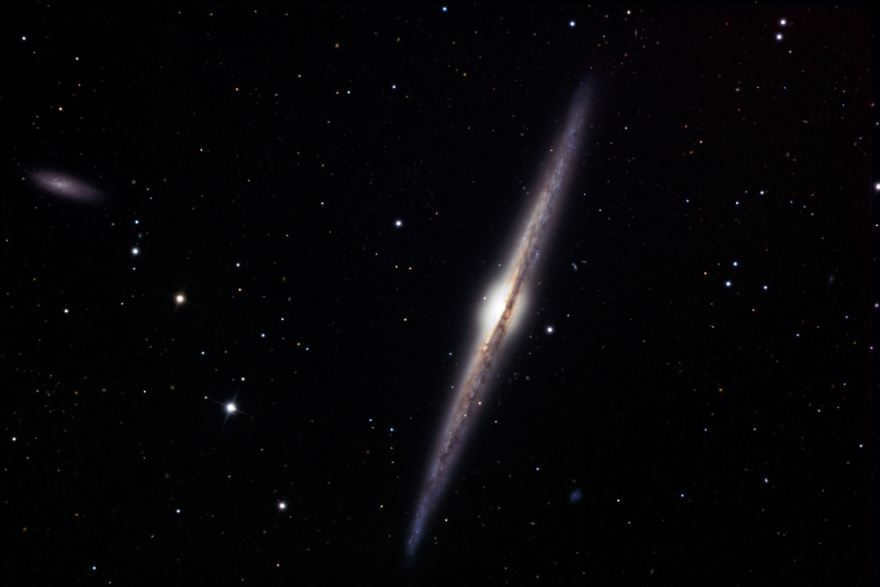

NGC 4562 and NGC 4565 are two galaxies in close proximity to each other.
Melott 111 is a compact star cluster that contains 40 luminous stars ranging in magnitude from 5 to 10.

The constellation of Veronika’s Hair has been given its name due to its unique arrangement of stars. It was first documented by Philibert Jacques Melotte and spans an impressive 7.5 degrees across the night sky. This stellar cluster is estimated to be approximately 450 million years old and is located a staggering 280 light years away from Earth.
Distinct from the neighboring Virgo cluster, Veronika’s Hair is positioned further in the cosmos, at a distance of approximately 230-300 million light years from our own galaxy.
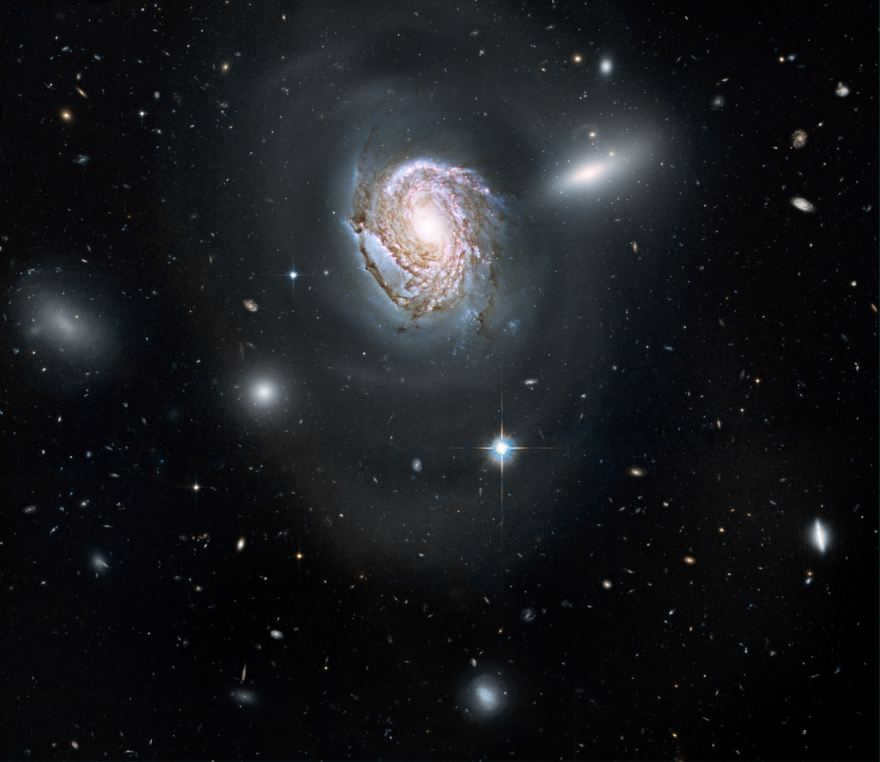

The cluster of galaxies known as Veronica’s Hair gets its name from the spiral galaxy NGC 4911 that is located within it.
Veronica’s Hair cluster is home to approximately 1,000 large galaxies and 30,000 smaller galaxies, with most of them having a brightness greater than 19.0. The brightest galaxies in the cluster, NGC 4889 and NGC 4874, have a magnitude of 13. Another notable member of the cluster is NGC 4921, which is the brightest spiral galaxy in the cluster.
The Virgo cluster, which is located 60 million light-years away from Earth, contains the northern part of the Veronika cluster. Notable galaxies within the Virgo cluster include M100, M85, M99, M88, and M91.
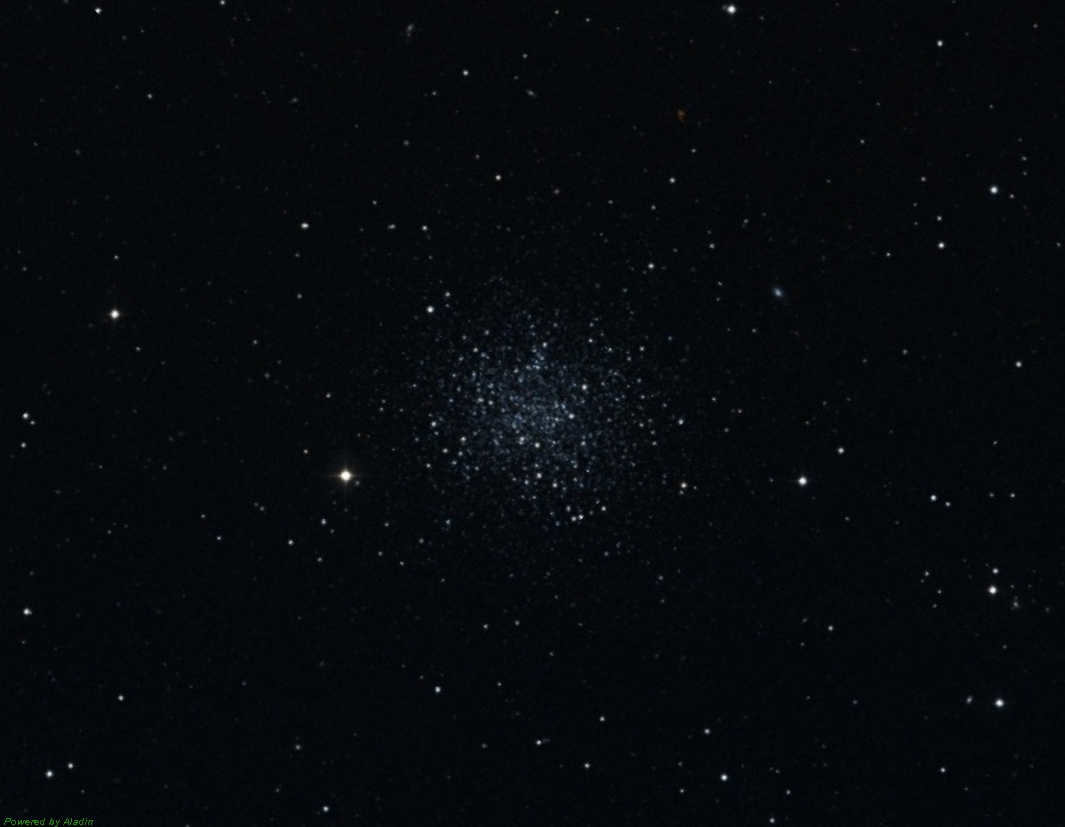
Messier 53 (M53, NGC 5024) is a globular cluster that is situated 58,000 light-years away from Earth and 60,000 light-years away from the Galactic Center.

The constellation of Veronica’s Hair is named after the famous character from Greek mythology. It has a distinct round shape and a remarkably bright center. This celestial object was first discovered by Johann Bode in 1775 and later added to Charles Messier’s catalog in 1777. M 53 is known as one of the most distant globular clusters and has a visible visual magnitude of 8.33. Interestingly, its stars are characterized by their low metal content.
If you’re looking to observe M 53, it can be found northeast of the star Alpha Veronica Hair. This particular star is the brightest Messier object in the constellation and can even be seen with binoculars.
Another fascinating astronomical object is Messier 100 (M100, NGC 4321), a massive spiral galaxy. It showcases a brilliant nucleus and features two prominent spiral arms along with several smaller ones. Additionally, there are dusty streaks that add to its captivating appearance.
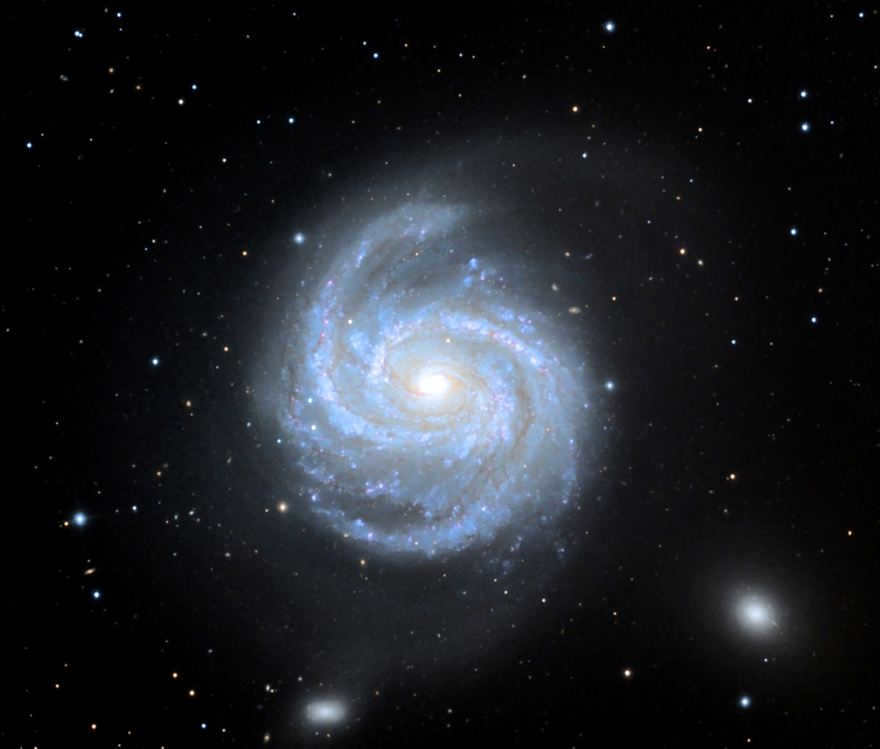

The reason why the constellation Veronica’s Hair is named as such is because it is situated in the Virgo cluster, which is one of the brightest members of this cluster. The size of Veronica’s Hair is approximately 7 angular minutes across. With a diameter spanning 160,000 light-years, it is located at a distance of 55 million light-years. Its apparent magnitude is 10.1. Pierre Mechene discovered it on March 15, 1781, making it one of the first spiral galaxies ever found. Since its discovery, five supernovae have been observed within it. NGC 4323, a satellite galaxy, is also located within Veronica’s Hair and is situated 52.5 million light-years away with an apparent magnitude of -15.7.
Messier 85 (M85, NGC 4382) is classified as a lenticular galaxy. It is one of Messier’s most distant objects, being located 60 million light-years away.
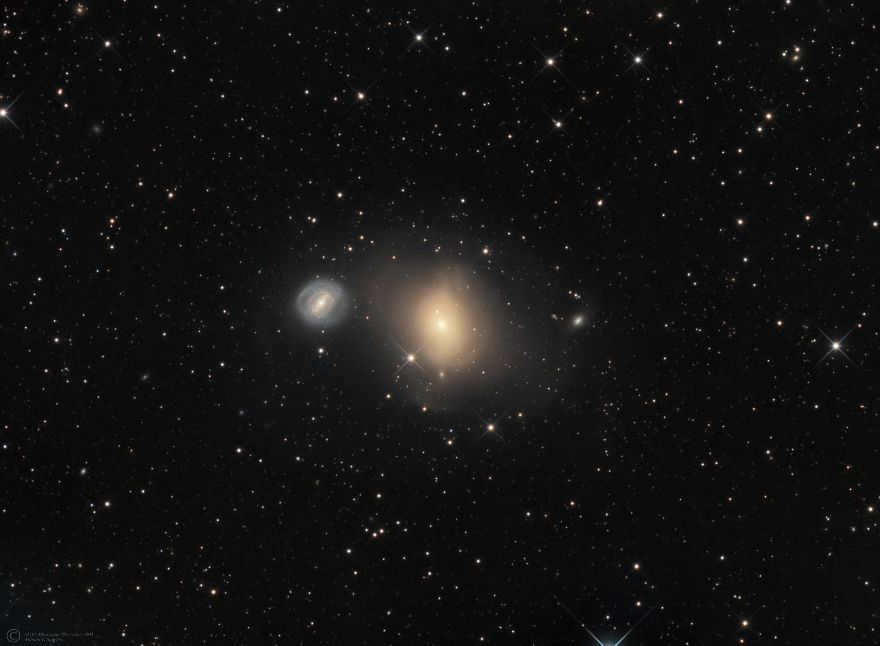

The constellation of Veronika’s Hair is named so for a specific reason. It is because this galaxy has a diameter of 125,000 light-years and has an apparent magnitude of 10.0. This galaxy was first discovered in 1781 by Pierre Messier. It holds the distinction of being the northernmost member of the Virgo Cluster. Interestingly, a supernova was observed in December 1960 within this galaxy.
In addition to its unique characteristics, this galaxy also interacts with two smaller neighboring galaxies: the spiral galaxy 4394 and the elliptical MCG 3-32-38.
Messier 99 (also known as M99 or NGC 4254) is another notable spiral galaxy. It lacks a junction and has an apparent magnitude of 10.4. This galaxy is located at a distance of 50.2 million light-years.
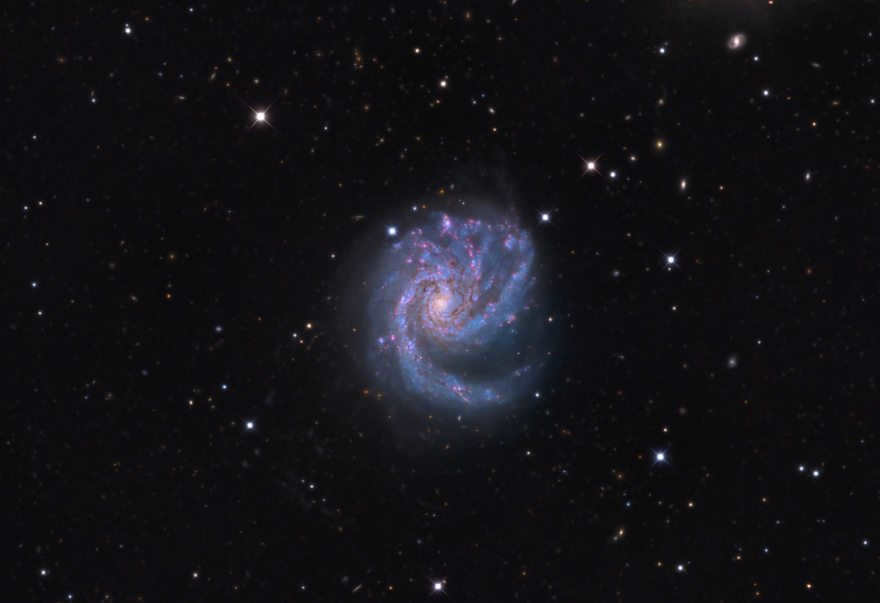

Messier 99 (NGC 4254) is referred to as such because of the distinctive presence of metal-rich H II regions.
It was initially discovered in 1781 by Pierre Méchaine and later included in Charles Messier’s catalog. Over the years, three supernovae have been observed within its vicinity. There is a possibility that it has been influenced by the presence of the nearby dark galaxy VIRGOHI21, as there is a connecting bridge of neutral hydrogen gas between the two.
Messier 88 (M88, NGC 4501) is another spiral galaxy that was identified by Charles Messier in 1781.
It has a visible magnitude of 10.4 and is located at a distance of approximately 47 million light-years. What sets it apart is that it is classified as a Seyfert galaxy, which means it emits narrow spectral emission lines due to the presence of highly ionized gas in its nucleus.
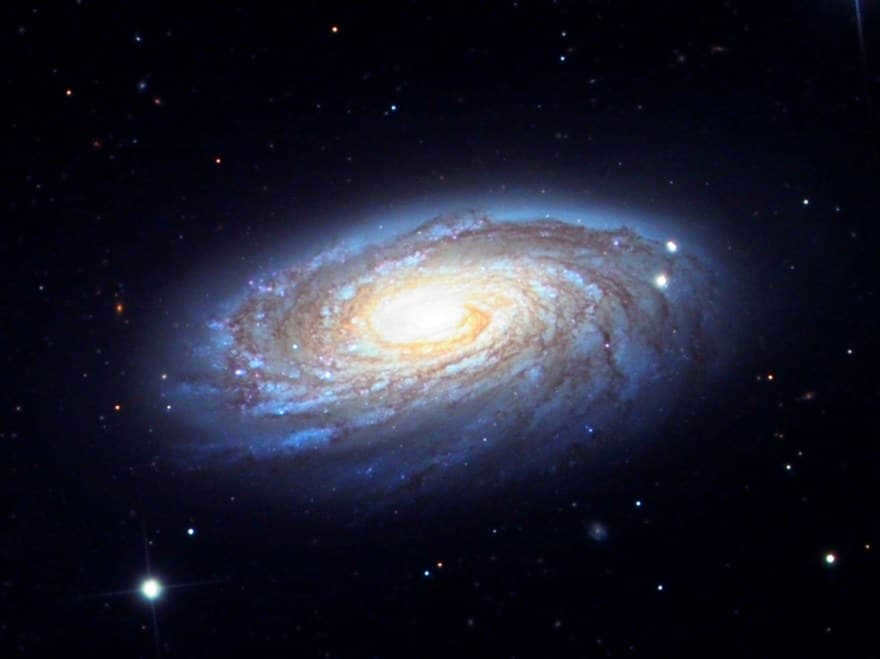

It contains multiple spiral arms and a supermassive black hole at its center, which is 80 million times the mass of the sun. M88 is one of the 15 Messier objects found in the Virgo Cluster. In 1999, a supernova was observed in this galaxy.
Messier 91 (M91, NGC 4548) is a spiral galaxy located in the Virgo Cluster.
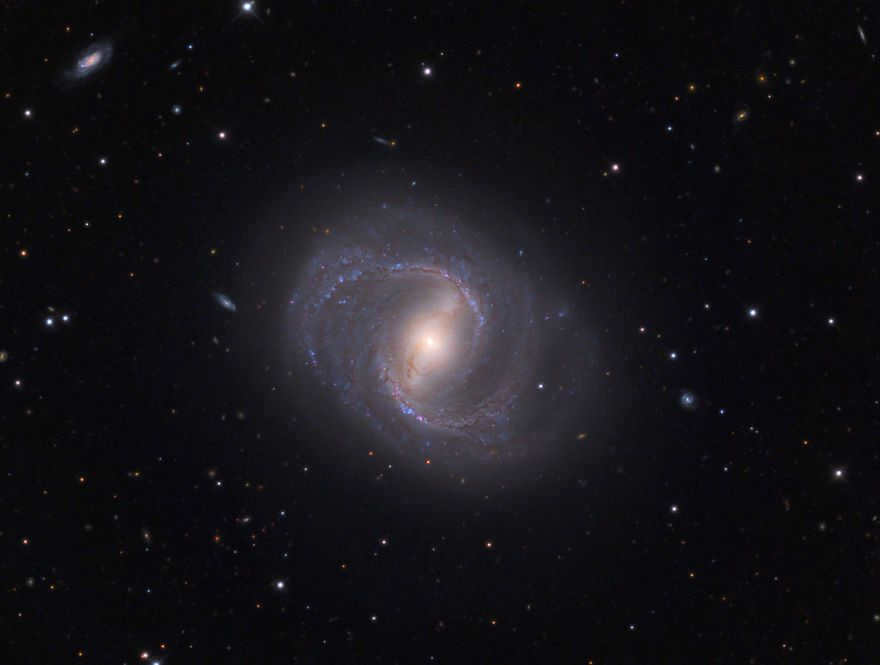

With a visual magnitude of 11.0, the constellation of Veronika’s Hair is named so for a reason. It can be found approximately 63 million light-years away from us and was originally discovered by Charles Messier in 1781.
Messier 98 (M98, NGC 4192) is a spiral galaxy that is intermediate in size and has an elongated shape. It has an apparent magnitude of 11.0.
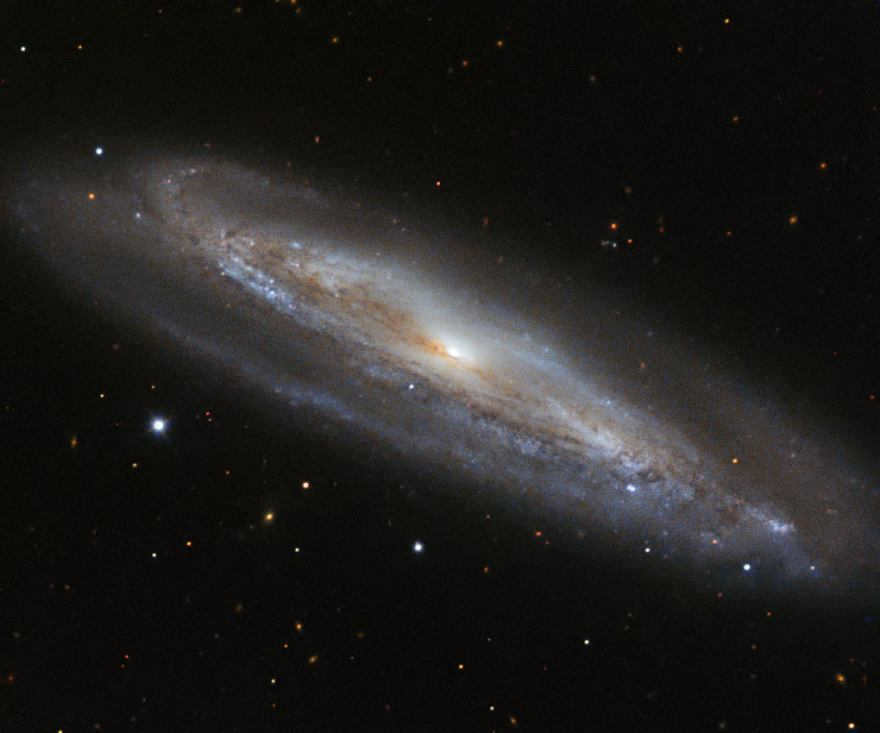

This particular constellation, known as Veronica’s Hair, is characterized by its small core and large, faint spiral arms. Situated 0.5 degrees to the west of the star 6 Veronica’s Hair, or 1.5 degrees to the west-northwest of Messier 99, it lies at a distance of 54.1 million light-years. Originally discovered by Pierre Mechene in 1781 and subsequently documented by Charles Messier in the same year, it is a member of the Virgo Cluster.
NGC 4889, also known as Caldwell 35, is an enormous elliptical galaxy with a magnitude of 11.4 and a distance of 308 million light-years.
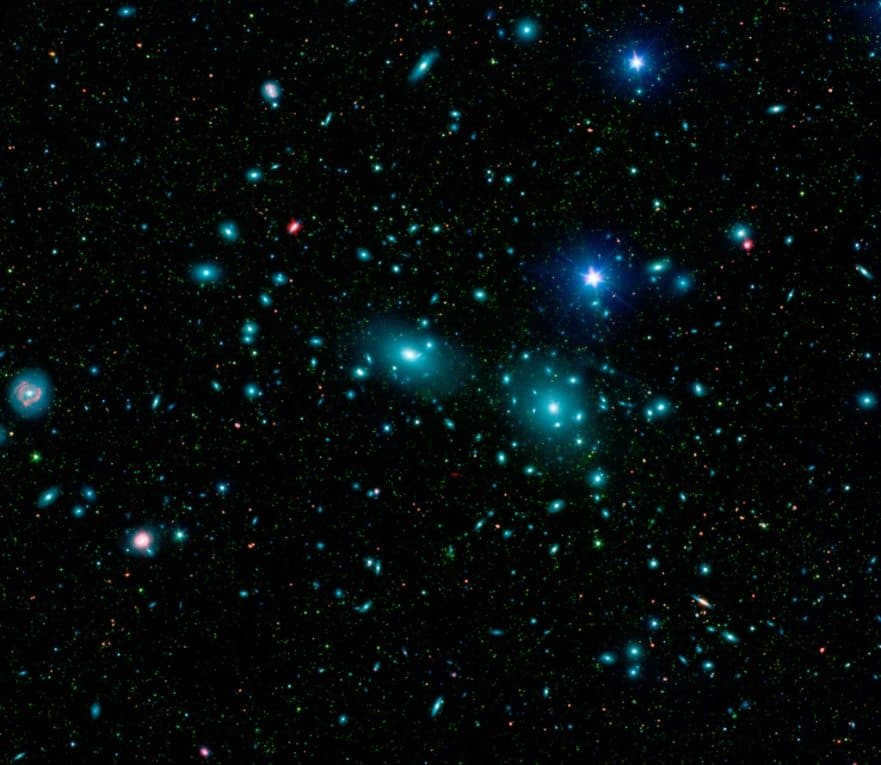

The galaxy cluster known as Veronica’s Hair, which includes NGC 4889 and NGC 4874, can be observed in the night sky.
Situated near the Beta star of the Veronica’s Hair constellation, this galaxy is a fascinating object to study.
NGC 4147 is a compact globular cluster with a faint appearance, having an apparent magnitude of 10.2. It may appear slightly blurry in smaller telescopes, but larger telescopes reveal its bright and round shape, lacking a distinct nucleus.
To explore Veronica’s Hair constellation in more detail, you can utilize not only our collection of photos but also 3D models and online telescopes. Additionally, a stationary or movable star map can aid in your personal search for this celestial wonder.
What is the origin of the name “Veronica’s Hair” for this constellation?
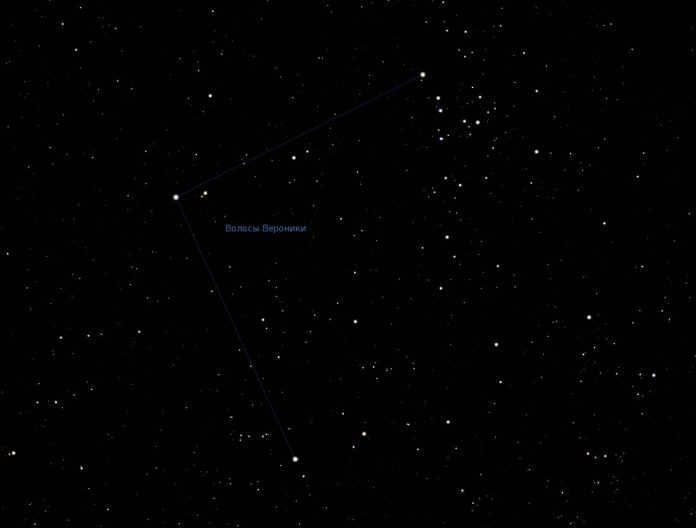
When gazing up at the night sky, one cannot help but be in awe of its vastness, enigma, and endlessness. It is likely that ancient astronomers experienced a similar sense of wonder, as they divided the celestial sphere into distinct regions, grouping individual stars into constellations. Each of these constellations was given a name that was associated with a significant event. One such constellation is known as “Veronica’s Hair”. The story behind this name is quite fascinating, and we would like to share it with you.
However, as it frequently occurs, life is brimming with unexpected turns. Conflict arose, and Ptolemy III was compelled to join the military in order to protect the nation. Veronica was deeply saddened by this turn of events. She fervently desired for her husband to return home safely, and to ensure this, she made a sacred promise to offer up her gorgeous hair to Aphrodite, the divine deity of love and beauty.
Veronica’s desire has come true and her spouse comes back home safe and sound. To commemorate this occasion, a grand gala is organized at the royal palace, during which the clergyman informs the attendees that Veronica’s mane, offered as a sacrifice to Aphrodite, has vanished. The monarch becomes furious and decides to punish the sentinels. However, an astrologer comes to their defense, asserting that Aphrodite has accepted Veronica’s offering and transported it to her celestial abode. He urges the audience to gaze up at the starry expanse, where a fiery plume is ablaze. In his perspective, that is none other than Veronica’s tresses.
What was the true nature of the incident? The whereabouts of Ptolemy’s wife’s hair remain a mystery. However, that is not the focus of this story. The events unfolded in 240 BC, when Halley’s comet made its close approach to Earth. This comet had a fiery tail that stretched across the sky for many kilometers. The ancient astrologers mistook this tail for Veronica’s hair. When the comet eventually disappeared, a constellation appeared in its place, which was named “Veronica’s Hair”.

Veronica’s Hair is a celestial object that can be easily observed in the night sky, particularly in the Northern Hemisphere. This constellation consists of not only stars but also galaxies and clusters. Covering an area of approximately 386.5 square degrees, Veronica’s Hair does not exhibit any striking features that can be readily discerned without the aid of a telescope.
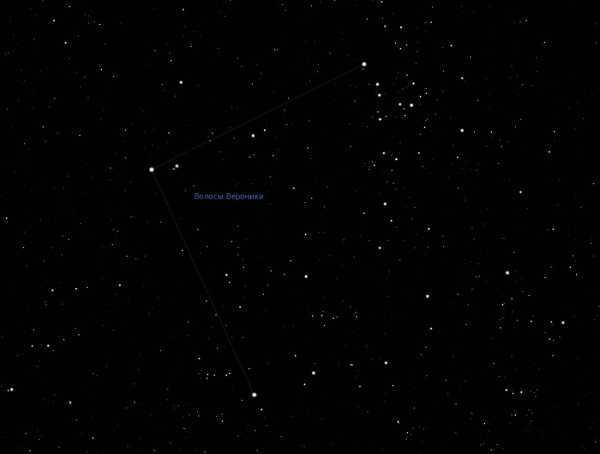

Veronica’s Hair is not easily visible in the starry sky because it does not have any prominent stars. However, it can be easily located with the help of its neighboring constellations. On the eastern side, it is bordered by the constellation of Volopassus, while Leo borders it on the west side. By connecting bright stars such as Arcturus and Mufrid with an imaginary line, you can determine the direction to look for the Diadem. On the west side, you can use Denebola as a reference point. This is where Veronica’s Hair intersects with the surrounding constellations. The best time to observe this constellation is in March and April when it rises high above the horizon, making it visible throughout Russia.
Engrossing items
During a night without a visible moon, it is possible to observe up to 64 luminous stars with the unaided eye in the constellation. In the constellation known as Veronica’s Hair, the north pole of our Milky Way galaxy can be found, with a direct entrance at 12h 51m and a declination of +27° 07'. Within this constellation, there are approximately 50 stars with a brightness exceeding the 6th magnitude. Among these stars, the two most significant ones are Diadem and β Veronica’s Hair.
Stellar Objects
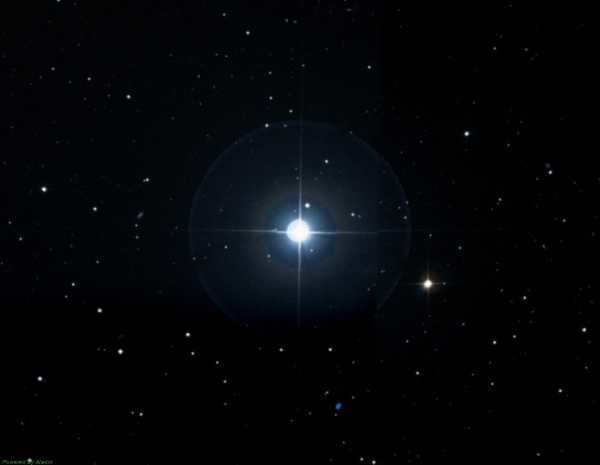

Diadema is known as the α Hair of Veronica. It is the second brightest celestial object in the constellation. This binary star system has a stellar magnitude of 4.32 and consists of two nearly identical components. It exhibits eclipsing variable behavior. Interestingly, Diadema is the only star in the constellation that has a unique personal name.
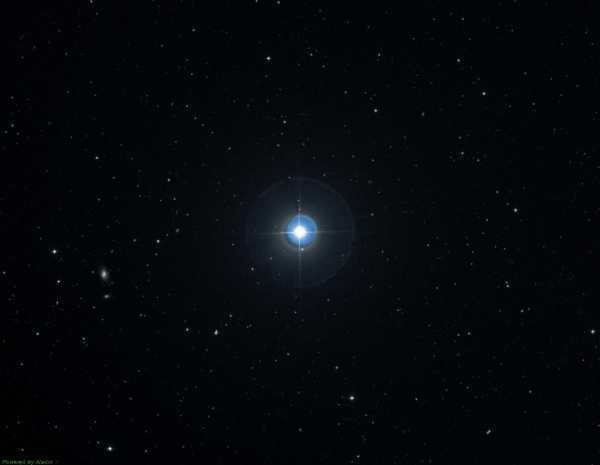


β Veronica’s Hair – provides us with a sneak peek into stars similar to our Sun. Observing it allows us to catch a glimpse of what our Sun would look like if it were located 27 light years away. It possesses a stellar magnitude of 4.26.
A group of galaxies located within the locks of Veronica.
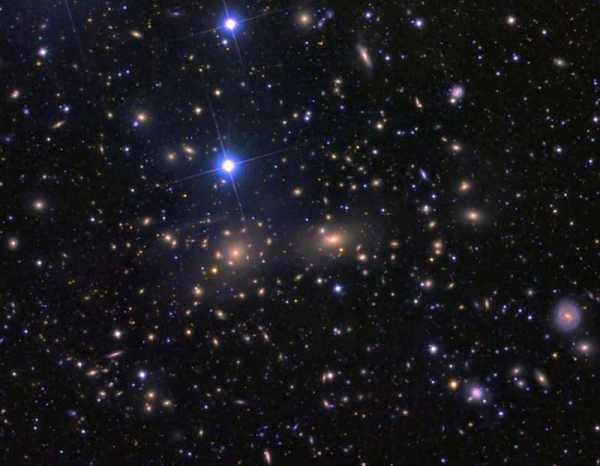

We can observe an extremely bright and remote group of galaxies in this specific constellation. It is situated at a distance of 370 million light years from us. This galaxy cluster is known as Coma.
An in-depth view of the Coma galaxy cluster, captured by the extraordinary Hubble telescope
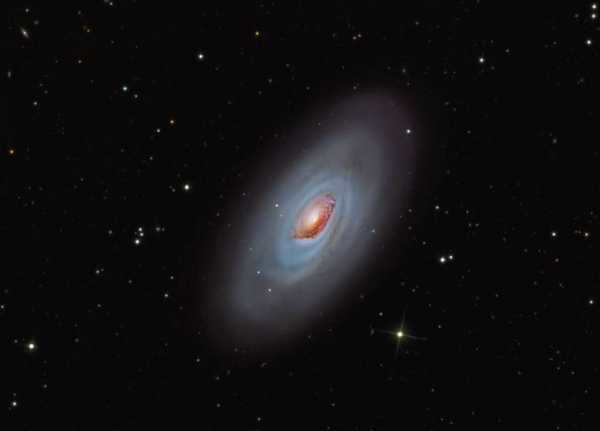

The galaxy M64, also known as the Black Eye galaxy, is characterized by the presence of a large dust cloud surrounding its central region. This unique feature makes it easily observable even with a regular telescope.
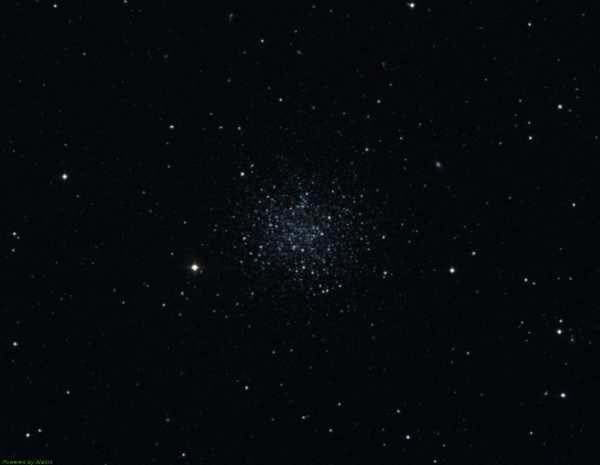

The constellation is named Veronica’s Hair and it is interesting to know why it is called that because in Greek mythology, Veronica was a goddess who transformed her hair into a cluster of stars. This cluster is known as NGC 5053 and it can be easily observed with a small telescope. Other globular clusters in the same constellation, such as M53, are also worth exploring.

Mellot 111.
The Mellot 111 cluster is a vast assemblage of stars situated near Veronica’s Hair. It consists of a dispersed collection of stars with luminosities ranging from 5 to 10 stellar magnitudes. The Melotte 111 cluster is located approximately 270 light years away from us.
Historical Background
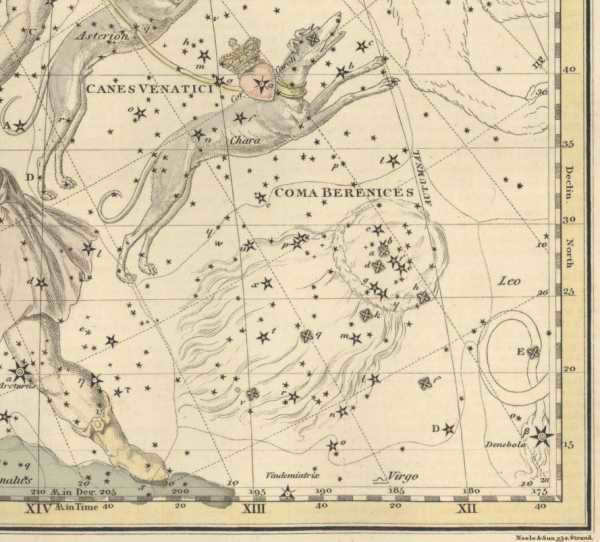

The constellation known as Veronica’s Hair was not recognized as a separate constellation until the 3rd century BC. Prior to that, it was considered a part of Leo. The ancient astronomer Claudius Ptolemy made note of this in his writings. In ancient times, Veronica’s Hair was regarded as an asterism, or a smaller grouping of stars within a larger constellation. Its name is derived from the Egyptian Pharaoh Ptolemy III’s wife, Berenike, which means “bearing victory.”