- Planets
Neptune, the eighth planet from the sun, holds the distinction of being the furthest planet in our solar system. Classified as a gas giant, Neptune is part of the outer solar system’s planetary category. After the demotion of Pluto, Neptune became the last planet in the lineup.
Due to its distance from Earth, Neptune cannot be easily observed without the aid of instruments. Its discovery came relatively recently, with the first observation made during the Voyager 2 flyby in 1989. Let’s explore some interesting facts about the planet Neptune.
Following Pluto’s reclassification as a dwarf planet, Neptune reclaimed the title of the farthest planet from the Sun. It orbits at an average distance of 4.5 billion kilometers from the star.
Interesting fact: It takes approximately 253 minutes for sunlight to reach Neptune at this distance.
The distance from Earth to the farthest planet is not constant, but rather varies between 4.3 and 4.553 billion kilometers. As time goes by, Neptune either gets closer or further away from us by 253 million kilometers. Due to this considerable distance, it is impossible for people to observe the planet with the naked eye. In order to catch a glimpse of Neptune, one would need a telescope with a minimum radius of 12.5 cm and a zoom capability of two hundred times. Even with such equipment, the planet would only appear as a tiny dot.
Neptune is known for its distinct blue hue, which is caused by the abundance of methane in its atmosphere. This gas absorbs the red colors that are present on the planet’s surface, rendering them invisible to our eyes. Additionally, Neptune holds the record for having the fastest winds in our solar system. Storms on the planet can reach speeds of up to 2400 km/h.
The dimensions, weight and path of Neptune, the planet

Neptune’s equatorial diameter measures 24,764 kilometers, making it four times larger than Earth. In terms of weight, Neptune is 17 times heavier than Earth but 19 times lighter than Jupiter. As a result, Neptune falls somewhere between the giant planets like Jupiter and Saturn and the terrestrial planets like Earth.
The planets closest to Neptune are Uranus, which is located closer to the Sun, and Pluto, which is now classified as a dwarf planet.
Neptune completes a full orbit in 164.79 Earth years, and in 2011 it achieved its first complete revolution since its discovery.
Neptune’s orbital inclination is 28.320, similar to that of Earth and Mars, resulting in seasonal changes that occur at a much slower pace on the gas giant. Each season on Neptune lasts approximately 40 Earth years.
The rotation period of Neptune is 16 hours, which coincides with the magnetic field rotation. However, due to its gaseous composition, the actual rotation rate varies at different latitudes. For instance, the widest equatorial belt completes a revolution in 18 hours, whereas the narrower middle and polar belts rotate at a faster pace. The circumpolar regions complete a revolution in 12 hours. This significant difference in rotation rates is more pronounced in Neptune compared to other planets.
Composition and Surface of Neptune

The ice giants Uranus and Neptune are classified separately for a good reason. Neptune has a rocky core composed of silicates and metals at its center, surrounded by an icy mantle made up of methane ice, water, and ammonia. Above the mantle lies an atmosphere consisting of helium, hydrogen, and methane.
However, it is important to note that Neptune’s mantle is not a frozen liquid. Despite its name, the mantle is actually very hot due to the immense pressure it experiences. The temperature reaches a range of 2000-5000 K, similar to the surface temperature of the Sun. Despite its high temperature, the substance formed under such extreme pressures is still referred to as ice, although it is a highly dense and hot liquid primarily composed of ammonia. This unique state is known as hot ice.
It is believed that, under immense pressure and temperature at a depth of 7000 km, methane transforms into diamond crystals, which then sink closer to the core. This process may even lead to the creation of a massive layer rich in diamonds.
The Earth’s Atmosphere

The upper layers of Neptune’s atmosphere consist of a mixture of hydrogen and helium, with a ratio of 4:1 between the two components. As the atmosphere gets closer to the ice shell, the presence of methane increases, giving the planet its distinctive blue color. In addition, clouds of ammonia and hydrogen sulfide form in the lower layers of the atmosphere.
Similar to other large celestial bodies in the solar system, Neptune’s atmosphere can be divided into four main regions: the troposphere, stratosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. In the troposphere, which is the layer closest to the surface of the ice giant, the temperature decreases to a minimum of -213°С before rising again to -103°С in the upper atmosphere. The thermosphere, on the other hand, experiences an anomalous warming, with temperatures reaching up to 470°С.
Weather and climate
Weather and atmospheric conditions
Weather and the Earth’s climate
The connection between weather and climate

The average temperature of Neptune cannot be calculated as it lacks a solid surface. The planet’s core reaches temperatures of 5500° C, while the mantle varies between 4700° C and 1700° C. The coldest area is the upper troposphere, which cools to -213°.
Neptune experiences seasons due to its similar axial tilt to Earth. However, these seasons last much longer, spanning over 40 years. Since 1980, the southern hemisphere has been in summer, and in 2020, the northern hemisphere will transition into its summer season.
Rings of Neptune

The discovery of Neptune’s ring system remained unknown for over 120 years after its initial discovery. It wasn’t until 1989, when the interplanetary probe Voyager-2 confirmed their existence.
Neptune, the eighth planet in our solar system, is home to a total of 5 rings. The closest ring to the planet’s surface is called the Halle ring, located approximately 42,000 kilometers away. Following the Halle ring are the Leverrier, Lascelles, and Arago rings. The last ring, named after the British mathematician Adams, is situated 63,000 km from Neptune and consists of five arcs known as Bravery, Freedom, Equality 1, Equality 2, and Fraternity.
Composed of water ice, silicon salts, and believed to contain organic matter, Neptune’s rings possess a distinct reddish hue.
Satellites
Satellites are objects that orbit around larger celestial bodies, such as planets or moons. They can be natural, like the Moon orbiting around Earth, or artificial, like the numerous communication and weather satellites that humans have launched into space.
Natural satellites form as a result of the gravitational pull between two objects. For example, the Moon orbits around Earth because of Earth’s gravitational pull. Artificial satellites, on the other hand, are man-made objects that are launched into space and placed into orbit around a celestial body. They serve a variety of purposes, such as communication, weather monitoring, navigation, and scientific research.
Satellites play a crucial role in modern society. Communication satellites allow for global communication, enabling us to make phone calls, send text messages, and access the internet from virtually anywhere on Earth. Weather satellites provide us with valuable data that helps us predict and monitor weather patterns, improving our ability to prepare for natural disasters. Navigation satellites, such as the Global Positioning System (GPS), allow us to accurately determine our location and navigate our way around the world.
Additionally, satellites are used for scientific research and exploration. They are equipped with various instruments and sensors that collect data about the Earth, the universe, and everything in between. This data is invaluable for scientists studying climate change, natural disasters, and the mysteries of space.
In conclusion, satellites are essential tools that have revolutionized the way we communicate, navigate, and understand the world around us. Whether they are natural or artificial, these orbiting objects have become an integral part of our daily lives and continue to contribute to our knowledge and advancement as a civilization.

The most distant planet in our solar system is home to a total of 14 natural satellites that have been discovered up until now. The largest moon of Neptune is Triton, which was found just 17 days after the planet itself was first observed. Its surface is covered in an icy shell and is home to numerous active cryovolcanoes.
Triton is the biggest moon that orbits in the opposite direction to its planet. It is this moon that prevents Neptune from being the coldest planet in our solar system. The tidal interaction between them raises the temperature of the planet, causing it to emit more heat energy than Uranus. Scientists predict that Triton is gradually getting closer to its “host” and will eventually be captured by its gravity, breaking apart in the process. This would make Neptune the planet with the most impressive ring system.
Nereid, the second moon discovered by Neptune, was named after the sea nymphs who were heroines in the ancient Greek myths. In terms of size, Nereid is the third largest among Neptune’s icy satellites.
Comparison between Earth and Neptune
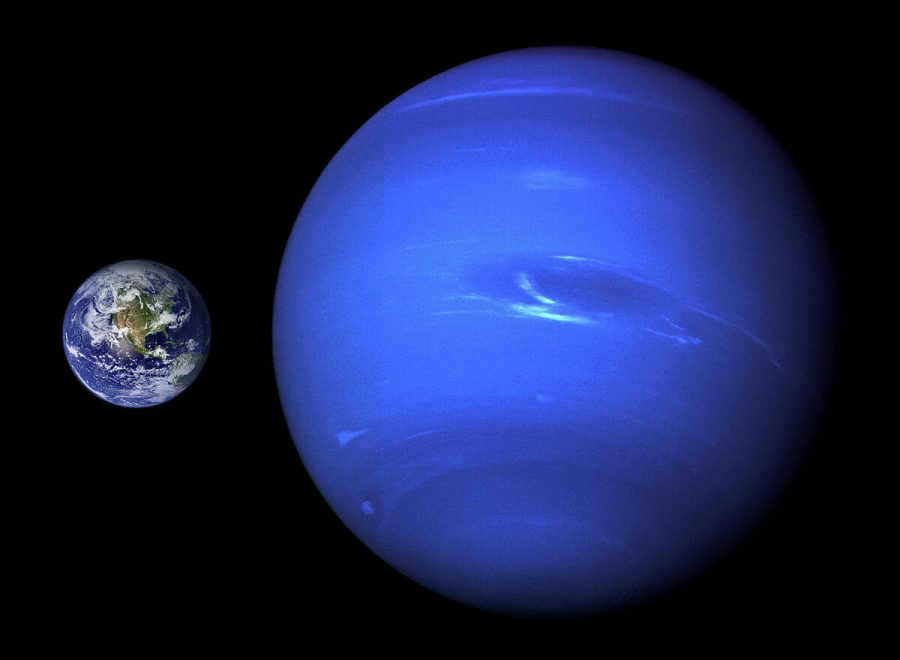

Let’s make a comparison between the third and eighth planets in our solar system:
- The ice giant has a mass 17 times larger than that of Earth, but its size is only 4 times larger.
- Both planets have a similar angle of inclination of their axis to the orbital plane, which leads to the occurrence of seasons.
- The maximum distance between the third and eighth planets is approximately 4.6 billion kilometers.
- The gravity on the ice giant is 1.13 times stronger than that on Earth.
- The orbital path of Venus is the only one less eccentric than that of the planet.
- In Greek mythology, Triton is the equivalent of the ancient Roman god Neptune.
- One hypothesis suggests that the ice giants used to be located closer to the Sun, but the enormous gravitational force from the resonance of Jupiter and Saturn’s orbits pushed them into farther orbits.
- Triton’s retrograde rotation is evidence of its past as an asteroid, while it continues to slowly approach its host.
- There are no current plans by any space agency to launch probes to study the “eight”.
- Pluto, with its more eccentric orbit, can sometimes be closer to the Sun than its neighboring planet.
- Deep within the ice giant lies the possibility of diamond deposits. The planet’s mantle layer, located approximately ten thousand kilometers below the surface, creates conditions that cause methane to break down into its simplest components. As a result, carbon crystallizes under extreme pressure and temperature, forming diamond hail.
- This gas giant is known for being the smallest in size. It ranks as the third smallest gas giant in terms of mass and the fourth smallest in terms of diameter among all the gas giants in the solar system.
- In honor of the discovery of the “eight,” a new element was added to Mendeleev’s periodic table one hundred years later. This 93rd element was named neptunium.
- When discussing planets outside of our solar system, Neptune and Jupiter are frequently used as metonyms. Exoplanets with similar sizes and masses are often referred to as “Neptunes” or “Jupiters.”
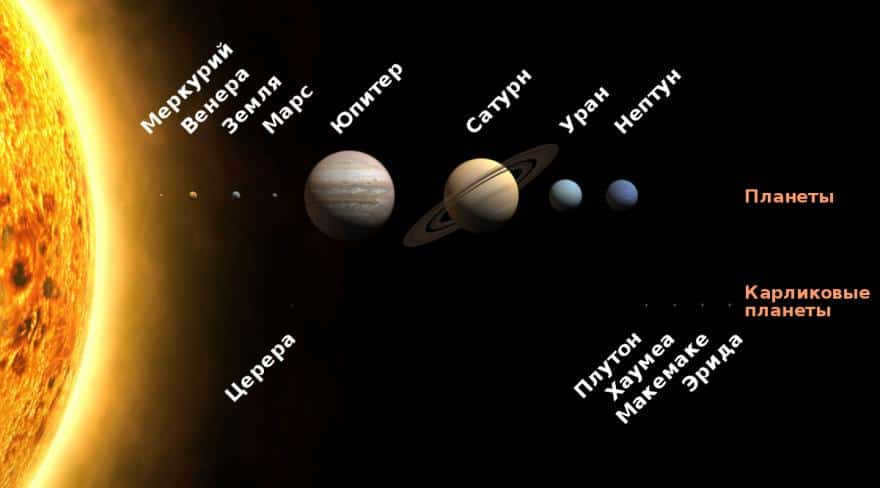




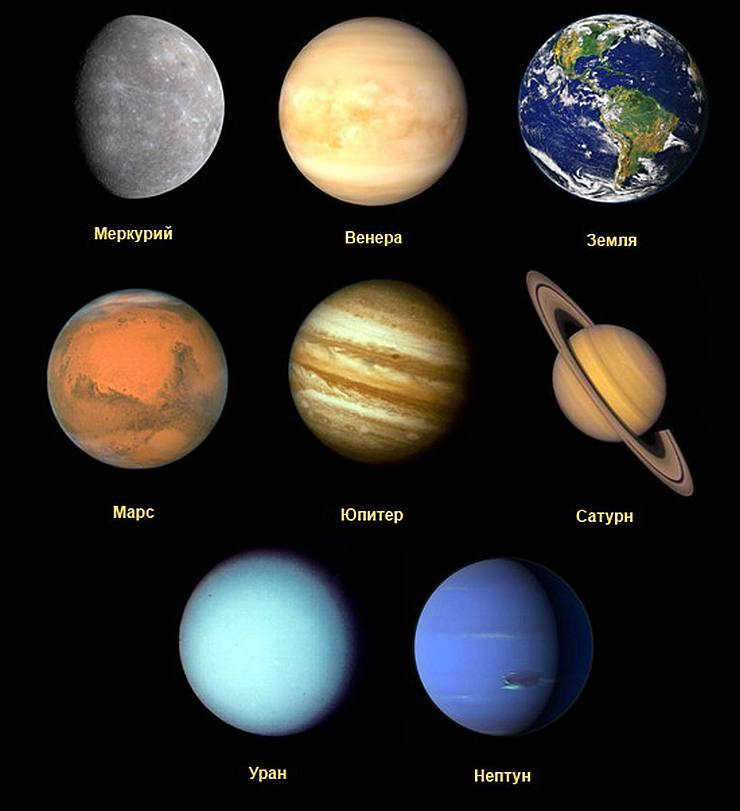
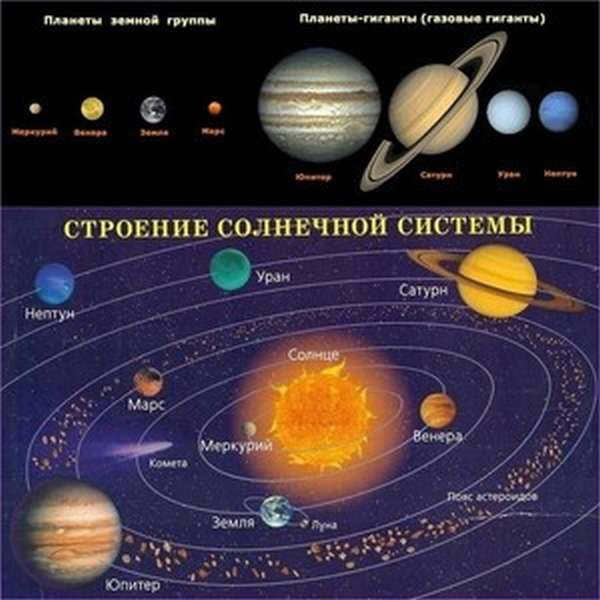
The sequence of planets in the solar system
As per the definition provided by MAC, there are a total of 8 known planets in the solar system, namely Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
All these planets can be categorized into two groups based on their physical attributes: terrestrial planets and gas giants.
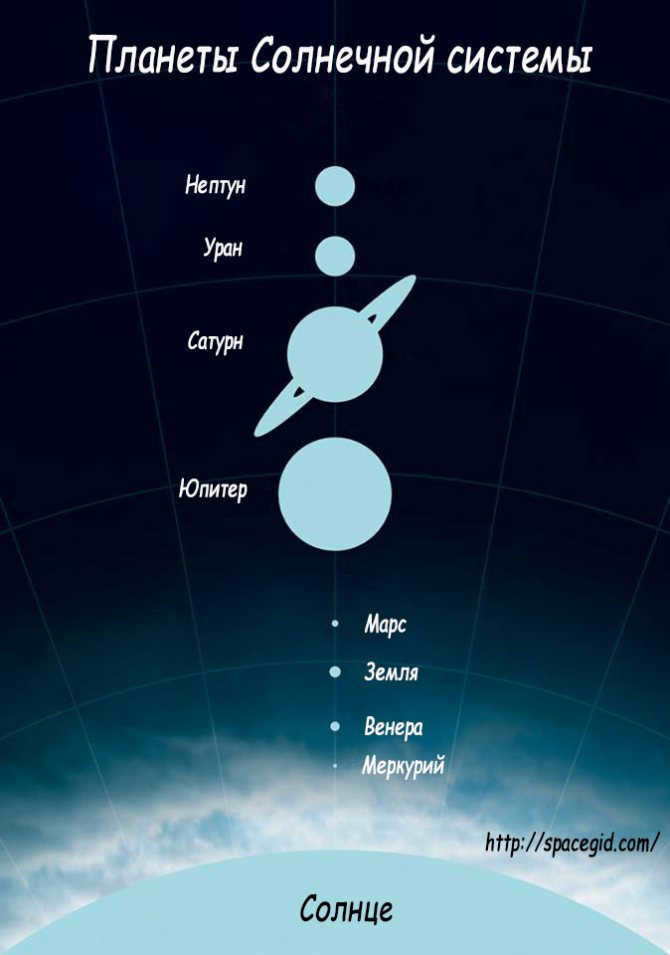
Illustration depicting the arrangement of the planets in the Solar System









The issue of precisely defining the boundary between the solar system and interstellar space is uncertain.
Two crucial factors that play a role in this determination are the solar wind and solar gravity. The outer limit of the solar wind is known as the heliopause, where the solar wind and interstellar matter blend together and merge.
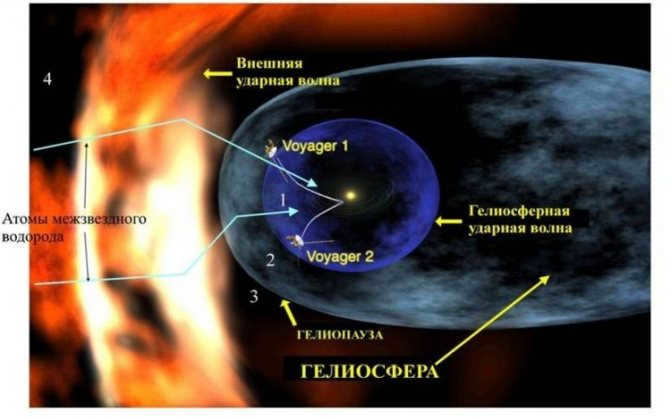
The heliopause marks the boundary between our solar system and the interstellar medium, and it is situated approximately four times beyond Pluto.
On the other hand, the Hill sphere, where the gravitational pull of the Sun is stronger than the gravitational pull of the galaxy, is believed to extend much further, around a thousand times.
There is still much about our solar system that remains unknown. It is estimated that the Sun’s gravitational influence surpasses that of nearby stars up to a distance of about two light-years (equivalent to 125,000 astronomical units).
The Oort Cloud
The Oort Cloud is a theoretical cloud of icy objects that is thought to surround the outermost regions of the solar system. It is believed to be the source of many comets that enter the inner solar system. The Oort Cloud is named after the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, who first proposed its existence in 1950.

The Oort cloud, a speculative cloud comprised of icy objects (potentially numbering in the trillions), acts as a reservoir for long-period comets. The estimated distance from the Sun to the outer boundaries of this cloud ranges from 50,000 AU (roughly equivalent to one light-year) to 100,000 AU (1.87 solar years).
It is believed that the objects that compose this cloud originally formed near the Sun and were subsequently dispersed into the far reaches of space by the gravitational influence of massive planets during the early stages of the solar system’s evolution.
Planets similar to Earth
Mercury
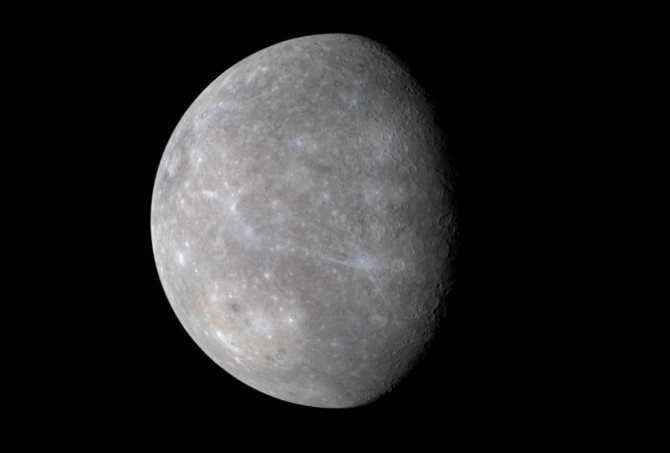
Mercury, depicted in color, presents an image of the MESSENGER spacecraft.
The immense proximity it holds to the Sun has resulted in Mercury undergoing the most significant temperature fluctuations among all the planets within our solar system. During the day, the average temperature reaches approximately 350 degrees Celsius, while at night, it plummets to a chilling -170 °C. The atmosphere of Mercury has been found to contain sodium, oxygen, helium, potassium, hydrogen, and argon. There exists a hypothesis suggesting that Mercury was once a satellite of Venus, although this claim remains unverified. Furthermore, it lacks any satellites of its own.
Venus
Venus is the planet that is closest to the Sun after Mercury. It has a unique atmosphere that is composed mostly of carbon dioxide. Due to its proximity to the Sun, Venus is often referred to as the Morning Star or the Evening Star. This is because it is the first star to become visible after sunset and remains visible before dawn when all other stars have vanished from sight. The atmosphere of Venus is primarily made up of carbon dioxide, with a concentration of approximately 96%. There is also a small amount of nitrogen, accounting for about 4% of the atmosphere. In addition, there are trace amounts of water vapor and oxygen present. Overall, Venus has a fascinating atmosphere that sets it apart from other planets in our solar system.
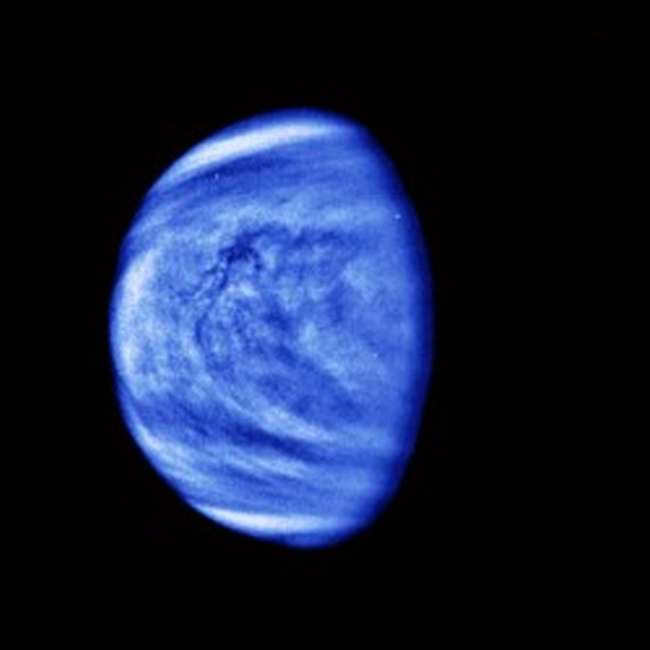

Venus is often referred to as Earth’s sister planet due to its similar mass and radius. It has a radius of 6052 km, which is 0.85% of Earth’s radius. The planet has no satellites, like Mercury. The atmosphere on Venus creates a greenhouse effect, resulting in surface temperatures reaching up to 475 °C, even hotter than Mercury. A day on Venus lasts 243 Earth days, which is nearly equal to a year on the planet, which is 225 Earth days.
Our Planet Earth
Earth, the third planet from the Sun, is a unique celestial body in our solar system. It is the only planet with liquid water on its surface, making it possible for life to thrive. Without this precious resource, life as we know it would not exist. With a radius of 6371 kilometers, Earth stands out among its planetary neighbors as more than 70% of its surface is covered by vast oceans. The remaining portion is made up of continents, providing diverse habitats for countless species.
One of Earth’s fascinating features is its tectonic plates, which lie beneath the planet’s mantle. These massive plates have the ability to move, albeit at a very slow pace, resulting in the ever-changing landscapes we see today. This geological phenomenon is responsible for the formation of mountains, valleys, and other landforms. Additionally, Earth orbits the Sun at a speed of 29-30 km/sec, contributing to the dynamic nature of our planet.
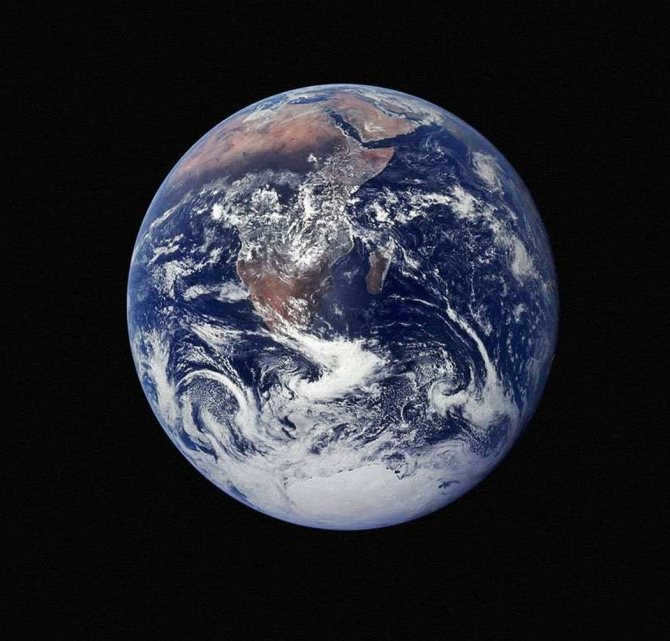

The duration of one complete rotation of this celestial body around its own axis is approximately 24 hours, while it takes a significantly longer time to complete a full orbit around its star compared to the planets in its immediate vicinity. The length of a day and a year on Earth is often used as a reference point for measuring time intervals on other planets, although it should be noted that this is purely for convenience. Additionally, Earth is accompanied by a natural satellite known as the Moon.
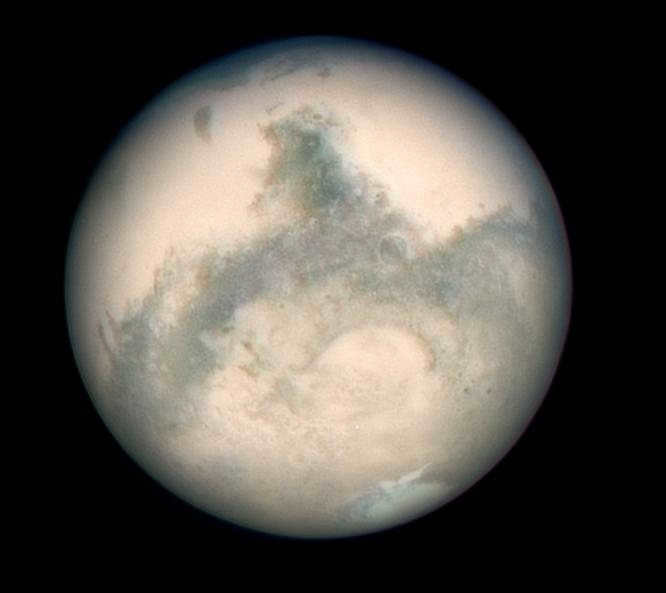

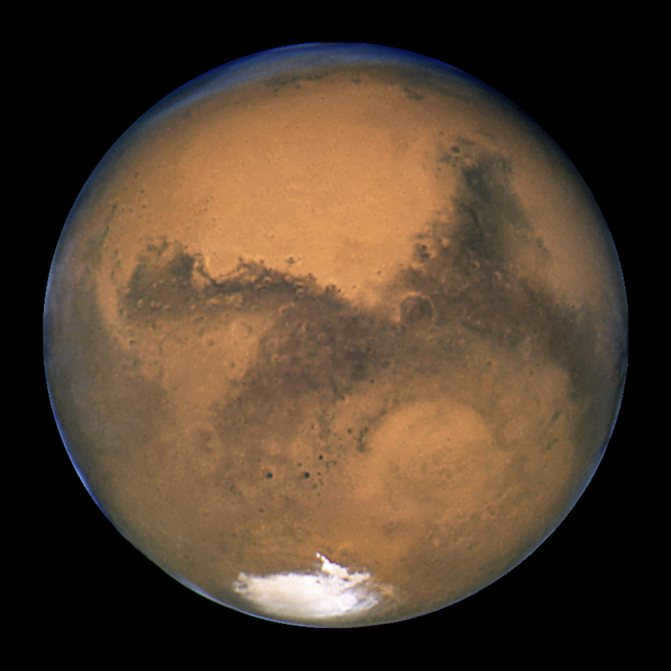
Mars, an image of the Hubble Space Telescope taken in 2003.
The fourth planet from the Sun, recognized for its thin atmosphere. Scientists from various countries, including the USSR and the United States, have been actively exploring Mars since 1960. Although not all exploration missions have been successful, the discovery of water in certain areas suggests the existence of primitive life on Mars, either currently or in the past.
Mars is bright enough to be visible from Earth without the need for any instruments. And every 15-17 years, during its opposition, it becomes the brightest celestial object, even surpassing Jupiter and Venus.
Mars has a radius of approximately half that of Earth, measuring 3390 km, but its year is much longer, lasting 687 days. It has two moons – Phobos and Deimos.







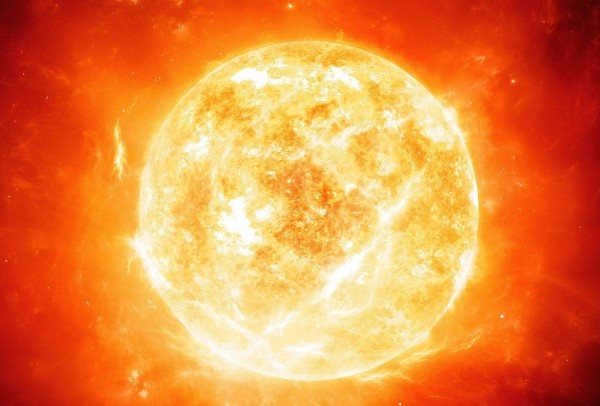
The Sun, which is composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, serves as the central star that governs the movements of all the planets and satellites within the solar system. With an age of 4.5 billion years, the Sun finds itself currently situated in the midst of its life cycle, steadily expanding in size. At present, the Sun boasts a diameter measuring 1,391,400 kilometers. In the coming years, this celestial body will continue to expand, eventually reaching the orbit of Earth.
In addition to its role in planetary motion, the Sun also acts as a vital source of both heat and light for our planet. Its level of activity experiences periodic fluctuations, growing stronger or weaker approximately every 11 years.
Due to the Sun’s exceedingly high surface temperatures, conducting a detailed study of this celestial body poses significant challenges. Nevertheless, ongoing efforts persist in attempting to launch specialized probes that can approach the star as closely as possible.
Mercury
Mercury, an incredibly hot planet closest to the Sun, is just a little bit bigger than Earth’s moon. Similar to the moon, Mercury has no atmosphere and is unable to erase the impact craters caused by meteorite collisions. Therefore, it is covered in craters, just like the moon. The side of Mercury that faces the Sun experiences extreme heat, while the side facing away from the Sun drops to temperatures hundreds of degrees below zero. Ice can be found in Mercury’s polar craters. It takes Mercury 88 days to complete one orbit around the Sun.
The Planet Jupiter
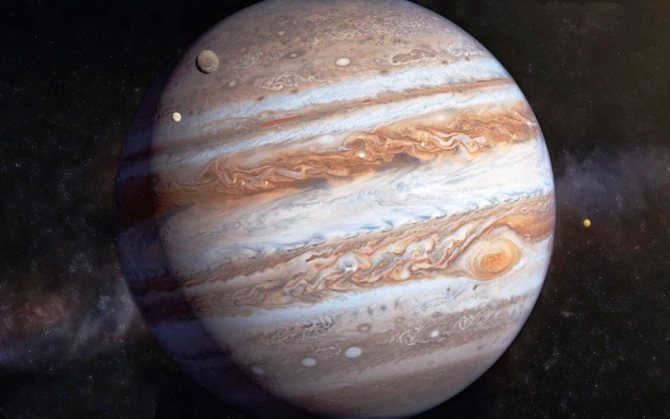

Photo: sciencepop.ru
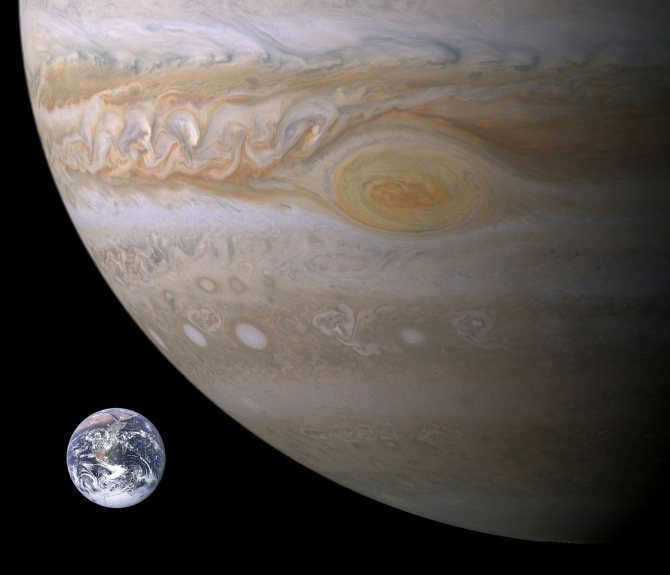
Jupiter is known as a gas giant and holds the title of being the largest planet in our solar system. Its immense size is truly mind-boggling, as it has the capacity to accommodate 1300 Earth-sized planets. However, it’s not just its size that sets Jupiter apart. The gravity on its surface is an astonishing 2.5 times stronger than that of Earth, meaning that a person weighing 100 kg on Earth would weigh 250 kg on Jupiter.
Another remarkable feature of Jupiter is its powerful magnetic field, which enables it to attract and deflect asteroids. Additionally, there is a massive storm known as the Great Red Spot, which has been raging on the planet for several centuries. Furthermore, Jupiter is known for its abundance of moons, with a total of 29 satellites orbiting around it.
The Red Planet
While it is challenging to observe the surface of Mars from Earth, telescopic observations have revealed that Mars experiences seasons and has bright spots at its poles. For numerous years, it has been widely believed that the light and dark areas on Mars are patches of vegetation, leading to speculation that Mars could support life and that water may be present in its polar caps. However, when the Mariner 4 spacecraft reached Mars in 1965, scientists were astonished to discover images of a desolate planet covered in craters, indicating that Mars is devoid of life. Nevertheless, more recent missions have unveiled a multitude of enigmas that Mars still conceals, waiting to be unraveled.
Small items
The Kuiper Belt
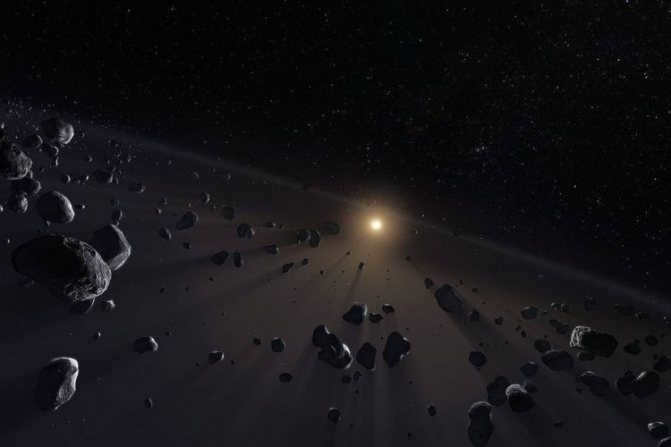

The Kuiper Belt, a region containing remnants from the formation of our solar system, is a vast expanse of debris resembling the asteroid belt, yet primarily consisting of frozen substances. Stretching between 30 and 55 astronomical units from the Sun, the Kuiper Belt is primarily composed of small celestial bodies. However, some of the larger objects within this belt, such as Quavar, Varuna, and Ork, may eventually be reclassified as dwarf planets once their characteristics are further defined. Within this region, there exists a multitude of small objects, predominantly comprised of ice.
These objects are composed mainly of methane, ammonia, and water, although there are also some containing rocks and metals.
Asteroids: A Unique Phenomenon in the Cosmos
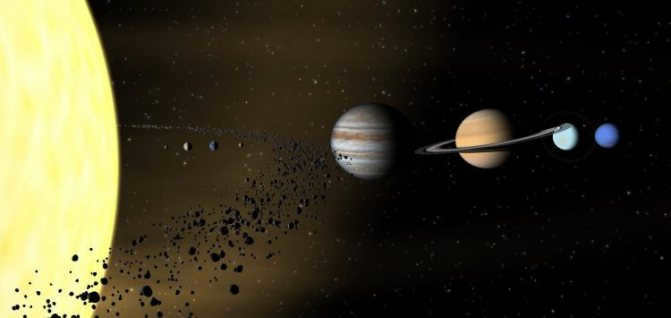
Asteroids – They are the most common small bodies in the solar system.
The asteroid belt is located between Mars and Jupiter. According to current theories, asteroids are remnants of the solar system’s formation that failed to come together to form a larger body due to the gravitational disturbances caused by Jupiter.
Asteroids vary in size, ranging from a few meters to hundreds of kilometers. Among them, there are both very small and large ones, such as Vesta and Hygeia. If they can be proven to maintain hydrostatic equilibrium, they may even be reclassified as dwarf planets.
The asteroid belt is home to tens of thousands, maybe even millions, of objects with a diameter larger than one kilometer. However, the combined mass of all these asteroids is unlikely to exceed one thousandth of Earth’s mass.
Meteors and meteorites

Meteorites are space objects of small size that periodically penetrate the Earth’s atmospheric layer until they descend. Once they enter the Earth’s atmosphere, they undergo a reclassification as meteors. Before falling to the surface, they burn up in the air, with only a small fraction making it to the ground.
Comets
Comets are celestial objects that orbit the Sun. They are composed of ice, dust, and small rocky particles. When a comet gets close to the Sun, the heat causes the ice to vaporize, creating a glowing coma (a cloud of gas and dust) around the nucleus. The dust and gas form a tail that can extend for millions of kilometers. Comets are often referred to as “dirty snowballs” because of their icy composition. They are believed to be remnants from the early solar system and can provide valuable information about its formation and evolution. Some famous comets include Halley’s Comet and Comet Hale-Bopp.
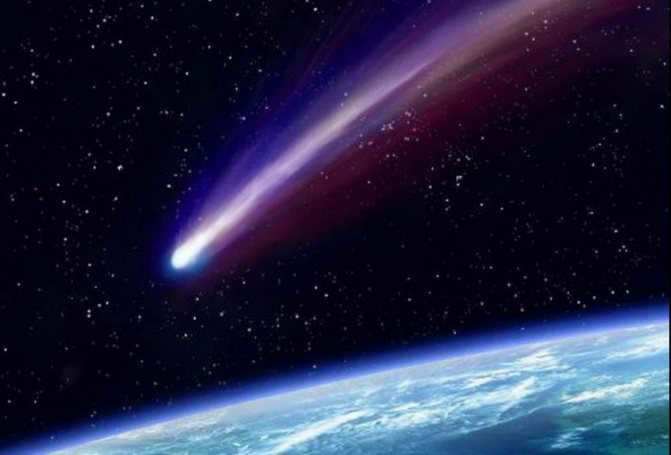

When you translate this term from Greek, you receive the word “long-haired.” And that is exactly what it is. As the icy traveler approaches the Sun, it extends a lengthy tail of evaporating gases for hundreds of millions of kilometers.
The comet also possesses a head, which consists of a nucleus and a coma. The nucleus is a frozen block of icy gases with traces of silicates and metallic particles. It is possible that certain organics are also present. The coma constitutes the gas and dust environment of the comet.
Enormous planets
There are four colossal gas planets situated past the orbit of Mars: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. They reside in the outer region of the solar system. They vary in their mass and composition of gases.

The proportions of the planets in the solar system are not accurate.
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet in our solar system. It has a radius of 69,912 km, which is 19 times bigger than Earth and only 10 times smaller than the Sun. The length of a year on Jupiter is not the longest in the solar system, as it lasts for 4,333 Earth days (equivalent to 12 years). A day on Jupiter is approximately 10 Earth hours long. The exact composition of the planet’s surface is still unknown, but it is known that Jupiter has much higher concentrations of krypton, argon, and xenon compared to the Sun.
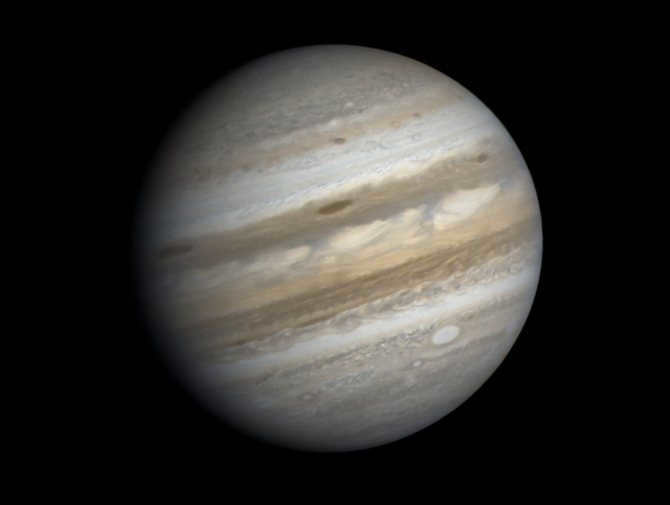

The planet Jupiter is believed to be a failed star, as it is one of the four gas giants. This theory is supported by the fact that Jupiter has the largest number of satellites compared to other planets in the solar system, with a total of 67. To understand how these satellites behave in Jupiter’s orbit, it is necessary to have an accurate and clear model of the solar system. The largest satellites of Jupiter are Callisto, Ganymede, Io, and Europa. Ganymede is particularly notable as it is the largest satellite of any planet in the entire solar system, with a radius of 2634 km, which is 8% larger than the size of Mercury, the smallest planet in our system. Io is also noteworthy as one of the three atmospheric satellites.
Further reading: Life on Mars: the latest discoveries bringing us closer to the possibility of relocating to the Red Planet and the estimated time it would take.
Saturn
Saturn is the second largest planet and the sixth largest in the solar system. It has a composition of chemical elements that is most similar to the Sun compared to other planets. The surface of Saturn has a radius of 57,350 km and its year is equivalent to 10,759 days, which is almost 30 Earth years. A day on Saturn is a little longer than on Jupiter, lasting 10.5 Earth hours. Saturn has 62 satellites, which is just slightly less than its neighbor Jupiter’s 67 satellites. Its largest satellite is Titan, which, like Io, has an atmosphere. Other satellites of Saturn include Enceladus, Rhea, Dione, Tefia, Japetus, and Mimas. These satellites are the most frequently observed objects and have been extensively studied in comparison to others.

The picture above shows Saturn, which was captured by the Cassini spacecraft in 2007.
For a considerable period, it was believed that the rings surrounding Saturn were a unique and exclusive feature of the planet. However, it has recently been confirmed that all gas giants possess rings, although they may not be as prominent as Saturn’s. The exact origin of these rings is still unknown, although there are several theories regarding their formation. Additionally, it has been recently revealed that Rhea, one of Saturn’s moons, also possesses some form of ring system.
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh largest planet in our solar system and it is also the third largest. It has a radius of 25267 km. One of the most unique features of Uranus is that it is known as the coldest planet. The temperatures on Uranus can reach as low as -224 degrees Celsius. Another interesting fact about Uranus is that its year is significantly longer than Earth’s year. In terrestrial calculation, Uranus has a year that lasts for 30,685 days, which is almost equivalent to 84 years on Earth. The day on Uranus is also quite long, lasting for 17 and a little hours. One peculiar characteristic of Uranus is its strong inclination of the axis. This causes the planet to appear as if it is not rotating like other celestial bodies in our solar system. Instead, it seems to roll like a ball. This phenomenon can be easily observed by anyone interested in astronomy. By examining a geometric model of the solar system, this effect becomes clear.
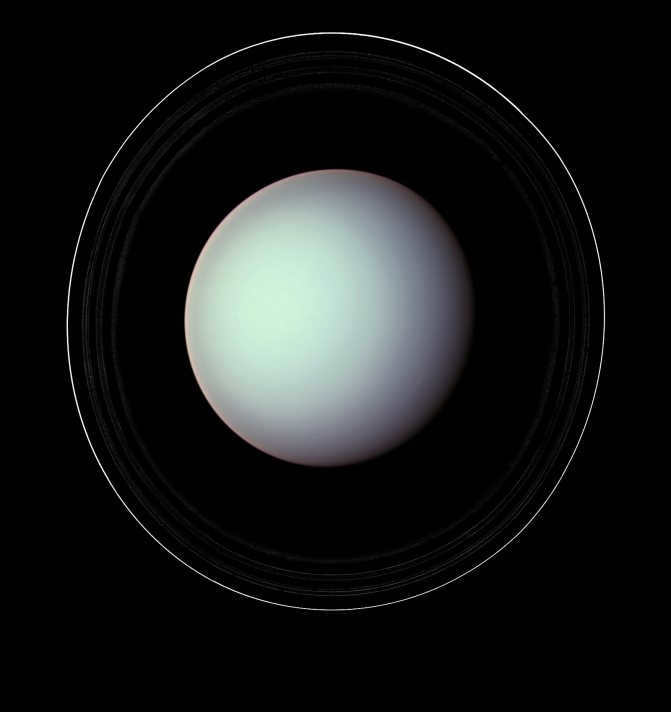

Uranus – Voyager 2 image from 1986
Uranus has a much smaller number of satellites compared to its neighboring planet Saturn, with a total of 27. The most well-known satellites are Titania, Ariel, Oberon, Umbriel, and Miranda. However, these satellites are not as large as the ones orbiting other planets.
Interestingly, when astronomer William Herschel first observed Uranus through his telescope, he initially mistook it for a comet rather than a planet.
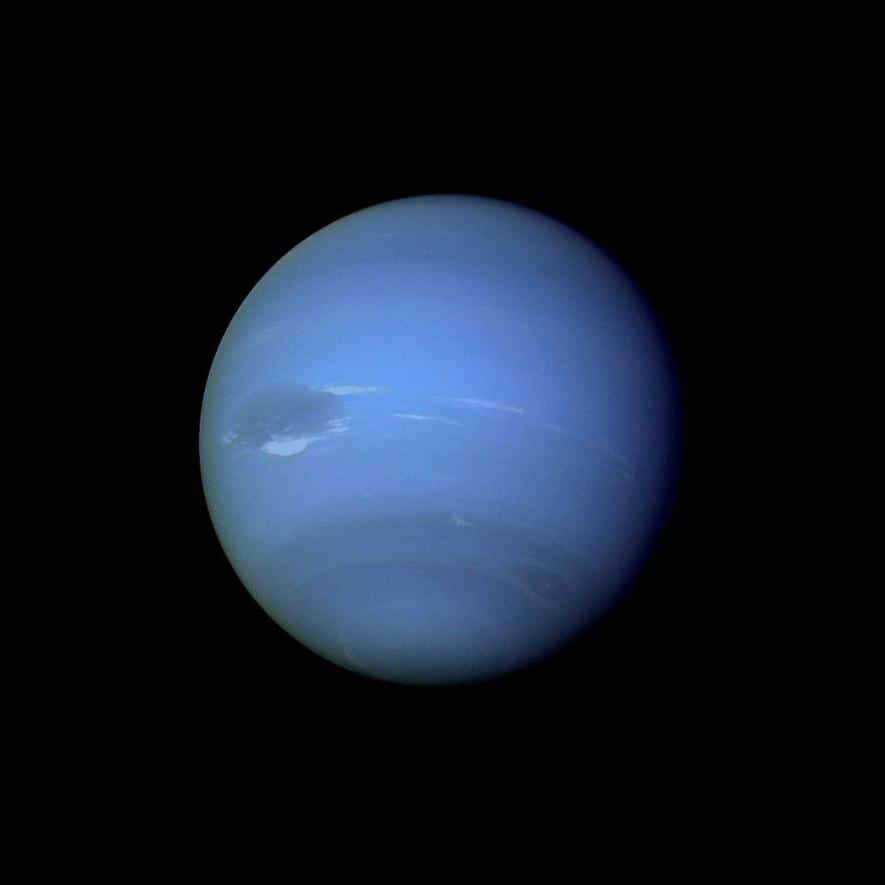
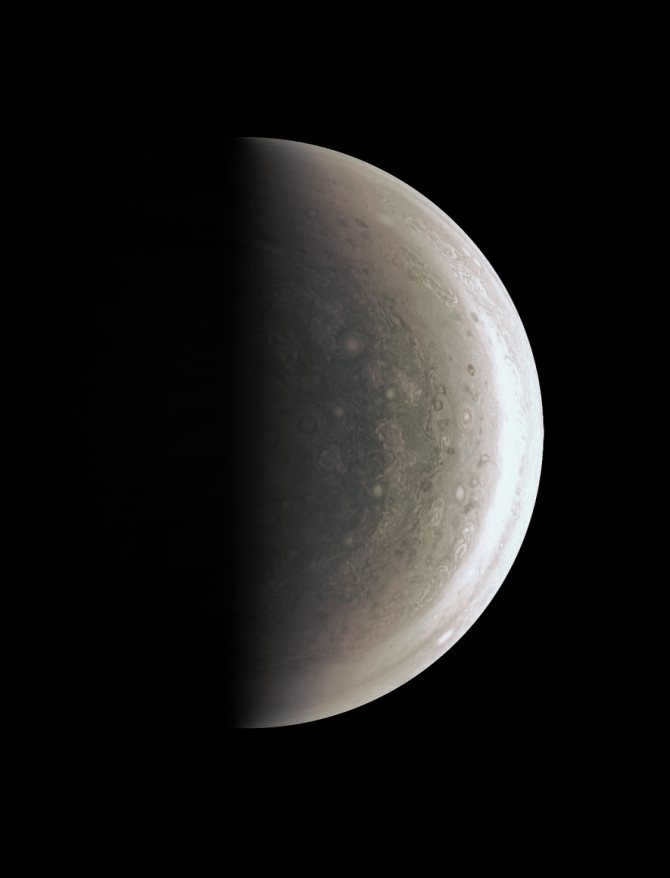
Neptune
The dimension of the eighth planet of the solar system, Neptune, is highly similar to its closest neighbor, Uranus. Neptune has a radius measuring 24547 kilometers. The planet takes approximately 60,190 days (equivalent to around 164 Earth years) to complete one revolution around the sun. It is worth noting that Neptune is home to the most powerful winds in our entire solar system, with speeds reaching up to 260 m/s.
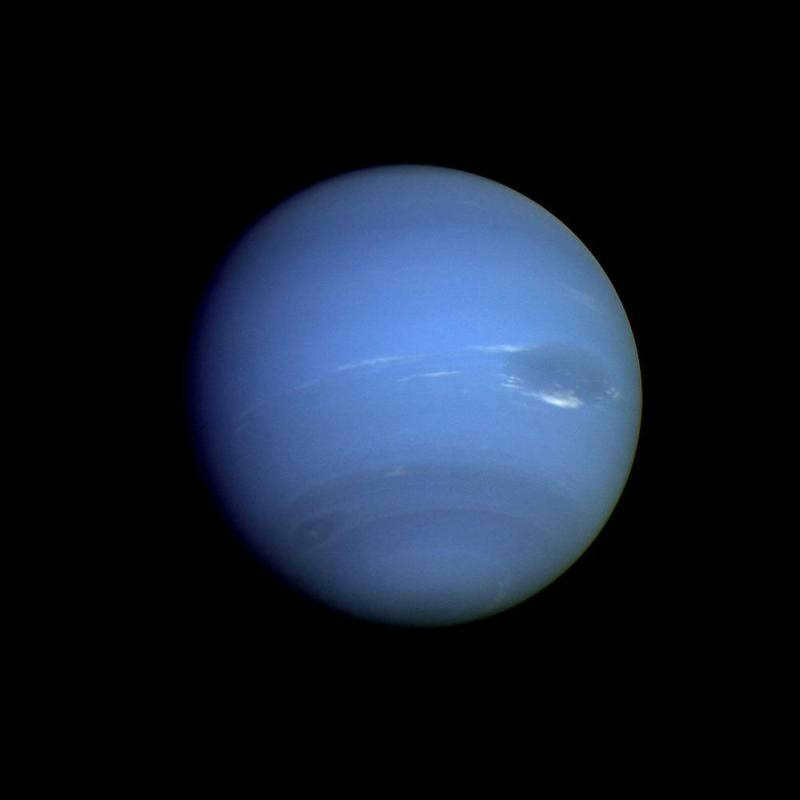

Unlike the rest of the gas giants, Neptune possesses a relatively small number of moons – just 14. Among these, the notable ones include Triton, the third moon in our solar system with its own atmosphere, as well as Proteus and Nereida.
Interestingly, Neptune stands out as the sole planet that wasn’t initially found by direct observation, but rather through mathematical calculations.
Venus
Venus, also known as the Evening Star or the Morning Star, is the second planet from the Sun in our solar system. It is named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty. Venus is often referred to as Earth’s sister planet because of their similar size and composition. However, Venus has a very different atmosphere compared to Earth, with a thick layer of clouds made up of sulfuric acid.
Venus is the hottest planet in our solar system, with surface temperatures reaching up to 900 degrees Fahrenheit (475 degrees Celsius). This extreme heat is due to the greenhouse effect caused by the dense atmosphere, which traps heat from the Sun. The atmospheric pressure on Venus is also about 92 times greater than Earth’s, making it a very inhospitable environment for humans.
Despite its harsh conditions, Venus has been the subject of many scientific missions and studies. NASA’s Magellan spacecraft, which orbited Venus from 1990 to 1994, provided detailed maps of the planet’s surface. The European Space Agency’s Venus Express mission, launched in 2005, studied the planet’s atmosphere and climate. These missions have helped scientists better understand the geology and dynamics of Venus.
Venus is often visible in the evening or morning sky as a bright star-like object. It is one of the brightest objects in the night sky and can even cast shadows on Earth when it is at its brightest. Venus is also known for its phases, similar to the Moon’s phases, as it orbits the Sun.

Photo: youtube.com
Venus, the second planet from the sun, has a mass that is almost similar to Earth. An interesting fact about Venus is that it is the only celestial body in the solar system that rotates counterclockwise, and its rotation is very slow – a day on Venus is equal to 243 Earth days.
The high density of Venus’ atmosphere is primarily due to the large amount of carbon dioxide present, which leads to the greenhouse effect. As a result, the temperature on Venus can rise up to 400 degrees Celsius. Additionally, Venus experiences severe thunderstorms that are even more intense than those on Earth. Although Venus has no natural satellites, there is speculation that one of them was once Mercury.
Uranus
William Herschel discovered the seventh planet in 1781 using a telescope, initially mistaking it for a comet. It was later confirmed to be a planet, and Herschel also discovered two of its 27 satellites, Oberton and Titania.
What was the name of the planet Herschel discovered? It was Uranus, a pale blue planet named after the Roman god of the sky. Despite being visible without special instruments, Uranus was often mistaken for a faint star before Herschel’s discovery.
This ice giant, with a radius of 25,567 kilometers, is the third largest planet in size. Uranus has opaque rings composed of macroparticles and dust.
The duration of a year on Uranus is 84 years. This seventh planet is composed of a small core made of iron-stone, surrounded by a mantle that contains water, ammonia, and methane. Enveloping the mantle is an atmosphere that consists of hydrogen, helium, and methane.
On Uranus, a day lasts a little over 17 hours.
The solar system is comprised of a collection of planets, with the Sun at its center – the most potent and brightest source of light and heat. The Sun is an enormous and scorching fireball consisting of plasma, helium, and hydrogen. One prevailing theory suggests that this celestial body was formed 4.5 billion years ago as a result of a supernova star’s explosion. This explosion created a dusty gas cloud, which then condensed into a disk where the Sun formed and the remaining planets began to orbit around it….
Different types of planets


There exist two types of planets – terrestrial ones (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars) and giant ones (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune).
The terrestrial representatives of the Solar System are not very large in size, they have a rocky surface, and they are positioned closer to the Sun compared to the giant planets. The planets that are closer to the Sun than Earth are Mercury and Venus.
The giant planets include Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. They consist of gas and have rings composed of icy dust and rocky particles.
In addition, there exists a ninth planet known as Pluto. It does not belong to any of the aforementioned groups due to its distance from the Sun, being the farthest one, and its smaller diameter of 2320 km (compared to Mercury, which has a diameter twice as large). Pluto is classified as a dwarf planet.
Let’s contemplate the primary celestial body of our galaxy and the respective positions of the planets in relation to the Sun.
The Sun is a yellow dwarf that has existed for approximately 4.5 billion years. It is currently in the midst of its lifespan. After 4 billion years, it will transform into a “red giant”, expanding in size and engulfing the Earth’s orbit (scientists predict that this will lead to the displacement of Earth and the extinction of life due to extreme temperatures). Ultimately, the Sun will conclude its existence as a “white dwarf”.

Sun
Mercury
Mercury is the smallest planet in size, and it is the closest to our sun. The planet’s rotation speed around its axis is extremely slow: it takes one and a half revolutions for the planet to complete a full revolution around the sun. The temperature on Mercury is extremely extreme, with nighttime temperatures dropping to minus 180 degrees Celsius and daytime temperatures rising to plus 430 degrees Celsius.
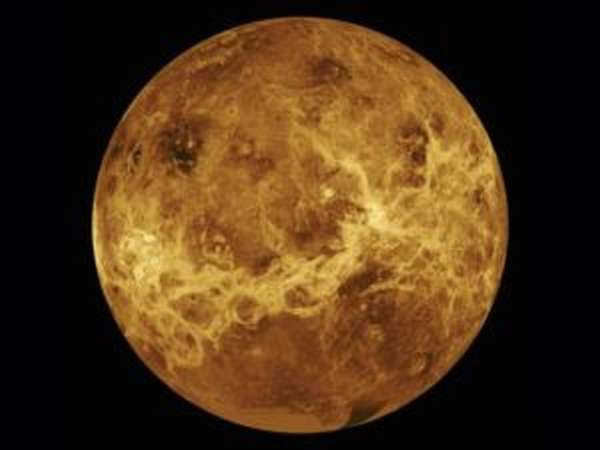

Mercury
Venus
The celestial body with this romantic name is covered in a dense carbon dioxide cloud. It bears a resemblance to our own planet in terms of mass and size. Which is closer to the sun, Mars or Venus? Venus takes the second spot in proximity to the star, while Mars is situated in fourth place. Out of all the planets, Venus holds the title for being the hottest due to its greenhouse effect.
Read more: MBA (Master of Business Administration) program essence, how to obtain a degree, tuition fees
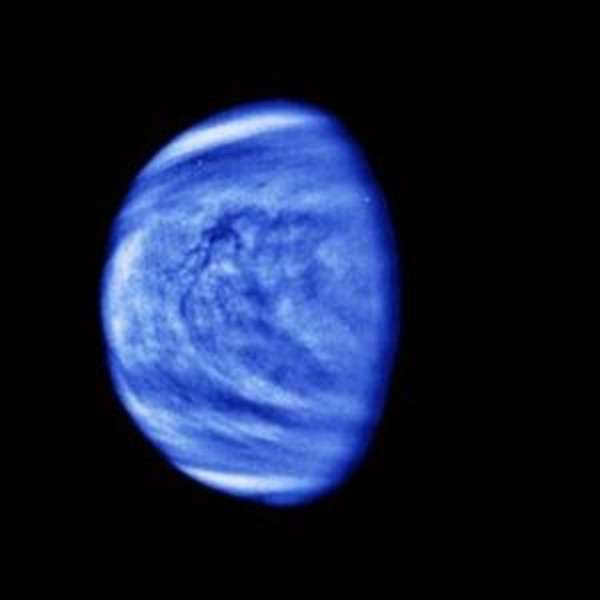

Venus
Earth
The birth of life on this planet can be attributed to its unique atmosphere composed of carbon and hydrogen, as well as the presence of oxygen and optimal temperature. How far is Earth located from the yellow dwarf? Earth is the third planet from the Sun, orbiting at a distance of 149 million kilometers from this massive star. It is this distance that has provided the ideal conditions for the emergence and evolution of life.
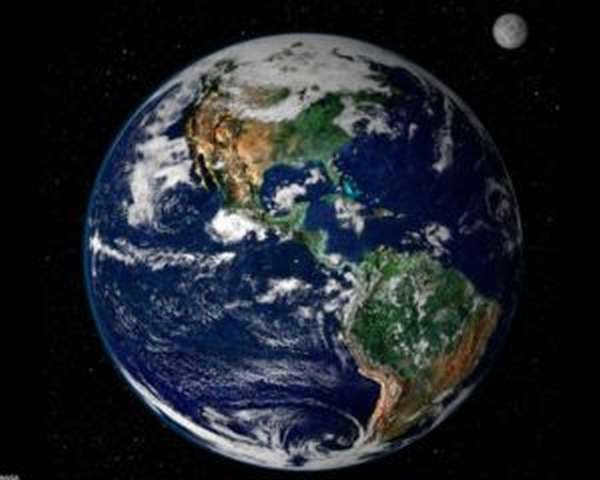
Earth
Mars
Mars shares a similar structure to Earth, but it is significantly smaller in mass and has half the radius. If Mars possessed water and an atmosphere, it would be capable of sustaining life. Its day length matches that of Earth, but its year is twice as long. Additionally, Mars is accompanied by two small asteroid-like satellites, Deimos and Phobos, which orbit around it. Notably, Mars is positioned closer to Earth than Neptune, contrary to the misconception that it is located closer to the Sun than Earth.
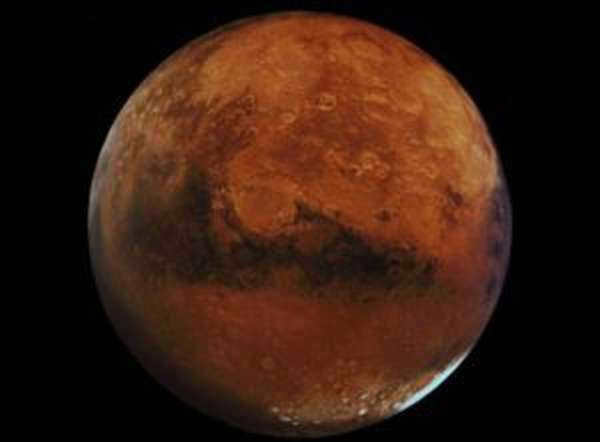

The Red Planet.
The Giant of the Solar System.
Being the largest planet in the solar system, Jupiter towers over all others. In fact, it is more than 300 times bigger than our home planet, Earth. If Jupiter’s mass were to increase significantly, it would no longer be classified as a planet, but as a star. Its atmosphere is composed mainly of hydrogen, with helium, sulfur, phosphorus, and ammonia making up the remaining 15%. Jupiter has a relatively short day, lasting only 10 hours, and a year that spans 144 months. Additionally, it boasts an impressive collection of over 60 satellites and four distinct rings.

Jupiter
Saturn
Saturn has a density that is lower than one. If there was an ocean that was several times the size of Saturn, the planet would not sink in it. Saturn is known for its magnificent ring system. Additionally, Saturn has several large satellites as its nearest neighbors. One of these satellites, Titan, is particularly interesting because its atmosphere is similar to that of Earth and its atmospheric pressure is only 1.5 times higher than ours.

Saturn
Uranus
With blue-green hues and positioned “sideways” due to its axis of rotation and the ecliptic plane being parallel to each other, Uranus boasts 27 satellites and 13 rings. It is famously known as the coldest planet (with a record low temperature of minus 222 degrees Celsius). The planet experiences extreme winds, with incessant gusts reaching speeds of up to 580 kilometers per hour. The exploration of Uranus by Voyager 2 has revealed that it possesses two primary magnetic poles and two secondary ones.

Uranus
Neptune
The gas giant is composed of methane, ammonia, and water. It possesses a solid rocky core. Because of the abundance of methane, Neptune appears blue in color. It is accompanied by 14 moons and 6 rings. Due to its considerable distance from Earth, limited knowledge is available about this celestial entity.
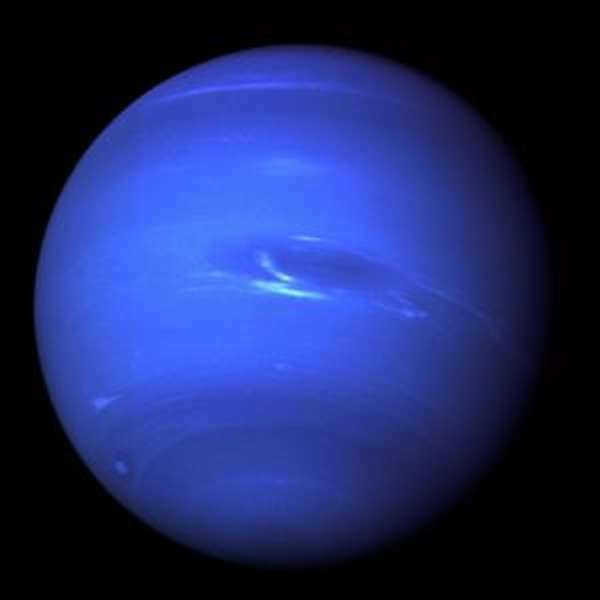

Caution! The discovery of Neptune was specifically due to mathematical calculations. It holds the distinction of being the most turbulent planet in our solar system, with hurricane winds reaching speeds of 700 km/h, as reported by the Voyager 2 spacecraft.
Pluto
Pluto is classified as one of the dwarf planets. Scientists theorize that beneath its surface lies a massive layer of ice, estimated to be around 200 kilometers thick. Limited information is available about Pluto due to its position as the farthest planet from the Sun. Its atmosphere is inhospitable, composed primarily of nitrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide. It has three known moons – Charon (previously believed to be the sole moon), Hydra, and Nikta. Pluto’s diameter is only a few times larger than that of Charon.

Pluto
Dwarf planets
Which planet is closer to the primary star if we only consider dwarf planets? There have been a total of five planets discovered with this classification. These include Pluto, Makemake, Erida, Haumea, and Ceres. Makemake is known for its incredibly flat icy surface, comprised of methane ice slabs. Erida is the heaviest dwarf planet, weighing about 27% more than Pluto. Haumea’s distinctive features include its oval shape and a surface covered in an ice layer. Ceres, on the other hand, is located in the asteroid belt, has a spherical shape, and orbits between Jupiter and Mars.
It’s crucial! Ceres is the nearest among all the dwarf planets that orbits the Sun at the closest distance.
The estimated distance from the Sun
- to Ceres – 414 million kilometers,
- Pluto is 5.9 billion kilometers,
- Haumea is 7.7 billion kilometers,
- Makemake is 7.9 billion kilometers,
- Erida is 10 billion kilometers.
Possibly, more dwarf planets will be discovered in the future.
Helpful video: what is the total number of planets in the solar system?
Helpful video: what are the essential things to know about the solar system?
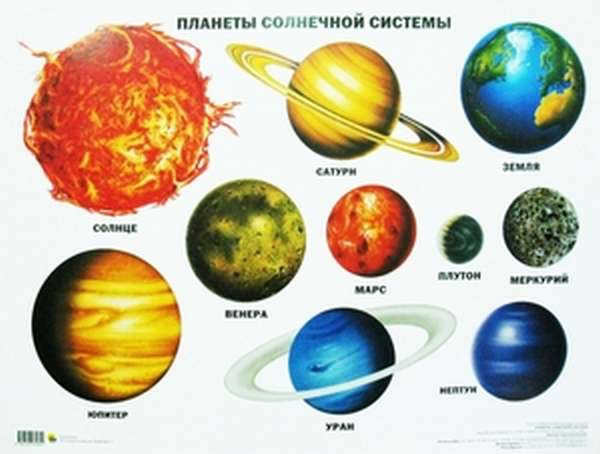
Every celestial object is positioned in the vastness of space with purpose, as billions of particles gradually come together over billions of years to form a single entity, allowing us to witness various phenomena in the night sky. The planets of our solar system, arranged in order from our star, the Sun, are: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune.
Understanding the sequence and composition of these neighboring cosmic bodies not only showcases a person’s knowledge, but also serves as a means of expanding our understanding of the universe, which directly impacts each and every one of us.
Nature, with its composition consisting of objects from the vast cosmos, is a intricate mechanism, where each element is intricately connected to other objects.
The solar system is comprised of a collection of objects that orbit around one central star, known as the Sun. It is an integral part of the Milky Way galaxy.
This is fascinating! How can we accurately translate the MPA of the atmosphere?
- The approximate age of the solar system is about 4,570,000,000 years.
- The total mass of all the elements within the system is approximately 1.0014 M☉ (solar mass).
- The combined mass of the planets accounts for 2% of the system’s total mass.
- Out of the 8 celestial bodies, 6 are accompanied by one or more satellites revolving around them.
Keep in mind! Apart from planets, there are also numerous small objects that constitute the planetary system.
The diagram represents the structure of the solar system.
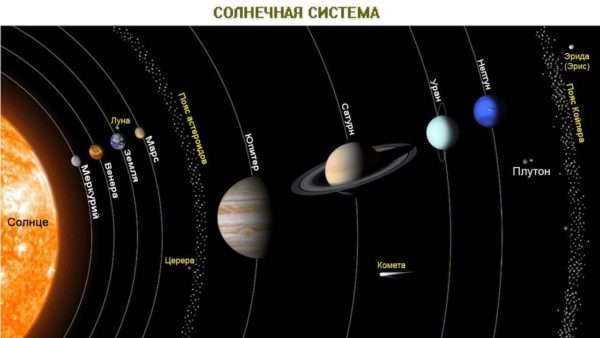
The organization of the planets in the solar system
Following the detection of significant celestial bodies in the Kuiper belt area in 2006, a decision was made to remove Pluto from the roster of planets. Pluto, along with Erida, Haumea, and Makemake, have been reassigned to the category of dwarf planets.
Interesting video: essential information about the solar system
The celestial bodies of the solar system
The field of astronomy is constantly progressing. With the advancements in physics and technological innovations, the precision of studying different celestial objects from a distance is improving. What was once confined to the pages of science fiction novels is gradually turning into reality with each passing year. Now, let’s examine all the planets of the solar system in chronological order.
The Sun, which is situated at the center of our planetary system, is a member of the group of yellow dwarfs known as G2-class stars. Over time, it has been gradually increasing in its luminosity. As a type 1 star belonging to the stellar population, the Sun formed during the later stages of the Universe’s formation and is characterized by a significant abundance of heavy elements, which are elements that are heavier than helium and hydrogen. Currently, there are multiple stars that share similarities with the Sun in terms of their structure, age, and composition.
- This is interesting! Here is a concise summary of the main points of Niels Bohr’s quantum postulates.
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram provides a visual representation of the variations in brightness, surface temperature, and size among stars.
Displayed in the photo is the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram.
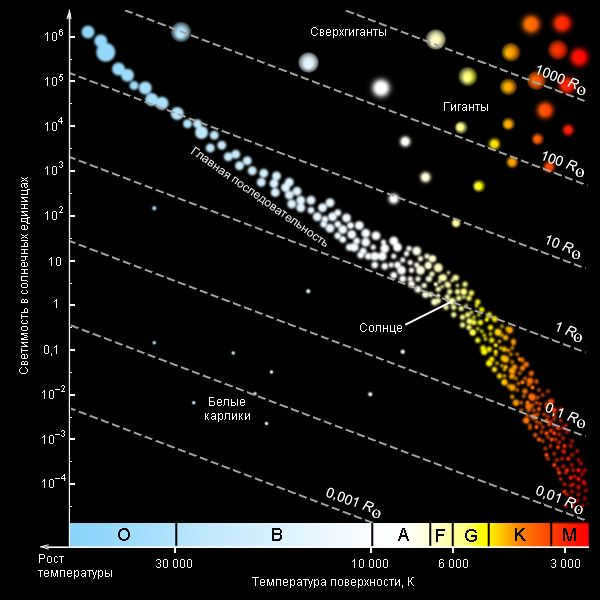
Diagram of Hertzsprung-Russell
The majority of the identified stars are not as luminous and emit lower levels of heat compared to the Sun (85%).

Stars go through a life cycle.
The solar system’s inner region
This area includes the group of cosmic bodies that Earth belongs to.
- They have a smaller diameter compared to the Sun and gas giants.
- They have a high density structure, solid surface, and a variety of elements in their composition.
- Most of them have an atmosphere, except for Mercury.
- They have a similar structure, including a core, mantle, and crust, except for Mercury.
- They have a relief surface.
- Some have no satellites or very few.
- They have weak gravity.
It’s important to remember that each planet is unique and amazing in its own way.
You can see the internal structure in the photo.
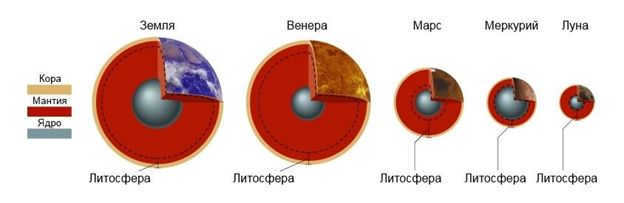
Mercury
Mercury is the initial extraterrestrial celestial body from our Sun.
- It completes an orbit around the Sun in 88 Earth days,
- has a day length of 59 Earth days,
- experiences an average temperature of +430 degrees Celsius during the day and -170 degrees Celsius at night,
- lacks any accompanying elements,
- displays impressive impact craters and ridges on its surface,
- possesses a sparse atmosphere.
This is fascinating! Could you explain the principle behind the Huygens Fresnel theory?

Mercury
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. Its composition is similar to that of our Earth, with a lithosphere, mantle, and core.
- It exhibits signs of internal activity,
- and possesses an atmospheric density that is 90 times greater than that of Earth,
- There is a small amount of water on its surface,
- the surface temperature exceeds 400 degrees Celsius,
- the length of a day on Venus is equivalent to 243.02 Earth days,
- Venus rotates in the opposite direction compared to most celestial bodies,
- and it lacks any natural satellites.
Venus lacks a magnetic field, but the high density of its atmosphere prevents the depletion of the planet.

Venus
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the sun and our home. It is known for its diverse range of living organisms.
- It has developed atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere.
- More than 70% of its surface is covered by water.
- It has a strong magnetic field.
- It takes 24 hours for one complete rotation around its axis and 365 days to complete a revolution around the sun.
- It has moving tectonic plates.
- The Moon serves as its satellite.
- Many properties of extraterrestrial objects (such as mass, rotation time, and surface area) are measured in relation to those of Earth.
The existence of life on other celestial bodies is still not fully understood.
Mars, which is the fourth planet from the Sun, is considerably smaller when compared to Earth or Venus.
- Mars completes a full revolution around its star in 687 Earth days.
- It possesses an atmosphere.
- There are traces of water and ice caps at the poles.
- The atmospheric pressure on Mars is 6.1 mbar, which is only 0.6% of Earth’s pressure.
- Volvanoes have been discovered on the surface of Mars, with the largest one (Olympus) measuring 21.2 km in height.
- Traces of geologic activity have been observed.
- Mars has two satellites, Deimos and Phobos.
Mars is the second most extensively studied celestial body in our solar system, following the Earth.
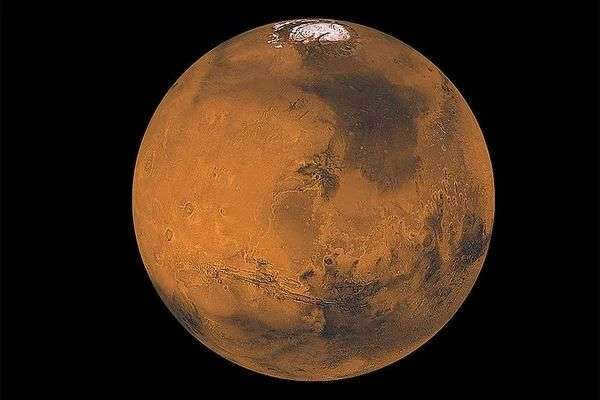
Red Planet
Giant gas planets
The outer region of the planetary system is comprised of giant gas planets, their moons, the Kuiper Belt, the diffuse disk, and the Oort Cloud.
Distinguishing features of giant gas planets:
- Impressive size and mass.
- Lack a solid surface, composed of gaseous substances.
- Their core is made up of liquefied metallic hydrogen.
- Rapid rotational speed.
- Notable gravitational pull.
- A multitude of moons.
- Possess rings.
Figure 1 illustrates the internal arrangement.
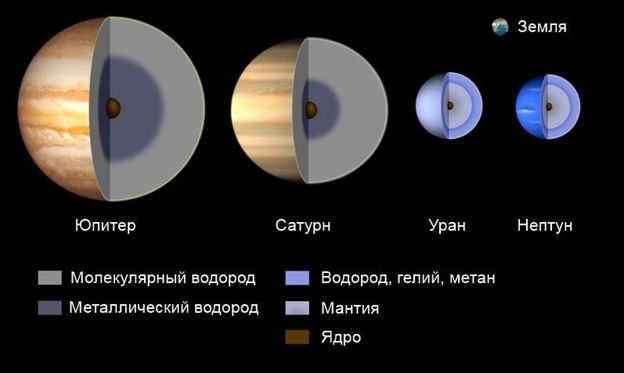
Structure within
Jupiter
Jupiter is the initial gas giant and the fifth planet from the Sun.
- It consists of hydrogen and helium,
- scientists have detected a high internal temperature,
- the star has an orbital period of 4333 Earth days,
- it completes one rotation on its axis every 10 Earth hours,
- the largest moons – Ganymede, Callisto, Io, and Europa – have a structure similar to that of the Earth’s moon group,
- Ganymede, the largest moon (with a radius of 2634 km), is larger than Mercury.
How fascinating! Let’s learn about planets: which one is the biggest?

Jupiter
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the star and the second gas giant. One of its most notable characteristics is the presence of rings, which can be seen from a great distance.
- It takes 10,759 Earth days for Saturn to complete one orbit around the star.
- A day on Saturn lasts for 10.5 Earth hours.
- It is the least dense celestial body in the entire system.
- Saturn’s moons Titan and Enceladus exhibit geological activity.
- Titan, one of Saturn’s moons, has its own atmosphere and is larger than the planet Mercury.
While Saturn’s rings were once believed to be a unique phenomenon, it has been discovered that all gas giants, including one of Saturn’s moons called Rhea, have rings as well.
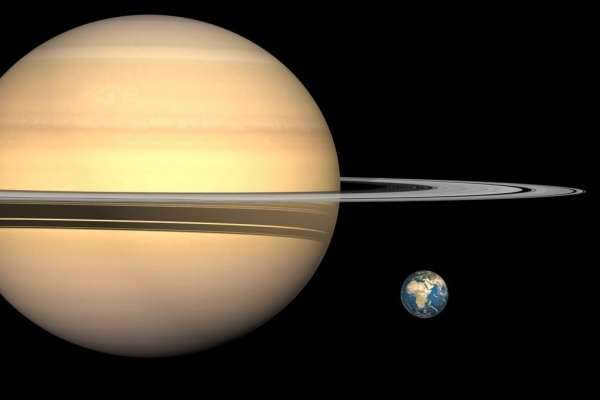
Saturn
Uranus
Uranus is the lightest of the gas giants and the seventh planet from our host star.
- with a surface temperature of -224 degrees Celsius,
- with an axis tilt of 98 degrees,
- It takes 30,685 Earth days to complete one orbit around its star,
- It takes 17 Earth hours to complete one rotation on its axis,
- the largest moons of Uranus are Titania, Oberon, Umbriel, Ariel, and Miranda.
Did you know? Due to its extreme tilt, Uranus appears to be rolling on its side.

Uranus
Neptune
Neptune is the final planet, located eighth in order from the Sun.
Notable characteristics of this heavenly body:
- It takes approximately 60,190 Earth days to complete one revolution around the Sun,
- Wind speeds on Neptune can reach up to 260 meters per second,
- The largest moon, Triton, displays geological activity and features geysers of liquid nitrogen and atmosphere,
- Triton rotates in the opposite direction compared to the other moons.
An astonishing fact is that the presence of Neptune was discovered solely through mathematical calculations. The positions of the terrestrial planets and the other gas giants were determined using powerful telescopes.
Summary
The universe is boundless and awe-inspiring, with countless galaxies and planets waiting to be discovered by humanity. This is why one of the primary goals of contemporary astronomy is to explore uncharted territory and investigate the potential existence of alternative life forms.

Our cosmic neighborhood is known as the Solar System, and its inhabitants are the planets. It is only fitting that each planet has its own unique name and place in this vast expanse.
In this article, we will explore the proper arrangement of the planets and delve into the reasons behind their chosen names.
Let’s start with the star of our Solar System: the Sun.
The Sun, the focal point of this article, derives its name from the Roman god Sol, who was revered as the deity of the celestial luminary. The word “sol” has roots in numerous languages, universally evoking thoughts of our modern-day Sun.
From this radiant star, we can trace the correct sequence of celestial objects, each possessing its own distinct characteristics.
Trivia: Have you ever wondered about the Earth’s rotational speed around the Sun?
The very first celestial body we focus our attention on is Mercury, which is named after the swift messenger of the gods, Mercury. And Mercury itself is far from being sluggish; due to its proximity to the Sun, it orbits our star at a faster pace than any other planet in our solar system, making it the smallest planet revolving around our radiant luminary.
Fascinating pieces of information:
- Mercury follows an elliptical orbit around the Sun, unlike the other planets that follow a circular path; furthermore, this orbit is constantly shifting.
- Mercury possesses an iron core that constitutes 40% of its mass and 83% of its volume.
- Mercury can be observed in the sky without the aid of a telescope.
Here’s an interesting fact: the distance between the Earth and the Moon.
The second house in our system is known as Venus. This planet was named after the goddess of love, Venus, who is admired for her beauty. Venus is slightly smaller in size compared to Earth. Its atmosphere is predominantly composed of carbon dioxide, with only trace amounts of oxygen.
Fascinating details:

- Mercury and Venus are both visible to the naked eye.
- Venus holds the title for being the hottest object, with surface temperatures reaching up to 475 degrees Celsius.
- About 70% of Venus’ surface is composed of water, while the remaining 30% consists of fully-formed continents, although their habitability remains uncertain.
Planet Earth
Our planet, Earth, is the only known space object that supports life. It is the third planet in our solar system and provides a perfect environment for living organisms with its suitable temperature, abundant oxygen, and vast water resources. The name of our planet is derived from the Slavic root “zem,” which means low. This name may have originated in ancient times when Earth was mistakenly believed to be flat, hence the reference to its low elevation.
Interesting Facts about Earth:
- Earth’s natural satellite, the Moon, is the largest among the satellites of the terrestrial group of dwarf planets.
- It is also the densest planet among the terrestrial group.
- Earth and Venus are often referred to as sister planets due to their similar atmospheres.
Mars, the fourth planet in our solar system, is known for its distinctive red color. It is named after the Roman god of war due to its blood-red appearance, although this color is actually caused by the high iron content on the planet’s surface. Despite being smaller than Earth, Mars has two moons, Phobos and Deimos.
Did you know?

- Mars has a fascinating array of formidable satellites in its orbit, true to its reputation as the god of war. Phobos and Deimos, which mean fear and terror in Latin, are among them.
- Scientists speculate that there may have been or still could be life on Mars, based on the discovery of water on the planet in the distant past.
- Mars has been the subject of extensive research, second only to our own planet Earth.
The asteroid belt
Situated between Mars and Jupiter, the asteroid belt serves as a demarcation line between the terrestrial planets and the giant planets. According to some experts, the asteroid belt is merely the remnants of a shattered planet. However, the prevailing theory suggests that the asteroid belt is a result of the Big Bang, the event that gave rise to our galaxy.
Jupiter, which is the fifth planet from the Sun, is approximately two and a half times more massive than the total weight of all the other planets in the galaxy. The name of this colossal planet is derived from the ancient Roman god, who was the king of all gods, probably due to its impressive size.
Fascinating information:
- There have been numerous scientific discussions regarding Jupiter. Some scientists propose that Jupiter is an unsuccessful star. In order to become one, it would need to increase its current weight by 88 times.
- Mapping out the distribution of satellites around Jupiter is exceedingly challenging due to the abundance of satellites orbiting it, up to 67 in total. This is the highest number recorded in our solar system. Among these satellites, Ganymede, Europa, Io, and Callisto could be considered as dwarf planets. Ganymede is even larger than Mercury!
- Jupiter’s satellite Io is one of the three satellites that has its own atmosphere.
Saturn
Saturn is named after the Roman god of farming. The symbol of Saturn is the sickle. The sixth planet is widely recognized for its magnificent rings. Saturn has the lowest density among all the celestial bodies orbiting the Sun. Its density is even lower than that of water.
Fascinating details:
- Saturn has a total of 62 satellites. The most well-known among them include: Titan, Enceladus, Japetus, Dione, Tefia, Rhea, and Mimas.
- Saturn’s moon Titan has the most substantial atmosphere compared to any other moon in the solar system, and Rhea also possesses rings similar to those of Saturn itself.
- The chemical composition of the Sun and Saturn is more similar than that of the Sun and any other object in the solar system.
The seventh planet in our solar system is Uranus. It is sometimes referred to as the “lazy planet” because it has a unique rotation. Unlike other planets, Uranus lies on its side during rotation, with its axis tilted at a 98-degree angle. Uranus is also known for being the lightest planet in our system. Its satellites are named after characters from the works of William Shakespeare and Alexander Pope. The planet itself is named after the Greek god of the sky.
Here are some interesting facts about Uranus:
- Uranus has a total of 27 satellites. Some of the most famous ones include Titania, Ariel, Umbriel, and Miranda.
- The temperature on Uranus can drop as low as -224 degrees Celsius.
- One year on Uranus is equivalent to 84 years on Earth.
The planet Neptune, which is the eighth and last planet in our solar system, is located relatively close to its neighboring planet Uranus. The name Neptune was chosen in tribute to the god of the seas and oceans, and this name was given to the planet because of its deep blue color that resembles the vastness of the ocean.
Fascinating details:
- The discovery of Neptune was made using mathematical calculations rather than observations, setting it apart from the other planets in our solar system.
- When compared to other gas giants, Neptune actually has a relatively small number of satellites, with just 14 in total.
- One interesting feature of Neptune is its moon Triton, which is the third moon in the solar system to possess its own atmosphere.
Since August 2006, Pluto is no longer recognized as a planet and has been reclassified as an asteroid due to its small size. Unlike other planets, Pluto’s name does not come from any god. It was actually named after the beloved cartoon character, Pluto the dog, by its discoverer, who named it after his daughter’s favorite character.
This article has provided a brief overview of the planet classification, and we hope you have found it to be both useful and informative.





