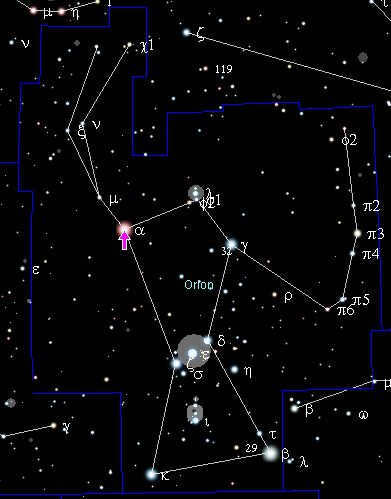
If you are situated in the temperate latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere, chances are you are familiar with the whereabouts of the Orion constellation. Recognized as one of the most prominent constellations in the night sky, alongside the Big Dipper, it never fails to capture one’s attention. The three stars that comprise Orion’s belt are particularly mesmerizing. Equally captivating is the star that forms the left shoulder of the Hunter’s celestial figure. This particular star emanates a brilliant red hue and goes by the name of Betelgeuse.
The red supergiant
This term is derived from the Arabic language. It signifies something akin to “dual hand.” Betelgeuse is located nearly 640 light-years away from Earth and stands as the tenth most luminous star in the nighttime sky. What’s more, it is remarkably enormous. Its mass is twenty times that of our own Sun, and its radius exceeds 1,000 times! Betelgeuse boasts 55,000 times the luminosity of our Sun, yet it is significantly colder, with a surface temperature of 3180 degrees Celsius – exactly half that of the Sun.
Betelgeuse is a comparatively young star compared to the Sun, as it is only 10 million years old. In contrast, the Sun is a whopping 4.5 billion years old. Interestingly, Betelgeuse has undergone a significant transformation in the last few tens of thousands of years, transitioning from a blue O star to a red supergiant.
This transformation occurred when the star depleted its hydrogen fuel in its core, causing it to collapse under its own gravitational pull. This collapse led to an immense increase in pressure and temperature within the core. The temperature became so extreme that the star could now fuse helium and carbon atoms, providing it with a new source of energy. As a result, Betelgeuse began to expand rapidly, growing much larger than its previous size. It continued to expand until it reached its enormous size today!
Enormous. Yet not compact
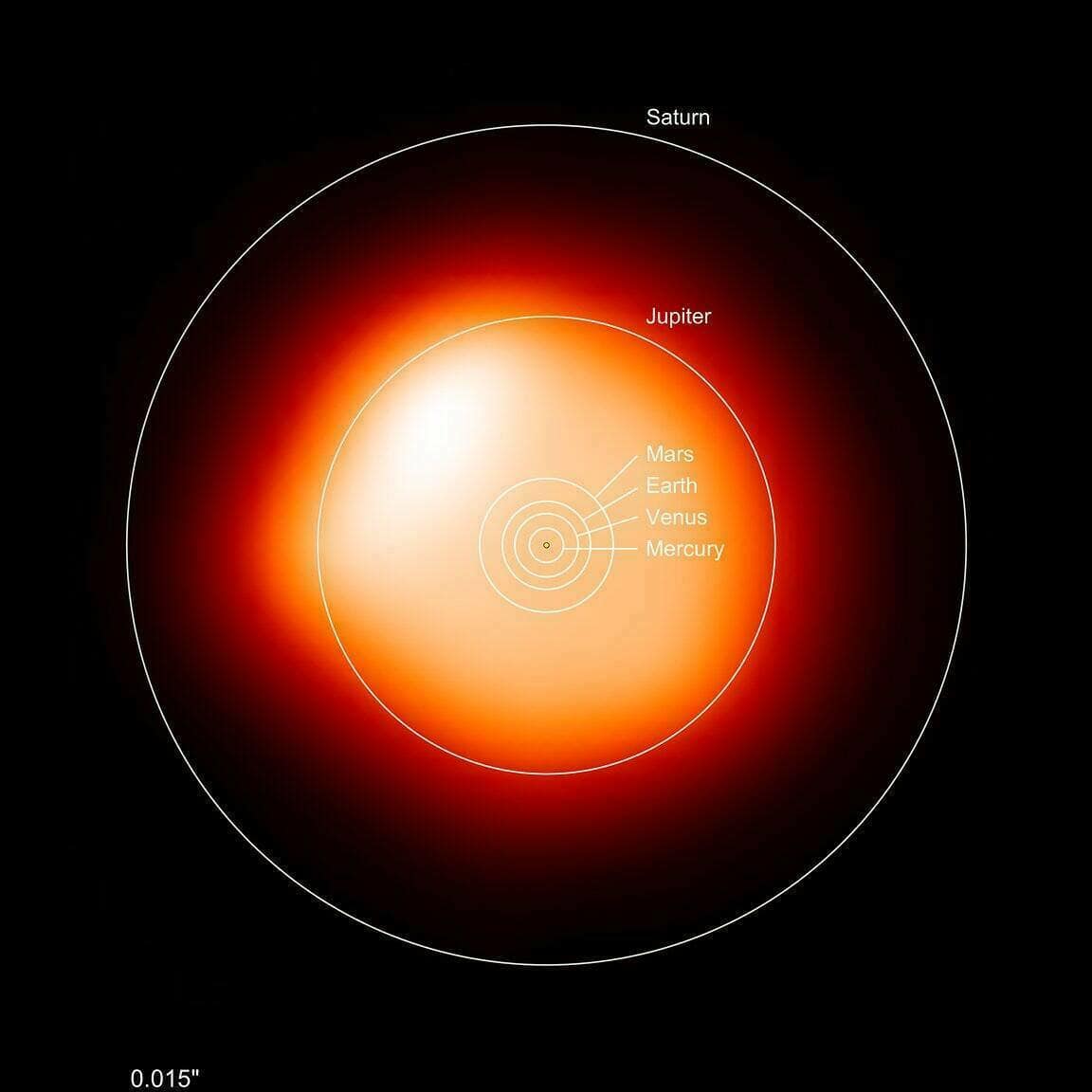
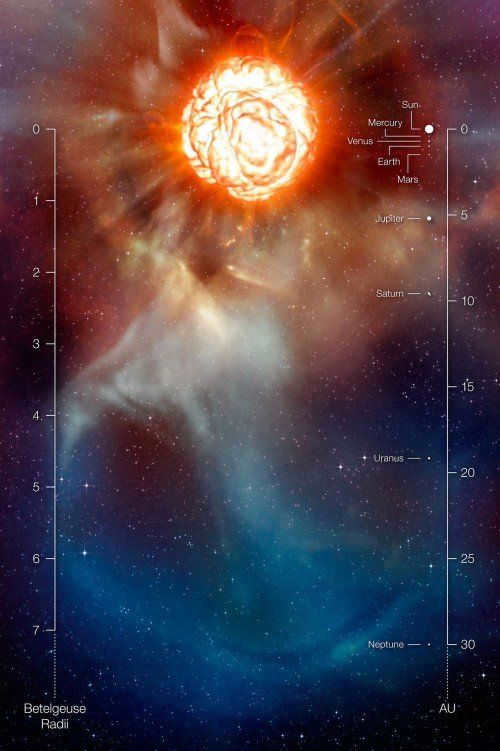
If Betelgeuse were placed in the position of the Sun, it would occupy almost the entire solar system, reaching the orbit of Jupiter. However, the density of Betelgeuse’s gas is significantly lower than that of the Sun. Furthermore, its density decreases over time due to the star’s intense heat generating a powerful stellar wind. The gravitational force, stemming from Betelgeuse’s own mass, is unable to counteract the radiation emitted from its hot core. As a result, the star continuously expels vast quantities of material into space.
In addition, Betelgeuse experiences changes in its luminosity. Approximately every 2070 days, it undergoes slight fluctuations in brightness.
Currently, the night sky still offers a view of the red supergiant Betelgeuse. However, it is predicted that this star may eventually disappear from our view. The reason for this is that red supergiant stars have a relatively short lifespan. They lack the necessary helium, carbon, and other atoms in their cores to sustain a fusion reaction for an extended period of time. Eventually, all available materials will be depleted, and energy production will come to a halt.
At this point, the outer layers of Betelgeuse will collapse into its core due to its own gravitational force. This will result in a magnificent event, known as a “supernova.” It will be one of the most powerful cosmic explosions ever witnessed, leaving astronomers in awe.

An explosive event of a supernova
When this occurrence transpires, the celestial body situated on the shoulder of Orion will be undoubtedly conspicuous. It will become one of the most luminous stars in the celestial sphere. Upon Betelgeuse undergoing a supernova explosion, it will radiate brilliance equivalent to that of the Moon for a certain period! Furthermore, this spectacle will not solely manifest itself during nighttime hours, but also during the diurnal hours.
The scale of this explosion will be so immense that it has the potential to impact our planet. Ionizing radiation may permeate the Earth’s atmosphere and potentially devastate crucial components such as the ozone layer, causing severe repercussions. As a result, until the ozone layer can regenerate, we will be subjected to cosmic radiation. This is a situation that we must take into account.
However, all of this is purely theoretical speculation. In reality, the likelihood of such an event occurring is highly improbable. This is largely due to the fact that the radiation emitted from such an explosion does not disperse evenly in all directions. Instead, it predominantly follows the imaginary axis along which Betelgeuse rotates. Furthermore, this axis is not aligned with Earth, thus eliminating any potential danger.
Moreover, the exact timing of Betelgeuse’s explosion remains uncertain. While the star is indeed on the brink of a cataclysmic event, the concept of “about to” in astronomy can encompass thousands of years.
Theoretically, this explosion could transpire tomorrow, or it could be delayed for a thousand years, or even a hundred thousand years. Regardless, the ultimate outcome will be the near annihilation of the red giant. It is conceivable that only a neutron star, spanning a mere few kilometers, will remain. Alternatively, it might even collapse into a black hole.
Exploring the Wonders of Betelgeuse
While we wait for further developments, let’s seize the unique opportunity to delve into the intricate details of Betelgeuse. This celestial object stands out from the rest, as it is one of the few stars that transcends the mere appearance of a luminous speck when observed through telescopes. Astronomers have the privilege of observing Betelgeuse in a resolved form, allowing them to witness the star as a diminutive disk.
During these observations, astronomers have already detected various structures and regions that exhibit a greater brightness compared to their surroundings. These areas are believed to be vast convection cells, where scorching material from within the star ascends to the surface.
Furthermore, extensive observations have revealed that between 1993 and 2009, Betelgeuse underwent a remarkable shrinkage of 15 percent without any noticeable change in its luminosity.
The red star located on the shoulder of Orion is sure to lead to more fascinating findings. It provides us with an opportunity to investigate the development of massive stars and their eventual demise. And if we are fortunate enough, we may even have the chance to witness that final stage firsthand.
However, it would be somewhat disheartening if Orion, a constellation renowned for its beauty, were to lose one of its most prominent stars…..
An explosion is the most probable outcome of a red star and a significant event in astronomy, which is why scientists are particularly interested in Betelgeuse. They have a unique opportunity to observe the state of the supergiant prior to the explosion.
2021: The star is in closer proximity to Earth than previously estimated
Through modeling, scientists led by experts from the Australian National University have reevaluated the size of the star and its distance from Earth. It turns out that the supergiant is slightly smaller and much closer to us than previously believed.
For a considerable amount of time, scientists were unable to determine the true dimensions of Betelgeuse – they could only speculate. Previous research led to the belief that it was slightly larger than Jupiter’s orbit. However, recent findings have shown that the star is actually smaller – it only takes up two-thirds of Jupiter’s orbit in size. Additionally, its radius is 750 times that of the Sun [1].
By obtaining more precise data on the physical dimensions of Betelgeuse, the researchers were able to make a more accurate calculation of its distance from Earth. It turns out that the star is actually only 530 light-years away, which is 25% closer than previous estimates. However, even if the scientists are mistaken and Betelgeuse were to explode in the near future, it would still be too far away to pose any threat to Earth. There is no expectation of a gamma-ray burst accompanying the explosion, and the X-ray and UV radiation emitted by Betelgeuse would have no impact on us. Nevertheless, 530 light-years is still quite a distance, and the explosion would primarily be of interest from an astronomical standpoint.
Scientists are feeling uneasy about a supergiant star located in the Orion constellation. Starting in late 2019, it experienced two instances of dimming. The initial decrease in brightness raised concerns of an imminent explosion, but by April 2020, the star’s brightness returned, albeit briefly. A few months later, Betelgeuse dimmed once again, although not to the same extent as the first occurrence.
The first dimming was likely the result of a cloud of dust being expelled by the supergiant star. The second episode, which was less intense, was investigated by an international team of astronomers led by experts from the Australian National University. These experts believe that the star’s pulsations were the cause of its dimming this time around.
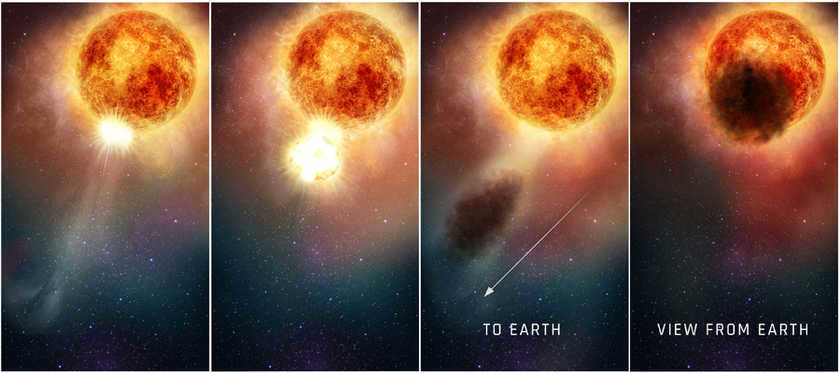
A video recorded the dimming of Betelgeuse as a result of a dust cloud in late 2019 and early 2020. Image: NASA, ESA, and E. Wheatley (STScI)
By creating a hydrodynamic model and simulating seismic processes on the surface of the supergiant, the scientists were able to determine that the star’s dimming, which is visible from Earth, is caused by pulsations generated by pressure waves.
The modeling also helped calculate the current phase of the red star’s life. Unfortunately, for those hoping for a celestial spectacle, the results indicate that Betelgeuse is currently in a phase where it is burning helium in its core, which means that it is not planning to explode anytime soon. In fact, the explosion of Betelgeuse is not expected for another 100 thousand years.
Remarks

Betelgeuse, one of the largest stars currently known to astronomers, is poised to conclude its life cycle and undergo a supernova. The exact timing of this event remains uncertain, but the resulting explosion’s intense brightness will likely illuminate a significant portion of the galaxy. The flash will be so powerful that it will be visible even during daylight hours. Over the course of a few weeks, an immense amount of energy will be released, equivalent to the Sun’s total energy output throughout its entire existence. The destructive impact will extend up to a radius of approximately 30 light years.
The Sun and Betelgeuse, a comparison
The constellation of the red giant Betelgeuse.
Betelgeuse and Rigel are two supergiants located in the constellation of Orion. Betelgeuse is classified as a red supergiant, while Rigel is classified as a blue supergiant.
The brightness of Orion’s Alpha, which includes Betelgeuse and Rigel, can vary in the night sky, with magnitudes ranging from 0.4 to 1.4. This means that Betelgeuse and Rigel can be seen as competing with each other in terms of luminosity. Additionally, it is worth noting that Orion’s Alpha can sometimes outshine Rigel in terms of luminosity.
Interestingly, the red supergiant Betelgeuse was originally intended to have a different name. However, due to a mistake, it ended up with its current name.
A colossal dream in the galaxy
The residue of a Type Ia supernova.
Undoubtedly, a brilliant luminosity in the celestial sphere would provoke individuals to contemplate their insignificance in the vast expanse of the universe. Just envision for a moment that the same cosmic eruption could be observed by potential inhabitants residing in remote systems within our expansive galaxy. Astronomers will undoubtedly derive genuine and irreplaceable advantages from such stellar revelations. As the long-awaited supernova explosion draws near in this century, the inquisitive gaze of various telescopes and other instruments will be fixated in its direction. In a frenzied state of excitement, scientists will inundate their databases with copious amounts of valuable information transmitted alongside the explosion’s radiance. Each passing day, news of the subsequent groundbreaking discovery will echo from every corner of the globe. However, these remain naught but elusive reveries.
Reality sets its own rules. The explosion of Betelgeuse is not something to be feared or even expected to be witnessed; it is something that can only be imagined. Even if the flame were to ignite before our eyes, it would hardly match the brightness of the full moon and would not cause us any significant harm. In the meantime, we have the opportunity to continue observing the red star of Orion and hope that astronomers will gain more knowledge without the occurrence of such rare and astonishing events.
Discover the latest astronomical findings and other noteworthy space news on our website. Subscribe, invite your friends, and be the first to catch the “supernews”!
Origin of the Name
The name of the red giant Orion has its roots in Arab countries. In Arabic, the giant was known as “Yad-al Jawza”, which translates to “twin hand”. However, during the Middle Ages, the Arabic letter “y” was often mistaken for the letter “b”.
As a result, the incorrect interpretation of “Beteljuz” became widely accepted. This name was translated to mean “house of twins”. In Arabic astronomy, the constellation Orion is referred to as “Gemini”.
Caution! This should not be confused with the actual Gemini constellation.
In addition to its original name, the red giant is known by various other names:
- Bashn (Persian for “hand”);
- Claria (Coptic for “bandage”);
- Ad-Dira (derived from Arabic word for “hand”);
- Ardra (in the Hindi language).
Notes
- ↑ 12
New photographs have revealed the presence of enormous bubbles on the surface of Betelgeuse. The information was reported by Lenta.ru on July 30, 2009, and was checked on August 13, 2010. The article has been archived since August 24, 2011. - Astronomers have successfully determined the mass of Betelgeuse. This information has been archived since September 24, 2011.
- Mohamed, S.; Mackey, J.; Langer, N. (2012). “3D Simulations of Betelgeuse’s Bow Shock”. Astronomy & Astrophysics541, id.A1
: A1. arXiv:1109.1555v2.pdf. DOI:10.1051/0004-6361/201118002. Bibcode:2012A&A…541A…1M. - ↑ 12345678910
The SIMBAD Astronomical Database provides further information on Betelgeuse. For more details, visit the following link: Link - J. Weiner, W. C. Danchi, D. D. S. Hale, J. McMahon, C. H. Townes.
Precision Measurements of the Diameters of Alpha Orionis and Omicr Ceti at 11 Microns // The Astrophysical Journal. — December 1, 2000. — Vol. 544. — pp. 1097–1100. — ISSN 0004-637X. — DOI:10.1086/317264. - Kunitzsch, P.; Smart, T.
A Dictionary of Modern Star Names: A Short Guide to 254 Star Names and Their Derivations. — 2nd ed., revised and expanded. — Cambridge, MA: Sky Pub., 2006. — ISBN 9781931559447. - Allen, Richard Hinckley (1963). Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning (Revised edition).
- A. A. Michelson, F. G. Pease.
Measurement of the diameter of alpha Orionis using an interferometer. // The Astrophysical Journal. – May 1, 1921. – Vol. 53. – ISSN 0004-637X. – DOI:10.1086/142603. - The structure of the surface and the darkening profile of Betelgeuse
- E. O'Gorman, P. Kervella, G. M. Harper, A. M. S. Richards, L. Decin, M. Montargès, and I. McDonald.
The non-uniform sub-millimeter atmosphere of Betelgeuse // arxiv.org : pdf. – 2020. – June 19. - ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)/E. O’Gorman/P. Kervella.
ALMA has captured images of the surface of Betelgeuse.
www.eso.org
(June 26, 2020). – The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) telescope has produced images of our neighboring star, Betelgeuse. These images represent the first-ever observations of Betelgeuse’s surface using ALMA, and they have achieved a higher resolution than any previous observations. The images were archived on June 30, 2020. - ↑ 12
Science News – R&D.CNews. www.rnd.cnews.ru. Verified July 1, 2020. - Computera: How can we revive people’s diplomacy? (Russian). science.compulenta.ru. Checked July 1, 2020.
- Popular Giant Star Shrinks Mysteriously, Space.com.
. Checked July 1, 2020. - The size of Betelgeuse changes over time. (source: astronet.ru – 06/30/2009; archived on August 24, 2011).
- Is Betelgeuse shrinking? (source: NewScientist – 10.06.2009; archived on August 24, 2011).
- A systematic change in the size of Betelgeuse over time, as stated by C. H. Townes et al.
- Oksana Gribanova comments on the news of the second Sun appearing (source: Rossiyskaya Gazeta – 2020 – May 18).
- The second Sun will be visible in the sky, as reported by STS.
- Arseny Tarkovsky’s star catalog.
How to Observe the Night Sky
One can catch a glimpse of Betelgeuse in the nighttime expanse of the Northern Hemisphere on Earth.
This colossal red supergiant is situated in the constellation Orion, which grants it a prominent position in the winter sky. It remains discernible even amidst the artificial glow of urban settings, particularly during the month of February.
Orion is classified as a winter constellation due to its exclusive presence in the southern region of the sky during the frigid season. Astronomers refer to this as its culmination. Amateur stargazers find it convenient to observe any celestial object located in the southern side of the sky.
It emerges in January on the eastern horizon shortly after sunset. By March 10th, it will have shifted to the southern sky, making it visible in the evenings. During this time of year, Betelgeuse can be seen from any part of the Earth.
Attention! In Sydney, Cape Town, and Buenos Aires, the red supergiant ascends to an elevation of 49 degrees in the celestial sphere.
Now let’s discuss the precise position of this star.
If you gaze directly at the three stars forming Orion’s belt, you will find that Betelgeuse is positioned to the left and slightly higher than the other two stars, which are aligned in a straight line. The brilliant light emitted by this star has a reddish hue. Betelgeuse represents the left shoulder of the mythical hunter Orion, while Bellatrix serves as the right shoulder.
The possibility of an explosion
The possibility of an explosion is acknowledged by scientists, although there is uncertainty regarding when it might occur. It could happen tomorrow, or it might take a million years, and there is also a chance that it might not happen at all. Despite the advancements in astronomy, our understanding of star life is still in its early stages. The existence of supermassive giants and the difficulties in modeling star formation in close systems challenge the existing scientific paradigms about star life. The discovery of objects that defy existing theories only raises more questions. Even Betelgeuse, a well-studied star, serves as an example of this.
Main features
The red supergiant is the ninth brightest object in the night sky. It has a variable luminosity ranging from 0.2 to 1.9 stellar magnitudes over a period of 2070 days. It belongs to the spectral class m1-2 la lab.
Size of the star
The star has a radius equivalent to 600 times the diameter of the Sun. It is 1400 times larger than the Sun and has a mass equal to 20 solar masses. Its volume is 300 million times that of the Earth.
Its atmosphere is thin and its density is significantly lower than that of the Sun. It has an angular diameter of 0.050 arc seconds, which varies depending on the giant’s luminosity.
Astronomers used a spatial infrared interferometer to measure the star’s radius. The star’s rotation period, which is 18 years, was also calculated.
Comparison of Betelgeuse’s size with other celestial objects
Temperature
The temperature of a red supergiant is 3,000 Kelvin (2,726.8 degrees Celsius). A red supergiant is significantly cooler than the Sun, which has a temperature of 5,547 Kelvin (5,273.9 degrees Celsius). The lower temperature of Betelgeuse is what gives it its reddish color.
Distance
The red supergiant is located 643 light-years from our solar system. This distance is considered to be quite significant.
When the star eventually explodes and transforms into a supernova, as predicted by astronomers, the resulting waves will have no impact on the essential functions of any organisms on Earth.
Additional information about the red supergiant can be found in the following table:
| Betelgeuse | Alpha Orionis |
| Constellation | Orion |
| Coordinates | 05h 55m 10.3053s (right ascension), + 07° 24′ 25.426″ (declination). |
| Apparent magnitude (visible spectrum) | 0.42 (0.3-1.2) |
| Apparent magnitude (J-band) | -2.99 |
| Spectral classification | M2Iab |
| Absolute magnitude | -6.02 |
| Distance | 643 light-years |
| Variable type | Semi-regular (SR) |
| Mass | 7.7-20 solar masses |
| Radius | 950-1200 solar radii |
| Luminosity | 120,000 times that of the Sun |
| Effective temperature | 3140-3641 K |
| Rotational velocity | 5 km/s |
| Age | 7.3 million years |
| Other names | Betelgeuse, Alpha Orionis, α Orionis, 58 Orona, HR 2061, BD + 7° 1055, HD 39801, FK5 224, HIP 27989, SAO 113271, GC 7451, CCDM J05552+0724AP, AAVSO 0549+07. |
Materials organized by topic
Supernova explosions are one of the cosmic events that are observed as they happen. In the field of science, there has never been a supernova explosion that has been predicted and anticipated in advance. Because of this, astronomers can only indirectly understand the processes that occur before the explosion.
When it comes to Betelgeuse, scientists confidently state that the star is in its final stage of life, where the current amount of carbon and other heavy elements can no longer support stable thermonuclear processes. Based on existing models, it is most likely that this will lead to the disruption of the star’s hydrodynamic equilibrium, in other words – a supernova explosion. There is also a possibility that Betelgeuse will not end its life in such a dramatic way, but instead gradually shed its outer layers, transforming into an oxygen-neon white dwarf.
Regardless, modern science is currently unable to determine an exact date for the explosion or dismiss the possibility entirely. The frenzy in the media surrounding the appearance of the “second Sun” began after the global astronomical community engaged in debates regarding the sudden decrease in average brightness and size of Betelgeuse. Numerous astronomers confidently asserted that this phenomenon could be attributed to an imminent supernova explosion, which, by cosmic standards, is expected to occur within the next two millennia. Others adopt a more cautious approach, attributing the star’s dimming to temporary or periodic processes. This unexpected dispute among astronomers highlights the vast amount of new and unknown information that scientists still need to uncover.
Facts about the red giant
The red giant known as Betelgeuse has an ever-changing radius, with a shape that fluctuates over time and features an asymmetrical shell with a slight bulge. This intriguing characteristic provides us with two important insights:
- Each year, the star loses mass as jets of gas erupt from its surface.
- There is a companion residing within the star that causes its eccentric behavior.
Observations made by scientists have revealed that since 1993, the size of Betelgeuse has decreased by 15%, while its brightness has remained constant.
Around the red giant, approximately five shells have been discovered. Additionally, in the ninth year of the twenty-first century, an emission of 30 astronomical units was detected.
In 2012, astronomers predicted that the red giant could encounter interstellar dust within twelve thousand years. Furthermore, the previous year, a scientist included it in the list of potential disasters that could occur in 2012.
Scientists acknowledge the following factors contributing to the reduction in size:
- An alteration in the luminosity of various regions on the surface of the supergiant. This can lead to a decrease in brilliance on one side and an increase on the other side of the star. On Earth, this can be conceptualized as a change in diameter;
- there is speculation that massive stars are not perfectly spherical, resulting in a bulge on Betelgeuse;
- a third hypothesis suggests that what astronomers are observing is not the actual diameter of the star but rather a layer of dense gas. The movements of this gas layer create the illusion of Alpha Orion changing in size.
Caution. Betelgeuse is surrounded by a gas nebula in the Orion constellation, which astronomers have previously overlooked due to the intense brightness emitted by Alpha Orionis.
Another fascinating fact is that Betelgeuse is part of the winter triangle, which consists of Procyon, Sirius, and this supergiant.
In cultures around the world
The star Betelgeuse has different names in various nations. Each nationality has its own beliefs and myths created by ancestors about the star’s origin.
For instance, in Brazil, it is called Gilcavai in honor of the hero whose wife tore his leg.
In Australia, it is named “owl eyes.” According to Australians, the two stars on Orion’s shoulders resemble the eyes of these nocturnal birds.
In South Africa, it is known as the lion that hunts the three zebras.
In literature and cinema.
The crimson supergiant is referenced in various literary works, poems, and movies by both Russian and foreign writers. For instance, in the renowned film “Planet of the Apes,” the planet Sorora orbits around this particular star. It is from this celestial body that the intelligent primates originated and journeyed to Earth.
One of the protagonists in the sensational movie “Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy” hails from and resides on a planet whose sun is Betelgeuse.
This star is also mentioned by the Danish author Niels Nielsen in his literary creations. His novel “Planet for Sale” narrates the tale of “planet hunters” who pilfered a minor satellite from Alpha Orion and transported it to Earth.
As early as 1956, Varlam Shalamov made a reference to this star in his Atomic Poem.
The star mentioned in Viktor Nekrasov’s work “In the Trenches of Stalingrad” is also described by him. The passage goes like this: “A train loaded with fuel is just two steps away from us, and during the day we can clearly see it from here. Kerosene continuously leaks out of bullet holes in the tank, forming thin streams. Soldiers go there at night to refill their lamps. I search the sky for familiar constellations out of habit from my childhood. Orion consists of four bright stars and a belt of three smaller ones. And then there’s one star that is very small and almost invisible. I can’t recall if it’s called Betelgeuse or not. Somewhere, there must be Aldebaran, but I’ve forgotten its location. Suddenly, someone places a hand on my shoulder, and I instinctively flinch.”
The famous novel "The Sirens of Titan" by Kurt Vonnegut also references the star. In this novel, the protagonist takes the form of a pulsating spiral wave that revolves around both the Sun and Betelgeuse.
Roger Zhelyazny wrote a novel called "The Light of the Sullen" which takes place on one of the planets orbiting the red giant star, shortly before its supernova explosion.
Arseny Tarkovsky’s 1998 poem "Star Catalog" also mentions Betelgeuse.
There are references to the star of Beetlejuice in the film Blade Runner. When the character Roy Batty dies, he mentions it as the shoulder of Orion: “I have seen something that you people simply won’t believe. Burning warships on the approaches to Orion’s shoulder. I saw the C-rays… flickering in the darkness near the gates of Tannhäuser. And all these moments will disappear in time like tears in the rain. It’s time to die.”
One of the writers is known as See Betelgeuse. He has written a poem dedicated to Alpha Orion.
The Ukrainian rock band Tabula Rasa has dedicated a song to the red giant called “Rendezvous on Betelgeuse”.
Some of the celestial bodies that captivate us are Jupiter, Aldebaran, Betelgeuse, M42, and the Pleiades.
Refocusing on Betelgeuse, we can provide a sort of conclusion to those sources that announce the imminent arrival of the most brilliant “farewell fireworks” in our atmosphere. Astronomers clarify that such an occurrence holds a genuine chance of happening right before our eyes, but the likelihood of this happening is incredibly slim, and it is unattainable to evaluate. Understandably, the media, seeking to engage the public, reshape these cautious statements in their own manner.
Comparison with the Sun
Betelgeuse is significantly larger than the Sun.
If Betelgeuse were placed in the solar system, it would extend all the way to Jupiter. As its size decreases, it would reach the orbit of Mars.
Betelgeuse is 100,000 times brighter than Earth and has an age of 10 billion years, while the Sun is only around 5 billion years old.
Scientists are increasingly puzzled by Betelgeuse’s behavior, as the red giant exhibits similar characteristics to the Sun. It has localized hot spots and cooler areas on its surface.
Despite the Sun being spherical in shape and Betelgeuse having a more irregular shape resembling a potato, this discrepancy continues to baffle the scientific community.
A supernova that is “extremely unpredictable”.
According to certain sources, Betelgeuse, which is located in the right shoulder of the constellation Orion, has the potential to unexpectedly explode in a brilliant supernova display, leaving behind a void that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
This extraordinary event would dramatically alter the appearance of the constellations that adorn the winter skies in our part of the world. Is it worth anticipating this event during our time on Earth, and is there any danger posed to our planet?
Various news outlets are reporting that an enormous supernova eruption may occur at any moment. Betelgeuse is set to dramatically increase in luminosity, shining thousands of times brighter and illuminating the night sky for several months. Eventually, it will gradually diminish in intensity, leaving behind the expansive Crab Nebula, with an unseen neutron star or black hole at its core. While this cosmic event poses no immediate threat to us, unless one of the star’s poles happens to be oriented towards Earth, the ensuing stream of gamma rays and charged particles could potentially disrupt the planet’s magnetic field and ozone layer. Should we place our faith in such reports, or is this merely another instance of sensationalist media speculation?
Provides the opportunity to attain a prominent position in the realms of sports, law, or the military, as well as public affairs. However, there is always the risk of losing everything in an instant. Interests and talents in the occult and mysticism, intense illnesses, and fevers; a magnificent and illustrious career concludes in ruin.
Cultivates an active intellect and immense determination, enabling the attainment of enduring popularity and happiness, as well as prestigious honors. Nevertheless, unforeseen setbacks cannot be ruled out and the potential for suffering as a result of any disagreements exists. Beneath the reserved exterior lies a rebellious spirit, success in the military accompanied by conflicts with superiors, and the opportunity to amass significant influence, accolades, and prosperity.
The seriousness of behavior and diligence are qualities that can help one establish themselves in the legal and financial fields. This may lead to fame, whether positive or negative, and there may also be a tendency towards self-destruction. Additionally, there is a seriousness and curiosity that inclines one towards science and literature, though there may be limited material wealth. Fame may be achieved through literary work or metal engravings, and overall good health is present despite facing adversity.
While popularity is favorable, there is a risk of experiencing domestic and family troubles. It is important to exercise caution to avoid becoming the cause of these issues. There may be some shyness and reticence, but also an exceptional talent for crafting fine jewelry and the potential for prosperity. However, there may also be some sorrow related to family matters.
Be cautious and restrained; possess the ability to lead, but also have intolerance for any interference in your affairs and a temper. You are a skillful leader and organizer, and you receive honors and high ranks in the military. However, there is a possible threat of death by lightning, fire, explosion, firearms, and other similar dangers.
You have a deep and inquisitive mind, which can lead you to dangerous and profitable occupations. You also have the potential for honors in the church or in the legal field. Your achievements in sports, literary work, and social work will be recognized by the public.
You are cunning, dodgy, and fraudulent. There may be betrayals of friends, and your life will be full of adventure, ups and downs. Eventually, you will attain wealth, but not luxury. This is an unfavorable time for family matters.
You have a quick, productive, and wicked mind. You can be a cunning villain, a celebrated swindler, and a forger. However, you are rarely caught by the hand. Outwardly, you have kind manners, generosity, and cordiality. You also have the ability to hypnotize and read other people’s thoughts.
He possesses clairvoyance and a talent for mechanics. He may have invented some remarkable device. He is also interested in spiritualism and may have experienced serious illness or bodily suffering. There is a possibility of mental illness. He does not possess great wealth, but he may achieve material success through a profitable partnership. His marriage and children will bring him happiness, but he may experience conflict with his siblings. In adulthood, he will face a severe test.
If this conjunction occurs with the ASC, it may indicate a threat of death by lightning, fire, explosion, firearms, etc. According to A. Eich.

Stars are massive spheres of fiery plasma. However, all except for the Sun appear as tiny specks of light in the celestial sphere. The Sun, although not the largest or smallest star in existence, is classified as a yellow dwarf. While it surpasses the combined size of all the planets, it is still considered average when compared to other stars. There are numerous stars that are significantly more massive and larger than our Sun. Some stars have expanded over time due to their evolution, while others have grown larger as they have aged.
A gigantic star with a vivid red color can be found in the constellation Shields and is currently acknowledged as the most enormous star within the Milky Way galaxy.
In 1860, German astronomers initially identified this star at the Bonn Observatory, but it was not until 2012 when astronomers observed UY Shields through a telescope in the Atacama Desert in Chile, that the accurate size of the star became extensively documented.
Following this incredible revelation, UY Shields was officially designated as the largest known star in the galaxy, surpassing previous record-holders like Betelgeuse and VY Big Dog.
Although there are other stars that are more luminous and compact than UY of the Shield, it stands out for its immense size, with a radius of 1708 ± 192 R. This measurement corresponds to a distance of approximately between 1,054,378,000 and 1,321,450,000 miles, which is roughly 1,700 times the radius of our Sun and 21 billion times its volume.
If UY of the Shield were to trade places with our Sun, it would engulf the entire orbit of Jupiter, consuming not only the Sun but also the first five planets of our solar system and the asteroid belt.
Betelgeuse
Betelgeuse is easily visible in the night sky from October to March on Earth. It has a radius that is a thousand times larger than our Sun, making it the most well-known red supergiant. One of the reasons for its fame is that Betelgeuse is about 640 light-years away from Earth, which sets it apart from other stars on this list.
Furthermore, Betelgeuse is situated in the renowned constellation Orion. This colossal star measures somewhere between 950 and 1200 solar radii and is anticipated to undergo a supernova event at any given moment.
VY of the Big Dog
This crimson hypergiant is among the most massive stars in our galaxy. Its approximate size is about 1,800 to 2,100 times larger than the Sun’s radius.
With such a colossal size, if VY of the Big Dog were placed in our solar system, it would extend beyond the orbit of Saturn. Situated approximately 3,900 light-years away from Earth, it is one of the numerous variable stars that can be observed in the constellation of the Big Dog.
VV Cepheus
This celestial body can be found in the region of the constellation Cepheus, situated approximately 6,000 light years away from our planet. It is an immense red hypergiant star, boasting a radius around one thousand times greater than that of the Sun.
In reality, this star forms part of a binary star system, with its companion being a diminutive blue star. The two stars gracefully revolve around each other in an intricate celestial waltz. As of now, no planets have been detected orbiting this particular star. The star has been named after the larger of the two stars in the pair, and it has gained recognition as one of the most colossal stars within the Milky Way galaxy.
This red supergiant has a radius approximately 1,650 times that of our Sun. Additionally, it stands out as one of the most luminous stars in the Milky Way galaxy, boasting a brightness 38,000 times greater than our Sun.
It is also affectionately known as “Herschel’s Garnet Star” due to its distinctive reddish hue.
V838 of the Unicorn
This red variable star resides in the constellation Unicorn and is situated approximately 20,000 light years away from Earth. Given its vast distance from the Sun, determining its actual size proves challenging.
Furthermore, it exhibits fluctuations in size, with its apparent size diminishing since its most recent outburst in 2009. Consequently, the range is typically cited as 380 to 1970 solar radii.
V354 Cepheus
This red hypergiant, which is slightly smaller than WOH G64, has a diameter of 1520 solar radii. V354 Cepheus can be found in the constellation Cepheus, approximately 9,000 light years away from Earth. It is classified as an irregular variable star, meaning that its pulsation occurs on an irregular schedule.
Astronomers who have extensively studied this star have concluded that it belongs to a large cluster of stars known as the Cepheus OB1 stellar association. This stellar association consists of numerous hot massive stars, as well as several cooler supergiants like V354 Cepheus.
RW Cepheus
This particular star might not appear to be significantly large when compared to its surrounding stars. However, there are only a few stars in our galaxy or in close proximity that can match its size.
With a radius of approximately 1600 times that of the Sun, this red supergiant would have an outer atmosphere that extends beyond the orbit of Jupiter if it were positioned in place of our Sun.