What is the magnitude of the Moon? In relation to Earth, the Moon is slightly more than a quarter of the size of our planet.
The Moon is the most luminous object in our nighttime sky. However, what is the size of the Moon? The Moon has an average radius of 1,079.6 miles (1,737.5 km) and an average diameter of 2,159.2 miles (3,475 km). According to NASA, in comparison to Earth, the Moon is one-third smaller in width than our planet. The equatorial circumference of the Moon is 6,783.5 miles (10,917 kilometers).
Initially, the Moon may appear quite large, but that’s solely due to its proximity to us – at an average distance of about 238,855 miles (384,400 km).
Moon size
- Radius: 1,079.6 miles (1,737.5 km)
- Diameter: 2,159.2 miles (3,475 km).
- Surface area: 14.6 million square miles (38 million square kilometers)
- Mass: 7.35 x 10^22 kg.
- Density: 3.34 grams per cubic centimeter (3.34 g/cm3)
The Moon is approximately one-fourth the size of Earth, making it significantly larger compared to other planets and their satellites. Among the satellites in the solar system, Earth’s moon is ranked as the fifth largest.
“If the Earth were the size of a nickel, the Moon would be the size of a coffee bean,” stated NASA.
The mass, density, and gravity of the Moon are unique and fascinating.
With a mass of 7.35 x 1022 kilograms, the Moon accounts for approximately 1.2% of the Earth’s mass. To put it in perspective, the Earth weighs a staggering 81 times more than the Moon. Additionally, the Moon has a density of 3.34 grams per cubic centimeter (3.34 g/cm3), which is roughly 60% of the Earth’s density.
When it comes to gravity, the Moon’s gravitational force is only 16.6% of the Earth’s gravitational force. This means that an individual on the Moon would weigh a mere six times less than they do on Earth. For instance, a 45-pound man on Earth would weigh 100 pounds, while on the Moon, their weight would plummet to a mere 16.6 pounds. The difference in gravity would make a long jump competition on the Moon quite fascinating. Someone capable of jumping 10 feet on Earth would be able to leap nearly 60 feet on the Moon.
While the Moon is the second densest satellite in the solar system, with a density of 3.34 g/cm3, it is surpassed by Jupiter’s satellite Io, which has a denser composition at 3.53 g/cm3.
Despite being the nearest and one of the most extensively researched celestial objects, scientists are still actively studying the Moon in order to uncover further details.
How does the Moon’s size compare to that of other satellites in the Solar System?
According to The Nine Planets, a science and education website that still recognizes Pluto, our Moon is the fifth largest satellite in the solar system in proportion to the size of its planet. The largest satellite in the solar system is Ganymede, which belongs to Jupiter.
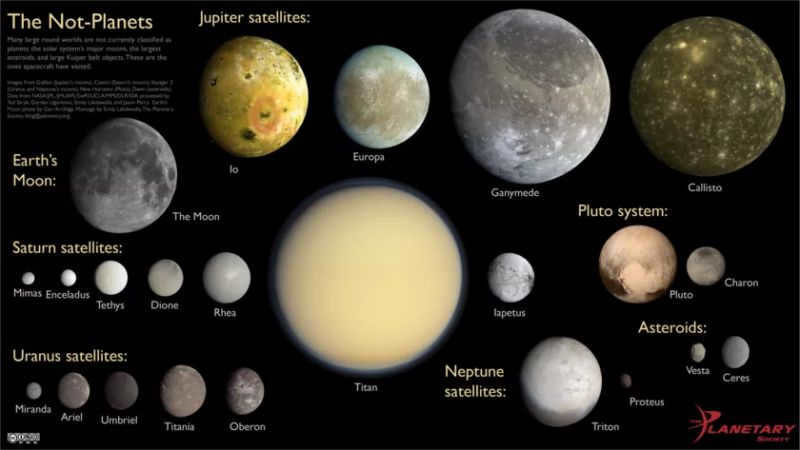

The 10 largest moons in the solar system
Position Moon Equatorial radius Parent planet
- 1 Ganymede with a radius of 1,635 miles (2,631 km) orbits Jupiter
- 2 Titan with a radius of 1,600 miles (2,575 km) orbits Saturn
- 3 Callisto with a radius of 1,497 miles (2,410.3 km) orbits Jupiter
- 4 Io with a radius of 1,131.7 miles (1,821.6 km) orbits Jupiter
- 5 Moon with a radius of 1,079.6 miles (1,737.5 km) orbits Earth
- 6 Europa with a radius of 969.84 miles (1,560.8 km) orbits Jupiter
- 7 Triton with a radius of 840.96 miles (1,353.4 km) orbits Neptune
- 8 Titania with a radius of 490.19 miles (788.9 km) orbits Uranus
- 9 Rhea with a radius of 474.91 miles (764.3 km) orbits Saturn
- 10 Oberon 473.11 miles (761.4 km) Uranus
What is a Super Moon?
Have you ever gazed up at the night sky and wondered, “Why is the moon so enormous tonight?”. The explanation lies in the moon’s orbit. Due to the fact that the Moon’s orbit is not perfectly circular, there are times when it is closer to Earth than others. When the moon is at its closest point to Earth – approximately 226,000 miles (363,300 kilometers) away – it is referred to as perigee, as stated in the NASA article. When a full moon coincides with perigee, we witness a super moon that appears 14 percent larger and 30 percent brighter than usual.

The term “super moon” was originally coined by astrologer Richard Nolle in 1979 to describe a new or full moon that occurs when the moon is within 90 percent of its closest approach to Earth. This phenomenon is scientifically known as perigee-sisigian moon. According to NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, “Sisigy refers to the alignment of three celestial bodies, namely the Sun, Moon, and Earth. However, the term “super moon” is much easier to say and remember.
It is not always easy to notice the difference: NASA states that “a 30 percent difference in brightness can easily be masked by clouds or the competing glare of city lights.”
“The primary explanation for the Moon’s non-circular orbit is the presence of numerous tidal or gravitational forces that exert attraction on the Moon,” explained Peter in an interview with Space.com. He added that the gravity exerted by the Earth, the Sun, and the other planets in our solar system all play a role in influencing the Moon’s orbit. “These various gravitational forces tug and push the Moon, allowing for these close encounters.”
A super moon occurs approximately every 414 days. However, this is just an average; in 2016, there were not one, but three supermoons. Although the Moon came close to Earth during the November 2016 super moon, it will not come as close until November 25, 2034.
What causes the Moon to appear larger when it rises or sets above the horizon?
Occasionally, the Moon may appear larger when it is rising or setting above the horizon.
This phenomenon is actually an optical illusion. There is a little-understood optical effect that can make the moon seem larger when it emerges from behind distant objects on the horizon. This optical trick, known as either the moon illusion or the Ponzo illusion, has been observed since ancient times but lacks a universally accepted explanation, according to NASA.
One theory suggests that we are accustomed to seeing clouds that are only a few miles above us, while we are aware that clouds on the horizon can be tens of miles away. If a cloud on the horizon appears to be the same size as the clouds directly above us, despite the significant distance, our brains interpret it as being massive. Similarly, since the moon appears to be the same size at the horizon as it does directly overhead, our brains automatically enlarge its perceived size to match.
One method to test the validity of this phenomenon is by placing your thumb next to the moon and comparing their respective sizes. As the moon ascends higher into the sky, repeat this observation and you will notice that its size will appear equal to that of your thumbnail.
The size of the moon – Earth’s natural satellite. Detailed information regarding its mass, density, gravity, actual and perceived size, occurrence of super moons, the moon illusion, and comparative photographs with Earth.
The moon is the most prominent celestial body (excluding the Sun) in the sky. From the perspective of an Earth observer, it may seem immense, but this is solely due to its proximity in comparison to other objects. In terms of dimensions, it encompasses approximately 27% of Earth’s size (at a 1:4 ratio). When compared to other satellites, it ranks as the fifth largest.
The average radius of the moon measures 1737.5 km. When multiplied by two, it yields the diameter (3475 km). The equatorial circumference totals 10917 km.

The moon’s total area is 38 million square kilometers, which is smaller than any continent.
Mass, Density, and Gravity
- The moon’s mass is 7.35 x 10^22 kilograms, which is 1.2% of Earth’s mass. In comparison, Earth is 81 times more massive than the moon.
- The moon’s density is 3.34 grams per cubic centimeter, which is 60% of Earth’s density. However, Saturn’s moon Io has a higher density of 3.53 grams per cubic centimeter, making it the densest moon in our solar system.
- The moon’s gravitational force is only 17% of Earth’s, meaning that an object weighing 100 kilograms on Earth would weigh only 7.6 kilograms on the moon. This is why astronauts can jump so high on the lunar surface.
The phenomenon of the super moon
Instead of following a perfectly circular orbit around the Earth, the moon traces out an ellipse, leading to variations in its distance from our planet. At its closest approach, known as perigee, the moon can appear significantly larger. When perigee coincides with a full moon, we are treated to the awe-inspiring sight of a super moon, which is approximately 14% larger and 30% brighter than a typical full moon. This celestial event occurs approximately every 414 days, adding an extra touch of magic to our night skies.
Illusion of the horizon
There exists an optical phenomenon that creates the perception of the Moon appearing larger than its actual size. This phenomenon occurs when the Moon rises behind objects that are far away on the horizon line. This intriguing phenomenon is commonly referred to as the moon illusion or the Ponzo illusion. Despite being observed for centuries, a definitive explanation for this illusion has yet to be determined. In the photograph provided, you can visually compare the size of the Moon and the Earth, as well as the Sun and Jupiter.
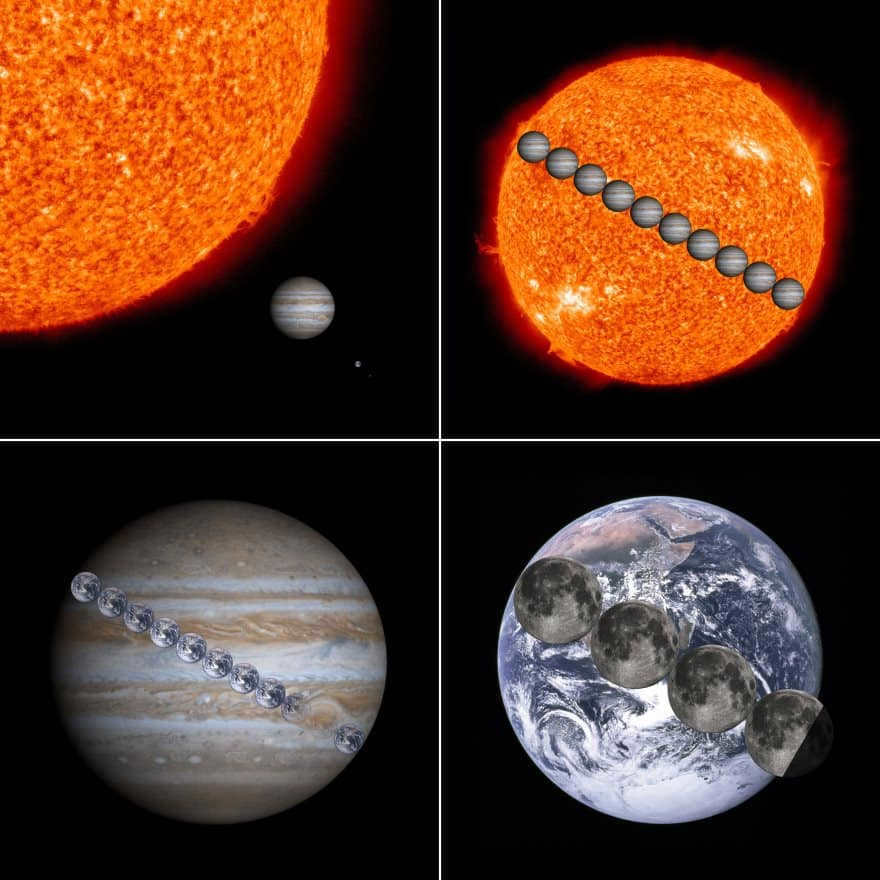
Comparison of the dimensions of the Sun, Jupiter, Earth, and the Moon
There is a theory suggesting that our perception of size is influenced by our experience of viewing clouds at a distance. When clouds on the horizon appear to be the same size as those directly above us, our brain interprets them as being massive despite their actual distance. However, when it comes to satellites, which appear the same size regardless of their position, our brain automatically tries to zoom in.
Not everyone agrees with this explanation, and there is another hypothesis. According to this hypothesis, the moon appears larger when it is close to the horizon because we have no point of reference to compare its size to, such as trees or other terrestrial objects. Without this comparison, the moon appears larger in our perception.
- Interesting facts about the Moon;
- What is the Moon?
- How was the Moon formed?
- How did the Moon come into existence?
- Constructing a Lunar Base: Part 1
- Constructing a Lunar Base: Part 2
- Constructing a Lunar Base: Part 3
- Constructing a Lunar Base: Part 4
- Can the moon be destroyed?
- How can we prove that the lunar landing was not a hoax?
- Is the Moon essential for our survival?
- How can one make money on the Moon?
- How did NASA document the departure of astronauts from the Moon?
- Which is a better destination: Mars or the Moon?
- Shouldn’t we return to the Moon?
- What is the actual name of the Moon?
The position and motion of the Moon
- The Moon’s orbit;
- The relationship between the Sun and the Moon
- Why doesn’t the Sun consume the Moon?
- What are the different phases of the Moon?
- What is a convex-shaped Moon?
- Why does the Moon appear so large to us?
- Why is the Moon gradually moving away from Earth?
- Why do we see both the Sun and the Moon simultaneously?
- How long does it take to reach the Moon?
- Distance between Earth and the Moon;
- The Moon’s rotation;
- The far side of the Moon;
- Earth’s second satellite is drifting away from us
Moon’s Structure
Moon’s Surface

The Moon is Earth’s one and only natural satellite. We observe it every day in the sky. The moon has a significant impact on our planet and even on human psychology. Scientists have been studying the satellite for more than 2,000 years, and this research continues today. Despite the advancements in technology, there are still many unanswered questions. Today, we will explore the size comparison between Earth and the Moon and speculate on the consequences if our planet were to lose its faithful companion. Let’s delve into this intriguing topic!
The moon exists.
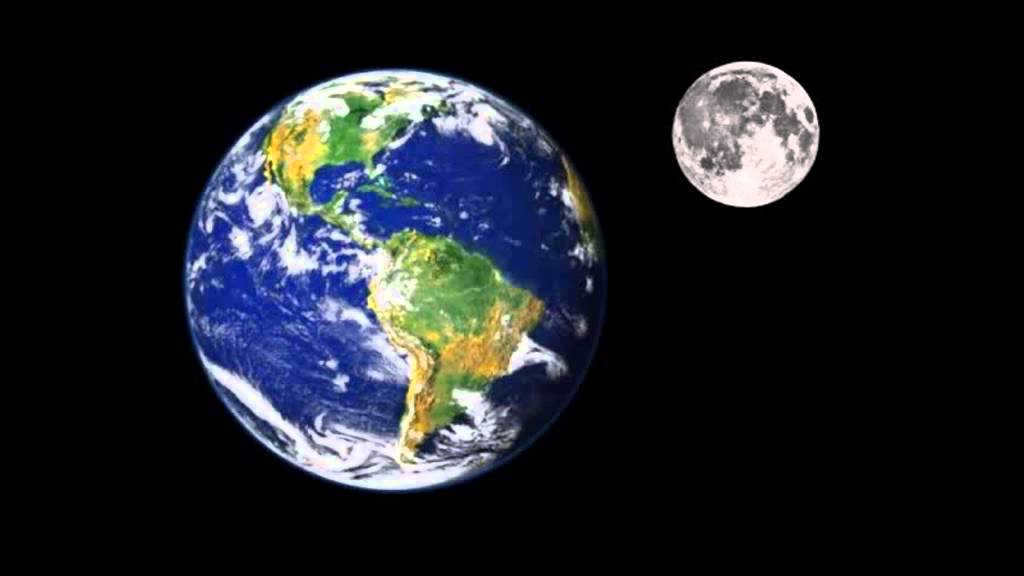
Despite being traditionally regarded as a natural celestial body, there has been recent speculation surrounding the Moon’s artificial creation. This speculation arises from certain man-made looking objects found on the lunar surface, which have puzzled scientists.
The Moon is known for its perpetually black sky, lack of atmosphere, and absence of sound. It boasts seas, oceans (formed by solidified lava), and even craters. The formation of the satellite and its current location continue to perplex scientists.
The Moon regularly “moves away” from Earth at a rate of 3.8 centimeters. Some scientists even suggest that in 50 billion years, the Moon will simply “drift away”. However, this theory is not widely supported by other researchers.
What is the size comparison between the Earth and the Moon?
Researchers have already determined that the Moon is six times smaller than our planet. By examining the photo, we can visually comprehend how many times the Earth surpasses the Moon in size. Visual information is often more easily understood. The scale of the Earth’s magnitude in comparison to the Moon is truly massive!
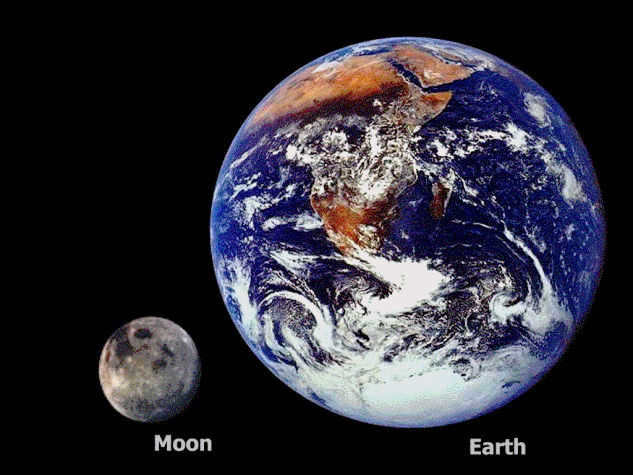
When viewed from Earth, the Moon appears relatively small, measuring about 30 cm in diameter. However, when observed from the horizon, its size becomes more impressive.
The Moon has a radius of 1737.1 kilometers, while the average radius of Earth is 6371.0 km. This means that the Moon is 3.667 times smaller than Earth.
So, how many times larger is Earth’s diameter compared to the Moon’s? It is 3,476 kilometers, which is the distance from Moscow to Tomsk. The equatorial diameter of Earth is 12,757 km, making the Moon four times smaller in terms of its cross-section. Specifically, the Moon’s cross-section is equal to 0.272 of Earth’s cross-section.
What is the difference in size between the Earth and the Moon in terms of area? The Moon has a surface area of 37.93 million square kilometers, while the Earth has a surface area of 510.1 million square kilometers. This means that the Moon is roughly equivalent in size to the combined areas of Russia, Canada, and China.
How much larger is the Earth than the Moon in terms of volume? The Moon is nearly 50 times smaller than our planet, occupying only 2% of the total volume.
The satellite’s density is 3.34 g/cm³, which is only 60% of the Earth’s density. The disparity in density can be attributed to the Earth’s larger size and the increased pressure within its interior. In fact, the Earth’s interior is comprised of a substantial core that holds 32% of its total mass, whereas the Moon’s core is limited to no more than 5% of its mass, making it roughly 350 kilometers in size.
How much greater is the Earth’s mass compared to the Moon’s? It is 81 times larger. Newton attempted to calculate the mass of a satellite, but his calculations actually exceeded the true values by a factor of 2. It is important to remind readers that an object’s mass is determined by the amount of matter it contains within a given volume. The more substance it holds, the greater its weight, and therefore, the more force is required to lift or move it.
The Splendor of the Celestial Body
The radiance of the celestial body is also worth taking into account. The albedo (i.e. the reflectivity visible to us from Earth) of the Moon is three times less than that of the azure planet. Consequently, the illumination provided by the celestial body is 41 times fainter than that of the Earth when observed from outer space. This equates to a discrepancy of four stellar magnitudes.
Imagining a World without the Moon.

Maybe life on the blue planet would never have emerged without it. The moon is responsible for the changing of seasons. If it didn’t exist, the temperature variations would be so extreme that African summer could easily be replaced by Arctic cold in the same region. Nights would be much darker than they are currently, especially when we observe a full lunar disk in the sky.
If there were no moon, people on Earth would not have had the chance to witness the extraordinary phenomenon of a solar eclipse. This is all due to the moon’s perfect placement, which completely blocks out the sun when it aligns with Earth.
On another planet, the length of a year would be quite distinct. The moon on this planet doesn’t just govern the tides, it also decelerates the rotation of our planet multiple times. If it weren’t there, a day would only span eight hours. Consequently, the duration of a year would be approximately one thousand days.
To clarify, the Moon doesn’t solely adorn the sky and evoke a romantic atmosphere. Despite its considerable distance (it takes three days to travel there), this satellite exerts a profound influence on our blue planet. Without it, the topography of mountains and plains, as well as life forms, would be entirely dissimilar.

Summary
There are numerous fascinating details about our planet’s satellite. We have examined the most captivating ones and discovered the exact number of times the Earth surpasses the Moon in size.

Every evening, we can easily observe the Moon, the celestial body that is closest to our planet, with our naked eyes. Throughout history, people have crafted numerous legends surrounding its pale radiance and the spots scattered across its surface. However, there is much more that we know about the Moon than just these myths.
Comparison between the Earth and the Moon in terms of size
It is a well-known fact that the Moon is a natural satellite of our planet Earth. This implies that the Moon is significantly smaller than the Earth in terms of its mass and size. Let’s analyze the comparative dimensions of these celestial bodies.
– On average, the Moon has a diameter of 3474 kilometers, whereas the Earth has a diameter of 12742 kilometers. In other words, the Moon’s diameter is only about 3/11th of the Earth’s diameter, making it 3.67 times smaller than the Earth’s diameter.
– The Moon’s surface covers 37.9 million square kilometers, while the Earth’s surface measures 510 million square kilometers. By comparing these numbers, we find that the Moon’s surface is 13.5 times smaller than that of the Earth. Even when comparing the Moon’s surface to the land area on Earth, it is still 4 times smaller than the continents and islands on our planet.

– The Moon’s volume is nearly 50 times smaller than that of the Earth, which means it occupies only about 2% of the Earth’s volume.
– The Moon’s mass is approximately 80 times less than that of the Earth, resulting in a lower average density for its rocks (about 60% of Earth’s density). There may be a significant amount of empty space within the Moon.
– The Moon’s gravity is only 1.6 m/sq. sec, which is 6 times weaker than Earth’s gravity (9.8 m/sq. sec). This difference in gravity allows for impressive jumping abilities on the Moon.
Indeed, the Earth is much larger in every aspect, which is why the Moon is a satellite of our planet and not the other way around.
Unique facts about the Moon
– To visually gauge the dimensions of the Moon, Earth, and Sun, we can juxtapose a regular pea (Moon), a five-ruble coin (Earth), and a double-leaf door (Sun) next to each other.
– A complete lunar day lasts for 29 Earth days, while it takes the Moon 27 of our days to complete a full orbit around the Earth.
– The Moon does not possess any natural satellites.
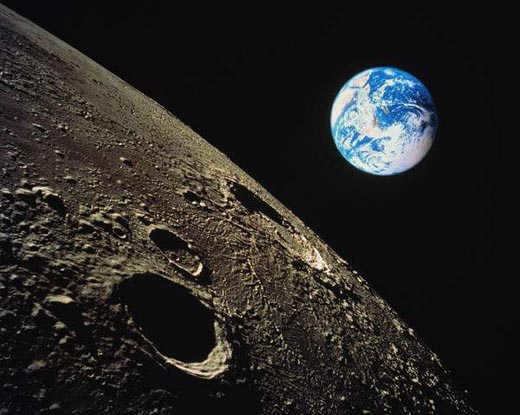

– The Moon does not have a significant atmosphere to shield our planet Earth from the impacts of random meteorites. As a result, the lunar surface is covered with numerous craters of varying sizes that were formed from collisions with celestial rocks.
– The lack of atmosphere on the Moon means that it experiences extreme cold temperatures during the night. As a result, water can only exist in a frozen state on the lunar surface. These harsh conditions make it impossible for any living organism to survive there. If there was ever life on the Moon, it has long since perished.
Discovering the Moon
The Moon has been extensively researched by humans, making it the most thoroughly studied celestial object. Researchers from various countries have launched over 100 different spacecraft to investigate its mysteries. Many of these spacecraft simply orbited the Moon and transmitted valuable data back to Earth.
In 1959, the Soviet Union made history by launching the Luna-1 spacecraft, which came close to the lunar surface and conducted the first direct measurements of its physical characteristics. This mission revealed that the Moon lacks its own magnetic field, setting it apart from the Earth.
The Soviet space program achieved significant success in their missions to the Moon, despite some unsuccessful attempts. Even the failed lunar modules managed to transmit images of the Moon’s surface, providing valuable insights.
Moreover, the Soviet Union successfully transported two Lunokhod modules to the Moon’s surface. The initial module functioned for approximately 10 months, covering a distance of over 10 kilometers on the Moon’s surface. Similarly, the subsequent module operated for around 4 months and traveled an impressive 37 kilometers.

The Moon has been the destination of multiple missions launched by the United States. These expeditions involved astronauts who landed on the lunar surface and safely returned to Earth. Before the Apollo manned program, American scientists made several unsuccessful attempts to land automatic stations on the Moon. Unfortunately, these vehicles crashed upon impact with the lunar surface.
All manned launches took place between 1969 and 1972, and were all successful. It is widely accepted that the first person to set foot on the Moon was American astronaut Neil Armstrong in 1969.
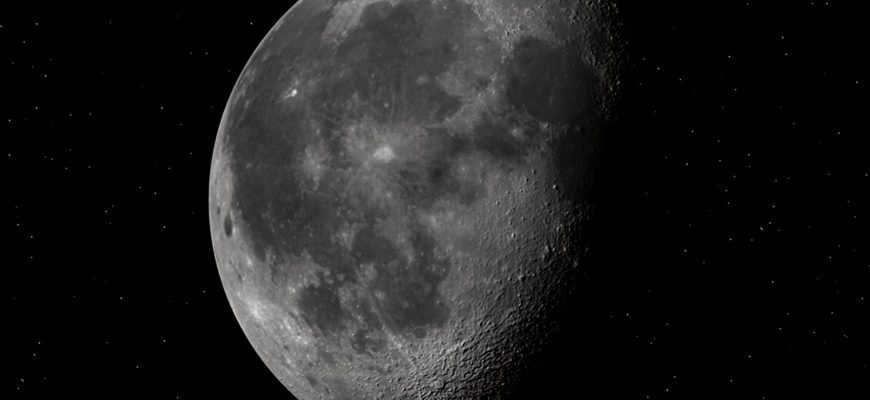

The Moon is a celestial body that orbits around the Earth. Its distance from our planet can range from 364397 to 406748 km. With a diameter of approximately 3475 km, the Moon is slightly larger than one-fourth of the Earth’s diameter. It has a mass of 7.36 × 1022 kg. Among the natural satellites in the solar system, the Moon ranks fifth in terms of size. Interestingly, the Moon is more strongly attracted to the Earth than to the Sun.
The duration of the Moon’s orbit around the Earth matches the duration of the satellite’s rotation on its own axis, resulting in only one side of this celestial object being visible from Earth. The side of the moon that remains unseen from our planet is commonly referred to as the back or dark side of the moon.
Terrain characteristics
The lunar landscape has remained virtually unchanged for millions of years. Meteorite falls and seismic activity occurred in the remote past.
The topography of the surface is shaped by mountains dotted with craters, which are evidence of meteorite impacts, as well as valleys. The plains are referred to as lunar seas, but they are actually solid areas formed by hardened lava that once erupted from the Moon’s interior. These “bodies of water” on the Moon have poetic names such as the Ocean of Storms, Sea of Clarity, Sea of Abundance, Sea of Tranquility, and Sea of Fertility. Craters are named after famous individuals like Gagarin, Korolev, Landau, Mendeleev, Pasteur, and others. Each mountain also has its own name, such as the Alps, Apennines, Carpathians, and Caucasus.
The Makeup of the Lunar Surface
The Moon’s surface is composed of different layers. The outermost layer is the lunar crust, which has an average thickness of approximately 68 km. Beneath the crust is a mantle that is about 1000 km thick. This mantle is made up of a mixture of magnesium, iron, silicon, and oxygen. At the core of the Moon is a solid inner core, which has a diameter of about 1500 km. The main component of this inner core is iron.
Additionally, the surface of the Moon is covered with a layer of regolith, which is a mixture of lunar soil, minerals, rock fragments, and even fragments of meteorites.
Composition of the Atmosphere: A Chemical Perspective
The atmosphere of the Moon can be described as highly rarefied. Our celestial neighbor is enveloped by a tenuous layer of gases, consisting of neon, nitrogen, helium, carbon dioxide, ammonia, methane, and argon. This lunar atmosphere emerged from a combination of the solar wind and the outgassing of gases during volcanic eruptions from beneath the lunar surface.
Gravity on the Moon
The gravitational pull on the Moon’s surface is significantly less compared to that on Earth. Nonetheless, the Moon’s gravitational forces can impact the occurrence of ocean tides on Earth for several reasons. These tides are specifically observed in the hemisphere of the Earth where the Moon is presently positioned.
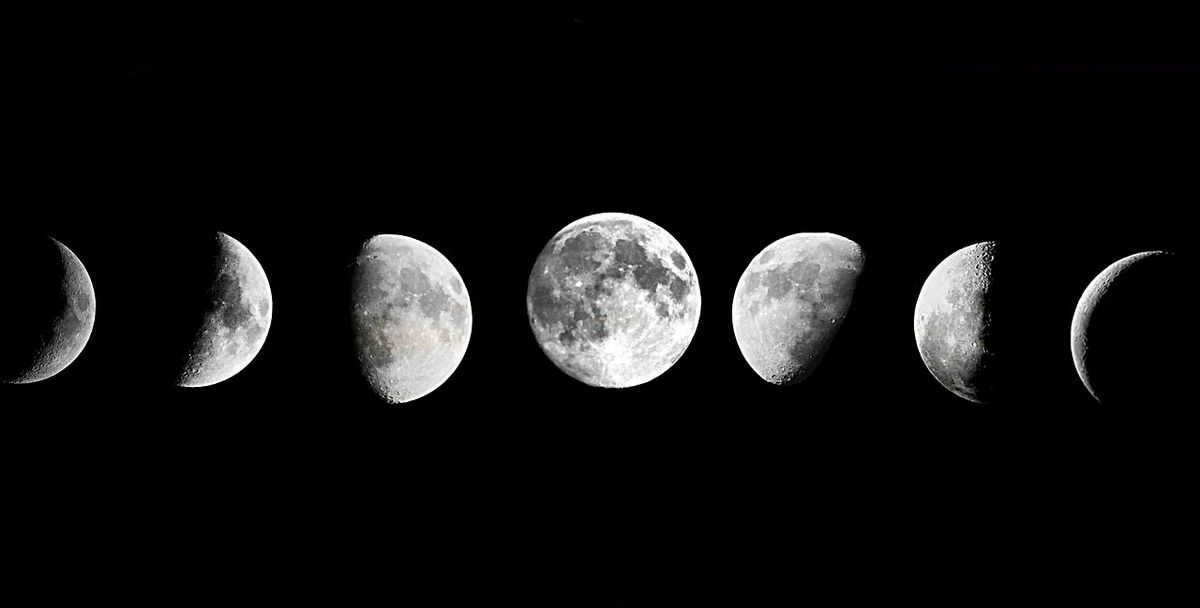
Lunar phases refer to the different appearances of the Moon as it moves and is illuminated by the sun’s rays. These phases occur in a regular pattern, making the Lunar Calendar historically reliable and accurate. Each lunar phase lasts approximately 7.4 days. There are four main lunar phases:
- The New Moon, when the Moon is not visible from Earth;
- The first quarter, when half of the Moon is visible (in the Northern Hemisphere on the right, and in the Southern Hemisphere on the left);
- The full moon, when the entire surface of the Moon is illuminated;
- The last quarter, when the other half of the Moon is visible.
The first two phases are known as waxing Moon phases, while the last two phases are known as waning Moon phases.

The Lunar Eclipse
One of the most fascinating astronomical occurrences is the lunar eclipse. When the Sun, Earth, and Moon align, the Earth’s shadow covers the surface of the Moon. A lunar eclipse can be classified as total, when the entire surface of the Moon is shaded by the Earth, partial (in this case, the Earth’s shadow cone covers only a portion of the satellite), or penumbral, where the Moon passes through the penumbra surrounding the shadow cone. It is common for the Moon to take on a red hue during eclipses, a phenomenon known as the “blood Moon”. Nowadays, precise dates for lunar eclipses are calculated well in advance.






