
Being one of the most ancient and captivating fields of study, astronomy offers humanity a chance to venture into the depths of outer space. Scientists in this field dedicate their time to examining the celestial bodies that make up our universe, not only in their current state but also in their distant past. Through this exploration, they acquire knowledge that helps them develop a scientific comprehension of the future of the vast macrocosm that surrounds us.

In today’s fast-paced world, simply relying on the school curriculum is no longer sufficient. It has become crucial to acquire valuable knowledge about finance and investments in order to secure one’s financial well-being.
Take control of your future by expanding your understanding and expertise in financial literacy today. Embrace the world of online FINANCIAL LITERACY.

Join now and celebrate your achievements.
What is the Study of the Universe
The study of the universe, also known as astronomy, focuses on understanding all the phenomena that occur within it. The word “astronomy” is derived from the Greek words “astron” meaning “star” and “nomos” meaning “law”. Astronomy is considered one of the oldest scientific disciplines, having originated thousands of years ago to fulfill practical needs. Ancient civilizations such as Babylon, China, and Egypt used early astronomical knowledge for navigation and timekeeping purposes.
The term “astronomy” itself was coined by ancient scientists Pythagoras and Hipparchus during the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC. In the modern world, astronomy can be divided into several distinct fields of study.
Astronomy is the study of the universe as a whole and its individual objects, such as stars, comets, planets, constellations, and galaxies. It also involves the examination of black holes, nebulae, and the celestial coordinate system.
The Relationship Between Astronomy and Other Sciences
Astronomy is closely connected to various other scientific disciplines, including mathematics, physics, chemistry, geography, biology, mechanics, and radio electronics. These fields of study are essential for modern astronomers, as the knowledge gained from them greatly aids in the understanding of astronomy as a subject.
In order to conduct astronomical research and calculate the coordinates and trajectories of celestial bodies, one must possess knowledge in mathematics and geography. Understanding chemistry is also necessary to determine the chemical composition of celestial luminaries and explain the chemical processes that occur in outer space. Physics is indispensable in order to comprehend the physical processes taking place on stars and to study the shape of celestial luminaries. Linguistics can aid in studying the meaning and origin of the names of constellations, stars, and planets. Radio electronics and mechanics are essential for learning to use a telescope, studying its structure, and conducting research in space. Biology provides an explanation for how sunlight affects all living organisms on the planet. History takes us back to the distant past and helps us understand the origins of celestial bodies, as well as introduces us to ancient astronomers.
Recent scientific research has provided evidence that the universe has limitations. Scientists have been able to measure its vastness in terms of light-years, estimating it to be approximately 45.7 billion. To put it into perspective, if we were to consider one light-year equivalent to 10 trillion kilometers, the immensity of the universe becomes even more mind-boggling.
The Diversity of Celestial Bodies in the Universe
The universe is teeming with an array of celestial bodies, also known as cosmic entities. These include:
The sizes of cosmic entities can range from minuscule to colossal. Among the smaller ones are meteorites, asteroids, and comets. Meanwhile, scientists continue to delve into the study of celestial bodies and have recently discovered the largest known entity in the universe – UY Scuti. This star boasts a radius 1700 times greater than that of the Sun.

Let’s examine celestial objects more closely and determine their characteristics.
Asteroids are chunks of rock that make up the asteroid belt, which is situated between the orbits of Jupiter and Mars. These rocky bodies have irregular shapes, with diameters ranging from 30 meters to several kilometers. To date, scientists have discovered over 97,853,768 of these small cosmic objects. Asteroids orbit around the Sun.

Comets consist of a compact core. When they approach the Sun, the nucleus starts to heat up and the substances it is made of begin to evaporate. This leads to the formation of a gas envelope and eventually a tail. As the comet moves away from the Sun, the tail and envelope dissipate. From time to time, comets can be observed with the naked eye. The most recent comet that was clearly visible in the night sky within the past 7 years was C/2020 F3 NEOWISE. This event took place in July 2020. In general, scientists use telescopes to study these celestial objects.

Meteoroids are compact cosmic entities that are bigger than an atom yet smaller than an asteroid. They can exist as individual entities or as fragments of other space objects, not just limited to asteroids. Celestial entities that collide with the Earth’s atmosphere are referred to as meteors. These meteors can comprise fragments from comets or asteroids.


A meteorite is the term used to describe a fragment of a meteoroid that has made it to the Earth’s surface. Essentially, it is any cosmic object that originated from space and has landed on the surface of another celestial body.

Meteorites create craters upon impact. The biggest known crater, Wilkes, measures 500 km in diameter.
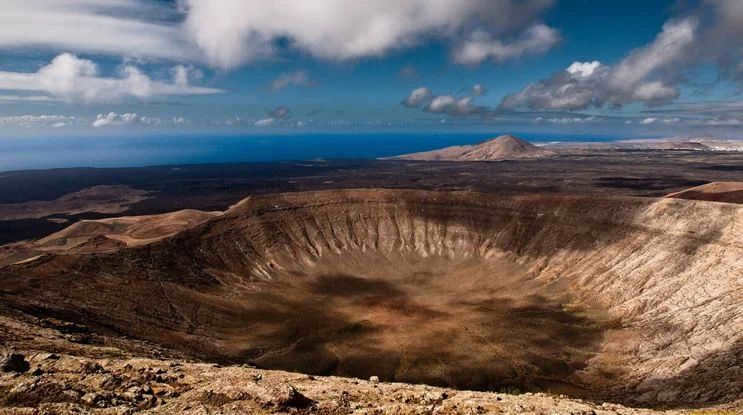

A meteorite created a crater.
Celestial bodies, such as stars, emit light and heat. They are massive gas spheres. The Sun is the closest star to Earth. When there are no clouds, a variety of stars can be seen in the night sky. Our ancestors recognized the importance of these “shimmering points” and used them to navigate in space. Stars were often the subject of myths and religious stories. Even without technology, ancient people saw images of various creatures in the stars and began to identify constellations. There are currently 88 constellations, including 12 zodiacal ones.
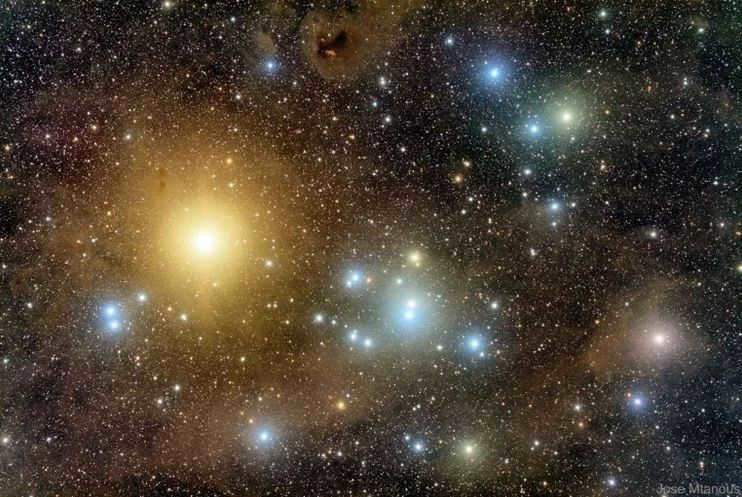

Planets are celestial bodies that orbit the Sun in a specific axis and are not satellites of any other astronomical object. The solar system consists of 8 planets:
- Mercury;
- Venus;
- Earth;
- Mars;
- Jupiter;
- Saturn;
- Uranus;
- Neptune.
Different Types of Telescopes: Land-based and Space-based
A telescope is a specialized device used for observing objects in space. Its primary function is to gather the maximum amount of light from a celestial body and increase the viewing angle for studying that celestial body. The amount of light captured by the instrument is directly proportional to its lens size. Therefore, a telescope with a larger lens has the ability to capture smaller objects.
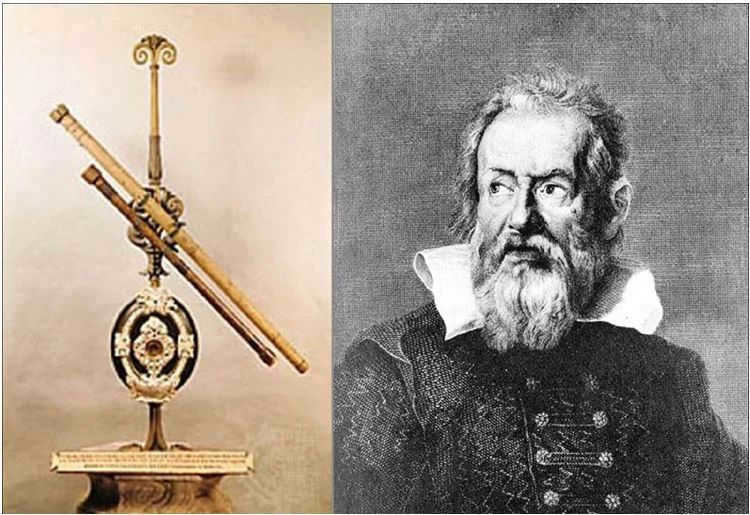
The scientist Galileo Galilei is credited with inventing the first telescope in 1609, although its principles of operation were similar to those of existing telescopes at the time. Galilei’s innovation lay in the use of more powerful lenses, which enabled a 20-fold increase in image magnification. This groundbreaking device played a crucial role in the early exploration of space, leading to important discoveries. Today, it is proudly displayed in a museum in Florence.

Ground-based telescopes are capable of observing the Sun, planets, and satellites, but they are unable to provide detailed information about the stars. Even the most advanced instruments can only capture stars as small, flickering dots.
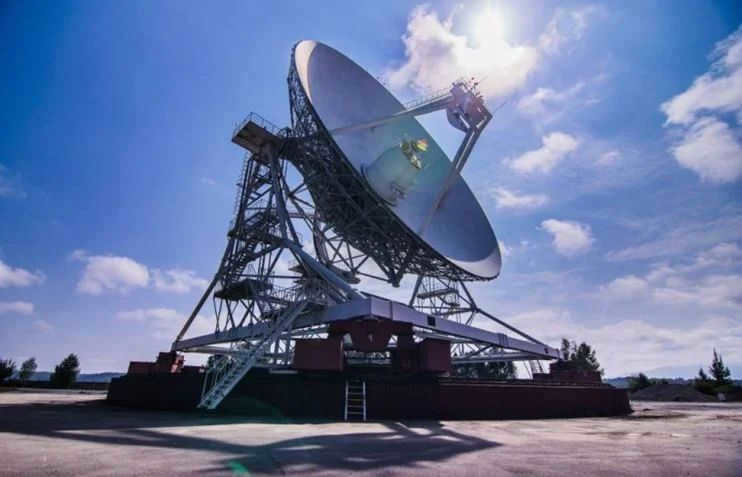

Astronomical observatories on the ground provide valuable insights into space and the universe. However, space telescopes, which are positioned in orbit, offer a more comprehensive understanding. These impressive instruments play a vital role in studying the history of the universe. The inaugural space telescope was launched in August 1957 and captured a highly detailed image of the Sun at an altitude of 25 kilometers.
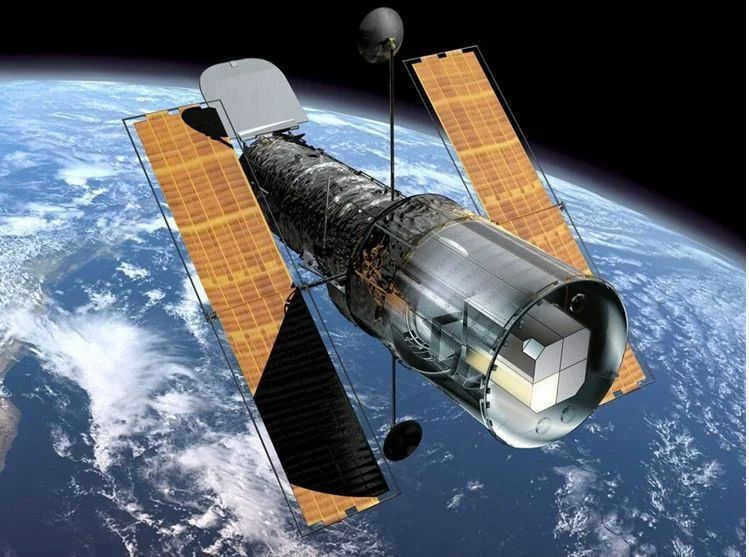

Telescopes in space
Contemporary telescopes in space and on the ground are furnished with computer software. This software transmits the visual representation to a screen, enabling one to perceive the image in its true form, devoid of any alterations.
Where can you find the biggest optical telescopes?
Usually, telescopes are situated in secluded areas far away from the noise of the city. Mountains or vast deserts are perfect locations for this purpose. Some of the largest telescopes in the world are:
- FAST – the most massive telescope on Earth. It has a diameter of 500 meters and is situated in China. This instrument is specifically designed for exploring the depths of the universe and searching for extraterrestrial intelligence.
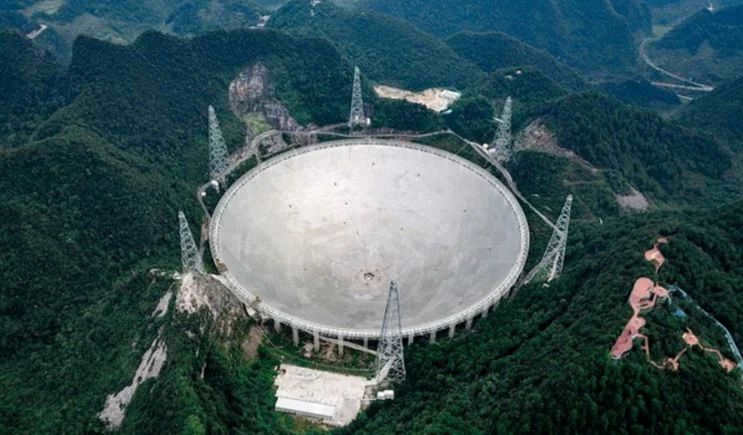

- The Arecibo observatory, situated in Puerto Rico, is home to one of the biggest telescopes with a diameter of 305 meters. It is primarily utilized for exploring the planets and the Sun.
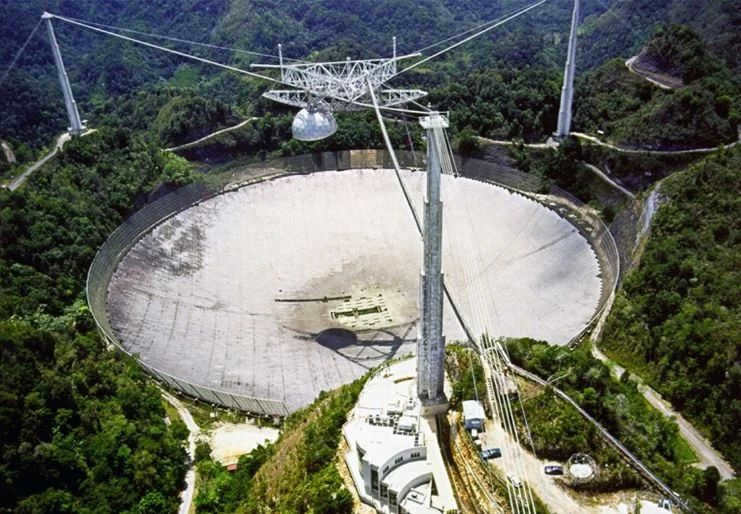

- GreenBank, which took 11 years to build, is one of the biggest telescopes in the United States with a diameter of 100 meters. This remarkable instrument has the capability to be aimed at any location in outer space.
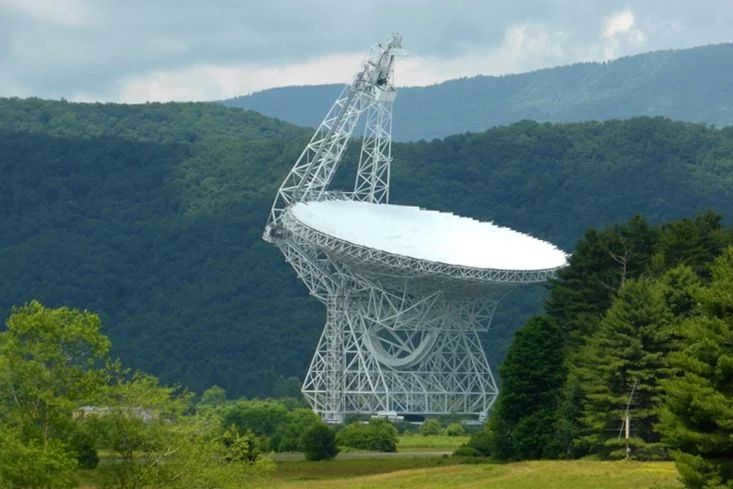


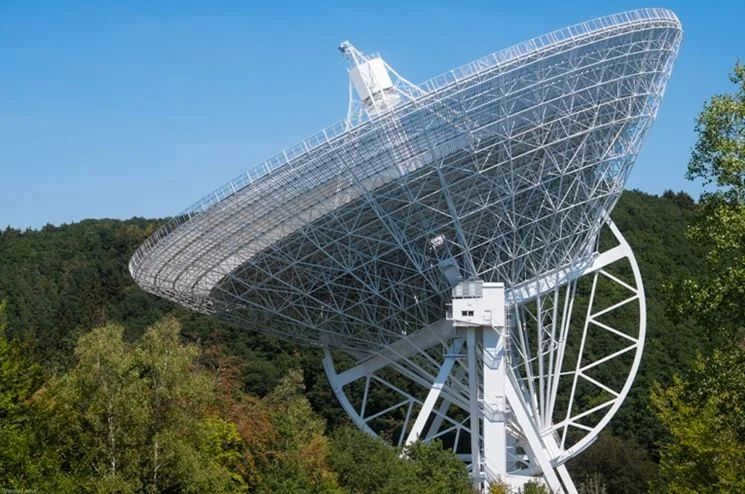
- Located in the western part of Germany, the Effelsberg Radio Telescope is a 100-meter diameter device used for astronomical observations.

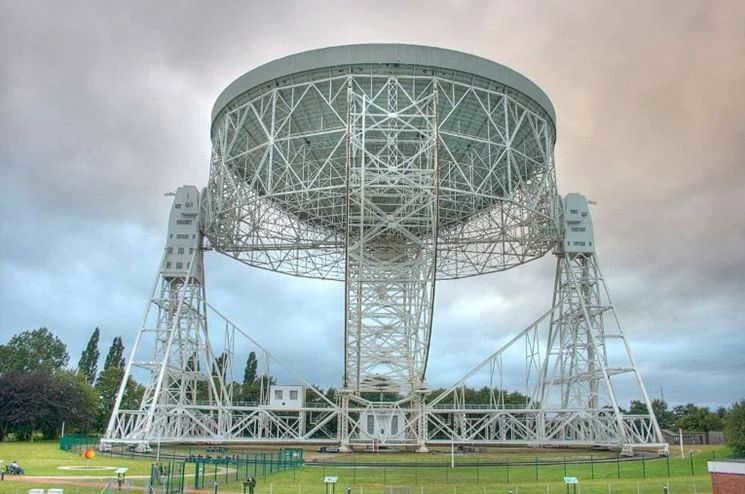
- The B. Lovell Radio Telescope, which was named after its creator, was constructed in the mid-20th century. With a diameter of 76 meters, this instrument has become an iconic symbol of scientific progress.


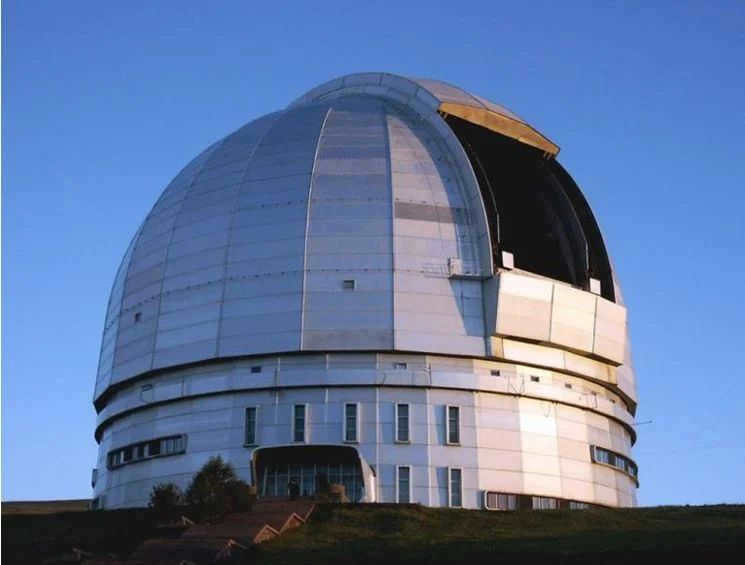
Situated in the mountains of Karachay-Cherkessia at an elevation of 2070 meters, Russia’s BTA (Big Telescope Alt-Azimuthal) stands as the country’s largest telescope. Its mirror boasts a diameter of 6 meters.

All-Wave Astronomy
In the past, astronomers relied solely on optical telescopes to explore the depths of outer space. As a result, their understanding was limited to what their naked eyes could perceive. However, the field of astronomy has made tremendous progress thanks to advancements in technology and knowledge. Scientists are now able to observe the universe across a wide range of wavelengths, leading to the emergence of new branches such as gamma-ray astronomy, radio astronomy, and X-ray astronomy.
Every celestial object emits a series of undetectable waves, which can be measured using specialized instruments. The importance of these measurements cannot be overstated. For instance, gamma and X-ray radiation, originating from space and reaching Earth, provide valuable insights into the colossal processes occurring in the deepest corners of the Universe. Due to the vast distances involved, it is impossible for humans to visually study all cosmic entities. Consequently, our understanding of the cosmos is primarily derived from the radiation emitted by celestial bodies. This radiation has enabled us to determine various characteristics such as the distance between objects, their composition, age, size, and more.
The concept of “all-wave astronomy” encompasses the idea that modern observations of cosmic bodies are conducted across all known ranges of electromagnetic radiation.
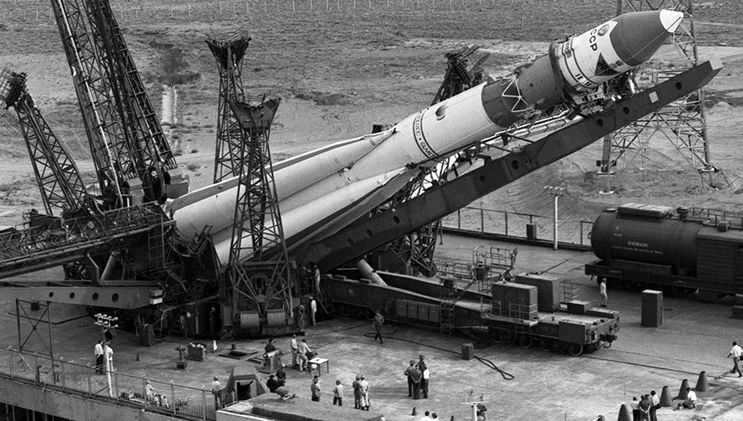
The origins of domestic space exploration can be traced back to the mid-20th century. In 1946, the establishment of Experimental Design Bureau No. 1 marked the beginning of a mission to develop satellites, launch vehicles, and ballistic missiles. By 1956, the bureau had successfully designed its inaugural carrier rocket, which later propelled the first artificial satellite into the Earth’s orbit.


Following the launch of the man-made satellite, the progress of space exploration took on a completely new speed. Some time later, another satellite was sent into space, but this time it carried a living creature – a dog named Laika.
Launches of interplanetary spacecrafts enabled the exploration of the Moon, and as early as 1959 a probe successfully landed on the surface of Earth’s satellite. During that time, the Soviet Union obtained images of the far side of the Moon, which allowed scientists to name almost all significant features on the lunar surface.
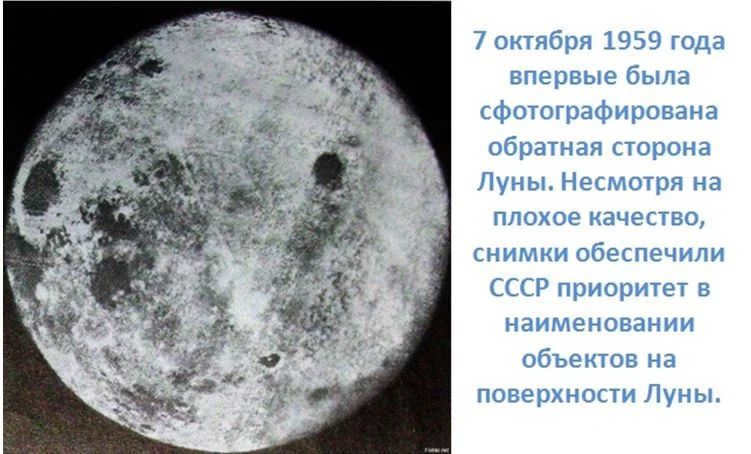
The initial image ever captured of the Moon’s far side
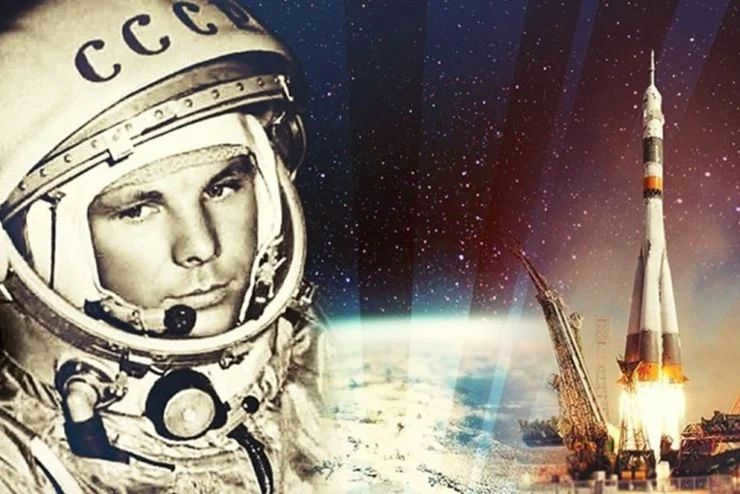
An significant milestone in the advancement of domestic space exploration was the historic mission of sending the first human into space. This momentous event occurred on April 12, 1961, when Yuri Gagarin piloted the Vostok spacecraft. Another significant achievement took place in 1965 with the first-ever spacewalk by a human.


Until 1991, the field of domestic space exploration witnessed numerous breakthroughs and accomplishments:
- In 1971, the world’s first orbital station, “Salyut-1,” was successfully launched with a crew on board.
- In 1977, a spacecraft successfully brought back soil samples from the Moon.
- Multiple interplanetary stations were launched, with some even landing on the surface of Venus to analyze its soil and capture images.
- Stations were also sent to Mars, enabling the capture of images of the planet’s surface and the measurement of its atmospheric composition.
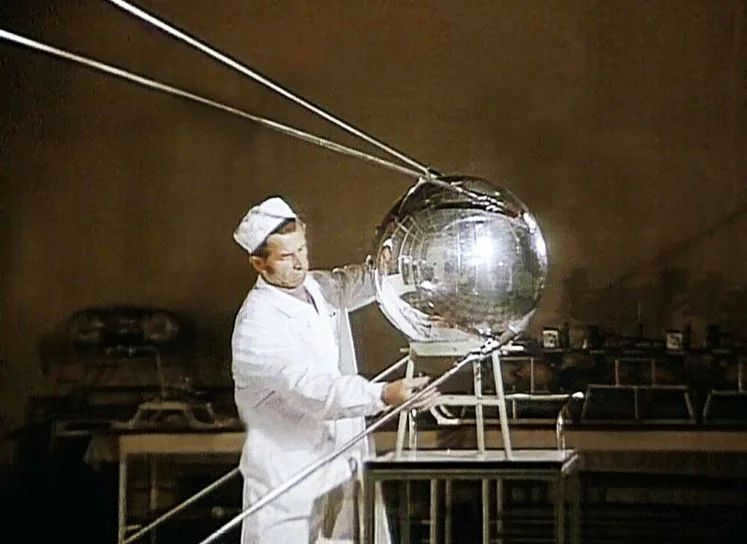
October 4, 1957 marked a major milestone in the field of space exploration. On this historic day, the world witnessed the successful launch of the first ever artificial satellite. This momentous event not only kickstarted the study of outer space, but also paved the way for groundbreaking advancements in both domestic and international space exploration.
Located in Kazakhstan, the Baikonur Cosmodrome served as the launch site for this groundbreaking mission. The R-7 launch vehicle was the chosen means of launching the first artificial satellite into space. The satellite remained in orbit for a remarkable 92 days, completing 1440 revolutions around the Earth. This provided scientists with an unprecedented opportunity to study the upper layers of the ionosphere and gather invaluable data. Furthermore, the mission allowed for crucial tests of the satellite’s hardware and verified calculations related to space conditions.

The initial man-made satellite of the Earth
Contemporary space exploration and its accomplishments
Modern space exploration has made a tremendous leap forward in its advancement. Nowadays, outer space is discussed as a tangible reality, rather than something incredibly distant. The launch of cutting-edge spacecraft and voyages into outer space have become routine events in the life of the Russian nation, despite being costly.
Space tourism no longer elicits surprise, as individuals can now embark on spaceship journeys for a certain fee. Space exploration is conducted at an elevated level, with contemporary scientists focusing on the development of solar power plants and the advancement of technologies aimed at influencing the climate of our planet.
Starting from 2016, the Vostochny Cosmodrome in the Amur Region has commenced its operations, thereby enabling Russia to conduct spacecraft launches from its own territory and become independent of other nations.
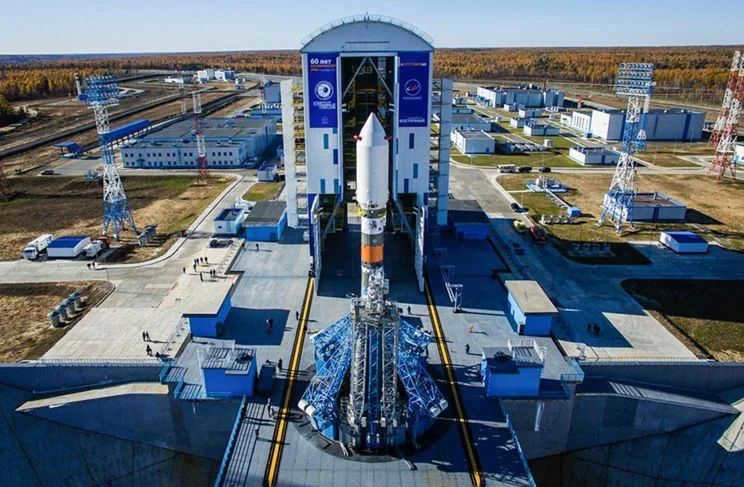

There are future plans to send manned spacecraft to the Moon, unmanned spacecraft for exploring space, and to execute the Sea Launch program.
Russia’s top priority is to advance its national space exploration, research the potential of the contemporary space industry, and position itself as a leader in the world.

Astronomy is among the most ancient fields of study, emerging alongside the advancements in trade, agriculture, and Earth sciences. Stargazers were the name given to astronomers in the past due to their focus on observing stars. However, in the present day, the scope of astronomy has expanded greatly, with more precise, varied, and powerful equipment being utilized. This article will delve into the advancements and discoveries of 21st-century astronomy.
What is the focus of astronomy?
Simply put, astronomy is the field of study that examines celestial bodies and planetary systems. It encompasses a wide range of objects, including the Sun, the Solar System, planets beyond it, comets, asteroids, galaxies, nebulae, and much more.
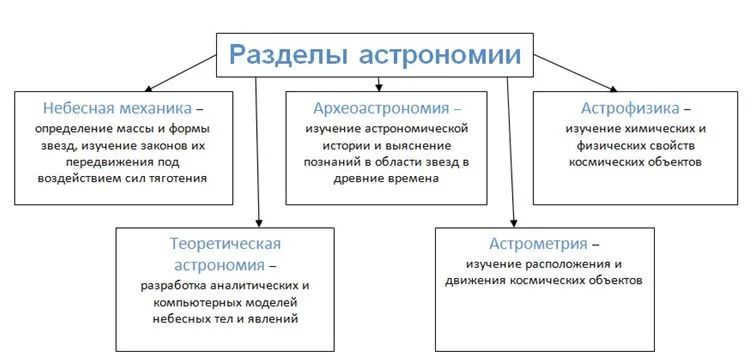
Astronomy can be divided into several subfields:
- Astrometry, which observes and tracks the visible movements of celestial bodies, determines their coordinates, and compiles reference books based on this data.
- Celestial mechanics, which explores the relationship between the motion of celestial bodies and gravitational forces, as well as the shape and mass of these objects.
- Astrophysics, which focuses on the structure, composition, and properties of celestial bodies.
- Cosmology, which studies the Universe as a whole and investigates its structure and evolution.

The Milky Way
Ancient Babylonians in the 2nd millennium BC were the first to compile astronomical tables, where they meticulously tracked the movements of celestial bodies such as the Moon, Sun, planets, and stars. Throughout history, astronomers have continued this practice, adapting their observation tools as technology advanced.
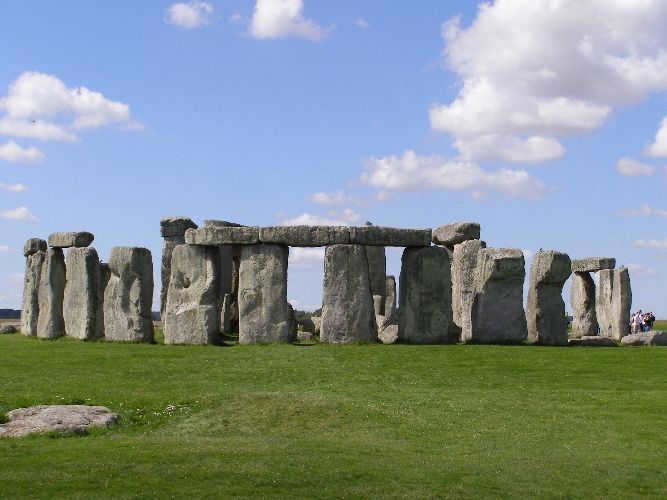
In the 18th century, a hypothesis emerged suggesting that the solar system could be part of a larger celestial object. English astronomer W. Herschel discovered that all visible stars from Earth are actually part of a massive star system known as the Milky Way, which is fixed in the sky.
By the 20th century, it was established that the Milky Way is a spiral galaxy with a lentil-like shape. It is estimated to contain between 200-400 billion stars, including our own Sun. The Solar System is located on the outskirts of this galaxy.


Astronomical Instruments
A device used to observe the celestial bodies is known as a telescope. The initial version of the telescope, invented by Galileo Galilei in 1609, resembled a tube. Over time, these telescopes underwent improvements, with a lens being replaced by a large mirror. Presently, the largest telescope has a mirror diameter of 10.4 m, as seen in the Great Canary Telescope.
In the 20th century, radio telescopes were introduced to receive radio waves from space. These telescopes consist of large bowl-shaped antennas equipped with advanced technology.
The Hubble Space Telescope, launched in 1990, has been operational and is expected to continue working until the end of 2021.

What knowledge have we gained?
The field of astronomy is dedicated to the examination of various celestial objects, encompassing a wide range of types and magnitudes. The four main branches of astronomy, astrometry, celestial mechanics, astrophysics, and cosmology, are succinctly outlined. To adequately prepare for upcoming lessons, fourth-grade pupils will require supplementary resources on the subject of astronomy.

When we gaze up at the night sky on a warm summer evening, we can’t help but wonder about the mysteries of the universe and our place within it. The vastness of cosmic existence and the fragility of our own earthly existence are humbling thoughts. We imagine the sky as a black velvet canvas, adorned with stars like drops of milk. And during the day, we expect to see clouds floating above. These musings are poetic, but astronomers approach the starry sky with a more scientific mindset. Their research consistently unveils remarkable findings, leaving us in awe. So, what exactly does the field of astronomy entail, and why is it so important?
What is the focus of Astronomy?
Astronomy is a field of science that explores the makeup of the universe. It examines the positioning, movement, physical characteristics, origins, and development of celestial bodies and systems. Additionally, astronomy investigates the fundamental properties of the surrounding universe. The study of astronomy encompasses various celestial objects like the Sun, stars, planets and their moons, black holes, galaxies and nebulae, quasars, asteroids, and more. Its objective is to elucidate the enigmatic phenomena occurring in the Universe and shed light on our existence.
Ever since telescopes were invented, scientists have been able to explore the Milky Way and discover countless other galaxies. The field of astronomy has made incredible progress since the early 20th century, with one of the greatest accomplishments being the development of the theory of the universe’s evolution. This theory explains how the universe expands over time.
What are the components of astronomy?

Astronomy, a field of scientific study that explores the vastness of the universe, encompasses various branches:
- Astrometry: This branch delves into the motion and positions of celestial objects.
- Celestial Mechanics: Focusing on stars, this area determines their mass and shape, and investigates the laws governing their movements under gravitational forces.
- Theoretical astronomy: Scientists in this field develop computer and analytical models to better understand celestial bodies and phenomena.
- Astrophysics: This discipline examines the physical and chemical properties of cosmic objects.
- Archaeoastronomy: By studying the historical aspects of astronomy, this branch seeks to uncover the astronomical knowledge of ancient civilizations.
Observation serves as the foundation of astronomy

Astronomical research does not involve conducting experiments like in physics. The primary source of information for astronomers is electromagnetic radiation.
Studying the universe is a highly intricate and lengthy endeavor that demands great attention, consistency, and focus. Thus, it is impractical to use meters and kilometers as units of measurement in astronomy.
When exploring the solar system, we utilize the astronomical unit. This unit represents the size of the Earth’s orbit’s major semi-axis: 1 a.u. = 149 million kilometers. In the field of stellar astronomy and cosmology, larger units of length such as the light-year and parsec, along with their derivatives (kiloparsec, megaparsec), are necessary. A light-year is the distance that a beam of light travels in a vacuum in the span of one Earth year. It is equivalent to approximately 9.5-1015 meters. The parsec is historically used for measuring distances to stars based on their parallax and is defined as 1 pc = 3.263 light-years = 206,265 a.u. = 3.086-1016 m.
Many of the techniques employed in other fields, like mathematics and physics, are also extensively utilized in the realm of astronomy. The vast expanse of space provides a unique environment where matter can manifest itself at temperatures reaching hundreds of millions of degrees as well as near absolute zero. This occurs within the vacuum of space and even within the dense cores of neutron stars. Moreover, the advancements made in the field of astronomy have also found applications in diverse disciplines such as geology, biology, geography, and history.

Astronomy and astronautics have always been a source of fascination and captivation for millions of individuals. The global community of amateur astronomers is immeasurable, and it is often their contributions that lead to numerous astronomical breakthroughs. One noteworthy example is Australian observer Anthony Wesley, who, while studying Jupiter in 2009, detected signs of a celestial object’s impact on the planet, potentially indicating the presence of a comet.
Astronomy allows us to comprehend the laws of nature and witness the gradual evolution of our universe. It significantly shapes people’s worldviews. In the early 21st century, there has been a surge in popular interest in space-related topics such as galaxies and extraterrestrial life. Unfortunately, this newfound fascination is often accompanied by misinformation and incompetence. Journalists lacking expertise in space matters and scientists making claims based on unverified facts lead many individuals to believe in pseudoscientific discoveries.
Nowadays, there is a vast array of top-notch scientific videos available on the subject of space, encompassing a wide range of topics such as stars, planets, and galaxies. These videos are carefully crafted, combining stunning graphics with actual footage from space, and are sure to captivate your interest, offering a deeper understanding of the captivating field of astronomy. Feel free to explore a selection of these fascinating movies below.
Author: Tatiana Sidorova, updated on March 15, 2018
Reproduction without an active hyperlink is strictly prohibited!
Also, read about the following topics:
- What is the field of astronomy?
- Observing the celestial bodies
- The International Day of Astronomy
- Distinctive features of the zodiac signs
- Phases of the Moon
- Solstice
- Calendar
- Aberration in Astronomy
- The mystery behind the planet Nibiru
- Nibiru: fact or fiction
- Why do stars fall and what are shooting stars?
- Stargazing in August and beyond
- How to become an astronaut?
- Mission to Mars
- Mars’ satellites: Phobos and Deimos
- Solar eclipse
- Meteor shower in Chelyabinsk
- Fantastic literature about outer space
Astronomy is a field of study that focuses on celestial objects and events. The term “astronomy” originates from the Ancient Greek language, with “astron” meaning “star” and “nomos” meaning “law” or “culture”. Therefore, it can be translated as the science that explores the laws governing the stars. Throughout the course of human history, astronomy has undergone periods of stagnation as well as periods of rapid advancement, marking a long and challenging journey.
Ancient Times

In ancient times, scientists believed that the Earth was at the center of the universe, but this ultimately limited their understanding of the cosmos.
The earliest astronomers could only rely on their naked eye to observe celestial objects such as stars, planets, the Moon, and the Sun. Archaeologists have discovered artifacts from ancient civilizations that suggest they were engaged in some form of astronomical observation. These studies likely served ceremonial purposes, such as determining the timing of rituals, as well as helping ancient people navigate the seasons for agricultural purposes.
Ancient Greek, Mesopotamian, Persian, Hindu, Chinese, Egyptian, and Central American civilizations were among the most advanced in terms of observing the sky. These civilizations were the first to create maps of the starry sky and trace the paths of planets and celestial bodies. Through their observations, ancient people formulated the initial hypotheses regarding the movements of the Sun, Moon, and planets. They believed that the Earth was the center of the universe, with all celestial objects orbiting around it. This geocentric model of the universe is famously known as Ptolemy’s.
The ancient Babylonians, who were pioneers in connecting mathematics and astronomy, played a significant role in advancing the field of celestial science. As an illustration, they discovered the recurring pattern of lunar eclipses, which happens every 18 years, 11 days, and 8 hours. Today, this cycle is referred to as saros.
The Medieval Period
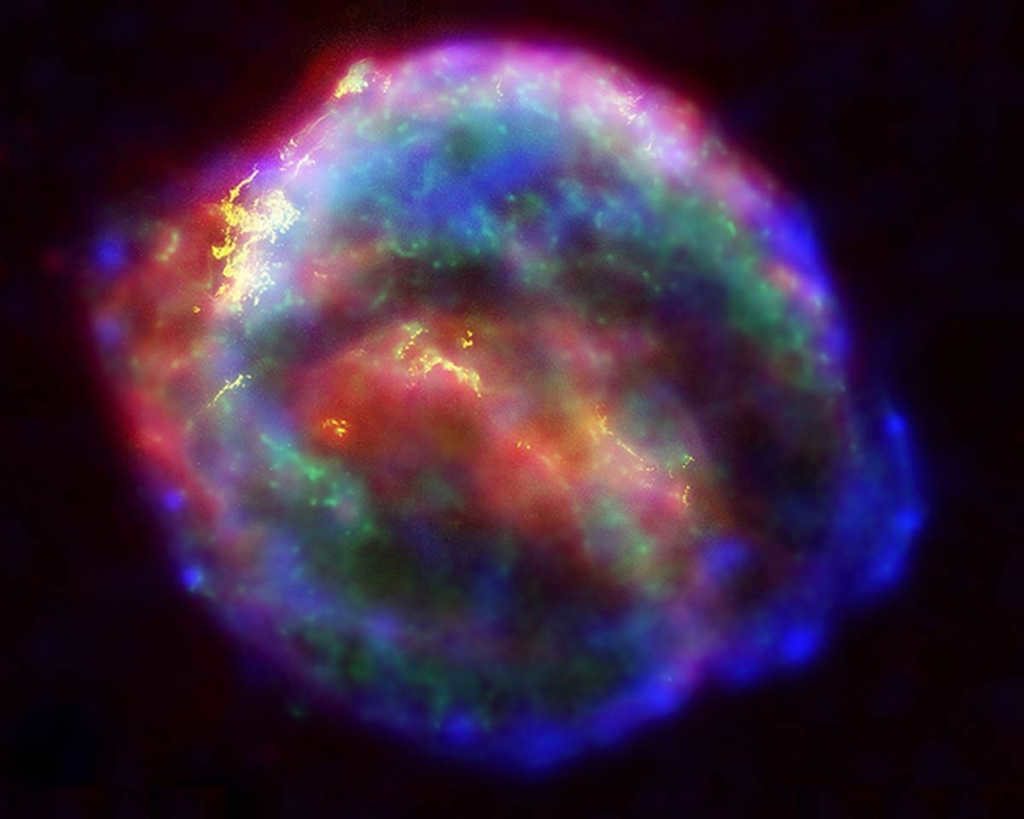

SN 1604, also known as Kepler’s Supernova, is a celestial event that occurred in the year 1604.
During the Middle Ages in Europe, astronomy remained stagnant until at least the 13th century. However, the field of astronomy thrived in the Islamic world and other regions around the globe. The advancements in astronomy during this time period led to the establishment of the first astronomical observatories in the Muslim world as early as the ninth century. In 964, the Andromeda Galaxy was discovered by the Persian astronomer Azofi. Additionally, in 1006, Arab astronomer Ali Ibn Ridwan and Chinese astronomers observed Supernova SN 1006, which is considered the brightest supernova in recorded history. Several influential Islamic astronomers, primarily from Persian and Arab backgrounds, made significant contributions to the field of astronomy. Some notable figures include Al-Battani, Tebit, Azofi, Al-Bumasar, Biruni, Arzakhel, Al-Biryandi, as well as the observers from the observatories of Samarkand and Maragheh. During this time period, many bright stars were given Arabic names by astronomers. It is believed that the ruins of Great Zimbabwe and Timbuktu may have served as astronomical observatories. For a long time, Europeans mistakenly believed that Arabs in Africa south of the Sahara Desert did not make any celestial observations. However, modern discoveries have shown that this assumption is incorrect.
Please note! The animation will only function on browsers that support the -webkit standard (such as Google Chrome, Opera, or Safari).
Astronomy. History of astronomy. The examination of astronomy

ASTRONOMY. HISTORY OF ASTRONOMY. STUDY OF ASTRONOMY
Astronomy (Greek. – star – law) is the field of scientific inquiry that focuses on the examination of the location, structure, properties, origin, movement, and evolution of celestial objects (such as stars, planets, meteorites, etc.), the systems they form (such as star clusters, galaxies, etc.), and the universe as a whole.
Characteristics of astronomy as a scientific discipline
Astronomy, as a scientific discipline, relies primarily on observation. Unlike physicists, astronomers do not have the ability to conduct experiments. Almost all the data about celestial bodies comes to us in the form of electromagnetic radiation. It is only in the past four decades that we have been able to directly study individual celestial bodies, such as probing the atmospheres of planets and examining the soil on the moon and Mars.
Astronomy is closely connected to other fields of science, particularly physics and mathematics, which are extensively employed in its study. However, astronomy also serves as a unique platform for testing numerous physical theories. Outer space is the sole location where matter can exist at temperatures reaching hundreds of millions of degrees Celsius, as well as near absolute zero, in the vacuum of space and within neutron stars. In recent times, the advancements made in astronomy have found applications in the fields of geology, biology, geography, and history.
The subject matter of astronomy encompasses a wide range of topics.
When exploring the vastness of the cosmos, astronomy is faced with three primary objectives that necessitate consistent resolutions:
- Examining the apparent and subsequent actual positions and movements of celestial entities in space, discerning their dimensions and configurations.
- Probing into the physical makeup of celestial bodies, encompassing the exploration of their chemical composition and physical conditions (such as density and temperature) on both their surfaces and interiors.
- Tackling the enigmas surrounding the origin and evolution of celestial bodies, including the potential future destinies of individual entities and their systems.
The questions of the initial issue are addressed through extensive observations that have been conducted since ancient times and are based on the principles of mechanics, which have been known for approximately 300 years. As a result, we possess a wealth of information in this field of astronomy, particularly regarding celestial bodies that are relatively close to Earth.
Our understanding of the physical composition of celestial bodies is far more limited. The resolution of certain questions related to the second issue only became possible just over a century ago, with the main problems being solved only in recent years. The Astronomy Division is responsible for this progress.
Modern astronomy is divided into numerous interconnected sections, and this division, to some extent, is arbitrary.
The primary divisions of astronomy include:
1. Astrometry is the branch of science that deals with the measurement of space and time. It encompasses two main areas: a) spherical astronomy, which focuses on developing mathematical techniques for determining the apparent positions and motions of celestial bodies using various coordinate systems, as well as studying the regular changes in their coordinates over time; b) fundamental astrometry, which involves tasks such as determining the coordinates of celestial bodies through observations, cataloging stellar positions, and calculating the numerical values of important astronomical constants. Theoretical astronomy provides methods for determining the orbits of celestial bodies based on their apparent positions, as well as calculating ephemeris (the apparent positions of celestial bodies) using known elements of their orbits.
2) Theoretical astronomy offers techniques for determining the paths of celestial objects based on their observable positions and techniques for calculating the apparent positions of celestial bodies based on the known elements of their paths (inverse problem).
3 Celestial mechanics investigates the principles governing the movement of celestial bodies under the influence of gravitational forces, determines the mass and shape of celestial bodies, and assesses the stability of their systems. These three disciplines primarily address the fundamental challenges of astronomy and are commonly referred to as classical astronomy.
5. The study of stars, stellar systems, and interstellar matter, taking into account their physical characteristics, is known as stellar astronomy. These two areas primarily focus on the second aspect of astronomy.
6. Cosmogony is concerned with the origin and evolution of celestial bodies, including our planet Earth.
7. Cosmology explores the overall patterns of the structure and progression of the universe.
By utilizing all the knowledge acquired about celestial bodies, the final two branches of astronomy address its third objective.
Astronomy is the scientific study of the structure, motion, physical properties, origin, and evolution of celestial bodies and the systems they form. It also explores the fundamental characteristics of the universe surrounding us. Unlike physicists, astronomers rely mainly on observation rather than experimentation. Almost all our knowledge about celestial bodies comes from the analysis of electromagnetic radiation. Only in the last four decades have we been able to directly study individual worlds, such as examining planetary atmospheres and analyzing the composition of lunar and Martian soil.
Astronomy has strong connections with other scientific disciplines, particularly physics and mathematics, which it heavily relies on. However, astronomy also serves as an invaluable platform for testing numerous physical theories. Outer space is the exclusive environment where matter can exist at extreme temperatures ranging from hundreds of millions of degrees to near absolute zero, as well as in vacuum voids and neutron stars. In recent times, the progress made in the field of astronomy has found practical applications in geology, biology, geography, and history.
There is no longer a need to navigate a ship using celestial bodies, anticipate the flooding of the Nile, or measure time with an hourglass: modern technology has replaced traditional astronomy. However, astronomy and space travel continue to be essential in communication systems, television, and the observation of Earth from space. Astronomy explores the fundamental laws of nature and the development of our planet, making it of significant philosophical significance. In essence, it shapes the way people perceive the world.
Astronomy has been a subject of fascination for ancient civilizations, including Egypt. The sky above us holds a wealth of knowledge and patterns that have been observed for centuries. It is believed that the first astronomers made their discoveries while sitting around primitive fires, observing the movements of the stars. The lunar phases, in particular, caught their attention, leading to the creation of the first lunar calendar. As their knowledge grew, they also discovered the movement of the Sun along the zodiac, giving rise to the solar year. Alongside these astronomical discoveries, ancient civilizations developed a rich mythology around the celestial bodies. The Sun, Moon, and other luminaries were deified, and rituals were performed to honor these heavenly gods and seek their help in times of need.
Ancient Egyptian Astronomy
Approximately four thousand years before the start of the Common Era, the Nile Valley was home to one of the most ancient civilizations on our planet – the Egyptians. After the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt, a mighty empire was established here, marking a new era in the region’s history. The Egyptian priests who studied astronomy made an intriguing observation: they noticed that two significant events consistently preceded the annual rise of the water levels. These events were the summer solstice and the reappearance of Sirius, also known as the “Dog Star,” in the morning sky after a period of seventy days of absence.





