
Currently, there are 58,742 educational establishments that provide supplementary cumulative rebates (ranging from 2% to 25%). To ascertain the applicable discount for all staff members at your educational institution, kindly access your personal Infoworks account.


Course for professional growth
Specifics of teaching computer science in elementary school according to the Federal State Educational Standard for Elementary Education.
We can combine your educational institution’s discount with this offer (the amount depends on how many of your colleagues have completed Infoworks courses).
Currently, 58,742 educational institutions are eligible for additional discounts (ranging from 2% to 25%). To find out the applicable discount for all employees of your educational institution, please log in to your personal Infoworks account.


Advanced training program
Contemporary concerns in the methodology of teaching folk plucked instruments at music schools and conservatories
We can apply a discount for your educational institution in addition to the existing discount (the amount of discount depends on the number of your colleagues who have completed Infoworks courses)
At present, 58,742 educational institutions are eligible for additional discounts (ranging from 2% to 25%). To find out the discount available for all staff members of your educational institution, please log in to your personal Infoworks account.


Organizational Matters in Family Education Administration
Overview of the Presentation in Slide Format:


One slide Astronomy is the scientific study of the universe and all its related phenomena.
“Astronomy is valuable because it lifts us beyond ourselves;
It is valuable because it is grand;
It is valuable because it is magnificent…”
/Henri Poincaré (1854-1912) was a French mathematician, physicist, and philosopher.

There are several objectives of astronomy. First, it aims to analyze and understand the changes in the global structure of the Earth. This involves studying the various shifts and transformations that occur within the Earth’s composition.
Another objective is to investigate the movements of continents and individual regions of the Earth’s surface through the use of radio astronomy. This allows scientists to track and monitor the shifting tectonic plates and understand the processes behind them.
Additionally, astronomy also focuses on studying the influence of the Sun and its activity on the Earth. This includes analyzing solar flares, sunspots, and other phenomena to understand their effects on our planet’s climate and environment.
A crucial objective is to study the asteroid danger and the potential for Earth’s collision with asteroids and comets. By monitoring and analyzing near-Earth objects, astronomers can assess the risks and develop strategies for planetary defense.
Lastly, astronomy aims to investigate the impact of the cosmos on the Earth’s life. This involves studying cosmic rays, interstellar dust, and other extraterrestrial factors that may affect the development and evolution of life on our planet.

Slide number 4 – How astronomy is related to other scientific disciplines:
Mathematics;
Physics;
Philosophy;





9 slide Measurement of distance in astronomy
1 astronomical unit (1a.u.) = 149 million kilometers.
1 light-year is the distance traveled by a light ray in a vacuum in 1 Earth year. It is equivalent to 9.5 x 10^15 meters.
1 parsec is the distance to stars determined by their parallax.
1 pc = 3.263 light years = 206,265 a.u. = 30.86 x 10^15m.

10 slide Measurement of time in astronomy
The duration of time during which the Sun completes a full rotation around the celestial sphere is known as a year.
The time period between the Moon’s orbit around the Earth is referred to as the sidereal or sideric month (27.3 days).
The time interval between two consecutive identical phases is referred to as the synodic month (29.5 days).
The tropical year is the duration of time in which the Earth completes one revolution around the Sun (365.24 days).

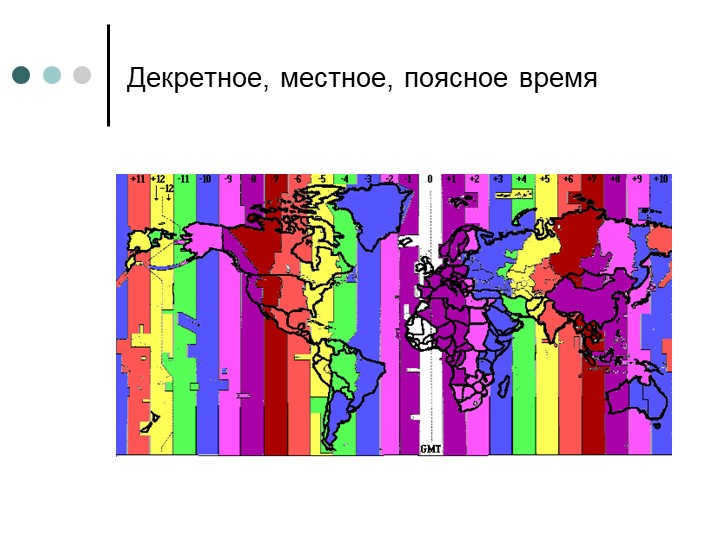
12 slide Time Zone
Time zones are geographical regions on Earth where the same standard time is observed.
The modern system of time zones was established in North America by Canadian engineer Sandford Fleming around 1879, and by 1929 it had been adopted worldwide.
Daylight saving time is the practice of adjusting one’s own time to align with universal time.
Ancient Egyptian timekeeping devices included water clocks, known as klepsydra.

Slide 13: The water clock known as a klepsydra was used to measure time
When water collected in the chamber, the float 5 with the number 6 on it would rise and indicate the hour on the column. Another figure (2) would release water from its eyes. After a day, the water would flow out through the siphon device 8 and turn the gear wheel 7, which in turn rotated the entire column.
The column would complete a full rotation in one year. The curved “hour” lines marked on the column were designed to ensure that the float’s steady rise corresponded to the varying lengths of day and night hours during different seasons.

Slide 14: Universal Time.
Universal time is a measurement of time that is based on the prime meridian (Greenwich). There is no distinction between world and local time at the North and South Poles.
The prime meridian runs through the Greenwich Observatory in London, England.
In Barnaul, the time difference from universal time is 7 hours in the winter and 6 hours in the summer.
Aviation and astronautics, such as NASA and TsUP, use world time.

16th slide of Ordinary Time
Decimal time is the time zone that is shifted 1 hour ahead.
It was implemented on June 16th, 1930 within the borders of the USSR.
Several countries around the world are situated across multiple time zones:
Russia – 9 time zones;
Canada – 6 time zones;
USA – 5 time zones, Greenland – 4 time zones, Australia and Mexico – 3 time zones, Brazil and Kazakhstan – 2 time zones.
Although China spans across 5 time zones, it observes a single standard time throughout its territory.
The Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) – 3 time zones.



The term “calendar” originates from the Latin word calendae, which was the name given to the first day of every month in ancient Rome. It was on this day that creditors would record interest in their debt ledgers.
Importance:
A functioning system of counting is essential for daily life to be possible;
measurement of space (metrology);
measurement of time (calendar and chronology).
Different types of calendars:
Lunar; based on the synodic month (the time it takes for the moon’s phases to change);
Solar;
Roman;
Gregorian;

There are 22 slides in the Lunar calendar presentation.
Muslims are the ones who use this calendar.
In 433 BC, the ancient Greek astronomer Meton made a remarkable discovery: every 235 lunar months, which is equivalent to 19 years, the new lunar year coincides again with the vernal equinox.
There are 12 months in a year.
All months consist of 30 days each.


Slide 23: The Roman calendar
The ancient Roman calendar consisted of 10 lunar months.
On the 1st day of each month, it was customary to settle any outstanding debts and pay interest.
On the 9th day of each month, the pontiffs would announce any holidays that were to be celebrated that month.
Around 700 B.C., Roman king Numa Pompilius added 2 months to the calendar, and the New Year was moved to March 1.
In 46 B.C., Julius Caesar further reformed the calendar by moving the start of the year to January 1.
To address the superstition that February was an unlucky month, Caesar made it the shortest month with 28 days.

On slide 24, the Gregorian calendar is discussed. In 1752, England made changes to the Gregorian calendar by moving from March 25 back to January 1. This adjustment resulted in 94 days being skipped. The Gregorian calendar remained in use in Russia until January 26, 1918, when a new style was adopted. After January 31, it was no longer February 1, but instead, it became February 14.

A unique feature of the Russian calendar is that it has 25 slides. Traditionally, the calendar in Russia began from the Nativity of Christ, with the year starting in March. However, Tsar Ivan III changed the New Year’s Day to September 1. Later, Peter I ordered that the beginning of the year be counted from January 1, following the Christian calendar, starting from 1700. Interestingly, the northern peoples did not have a concept of counting the time of life, as it was not considered significant.

Slide number 26 is dedicated to the topic of the seven-day week and its origins. The concept of a seven-day week can be traced back to the ancient Babylonian priests who assigned each day to a specific celestial body – Sun, Moon, Mars, Mercury, Jupiter, Venus, and Saturn. It is interesting to note that Saturday, associated with Saturn, was considered the unluckiest day of the week, and people would typically refrain from working on this day, making it a day off. Sunday, on the other hand, was known as Solntsev day, meaning the day of the sun.

Slide 27 Control Questions:
The matron saint of astronomy.
What is the purpose of studying astronomy?
What is a calendar? Can you name any?
What do ordinance, local, universal, and zone time mean?
What is a time zone?
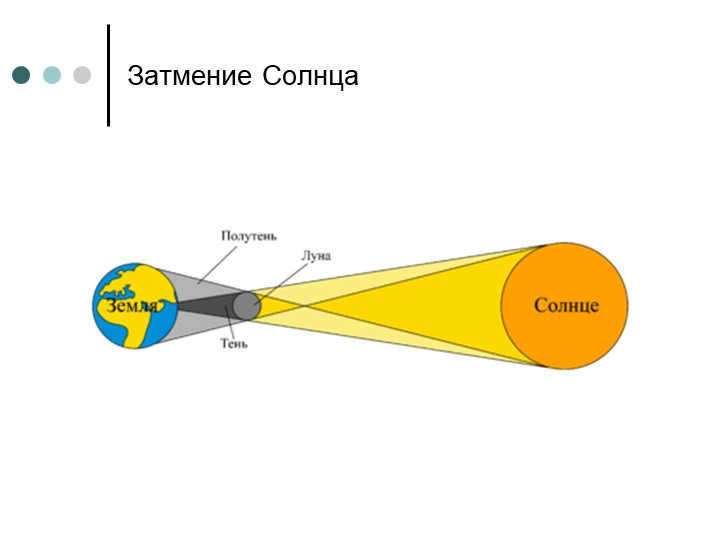
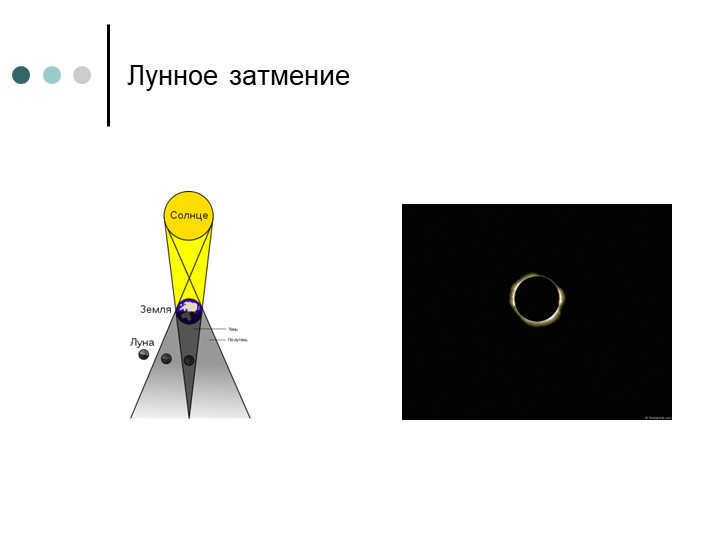
How do solar and lunar eclipses occur?
What were the days of the week called in the Old Slavonic calendar?
How many time zones are there in Russia? Which time zone is Altai Krai in?
The field of science that explores the cosmos, the Universe, including its structure, motion, space, origin, and the development of celestial objects and systems, is known as astronomy.
Derived from ancient Greek, the term astronomy refers to the study of the celestial bodies’ laws.
Astronomy encompasses the study of the Sun, Earth, other galaxies, planets within the solar system, stars, comets, asteroids, and meteorites.
The exploration of the universe began on our planet when humans started contemplating and questioning the origins of humanity and the functioning of the world. As early as the 6th century BC, people initiated the examination of the stars, and by 1500 BC, the first calendars and astronomical tables emerged. Pioneering scientists like Pythagoras and Galileo made significant contributions to the advancement of astronomy. They posited that our planet possesses a spherical shape.
Astronomy can be categorized into five main disciplines:
– The branch that investigates celestial objects as a whole is known as astrometry;
The second branch of astronomy is known as celestial mechanics, which focuses on studying the laws of motion, mass, volumes, and shapes of celestial bodies.
The third area of study in astronomy is theoretical astronomy, which involves computer modeling and creating models of celestial bodies and systems.
Astrophysics is the field of astronomy that examines the chemical composition and physical properties of celestial bodies.
Archaeoastronomy is the branch of astronomy that investigates the history of the origin of celestial systems, objects, and the Universe.
Observation plays a fundamental role in the work of astronomers. Almost all information about celestial systems and bodies is obtained through observations.
The task of astronomers is to observe celestial objects and the universe, which is a challenging and demanding process that necessitates intense focus, attention, and consistency.
The objects being studied are located at vast distances from the observers, which cannot be measured in mere millions of kilometers. As a result, scientists have established their own unit of measurement, known as the astronomical unit, to study objects within the solar system and other celestial bodies. The astronomical unit is defined as the distance of the Earth’s large semi-major axis, which is 140 million kilometers.
The field of astronomy is a scientific discipline that allows us to comprehend the inexplicable phenomena and situations that occur on our planet Earth.
Alternate Message
Astronomy is the study of celestial bodies and their motions in space. This branch of science has numerous practical applications, ranging from unraveling the origins of the universe to facilitating space exploration.
Throughout history, astronomy has been one of the earliest sciences practiced by humans. Ancient civilizations utilized their understanding of the sun, moon, and stars’ movements to create calendars and determine the changing of seasons. They also observed celestial events like eclipses and comets, associating them with various mythological and religious beliefs.
Modern astronomy utilizes a variety of tools and technologies to explore the vastness of the cosmos. Space-based telescopes, like the renowned Hubble, offer intricate imagery of far-off galaxies and celestial objects. On the other hand, ground-based telescopes employ specialized instruments to analyze the various properties of light emitted by stars and galaxies.
Moreover, astronomy finds practical applications in numerous scientific domains. For instance, the study of space weather plays a crucial role in safeguarding spacecraft and satellites against the hazardous effects of solar wind. Furthermore, investigating planets and celestial bodies aids in unraveling the mysteries surrounding the origin of life in the universe.
All in all, astronomy stands as an extraordinary and captivating scientific field that enriches our understanding of both our planet and the vast cosmos surrounding it.
Science Astronomy: Enhancing Communication with Visuals

Hottest subjects nowadays

- Over the years, tea has become a popular beverage in Russia and other countries both near and far abroad. The term “tea” refers to a drink that is made by brewing the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant.
- Tourist camping is an appealing and promising activity. Many young people have experienced the joy of camping, with guitars, tents, campfires, and heavy backpacks. It is a romantic way of life and a test of endurance.
- The white mushroom is a member of the Borovik family and is known for its edible nature. It has a convex cap that can range from 8 to 30 cm in diameter. Some particularly large and unique specimens have been discovered with distinctive features.
- The Constitution of the Russian Federation has been created and improved by mankind throughout its existence. It serves as a foundation for politics, political systems, and the relationships between people within the state.
- A.S. Pushkin is a renowned poet, known not only in Russia but also globally. His literary works are a treasure trove within world literature, and his life story is filled with numerous intriguing facts.
- Physics is a scientific discipline that encompasses the study of material phenomena in our surroundings. One such phenomenon is the effect of a body’s weight on a support or suspension.

I developed a deep fascination for astronomy at the tender age of 10. Fond memories of my dad returning home from work in the evenings with a new book on the subject still linger in my mind. He would often surprise me with these thoughtful gifts, and on this particular occasion, it was a captivating tome on constellations. I was absolutely enthralled by its contents, as the author had a way of describing the stars and planets that truly captured my imagination. Recognizing my keen interest, my dad suggested a trip to the planetarium. To this day, I can vividly recall the sheer joy and wonder I experienced during those magical childhood visits. From that point forward, astronomy became my lifelong passion.

What does astronomy study?
Therefore, astronomy is a discipline that originated four centuries ago. During that time, scientists possessed extensive knowledge. They understood that stars and planets were distinct entities, and that some celestial bodies were closer to Earth while others were farther away. Additionally, they were capable of predicting solar and lunar eclipses. However, each new discovery contradicted the teachings of the church, resulting in astronomers being persecuted and incarcerated.
Those days are long gone, and nowadays, astronomy is a sophisticated field encompassing various disciplines. It examines the structure of the universe, the laws governing stellar motion and origin, and even contributes to satellite launches.

The connection between astronomy and science and technology
Today, the field of astronomy is closely intertwined with the disciplines of physics and mathematics. Throughout the 20th century, groundbreaking discoveries were made in the realms of X-rays, electrons, and the transformation of elements. These revelations shed light on the fact that matter in the vast expanse of the universe can exist in states that were previously unimaginable. These unique states of matter cannot be replicated on Earth; rather, they manifest on a grand scale within stars and nebulae. It is the duty of astronomers to meticulously study and analyze these phenomena. Such studies inherently involve extensive mathematical calculations, such as determining the orbit and trajectory of celestial bodies. In this regard, calculating machines have proven to be invaluable tools. Entire scientific institutes, known as observatories, have been established to facilitate this research. One notable example is the largest observatory in the world, located in Chile. This state-of-the-art facility will significantly contribute to the study of galaxies that formed within the first hundred million years following the Big Bang.

Each year, astronomers are delving deeper into the vastness of the Universe, revealing unseen realms that lay before them. Just as the universe itself is boundless, so too are the enigmas that astronomers strive to unravel. This timeless field of study will forever remain ageless.
I have an immense passion for all things related to space, and I have been avidly keeping abreast of all the latest developments in astronomy. I am even contemplating the purchase of a telescope and immersing myself in the world of amateur astronomers. In the subsequent paragraphs, I will delve into the subject of what astronomy entails and shed light on the realm of amateur astronomers.

Astronomy: The Study of the Cosmos
In the past, astronomy played a crucial role in plotting ship routes, predicting river floods, and determining favorable times for sowing. While other sciences have taken over these practical applications, astronomy remains important in the modern era, especially since the advent of space exploration. Contemporary astronomy encompasses various fields of study, including:
- Celestial Mechanics: The study of star motion and the determination of their mass.
- Astrometry: The analysis of celestial body movements.
- Theoretical Astronomy: The construction of models to understand celestial objects and phenomena.
- The study of the evolution of celestial objects and the patterns of their spatial arrangement is a task that is undertaken by several other areas of study.
- Amateur astronomy is simply a hobby where individuals who are not involved in science make their own observations.
- Despite the fact that amateurs do not have a scientific background or the resources of a research center, their contribution to the common cause is significant.
Amateur astronomy
Amateur astronomy is essentially a hobby pursued by individuals who are not involved in science. Despite their lack of scientific background or access to research facilities, their contribution to the common cause is substantial.

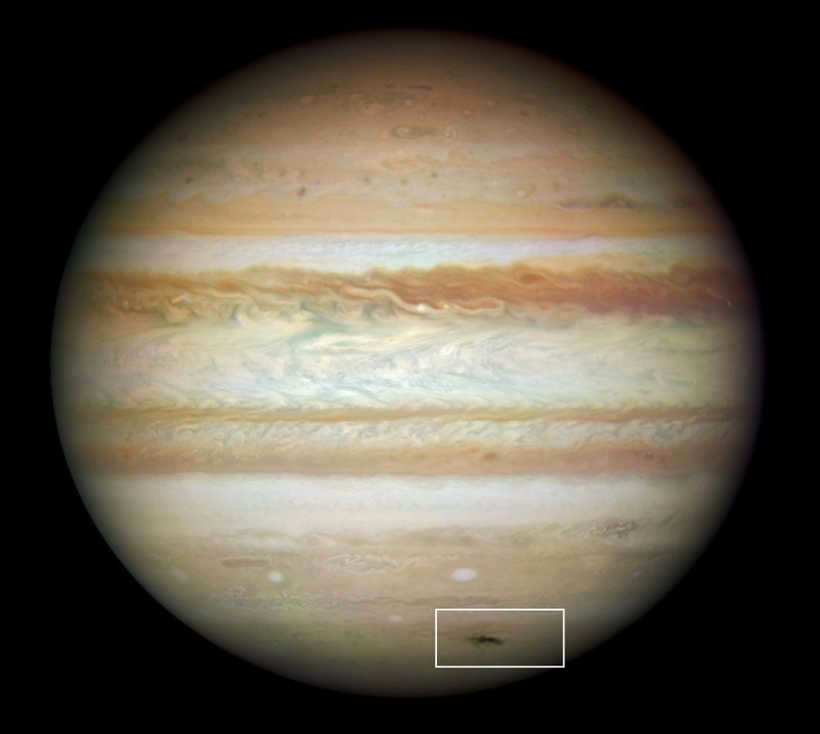
Anthony Weasley made an extraordinary finding by observing the cosmos from his own backyard – a massive hole on Jupiter, equivalent in size to planet Earth. He promptly reached out to NASA and provided them with the captured images, which were later verified by experts using advanced equipment. This groundbreaking discovery was identified as “Jupiter’s scar,” resulting from the impact of a comet.
At times, a telescope is unnecessary. As an illustration, regular schoolteacher Hannie van Arkel. was examining images of galaxies that are available to the public on the internet. She observed an unsettling congregation of gas in one of the pictures. a congregation of gas that bore resemblance to a galaxy but possessed a colossal aperture at its core. Upon reaching out to scientists, she greatly embarrassed them – the photograph unequivocally exhibited the outcome of a so-called outburst from a black hole. outburst from the black hole.

Astronomy is a field of scientific study that focuses on the examination of celestial bodies, including their history, origin, motion, and structure. It encompasses the exploration of space, other planets, interstellar space, and galaxies. By delving into the study of astronomy, one can gain knowledge about various cosmic phenomena such as black holes, nebulae, comets, and the intricate structure of our solar system.
Contemplating the night sky has always sparked curiosity in individuals, regardless of age. The stars and the vastness of the universe have captivated the minds of many, and these inquiries are both captivating and thought-provoking. Fortunately, the science of astronomy provides the answers to these puzzling questions, offering a deeper understanding of the cosmos.

What is the name of the science that explores space?
Astronomy is currently a highly diverse field of study that has been in existence for over four hundred years. This scientific discipline examines everything visible in the night sky, including stars and constellations, planets and galaxies, as well as their interconnections, structure, and movements within the universe.
In essence, astronomers investigate the wide range of celestial bodies that exist within the cosmos.
In ancient times, astronomy was utilized for navigating ships, predicting weather patterns, and forecasting solar and lunar eclipses. Today, thanks to this field of science, we have extensive knowledge about stars and comets, the ability to venture into space, and the opportunity to explore new planets.
What is included in modern astronomy
Astronomy, like many other sciences, has undergone rapid evolution over time. It has transitioned from simple observation to practical study. Today, astronomy is closely intertwined with the fields of chemistry, physics, and mathematics. These disciplines enable a more in-depth exploration and comprehension of celestial entities. Currently, astronomy encompasses the following areas:
- Astrometry – the investigation of celestial bodies’ motion in space;
- Celestial mechanics – the examination of stars, including their shape, mass, and movement;
- Theoretical astronomy – the development of computer programs to simulate cosmic processes;
- Astrophysics – the exploration of the physical and chemical characteristics of cosmic bodies.
Astronomy in Russia
Currently, Russia boasts a range of observatories, planetariums, and institutions of higher learning dedicated to the study of astronomy. Among the most renowned are the Main Space Observatory in St. Petersburg, the Sternberg State Astronomical Institute in Moscow, and the Moscow Planetarium. In addition, there are several other notable establishments such as the P.K.Sternberg State Astronomical Institute in Moscow.

If you have an interest in the field of astronomy, there are also various astronomical publications available in Russia, such as “Letters to the Astronomical Journal” and “Earth and the Universe”.
In my personal opinion, there is nothing more breathtaking than the vast expanse of the night sky. It is truly magnificent to step out onto the porch in the countryside and gaze endlessly at the shimmering display of distant celestial bodies. However, the stars are not just a source of wonder for us dreamers, but the subject of an entire scientific discipline known as astronomy.
 What is the name of the science that studies space
What is the name of the science that studies space
Astronomy is an ancient scientific discipline that has captivated humans for centuries. Our ancestors were fascinated by the mysteries of the cosmos and sought to understand the laws that govern celestial bodies and their impact on our world.
Today, astronomy has made significant progress. From my early years until now, I have always enjoyed exploring space encyclopedias and learning about:
Astronomy is concerned with the examination of these celestial entities and events, along with numerous others: the genesis and demise of stars, their categorization, objects such as meteorites and comets, and the enigma surrounding the inception of the universe. Vast quantities are often referred to as astronomical, and this is not without reason: this discipline continuously grapples with immense figures. This is simply how the colossal (and conceivably boundless) cosmos operates. All these magnitudes and contemplations about “what existed prior to the Big Bang” cause me great distress and engender a profound sense of unease regarding my own insignificance.
This subject was not included in our school curriculum. A lot of individuals were pleased by this decision: why bother learning something that seems so distant from us? I can relate to their perspective, just like Sherlock Holmes, who once mentioned that it was pointless to clutter one’s mind with information that has no relevance to them.
However, is that truly the case? In reality, we are actually situated within space itself. It surrounds us, and in a way, we are also a part of it.

My fascination with the stars has always been present. I’m not sure why, but ever since I was a child, I have had a deep appreciation for gazing at the night sky. Living on the outskirts of the city, we were fortunate to have minimal streetlights, allowing for clear views of the stars. I remember even taking my neighbor’s astronomy textbook and delving into its pages, searching for constellations that I could identify in the expansive sky. To this day, I can still locate some of those familiar constellations when I look up at the night sky.

The Scientific Field of Astronomy
Astronomy is a scientific discipline that focuses on exploring the vast expanse of the universe and investigating various celestial bodies and objects within it. These encompass a wide range of entities:
Astronomy delves into not only the composition of these celestial bodies, but also their origins, evolution, and movements.
It is one of the most ancient sciences. And what is so challenging about it: you simply raise your head up in the sky and observe. That is what people did in ancient times, until they began inventing various methods to observe the sky.
Since ancient times, the study of the sky has been beneficial to people. The positioning and movement of celestial bodies allowed for determining the start of seasons, creating calendars, predicting weather, navigating at sea, and much more.
The ancient Greeks were the ones who were ahead of the curve when it came to the development of astronomy. Pythagoras, one of the Greek scholars, suggested that the Earth had a round shape. Another Greek scholar, Aristarchus, proposed that the Earth revolved around the Sun, which was contrary to the prevailing belief at the time. Unfortunately, Giordano Bruno, an Italian philosopher, faced severe consequences for his suggestion about the infinity of the universe. The Catholic Church burned him at the stake and imprisoned him for seven years, in an attempt to make him renounce his ideas. Clearly, this was not how the Catholic Church envisioned the structure of the universe.

What is the name of the science studying the cosmos
In the previous century, the field of astronomy was broadly split into two categories: observational and theoretical. Theoretical astronomy involves the development of computer, mathematical, or analytical models for the purpose of studying the cosmos.
However, observing the stars is even more thrilling. Simply gazing at the night sky is enjoyable, but examining the heavens through a telescope adds an extra layer of fascination. Therefore, there are numerous individuals worldwide who engage in amateur stargazing. Surprisingly, even these amateurs contribute to scientific knowledge! While their equipment may be less advanced (as huge telescopes are not readily available for purchase), their sheer volume of observations is substantial. In fact, some scientists in this field originated from amateur backgrounds.

In the past, during the time of the Soviet Union and even afterwards, astronomy used to be taught as a distinct subject in high schools. However, for approximately 15 years now, this subject has been absent. It is unfortunate because, according to statistics, 30% of Russians once again believe that the Earth revolves around the Sun, rather than the other way around.
Ever since I was a child, I have been a regular visitor to the planetarium. Nowadays, of course, the planetarium has greatly evolved – it is now digital and provides detailed information about the latest advancements in the field of astronomy. In the following paragraphs, I will explain the nature of this science and what astronomers investigate.

Areas of focus in astronomy
The essence is revealed in the precise description of the field known as “astronomy”. Consequently, it encompasses the scientific exploration of celestial objects, and based on this, its nature becomes evident:

- Stars, including our sun;
- Planets and moons;
- Interstellar material;
- Interplanetary material;
- Comets;
- Asteroids;
- Pulsars;
- Galaxies;
- Black holes;
- Quasars and various other objects in the universe.
A peek into the past
When scientists gaze at the vast expanse of the night sky, they are essentially gazing back in time. This concept is not surprising, as the light emitted by stars and reflected by planets can travel for tens to billions of years before reaching us. Therefore, we observe these celestial bodies as they appeared in the past, precisely the amount of time it took for their light to reach us. This principle forms the basis of a method used to determine the distance of galaxies from our planet: the faster a galaxy is moving away, the farther it is from us. However, how far away are these galaxies exactly? Currently, science has established three key facts about the universe:
- “It originated from a single superdense point;
- It is expanding;
- It is expanding at an accelerating rate.”
Over the course of billions of years, the universe will undergo expansion, causing galaxies to experience an acceleration until they reach the ultimate speed of light. At this point, a truly awe-inspiring event will occur – they will vanish from sight, rendering them utterly impossible to detect. This phenomenon is projected to take place after approximately 3 trillion years, at which point they will no longer be visible in our celestial expanse. In the far future, scientists will only have the opportunity to study a solitary assemblage of stars known as the Milky Way.
The Future of Astronomy.
However, what can we anticipate from this discipline in the coming decades? Not long ago, light was the sole means of obtaining information about the workings of the Universe. Nevertheless, modern scientists are now investigating objects in the “undetectable” segments of the electromagnetic spectrum. A prime example of this is the recent breakthrough in the field of radio astronomy. As the name suggests, this branch of science involves the study of radio waves emitted by celestial bodies. The achievements in this field have been remarkable, yielding a wealth of data on interstellar matter, the dynamics of our own galaxy, and the ramifications of cosmic catastrophes, such as nebulae, among other phenomena.

However, the most thrilling aspect will arise when it becomes feasible to launch space telescopes. There is no sound or bending of our planet. Nor is there the curvature of our planet.. There is only one thing – the stillness of the void.
Astrophysics is a intricate examination of our cosmos from a scientific and philosophical standpoint. Its inception commenced in ancient times. Ancient civilizations were deeply engrossed in myths, worship of deities, the initial exploration of celestial bodies, and so on. Thanks to these early societies, we became aware of the existence of the first planets. The study of astrophysics is grounded in the comparison of the physical characteristics of the universe.

The Science of Cosmology
Cosmology is a scientific field that combines aspects of astrophysics and astronomy. It involves the study of the universe through the observation of astronomical phenomena. In order to gather data, scientists utilize the principles of relativity, originally formulated by Albert Einstein. Previously categorized as a branch of philosophy, cosmology became recognized as a rigorous scientific discipline in the 1920s. Today, modern cosmology is gaining popularity as it incorporates new discoveries from physics, astronomy, astrology, and philosophy. One of the most recent advancements is the Big Bang theory, which posits that our universe is constantly expanding due to high density and temperature.
Historical origins of this field of study
In the early 1900s, prior to announcing his groundbreaking findings, the researcher had to provide both theoretical and empirical evidence to establish the distinctiveness of the outcomes. However, let us travel back to ancient times when humanity was just embarking on its initial forays into the realm of astronomy. In ancient Egypt, China, India, and Greece, scholars dedicated themselves to observing celestial phenomena. This led to the creation of the lunar calendar, which served as a guiding tool for people on Earth for an extensive period of time.
The study of the cosmos, known as cosmology, has a rich history deeply rooted in ancient myths and legends. One of the early pioneers of this field was Aristotle, who proposed the theory of homocentric spheres. According to this theory, our planet is situated on the surface of a hollow sphere, with the center of the Earth serving as the center of the universe. This model, which emphasized the divine origins of the Earth, gained significant popularity during that time.
Over the centuries, the doctrine of cosmology underwent significant transformations. Early ancient physicists believed in a geocentric model, where the planets revolved around the Earth, placing our planet at the very center of the Universe. However, these were mere theories without any practical evidence to support them.
The Advancement of Cosmology as a Scientific Field
In the 15th century, Nicolaus Copernicus made a significant breakthrough by consolidating the existing knowledge of his time. His theory proposed that the Sun is at the center of our universe, with planets, including the Earth and the Moon, orbiting around it. Copernicus drew inspiration from the works of prominent scientists such as Aristarchus of Samos, Leonardo da Vinci, Heraclitus, and Cuso.

Kepler made a significant advancement in the progress of this field. He formulated his renowned three theories, which later served as the foundation for Isaac Newton’s laws of dynamics. These laws revolutionized the understanding of planetary movement in the cosmos. Hence, it can be inferred that cosmology and physics have a strong interconnection. Cosmology succinctly provides a general overview of the phenomena taking place in our universe.
From ancient times, humans have been seeking to understand the role of our surrounding world in the vast universe. The Bible suggests that our universe was initially unseen and unremarkable. Einstein put forth the notion that the universe was motionless and stationary. However, scientist Friedman later demonstrated that it is actually in a state of gradual expansion and contraction. Astronomer Hubble’s research allowed for precise measurement of the distances to galaxies, leading to the development of the Big Bang theory.

The Basics of the Big Bang Theory
According to the principles of this theory, the age of the Universe is calculated from the moment of the nuclear explosion. As a result, scientists have determined that the Universe is 13 billion years old. Currently, the principles of astrophysics in cosmology are purely theoretical. In the initial moments after the Big Bang, there was the emergence of particles known as “quanta”, followed by the appearance of quarks with various types of interactions. It was only 0.01 seconds after the explosion that the formation of stars, galaxies, and even the solar system itself began.
What is the subject of study in cosmology?
Cosmology is an interdisciplinary field that incorporates principles from physics, mathematics, astronomy, and philosophy. Its primary focus is the study of the universe as a whole. Cosmologists examine the characteristics and behavior of celestial bodies such as planets, the Sun, the Moon, meteorites, and star clusters. The theoretical aspects of cosmology are derived from astronomy, and sometimes even geology, while the practical aspects are rooted in physics.
The idea of the cosmos in the field of cosmology
According to scientific theories, the cosmos is composed of various entities such as galaxies, stars, and planets. These entities have each undergone a unique process of development:
- Galaxies, in their early stages, were known as proto-galaxies;
- Stars began as protostars;
- Planets formed from protoplanetary clouds.

The metagalaxy is currently the most extensively researched area. It is a combination of numerous galaxies that fall within the astronauts’ visual range. The distribution of these galaxies is uneven, a fact that has been experimentally confirmed in the field of astronomy. Presently, scientists are focused on investigating the vast expanse of space that lacks any galaxies whatsoever. The metagalaxy’s age is estimated to be similar to that of the Universe.
A galaxy is a celestial structure that consists of stars and other celestial objects. It is a vast collection of stars that are held together by gravitational forces. Galaxies come in different shapes and sizes, with the Milky Way being the most well-known. The Milky Way is visible to everyone on Earth and is made up of stars, gas, and cosmic dust.
Stars in galaxies have varying ages, with some being as old as the universe itself and others being newly formed. The formation of stars is influenced by gravity, magnetic forces, and other factors. The study of galaxies and their formation is an area of cosmology that holds a wealth of knowledge but also many unanswered questions. Only the brightest and most brilliant scientists can hope to unravel the mysteries of the universe.
The Challenges of the Big Bang Theory
Cosmology is a relatively nascent field of study, having emerged as a distinct scientific discipline only in the mid-20th century. Its foundational principles are supported by empirical evidence collected by astronomers who have observed our vast Universe. Cosmology is a dynamic and ever-evolving field, constantly pushing the boundaries of knowledge. The theoretical concepts proposed several decades ago have already been subjected to experimental verification or debunking.

For instance, during the time of Einstein and Friedman’s teachings, the density of the Universe had the potential to possess any value. Nowadays, it has been scientifically established that this value corresponds to the critical value of pkr. Numerous similar instances can be provided.
There exist several fundamental cosmological issues that continue to be relevant in the present:
- the flatness of the Universe;
- the universality of the Universe’s horizon (appears the same from different directions);
- the origin of the gravitational compactifications that gave rise to galaxies;
- the actual composition of the substances that make up our Universe;
- according to the theory of quantum gravity, the cosmological constant should be 120 times higher;
- Cosmology studies the universe as a whole, while astronomy focuses on the study of celestial bodies.
- Astronomy has been practiced by ancient civilizations since ancient times, where people used the stars for navigation and worshiped ancient gods.
- Cosmology integrates knowledge from astrophysics, physics, philosophy, geology, cosmogony, and astronomy.
- In cosmology, scientists develop theories that apply to the entire universe rather than specific planets.
- Astronomy does not heavily rely on the laws of physics, while cosmology is built upon many physical principles.
- Unlike astrology, cosmology is not considered a rigorous science, as some of its assumptions lack practical confirmation.
- Astronomy encompasses the study of celestial phenomena, while cosmology seeks to understand the underlying principles behind them.
- Theoretical astronomy is a scientific discipline that focuses on the study of the movement of celestial bodies in their orbits. It aims to determine the position of planets based on their current location.
- Astrometry relies on the concepts of space and time. It utilizes mathematical methods to calculate the apparent positions and motion of objects in space. It also investigates the changing coordinates of celestial bodies.
- Celestial mechanics is concerned with the laws governing the motion of objects in space and their formation into systems.
- Gamma-ray astronomy investigates celestial objects through their radiation emissions.
- X-ray astronomy, similar to the aforementioned branch, focuses on studying X-rays emitted by celestial bodies.
- predicting the weather;
- facilitating maritime and aviation navigation;
- determining the precise dates of significant historical events;
- creating detailed maps of the Earth’s surface, constructing topographic charts.
Difference between astronomy and cosmology
However, even in the present day, numerous scientists maintain that cosmology is a subset of astronomy and do not regard it as a distinct discipline.
Many discoveries have been made in the field of modern science, which have greatly expanded our understanding of the universe. Some of these theories have been experimentally confirmed by scientists from around the world. However, there are still numerous areas that require further study and a solid empirical foundation. Even to this day, there remains a lack of consensus on the nature of the universe and the composition of its substances. This is a key challenge faced by scientists working in the field of cosmology and related disciplines. Our knowledge of the world around us is rapidly expanding, but as it does, new questions continue to arise. This is a natural part of the development and evolution of cosmology as a distinct scientific field.
Until recently, astronomy was not included in the school curriculum at all. However, it is now considered to be a mandatory subject. The way astronomy is introduced varies among different schools. In some cases, it is first introduced to seventh-graders, while in other schools it is only taught in the 11th grade. Many students wonder why they need to learn astronomy. So, let’s explore what this field of science is all about and how knowledge about the cosmos can benefit us in our lives?
The science of astronomy and its focus of study
Astronomy is a branch of natural science that delves into the mysteries of the universe. It is dedicated to exploring and understanding cosmic phenomena, processes, and objects. Through the lens of this scientific discipline, we gain insight into the nature of stars, planets, satellites, comets, asteroids, and meteorites. Furthermore, astronomical knowledge grants us a deeper comprehension of the cosmos itself, including the arrangement of celestial bodies, their movements, and the formation of their systems.

Astronomy is a scientific discipline that seeks to elucidate the inexplicable phenomena that are an inherent aspect of our existence.
The genesis and progression of astronomy
The initial human conceptions of the cosmos were exceedingly rudimentary, rooted in religious convictions. Individuals held the belief that the Earth occupied the central position in the universe, with the stars affixed to the firmament.
Throughout its evolution, this field of study has undergone various transformative periods, each referred to as an astronomical revolution.
The initial revolution occurred at various times in different parts of the globe. It started around 1500 years BC and was sparked by advances in mathematics. This led to the emergence of spherical astronomy, astrometry, and accurate calendars. The major breakthrough during this period was the development of the geocentric theory of the universe based on ancient knowledge.
The second revolution in astronomy occurred between the 16th and 17th centuries. It was driven by the rapid progress in natural sciences and the discovery of new insights about the natural world. During this time, the laws of physics were applied to explain astronomical processes and phenomena.

Astronomy, which is the study of celestial objects and phenomena, has made significant progress throughout history. One of the major breakthroughs was the establishment of the laws of planetary motion and universal gravitation. Additionally, the invention of the optical telescope greatly enhanced our ability to observe and understand the universe.
As astronomy advanced, new discoveries were made, such as the identification of new planets, asteroids, and star systems. These findings further expanded our knowledge of the cosmos. Furthermore, the development of space science led to the invention of new techniques that aided in astronomical research.
One significant advancement was the ability to study the chemical composition of celestial bodies. This breakthrough confirmed the interconnectedness and unity of the entire cosmic space. With each new discovery, our understanding of the universe continues to grow.
In the 1970s to 1990s, a significant astronomical breakthrough occurred, driven by advancements in engineering and technology. This era witnessed the emergence of all-wave, experimental, and corpuscular astronomy, enabling the study of celestial objects through the analysis of the electromagnetic waves and corpuscular radiation they emit.
Branches of astronomy
Astronomy, being an ancient science, has developed over time and has formed a complex structure. The field of classical astronomy can be divided into three main branches:

Aside from these primary sections, there are additional ones:
New trends and contemporary advancements in the field of astronomy
As of late, due to the rapid progress in various scientific disciplines, innovative branches dedicated to highly specific research in astronomy have emerged.
Introduction to Astronomy
What are the fundamental principles of this scientific field? In order to delve into the study of astronomy, it is necessary to become acquainted with its basic concepts.
Space encompasses a collection of stars and the interstellar regions. Essentially, it represents the entire universe.
A planet is a specific celestial body that revolves around a star. This designation is reserved for massive objects that can attain a rounded shape due to their own gravitational forces.
A star is a massive spherical entity composed of gases, within which thermonuclear reactions occur. The Sun, our closest and most familiar star, serves as an excellent example.

An object in the field of astronomy that is in orbit around a larger object due to gravity is referred to as a satellite. Satellites can occur naturally, such as the Moon, or can be artificially created and launched into orbit to provide essential information.
A galaxy is a cluster of stars, star clusters, dust, gas, and dark matter held together by gravity. All objects within a galaxy move in relation to its center.
In the field of astronomy, a nebula refers to interstellar space that emits distinctive radiation and stands out against the background of the sky. In the past, galaxies were often mistaken for nebulae before the development of powerful telescopic instruments.
The celestial bodies possess a natural attribute known as declination in the field of astronomy. This attribute serves as one of the two coordinates that indicate the angular distance from the celestial equator.
The contemporary language used in the field of astronomy
The introduction of innovative research methods, as mentioned before, has led to the development of new astronomical terminology:
“Exotic” entities – sources of optical, X-ray, radio, and gamma-ray radiation found in the vast expanse of space.

A quasar, in simple terms, is a celestial body that emits powerful radiation. Its energy output can surpass that of an entire galaxy. Even at considerable distances, we can observe such an astronomical object through a telescope.
A neutron star represents the final stage in the life cycle of a celestial body. This cosmic entity possesses an unfathomable density. To provide some perspective, the matter contained within a neutron star, which can fit into a teaspoon, would weigh 110 million tons.
Astronomy is a field of study that is intricately connected to a wide range of disciplines. Its research draws upon the advancements made in various branches of science.
Chemistry and astronomy are closely intertwined when it comes to understanding the distribution of chemical elements and their compounds on Earth and in space. Furthermore, scientists are highly interested in investigating the chemical processes that occur in outer space.
Geography and geophysics are also linked to astronomy, as the Earth can be viewed as one of the planets within our solar system. Geographers rely on astronomical knowledge to study phenomena such as the Earth’s topography, climate patterns, seasonal changes, magnetic storms, global warming, and ice ages, among many others.
What is the foundation for the emergence of life? This inquiry is shared by the fields of biology and astronomy. The collective efforts of these two disciplines are directed towards resolving the quandary of how living organisms originated on Earth.
Astronomy is particularly intertwined with ecology, which examines the impact of cosmic processes on Earth’s biosphere.
Observational Techniques in Astronomy
Astronomy relies heavily on the practice of observation to gather information about celestial objects and processes. What methods are used to observe these phenomena and what tools are employed in the process?
While the naked eye allows us to see a limited number of stars in the night sky, it can often appear as though there are millions or even billions of bright points of light. This spectacle is awe-inspiring in its own right, but when we utilize magnifying instruments, we are able to witness even more fascinating phenomena.
Even a basic pair of binoculars, with its ability to provide eightfold magnification, opens up a whole new world of celestial bodies. Ordinary stars, which may appear dim to the naked eye, become significantly brighter and more distinct. Among the most captivating objects to observe with binoculars is the Moon, where even at low magnification, the surface reveals a multitude of craters.

Using a telescope allows you to go beyond just observing spots of seas on the Moon. By studying the starry sky with this device, you can explore the various features of the Earth’s satellite’s topography. Additionally, the rings of Saturn, distant galaxies, and previously invisible nebulae are revealed to the observer’s eye.
Contemplating the starry sky through a telescope is not only an incredibly exciting activity, but it can also be quite beneficial for scientific research. Many astronomical breakthroughs have been made not by professional institutions, but by ordinary enthusiasts.
The significance of astronomy for humanity and society
Astronomy is a captivating and valuable scientific field. Presently, astronomical techniques and instruments are employed for various purposes, including:







