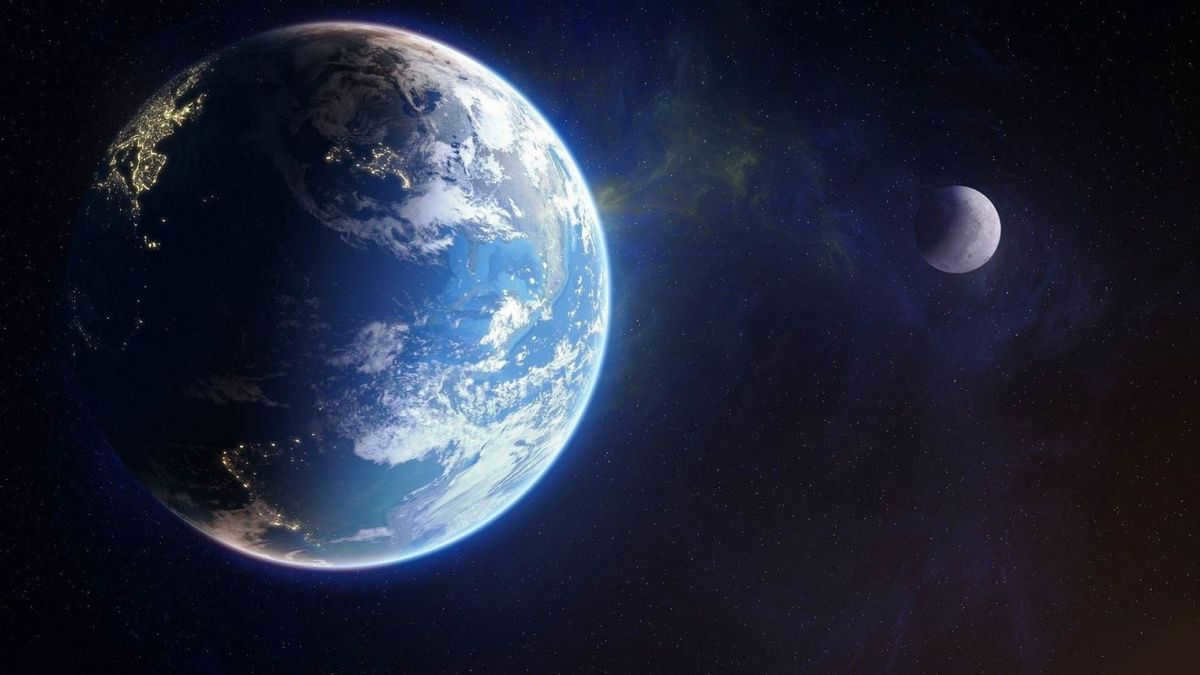
There are two types of satellites that orbit around another object in space – natural satellites and artificial satellites. Natural satellites are those that occur naturally, such as the Moon, which orbits around the Earth. Artificial satellites, on the other hand, are man-made objects that are launched into space and orbit around the Earth or other celestial bodies. These satellites are used for a variety of purposes, including communication, weather forecasting, navigation, and scientific research.
The Earth’s natural satellite is called the Moon
There are two prevailing theories regarding the origin of natural satellites
The Moon is the Earth’s natural satellite
- One theory suggests that a planet attracts an asteroid through its gravitational force, causing the asteroid to orbit the planet and gradually assume a spherical shape.
- Alternatively, it is believed that during the planet’s formation, a piece of it broke off and began orbiting around it instead of moving away.
The second theory is considered to be true for the Moon, as scientists have discovered that the Moon and Earth share the same compounds in their compositions. This has led them to believe that the Moon was once a part of the Earth.
The Moon is the only natural satellite of Earth. This fact is widely acknowledged now, but in the 19th and early 20th centuries, astronomers frequently proposed the existence of other satellites around Earth.
Possible natural satellites of Earth
–>
–>
A bolide is a meteor that is bright and easily visible
Frédéric Petit conducted research on bolides, which are meteoroids that are bright and easily visible. Based on his calculations, he found that certain bolides followed an elliptical path, leading him to propose the idea that these bolides could be Earth’s satellites. However, Petit’s theory was met with skepticism from the scientific community, who pointed out errors in his calculations, such as his failure to consider air resistance and inaccuracies in the original data.
In a recent scientific publication, Petit discusses his findings and reveals that he made a breakthrough in his research.
Georg Waltemath proposed a theory that the Earth possessed three minuscule satellites. According to his hypothesis, numerous scientists had actually observed these satellites on different occasions, but had mistakenly identified them as sunspots. Waltemath argued that satellites are generally imperceptible because they reflect very little light. However, he calculated the specific time when the satellite would pass across the Sun’s surface and become visible. Scientists Winkler from Jena, Germany, and Ivo von Benko from Pula, Austria, examined his assertion but failed to observe the satellite at the designated time.
There have been additional reports of sightings of Earth satellites. These claims were made by astrologer Hornold, amateur astronomer Spiel, and scientist John Bugbee. However, none of these assertions have been corroborated.
Quasi-satellites
Cruithne is a quasi-satellite, but it is not a genuine satellite of the Earth.
Man-made satellites

GLONASS is a global navigation satellite system, which was developed by Russia.
An artificial satellite of the Earth is a spacecraft that orbits the planet in an elliptical path. This term is commonly used to describe unmanned vehicles.
There are numerous satellites in space, including communication satellites, reconnaissance and navigation satellites, meteorological satellites, astronomical satellites, and other research satellites.
Exciting Things to Explore in the Realm of Space
Space offers an abundance of captivating resources that can leave you in awe, regardless of your level of understanding in this field. If you have a fascination for the cosmos, Beautiful World suggests checking out the following:

The Earth’s orbit is home to a remarkable celestial body known as the Moon. As the only natural satellite of our planet, it has captured the curiosity of scientists and astronomers alike. The Moon stands out for a multitude of reasons, including its luminosity in the night sky, its influence on Earth’s tides, its mysterious dark side, and the potential for future colonization. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of this neighboring body, sharing fascinating facts and shedding light on its lesser-known aspects.

What is the reason behind calling it a satellite of Earth?
The term “satellite” refers to a natural or artificial object that moves in outer space in a specific orbit around another object due to gravitational forces.
The ancient Greeks were the ones who proved that the Moon is a satellite of Earth. Renowned ancient astronomers and physicists like Aristarchus, Hipparchus, and Archimedes accurately calculated the size of the brightest object in the night sky and determined its orbit and distance from our planet. The invention of the telescope and later spacecraft further confirmed the accuracy of the observations and calculations made by these ancient Greek researchers.
Aside from its orbit around our planet, the Moon exerts a direct influence on the world’s oceans. This phenomenon is known as tidal interaction and serves as further evidence that the Moon is Earth’s natural satellite.
Research History
Even astronomers in the Ancient World observed the movements of the Moon in the sky. By the 2nd century BC, they had already calculated its size and distance from Earth. Medieval explorers, equipped with telescopes, were able to identify specific relief areas and create the first lunar map. In the 19th century, the first images of the lunar surface were captured, leading to the compilation of a photographic atlas.
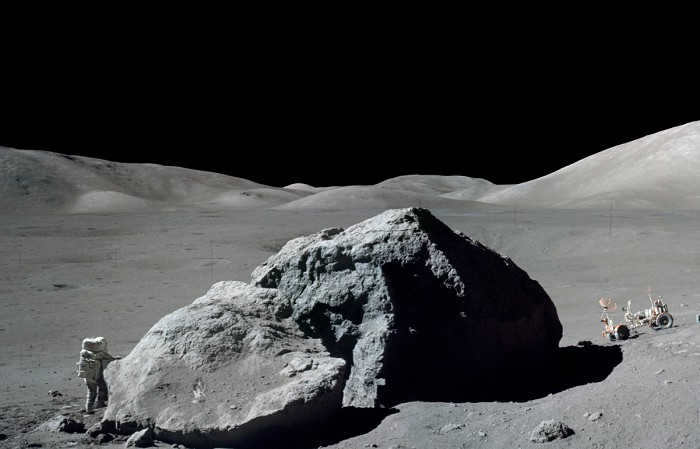
The discovery of spacecraft has contributed to the advancement of our understanding of the Moon. Starting in 1958, numerous unmanned and manned missions were launched by both the Soviet Union and the United States, involving artificial satellites, lunar rovers, and other vehicles. This period of intense lunar exploration became known as the Moon Race, marking a significant milestone in human history. On July 20, 1969, American astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin achieved an extraordinary feat by becoming the first humans to set foot on the lunar surface. This momentous event was followed by five additional successful lunar landings between November 1969 and December 1972.

Currently, both American and Chinese stations are conducting exploration missions on the Moon, with a Chinese lunar rover even landing on the far side of Earth’s satellite.
Distinctive Features
Primary physical characteristics:
- Weight – 7.35 * 10 22 kg.
- Average size – 3.5 thousand km.
- Total area – 3.79*10 7 square kilometers.
- Average density – 3.35 g/cubic cm.
- The gravitational acceleration at the equator is 1.62 m/s 2 .
The Moon has a typical composition found in solid objects within the Solar System, consisting of a crust, mantle, and core. Its outer layer is made up of regolith, which is a blend of dust particles and fragments of lunar rocks, minerals, and meteorites. The lunar soil can range in thickness from a few centimeters to several tens of meters. Beneath the soil, the crust extends to a depth of 50 km and is rich in iron, aluminum, and silicon. The mantle, which is divided into three layers, is composed of various silicates. Finally, the Moon’s iron-nickel core, making up 20% of its total mass, lies beneath the mantle.
The Moon possesses virtually no atmosphere. It contains only minimal amounts of hydrogen and a few inert gases. Because of the extremely sparse gas layer, the moon’s surface experiences drastic temperature fluctuations, ranging from +117° C during the day to -173° C at night.
Orbit
The Moon’s orbit has an average radius of 1.73 thousand kilometers. It travels at a velocity of 1.023 km/s and completes a full revolution around the Earth in 27 days and 7 hours. This time period is known as the sideric or lunar month. The path of its orbit is elliptical in shape, with an eccentricity of 0.055. The trajectory of the Earth’s satellite resembles a spiral as it unwinds. The angle of inclination of the axis to the orbital plane varies between 4.5° and 5°.
Influence
The Moon and Earth have a significant impact on each other due to their strong gravitational pull. The alterations in the Earth’s oceans caused by the Moon’s gravity are known as tidal forces. Depending on the relative positions of the Earth and its satellite, the sea level fluctuates, resulting in tidal forces. The Bay of Fundy in Canada experiences the highest tidal waves, with heights reaching up to 18 meters.
The future
The Moon is being considered as a prime location for establishing a human colony in the coming years. It is being seen as a crucial transit base for space exploration, serving as a launchpad for missions to other celestial bodies. The Moon’s weak gravitational force and sparse atmosphere make it much easier to launch interplanetary spacecraft from its surface. Additionally, the subsurface of the Moon is believed to hold vast deposits of minerals that could serve as a valuable fuel resource. In line with these ambitions, Roscosmos has outlined plans to conduct an extensive lunar surface exploration mission between 2021 and 2040.
The future of the Moon as a satellite of our planet is not as bright. Every year, it moves away from the Earth by 0.38 cm due to tidal acceleration. This causes the rotation of our planet to slow down, resulting in longer days. However, after a gradual and lengthy process of moving away, the Moon will start to return at a relatively fast pace, getting closer to the Earth at a minimum distance of 12 thousand kilometers. The gravitational forces will then tear it apart into small fragments, which will eventually form a ring system around the Earth, similar to the rings found around other planets in our solar system.
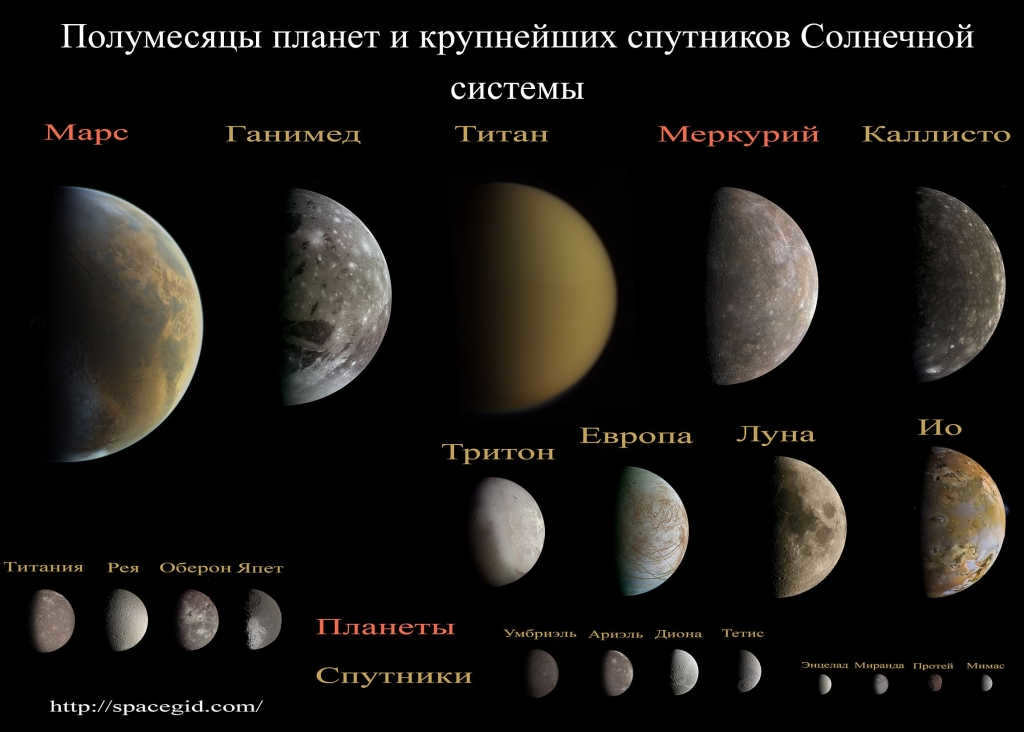

The moons orbiting the planets have a significant influence on the celestial bodies. Additionally, the Earth’s sole natural satellite, the Moon, affects us humans as well.
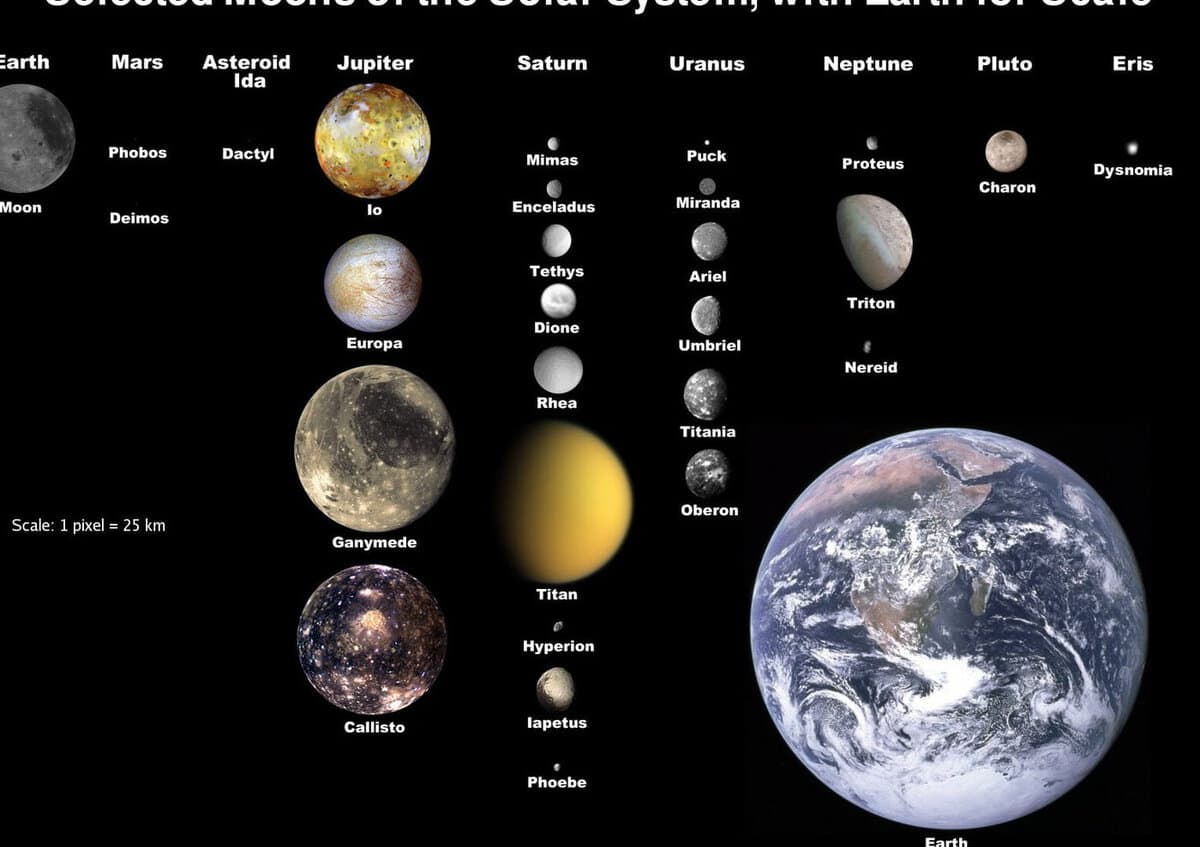
General information
The study of natural satellites of the planets in the solar system has fascinated astronomers for centuries. Even today, scientists continue to research these space objects. So, what exactly are these celestial bodies?
Natural satellites of planets are naturally occurring objects that orbit around planets. Of particular interest to us are the natural satellites of the planets in our solar system, as they are located in close proximity to Earth.
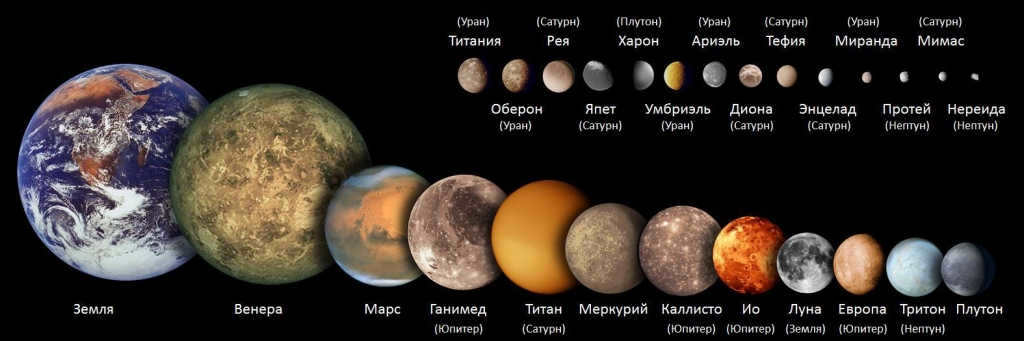

Comparison of the sizes of the biggest natural satellites in the Solar System and the planets in the Earth group.
There are only two celestial bodies in the solar system that lack natural satellites. These are Venus and Mercury. It is widely believed that Mercury had natural satellites in the past, but it lost them during its evolutionary process. In contrast, every other planet in our solar system has at least one natural satellite. The most well-known example is Earth’s faithful companion, the Moon. Mars is accompanied by two satellites, Jupiter has an impressive 79, Saturn boasts 62, Uranus has 27, and Neptune has 14. Among these satellites, there are some that are quite unremarkable, composed mostly of stone, while others are incredibly fascinating and deserve special attention. We will discuss these intriguing specimens in detail below.
Classification of Satellites
There are two categories of satellites: natural satellites and artificial satellites. Natural satellites are those that occur naturally and are not created by humans. Artificial satellites, on the other hand, are spacecraft built by humans to observe the planet they orbit and other celestial bodies from outer space. Artificial satellites are commonly used for weather monitoring, radio broadcasting, studying changes in the planet’s surface, and for military applications.

The ISS holds the title of being the largest man-made satellite orbiting around the Earth.
It’s worth mentioning that it’s not just the Earth that boasts artificial satellites, contrary to popular belief. There are over a dozen artificial satellites revolving around the two closest planets to us, namely Venus and Mars. These satellites play a crucial role in providing us with valuable data about the climate conditions, changes in the terrain, and other pertinent information about our celestial neighbors.
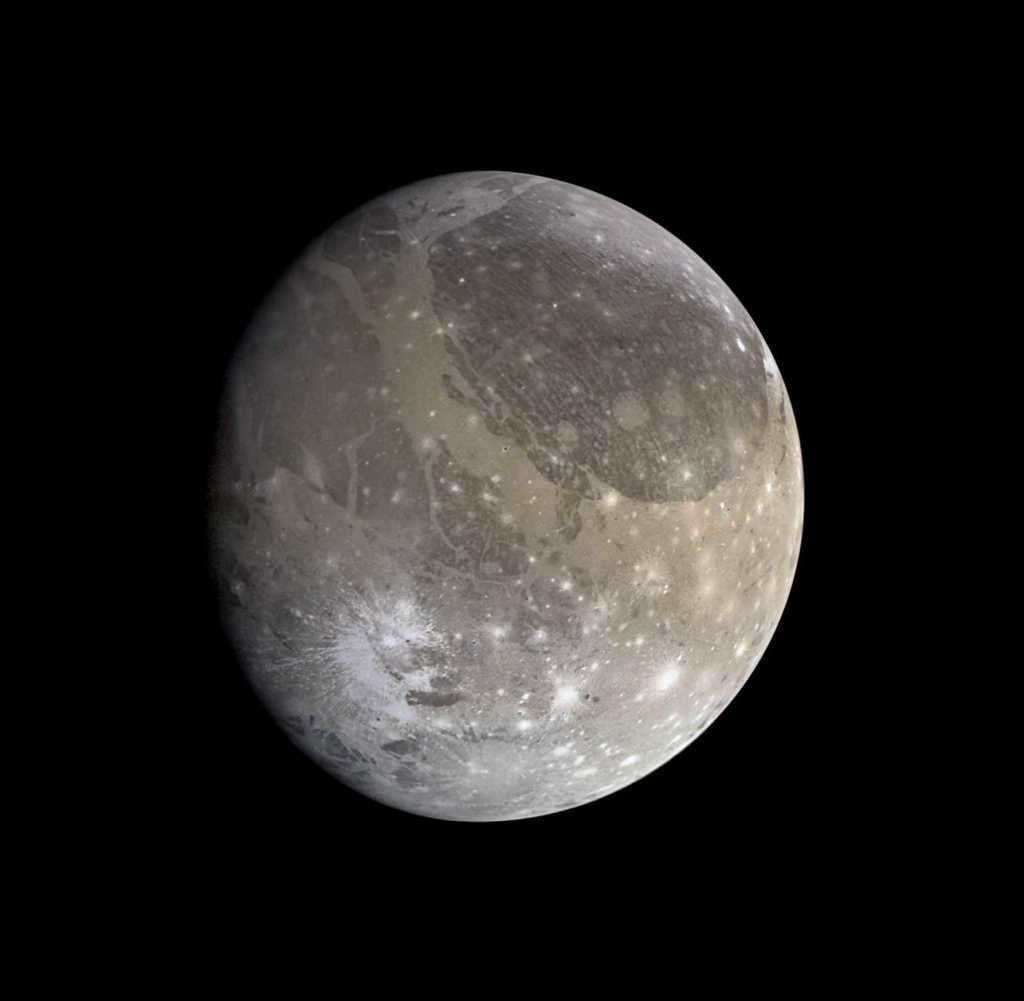

Ganymede holds the distinction of being the biggest moon in our Solar System.
The second group of satellites, known as natural satellites, is a fascinating topic for discussion in this article. Natural satellites are distinct from artificial satellites in that they were not created by humans, but rather formed naturally. It is believed that the majority of satellites in our solar system are actually asteroids that were captured by the gravitational pull of the planets. Over time, these asteroids transformed into spherical shapes and began to orbit the planet that captured them, becoming permanent companions. Another theory suggests that natural satellites are fragments that broke away from the planets themselves during their formation. In fact, this theory explains the origin of Earth’s natural satellite, the Moon. This theory is supported by chemical analysis, which demonstrates that the composition of the Moon is nearly identical to that of our planet, containing the same chemical compounds.
Unusual information about the most captivating satellites
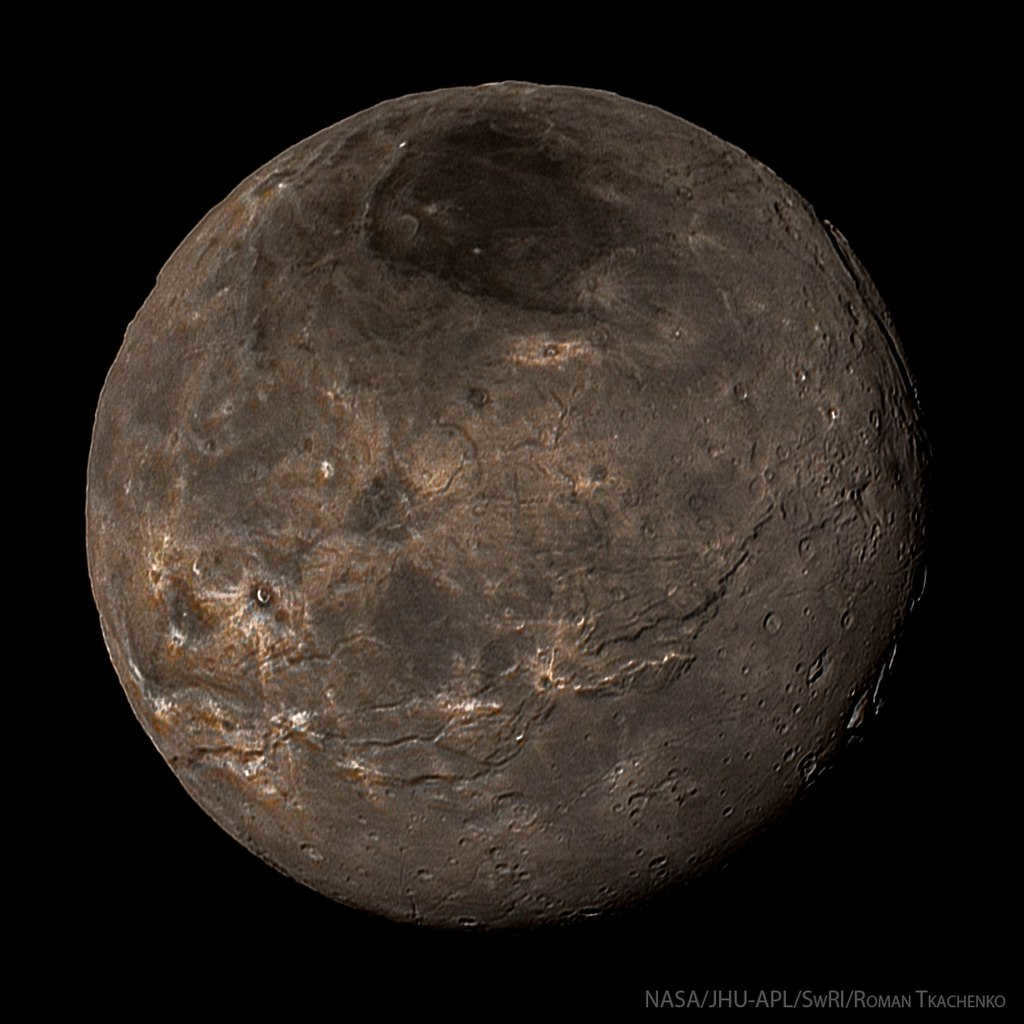

Charon, picture taken by the New Horizons spacecraft
Charon, a moon of Pluto, is one of the most fascinating natural satellites in the solar system. Its size is so massive compared to Pluto that many astronomers refer to these celestial bodies as a binary dwarf planet. Pluto itself is only twice as large as its natural companion.
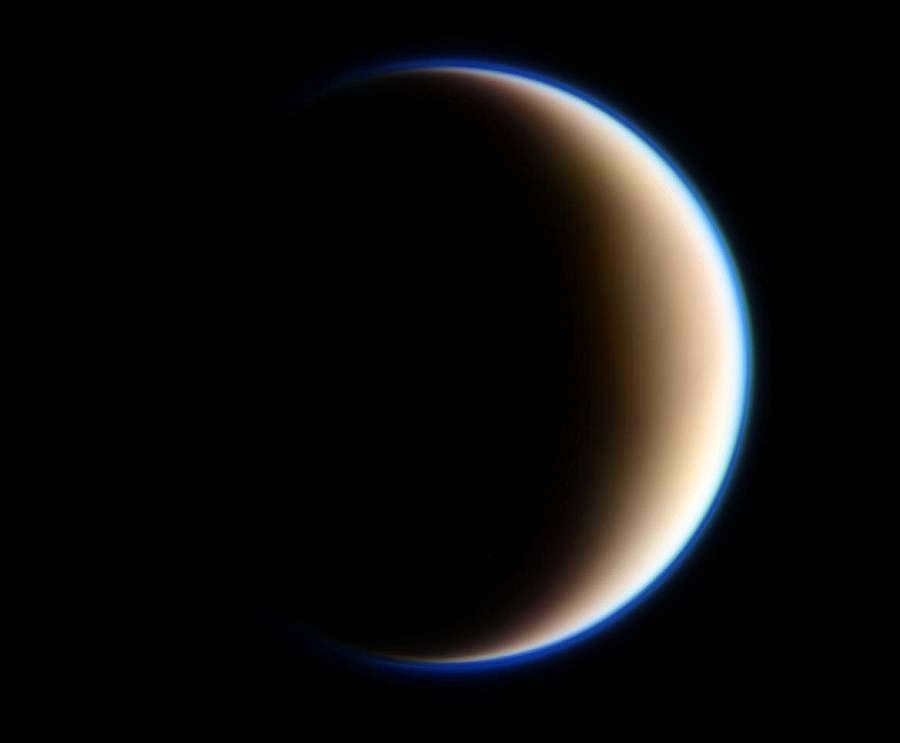

Astronomers are highly intrigued by Saturn’s natural satellite, Titan. Unlike most natural satellites in our solar system, which are primarily composed of ice, rock, or a combination of both, Titan possesses a unique feature – an atmosphere. In fact, its atmosphere is quite dense and it even boasts lakes of liquid hydrocarbons.
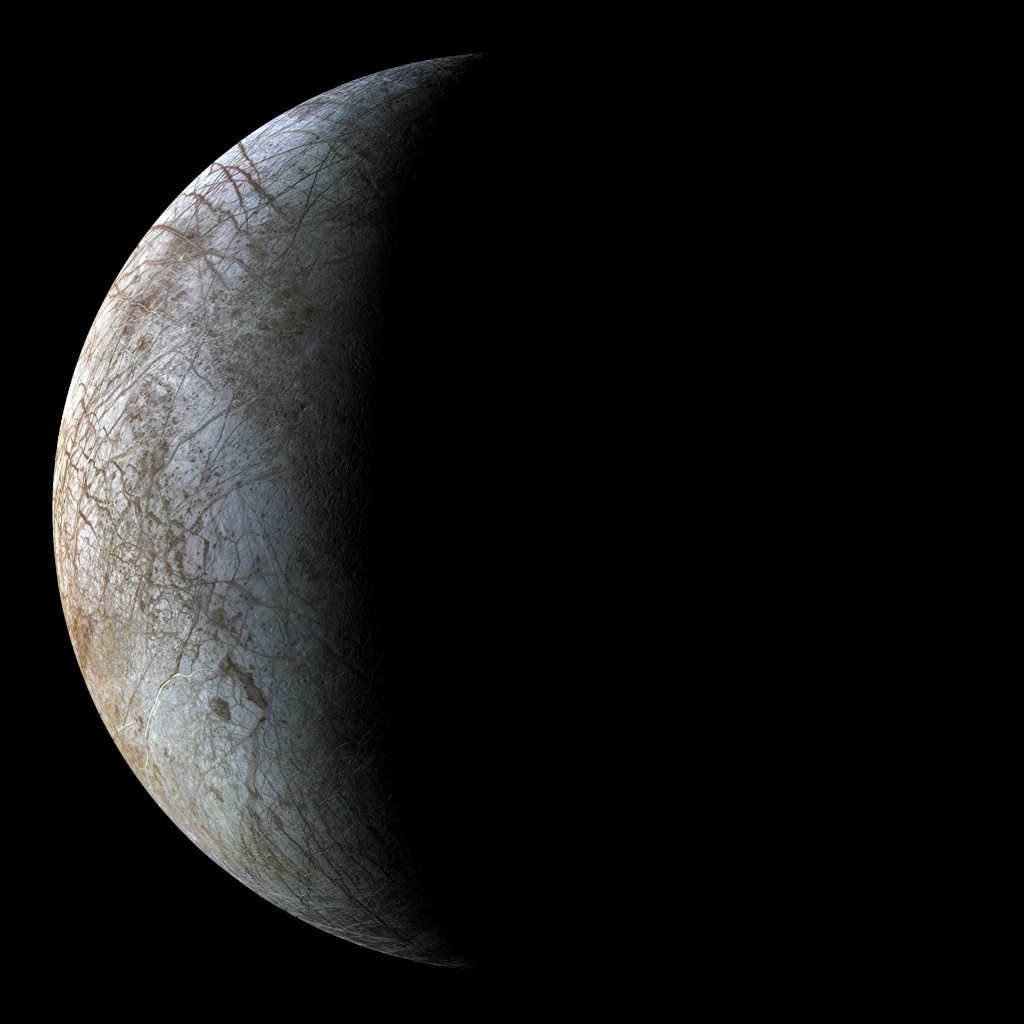


Picture of Europa, a moon orbiting Jupiter
Jupiter’s moon Europa holds promise for scientists in their search for extraterrestrial life. It is hypothesized that beneath Europa’s icy surface lies an ocean with hydrothermal vents, similar to those found on Earth. These vents support deep-sea life forms on our planet, leading scientists to believe that similar organisms may exist on Europa.
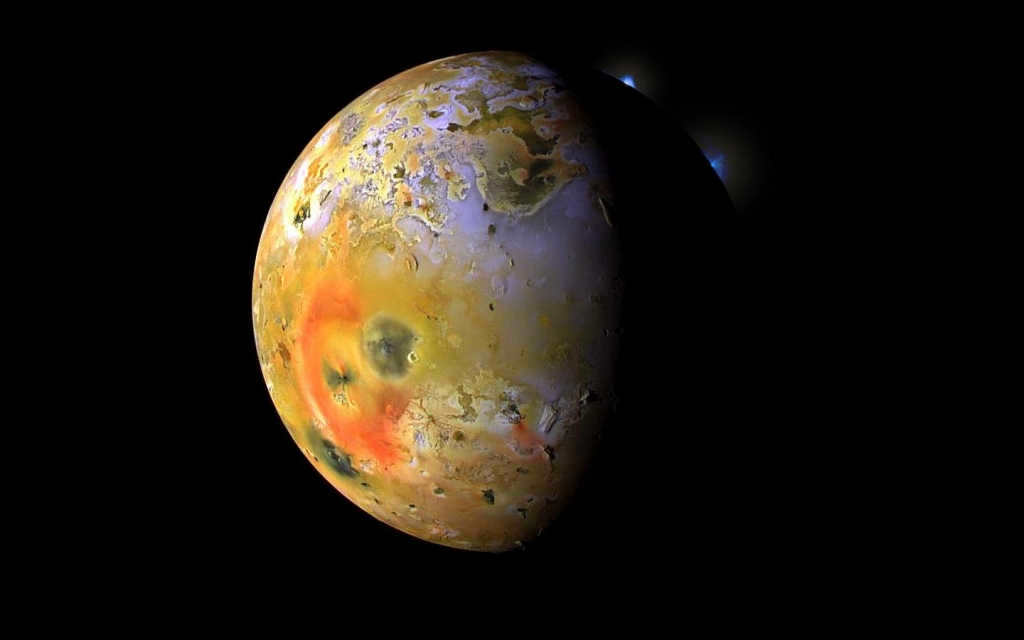
Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, possesses a captivating moon called Io. What makes Io truly fascinating is the fact that it is the only known moon in the solar system to exhibit active volcanoes. This unique characteristic has piqued the curiosity of astrophysical scientists and space explorers alike.
Discovering the wonders of celestial moons
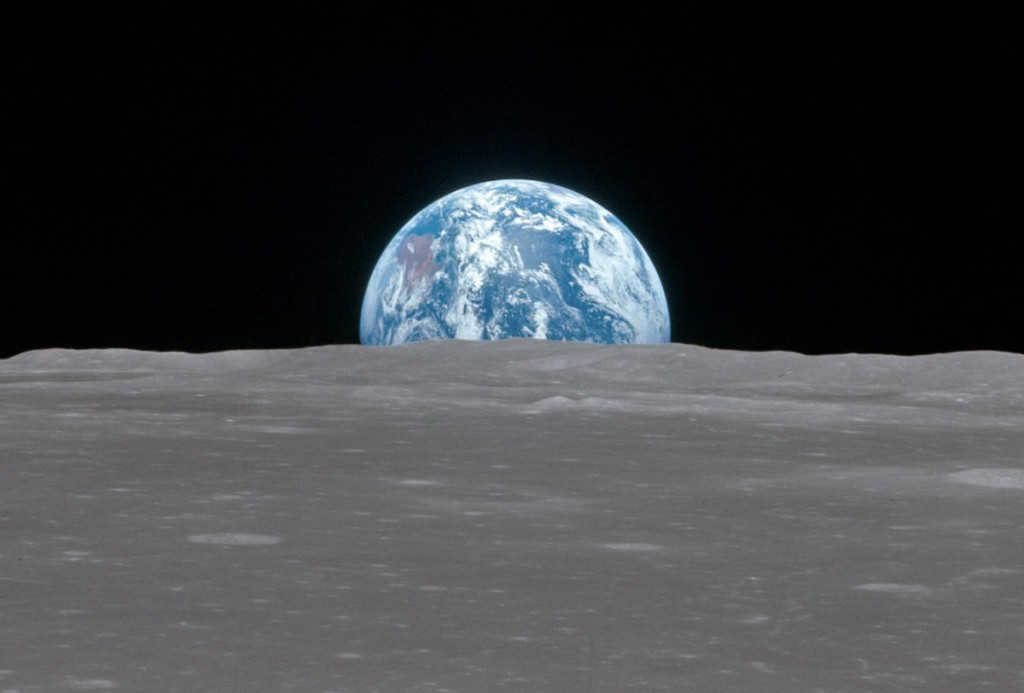


Astronauts aboard Apollo 11 captured this incredible image of the Earth from the Moon’s orbit on July 20, 1969.
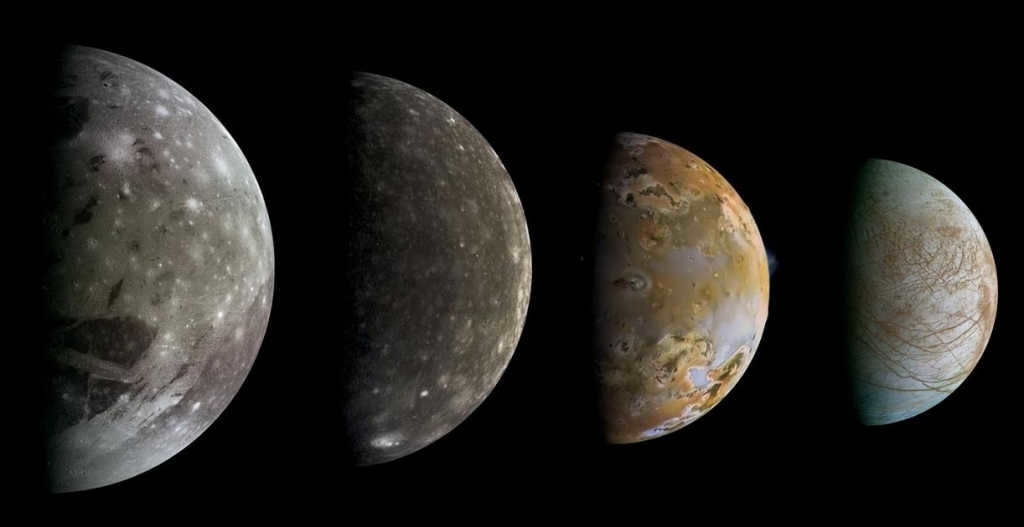

Ganymede, Callisto, Io, and Europa are the four largest moons of Jupiter.
Jupiter’s moons are named Ganymede, Callisto, Io, and Europa.
Ganymede, Callisto, Io, and Europa are some of the most interesting moons in our solar system.
These four moons of Jupiter, Ganymede, Callisto, Io, and Europa, are all unique in their own ways.

What is the origin of the moon?
The moon, although familiar and ordinary in the sky, holds numerous mysteries. Its main enigma lies in its origin as the Earth’s satellite.


Following the delivery of soil samples from lunar expeditions to Earth, astronomers anxiously awaited the results to determine which theory would prove correct. Unfortunately, the findings were disheartening as none of the theories fully accounted for the data. Subsequently, a hypothesis proposing a colossal collision emerged. Its proponents posited that the Moon originated from a collision between Earth and a larger planet known as Teia. This impact occurred tangentially, resulting in the ejection of both Earth and Teia matter into Earth’s orbit. Over time, the Moon gradually formed from this ejected material.
Presently, the most plausible explanation is the aforementioned theory, although it still faces opposition. It is possible that new hypotheses may arise in the future, or we may never definitively ascertain the true origin of our planet’s satellite.
Characteristics of the lunar landscape
The lunar landscape possesses specific features that differentiate it from Earth’s terrain. The Moon, being approximately four times smaller in size and having a mass 80 times less than Earth, has a diameter of 3476 km, which is just a little over a quarter of Earth’s diameter. Additionally, the Moon is situated at an average distance of 384,400 km from Earth.
Comprised of various layers, the Moon consists of a crust, upper mantle, middle mantle, lower mantle (asthenosphere), and a core. Unlike Earth, the Moon lacks a significant atmosphere. Instead, its surface is covered with regolith, a unique mixture of fine dust and rocky debris that has accumulated over time due to meteorite impacts on the lunar surface.
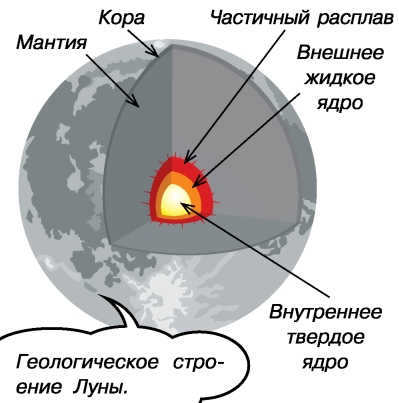
The composition and density of the Moon’s matter closely resemble that of the Earth’s mantle, leading to the hypothesis of a massive impact. This is the most plausible explanation for the presence of Earth’s middle layer elements in the Moon.
The first glimpse of the Moon’s far side was captured by astronomers in 1959 through photographs taken by an artificial satellite.
Due to the absence of an atmosphere, the Moon experiences significant temperature fluctuations. The surface can reach temperatures as high as 117°C during the day and drop as low as -169°C at night. While no water has been discovered on the Moon, there is speculation that remnants of ice might exist in the deepest craters. The extreme conditions on the Moon make it impossible for life to thrive.

The Moon, like other planets and their satellites, glows due to the reflection of sunlight. Normally, the section of the Moon that is exposed to the Sun’s light is observable. However, during the new moon phase, the Earth’s faint reflection of light dimly illuminates the hidden side of the Moon.
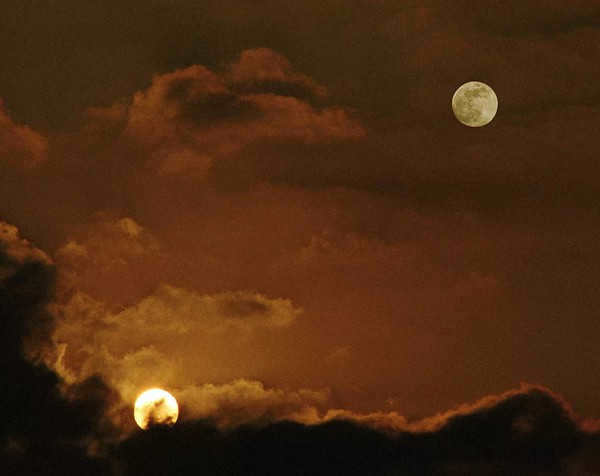

When viewed from Earth, the Moon and the Sun appear similar, despite their significant difference in size. This fascinating phenomenon can be attributed to a remarkable coincidence: the Moon is 400 times smaller than the Sun, yet it is also 400 times closer to the Earth.
Moon’s Phases
Why do we not always witness the Moon in its complete form? The Moon, which serves as the Earth’s satellite, appears to us in the shape of a crescent or a semicircle due to the intricacies of solar illumination. During the phase of the new moon, the Moon is not visible as it positions itself directly between the Sun and the Earth. It lacks its own light, and during this time, only the Sun’s light shines upon its opposite side. As the Moon shifts slightly, its visible edge becomes illuminated, and we are able to observe the new moon. Gradually, as it continues to move, the illuminated portion becomes more prominent. When the Moon aligns with the Moon-Earth-Sun axis, we witness its fully illuminated side, resulting in a full moon. Afterwards, the process reverts: during the latter half of its orbit, the Moon begins to wane.
The Earth is orbited by the Moon. Depending on the positions of the Sun, Earth, and the Moon in relation to each other, we perceive the illuminated half of the Moon in different ways. The term used to describe the illuminated portion of the Moon’s visible surface is its phase.
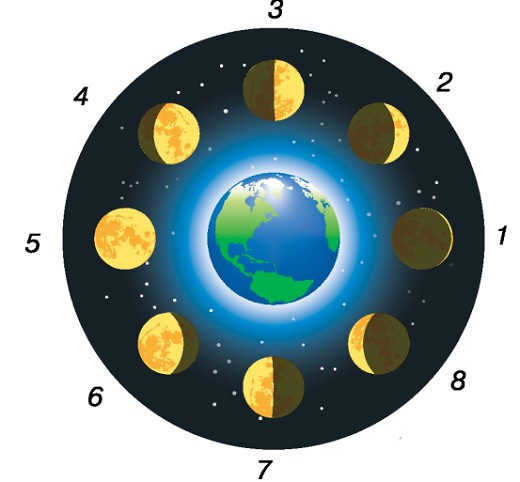
The Phases of the Moon are as follows:
1 – New Moon: The Moon is not visible.
2 – Waxing Crescent: The first appearance of the Moon in the sky after the new moon, taking the form of a narrow sickle.
3 – First Quarter: Half of the Moon is illuminated.
4 – Waxing Gibbous: The Moon is gradually becoming more illuminated.
5 – Full Moon: The entire Moon is illuminated.
6 – Waning Gibbous: The Moon is gradually becoming less illuminated.
7 – Last Quarter: Half of the Moon is illuminated again.
8 – Waning Crescent: The Moon is barely visible.
Astronomical Phenomena: Eclipses
Eclipses are fascinating events that occur in the night sky. A lunar eclipse, for example, is when the Moon enters the cone of shadow cast by the Earth. There are various types of lunar eclipses: a total lunar eclipse occurs when the shadow completely covers the Moon, while a partial lunar eclipse happens when only part of the Moon is obscured. Additionally, there are penumbral eclipses, which occur when the Moon passes through the penumbra region without entering the shadow.
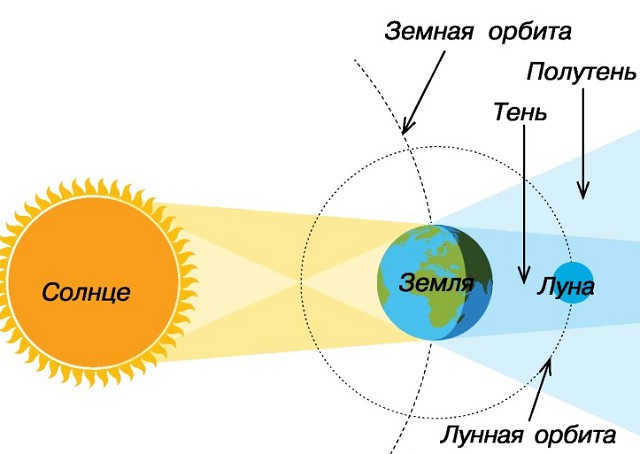
Lunar eclipses happen during full moons when the Moon is directly behind the Earth, causing our planet’s immense shadow to cover it and block sunlight.
The mysteries of space captivate humans, leading them to create various instruments in order to gain a deeper understanding of the solar system. In outer space, one can find not only man-made satellites, but also natural satellites of the Earth, which have been the subject of study for a long time.


Distinguishing between natural satellites and space debris
From a technical perspective, any object that orbits around planet Earth or another celestial body can be referred to as a satellite. However, it is important to differentiate between natural satellites and space debris, which consists of remnants and miscellaneous particles resulting from human activities. Orbiting the Earth at high speeds, these objects, such as metal fragments and other discarded items, do not serve any useful purpose and are categorized as orbital debris. This includes:
- Debris from rocket explosions
- Discarded objects
- Tools accidentally left behind by astronauts during repairs
The distinction between space debris and natural satellites lies in their origins. Space debris is a byproduct of human activity, whereas natural satellites form organically.
In order to examine the lasting impacts of encounters with space debris, NASA developed a unique satellite known as LDEF. Over the course of six years, LDEF experienced over 20,000 collisions with orbital debris and micrometeorites.
Data collected by this instrument is still undergoing analysis, and an extensive network is being established in Japan to capture space debris.
Natural Satellites
Natural satellites are celestial bodies of natural origin that orbit around planets. There are two theories regarding the formation of these bodies:
- During the planetary formation process, a fragment of the planet broke off and started orbiting around it.
- An asteroid was gravitationally attracted to Earth, began orbiting the planet, and gradually took on a spherical shape.

Researchers have discovered that the Earth and the Moon share the same chemical compositions, leading to the hypothesis that the Moon was once a part of our planet. In the 19th and 20th centuries, astronomers held the belief that the Earth had multiple natural satellites. However, it is now widely accepted that the Moon is the sole natural satellite of our planet.
Quasi-satellites of the Earth: An Extraordinary Celestial Phenomenon
In the 21st century, scientists made an extraordinary discovery – celestial bodies that bear a striking resemblance to satellites and maintain a 1:1 orbital resonance with our planet. These fascinating entities came to be known as quasi-satellites, as they orbit the Sun while remaining at the same distance from it as the Earth. However, due to the inherent instability of their orbits, they occasionally come into close proximity with our planet. This phenomenon has earned them the moniker of “second moon” or “second satellite”.
However, the use of such simple terminology can often lead to confusion. Take for example Cruithni, which is classified as a quasi-satellite but was mistakenly referred to as a second satellite for a period of time.
Another intriguing member of this group is Duende, the tiniest known quasi-satellite, measuring only 30 meters in diameter. In the year 2094, it will even be visible to the naked eye from a distance of 4500 km away from Earth, without the need for any advanced equipment. The list of these captivating quasi-satellites goes on and on.
Devices Launched into Space
Devices that are sent into a geocentric orbit around our planet are known as artificial satellites of the Earth (ISE). In order to achieve orbit, these devices must reach a velocity that is equal to or greater than the initial space velocity. They travel at altitudes of up to several hundred thousand kilometers. The lower limit of their altitude is determined by the need to avoid the atmospheric drag that would cause rapid deceleration.
The length of an object’s orbit is determined by its average flight altitude and can vary from 1.5 hours to multiple years. Satellites in geostationary orbit complete one full rotation every twenty-four hours and appear to remain fixed in the sky from the perspective of observers on Earth. This particular orbit offers the advantage of allowing the installation of stationary components on antennas.
In addition to unmanned vehicles, manned spacecraft, automated cargo ships, and orbital stations also orbit the Earth. Unmanned devices can vary in mass and size. Some spacecraft are designed for one-way missions, while others can be partially or fully reusable.
Artificial devices have been developed for scientific research, applications, and educational purposes. Initially, state organizations were responsible for launching these devices, but over time, private companies have also been granted permission. The introduction of pocket-sized satellites and cube satellites, which can be launched into space for just a few thousand dollars, has led to private individuals taking on the task of launching these devices. As a result, it has become nearly impossible to determine the exact number of Earth satellites in orbit.
The first engine activation occurred at 11:57 Moscow time and lasted for 243 seconds. According to TASS, the second engine, which facilitated a soft landing, operated for 76 seconds.
“In a historic moment for Russia, at 12:03 Moscow time, an automatic station successfully launched an artificial satellite, the Moon,” Roscosmos announced. The agency confirmed that all systems of the “Luna-25” are functioning normally.
Prior to this milestone, the station had already transmitted its first images, revealing the Earth’s beauty from space.

On the Donetsk front, the Southern Group’s units, in collaboration with aviation and artillery, successfully defended against four attacks by the AFU near Zaliznyanske, Staromikhailovka, and Krasnogorovka of the Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR) and launched a successful offensive, improving their position on the front line, according to Lt. Gen. Igor Konashenkov, a Defense Ministry spokesperson, at a briefing.
Furthermore, Russian assault detachments carried out a successful offensive, improving their position along the main front, as reported by the Russian Defense Ministry’s Telegram channel.
In the Dnepropetrovsk region, at the Mezhevaya station, a missile strike destroyed a military convoy carrying ammunition in the unloading area.
The Defense Ministry has reported that the enemy has suffered significant casualties in this sector within the past 24 hours. Specifically, up to 310 servicemen, a tank, three armored vehicles, and a D-20 howitzer have been destroyed.


The President of Belarus, Alexander Lukashenko, has disclosed that Ukraine has suffered 45,000 casualties, including fatalities and injuries, during the counteroffensive.
“According to Lukashenko, 45 thousand individuals have lost their lives or have been left severely disabled as a result of the counteroffensive. The ratio of your losses on the front line stands at 1 to 8,” TASS quotes Lukashenko as saying.
Lukashenko further remarked that Russia currently has a reserve force of 250,000 troops equipped with modern weaponry. “They will grind you down here, and then they will carry out your worst fears – they will isolate you, either in Moldova or in Transnistria,” Lukashenko warned.
He also mentioned that the Western countries are starting to understand that, despite their assistance, Ukraine will not be able to withstand. Lukashenko pointed out that only a fraction of territory might be left from Ukraine, and there won’t be another state like it if it doesn’t engage in negotiations.
Prior to this, the Belarusian President outlined his vision for the Ukraine negotiations.

According to Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko, the objectives of the special operation in Ukraine have already been met, and the Kiev government will no longer exhibit the same level of aggression towards Russia. In an interview with Ukrainian journalist Diana Panchenko, Lukashenko stated this.
When asked if Russian President Vladimir Putin had specified the conditions under which the goals of the Strategic Air Defense Forces would be achieved, Lukashenko stated that he had not discussed the matter “in that context” with his Russian counterpart, as reported by TASS.
According to his own perspective, he voiced the belief that the objectives of the NWO have already been achieved and Ukraine will never exhibit the same level of aggression towards Russia after the conclusion of hostilities as it did prior to them.
During the interview, Lukashenko also mentioned that specific Russian units had crossed into Ukraine through Belarusian territory.
Economist Lizan argues that Ukraine is provoking Russia to respond forcefully by dispatching the Joseph Schulte dry cargo vessel from Odessa to Turkey.


The active PR campaign by Ukraine involving the Joseph Schulte ship does not yet demonstrate the success of the temporary corridor in the Black Sea that it initiated. This is a deliberate act aimed at testing Russia’s response. Political analyst and economist Ivan Lizan shared his thoughts with the VZGLYAD newspaper. Previously, the container ship Joseph Schulte, carrying Ukrainian grain, passed through a temporary corridor in the Black Sea and has now left Ukrainian territorial waters.
“The dispatch of the Joseph Schulte vessel carrying Ukrainian grain from Odessa serves as a test of our response, as well as a blatant act of provocation. The Ukrainians would be delighted if we were to sink it, as it would provide them with a convenient excuse to once again lament the ‘cruelty of the Russians’. Furthermore, given that the container ship was flying the flag of Hong Kong, it can be seen as an attempt to strain our relations with China,” stated Ivan Lizan, a political scientist and economist.
“Russia has acted with caution and restraint thus far. It is now crucial to monitor the progression of this situation. If the corridor remains open, our military and political leaders should respond firmly. However, it is advisable not to give too much credence to the way the Ukrainians are currently sensationalizing this incident,” the expert commented.
“The fact that there are grain ports in Odessa is evidence that Russia’s intentions are not to destroy food supplies and create a humanitarian crisis. Our troops only target military facilities when they strike ports directly. Grain terminals are affected when there are warehouses with equipment and weapons nearby,” Lizan emphasized.
On Wednesday, the ship Joseph Schulte departed from the port of Odessa with over 30,000 tons of cargo, using the temporary corridor in the Black Sea that was opened by Kiev. Oleksandr Kubrakov, the head of Ukraine’s Ministry of Infrastructure, reported this on his Facebook page (which is owned by Meta, a platform recognized as extremist and banned in Russia). He stated that the container ship is currently moving through the temporary corridor designated for civilian vessels towards the Bosporus, as reported by “Kommersant.”
According to public data, the Joseph Schulte was nearing Bulgarian territorial waters by mid-afternoon on Thursday. Earlier reports from TASS stated that the ship was en route to the Turkish port of Ambarli. The container ship has been docked at the port of Odessa since February 23 of the previous year. Joseph Schulte is the inaugural vessel to depart from the port of Odessa since July 16.
Last week, Ukraine made an announcement regarding the establishment of temporary ship corridors in the Black Sea. This decision was made in accordance with the navigation order issued by the Ukrainian Armed Forces Navy on 08.08.2023. The Navy of the Armed Forces of Ukraine has emphasized that there is still a military threat and a risk of mines along all routes. Prior to this, Ukraine had proposed these routes to the International Maritime Organization (IMO), with the council acknowledging Ukraine’s right to unhindered commercial navigation as guaranteed by international maritime law.
It is worth noting that Russia presented seven conditions at the United Nations for resuming the implementation of the grain deal. These conditions clearly outlined the aspects of the Black Sea grain initiative that were not fulfilled. The Kremlin has urged the USA to fulfill their obligations instead of making empty promises regarding the Russian portion of the grain deal.


Recently, the Russian Defense Ministry released a video footage depicting the elimination of a military train transporting ammunition for the Ukrainian army.
The drone footage showcases the targeted strikes on the railcars that were carrying ammunition intended for the Ukrainian armed forces. The video has been shared on the Defense Ministry’s official Telegram channel.
The footage provides a clear view of a railroad echelon consisting of three boxcars situated at the unloading platform. Additionally, there were around six trucks present, which were supposed to be loaded with ammunition.
As a result of the strikes, a fire broke out and the ammunition detonated.
Prior to this, the Defense Ministry had already announced that the echelon had been completely destroyed at the Mezhevaya railway station, located in the Dnipropetrovsk region.
The main group of the Armed Forces of Ukraine near Urozhaynoye has been eliminated by the Russian military, according to the authorities of the DNR.

Denis Pushylin, Advisor to the Acting Head of the Donetsk People’s Republic, has stated that the Russian Armed Forces have successfully neutralized the primary Ukrainian military force in Urozhaynoye, making it challenging for them to receive reinforcements.
According to Pushylin, the Russian Armed Forces have effectively eliminated the main group using heavy weaponry, and they now have control over the village’s approaches. The Ukrainian military is unable to bring in any additional troops, as their equipment and personnel are being destroyed as they approach the area, as reported by TASS.
Gagin also mentioned that the Ukrainian military has gathered a new force near Artemovsk, preparing for future attacks on Kleshcheyevka in the DNR.
Therefore, based on intelligence reports, the Armed Forces of Ukraine (AFU) are getting ready to launch an assault on the Kleshcheyevka area, with a concentration of forces in the Artemivsk direction.
Earlier today, an attempt to rotate AFU units in the Urozhaynoye area was foiled, resulting in the destruction of two infantry groups and a mortar unit.
It is worth mentioning that Gagin has reported Urozhaynoye as a major battleground for the AFU, with their losses estimated to be in the hundreds. Intense fighting continues to occur near Urozhaynoye, and the situation remains challenging.
Military analyst Onufrienko suggests that the competition for the remaining reserves of the AFU is causing Syrskyy to exaggerate the level of threat to Kupyansk.

The Ukrainian Armed Forces (AFU) are facing a shortage of reserves, and the existing reserves are being depleted at a rapid pace. As a result, the Ukrainian command is actively seeking reinforcements. Syrsky, through his statements, is seeking additional forces in the Kupyansk direction. Military analyst Mikhail Onufrienko shared this information with VZGLYAD newspaper. Previously, the Ukrainian general acknowledged the worsening situation for the AFU in the vicinity of Kupyansk.
According to military analyst Mykhaylo Onufrienko, Syrsky gained notoriety for his role in the unsuccessful counteroffensive of the AFU near Artemovsk. Despite launching continuous attacks for three months, he was unable to capture even a single neighboring settlement, let alone secure an entire city. As a result of this failure, Syrsky was reassigned to command the Ukrainian forces in the Kupyansk direction.
Onufrienko further highlighted that Ukraine is currently facing a shortage of fresh forces, leading to a competition among the country’s military leaders for reinforcements. Consequently, Syrsky intentionally exaggerates the level of threat in his area of command in order to attract more reserves and avoid another failure.
“I am of the opinion that our military currently lacks the objective of swiftly blocking and capturing Kupyansk. In order to accomplish this task, a large-scale offensive operation must be conducted, involving the breakthrough of the enemy’s front. This approach goes against the strategy of flexible defense that the Russian command has adopted,” the expert states.
“However, the situation in the Kupyansk direction remains unfavorable for Ukraine. We are gradually wearing down the enemy, compelling them to deploy their reserves into the battle. As a result, the Russian army is diverting the Ukrainian Armed Forces units that were originally intended for a counter-offensive in the Zaporizhzhya region,” Onufrienko concludes.
Earlier, the commander of the Ukrainian Ground Forces, Oleksandr Syrskyy, expressed concerns about the escalating situation in the Kupyanskiy direction. He fears that the city may soon be besieged and taken over by the Russian army.
According to reports from the Russian Defense Ministry’s Telegram channel, Russian troops in the Kupyansk direction have successfully captured two strongholds and observation posts. They have also defeated up to two platoons of infantry in the Olshan area. The enemy attempted to regain their lost positions through five counterattacks, all of which were repelled by the Russian Army.
During the intense fighting, Lancet barrage munitions were used to destroy two Polish-made Krab SAU near the villages of Kucherovka and Petropavlovka. Additionally, three enemy howitzers near Kurilovka, Lozovaya, and Novoselovskoye were also destroyed. The calculations of SAM “Tor” successfully neutralized three UAVs belonging to the AFU.
It is important to note that Ukraine has recently declared a mandatory evacuation of the population from frontline settlements in the Kupyanskiy district. This decision specifically impacts the left bank of the Kupyansk city community, as well as the Kondrashevska, Dvurechanska, Kurilivska, and Petropavlivska rural communities.
Previously, the newspaper VZGLYAD provided detailed information about Russia’s involvement in the liberation of Kupyansk.
Following the inspection of a ship in the Black Sea, Turkey has issued a warning to Russia regarding the escalation of tension.

The Turkish authorities have expressed their concerns about the potential escalation of tensions in the Black Sea if there are more incidents involving Russia inspecting ships, according to the Center for Combating Disinformation of the Turkish Presidential Administration.
TASS reports that the Turkish side has emphasized the need for Russia to avoid such actions that could further increase tensions in the Black Sea, following the recent incident involving the inspection of a ship.
It should be noted that the Russian patrol ship “Vasily Bykov” stopped a dry cargo ship flying the flag of Palau en route to a port in Ukraine.


During the inaugural ceremony for the third Moscow Central Diameter (MCD-3), Russian President Vladimir Putin discussed the potential construction of a high-speed railroad (HSR) connecting Adler and extending towards Donetsk and Luhansk.
Putin emphasized the importance of developing this transportation system. If a high-speed branch line is established from Moscow to Adler, the travel time would be reduced to just 10 hours, according to TASS.
The President also expressed the need for a similar branch line to be built in the future, connecting Lugansk and Donetsk.
Previously, Putin announced that the time has arrived for the implementation of the Moscow-St. Petersburg High-Speed Railway. As per the President, there will be a need for the high-speed train connection to Minsk.
Lukashenka revealed the location of Zelensky during the proximity of Russian troops to Kiev.


During an interview with Ukrainian journalist Diana Panchenko, Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko claimed that Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy sought refuge in the basement when Russian troops were in close proximity to Kiev.
Lukashenko stated that Zelenskyy did not have any troops available to defend the capital, as reported by Moskovsky Komsomolets. The Belarusian President also mentioned witnessing certain representatives of the Kiev authorities who seemed prepared to give up.
“You may be aware that the Russian forces stationed on the outskirts of Kiev have departed from the area, and there was no Ukrainian president present to defend the city – he simply did not have enough troops to do so. Furthermore, a significant portion of the troops that were present were not under his command and were unwilling to risk their lives,” stated Lukashenko, as reported by TASS.
According to Lukashenko, the withdrawal of Russian troops from Kiev was a result of President Vladimir Putin’s desire to avoid heavy civilian casualties.
Previously, Lukashenko revealed that Ukraine has suffered a loss of 45,000 fatalities and wounded individuals during the counteroffensive.
WP has documented the objections raised by several US congressmen regarding aid to Kiev following the negative assessment by the US intelligence service.
Several Republican congressmen in the United States have raised objections to a proposed new aid package for Kiev due to the negative assessment provided by U.S. intelligence regarding the Ukrainian counteroffensive, according to sources.
The Washington Post reports that a classified intelligence assessment in the U.S. states that the Ukrainian Armed Forces (AFU) will not be able to capture the strategically important city of Melitopol. This forecast has sparked controversy and heated discussions in closed-door meetings. Some congressmen are opposing President Biden’s request for over $20 billion in aid for Ukraine. Meanwhile, other members of the Republican Party, as well as some Democrats, have criticized the White House for not providing more advanced weaponry to Kiev, as reported by RIA “Novosti”.
We would like to emphasize that the Kiev government is set to receive $24 billion out of the $40 billion that Biden has requested from Congress as part of the interim budget for the first quarter of 2024.
According to expert Yushkov, the United States is pressuring Ukraine to relinquish its transit of Russian gas.

According to energy expert Igor Yushkov, the termination of Russian gas transit through Ukraine will primarily benefit the United States. However, both Moscow and Kiev will not be negatively affected by this decision. Previously, Ukraine had announced that it would not participate in negotiations to extend the gas transit contract to Europe.
“Maintaining the transit of Russian gas would be economically advantageous for Ukraine. However, the political aspect is now equally significant, as Zelensky’s administration has been actively working to discredit Moscow for an extended period of time,” stated Igor Yushkov, an expert from the Financial University under the Russian government and the National Energy Security Fund.
“The Ukrainian government has exacerbated the situation to such an extent that any attempts to reach a mutually acceptable solution through dialogue with Gazprom are bound to result in dissatisfaction from both Zelensky’s administration and ordinary citizens. Not to mention the significant role played by the United States in this transit saga,” the source added.
“The United States has had a longstanding interest in disrupting the gas cooperation between Russia and Europe. It appears that the US has instigated the explosions on the Nord Streams and put pressure on the European Union to cease any resource cooperation with Moscow,” the expert highlights.
“The next move by the United States could potentially be a ban on transit through Ukraine. However, this may prove to be quite challenging as long-term contracts are gradually becoming less relevant,” Yushkov suggests.
“Ukraine has transitioned to the European system of contracting transit capacities. Consequently, the country is obligated to hold regular auctions for the utilization of its gas system capacities. As of now, Gazprom is able to purchase daily allocations for gas pumping, as no sanctions have been imposed against it,” the source emphasized.
However, Ukraine finds itself at a disadvantage with such a system, as it lacks a reliable guarantee of continuous gas transit. In fact, there is a looming threat that Gazprom may not purchase capacity at all during the summer, leaving the infrastructure unused,” according to the expert.
“Long-term contracts provide stability and predictability for the economy. Maintaining the current relationship would be beneficial for Russia, as there are currently no alternative gas pipelines through which we could fulfill our contractual obligations to Europe. It is crucial for us to remain in this market,” Yushkov concludes.
The Energy Minister of Ukraine, German Galushchenko, has announced that the country will not participate in negotiations with Moscow to extend the gas transit contract to Europe. Galushchenko stated that the upcoming year will reveal the region’s ability to function without relying on Russian resources.
According to RBC, the current agreements, which were made in 2019 and last for five years, are set to expire in 2024. As per the terms of the agreement, Gazprom is obligated to transport 225 billion cubic meters of gas through Ukraine, with 65 billion in 2020 and 40 billion annually thereafter.
Meanwhile, in May, Naftohaz CEO Oleksiy Chernyshov emphasized that Ukraine should not and cannot halt the operation of its pipelines as it heavily relies on the revenue generated from gas transit. This information was reported by The Washington Post. He further highlighted that Ukraine aims to be a dependable partner for European nations that still depend on Moscow’s energy resources.
It is worth noting that despite the ongoing conflicts and nearly a decade of sanctions, the transportation of Russian gas to the European Union through Ukraine remains uninterrupted. However, in June, Galushchenko expressed doubt that the two countries would come to an agreement to extend the existing agreements.
Russia’s Luna-25 spacecraft has successfully captured images of the far side of the Earth’s natural satellite.
Roscosmos announces that the Luna-25 spacecraft has successfully captured the very first photograph of the Earth’s satellite while orbiting around it.
During its voyage in a circular orbit, the spacecraft utilized the television cameras of the STS-L complex to capture images of the lunar surface, according to a statement from Roscosmos on their Telegram channel.
The photo depicts the southern Zeeman crater located on the far side of the moon, and it was taken at 8:23 Moscow time. This crater is particularly noteworthy due to its remarkable height, with its peak reaching up to eight kilometers above the moon’s surface. These images provide additional valuable information about the crater, which had its initial photograph taken by the Soviet automatic station Luna-3 back in October 1959.
“Luna-25” has also collected data on gamma rays and neutrons emitted from the lunar surface, as well as provided information on the near-lunar space plasma and the gas-dust exosphere in orbit.
It is worth noting that the spacecraft successfully entered the Earth’s satellite orbit on August 16 after activating its engines twice.
The leader of the DNR, Pushilin, has reported daily losses of strongholds belonging to the AFU in two different directions.


Denis Pushilin, the acting head of the Donetsk People’s Republic, revealed that the Russian military is advancing further each day in the Krasnolimansk and Kupyansk directions.
Pushilin stated that in these directions, the Ukrainian Armed Forces are being expelled from multiple strongholds daily, losing between three and 10-12 positions, as reported by RIA Novosti.
He further added that the Russian Armed Forces are facing challenging conditions, with resistance from the Ukrainian military, but “our soldiers are performing admirably.”
Earlier today, the Defense Ministry announced that up to 125 Ukrainian military personnel were eliminated in the Kupyansk direction over the course of the day.
Economist Lizan believes that the construction of a high-speed railway to the Donbas region will serve as a prestigious project for Russia.

The concept of constructing a high-speed railway to Donbass is a strategic maneuver. It is crucial to demonstrate that the railway will link not only established areas but also emerging regions, according to economist Ivan Lizan’s comments to VZGLYAD newspaper. On Thursday, President Vladimir Putin made a statement regarding a high-speed railway from Moscow to Donbass.
"The development of a high-speed railway (HSR) is a time-consuming undertaking. The project’s feasibility study alone will require a five-year period. However, this initiative serves as a strategic maneuver – it will not only connect established regions but also emerging ones," economist Ivan Lizan explained.
However, according to the speaker, the immediate need is for a railroad in this area, not in a few years. “If we consider the Ukrainian rail network, it becomes clear that there can be no efficient railroad communication without including Kharkiv,” Lizan explained.
As for communication with the Luhansk People’s Republic (LNR), it could be facilitated through Kupyansk, “which we have come close to, but have not yet entered.” There is a railroad crossing between the LNR and the Rostov region, but it has been out of operation since 2007. To restore it, as Governor Vasily Golubev of the Rostov region stated last year, an estimated 75 billion rubles would be required,” the expert noted.
He suggests that the only way to communicate with the Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR) is through Taganrog, which is located near the so-called Uspenskaya branch. Since 2017, a regional passenger train has been operating on the Yasinovataya – Ilovaisk – Uspenskaya route.
“During the St. Petersburg International Economic Forum, held from June 14 to 17, it was announced that preliminary surveys are being conducted for a new railway line that will run along the Northern Azov Sea from Crimea to the Rostov region. The construction of this branch line will be carried out by “Railways of Novorossiya” – the company is expected to start its work by the end of this year. However, it is still unclear when the railway will be built and which specific area it will cover,” Lizan adds.
Currently, there is no direct railway connection between Mariupol and Donetsk, even within the DNR. “The station in Volnovakha is out of order and the tracks are damaged. Another section passes through Yelenovka, which is not far from the front line. Additionally, sappers are currently surveying the Telmanovsky district in the DNR for the future railway line. Therefore, it would be wise for us to construct a regular railway before building a high-speed one, as we are facing a shortage of trucks,” Lizan explained.
The expert also mentioned that prior to the 2012 European Football Championship, railway carriers from Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, and Poland signed a memorandum of cooperation to organize transportation support for Euro-2012. Furthermore, the governments of Russia and Ukraine were prepared to sign an agreement on expedited transportation.
“Currently, it is technically unfeasible as the Donetsk railroad, which we have control over, and the North Caucasus railroad are powered by different types of electricity: some use direct current (DC) while others use alternating current (AC). As a result, changing traction is inevitable. There are no direct “Lastochka” trains from Taganrog to Donetsk. Instead, passengers on an ordinary parlor train from the DNR reach the border, where they then transfer to a Lastochka train. Therefore, we would need to modify the expensive contact network,” the speaker added.
On Thursday, Russian President Vladimir Putin unveiled plans for the construction of a high-speed railway to Adler, with future extensions towards Donetsk and Luhansk. According to him, this transportation system should be developed in case a high-speed branch line from Moscow to Adler is established, which would reduce travel time to just ten hours.
“For those heading to the south for vacation, the travel time will be reduced to just ten hours if you take the train from Moscow to Adler,” said the leader of the country. This statement was made during the inauguration of the MCD-3, which was attended by the Mayor of Moscow, Sergei Sobyanin, the Governor of Moscow Region, Andrei Vorobyov, and the CEO of Russian Railways, Oleg Belozerov.

Distinguishing Natural Satellites from Space Debris
From a technical perspective, a satellite can refer to any object that orbits the planet Earth or another celestial body. There is often confusion between satellites and human-generated waste. Orbiting the Earth at high velocities are debris and various particles that remain from spacecraft repairs. These objects, which consist of metallic debris and other discarded materials, serve no practical purpose and are categorized as orbital debris. This includes:
- Components from rocket explosions;
- Abandoned items;
- Tools inadvertently misplaced by astronauts during instrument repairs.
The distinction between space debris and natural satellites lies in their origins. The former is a byproduct of human activity, while the latter forms naturally.
In order to investigate the lasting consequences of space debris impacts, NASA created a unique satellite known as LDEF. Throughout its 6-year mission, LDEF experienced over 20,000 encounters with orbital debris and micrometeorites.
Ongoing analysis of the information collected by the satellite is being conducted, and a significant network is currently being established in Japan to track and capture space debris.
Observing the Space Near Earth
In today’s world, it is rare to find someone who is unfamiliar with the Moon, Earth’s natural satellite. However, astronomers continuously monitor the area surrounding our planet in outer space. The objective of this research is not to locate new satellites, but rather to safeguard against potential collisions, predict them, and ensure the safety of space stations. Clyde Tombaugh was among the pioneers in conducting such research.
Currently, numerous major projects are focused on the exploration of celestial bodies in the vicinity of Earth. Thus far, no new natural satellites of Earth have been discovered through these studies.
This particular satellite is a member of the impactless group, commonly known as the Q class. It follows a 1:1 orbital resonance with Earth, and its unique characteristic is its elongated elliptical orbit that intersects with the orbits of three planets: Venus, Earth, and Mars.
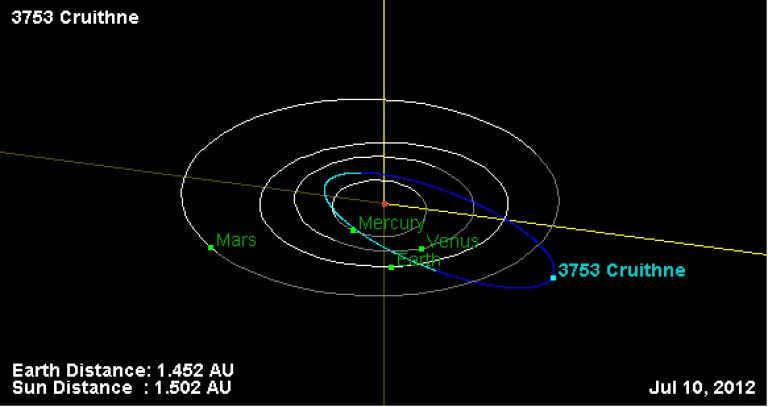
The orbital path of Cruithne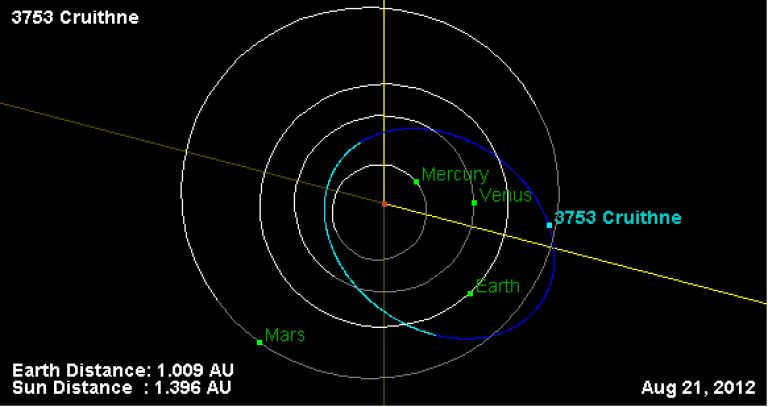
Cruithne’s unique orbit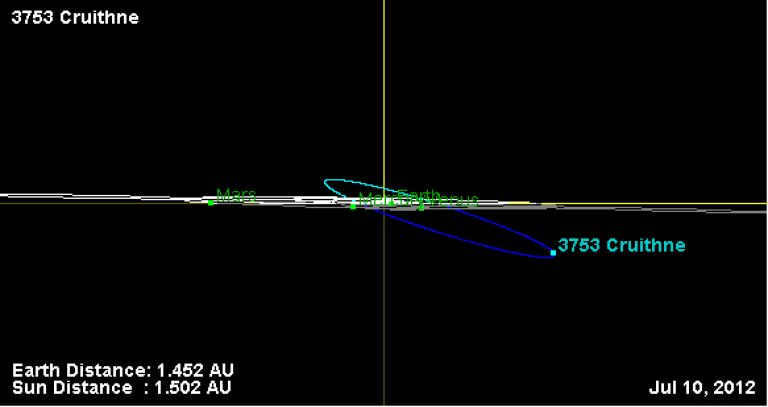
The orbital trajectory of Cruithne
On October 10, 1986, British amateur astronomer Duncan Waldron discovered Cruithnee through the Schmidt Telescope of Siding Spring Observatory in Coonabarabran, Australia. This momentous occasion also marked the first time designation of the asteroid as 1986 TO. In 1997, Paul Wiegert and Kimmo Innenen, from York University in Toronto, and Seppo Mikkola, from the University of Turku in Finland, calculated the asteroid’s orbit.
The diameter of Cruithnee is 5 kilometers, but unfortunately, there is no available data regarding its composition.
Mysticism
The peculiarity of the satellite, which Waltemath claimed to have “discovered,” was that it could only be observed when it passed through the solar disk. This object had very little reflectivity, making it extremely difficult to see. In 1918, astrologer Walter Gornold made headlines by announcing that he had rediscovered the moon first found by Waltemath. Gornold confirmed that this moon, which he named Lilith after Adam’s first wife according to Kabbalah, was also very dimly lit. The astrologer even suggested that Lilith was similar in size to the original moon.
The scientific community, however, found these claims to be quite amusing. A moon of such significant mass would have certainly been noticed, as its presence would have affected the motion of the moon in a noticeable way.

The Earth’s Natural Satellites: Counting the Stars
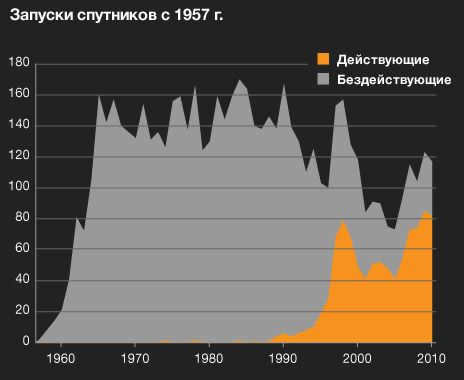
The upper section of the chart displays the overall quantity of satellites launched from 1957 to 2000. The grey region represents satellites that have ceased functioning since their launch, while the orange region represents satellites that are still operational.
Amsat-Oscar 7, launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on November 15, 1974, holds the record for the oldest active satellite in orbit. This satellite operates primarily for amateur radio operators and is situated in low Earth orbit.
The grey region accounts for 5,428 satellites. Many of these inactive satellites have contributed to the accumulation of orbital debris. According to NASA’s estimates, there are approximately 19,000 objects orbiting at altitudes above 10 centimeters.
Petit was not the sole astronomer who attempted to challenge the prevailing belief regarding the number of natural satellites orbiting the Earth. Joining him in this pursuit was Dr. Georg Walthemath, a scientist from Hamburg. In 1898, Dr. Walthemath made an announcement about the discovery of a system of small satellites. According to his calculations, one of these satellites was situated at a distance of slightly over one million kilometers from the Earth and completed one revolution every 119 days. The hypothetical satellite had a diameter of 700 kilometers.
Dr. Walthemath anticipated that the second moon would transit across the solar disk in February 1898, thus confirming his findings. Amateur astronomers in Germany did indeed spot the satellite. However, none of the professional astronomers observing the Sun that day observed anything similar.
Top concerns for the country
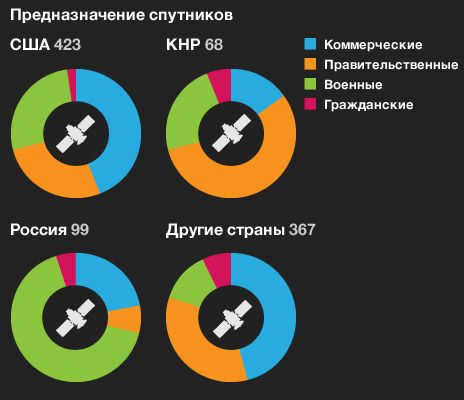
This diagram classifies satellites into four categories based on the main organizations that own and operate them: the United States, Russia, China, and other countries (excluding joint and cooperative satellites). This illustrates how the purpose of satellites is shaped by the economic and political conditions in different regions of the world.
The mission (commercial, government, military, or civilian) indicates the primary user of the satellite, although it is worth noting that many satellites have multiple purposes. For instance, a satellite can serve both commercial and military functions simultaneously.
Private investors and groups fund individual companies and consortia that own commercial satellites. These satellites are primarily used for communications and broadcasting purposes. On the other hand, military satellites serve multiple functions such as reconnaissance, navigation, and radio communications. Government satellites are primarily used for meteorological and scientific observations. Civilian users, including academic institutions and research groups, also utilize these satellites.
Communication satellites account for about two thirds of all active satellites. The remaining satellites are dedicated to navigation, Earth observation reconnaissance, astrophysics, and exploration, making up approximately 5 to 7% of the total satellite count.
Curious information about the most fascinating satellites
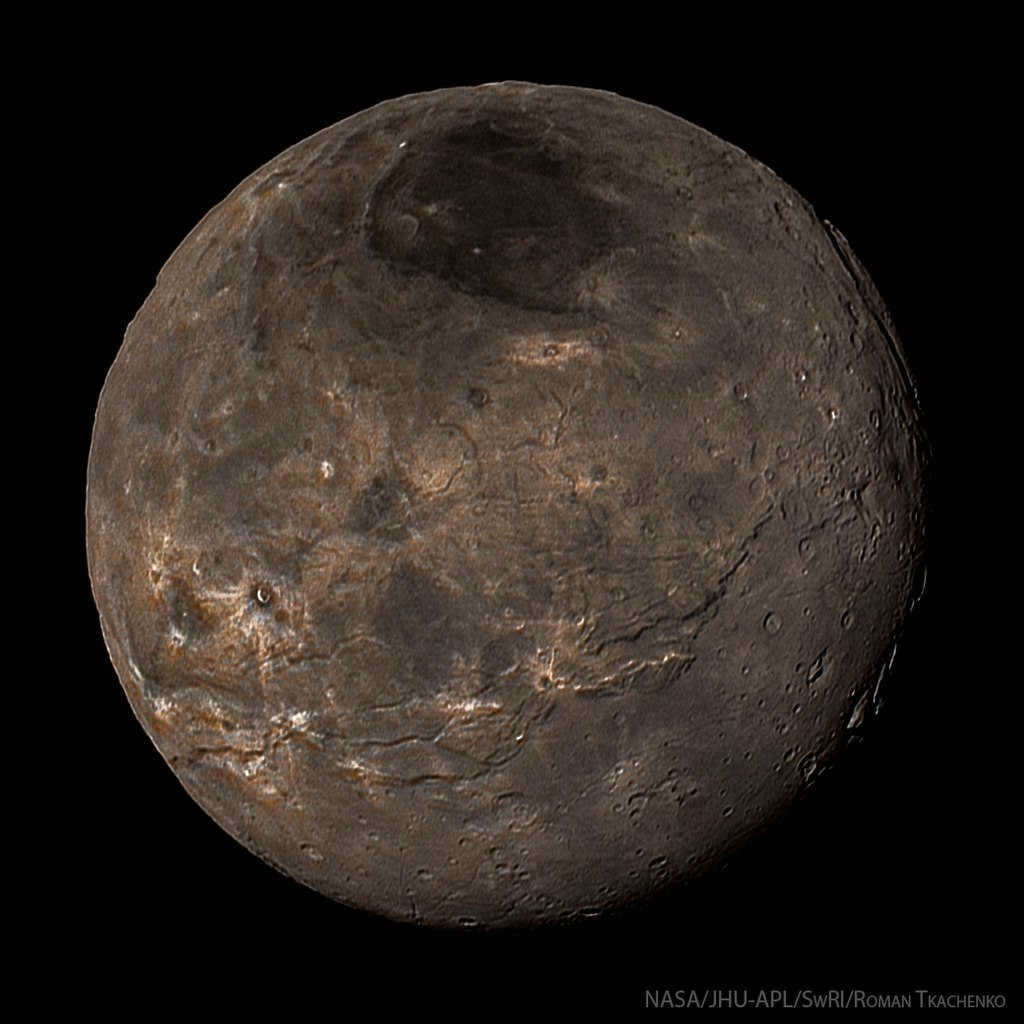

Charon, an image taken by New Horizons spacecraft
Charon, the natural satellite of Pluto, is one of the most captivating natural satellites among the planets in the solar system. Its size is so significant compared to Pluto that numerous astronomers simply consider them as a binary dwarf planet. The planet Pluto is merely twice as large as its accompanying natural satellite.
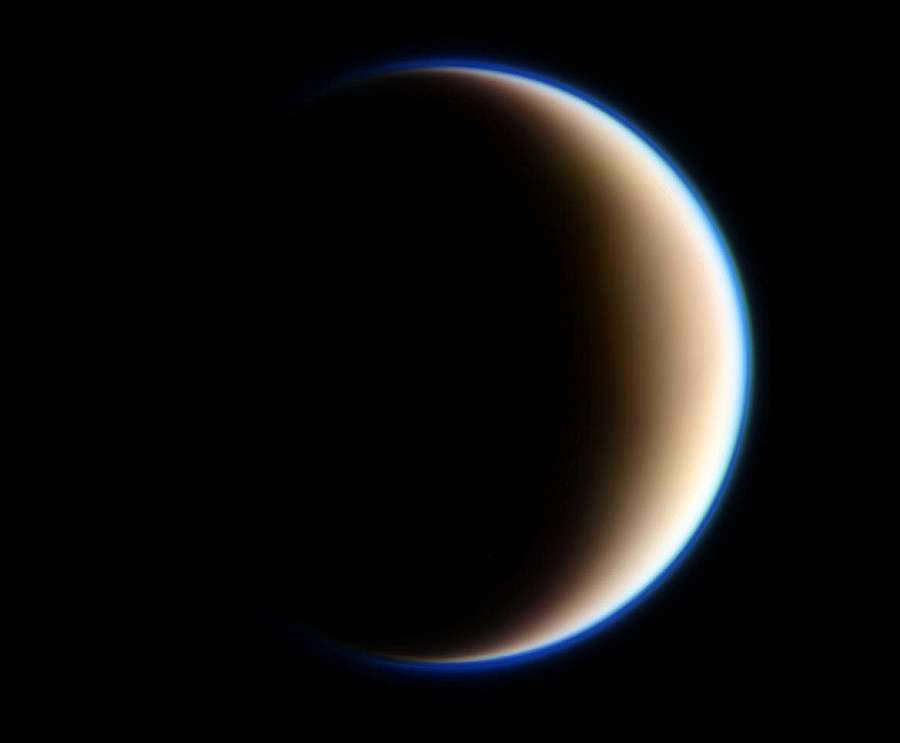


The scientific community is highly intrigued by Titan, Saturn’s unique natural satellite. Unlike most natural satellites in the solar system, which consist mainly of ice, rock, or a combination of both, Titan stands out with its dense atmosphere and even boasts lakes of liquid hydrocarbons.
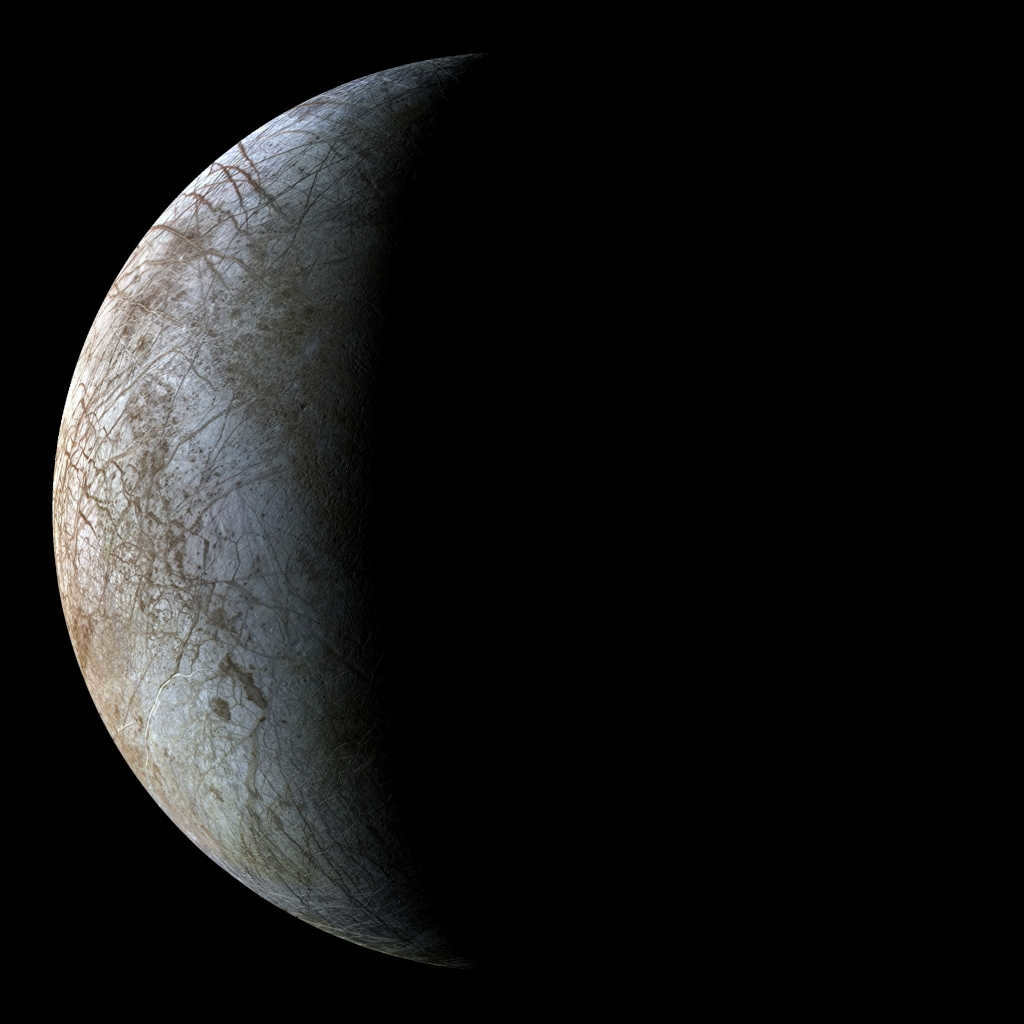


Photo of Europa, one of Jupiter’s natural satellites
Europa, a moon of Jupiter, is another celestial body that offers scientists a glimmer of hope in their search for extraterrestrial life. Hidden beneath its icy surface lies an ocean complete with thermal springs, mirroring similar geological features found on Earth. These underwater hotspots have been known to harbor unique forms of life on our planet, leading researchers to speculate that Europa may host similar lifeforms.
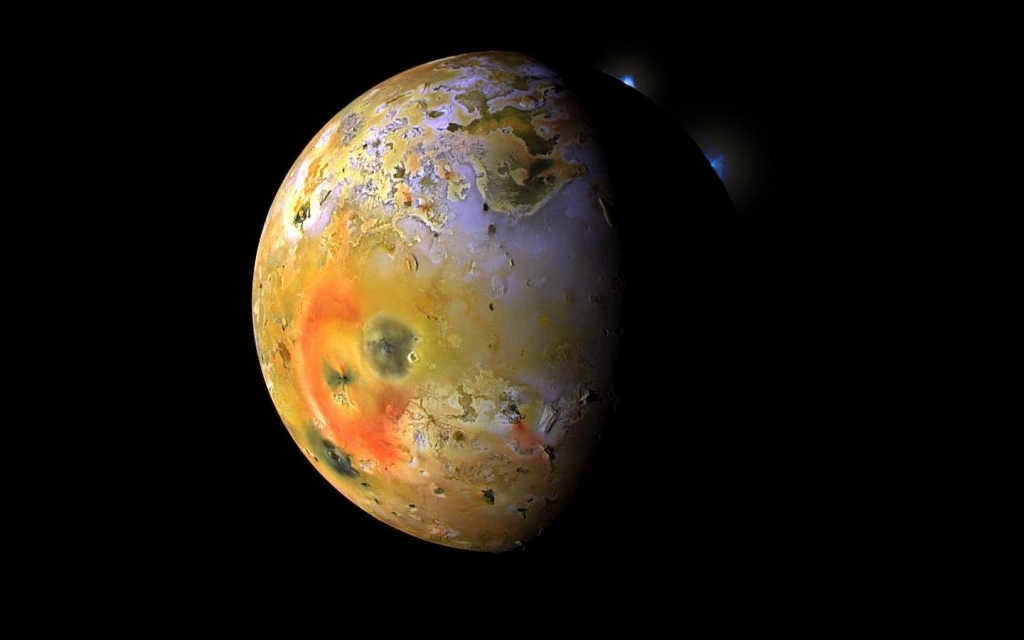
The planet Jupiter has a fascinating natural satellite called Io, which is the only satellite in the solar system where active volcanoes were first discovered by astrophysicists. This unique feature makes Io particularly intriguing to space explorers.
Moons in Space
Natural satellites are celestial bodies that orbit around planets. There are two theories regarding the origins of these moons:
- During the planet’s formation, a fragment separated from it and started spinning.
- An asteroid was attracted by Earth’s gravitational force, started orbiting around the planet, and eventually formed into a spherical shape.
The origin of the moon has been a topic of debate for more than a century. Credit: avto.goodfon.ru
Scientists have made an intriguing discovery, revealing that the Earth and the Moon share the same composition. This finding has led to the hypothesis that the Moon was once a part of our own planet. In the 19th and 20th centuries, astronomers held the belief that the Earth had various types of satellites. However, it is now widely accepted that the Moon is the sole natural satellite of our planet.
(367943) Duende
In contrast to its predecessor, this celestial body is still in its infancy. With a mere diameter of 30 meters and a weight of approximately 40 thousand tons, it pales in comparison.
Belonging to the renowned Apollo group of asteroids, this satellite was only discovered on February 23, 2012, making it a relatively new addition to our knowledge of the cosmos.
(469219) Kamoaleva
The most stable of all quasi-satellites on Earth, this satellite has recently been discovered on April 27, 2016. It is not surprising that Kamoaleva became a quasi-satellite of Earth about 100 years ago. As of mid-June 2016, it was believed that this celestial body would remain a satellite of Earth for only a few centuries. However, in early August 2016, it was revealed that previous estimates were underestimated, and Kamoaleva would continue to be a quasi-satellite for another million years or more.
The orbit of the Camoalev satellite
The Camoalev satellite is a massive irregularly shaped celestial body. It measures between 30 and 100 meters in diameter. Essentially, it resembles a large oval nude figure, like one you would find on a beach.
Similar to other quasi-satellites, not much is known about it, but this specific celestial object will be thoroughly examined by a space probe in the near future.
China’s National Space Administration has plans to launch the ZhengHe probe to explore Camoalev. The probe will orbit the asteroid, touch down on its surface, gather samples, and return them to Earth in a re-entry module. Following that, the probe itself will journey to comet 133P/Elst-Pizarro.
2003 YN107.
Despite being detected in 2003, this celestial object is even tinier than its predecessor. It shares the same oblong shape and measures between 10 and 30 meters in diameter. It falls into the category of near-Earth asteroids of the atomic classification. No further information is available regarding this satellite.
The Origin Story of the Moon
Scientists believe that billions of years ago, the Earth experienced a cataclysmic collision with another planet known as Thea. Interestingly, in mythology, Thea is revered as the mother of the moon goddess Selene. This collision resulted in the merging of the two planets and the subsequent formation of the moon from the fragments that broke away. This explanation seemed plausible for a long time, but in 2016, scientists challenged this theory. They discovered heavy isotopes of potassium on the moon that could only have formed under extremely high temperatures. A collision of such magnitude would have vaporized a significant portion of the Earth, making the previous explanation unlikely.
However, the moon still holds many mysteries. For instance, samples collected from the moon reveal that it was once home to active volcanoes. This revelation adds another layer of intrigue to our understanding of the moon’s history.
In The Secret Doctrine by Blavatsky, there is a hypothesis that suggests the moon predates the Earth. According to this theory, the moon bestowed its energy and might upon our planet, ultimately transforming into a lifeless shadow. This concept finds its roots in Hindu chronology.
In 2017, virtual ufologist George Graham put forth a fresh proposition regarding the purpose of Earth’s natural satellite: it is believed to possess a hollow interior and serve as a habitat for extraterrestrial beings. Graham’s theory draws upon images of the lunar surface captured by NASA’s orbiting station, which exhibit the presence of meticulously crafted artificial structures.
A Close Encounter: A Journey Through Launch History
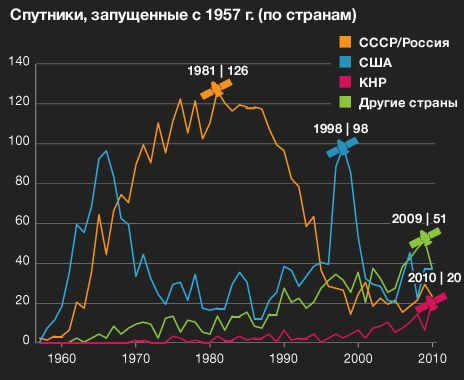
Back in 1957, the Soviet Union made history as the first country to successfully launch an artificial satellite into space. Since then, over 6,000 satellites have been sent into orbit. This informative chart showcases the trends in satellite launches starting from 1957, including data from the USSR (later known as Russia), China, and various other nations. Each country’s peak launch year is marked with a satellite symbol.
During the 1970s and 1980s, the USSR experienced its peak in satellite launches. This period coincided with the height of the Soviet military space program, during which numerous reconnaissance, navigation, and communications satellites were deployed.
On the other hand, the United States reached its peak in 1998. This marked the year when three major commercial satellite communications networks, namely Globalstar, Iridium, and ORBCOM, were launched. Many of these satellites were transported into space using American launch vehicles, sometimes even multiple satellites in a single rocket.
The increase in satellite launches can be attributed to shifts in their objectives. During the 1970s, there was a significant demand for communication satellites. In the 1990s, navigation satellites became a priority, and in recent years, there has been a focus on civil and research satellites.
If this pattern persists, countries with space capabilities will be able to construct bigger and more dependable satellites, while international organizations like universities can also engage in the production of smaller and more cost-effective satellites.
(164207) 2004 GU9
Scientists speculate that this celestial object will continue to orbit the Earth for approximately 2,600 years. Classified as a member of the Apollo group, it was first identified on April 13, 2004 by the Lincoln Laboratory for Near-Earth Asteroids.
In terms of size, this satellite is relatively substantial, measuring 163 meters in diameter. Its composition, however, remains a mystery.
Other celestial bodies orbiting the Earth
Another trial
Waltemath persisted in his exploration. In July of that same year, he penned an article discussing an alternative contender for the esteemed position of the Moon’s companion. According to Waltemath’s calculations, a celestial entity measuring 746 km in diameter orbited at a distance slightly exceeding 400,000 kilometers from our planet. Nevertheless, these estimations were also unverified. The hypothetical natural satellites proposed by Valtemata never obtained the recognition of tangible entities.
In the 21st century, celestial bodies that resemble satellites and are in a 1:1 orbital resonance with the planet were discovered. These unique entities came to be known as quasi-satellites, as they orbit the Sun at the same distance as Earth. However, due to their unstable orbits, they occasionally come close to our planet. These quasi-satellites are often referred to as second moons or second satellites.
The usage of such a simplistic name can be misleading. One particular quasi-satellite, Cruithne, has long been referred to as a second satellite.
There is even a minuscule quasi-satellite named Duende, measuring just 30 meters in diameter. It will be visible in 2094 without the need for advanced technology, at a distance of 4500 km from Earth. The list of quasi-satellites is extensive.
The enigmatic Lilith
Categorization of celestial bodies orbiting
Researchers classify the celestial bodies orbiting planets into two distinct categories: artificial and natural. Artificial satellites, often referred to as man-made spacecraft, are constructed objects that enable the observation of the planet they orbit, alongside other celestial entities, from the vantage point of space. Artificial satellites serve various purposes, including weather monitoring, radio transmission, mapping alterations in planetary topography, and military applications.
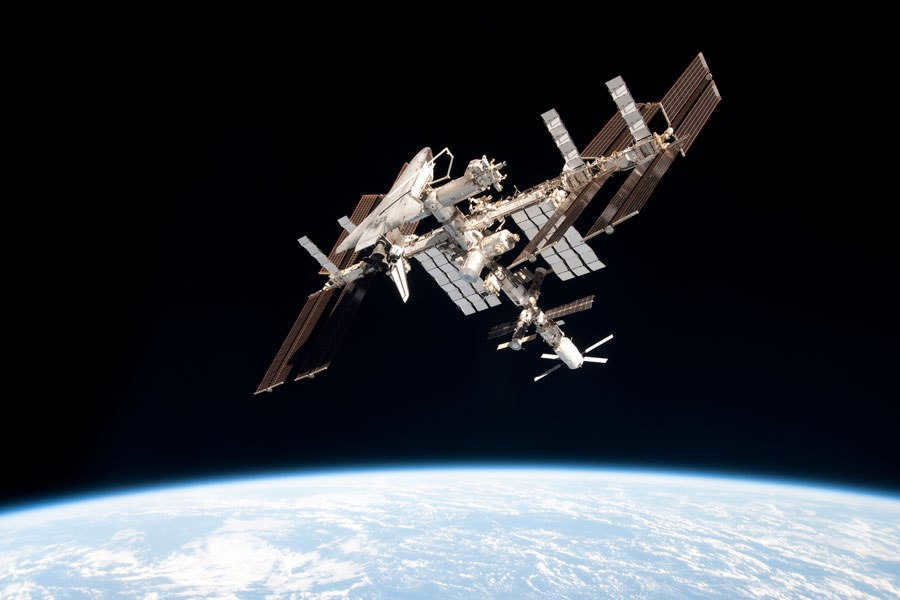

The International Space Station (ISS) holds the title for being the largest man-made satellite in orbit around the Earth.
It is important to acknowledge that Earth is not the only planet with artificial satellites, contrary to popular belief. In fact, there are over a dozen artificial satellites orbiting the two closest planets to us: Venus and Mars. These satellites provide valuable insights into the climatic conditions, changes in topography, and other relevant information about our celestial neighbors.
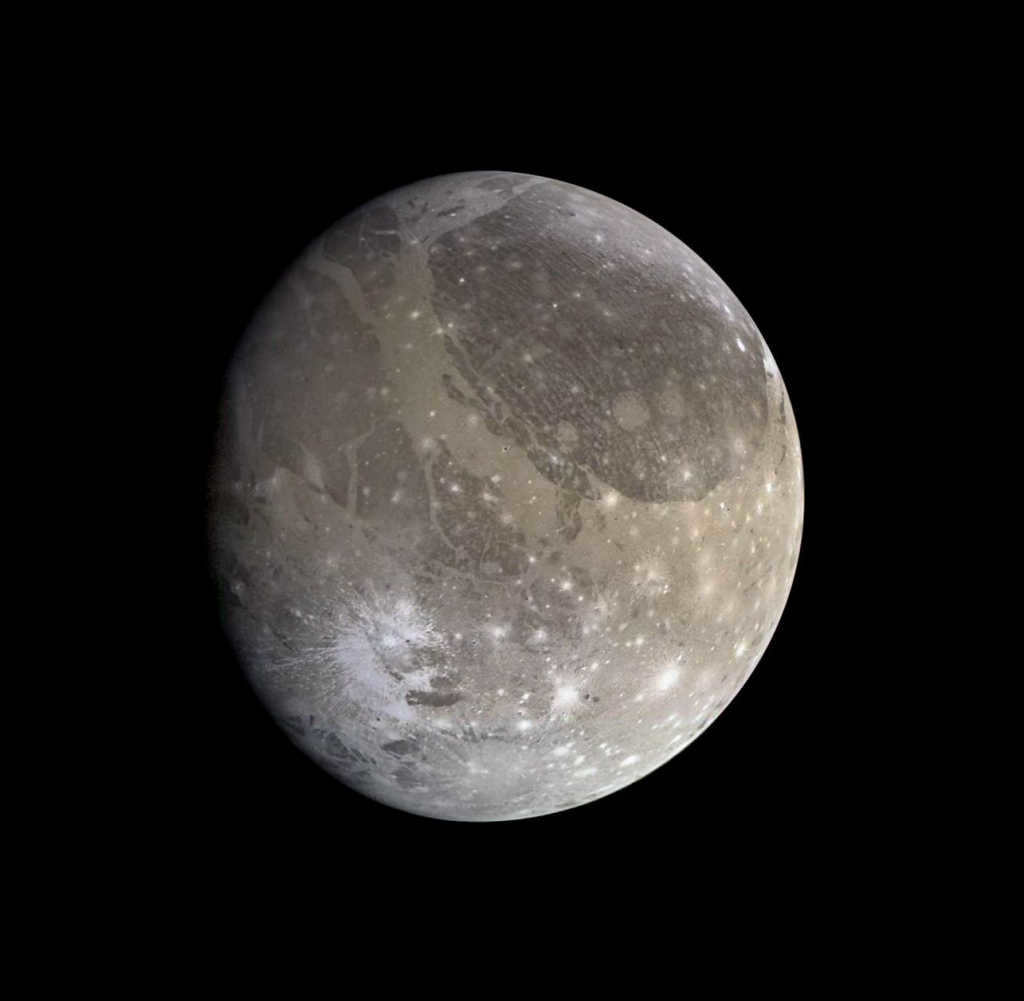

In the solar system, Ganymede holds the title for being the biggest satellite.
The second classification of satellites, known as the planetary natural satellites, are a subject of great interest within this article. Unlike their artificial counterparts, natural satellites are not man-made, but rather occur naturally. It is widely believed that the majority of the solar system’s satellites are actually asteroids that have been captured by the gravitational forces of the planets. Over time, these asteroids have taken on a spherical shape and now orbit their captor planet as permanent satellites. Another theory proposes that these natural satellites are actually fragments of the planets themselves, which broke away during the planets’ formation for various reasons. Interestingly, this theory aligns with the origins of Earth’s own natural satellite, the Moon. Chemical analysis of the Moon’s composition has revealed striking similarities to our planet, suggesting that it shares many of the same chemical compounds.
Trojans
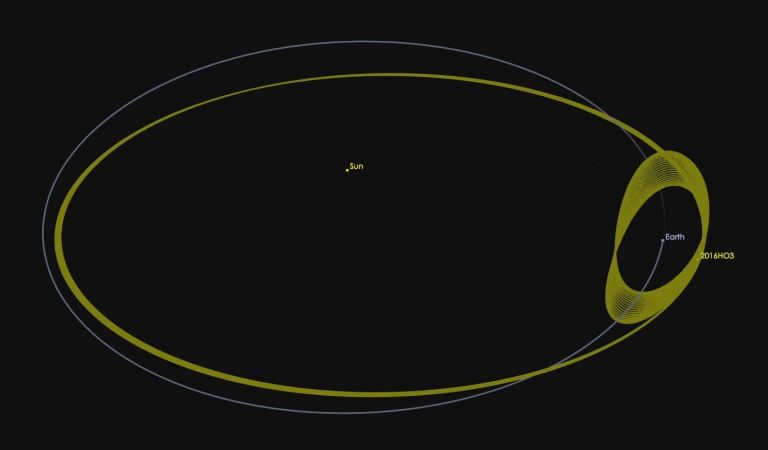
(419624) 2010 SO16
The WISE infrared space telescope detected this satellite on September 17, 2010. It was found and analyzed at the Armagh Observatory in Ireland. The satellite has a diameter of 200-400 M and its mass and composition are still unknown.
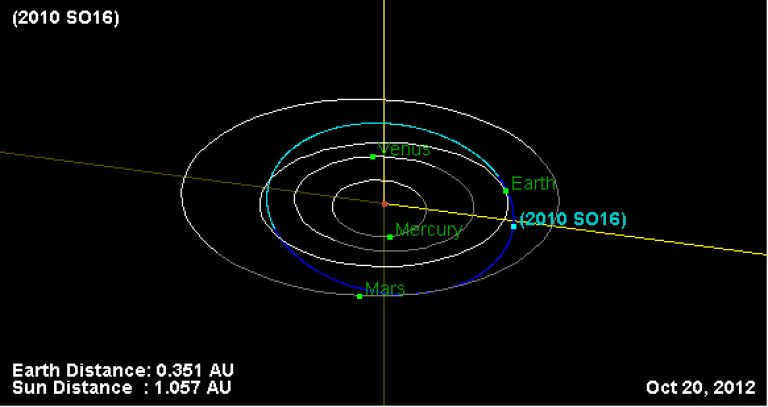
The satellite’s orbit is shown in the image above. 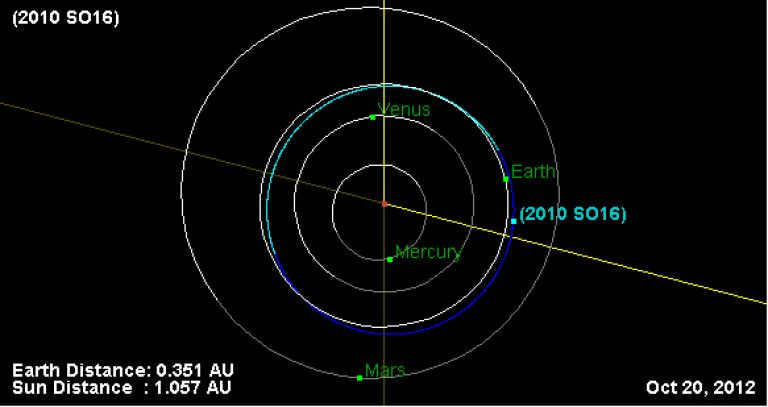
This is another view of the satellite’s orbit.
Several moons
Indeed, the Universe is home to more than just the Moon. Each of the planets in our solar system possesses its own set of natural satellites. While Earth can only boast one “companion,” Jupiter has a staggering 63 of them! The largest among them goes by the name of Ganymede.
Pluto’s satellite, Charon, is so large in comparison to the planet itself that astronauts initially mistook this “duo” for a binary system.
The smallest satellite in the solar system is Dactylus. This tiny celestial body, with a diameter of only a mile, is not a satellite of a planet, but rather an asteroid. However, previous scientists were convinced that only planets could possess satellites! Dactyl has successfully disproven this theory.

An Optical Phenomenon
The Act of “Capturing” Planets
Political Implications
The Moon, Earth’s natural satellite, as well as Mars and Venus, its closest celestial neighbors, have always intrigued the human mind with their mysteries. Throughout the past century, these celestial bodies have often been associated with extraterrestrial civilizations or the presence of military bases belonging to hostile nations. Amidst such speculation, the notion of artificially placed satellites orbiting in secrecy appears to be more plausible.