The vast expanse of the cosmos is far from empty. It is filled with an incredible variety of celestial bodies, each with its own unique characteristics and names. These include meteors, meteorites, comets, bolides, planets, and stars. Within each category, there are further distinctions that may only be discernible to experienced astronomers. In this article, we will explore the fundamental differences between stars and planets.

The primary distinction
The initial, fundamental, and indisputable distinction is the ability to emit light. Stars always emit light, whereas planets do not possess this characteristic. Of course, nearby planets may appear as glowing spots – Venus is a striking example. However, this glow is not inherent to the planet itself; it is merely a reflection of the light from the true source – the Sun.
Incidentally, this method is an excellent technique for distinguishing between a planet and a star solely through visual observation, without the need for any additional optical instruments. If a bright point in the nocturnal heavens “twinkles” or flickers, it can safely be assumed that it is a star. Conversely, if the illumination emanating from the celestial body remains steady and uniform, it indicates that the object is a planet, reflecting the light of its closest luminary. This fundamental distinction serves as the primary and most apparent indicator of the disparities between stars and planets.
The next distinction, derived from the initial one
Only extremely hot surfaces possess the capability to radiate light. To illustrate this point, let’s take the case of a metal that doesn’t naturally emit light. However, when heated to the appropriate temperature, the metal object starts to emit a faint glow.

One of the main distinctions between stars and planets is their incredibly high temperatures. It is this high temperature that allows stars to emit light. Even the coldest star has a surface temperature that does not drop below 2000 degrees K. Stellar temperatures are typically measured in Kelvin, rather than Celsius.
Our own Sun is even hotter, with its surface reaching temperatures of 5000 to 6000 K during different periods. In terms of Celsius, this would be an impressive range of 4726.85 to 5726.85 degrees.
These temperatures are unique to stellar surfaces. Another factor that sets stars apart from planets is their significantly higher internal temperatures compared to their external temperatures. Some stars have surface temperatures as high as 6000 K, while it is believed that the center of stars can reach millions of degrees Celsius! Currently, there is no capability, technique, or formula available to calculate the internal “degreeness” of stars.

Comparing Size and Movement
The sizes of stars and planets vary greatly. When compared to stars, planets are tiny in comparison. This applies to both their weight (mass) and volume. If we were to replace the Sun with an average-sized apple in empty space, the Earth would be represented by a pea located hundreds of meters away. Comparing the sizes of planets and stars reveals that the volumes of stars are thousands or even millions of times larger than the space occupied by planets. The mass ratios between stars and planets are also significantly different. This is because all planets are solid while stars are mostly gaseous. Without these high temperatures, which allow for thermonuclear reactions, stars would not be able to exist.

Other Indications
The size of stars and planets cannot be determined by the naked eye. However, there are certain distinguishing factors that require more specific equipment. For instance, the chemical composition, which can be determined through spectral analysis, can accurately determine whether we are dealing with a planet or a star. This is because stars are composed of light elements, as they are gaseous giants, while planets consist mostly of solid components.
Another indication can be the presence of a satellite (or even multiple satellites). Only planets have satellites. However, the absence of a companion does not necessarily mean that we are definitely dealing with a star – some planets can exist without such “neighbors.”
Astronomers have a new criterion for identifying whether a recently found celestial object is classified as a planet. The trajectory on which it orbits must be free from any foreign matter, colloquially referred to as debris. Satellites are not considered in this sense, as they are sufficiently large to avoid falling to the surface. This regulation was only established in 2006. As a result, Erida, Ceres, and notably, Pluto, are now recognized as dwarf planets rather than full-fledged planets.

Astronomical Calculations
Scientists possess an insatiable curiosity. Despite their well-founded knowledge of the distinctions between stars and planets, they remain intrigued by what occurs when a planet’s mass surpasses that of the Sun, for instance. It has been discovered that such an expansion in a planet’s size would result in a dramatic surge in pressure within its core. Consequently, the temperature would soar to a million degrees or more, triggering nuclear and thermonuclear reactions. The end result would be the birth of a new star instead of a planet.
There is an abundance of stars in the night sky! And each of them appears to be quite diminutive! On the other hand, the Earth is immensely vast. Hence, the question arises: which entity is larger, a star or a planet? In order to address this inquiry, it is imperative to comprehend the nature of each of these celestial objects.

Stellar Objects
Astronomers use the term “star” to describe a celestial body where thermonuclear reactions take place. These objects are colossal spheres of gas, radiating inconceivable amounts of light and heat. They form through the gravitational compression of gas and dust that fills the expanse of space. Within the depths of stars, at temperatures reaching several million Kelvin, hydrogen undergoes thermonuclear reactions, transforming into helium.
Despite their immense heat, the surface of stars is relatively cool, with temperatures ranging from a few thousand to tens of thousands of Kelvin. Stars are the primary constituents of the Universe, emitting the majority of light present in nature. Even with this limited information, we can determine that stars are larger than planets.
All celestial bodies in stellar systems revolve around a central star. In our solar system, the planets revolve in the same direction as the Sun rotates on its axis.
The formation of a star
However, scientists worldwide have access to more than just this data about stars. The question of what is larger, a star or a planet, has long been answered. Additionally, the process of star formation has been discovered. Stars are actually born from interstellar gas. As the cloud of this substance slowly contracts under the force of its own gravity, gravitational energy is transformed into thermal energy. Once the temperature at the core reaches millions of Kelvin, the contraction stops and nucleosynthesis begins. This phase, which is the longest in a star’s life, continues until the core runs out of fuel. At that point, when the hydrogen in the core is converted to helium, fusion continues on the periphery of the helium core.
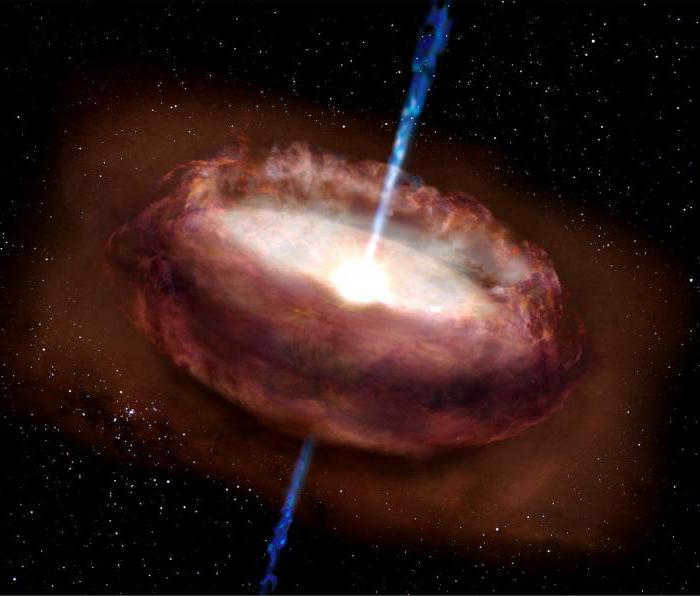

During this period, the star undergoes a transformation in its structure. Its luminosity increases, causing the outer layers to expand beyond their usual limits, while the inner layers contract even further. As a result, the brightness of the star decreases. Once the surface temperature naturally decreases, the star is referred to as a red giant. This phase lasts for a relatively short period of time.
An example of star formation in the present time can be observed in the gas cluster near the constellation Orion. This complex encompasses nearly the entire area of the constellation and includes a significant amount of molecular and neutral gas, dust, and multiple nebulae. Stars have been forming here for millions of years and continue to do so to this day.
It is common knowledge that planets and stars are both formed from the same dust cloud, but it is debated which one is larger: stars or planets. Planets, in general, are celestial bodies that orbit around a star. They have enough mass to become spherical in shape, but are not massive enough to undergo thermonuclear reactions. Additionally, planets have the ability to clear their orbital space of smaller objects known as planetesimals.
In the past, scientists were uncertain about the existence of planets in other star systems. However, with the advent of powerful space telescopes, researchers have now discovered a significant number of these celestial bodies, known as exoplanets.
The fact that we are able to observe stars, yet not the planets that orbit them, is a testament to the significance of stars in comparison to planets. Conversely, there are instances where we can observe certain planets within our solar system, but this does not imply that they are larger than our star. Rather, it is due to the proximity of these planets to Earth in comparison to our star.

The central object of a star system is much larger than the celestial bodies that orbit it. If this were not the case, the planets would not revolve around the star, but rather the star would revolve around the planets, which goes against the laws of the universe.
Conclusion
Based on the findings of scientists regarding the structure of not just our own, but also other stellar systems, it is clear that a star is larger than a planet. This is because smaller celestial bodies orbit around larger ones. In the case of a star and a planet, the planet orbits around the star, indicating that the star is significantly larger in both size and mass.
Furthermore, the same principle applies when comparing a star, a planet, and a satellite. The satellite initially orbits around its planet, and then both the planet and the satellite revolve around their star, emphasizing the superior size of the star.

A celestial body known as a planet
Planets are cosmic entities that revolve around stars, characterized by their large size. Interestingly, the word “planet” comes from the Greek word “wanderer,” suggesting that these celestial bodies wander through the vast expanse of the universe. Planets can be classified into two main categories: giants and terrestrial planets. The former category consists of gas giants, which are significantly larger than their terrestrial counterparts, including Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Gas giants often have numerous satellites, while terrestrial planets either have none or only one, such as Mars and Earth. Despite their differences, both groups have representatives that share similar structures and properties. It is worth noting that Pluto was previously considered a planet.

Distinguishing Stars from Planets
Stars are massive celestial bodies that emit radiant light. While stars are visible in the night sky, they are situated at significant distances, with the Sun being the closest one to us. Furthermore, the Sun is the sole star in our solar system. Stars possess extremely high temperatures, reaching thousands of degrees.
If we discuss the nearest star compared to the Sun, we would be referring to Proxima Centauri. Despite its proximity, the distance to Proxima Centauri is approximately 39 trillion kilometers. In the sky of each hemisphere on Earth, we can observe around 3,000 stars. To sum up the distinctions between these celestial bodies and planets, I would like to state the following:
- Stars possess the capability to emit light;
- Planets have significantly lower temperatures compared to stars;
- Planets are much smaller in size compared to stars.
Lastly, it should be noted that stars and planets greatly differ in their composition.
My fascination with space and the dreams it evokes began in my early childhood, when a close friend of mine (now an aeronautical engineer) introduced me to the wonders of constellations. Since then, I have delved into numerous books and watched countless movies on the topic. To truly grasp the distinctions among these celestial entities, it is imperative to comprehend the processes behind the birth of stars and planets.

The inception of stellar systems
The procedure delineated beneath is reiterated up until the present moment, giving rise to every novel assemblage.
Hydrogen is the fundamental constituent of the universe. A substance made up of a single proton in its nucleus is spread out across space. Drawn together by the force of gravity, it congregates into clouds. The mutual attraction and resulting energy from the fusion of lighter materials give rise to a newborn star. However, this is merely the inception of its existence. Through a thermonuclear reaction, lighter elements are transformed into heavier ones and become part of a celestial body’s core. The larger the mass of the material, the more difficult it is to fuse. Consequently, towards the end of a star’s life, two forces contend within it: gravity, which compresses the body, and the chain reaction’s force, which expands it. The subsequent fate of the star hinges on which force “triumphs” over the other:

When a white dwarf explodes, it gives rise to a brand new star.
The birth of planets and the emergence of life

As you may be aware, planets are a result of the life cycle of stars. Their orbits are established during the supernova’s birth. The formation processes are also influenced by gravity. The existence of life on planets is determined by multiple factors:
- Distance from the star.
- Characteristics of the atmosphere and surface.
- The force of gravity.
- The speed of movement.
- The number and intersection of orbits of other celestial bodies.
Space is a subject that greatly intrigues me, and I thoroughly enjoy devouring articles on the topic. When I came across this particular question, my brother and I were compelled to pool our knowledge and organize it meticulously.
What is a star?
A star is a massive celestial object made up of compressed gas. It is believed that stars were formed after the Big Bang when atoms, primarily consisting of hydrogen, helium, and lithium, came together. The immense gravitational force acting on the hydrogen causes it to compress, converting gravity into kinetic energy. As a result, the star’s temperature and pressure increase, leading to the process of nuclear fusion. During nuclear fusion, elements such as carbon, magnesium, and others up to iron are produced. In fact, the first 26 chemical elements are formed within the core of a star. When the core reaches the point of being predominantly composed of iron, the star undergoes an intense compression that causes it to rebound. This rebounding force results in a spectacular explosion, known as a supernova, which propels the majority of the star’s material out into space.

Planets: Their Formation and Characteristics
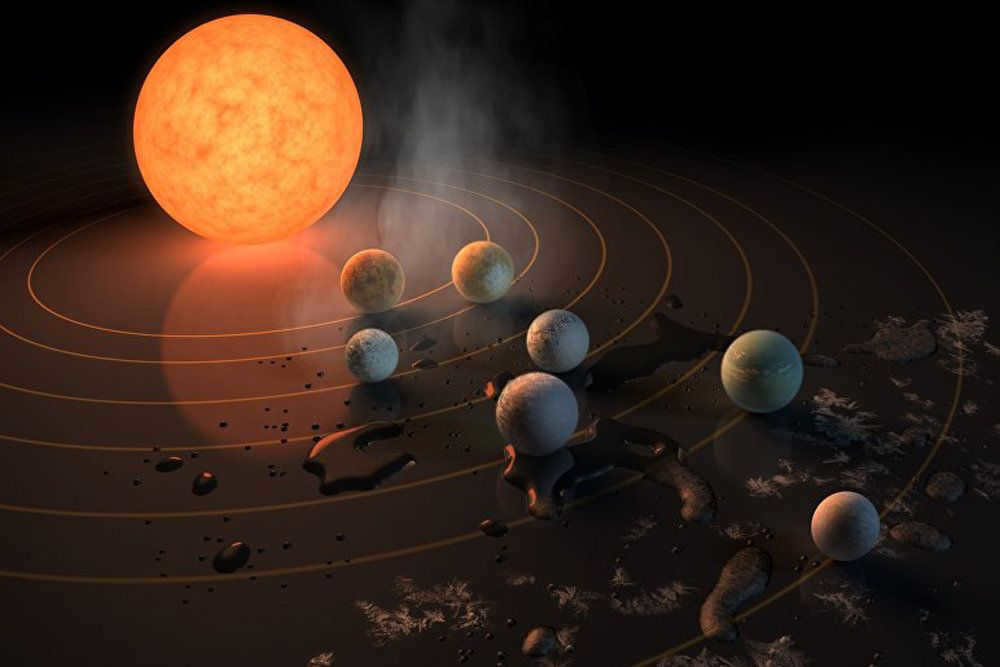
A planet is a celestial body that orbits around a star and rotates on its own axis.
When a supernova star explodes, the material expelled into space undergoes chemical reactions and transforms into molecules and minerals. These clusters, influenced by the gravitational force, come together to form a cloud of gas and dust. As a shock wave from a nearby star’s explosion passes through this cloud, a new star begins to take shape. Eventually, it absorbs most of the cloud’s mass and the majority of its hydrogen, leaving behind a remaining dust that orbits in the same direction as the star. Over time, this dust coalesces to form planetesimals, which develop iron cores and atmospheres.

Comparing Stars and Planets
When examining the origins and characteristics of stars and planets, it becomes clear that they have distinct differences:

- The primary components of a star are hydrogen and helium, whereas a planet is composed of other elements with a small proportion of hydrogen.
- A star undergoes the process of nuclear fusion.
- When a star reaches the end of its life, it either emits a bright flash or simply fades away. On the other hand, a planet’s demise occurs as its core cools down, resulting in it becoming a solid entity without an atmosphere.
- A star emits energy into space, while a planet does not possess this capability.
- A planet orbits around its respective star, which in turn orbits around the center of the galaxy.
When gazing at the sky on a cloudless evening, one can observe an array of twinkling stars. It is often overlooked that each of these celestial bodies has the potential to be either a star or a planet within our own solar system, or even a distant galaxy. In the following passage, I will delve into the distinct characteristics of stars and planets.

The Definition of a Star
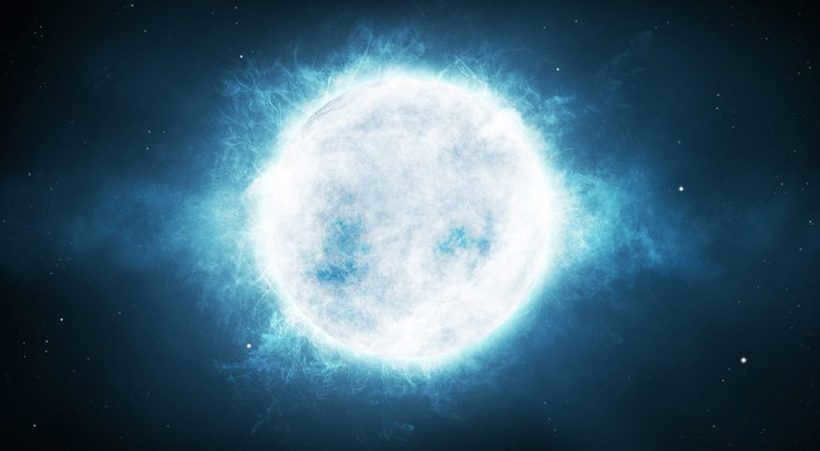
A star is an enormous, colossal. mass of gas created from a gas-dust nebula (primarily composed of hydrogen and helium) by the force of gravity. The energy within stars is released through thermonuclear fusion reactions, where hydrogen is converted into helium, or helium is converted into carbon, at extremely high temperatures within the core, which can reach tens of millions of degrees Celsius. As a result of these reactions, stars emit powerful light and heat radiation. Stars serve as the primary sources of light in the universe.

What defines a planet?
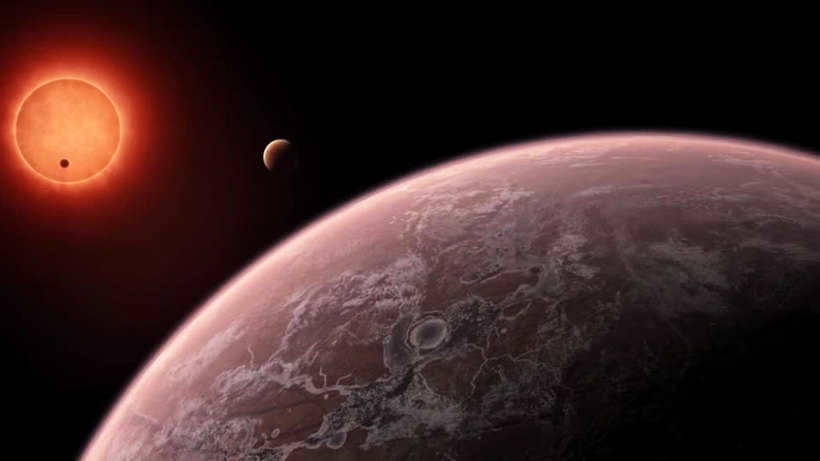
Celestial objects that have sufficient mass to be shaped like a sphere due to gravity, but not enough to trigger thermonuclear reactions, are known as planets. Planets revolve around a star. The definition of planets has evolved over time, and even now scientists are reevaluating previously designated planets like Pluto. Since August 24, 2006, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) has provided a precise definition for the term “planet,” and Pluto does not meet this definition; instead, it is classified as a type of “dwarf planet.”

The primary distinctions between stars and planets
After comprehending the definitions of stars and planets, we can highlight their main distinctions.
- Stars have significantly larger diameters compared to planets.
- Stars are much more massive than planets, often tens or even hundreds of thousands of times more.
- Planets are celestial bodies that orbit stars.
- While planets consist mostly of solid matter (except gas giants like Jupiter, which bear resemblance to the composition of stars and are sometimes referred to as failed stars by scientists), stars are composed of gas and lack solid surfaces.
- Planets do not undergo thermonuclear reactions like stars.
- Planets do not produce light like stars, but rather reflect it from their surfaces, so their temperature is influenced by their distance from the star.
That is all, thank you for your attention!)

The enigmatic expanse of space still holds many secrets yet to be unraveled by mankind. Today, I will shed light on the distinction between planets and stars, knowledge that everyone should possess. So, let’s embark on this enlightening journey!

The primary distinctions
The primary distinctions are that stars possess immense temperatures and undergo numerous chemical reactions every second. However, there are planets that harbor chemically reactive life forms. Nevertheless, this is not the case when considering our central star, the Sun. The energy emitted by these stars extends to neighboring celestial bodies, whereas the energy of planets remains confined within the planet’s boundaries.

That’s the reason why the Sun is observable from Earth, while the other planets that are visible cannot be seen. However, within the star, it is hotter. This is also the explanation for why we cannot launch a satellite to the Sun, as it would simply disintegrate due to the extreme heat.
Earth, the celestial body, revolves around the sun, the celestial object. And we observe another distinction. The magnitude of the celestial object is so immense that its gravitational force causes objects to rotate on their axis.
A brief overview of celestial bodies
However, what comes to mind when you hear the term celestial body?! A regular spherical entity, perhaps with various colors and composition. But there exist some highly extraordinary celestial bodies that scientists are currently uncovering, and their number is increasing. and they’re truly awe-inspiring our imagination.
- For instance, there exists a solitary celestial body orbiting its celestial object at a distance of 96 billion kilometers.
- And then there is a dark celestial body have you ever come across a dark celestial body? It reaches temperatures of about 1,000 degrees. There it is!
- What if there was a planet where it precipitates precipitates rocks?
- However, we have also discovered a planet that humans could potentially inhabit, as it is remarkably similar to our beloved Earth.

There is no end to the possibilities.
Some information about stars
The number of remarkable stars is countless! As an illustration.
Is it astonishing? However, this enormous entity has already diminished by 15%! 🙁 Eventually, it may become as small as the sun.
And this is the remaining portion of the azure supergiant:
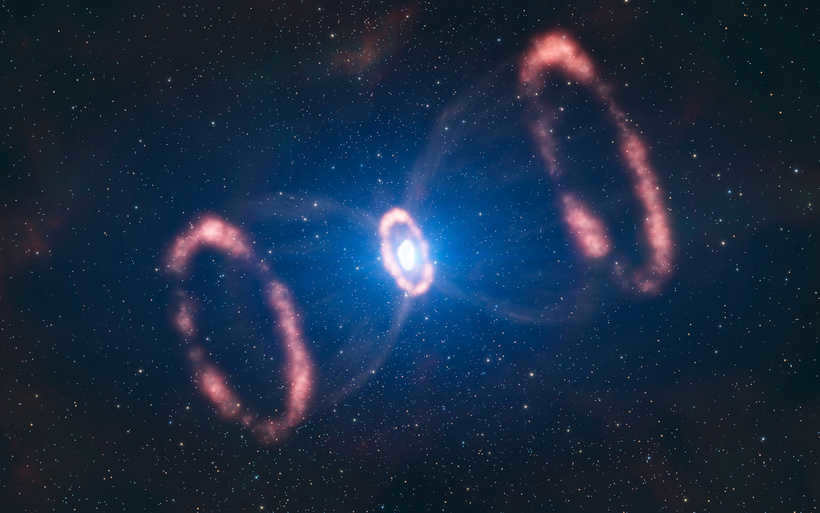
In the 1980s, there was an observable burst of light on our planet. The atoms involved in this phenomenon were grouped in circular formations, and researchers are currently conducting measurements on them.
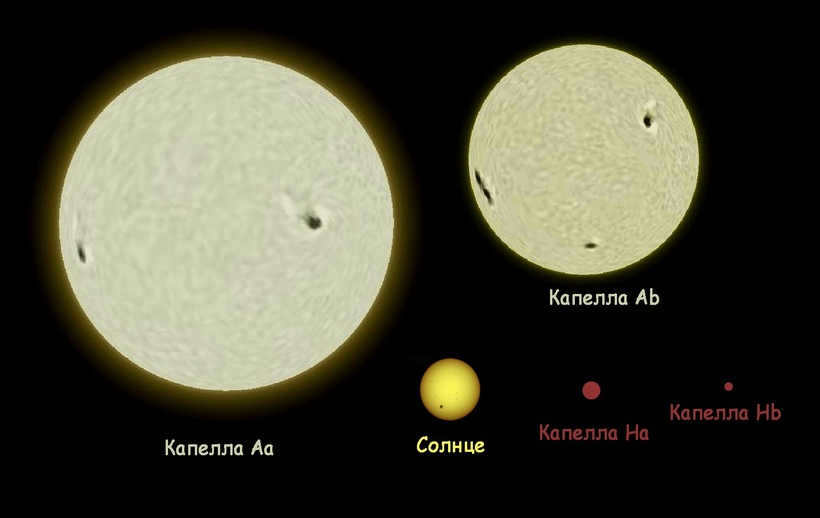
There is a magnificent celestial formation right here. It’s not just larger than our Sun and has been observed by humans for a long time, but it has also captured satellites in its orbit. This star is a spectrally binary system.
Every planet is distinct, just like each star has its own uniqueness.

When I was a child, I always had a fascination with gazing up at the night sky, observing the constellations, and letting my imagination run wild. It was no surprise then, that when elective courses were offered at school, I eagerly chose astronomy. And I can confidently say that it was a decision I never regretted. The classes were captivating and enlightening, which allowed me to gain extensive knowledge about the celestial bodies, particularly the distinctions between planets and stars. Allow me to share more about this fascinating topic.

What separates a planet from a star?
A planet, in simple terms, is a large celestial object that orbits around a star and has a spherical shape.
On the other hand, a star is a colossal celestial body primarily made up of gas and emits light and heat through thermonuclear reactions.
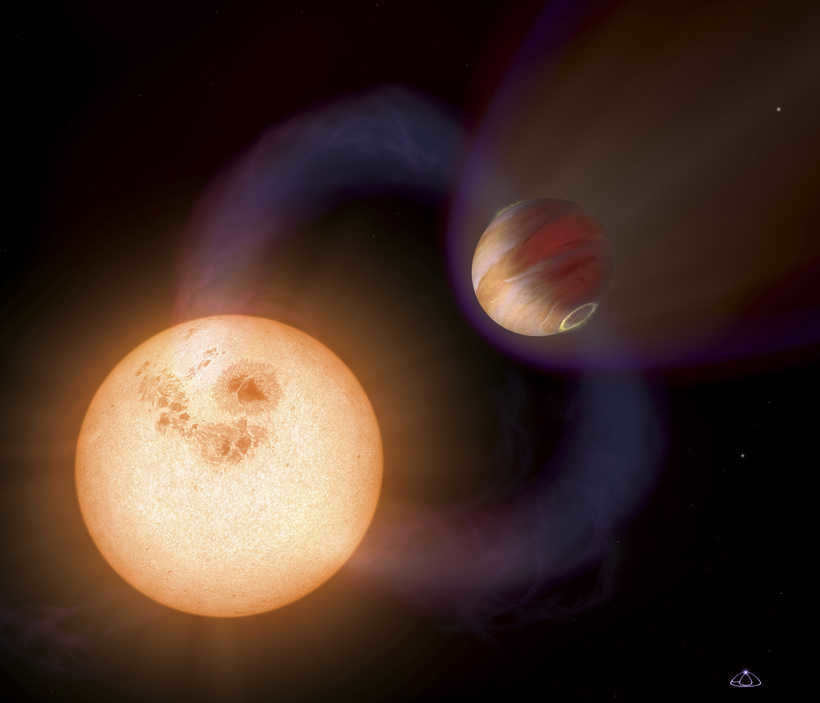

Notable Differences Between Planets and Stars
While planets and stars may appear similar at first glance, they possess numerous distinguishing characteristics:

- The primary distinction between a star and a planet is their ability to emit light. Stars emit their own light as a result of thermonuclear processes occurring within them, while planets are mostly dark celestial bodies. Although there are planets that glow, this is only due to the reflectivity of their surface.
- The temperature of stars is significantly higher than that of planets. Some stars can reach temperatures of up to 40,000 degrees, even on their surface. In contrast, planets have much lower temperatures, with the closest planet to the Sun, Venus, reaching only 460 degrees. The temperature of planets decreases as their distance from the Sun increases.
- One more significant difference lies in the movement of the planets around the stars, as the stars remain stationary.
- The stars are primarily composed of light chemical elements, such as various gases. On the other hand, planets are predominantly composed of solid elements and have a solid outer layer.
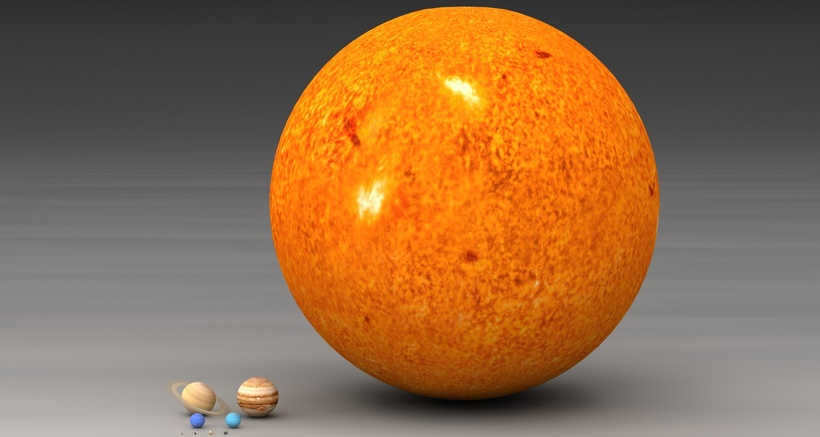
- Size and weight. While stars may appear small when observed from Earth, they are actually much larger, being thousands of times the size of planets. To visualize this, you can compare a pea to an apple, with the apple representing a star and the pea representing a planet. It’s truly impressive, isn’t it?
There are moments when I feel a sense of remorse for not being able to fully comprehend the vastness of the world. During my childhood, I received a remarkable present in the form of a book devoted to the topic of outer space. I distinctly recall being captivated by the spherical shapes of the planets, with the most prominent one being the Sun. It was at this point that my journey to understand the disparities between our Sun and the other celestial bodies, such as the planets, commenced. Differentiating them solely based on visual depictions proved to be a challenging task.

There are more differences than similarities between planets and stars.
Even though encyclopedia pictures may not show many visible differences, they do exist. And they are quite significant.
- Firstly, there is a difference in temperature.
- The second difference is in luminosity.
- Thirdly, there is a difference in size.
- Lastly, there is a difference in motion path.


Dimensions
The primary observation that leads us to consider the notion that stars are greater in size than planets is their visibility from Earth. Stars are easily visible in the night sky, while planets are less frequently observed, and usually only those within our solar system.  This distinction is not solely due to the fact that stars emit light and planets do not. It is also a consequence of the laws of physics, which state that an object with greater mass will not orbit around something smaller. Satellites orbit around planets, and planets orbit around stars. This is a direct result of the stars being larger than planets.
This distinction is not solely due to the fact that stars emit light and planets do not. It is also a consequence of the laws of physics, which state that an object with greater mass will not orbit around something smaller. Satellites orbit around planets, and planets orbit around stars. This is a direct result of the stars being larger than planets. 
Movement
In addition, a planet is distinct from a star. Unlike a star, a planet follows a specific orbit, which it repeats regularly. It is impossible for a planet to deviate from its predetermined path; it is fated to revolve around its star for its entire existence. How often do we find ourselves stuck in the same patterns in our own lives? In comparison to planets, our lives are a testament to diversity.
The other day, my son asked me just before bedtime about the dissimilarity between a planet and a star. This question led to us being late for school the following morning.

The distinction between a planet and a star
After pondering over it, I found myself at a loss for an answer. Consequently, we opted to consult the all-knowing Google for a solution. We stumbled upon a wealth of information on this topic. Evidently, the following differentiates a star from a planet:
- A star surpasses a planet in size;
- A star outweighs a planet;
- Stars emit light, while planets merely reflect it;
- Stars remain motionless, whereas planets orbit around stars.
We also learned that stars and planets are classified into distinct categories.

Categories of stars
As I gazed up at the night sky, I beheld numerous stars shining with equal brilliance. Although they may appear the same to us from our vantage point on Earth, in reality, they come in a wide array of forms. Here are several examples:
- A star classified as a red giant.
- A compact star known as a white dwarf.
- A small, dim star called a red dwarf.
- Highly dense celestial objects known as neutron stars.
- Massive stars referred to as supergiants.
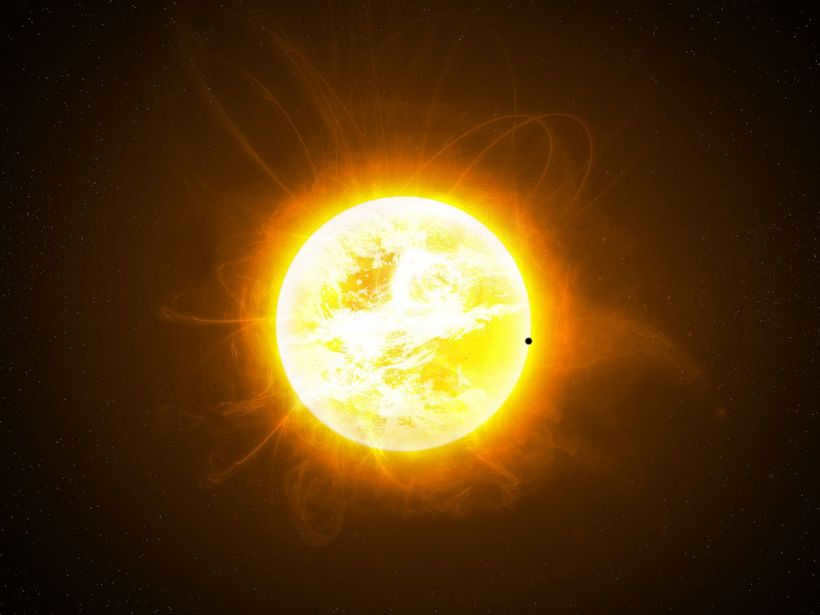

The Sun: A Unique Star
Undoubtedly, the Sun deserves our attention as we witness its presence almost every day. Upon learning more about the Sun, I was truly amazed by its extraordinary nature. Distinguishing itself from other stars, the Sun exhibits a fascinating rotation on its axis.
Being the largest entity in our solar system, the Sun stands as the sole star among the planets. However, it is essential to note that when compared to numerous other stars, the Sun is relatively small.
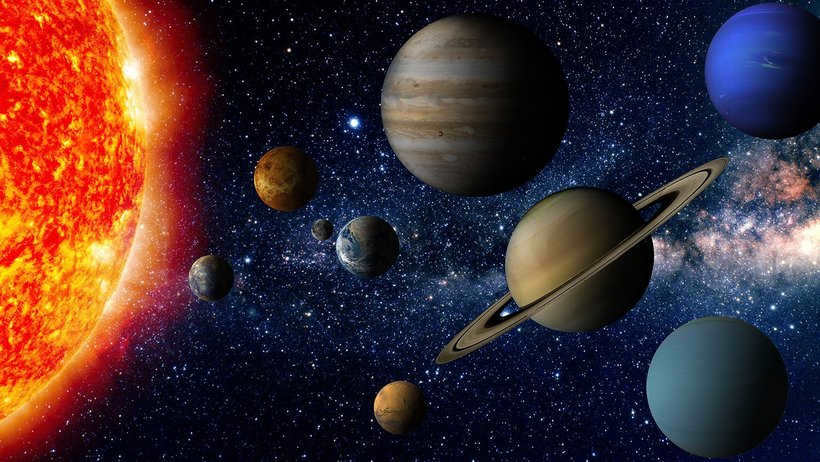

What types of planets exist?
There are two categories of planets: terrestrial planets and gas giants. Terrestrial planets include Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. They are smaller in size and located closer to the Sun. While Mercury and Venus have no moons, Mars has two moons, and Earth has one, which we commonly refer to as the Moon.
On the other hand, gas giants consist of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. These planets are significantly larger than terrestrial planets and are located farther away from the Sun. Gas giants have numerous moons and possess strong magnetic fields. Jupiter, being the largest planet, is followed by Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
After learning about stars and planets, my son has developed a keen interest in space. I anticipate that we will delve deeper into this subject in the future.
Ever since I was a child, from the very first episodes of Doctor Who, my eyes have been ablaze and my heart has been filled with excitement at the mere mention of these almost enchanting phenomena that populate the universe. Remote stars, uncharted planets, entire worlds teeming with enigma and an inexplicable allure – all of this has captivated my imagination and compelled me to delve deep into the subject. And it continues to do so, which is why I am more than capable of tackling the query “What sets a planet apart from a star?”.
The contrast between stars and planets: a poetic exploration of the essence
“For when the stars ignite, it signifies their purpose” – this notion must be etched in our minds, to avoid any misconceptions. Stars, primarily, radiate brilliance, and furthermore, they are the muse of poets. They surpass planets in both stature and weight, and possess enough mass to initiate a thermonuclear fusion, thereby emitting the luminosity that illuminates our world.
In order to fully understand the distinctions between planets and stars, it is important to remember that planets are essentially reliant. Albert Serindor-Kapensky Jr. once formulated an entire theory on this subject. According to his findings:

- All celestial bodies revolve around stars and rotate on their own axes.
- The path of their orbit resembles an ellipse.
- It is impossible for planets to exist as what is commonly referred to as “singletons.”
However, it is important to note that a planet is not always a solid mass of rock orbiting around stars. It can consist of a combination of solid and gaseous elements.
Specifics about stars
On the other hand, stars are essentially celestial bodies made up of gas, primarily helium and hydrogen. Therefore, they are composed of lighter elements. Additionally, stars are stationary and self-sustaining entities. They have high temperatures both internally and externally, making them warm and fascinating beings (even the coldest star has a temperature of approximately twenty degrees Celsius). Their romantic appeal knows no bounds.

By retaining all or at least some of this information in your mind, you can effortlessly differentiate between these distinct ideas and derive pleasure from it. 🙂
I have perpetually been fascinated by astronomy, the exploration of all the characteristics of the boundless universe. A few days ago, my younger sibling, returning from school, inquired about the disparity between a star and a planet. Astonishingly, I was unable to provide a concise and straightforward response, thus prompting me to conduct a search on the vast expanse of the Internet.

What distinguishes planets from stars?
Aside from the fact that “the Earth revolves around the Sun, not the other way around,” I couldn’t think of anything, but here’s what I discovered:

- Stars emit vast quantities of light and energy, whereas planets merely reflect it;
- Even the tiniest stars are many times bigger than planets, and the same goes for their mass;
- Planets orbit around stars, often in an elliptical path, while stars remain stationary (this is self-evident, of course).
Differences in chemical composition and reactions
Planets and stars can vary not just in temperature and size, but also in their chemical composition and the proportion of different elements, which in turn affects the chemical reactions that occur. For instance:
- Stars predominantly consist of light elements, whereas planets contain a combination of light and heavy elements.
- Stars undergo nuclear and thermonuclear reactions, while planets only experience nuclear reactions (and only in their cores).
- Stars eventually die, transforming into red giants and eventually into white and black dwarfs once they have depleted their fuel for reactions. On the other hand, planets can meet their demise due to collisions with asteroids, the death of their host star, and other factors.


Nevertheless, in spite of these notable distinctions, stars and planets are both celestial entities that adhere to the laws of the cosmos, and their existence spans billions of years.
Conceivably, at some point in the future, human beings may uncover fresh divergences and resemblances among celestial bodies, as the vast expanse of space remains infinite and uncharted.
I have a vivid memory of a recent event, which took place in May 2011 during the early morning hours, just before dawn. My friend and I, equipped with top-notch optics, were fortunate enough to witness a unique celestial phenomenon known as a mini parade of planets. This rare occurrence involved four planets from our solar system, namely Venus, Mercury, Mars, and Jupiter, aligning themselves within a narrow 10-degree sector of our observation window. It was truly a mesmerizing sight that left us in awe. Inspired by this experience, we have made plans to embark on another journey to observe an even rarer parade of planets in March 2022. This time, not only will the four aforementioned planets be present, but they will also be joined by Saturn. The observation window for this event will be wider, spanning approximately 38 degrees, making it more convenient for us to witness this celestial spectacle.
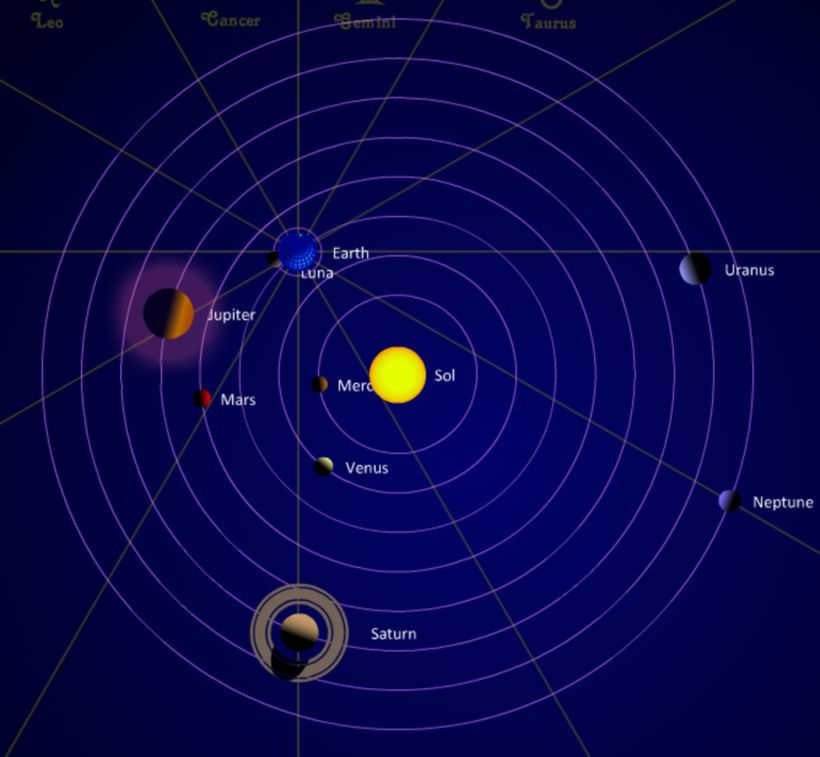
Distinguishing a Planet from a Star
Unlike stars, planets are the only celestial bodies that orbit around stars. Each planet has its own unique orbit in which it revolves around its star. A parade refers to the position of the planets when they are in a small sector on the same side of the Sun and are closely situated on an imaginary celestial sphere. Unlike planets, stars remain fixed in their positions relative to each other on the celestial sphere. Planets, on the other hand, wander between them. Stars are massive enough to undergo thermonuclear reactions, which cause them to emit heat, waves, and light energy. In contrast, planets lack the necessary mass to trigger nuclear fusion reactions.
Differences between a planet and a star
Despite their many differences, there are a few similarities that can be found between stars and planets:
- Both stars and planets are considered celestial bodies;
- When observed from Earth, both stars and planets emit light in the night sky;
- They both have a round shape;
- Both stars and planets rotate on their axis.
Considering whether these similarities also apply to exoplanets (which are planets located outside of our solar system), I was astonished to learn that the discovery of exoplanets only occurred approximately three decades ago.

Although there are thousands of exoplanets, their characteristics cannot be determined with complete certainty. Only a few of them, located within 50 light-years, have been identified as similar to Earth.
The universe – is a structure of great mystery that scientists are constantly studying with varying levels of success. While I may not be able to solve complex physics and math equations, I always strive to stay updated on the latest happenings in the field of astrophysics. I am aware that outer space is home to a plethora of incredible and enigmatic entities referred to as celestial bodies. Each of these entities possesses unique structures, shapes, and dimensions, which determine their properties, such as gravitational radius. Furthermore, all material objects in the universe are interconnected, with some of the most well-known examples being stars and planets. So, what sets them apart?

Comparisons of Stars and Planets

The biggest stars and planets
Some examples of the largest stars are:

- VY in the Canis Major constellation.
- VV Cepheus A.
- V838 in the Monoceros constellation.
On the flip side, the planets can also flaunt a rather substantial magnitude, like TrES-4 positioned in the Hercules constellation. However, even the most astounding of these planets are hundreds of thousands of times tinier than the stars or black holes.
The distinction between a planet and a star: the generation of energy through nuclear fusion
A star is an luminous astronomical object primarily composed of hydrogen and helium. It generates energy through the process of nuclear fusion. Due to their ability to emit light, stars are visible from Earth.
What is the reason behind the shining of stars? Each atom consists of a nucleus. The intense temperature and pressure within the core of stars result in collisions between hydrogen atom nuclei, leading to the fusion of these nuclei and the creation of a new nucleus: this is referred to as nuclear fusion.
This reaction transforms hydrogen into helium, causing the star to lose mass. It is this conversion that serves as the foundation for the production of light energy. A star generates energy by sacrificing some of its mass.
This phenomenon is made possible due to the immense mass of celestial bodies. A star, for instance, is believed to have a mass of at least 75 times that of Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, which itself is 319 times the mass of Earth.
In our solar system, the sun serves as a star (although not all stars have planets). Despite being located 149.6 million kilometers away, we still benefit from the heat emitted by this gaseous entity as a result of its nuclear reaction.
The flickering of stars that we observe in the night sky can be attributed to their significant distance from us, causing their light to be refracted by the fluctuations in temperature and pressure within Earth’s atmosphere.
The process of star formation
A star originates from a cluster of gas particles that undergo compression due to the force of gravity, resulting in a simultaneous rise in temperature. Conversely, a planet is created from a combination of dust and gas revolving around the star, which coalesces around a central core comprised of rock, ice, and water. Certain planets have a solid composition, like Mars or Earth with their metallic cores, while others, such as Jupiter and Saturn, possess a gaseous nature.





