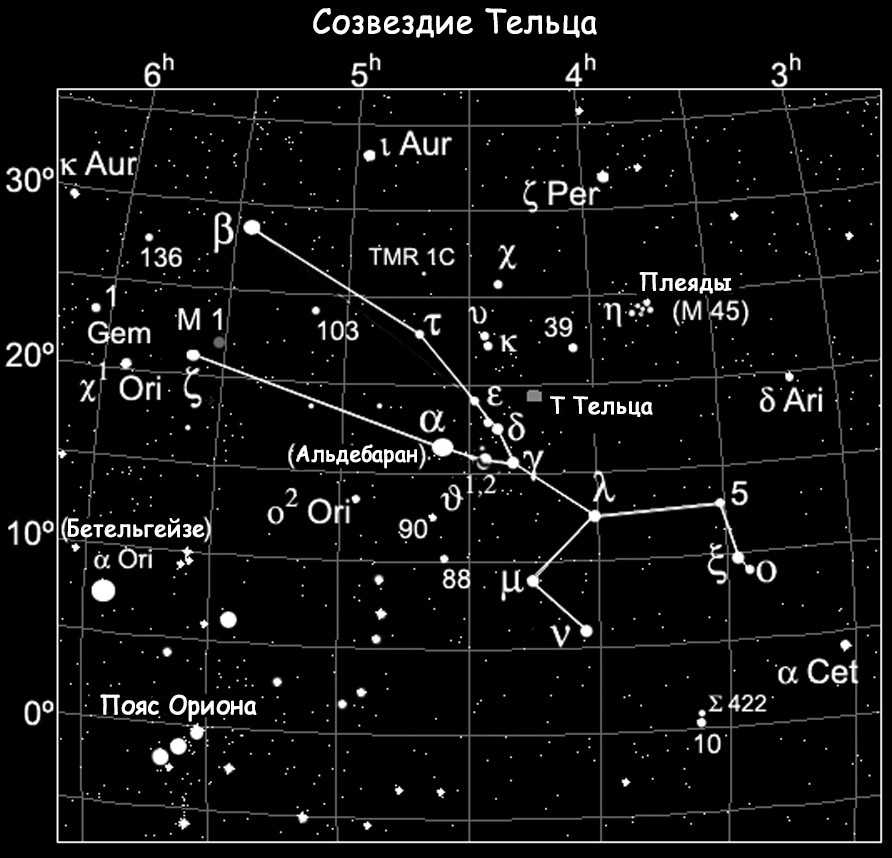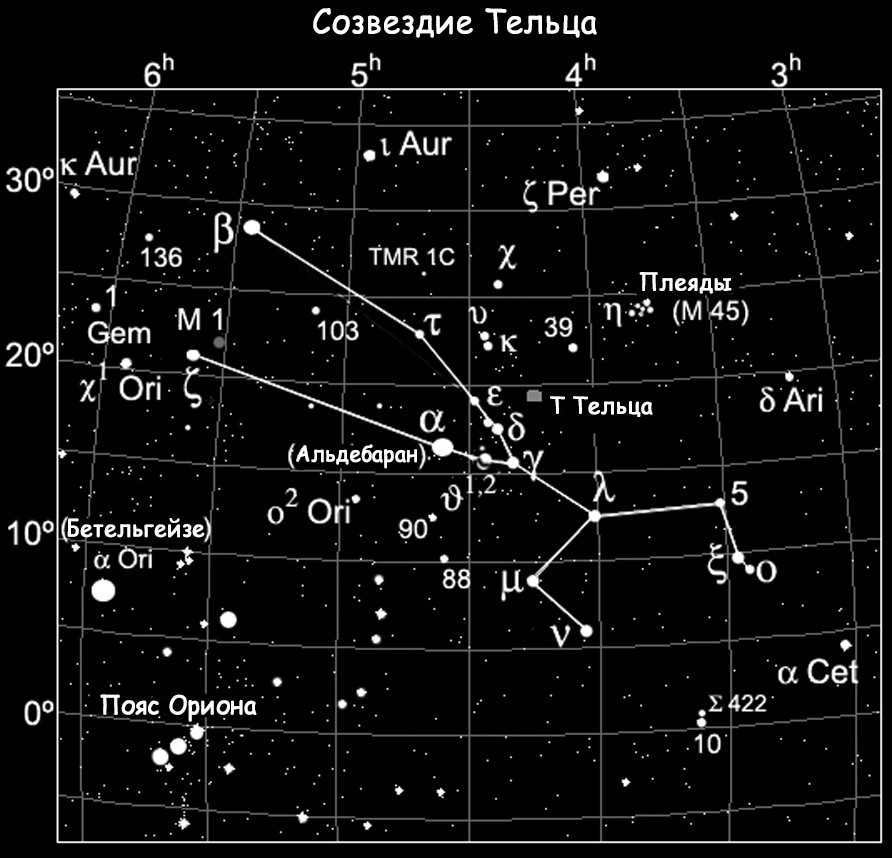
Taurus is one of the most star-rich constellations among the zodiacal constellations. Situated in the Northern Hemisphere, Taurus is most visible during the months of November to January.
The original bull in the celestial sky
It is incredible to think that without any optical instruments, one can observe a whopping 216 stars in this constellation. Taurus occupies almost 800 square degrees of the sky.
Take a look at the Taurus constellation in a planetarium program.
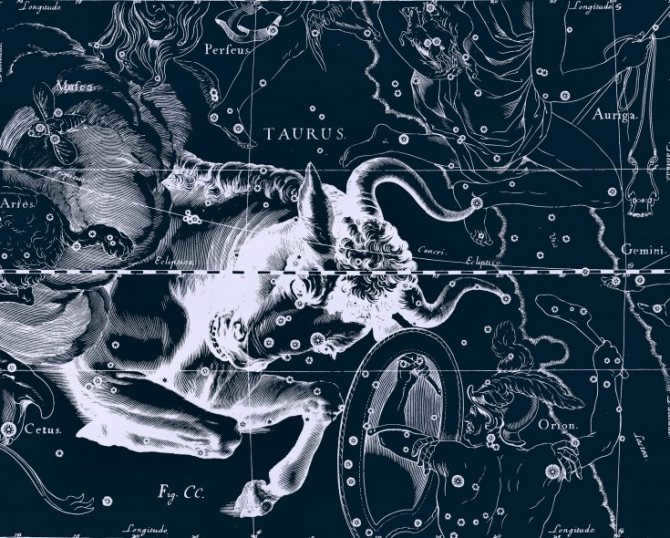
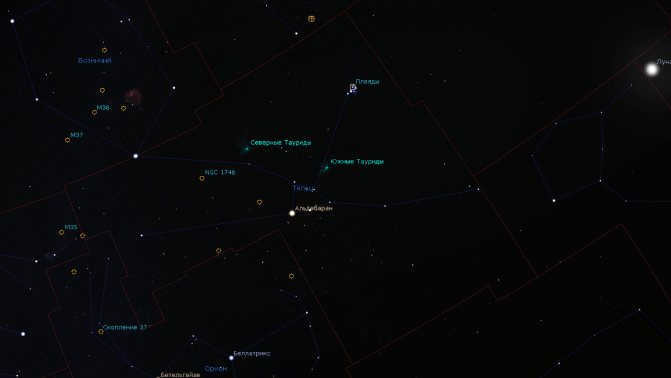
The constellation Taurus is situated between the constellations of Aries and Gemini, to the northwest of the constellation Orion, in terms of its territorial position. Taurus is also in close proximity to the constellations of Eridanus and Whale, Perseus and Ascendant. This particular constellation can be easily observed from various parts of Russia. It is visible for most parts of the year in the middle latitudes, with the exception of the latter part of spring and the initial part of summer. In terms of the Sun’s position within Taurus, it remains in this constellation from the middle of May (specifically the 14th) until the middle of June (specifically the 19th).
Star that will provide a significant advantage to the Sun
Image of Aldebaran, a star captured from the DSS catalog.
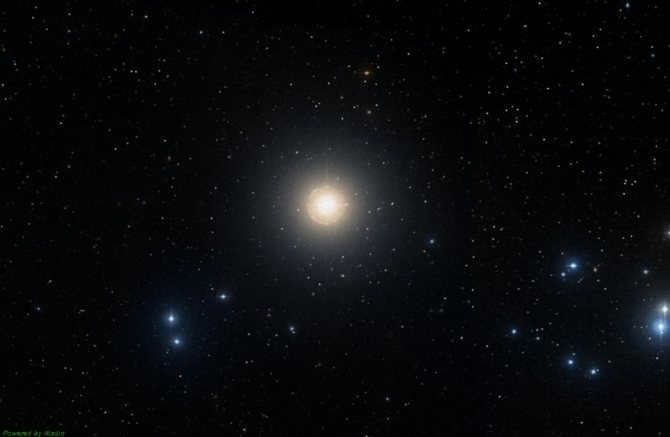
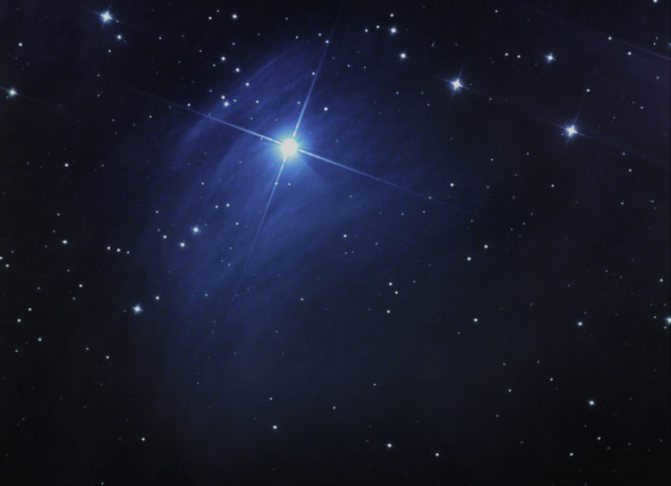
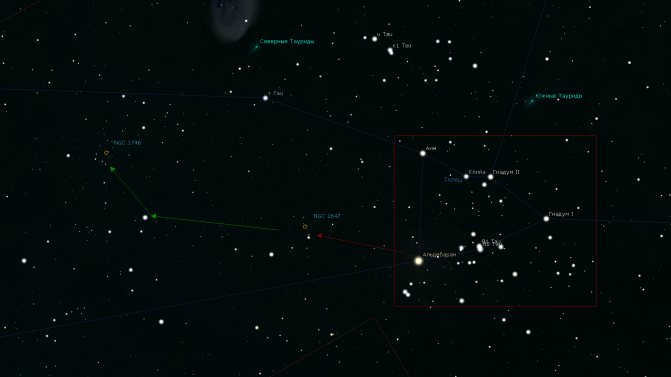
Aldebaran, the brightest star in the Taurus constellation and one of the brightest among all 12 zodiacal constellations, is known for its captivating name. This first magnitude (0.85m) alpha star of Taurus is highly visible in the night sky and is situated at the forefront of the constellation. It has been referred to as the “eye” of Taurus in the past. Other notable names for this celestial body include Lamparus and Palilius.
At present, Aldebaran is undergoing active helium burning, resulting in a growth in its size. Currently, the diameter of Taurus Alpha has expanded to 38 times that of our Sun. Aldebaran possesses a mass equivalent to 2.5 times that of our Sun and a luminosity 150 times greater than that of the Sun. Alpha Taurus is a star with variable luminosity, displaying irregular and minor fluctuations. The range of variation in stellar magnitude is a mere 0.2m.
Second brightest, second in the alphabet
Photograph Star Nat or Beta Taurus
Another luminous star in the Taurus constellation is the star Nat or beta Taurus, with a magnitude of second (1.65m). This star is often known as El-Nat, which translates to “bull’s horns” in Arabic. It is located very close to the Ascendant constellation. Ptolemy mentioned this star in his Almagest, as it was one of the few celestial objects that belonged to two different constellations simultaneously. In this case, both Taurus and Ascendant.
Nat’s star is classified as B7 III and is situated 131 light-years away from Earth. Beta Taurus is a binary star system, with its companion belonging to a different spectral class (B8) and located at an angular distance of 33 arc seconds from the primary star. The surface temperature of this star, which is undergoing a gradual transition into a giant, is 13600 K. In addition, El-Nat has a mass that is on average 4.5 times greater than the Sun, a luminosity that is 700 times higher, and a radius that is 5-6 times larger than the Sun.
This and Zeta “horned” constellation
Stars of the Pleiades scattered cluster
Taurus is intriguing due to the presence of two additional stars that have names starting with the same letter, thanks to the Latin alphabet. The first of these stars is known as Eta Taurus or Alcyone. This celestial body is part of a multiple star system, consisting of four components: A, B, C, and D. The primary component, Alcyone A, is classified as a Ve star. Its rapid rotation causes it to have an ellipsoidal shape rather than a spherical one. Alcyone A is classified as a blue-white giant and has a spectral class of B7IIIe. Its apparent magnitude is approximately 2.87m.
Zeta Taurus
Zeta Taurus is situated at a distance of 417 light-years from our planet. This binary system is also significant as it represents Ve stars in Alcyon A. Zeta Taurus has not been given a conventional name. It possesses a third stellar magnitude (2.97m) and falls into the B4IIIpe/G8III classification on the spectrum. As a bright blue-white giant in the zeta Taurus double system, it showcases an exceptionally strong luminosity that is approximately 5,700 times more powerful than that of the Sun.
Image of Zeta Taurus and the Crab Nebula
T Taurus
Photograph of T Taurus showcases its unique and captivating nature as a variable star located in the Taurus constellation.
Renowned for its variability, T Taurus serves as the quintessential example of T Taurus-type variable stars. This particular star is currently in its early evolutionary stage, as its stellar matter gradually precipitates from a slowly rotating circumstellar disk and condenses into a protostar at its core. Acting as the central component within a vast gas and dust cloud, this protostar possesses an immense mass of approximately 1000 solar masses, steadily contracting under the influence of its own gravitational force.
Scattered groups of stars in Taurus
Taurus constellation is home to two well-known scattered groups of celestial lights that have been observed since ancient times.
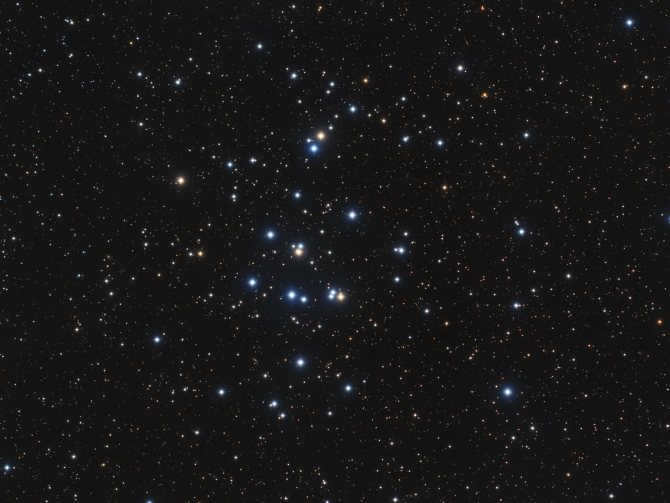
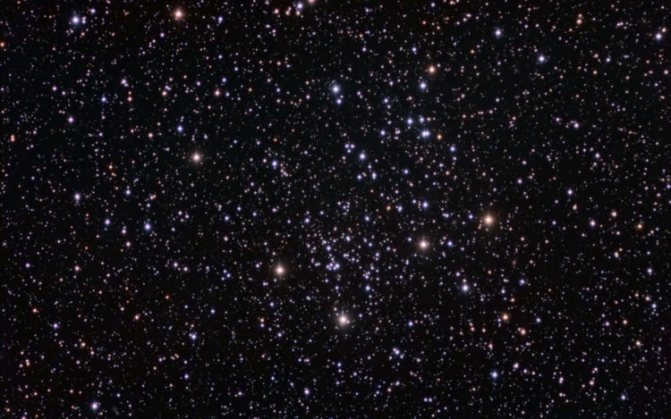
The Hyades
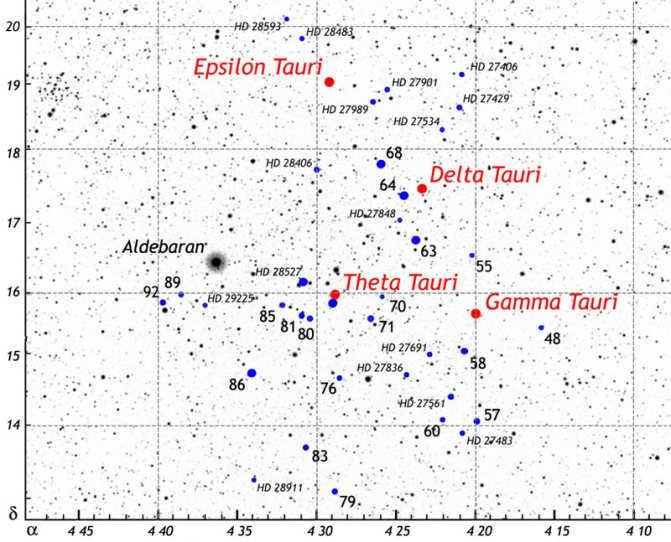
The first of these groups is called the Hyades. It can be easily spotted with the naked eye, as the brightest star in Taurus, Aldebaran, is situated in the most densely populated area of stars. The alpha star of the constellation is not part of the cluster itself, but is only projected onto it. In total, there are approximately two hundred stars in this constellation, with about four dozen considered to be the brightest.
The estimated size of the Hyades cluster is approximately 70 light-years, while its distance from Earth is 130 light-years. The cluster is thought to be around 620-650 million years old. The most luminous stars in the cluster are Epsilon, Gamma, Theta, and Delta Taurus.
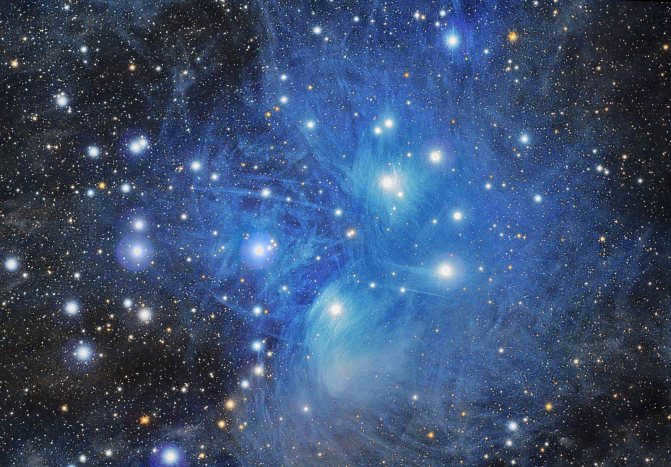
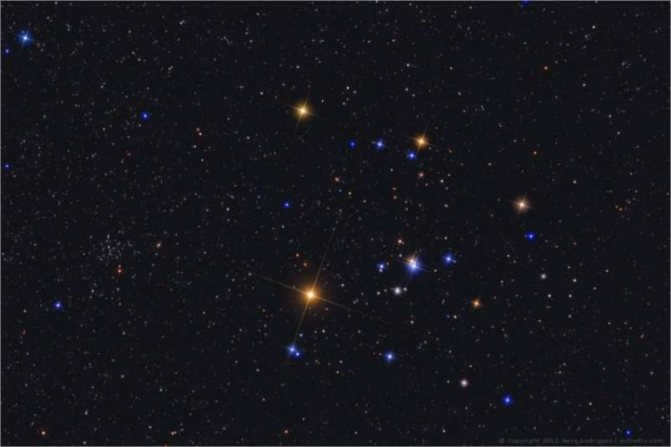
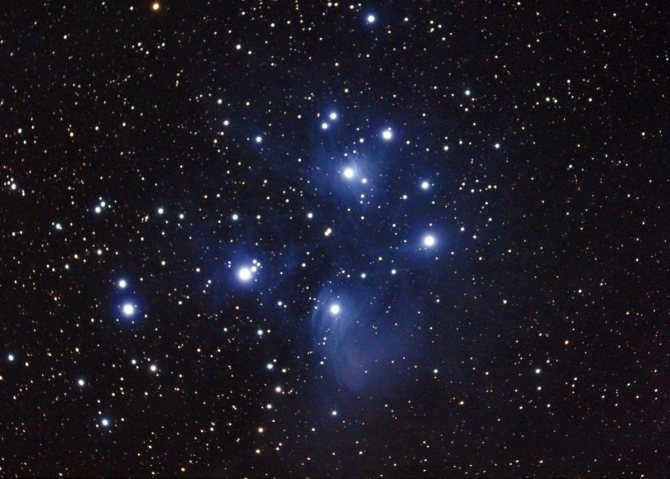
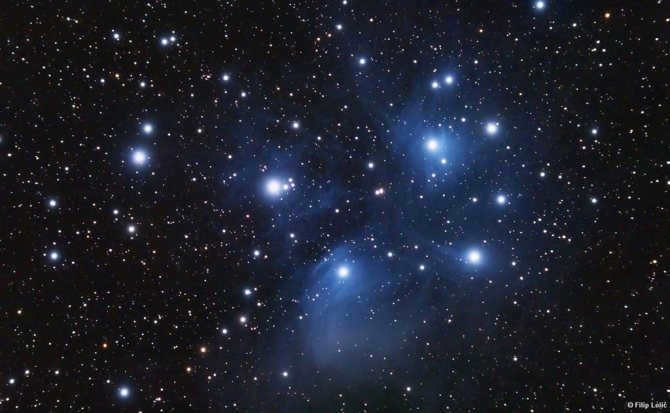
The Pleiades, also known as M45 in Messier’s catalog, is a fascinating cluster in Taurus. This cluster is easily visible in the night sky, even without binoculars, due to its abundance of hot and bright blue stars. Located approximately 440 light-years away from us, the Pleiades consists of around 1000 stellar bodies.
Its name derives from the nine brightest stars within the cluster, with seven named after the mythical Greek sisters (the Pleiades themselves) and the remaining two named after their parents. Scientific research has confirmed that the Pleiades are a physically connected group of stars, rather than a random assortment of stars in close proximity. These stars can be clearly observed in the winter months in the Northern Hemisphere and during summer in the Southern Hemisphere.
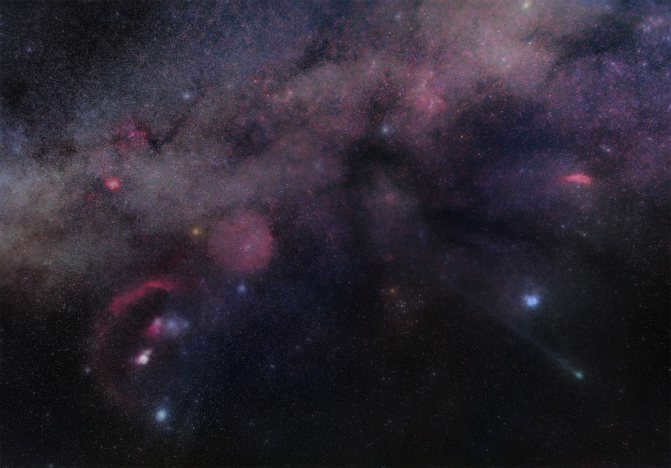
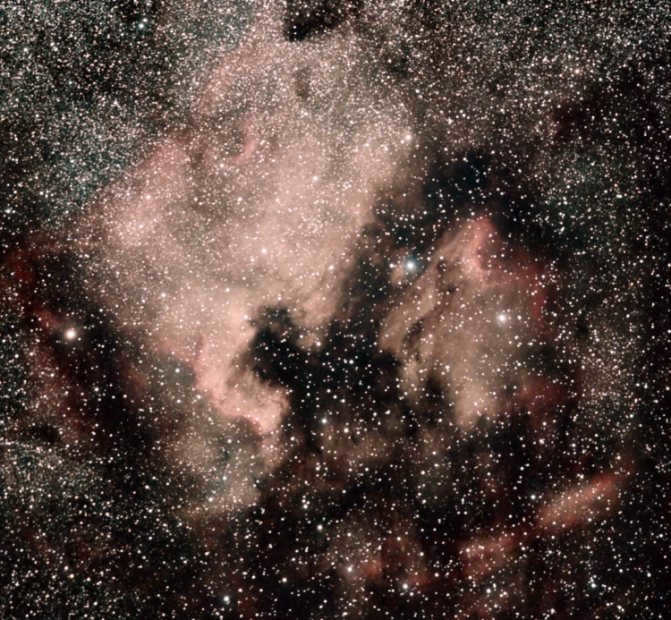
Crab Nebula
High-resolution photo of the famous Crab Nebula
An explosion of a supernova known as SN 1054 caused the creation of a colorful diffuse nebula in the night sky. This nebula is commonly referred to as the Crab Nebula and is listed as Messier object M1 in astronomical catalogs.
Photo of the Crab Nebula M1
The discovery of this nebula dates back to 1731. It is located approximately 6500 light-years away from Earth. Currently, its diameter is around 11 light-years, and it continues to expand at a rate of about 1500 kilometers per second. The nebula is also known as a pulsar due to the presence of a pulsar at its center. The pulsar is a neutron star that emits radio waves, gamma rays, and stellar wind as it rotates, providing sustenance to the entire nebula.
Background
The history of Taurus constellation can be traced back to ancient times. It is believed to have been observed by mathematician Eudoxus, who lived prior to the start of our era. However, it is more likely that he was simply the first to document the constellation. Taurus is also included in the Almagest catalog by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy. According to Greek mythology, Taurus represents the bull that Zeus transformed into to abduct Europe. Zeus transported the goddess across the sea to the Greek island of Crete.
- Constellations
Taurus is a constellation of the zodiac located between Gemini and Aries, situated to the northwest of Orion. The most prominent stars in Taurus include Aldebaran (with an apparent sidereal magnitude of 0.87), Nat (1.65), Alcyone (2.85), and ζ of Taurus (2.97). Within the Taurus constellation, you can find the scattered star clusters known as the Hyades and Pleiades, as well as the Crab Nebula which contains the pulsar PSR B0531+21.
Even without the aid of optical instruments, the human eye can observe up to 216 stars within this constellation. In the night sky, Taurus spans across an area of 800 square degrees.
The Taurus constellation: debunking the myth

The constellation Taurus has a long history and is mentioned in ancient Greek mythology. According to the Greeks, it was attributed to Eudoxus, although he may have only been the first to describe it. The constellation is also included in Claudius Ptolemy’s Almagest catalog of the starry sky.
According to ancient Greek myth, Taurus represents Zeus, who transformed into a white bull in order to abduct Europa and take her to the island of Crete. Another version of the myth suggests that Taurus symbolizes the Cretan bull defeated by Hercules during his seventh labor, which may be the same bull that Zeus transformed into. It is said that after the bull’s defeat, it was immortalized as a constellation. There is also a version of the myth that connects the name Taurus to the ferocious fire-breathing bulls that Jason tamed in Colchis.
The Pleiades derive their name from Greek mythology, specifically from the Pleiades, who were the daughters of the titan Atlanteus and the oceanid Pleione. Their names are Alcyone, Sterope, Maia, Merope, Taygeta, Keleno, and Electra. These sisters were taken to heaven by Zeus, who saved them from Orion’s pursuit. On the other hand, the Hyades are the daughters of Atlanteus and Ephra, making them half-sisters to the Pleiades. Zeus transformed them into the asterism known as the Hyades in honor of their love for their brother Gias, who died sorrowfully after his demise during a hunt. This particular interpretation of their myth is a result of folk etymology, as the name “Hyades” means “it’s raining” in ancient Greek. The Hyades, located low above the horizon in the Greek sky during the rainy season, were seen as a sign of inclement weather. In ancient astronomy, both the Pleiades and sometimes the Hyades were regarded as independent constellations.
In the ancient Slavic religion, the Pleiades star cluster found in this constellation was linked to the deity Veles, who was worshipped as the god of livestock. The Latin name for this constellation, Taurus, has a similarity to the Russian word “tur,” which refers to a wild bull. Nonetheless, it is now commonly known as Taurus in Russian.
The primary stars of the Taurus constellation
A celestial body that will provide numerous advantages to the Sun

The brightest star in the constellation Taurus, and indeed the brightest among all 12 zodiac constellations, goes by the beautiful name of Aldebaran. Aldebaran is the alpha star of Taurus, with a magnitude of 0.85m, and is one of the most easily visible stars in the entire night sky. Situated at the head of the constellation, it was often referred to as the “eye” of Taurus in the past. Other well-known names for this celestial body include Lamparus and Palilius.
Aldebaran is classified as a K5 III star and falls into the category of normal giants, boasting an orange hue. Orbiting around this star at a distance of several hundred astronomical units is a companion star, which happens to be a red dwarf of the M2 class. The distance between Aldebaran and our planet is estimated to be around 65 light years.
Presently, Aldebaran is undergoing active helium burning, resulting in its size expanding. At present, Taurus Alpha has enlarged its diameter to 38 times that of the Sun. Aldebaran possesses a mass equivalent to 2.5 solar masses and a luminosity 150 times greater than that of the Sun. Alpha Taurus is a variable star with an irregular and minor fluctuation in brightness. The range of luminosity variation in stellar magnitude is merely 0.2m.
Second brightest, second in the alphabet
El-Nat, also known as Beta Taurus, is the second brightest star in the constellation of Taurus with a magnitude of 1.65m. Its name, El-Nat, comes from Arabic and means “bull’s horns”. This star is located very close to the constellation of Ascendant. Ptolemy mentioned El-Nat in his Almagest, noting that it is one of the few stars that belongs to both Taurus and Ascendant simultaneously.
Nat’s star is classified as a B7 III and is situated 131 light years from Earth. Beta Taurus is a binary star system, with its companion belonging to a different class (B8) and being separated from the primary star by an angular distance of 33 arcseconds. The surface temperature of this slowly evolving giant luminary is 13600 K. El-Nat’s mass is, on average, 4.5 times greater than the Sun’s, its luminosity is 700 times higher, and its radius is 5-6 times larger than that of the Sun.
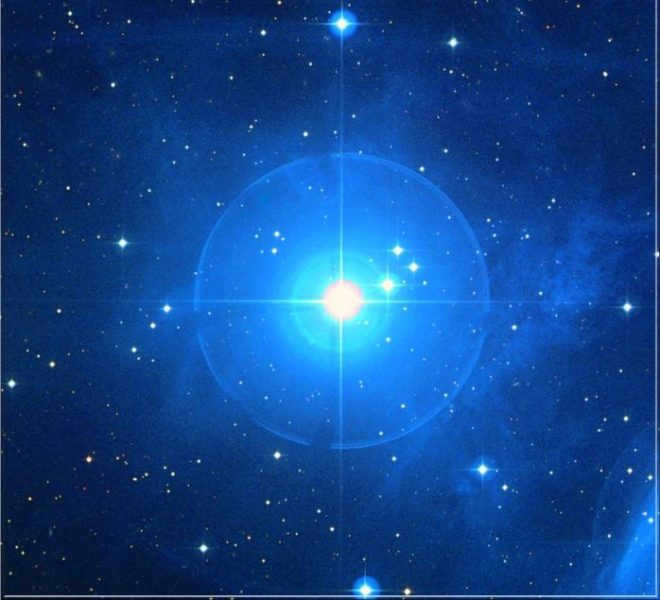

Taurus is fascinating because it has two more stars with consonant names, thanks to the Latin alphabet. The first of these stars is also known as Taurus or Alcyone. This particular star is part of a multiple star system and consists of four components: A, B, C, and D. The first component, Alcyone A, is a Ve-star. Due to its rapid rotation, its shape is not spherical but ellipsoidal. Alcyone A is classified as a blue-white giant and has a spectral class of B7IIIe. Its apparent stellar magnitude is approximately 2.87m.
Stars B and C in the Zeta Taurus system belong to the main-sequence category A0. Star B has a stellar magnitude of 6, while star C has a stellar magnitude of 8. The third star in the system, Alcyone C, is a variable star that undergoes changes in luminosity of approximately 0.05m every 1.5 hours. The final star, Alcyone D, is a white-yellow dwarf of spectral class F2. It has an apparent stellar magnitude of 8.7m. With the use of a telescope, all four stars in the Zeta Taurus system can be easily observed.
Zeta Taurus
Zeta Taurus can be found 417 light-years away from our location. This binary star system also serves as a representative example of Ve stars within the Alcyon A constellation. Zeta Taurus does not possess a traditional name. It possesses a stellar magnitude of 2.97m and is classified as a B4IIIpe/G8III based on its spectrum. Taurus is a vibrant blue-white giant within the double star system of zeta Taurus, and it possesses an exceptionally powerful luminosity that is approximately 5,700 times stronger than that of the Sun.
Taurus
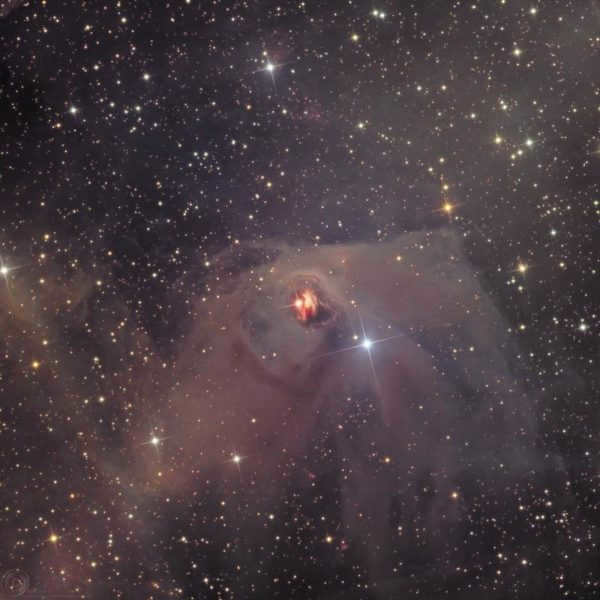

T Tauri-type variable stars are represented by a renowned variable star that serves as their prototype. This particular star is currently in the early stages of its evolution, as its stellar material gradually settles from a circumstellar disk with a slow rotation, eventually forming a star. Within its core, hydrogen condenses and transforms into a protostar. The protostar acts as the central component of an immense cloud composed of gas and dust, boasting a mass equivalent to approximately 1000 solar masses. As time progresses, this massive cloud gradually shrinks due to the force of its own gravity.
119 Taurus
This star, known as 119 Taurus, is a red supergiant classified as M2Iab-Ib. It has a visual magnitude of 4.32 and is located approximately 1,802 light-years away. Its diameter is a staggering 600 times larger than that of the Sun. With a color index of 2.07, it is recognized as one of the most prominent red stars in the sky.
119 Taurus exhibits a semi-regular variability, with its brightness ranging from 4.23 to 4.54 over a period of 165 days. Due to its proximity to the ecliptic, it is occasionally obscured by the Moon and other planets.
Ro Taurus
Ro Taurus is a white main-sequence star (A8V) located at a distance of 152 light-years. It has a visual magnitude of 4.65 and surpasses the mass of the Sun by a factor of 1.88. The star has a fast rotational velocity of 117 km/s and completes one rotation every 488.5 days. Additionally, Ro Taurus is classified as a Delta Shield type variable star, exhibiting a brightness fluctuation of 0.01 magnitude approximately every 1.61 hours.
A binary system containing two main-sequence stars, F8 V and K5 V, that emits X-ray radiation. It has a combined apparent magnitude of 5.1149 and is located 46.9 light-years away.
Omicron Taurus
This astronomical object, known as Omicron Taurus, is a giant star of spectral type G6 III Fe-1. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.61 and is situated at a distance of 212 light-years. Omicron Taurus is a double star with an orbital period of 1655 days, and it completes one axial revolution every 533 days. It has a radius 18 times that of our Sun, a mass three times greater, and is 155 times brighter.
Atlas (27 Taurus)
This particular star is a triple star system, known for its visual magnitude of 3.62 and its location at a distance of 381 light-years. Its name, Atlas, was inspired by Titan, who was the father of the Pleiades. The primary object in this system is a blue-white giant (B8 III). It is a spectroscopic double system, consisting of two components with visual magnitudes of 4.1 and 5.6 respectively. The orbital period of this system is approximately 1250 days. Additionally, there is also a faint companion located at 0.4 angular seconds, with an apparent magnitude of 6.8.
Electra
Electra, also known as 17 Taurus, is a massive blue-white giant star located in the Taurus constellation. With an apparent visual magnitude of 3.705, it is the third brightest star in its cluster. Situated approximately 600 light-years away from Earth, Electra exhibits a rapid rotation rate of 181 km/s, causing it to flatten at the poles and stretch at the equator. This unique characteristic gives the star its distinct shape. Furthermore, Electra emits a noticeable excess of radiation in the infrared spectrum, indicating the presence of a gas disk surrounding it. This disk is believed to have formed as a result of mass loss caused by the star’s high rotation rate. It is worth noting that Electra occasionally appears to be overlapped by the Moon and planets, adding to its celestial allure.
Maya
Maya, also known as 20 Taurus, is a massive blue giant star (B8III) located approximately 360 light-years away. With a visual magnitude of 3.871, it shines brightly in the night sky. This star is a part of the stunning Maya Nebula, officially known as NGC 1432.
Maya is an intriguing celestial object due to its unique chemical composition. It is classified as a mercury-manganese star, which means it contains high levels of mercury and manganese elements. This composition is evident in its prominent spectral line caused by the absorption of ionized mercury. In terms of size and brightness, Maya surpasses our Sun by a significant margin. It has a mass four times greater than that of the Sun, a radius 5.5 times larger, and shines 660 times brighter.
Merope
Merope is the name of a star in the constellation of Pleiades. It is one of the seven sisters in Greek mythology. Merope is also the name of a character in the Harry Potter series, who is one of the Black sisters. She is the only one of the sisters who is not a member of the Death Eaters. In astronomy, Merope is classified as a B6e star, which means it is a blue star with emission lines.
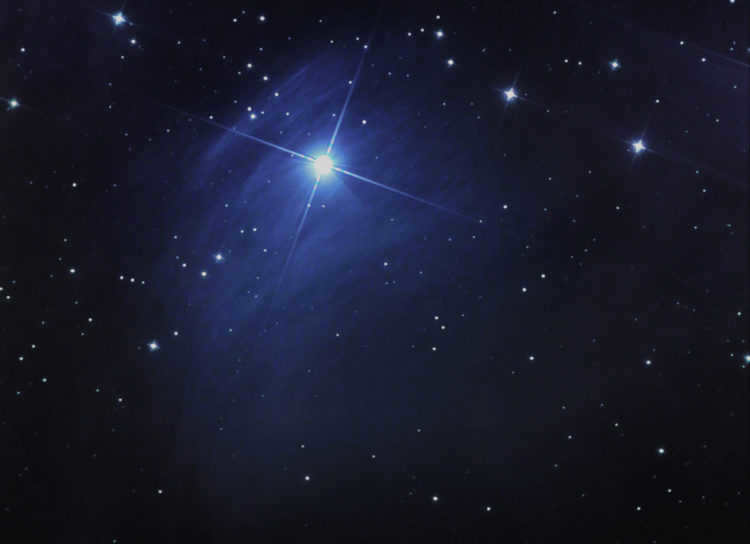

It is a blue-white subgiant (B6IVe) with a visual magnitude of 4.113 and a distance of 360 light-years. It has a mass of 4.5 times that of the Sun, is 4 times larger in size, and shines 630 times brighter. This star has the characteristics of a Beta Cepheus-type variable, with its brightness fluctuating by 0.01 magnitude. It is situated in the midst of the Merope Nebula, which surrounds it. Currently, the Pleiades cluster is passing through this nebula.
Taygeta
Taygeta, also known as 19 Taurus, is a remarkable triple star system located approximately 440 light-years away. With an apparent visual magnitude of 4.30, Taygeta shines brightly in the night sky. The main star, known as A, is a fascinating spectroscopic double star. It is classified as a blue-white subgiant of spectral type B6IV. The components of this double star have magnitudes of 4.6 and 6.1, and they are separated by a mere 0.012 arc seconds. Remarkably, this double star has an orbital period of 1313 days. Additionally, Taygeta has a companion star with a magnitude of 8, which is separated from the main star by 69 angular seconds.
Pleione
This particular celestial object is known as Pleione, and it is classified as a double star with a visual magnitude of 5.048. Located at a distance of 392 light-years, Pleione is in close proximity to the bright Atlas, making it challenging to observe directly.
Pleione is categorized as a hot B-class star and is considered a classical Ve star due to the presence of hydrogen emission lines in its spectrum. It shines with a brightness that is 190 times greater than that of our Sun. Additionally, Pleione is a variable star, similar to Gamma Cassiopeia, experiencing fluctuations in brightness from 4.8 to 5.5.
Celeno
Celeno, also known as 16 Taurus, is a subgiant star (B7IV) with a striking blue-white color. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.448 and is located approximately 430 light-years away from Earth. This star is often referred to as the “Lost Pleiades” due to its difficulty in being located. Celeno is an impressive star that is four times larger than our own sun, and it has a rotational speed that can reach up to – 185 km/s.
There are two stars that are 0.04° apart and are situated 440 light years away from us. One of them is 21 Taurus, which is classified as a main-sequence dwarf (B8 V) and has an apparent magnitude of 5.76. The other star is 22 Taurus, also a main-sequence dwarf (A0Vn), with an apparent magnitude of 6.43.
The constellation Taurus offers a variety of intriguing celestial objects to observe
The Hyades: A Cluster of Stars Dispersed Across the Sky
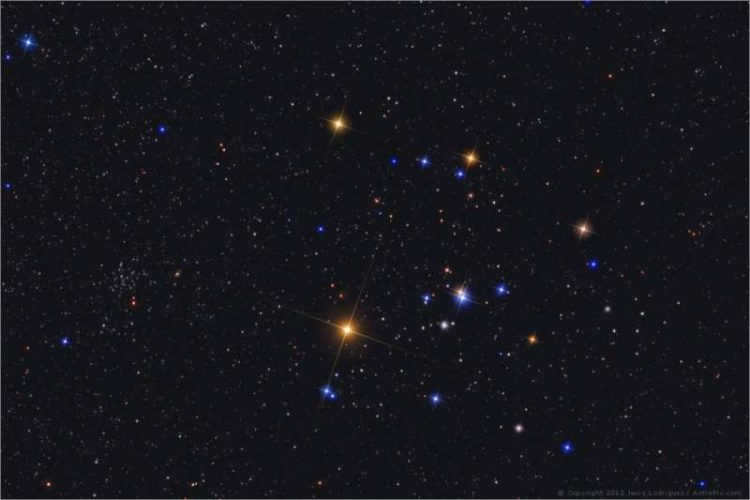

The Hyades is a massive star cluster spanning an area of 8° in the night sky. It is home to approximately 200 stars and is located about 150 light-years away from the Sun. The Hyades is recognized as the nearest dispersed star cluster to our solar system. Interestingly, the bright star Aldebaran is not physically associated with the Hyades, but happens to be in close proximity to it, much to the delight of stargazers. What’s unique about the Hyades is that it does not have any other official name in astronomical catalogs and has not been assigned an ordinal number. The Hyades often make appearances in science fiction literature, with spacecrafts passing through the cluster or the plot unfolding on one of its planets.
To observe the Hyades, no specialized astronomical equipment is necessary. In some cases, binoculars can be useful for studying specific regions within the cluster in greater detail.
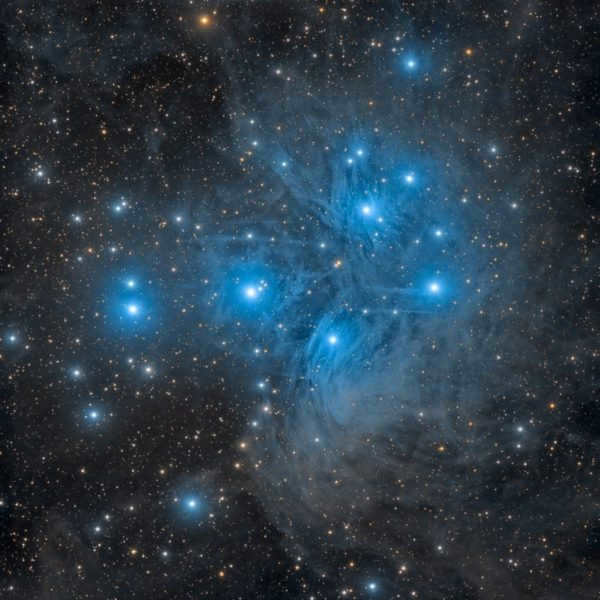

It may be difficult to come across someone who has any fascination with astronomy and has not yet laid eyes on this magnificent star cluster. This cluster is easily visible to the naked eye, resembling a small bucket filled with seven radiant stars. This is why it is commonly referred to as the Seven Sisters, or M 45. A plethora of information about this scattered cluster can be found across various sources on the internet, so there is no need to reiterate it all. It is worth mentioning, however, that the cluster is comprised of approximately 400-500 stars and spans an area slightly larger than 1.8 degrees in the sky. It is located at a distance of 407 light years from the Sun. This cluster is relatively young, with an age not exceeding 50 million years. The majority of its stars are intensely hot and blue, falling into the B5 spectral class.
The cluster M 45 is encompassed by a nebula that reflects the light of the stars within. This phenomenon is easily observable with a telescope set at low magnifications, provided that one has a wide-angle eyepiece and is fortunate enough to have an impeccably dark sky. Locating the Pleiades cluster is a simple task; one need only refer to the overview of the Taurus constellation depicted above. From the vantage point of Aldebaran, there is a splendid perspective of this celestial “bucket”.
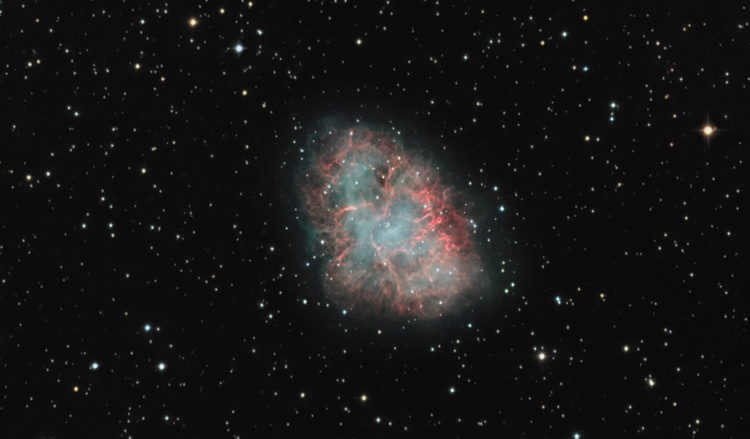

M 1 is a remarkable instance of a supernova star that burst in 1054. This nebula is situated approximately 9-10 light years away from the Sun. Positioned at the core of the nebula is a pulsar known as NP 0532, which has a pulsation period of 0.033 seconds. In the visible spectrum, the pulsar exhibits a luminosity ranging from 14.4 to 17.7 m. The linear dimensions of M 1 are roughly 6 × 4′, with a brightness of 8.4 m. Nevertheless, don’t expect it to be an easy target, as this object harbors numerous secrets and may prove elusive to first-time observers. To spot it, you’ll need a clear sky, devoid of city lights and moonlight. It’s relatively simple to locate the star ζ (zeta) Taurus and then raise your telescope slightly higher.
A duo of dispersed star clusters NGC 1807 and NGC 1817
A pair of compact, luminous, stunning dispersed star clusters NGC 1807 and NGC 1817 can be observed with the naked eye under optimal weather conditions, and when using binoculars, both can be simultaneously seen in the same field of view. The first cluster covers an area of 17′ and has a magnitude of 7 m, while the second cluster spans 16′ in the sky and possesses a brightness of 7.7 m. It is situated on the boundary with the Orion constellation and can be easily located using nearby prominent stars.
NGC 1514: An Extraordinary Planetary Nebula

NGC 1514 is known as the “Crystal Ball” in the Taurus constellation. Despite its small size (1.54′) and low brightness (10 m), this nebula is located in the northern part of the constellation, near the foot of Perseus, at a distance of 800 light-years from the Sun. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1790. You can observe this “planetary” nebula using a telescope in two different ways: either start from the Pleda cluster or from the star ζ Perseus, which has a brightness of 2.8 m. The map below shows the arrows that indicate the path to the target. In a 150 mm telescope, NGC 1514 will appear as a small cloudy spot with a noticeable bright center. In a 250 mm telescope, under favorable weather conditions, you will be able to observe variations in brightness and blurred contours of the nebula.
An unfilled dispersed group of stars, known as NGC 1647, contains slightly more than 150 stars and has a combined surface brightness measurement of 6.4 m. It spans an angular size of 45′. Due to its close proximity to other stars, it is unlikely to be visible to the naked eye. However, it can be easily located with binoculars, even by beginners. To find NGC 1647, simply shift your view to the left side from the Hyades (or the star Aldebaran).
NGC 1746 is an example of a scattered star cluster.
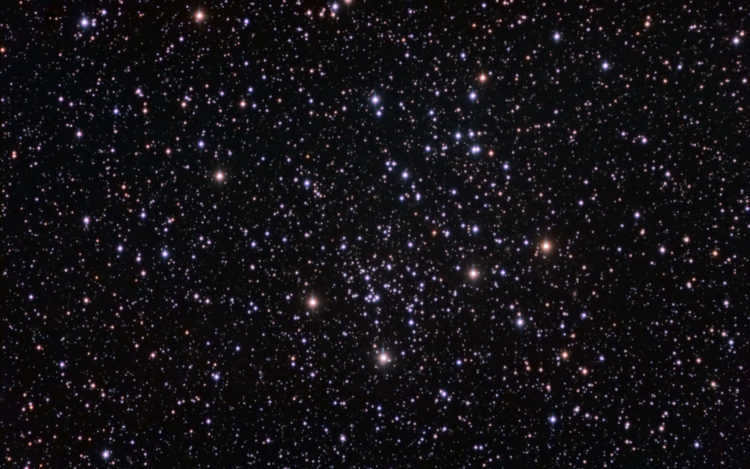

When it comes to luminosity and size, NGC 1746 is on par with the previous cluster. It consists of approximately 200 stars, with a few standout ones that adorn its perimeter, giving the cluster a memorable appearance. If we continue in a straight trajectory from the Hyades, passing through NGC 1647, we will eventually encounter NGC 1746.
Double star 118 Tau.
A binary system, known as 118 Tau, consists of two stars with a combined luminosity of 6.7 m. These two stars have individual luminosities of 6.6 m and 5.8 m, respectively. The angular separation between them is very small, measuring less than 5″. Using a basic binocular or telescope will not be sufficient to distinguish the two stars, but with a 150mm instrument and a magnification of 100+, it becomes feasible to resolve the double star into its individual components.
How can we locate Taurus in the celestial sphere?
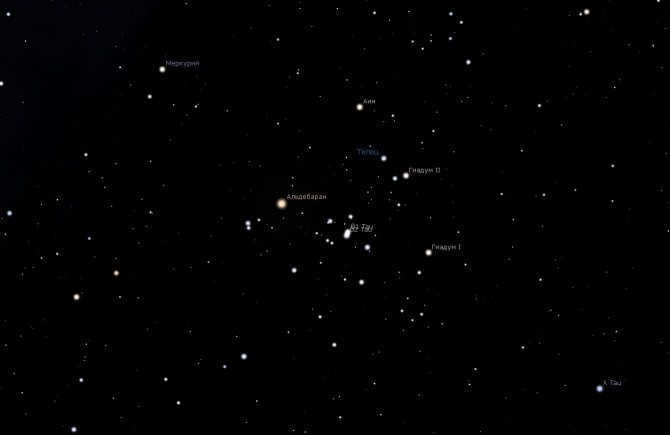
Finding the Taurus constellation in the sky is a relatively simple task. Taurus is positioned at a high altitude and is easily visible all across Russia, although the optimal viewing conditions are in November and December. A useful guide for identification is the prominent “fiery ladle” formed by the Pleiades star cluster, along with the reddish-orange Aldebaran. Towards the east, one can spot the bright Gemini constellation, while to the south, the distinctive pattern of Orion becomes visible. Taurus also shares its borders with the “circlet” of Perseus to the north, as well as Aries and Whale towards the west. The Sun enters the Taurus constellation on May 11.
Remember this – SPIRITUAL HORROR Remember this – SPIRITUAL HORROR In case you have an interest in .
DO NOT FORGET THE SPIRITUAL Pride Who is this genius of provincial thought, who declared: &.
The Word That Ruins Relationships There are numerous individuals around us with whom we.
"There are no champions in this situation". Alexander Lukashenko talked about the incidents in Russia and their impact.
June 22, 1941. The initial hours of the Great Patriotic War: sequence of events. .
–Photo album
 The series of photos titled Slutsk Spring was taken at 12:09 on 06 March 2023. There are a total of 10 photos in the series.
The series of photos titled Slutsk Spring was taken at 12:09 on 06 March 2023. There are a total of 10 photos in the series.  The series of photos called Flowers was captured at 10:18 on 12 October 2021. It consists of 12 photos.
The series of photos called Flowers was captured at 10:18 on 12 October 2021. It consists of 12 photos.  The series of photos named Winter Fairy Tale was taken at 22:26 on 19 January 2020. It includes 7 photos.
The series of photos named Winter Fairy Tale was taken at 22:26 on 19 January 2020. It includes 7 photos.
–Latest News
–Exciting Applications
- PostcardsA brand new collection of postcards for all occasions
- I am a photographerA plugin for sharing and showcasing your photos in your diary. Minimum system requirements: Internet Explorer 6, Fire Fox 1.5, Opera 9.5, Safari 3.1.1 with JavaScript enabled. It should work smoothly
- Music player
- VocabularyThis application displays the 100 most frequently used words in your diary or your friends’ diaries as a word cloud. Each word is a clickable link that allows you to search for that word in your diary
- Yandex.blogs rating buttonsAdds Yandex rating buttons to your profile. Additionally, there will be graphs showing the rating changes per month in the near future
–Search by journal
–Subscribe via email
–Areas of interest
The Taurus constellation in the fields of astronomy, astrology, and mythology
After discussing the previous zodiac sign, Pisces, and the first one, Aries, it is now time to focus on the next sign, which follows Aries. This sign is Taurus, and it spans from April 21 to May 20.
Before we begin, let’s discuss the distinction between astronomical constellations, which vary in size, and astrological signs, which are all 30 degrees in extent.
An astronomical constellation is a designated grouping of stars (in 1922, the International Astronomical Union identified 88 constellations on the Celestial Atlas, with 13 located along the ecliptic in the same sequence as the zodiac signs:
12 zodiac signs.
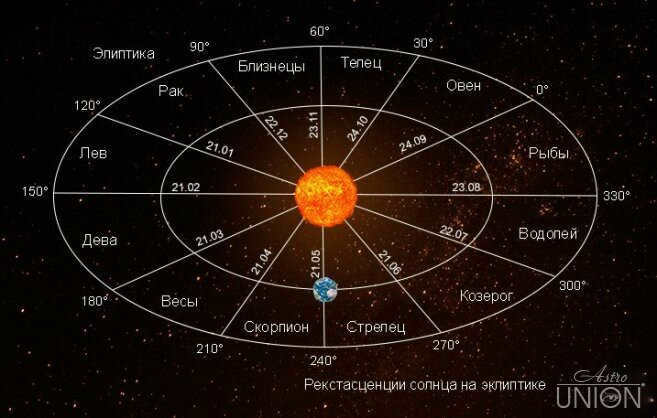
Astrology divides the ecliptic, which is the plane of the Earth’s orbit, into 12 sectors of 30 degrees each. The point of the vernal equinox, which shifts by about 50 seconds every year in the opposite direction of the zodiacal signs due to the precessional movement of the Earth, serves as the origin of coordinates. These 12 sectors are named “Aries” to “Pisces” and together form the Tropical Zodiac, which is used in classical Western astrology.
About Taurus Astronomical:
Located in the northwestern region of Orion and situated between Gemini and Aries, the Taurus constellation encompasses an area of 797.2 square degrees in the celestial realm. It boasts a multitude of over two hundred stars that are visible to the naked eye. The most brilliant among them is known as the Eye of the Wolf, or Aldebaran, a name derived from the Arabic word meaning “following.” This name references its motion behind a star cluster called the Pleiades, which is also referred to as Stozhary in Russian tradition.
The Pleiades cluster is engulfed in a cloud of cosmic dust and resides within the vastness of space. It spans several lunar disks and is situated approximately 400 light years away from Earth, with a length of only 13 light years.
Aldebaran is classified as a giant star, and its immense size is truly remarkable. To put it in perspective, the diameter of this “eye” is 38 times larger than that of the Sun, despite being located at a distance of 65 light years away from Earth. Furthermore, its luminosity surpasses that of our Sun by 150 times. Surrounding Aldebaran are 200 dazzling “beads” that form another star cluster, known as the Hyades, which depict the face of the bull. The Hyades are situated 132 light years away from Earth.
That reminds me:
There is a star called Janetta that is white in color.
If one were to travel at the speed of light, it would take ten years to reach it.
If one were to travel at the speed of light
♪ There is also a star called Janetta that is blue in color ♪
If one were to travel at the speed of light
It is located a hundred years away
If one were to travel at the speed of light
So, which star should you and I choose to fly to?
The white one or the blue one?
The most well-known “landmark” in Taurus is the Crab Nebula, which is the leftover of a supernova explosion in 1054. Interestingly, it was initially detected by J. Bavis in 1731 and later by Messier in 1758. Experts state that the diameter of the nebula expands by 80 million kilometers every day, which is quite challenging for ordinary individuals to comprehend. Moreover, the Crab Nebula emits powerful radio and X-ray waves. At its core, you’ll find the pulsar PSR B0531+21, which emits electromagnetic pulses with remarkable regularity. This pulsar is one of the earliest neutron stars identified by astronomers.
Taurus also features a nebula with the enigmatic name Ghost, as well as another nebula known by multiple names – Hinda, Variable Hinda, and Struve’s Lost Nebula.

The star Elnath (known as the Kicker in Arabic) also possesses alternative names, such as the “Ankle of the Holder of the Leash” (referring to the Ascendant). Consequently, it appears to have dual designations: in Taurus and in the Ascendant. Ptolemy even described it as “the star located at the end of the northern horn, which is identical to the star found on the right foot of the Ascendant”. Additionally, the Ruby Star is renowned for being one of the reddest stars. The only star that surpasses it in terms of redness is the Garnet Star of Cepheus.
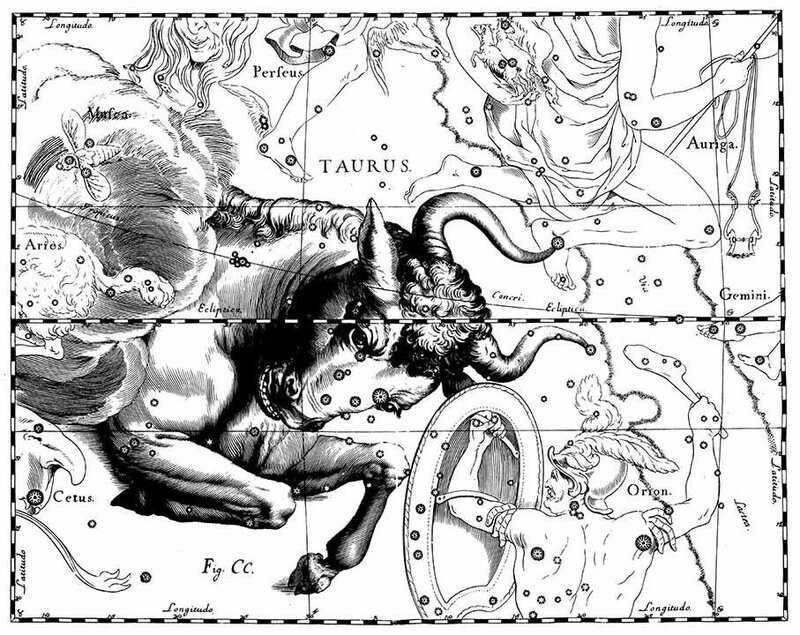
About the legendary Taurus:
The prevalent account of the inception of this extraordinary constellation is connected to the deity Zeus, who developed strong affection for the stunning Europa. To abduct her, he assumed the form of a bull and carried the beloved on his bovine spine to the island of Crete.
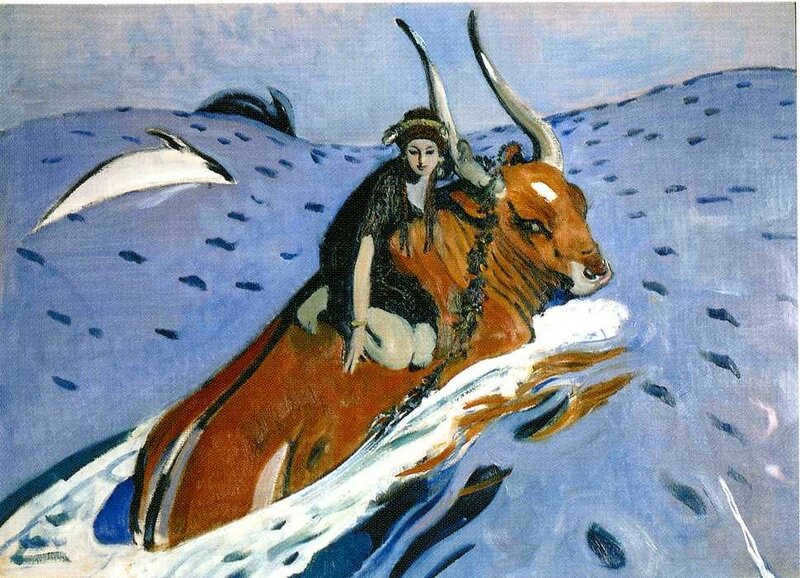

There is another version that is related to the seventh labor of Heracles and is also linked to Crete. Poseidon sent a magnificent white bull to the king of Crete, Minos, as an offering for him, Poseidon. The clever ruler deceived the god by substituting the bull with another, and as a result, Poseidon became furious and inflicted madness upon the hidden sacrifice. This madness caused the deaths of numerous individuals until Heracles managed to subdue the raging animal.
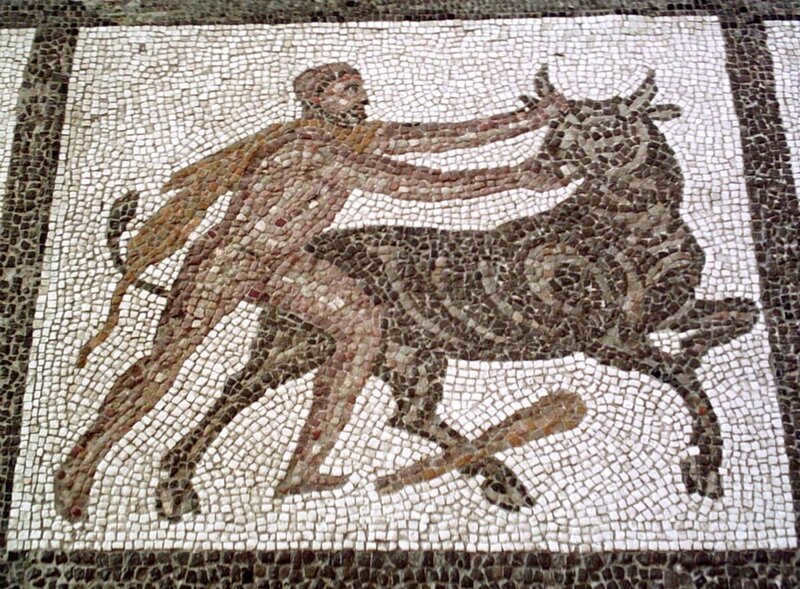

There is a beautiful mosaic located in the ancient city of Kition in Cyprus.
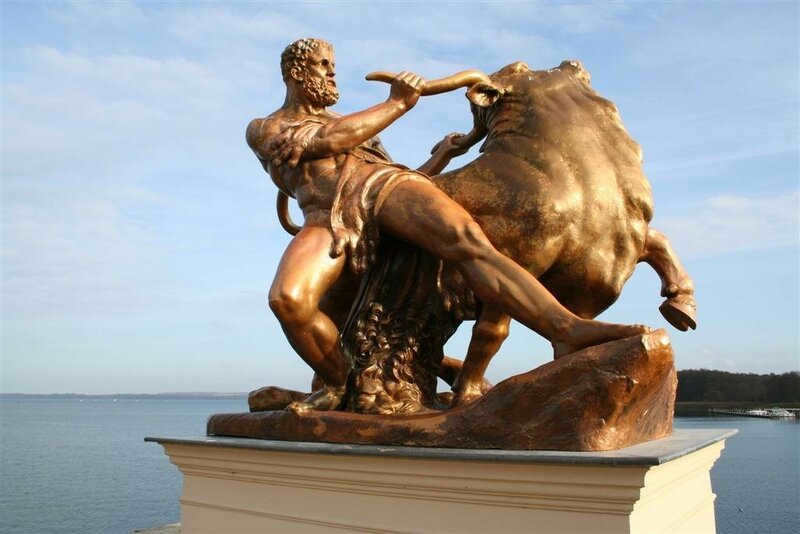

A statue depicting the mighty Heracles conquering the menacing Cretan bull, can be found in the enchanting gardens of Schwerin Castle located in Germany.
Additionally, there exists an alternative version of the myth involving the unfortunate Io, who was transformed into a cow by the formidable Hera in order to prevent any further betrayal by her lover Zeus. This alternate version suggests that Taurus might actually represent Thelitsa.
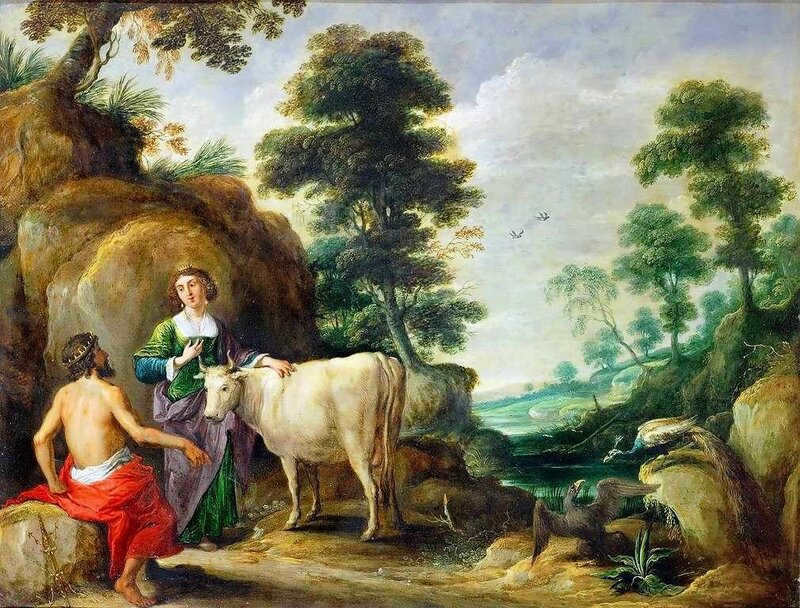

David Teniers I – Juno with Io transformed into a bovine, and Jupiter.
The Pleiades were previously regarded as a separate constellation rather than just an asterism.
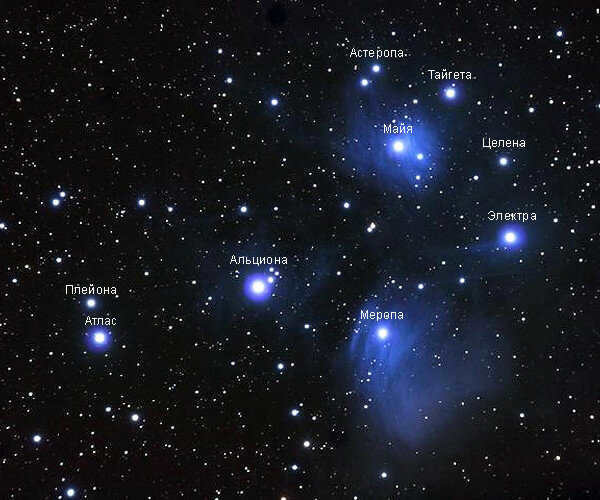

The Pleiades, known as the Seven Sisters, are named Alcyone, Keleno, Electra, Taygeta, Maia, Sterope, and Merope. Interestingly, Merope was married to Sisyphus, a man condemned by the gods to the eternal punishment of pushing a boulder up a hill, only to have it roll back down every time it nears the top.

Ovid noted that the seven strings of Hermes’ lyre represented the seven stars of the Pleiades, meaning that they produced celestial music – the music of the universe. Hesiod also advised farmers: “When the Atlantis-Pleiades rise in the east, it is time to harvest; and when they start to set, it is time to sow.”
Regarding the astrological sign Taurus:

The fortunate color associated with Taurus is Blue, Blue-Green.
Taurus can be likened to a transparent manuscript, for those who possess the art of interpretation. Let us explore the contents of this manuscript, specifically the tale of Zeus, who metamorphosed into a bull in pursuit of the captivating Europe.

First of all, this constellation is linked to beauty, being a true representation of Venus, and secondly to passionate love and the longing to possess. After all, Taurus, just like the mighty Zeus, is characterized by possessive instincts, and at the same time, Taurus is incredibly alluring – just like Zeus was able to captivate Europe in the form of a bull.
Furthermore, Taurus is considered to be the most fertile and productive sign in astrology. In fact, Europe bore three sons from Zeus. Interestingly, individuals whose planets are connected to the stars of this constellation may have children outside of marriage, and their first child may achieve great success and fame.
Additionally, it is also likely for there to be a distant journey or emigration due to a loved one in the fourth sign. However, if we strictly follow the legend, the union of Europe and Taurus did not prove to be long-lasting.
However, the Taurus sign is not only associated with love, but also with financial opportunities and money.
Individuals who were born under the Taurus zodiac sign are known for being practical and pragmatic. They tend to set goals for themselves that revolve around accumulating both material and spiritual wealth. It is rare to find a Taurus who is unemployed, as they are determined to steadily and securely build their own empire. They understand the importance of establishing a strong foundation and work diligently to grow their businesses step by step.
It is worth mentioning that Taurus individuals possess the ability to fully concentrate on a problem and devote maximum effort to achieving their goals, which is the key to their success.

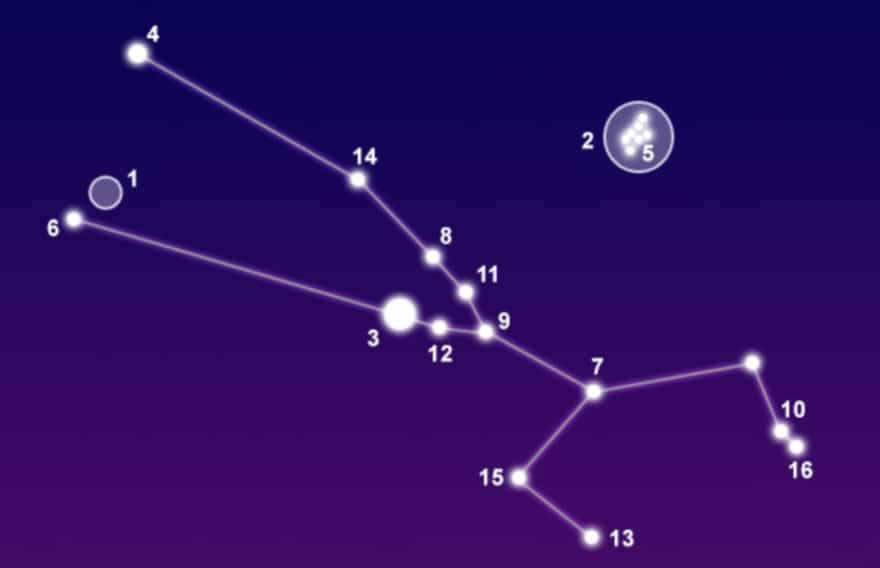
Taurus is a constellation in the zodiac, situated between Gemini and Aries, to the northwest of Orion. The most notable stars in Taurus include Aldebaran (with an apparent sidereal magnitude of 0.87), Nat (1.65), Alcyone (2.85), and ζ Taurus (2.97). This constellation is home to the Hyades and Pleiades star clusters, as well as the Crab Nebula, which features the pulsar PSR B0531+21.
Even with the naked eye, it is possible to observe up to 216 stars within the Taurus constellation. In the night sky, it covers a vast area of approximately 800 square degrees.
Taurus is positioned between Aries and Gemini, with the constellation Taurus being adjacent to Orion in the northwestern direction. It is also encompassed by a cluster of other neighboring constellations: Eridanus, Cetus, Auriga, and Perseus. This magnificent constellation can be observed throughout the entirety of the Russian Federation. It is particularly favorable for observation in Central Russia, where it remains visible year-round, except for a brief period in spring and summer when it becomes unobservable.
In the northern hemisphere, the constellation of Taurus can be seen in the sky from November to March, but its visibility is highest in January.
- Taurus occupies an area of 797 square degrees.
- Its right ascension is 4 hours.
- Its declination is 15 degrees.
- The best viewing locations for Taurus are between latitudes 90 degrees and minus 65 degrees.
People living in Russia are particularly lucky, as they have the opportunity to observe the Taurus constellation all across the country.






The legend of Zeus transforming into a majestic bull

The constellation Taurus is connected with Greek mythology. Similar to many Greek legends, it revolves around the romantic interest of Zeus, the king of the gods.
This particular tale focuses on Zeus’s infatuation with Europa, who is the daughter of King Agenorus. Zeus often employs disguises to win over his love interests, and this narrative is no exception. In this instance, he transforms himself into a magnificent bull and becomes a part of King Agenor’s herd.
One day, Europa spots the bull and is captivated by its beauty. She approaches it and even climbs on its back. To her surprise, the bull heads towards the beach and jumps into the sea, carrying her to the island of Crete. Once there, the bull reveals its true identity as Zeus and declares that Europa will become his mistress.




When and where can you observe Taurus?
Taurus is easily visible from Russia and is one of the most easily recognizable constellations.
Even in well-lit urban areas, the V-shaped formation of the bull’s horns is quite easy to locate. A helpful guide for orientation is the small constellation known as the Pleiades: it stands out prominently, and Aldebaran shines so brightly in the night sky that it is difficult to miss.

It is not difficult to locate the shape of the bull in the celestial sphere.
Taurus is visible throughout the year in the middle latitudes, except for the summer season, as it appears prominently above the horizon. The optimal time for observing this constellation is in the late autumn and early winter months.
Aldebaran, Elnath, and Alcyon are the most luminous celestial bodies
Also referred to as Alpha Tauri, Aldebaran is located approximately 65 light years away from Earth and serves as the most luminous star in the constellation. It takes the form of a red giant star and boasts a diameter that is roughly 45 times larger than that of our Sun.
Also recognized as Beta Tauri, this star is situated on the border between Taurus and Ascendant, which is why it is sometimes known as Gamma Ascendant. Elnath, a blue giant star, can be found around 130 light-years away from Earth.
Alcyon, the third brightest star in its constellation, is also the brightest star in the Pleiades or Seven Sisters. Its name translates to “Central.” In Greek mythology, Alcyon represents the nymph of Atlantis who later became the mother of Gireos. Alcyon is a multi-stellar system composed of four stars that have a radius ten times that of the Sun.







Popular topics for posts
- The History of Coffee
Coffee is the preferred beverage for many adults. So, when and where did it first originate? The birthplace of coffee can be confidently identified as Ethiopia. As early as 900 A.D., the inhabitants of this country discovered the miraculous properties of the coffee plant. - The Fascinating City of Vladivostok
In 1860, the city of Vladivostok had its humble beginnings. It emerged from a barracks constructed on the shores of the Golden Horn Bay. During that time, this area was renowned for hunting, and the streets were named not just for amusement, but after the significant events that occurred on them. - Reproductive Health in Humans
Human health, in the broadest sense, encompasses not only the absence of any notable ailments but also the balanced and steady development of one’s psychological, physical, mental, and other aspects of life.
The constellation that houses the Crab Nebula

The M1 Nebula, commonly referred to as the Crab Nebula, is the aftermath of an enormous supernova eruption observed by astronomers from the Far East during the 11th century. Nebulae that originate from such violent occurrences are classified as supernova remnants.
The Crab Nebula is immense, estimated to span approximately 10 light years in diameter and is located roughly 6000 light years away from our planet.
January lunar calendar, February lunar calendar, March lunar calendar
The Taurus sign, in its entirety, is a representation of temperature and heat in general. However, when examining its different parts, the leading section, particularly near the Pleiades, is linked to earthquakes, winds, and fogs. The middle section is associated with moisture and cold, while the last portion, close to the Hyades, is connected to fire, thunder, and lightning…
Claudius Ptolemy – On the Weather – “Tetrabiblos”
Fig.1 The symbol for Taurus
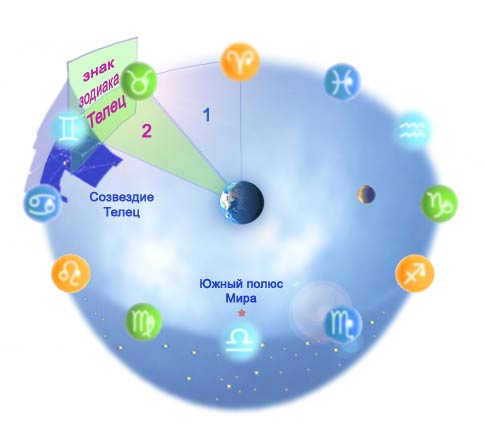
Fig. 2 Taurus zodiac sign, Taurus constellation, and their relative positions in a spherical projection (according to the ancient belief, the sky consisted of several nested spheres).
In the view of ancient astronomers, zodiac signs are used to designate different sections of the night sky near the ecliptic. The section of the sky corresponding to the Taurus sign can be visualized as follows:
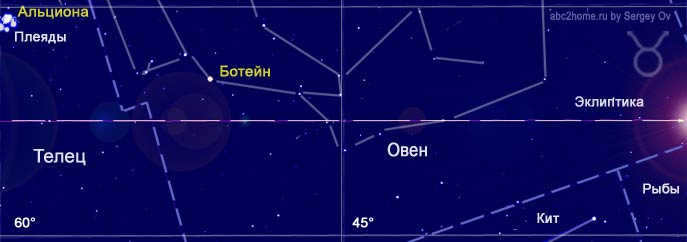
Figure 3. The Taurus zodiac sign represents a section of the starry sky that corresponds to the Taurus sign. The Taurus sign mainly encompasses the Aries constellation and the northwestern part of the Taurus constellation (with the Pleiades marking the left border of the sign’s area), as well as small portions of the Pisces and Cetus constellations.
Ancient Greek philosophers attributed the following characteristics to the Taurus zodiac sign:
– The Taurus zodiac sign, which inherits many of its qualities from the masculine and powerful Taurus constellation (Bull – Greek Tauros lat. Taurus), paradoxically represents a female sign. This is because the ancient Greeks associated it with the dwelling place of Venus.
– The symbol representing Taurus embodies the essence of the element Earth, which is characterized by its cold and dry nature. Individuals born under this sign are associated with the phlegmatic temperament, which is the predominant component.
– In ancient times, Taurus was also recognized for its specific characteristics and properties. It is considered a southern sign due to its location relative to the equatorial plane when the Sun passes through it. In terms of seasons, Taurus is associated with spring. The sign of Taurus is in harmony with certain elements, such as copper (associated with Venus) and gold (associated with Zeus). Precious stones like emerald and agate are also associated with this sign. Additionally, Taurus has a unique quality in that it enhances the strength of the Moon, which is known as its “exaltation”.
Eudoxus is credited with writing the initial account of the constellation.
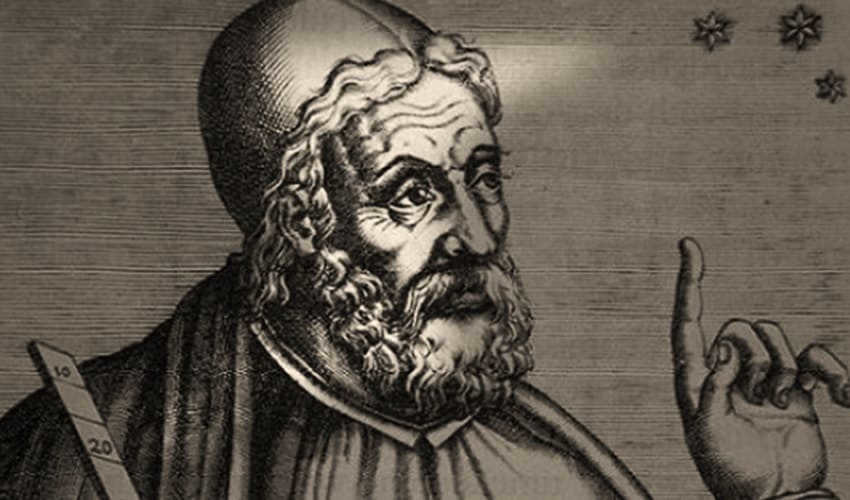

Eudoxus, a disciple of Plato, provided an account of our constellation system approximately between 400 and 350 BC. He bequeathed to his successors a celestial globe referred to as the Eudoxus Sphere. Unfortunately, Eudoxus’ work, including the globe itself, has been lost, but we have knowledge of his concepts thanks to a report by Aratus written around 220 BC.
In Aratus’ writings, we can find explanations of Orion, Sagittarius, Scorpius, Gemini, Taurus, and numerous other constellations that continue to adorn our star charts to this day.
Taurus: The Practical and Steadfast Zodiac Sign
According to astrology, individuals born between May 14 and June 21 possess a strong practicality and unwavering nature. This can be attributed to the fact that Taurus is an earth sign. Taurus individuals highly value material possessions and possess the knowledge and drive to attain a comfortable life.
Furthermore, Taurus individuals excel in planning for the future, setting clear goals, and showcasing a business-oriented mindset. They are known for their independence, honesty, and dependability, but also for their self-interest. Taurus individuals are unlikely to engage in activities that do not provide personal benefits.

The Zodiac’s second sign is Taurus.
He has no interest in horoscopes, does not partake in self-discovery, and prefers to depend on his own abilities in all aspects.
In the constellation, there are dispersed groupings of stars: the Hyades and the Pleiades
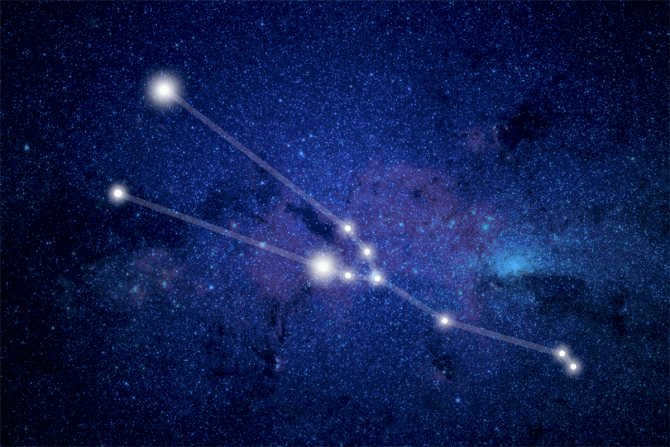

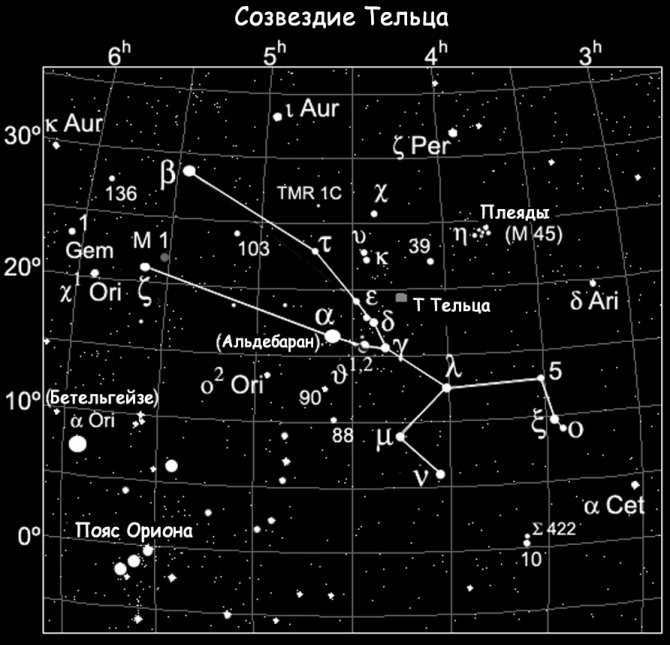
The Hyades cluster can easily be located by using Orion’s Belt, which consists of three blue-white stars in the constellation Orion the Hunter. To find the cluster, simply draw a line westward (generally in the direction of the sunset) through the Belt stars. This line will lead you to the bright reddish star Aldebaran, also known as the fiery red eye of the Bull.
Although Aldebaran is not technically a member of the Hyades star cluster, it serves as an excellent marker for locating the cluster. Interestingly, Aldebaran is only 65 light-years away, while the Hyades are located approximately 2.5 times farther away.
In the Taurus constellation, there is another bright star cluster called the Pleiades. The Hyades and the Pleiades are both easily visible to the naked eye, but they are more than 430 light-years apart. To see them, just use binoculars.
The Pleiades cluster is made up of young and very bright stars that began forming around 100 million years ago. It is one of the closest star clusters to Earth, located about 400 light-years away. With hundreds of stars, the Pleiades cluster spans over 10 light-years in width.


Multiple star systems
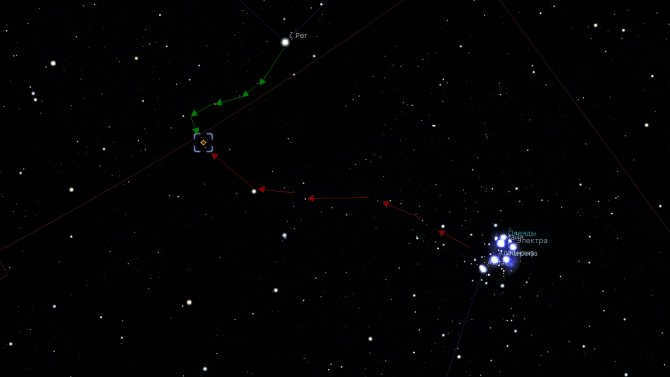
8.1 Double star 118 Tau
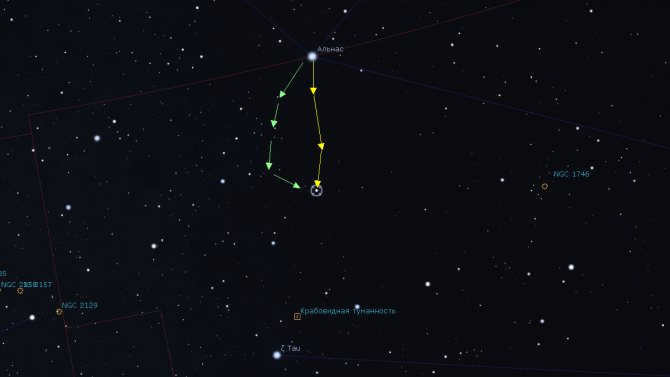
A pair of stars known as 118 Tau form a system with a combined luminosity of 6.7m. The two stars have individual luminosities of 6.6m and 5.8m respectively. The angular separation between them is extremely small, measuring just under 5″. A basic binocular or telescope will not have enough power to resolve the double star into its individual components. However, with a 150mm telescope and a magnification of 100+, it becomes possible to observe them separately. I have marked the location of the system on the map above. To find it, start from the star Alnas and move downwards.
I am confident that you will revisit this cluster many times. Other scattered clusters like Pleiades and Hyades will keep you company on many nights. It is always satisfying to have something new to observe through a telescope, especially outside of the well-known star clusters. Explore, discover, and share your observations and experiences.
The legend of the Pleiades, the offspring of Atlanteus.
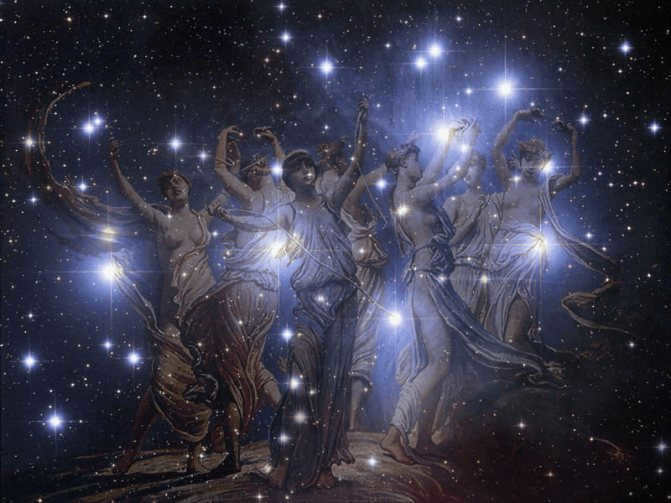

The Pleiades consisted of seven daughters born to Atlanteus and Pleione. They were the half-sisters of the Hyades, whose mother was Etra. It is possible that they were also half-sisters of the Hesperides, who were the daughters of either One Night or Atlante and Hesperis. Both Pleione and Etra were Oceanides, daughters of Oceanus and Thetis, the titans who ruled the outer seas before being succeeded by Poseidon.
The Pleiades were also nymphs in the lineage of Artemis, and along with the seven Hyades, they were referred to as Atlantids, Dodonids, or Niciads. They served as nannies and teachers to the infant Bacchus.