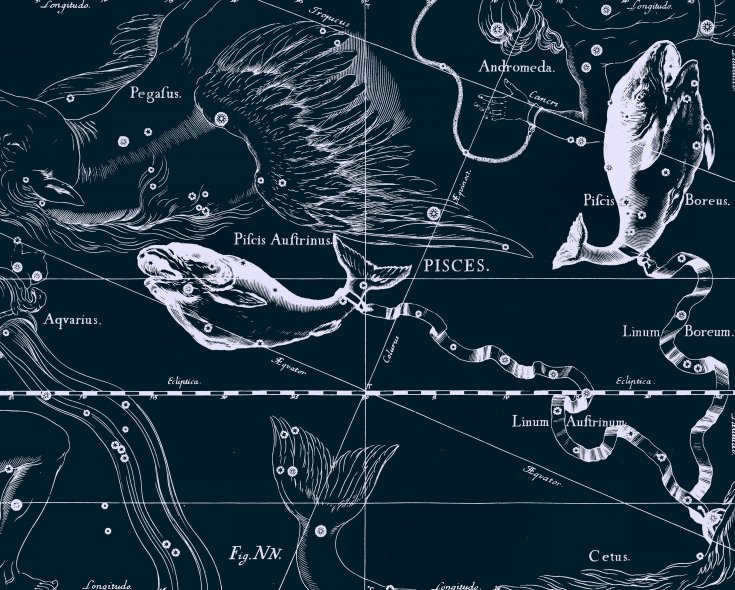
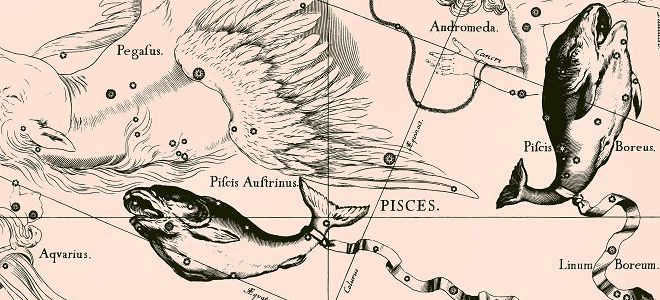
It is common knowledge that the zodiacal constellation Pisces is situated in the night sky. Due to its position between Aries and Aquarius, it is often divided into its northern and western parts. The northern part is located beneath Andromeda, while the western part lies in the region between Pegasus and Aquarius. In actuality, these are two separate groups of stars. And the western part of Pisces is referred to as the Crown by Arab astronomers.
By the way, the Pisces constellation is quite expansive in the celestial sphere.

The tale of the Pisces constellation
Naturally, what would it be without mythology?
Countless cultures have associated the constellation with the goddess of beauty, Aphrodite, and her son Eros. It is believed that they transformed into fish in order to elude the monstrous dragon Typhon.
Some believed that the fish beneath the water helped the goddess and her son to conceal themselves, leading them to ascend to the heavens.

However, there exists a myth surrounding the love between Cyclops and the exquisite Galatea. As the legend goes, he caught sight of her with another and pursued her. In their attempt to evade him, the enamored pair perished. Yet, love did not separate them, but rather united them in the celestial expanse.
In any case, each tale is imbued with love. Therefore, Pisces in the astral sphere embodies and symbolizes this splendid emotion.
I must admit, I’m uncertain as to why, but gazing at the stars always evokes a desire to dream.
– Vincent van Gogh
It’s surprising that the constellation doesn’t have the brightest star. It does have bright stars, but they don’t make the top of the brightness list. Despite having over 160 stars, only a few can be considered the brightest.
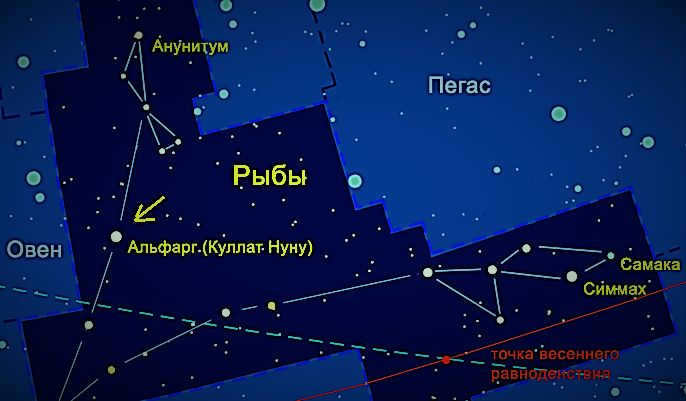
Al Pherg (Kullat Nunu) is considered the first star in the constellation. It is a giant star of the fourth magnitude. Interestingly, its brightness is over 300 times stronger than the sun. However, it is located 294 light years away, so it appears as an ordinary point in the night sky to observers on Earth.
AlphaAlricia marks the beginning of Pisces. It is interestingly represented by two white twin dwarf stars, which translates to “twine” or “rope”.
Omega is a binary star system. It is a small star, located 106 light years away from our planet.
Gamma is a giant star with a yellow color. It can be found at a distance of 130 light years. Interestingly, it is also the second brightest star.
TX Pisces is a unique star known as a carbon star. One of its fascinating characteristics is its dark red color.
Iota is a yellow dwarf star. What makes it even more interesting is that it is the closest star to Earth, being only 45 light years away.
Beta, on the other hand, holds the title of the farthest star from our planet. Its distance is an astonishing 492 light years. Interestingly, it is commonly referred to as the “mouth of the fish.”
The star that holds the title for being the closest to us is actually van Maanen’s star. In astronomical terms, it is located 14 light years away from us. This white dwarf star lies in the direction of the Western Fish.
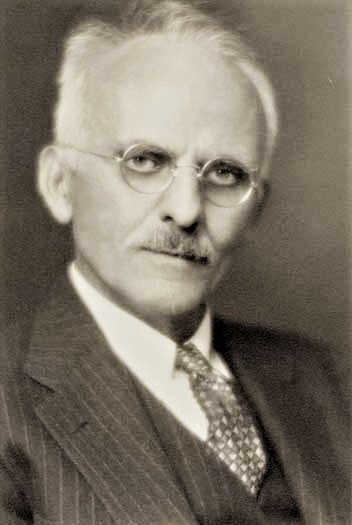
Adrian Van Maanen, who was born on March 31, 1884 and passed away on January 26, 1946, was a renowned astronomer from the Netherlands. In the year 1917, he made a groundbreaking discovery of a star with an exceptionally high proper motion, which was later named in his honor.
Other celestial bodies
Messier 74 (M 74) is a captivating spiral galaxy that exhibits active star formation. Recent scientific research has revealed that within the past decade alone, this galaxy has witnessed the birth of two supernovae. Moreover, it has been recently discovered that there is an immensely powerful X-ray emitting black hole located within Messier 74.
Another noteworthy spiral galaxy in the cosmos is NGC 524. It falls under the category of lenticular objects, which are characterized by their peculiar shape.

However, there exists another spiral galaxy that deserves attention – NGC 488. Despite its small size and dimness, it possesses a dense core, which makes it visible as a hazy spot through a telescope.
NGC 660, on the other hand, is characterized by a spiral ring structure, with two stellar disks rotating at different angles.
This group of galaxies located near Andromeda is also worth mentioning. It consists of 8 elements labeled NGC: 375, 379, 380, 383, 384, 385, 386, 388. However, each of them was discovered at different times, and unfortunately, they are nearly impossible to examine in detail.
Furthermore, it is important to mention the binary star system ζ Psc. This system is comprised of a giant star and a main-sequence star.
Stars reveal to us the magnificence and allure of the cosmos, in which we, perpetual explorers of the celestial realm, endeavor to discover our own guiding star.
Valentin Petrovich Rychkov
Observation
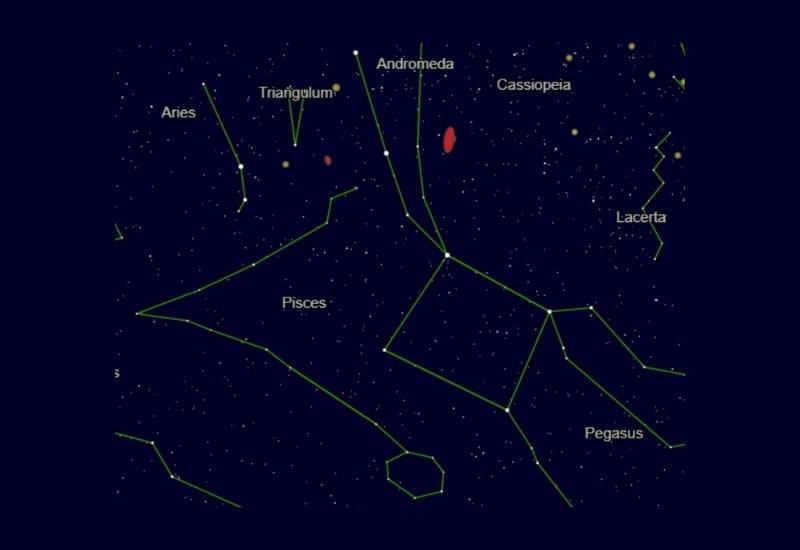
By the way, in the night sky, the constellation Pisces has some famous neighboring constellations such as Aries, Whale, Pegasus, Andromeda, Aquarius, and Triangle. It has a long history and is well-known. With its enduring popularity, many people are curious about how to locate it in the starry sky.
In the northern hemisphere, Pisces can be observed during the autumn season. Although it may not be particularly striking, it contains numerous fascinating astronomical objects.
As mentioned, Pisces can be found between Aquarius and Aries. Its geometric shape consists of two rays that form an acute angle. One of the rays, pointing northward, is enclosed by a triangle. The other ray, facing west, terminates in a pentagon.
Furthermore, Pisces is the location of the vernal equinox point. This means that the Sun is in Pisces from March 12 to April 18.

The cosmos is a stunning and unfathomable entity to mankind in its entirety. However, every bit of knowledge we attain brings us closer to unraveling the existence of the universe.
While a constellation may not appear remarkable in the night sky, it holds a significant place in the exploration of the cosmos. A seemingly unremarkable patch of the sky reveals astounding beauty when observed up close. Furthermore, the celestial objects that comprise it are astonishingly exquisite.
Even though the stars of Pisces may be challenging to distinguish for stargazers, they still hold considerable intrigue. One could argue that the elusive nature of the constellation adds to its allure. Perhaps, to some extent, this contributes to its popularity.

One of the sectors of the zodiac that encompasses the Pisces constellation serves as a marker for the Sun’s annual journey. It has been widely known for centuries that this particular constellation can only be seen in the northern hemisphere and is not visible from all continents or at all times.
What is the appearance of the Pisces constellation?
There is a lack of awareness among many individuals regarding the visual representation of the Pisces constellation in the celestial sphere, primarily due to the absence of luminosity in its stars. The constellation itself is relatively faint, making it difficult to observe throughout the year. By mentally connecting the most prominent stars, one can form an acute-angled triangle. Additionally, three faint but perceptible points along a horizontal line depict the zodiacal sign, visible to the naked eye.
How to locate the Pisces constellation in the night sky?
Finding the Pisces constellation can be quite challenging, especially on days when the sky is cloudy. However, during clear nights, it becomes visible, although its faintness often causes it to be overshadowed by other zodiacal signs. In Russia, it can be observed in September and October, as the stars come closer during the autumn season. Interestingly, on March 11, when the Sun passes through Pisces, it becomes practically invisible in the sky.
Looking for neighboring celestial bodies can aid in the search for Pisces. This constellation is situated near Andromeda and Pegasus, forming a distinctive square shape. From this square, a chain of stars extends towards the northeast, resembling a hand that covers Pisces. Another useful guide is Perseus, who is easily visible from all continents. His right foot points towards Aries, and just behind Aries lies Pisces.
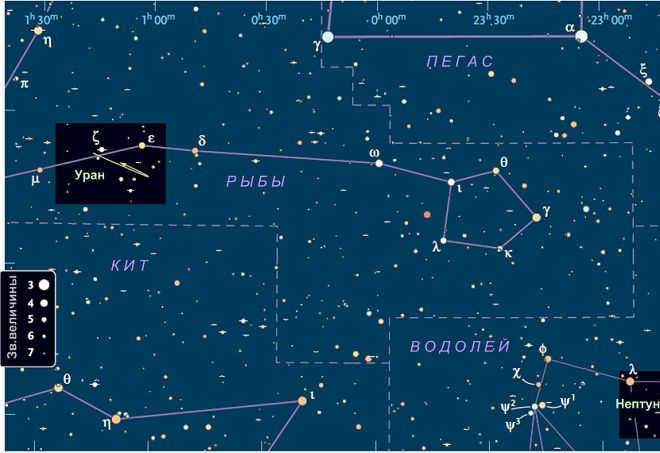
The constellation Pisces – the stars’ moniker
All the stars within the Pisces constellation are unassuming and frigid, much like individuals born under this astrological sign. There are a total of 75 stars and they can be observed using a basic amateur telescope during a clear night. The primary distinguishing factor is the position of the vernal equinox, which marks the Sun’s initiation of longer daylight hours in the Northern Hemisphere and shorter daylight hours in the Southern Hemisphere.
The star Alrisha, located in the third position in terms of brightness, played a key role in paving the way. What makes it fascinating is the fact that it actually consists of two small dwarf stars. Following Alrisha is Omega Pisces, a dwarf star located 106 light-years away from the sun. This star system includes the carbon star TX Pisces, which displays a mesmerizing dark red twinkle. Van Maanen, a yellow dwarf, is the closest star to us, while Beta, known as the mouth of the fish, is the farthest. In addition to these, there are several other stars available:
- Iota;
- Eta Pisces;
- Alpha Aries.
The Pisces constellation: a tale of gods, monsters, and love
In ancient Greece, the sky was believed to be home to the gods. According to Greek mythology, the Pisces constellation represents the goddess Aphrodite and her son, who took the form of fish to escape from the monstrous Typhon. It was said that the fish carried the gods to safety in the sky, protecting them from danger.
Other cultures tell a different story about the origin of the Pisces constellation. They speak of Galatea, a maiden who drowned with her lover. The Cyclops, a giant with a fiery passion for Galatea, wanted her to choose him. However, she defied his wishes and chose a handsome young man instead. The Cyclops pursued them relentlessly, and in their attempt to escape, the lovers sought refuge in the sea, where they met their tragic end. It is said that their love was so powerful that it immortalized them as stars in the sky, forming the constellation of Pisces.
It may sound strange, but the constellation of Pisces has a star that is barely visible from Earth, yet it manages to stand out among the rest. What sets it apart is a small galaxy called Messier 74, which is located within it. This galaxy is known for its continuous process of star formation, and in the past ten years alone, it has given birth to two new stars. While it was first discovered in 1780, it is only with the help of modern astronomers that a black hole has been observed within it. Additionally, there is a white dwarf in this constellation, which is considered to be the closest to Earth.
When it comes to compatibility, the signs Sagittarius and Capricorn tend to have a low level of compatibility. Although different people can eventually find common interests and develop strong friendships or romantic relationships, certain character traits often lead to short-lived unions.
Taurus and Gemini, two individuals with different personalities, may encounter various challenges that will depend on numerous factors in different areas of their lives. In order to establish a connection, both parties will need to make compromises and put effort into personal growth.
Scorpio and Pisces, on the other hand, have a high level of compatibility and can form a strong bond in both romantic and platonic relationships. They can also work well together, as long as each person is able to choose the right role and avoid conflicts.
Aries and Aquarius make for a good match, not only in terms of romance but also in the realms of work and friendship. While there may be occasional disagreements and relationship problems, these can be managed by following the advice of astrologers.
Throughout history, individuals have witnessed the annual celestial rotation of twelve constellations known as the zodiac, with Pisces being among them. At first glance, this constellation may not appear particularly remarkable, as it is often regarded as one of the faintest. Nevertheless, upon closer examination, numerous intriguing elements can be uncovered within its boundaries.
Appearance and Location of the Pisces Constellation
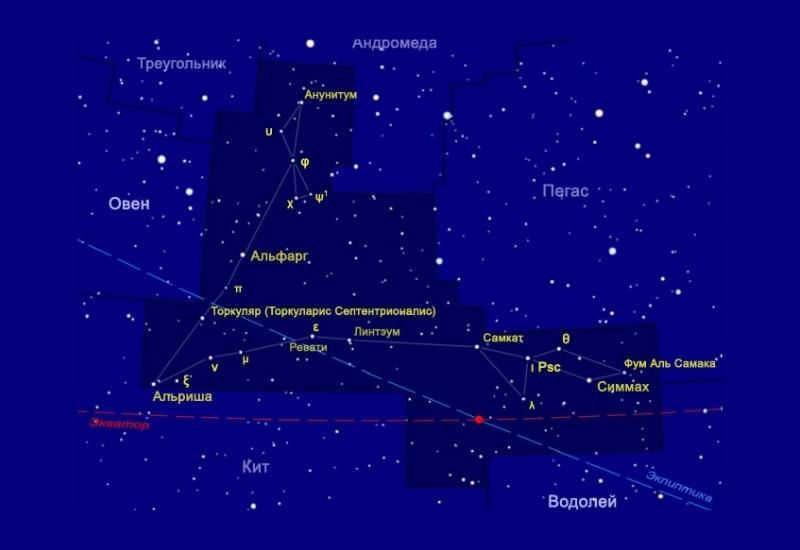
The Pisces constellation can be found in the northern hemisphere and is comprised of a total of ten stars. These stars come together to form two distinct rays that emanate from a single point – the Northern and Western Pisces. These rays are connected by an imaginary ribbon that stretches between them. The Northern Pisces ray almost touches the Andromeda constellation at its endpoint, while the Western Pisces ray extends towards the Pegasus constellation.
Pisces is one of the twenty largest constellations, covering an area of nearly 900 square degrees.
The constellation Pisces can be located in the space that lies between the two adjacent zodiac constellations, namely Aries and Aquarius. This particular constellation is of considerable size and covers a significant portion of the celestial sphere. Alrisha is the star that serves as the foundation of this constellation. While a regular individual may observe the Pisces constellation in a photograph, the opportunity to truly marvel at its beauty in person requires the use of a powerful telescope.
Identifying the Pisces constellation in the night sky
The Pisces constellation becomes visible in the sky during the early autumn season and can be observed until December. However, the prime time for spotting it is from late September to early October. You don’t require any sophisticated equipment to appreciate Pisces; a regular amateur telescope will suffice.
It is impossible to observe the constellation Pisces with the naked eye due to its dimness, which causes it to be overshadowed by its brighter neighboring constellations.
Nevertheless, locating Pisces becomes easier by looking at its neighbors. The prominent constellations Andromeda and Pegasus can be easily spotted without any optical aid. Positioned above Pisces, these two constellations effectively obscure Pisces and provide a convenient reference for orientation.
The most notable stars in the Pisces constellation
Despite the limited number of bright stars in the Pisces constellation, there are a few that capture the attention of both amateur and professional astronomers.
The star Kullat Nuni or η Pisces (Alfargus)
η Pisces is the most luminous star in the entire constellation. Al Pherg is classified as a giant and falls into the fourth magnitude category. It shines over 300 times brighter than the Sun, despite having a mass only 3-4 times greater. Located approximately 294 light-years away from Earth, it stands out as a remarkable celestial object.
γ Pisces (Gamma Pisces) – A Bright Star in the Pisces Constellation
Gamma Pisces, the second brightest star in the Pisces constellation, shines with a brilliance 60 times greater than that of the Sun. It also boasts a mass that is ten times larger than our own star. What makes it even more remarkable is its proximity to our solar system. Gamma Pisces is a mere 138 light-years away from the Sun, making it more than twice as close as Alfargus.
In addition to its brightness and proximity, Gamma Pisces is also a member of a cluster of fainter stars known as the Crown of Fish. This cluster forms the head of one of the fish found near the constellation Pegasus.
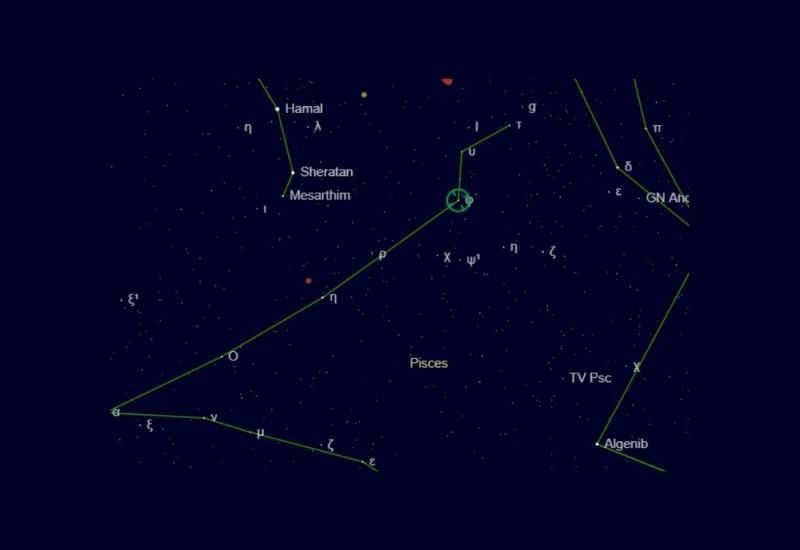
α Pisces or Star of Alrish (Okda, Kaitain)
At the foundation of the constellation lies this binary star system. The two stars are positioned 1.8 arc seconds apart. Both stars possess a blue hue and are relatively equal in size, although the larger star outshines its companion. It takes approximately 700 years for the stars to complete a full orbit around each other.
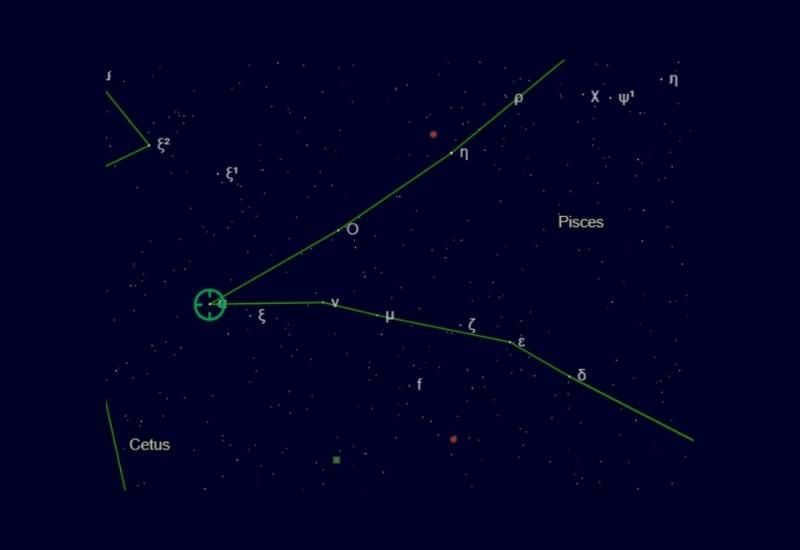
Alternative titles for this star may be rendered as “cord” or “ligature” as it symbolizes the figurative knot of the cord that binds two fish together.
Star 54 Pisces (54 Psc).
In 2002, scientists detected a planet revolving around Star 54 Pisces (54 Psc), and four years later, they made another exciting discovery – a brown dwarf also in orbit around the star. Despite the fact that the brown dwarf’s brightness is less than half that of the Sun, it shares similarities with the Sun in terms of size and mass.
The mass of the brown dwarf in its orbit is a mere 5% of the Sun’s mass, yet it is a staggering 50 times more massive than Jupiter.
The exoplanet situated near 54 Psc revolves around its star in a path resembling that of Mercury and completes one full orbit in a span of 52 days. Simultaneously, the mass of this celestial body is similar in magnitude to that of Saturn.
Besides the stars, there are various other celestial objects in the Pisces constellation that are worth mentioning.
Messier Galaxy 74 (M74, NGC 628)
Situated 30,000,000 light-years away from Earth, this typical spiral galaxy is believed to harbor at least 100 billion star systems and individual luminaries. Its low brightness makes it challenging to observe with an amateur telescope, but it can be detected near η Pisces when using professional equipment.
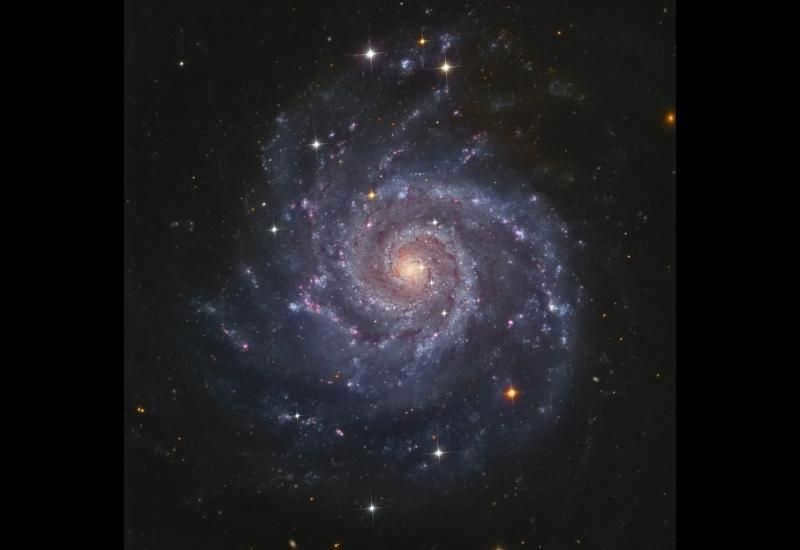


In the early 2000s, astronomers observed two supernovae of an uncommon type in this galaxy. These stellar explosions emitted immense amounts of heat, energy, and gamma rays. These events are considered some of the largest ever witnessed by humanity.
Simultaneously, researchers detected a source of extremely powerful X-ray radiation. Its intensity surpassed that of a neutron star and was later identified as a black hole with a mass 10,000 times greater than that of the Sun.
Twinned galaxy 3C 31 (NGC 383).
This galaxy bears a striking resemblance to a quasar. At its core lies a black hole, believed to be responsible for emitting jets of matter in two opposing directions across vast distances. As a result, NGC 383 emits the most powerful radio waves. Situated 237 million light years away from our own system, it remains a fascinating celestial entity.
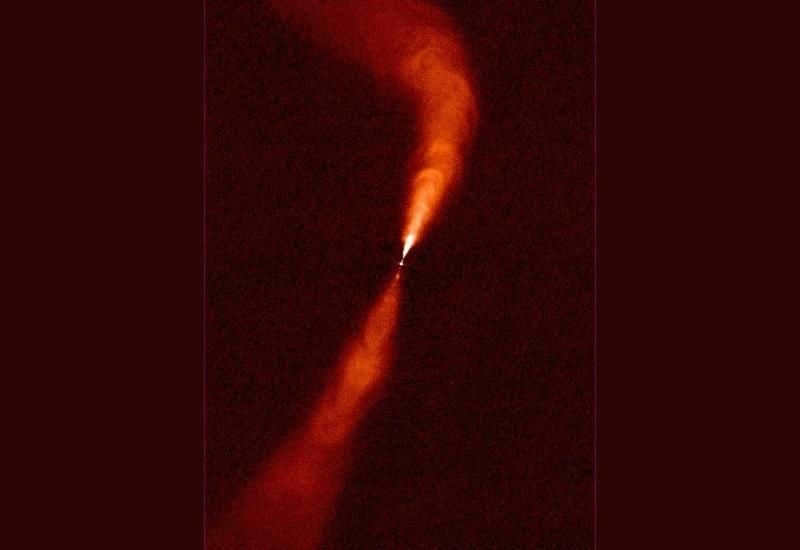
PGC 3792, also known as The Pisces dwarf galaxy.
This particular galaxy is the nearest among the collection of galaxies being examined, with a distance of only 2.51 million light-years from Earth. Its discovery can be credited to V.E. Karachentseva during the 1970s.
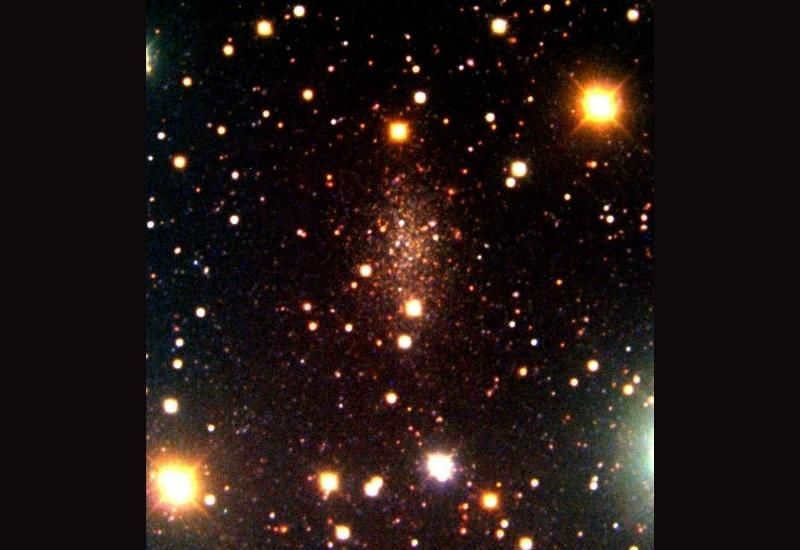

Over the course of 10 billion years, the process of celestial body formation in PGC 3792 has gradually decelerated. While the majority of stars emerged approximately 8-9 billion years ago, there are still small clusters of young and hot stars present on the outskirts of the galaxy.
The Mythology Linked to the Pisces Constellation
The name Pisces originated from ancient Babylon. Astronomers who observed the constellation noticed that it resembled a pair of fish connected by their tails with a thread.
This comparison stemmed from the ancient Greek legend of Typhon, in which the Earth goddess Gaia compelled her monstrous son Typhon to lay waste to Olympus. As a result, the gods, including Aphrodite and her son Eros, were forced to flee Olympus. When they reached the river, they tied themselves together with a ribbon and transformed into fish, enabling them to swim away from danger.
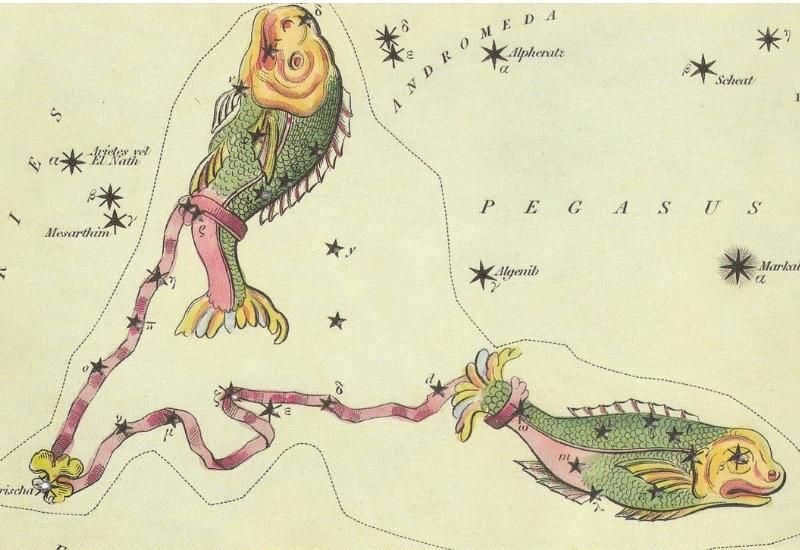
The constellation of Pisces is represented in mythology by a star named Alpha Pisces. This star is also known as Alshera, which translates to “cord,” symbolizing the knot of a thread.
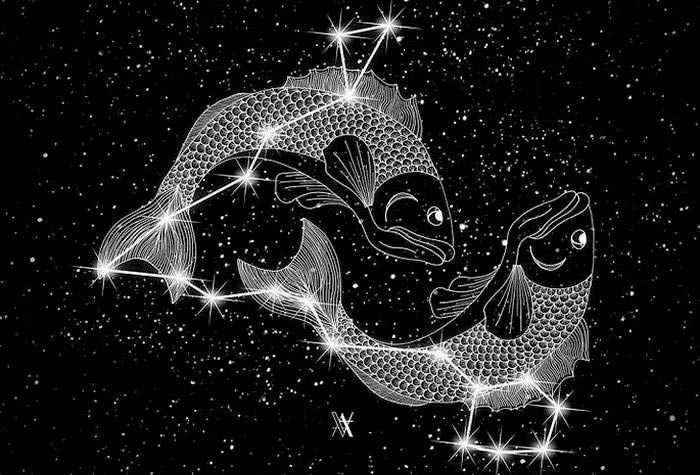

Pisces (Latin. “Pisces”) is a large constellation of the zodiac that represents a water sign. On star atlas maps, the constellation is depicted as two fish connected by a rope on their tails. One fish is facing north while the other is facing west.
Situated between the clusters of stars Aries to the east, Pegasus to the south, and Aquarius to the west, Pisces is easily recognizable in the night sky.
- It reaches the meridian at 21:00 on November 10th.
- Visible between latitudes: 90 and -65 degrees.
Pisces symbolizes spirituality and the mysticism of the celestial realm. In ancient times, it was believed that the stars of this constellation determined the fate of sailors.
A glimpse into the past
Pisces was among the first 48 constellations to be extensively studied by the Greco-Roman astronomer Claudius Ptolemy in the second century. Its presence can be traced back to around 2300 B.C., as it adorned the surfaces of ancient Egyptian sarcophagi and was inscribed on Babylonian cuneiform tablets.
Fascinating trivia:
“The vernal equinox point, which used to be located within the constellation Aries, has now shifted to Pisces due to the Earth’s axial precession, also known as the Earth’s wobble.” Jan Ridpath, an esteemed astronomer and accomplished author of numerous astronomy books, shares this insight.
Greek myth
Typhon, a notorious titan, attempted to seize control of Mount Olympus, prompting the gods to scatter in various directions. In order to elude the titan, Aphrodite, the goddess of love, and her son Eros sought assistance from Zeus, who transformed the mother and son into fish. Aphrodite and Eros connected their tails to ensure that they would remain together. Following their rescue, Athena positioned the gods in the heavens, where they now appear as a pair of linked fish.
Roman myth
The storyline of this myth bears resemblance to its Greek counterpart, however, the central figures in this tale are the Roman deity of love – Venus, and her offspring Cupid. In order to evade impending peril, the gods sought refuge by mounting on the backs of aquatic creatures.


How to locate the Pisces constellation
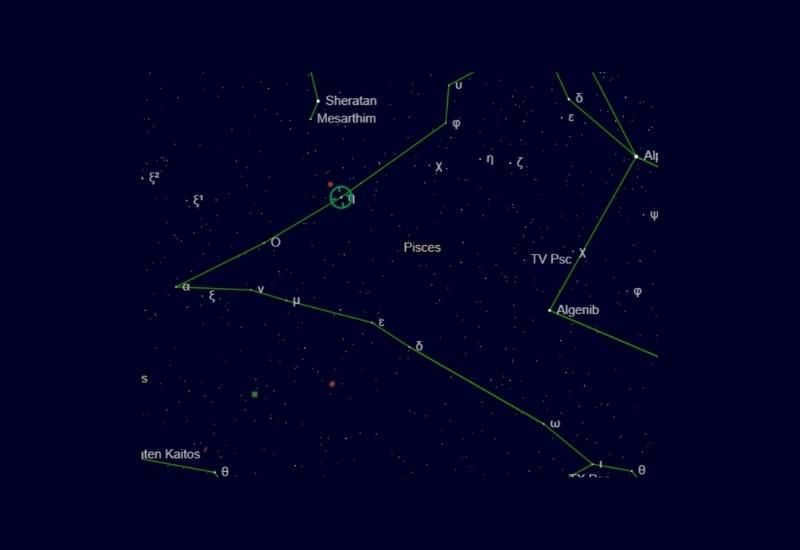
Locating the Pisces constellation can be challenging due to the dimness of its stars, despite occupying a significant portion of the sky. It bears a resemblance to the letter “V,” with the right side forming an “O” shape and a small triangle visible on the left side.
Astronomers typically search for a circle of five stars in the sky, known as the Wreath asterism, which is the most recognizable pattern of Pisces. This asterism also represents the head of Western Pisces.
To assist in finding Pisces, astronomy enthusiasts often rely on star charts or mobile apps that provide directions based on their location.
Pisces astrological sign
In the ancient Roman era, around the first century AD, an astrologer named Manilius described individuals born under the Pisces zodiac sign as having a deep affinity for the sea. He stated that they would wholeheartedly embrace the vastness and mysteries of the ocean, entrusting their lives to its depths.
Pisces, as a zodiac sign, is intricately linked to the ever-changing nature of the oceans and seas. Consequently, those born under this sign experience a life filled with unpredictable circumstances and constant fluctuations.
Manilius further elaborated on the characteristics of Pisces individuals, mentioning their ability to have numerous offspring, their amicable nature, their agility, and the perpetual potential for change that defines their lives.
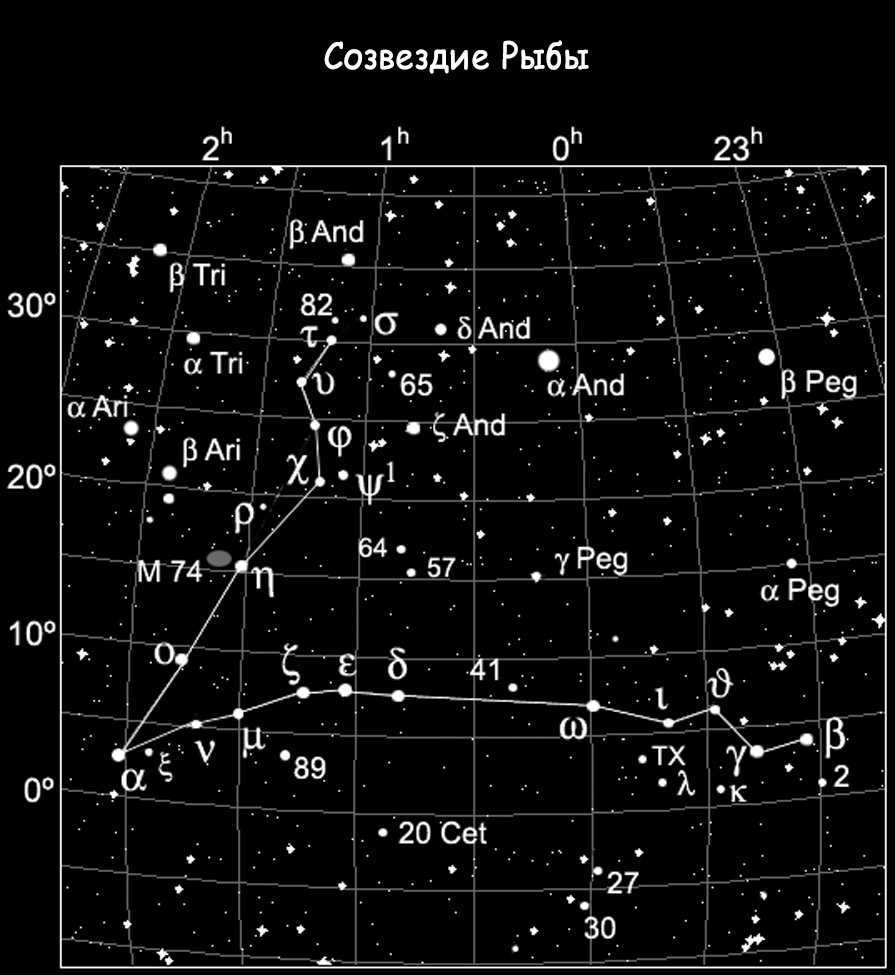 The constellation Pisces is home to galaxies and stars
The constellation Pisces is home to galaxies and stars
Pisces, the zodiac sign, contains a total of ten stars with their own planetary systems, as well as a mesmerizing spiral galaxy known as Messier 74 (NGC 628), which boasts an impressive 100 billion stars.
Located between the stars Eta Pisces and Alpha Aries, this constellation has caught the attention of scientists due to its X-ray emissions, which have been attributed to the presence of a black hole galaxy.
The name Messier 74 was given by the astronomer Charles Messier, who dedicated his time to identifying various objects in the night sky and creating the renowned “New Messier General Catalog”.
In addition to M74, numerous other celestial objects have been observed within the Pisces constellation:
| Name | Type | Magnitude |
| Messier 74 | Galaxy | 9,5 |
| NGC 660 | Galaxy | 11,2 |
| NGC 315 | Galaxy | 11,2 |
| NGC 520 NED01 | Galaxy | 11,4 |
| NGC 410 | Galaxy | 11,5 |
| NGC 524 | Galaxy | 11,5 |
| NGC 474 | Galaxy | 11,5 |
| NGC 266 | Galaxy | 11,6 |
| NGC 514 | Galaxy | 11,6 |
| NGC 718 | Galaxy | 11,7 |
| NGC 470 | Galaxy | 11,8 |
| NGC 467 | Galaxy | 11,8 |
| NGC 676 | Galaxy | 12 |
| NGC 7715 | Galaxy | 12,1 |
| NGC 383 | Galaxy | 12,1 |
| NGC 499 | Galaxy | 12,3 |
| NGC 520 NED02 | Galaxy | 12,4 |
| NGC 693 | Galaxy | 12,4 |
| NGC 706 | Galaxy | 12,5 |
There are over 160 stars in the constellation, with the 3 most well-known ones being:
- The brightest star within the entire constellation.
- It is a binary star situated near the tail of the Northern Fish.
- Its brightness is 300 times greater than that of the Sun.
- Based on the astrological characteristics of the star Kullat Nuni, it imparts traits such as determination, ambition, and a drive for success to the zodiac sign.
- It falls into the fourth magnitude category of stars.
- Its distance from Earth is approximately 294 light years.
- A binary star that represents the intersection of the two threads that bind the fish.
- The renowned scientific publication “The King of Astrology” suggests that individuals born between the end of February and the end of March possess an innate sense of self-awareness and a clear understanding of their life’s purpose, all thanks to this particular star.
- The star’s name can be translated as “knot” or “rope,” which is fitting considering that it is from this celestial body that the zodiac sign Pisces originates.
- It is located approximately 169 light years away from Earth.
- Located to the east of the Constellation Wreath, specifically serving as the head of the western fish.
- This star is classified as a dwarf star.
- Its distance from Earth is approximately 106 light years.
Other stars in the Pisces constellation
- Pisces TX. – A bright red Carbon star located about 900 light-years away from the sun.
- Van Maanen’s star – Named after the Dutch astronomer who discovered it, this is a white dwarf located 14 light-years away.
- Gamma Pisces – A yellow giant located 130 light-years away.
- Beta Pisces – The furthest star, located 492 light-years away. Arab astronomers refer to this star as the mouth of the fish.
- Iota – A yellow dwarf located 45 light-years away.
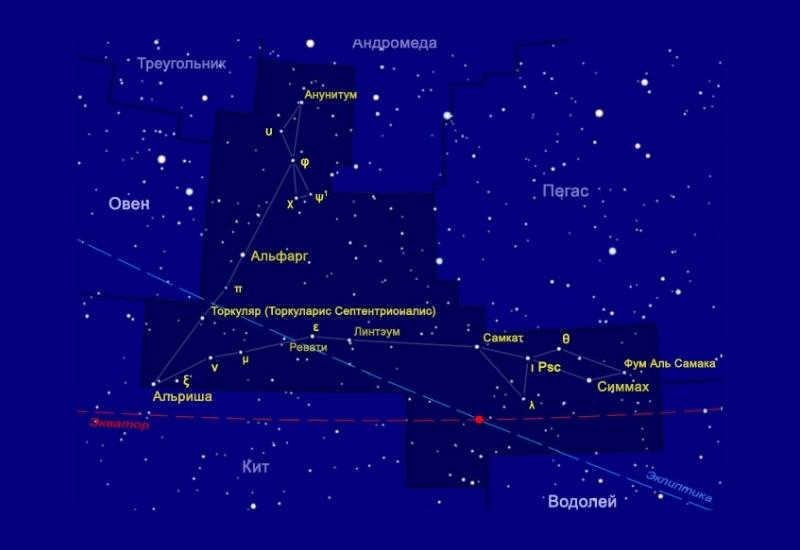
Even though Pisces constellation is known for its dim stars, it is also home to numerous stars and galaxies. One of the most remarkable ones is M74, which can be observed with a high-quality telescope and is sure to captivate anyone who sees it.
Messier 74 resembles a miniature version of our own Milky Way, and its spiral arms are rich in gases and dust, where new stars continue to form to this day.
Without a special instrument, it is impossible to identify and observe the constellation, as the brighter celestial neighbors overpower the fainter stars with their light. Having a professional telescope is not a requirement for Pisces, as an amateur can handle the task just fine.
Individuals born under this zodiac sign possess emotional sensitivity, determination, and kindness. Astrologers believe that Pisces’ differing orientations towards the North and West are indicative of their changeability and occasional fickleness.
The opposing orientations of Pisces symbolize the constant split of attention between a person’s fantasies and reality.
The Christian symbolism for Jesus Christ also incorporates the astrological designation of Pisces. This connection originated in the early days of Christianity when believers would undergo baptism in water, metaphorically identifying themselves as fishes. Additionally, the word “Ikhthus”, which bears resemblance to “Jesus”, served as a coded reference to Christ. In Greek, “Ikhthus” translates to “Pisces”.
To observe the Pisces constellation, individuals in the Northern Hemisphere can view it from August to February, with November being the optimal time. In the Southern Hemisphere, it is visible during the spring season.
Scientific Facts: A Video Review
The constellation Pisces is one of the twelve constellations that the Sun passes through on its annual journey, known as the zodiac. Humans have been aware of this constellation for thousands of years.
Position on the star chart
Pisces is located in the Northern Hemisphere and can be observed in early autumn in our country. It is not particularly noticeable in the night sky, appearing dim. However, there are many fascinating objects within this constellation.
Check out the planetarium program for a different perspective
Located between Aries and Aquarius on the star chart, Pisces can be seen reaching out towards Andromeda and Pegasus. This constellation is connected by an imaginary ribbon, with the star Alrisha marking the starting point.
Over a period of 38 days, the Sun travels across the background of Pisces. In the modern calendar, this occurs from March 12 to April 18.
Pisces is made up of two distinct groups: North Pisces, consisting of three stars, and West Pisces, consisting of seven stars.
Adjacent Constellations
Aries, Triangle, Whale, Andromeda, Pegasus, and Aquarius are the closest constellations to Pisces.
If you imagine the Pisces constellation in a geometrical sense, it can be visualized as two rays intersecting at an acute angle. The northern ray terminates in a triangle with obtuse angles, while the western ray does not form an equilateral pentagon.
The more prominent and larger neighboring constellations of Pisces include Aquarius, Aries, Triangle, Andromeda, Pegasus, and Whale.
Where can I locate the Pisces constellation?
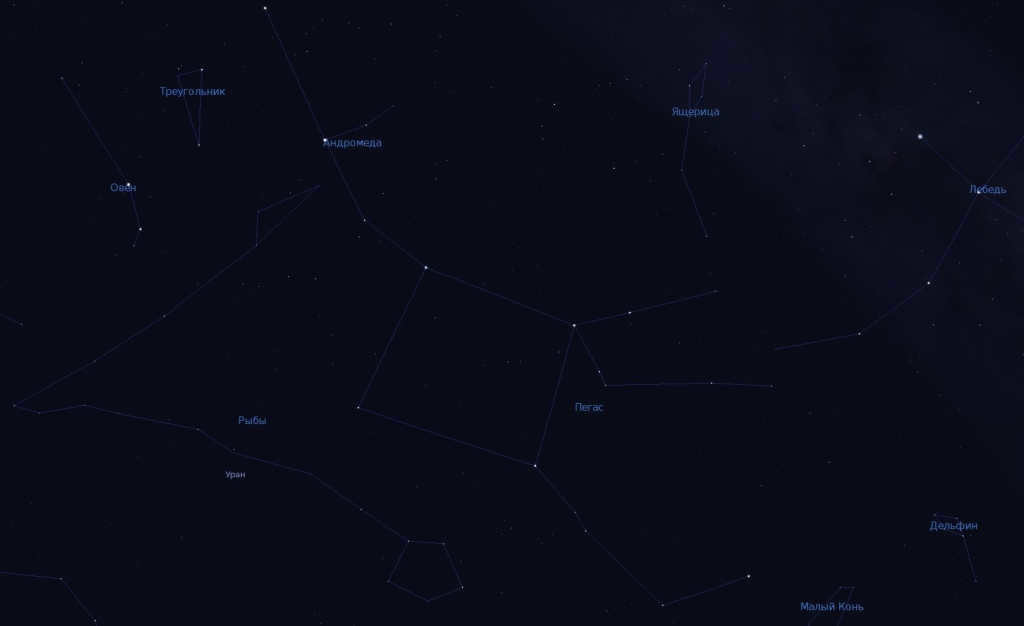
One can locate it by observing its more prominent celestial neighbors. The attention is easily drawn to the expansive and luminous formation created by Andromeda and Pegasus. These two constellations appear to envelop Pisces. The Pisces constellation, consisting of five stars, is situated in closer proximity to Pegasus. On the other hand, there is a three-star fish that can be observed next to Andromeda.
It becomes even more effortless to locate the radiant Perseus, as it serves as a guide to Aries, which is positioned adjacent to the Pisces constellation.
Directly beneath the acute angles of Cassiopeia (which is impossible to overlook), lies Andromeda, with Pisces situated below Andromeda.
Observing in the Northern Hemisphere from the beginning of autumn until the start of winter is a wonderful experience. The ideal months for observation are September and October, as long as the weather conditions permit.
Discovery timeline


These stars bear a strong resemblance to the constellation of Pisces!
Ancient Phoenician legends make mention of these stars. Information about the Pisces constellation, albeit in a slightly modified form, is documented on Babylonian cuneiform cylinders. The present form and description of the constellation have been passed down to us from the enlightened Greeks. Pisces was distinguished and mentioned as an independent constellation in the second century by Claudius Ptolemy in his catalog of the night sky, known as the “Almagest”.
This group of stars is particularly visible in the sky during rainy seasons and floods when the Earth’s surface is saturated with moisture. It is during these times that water-dwelling creatures thrive. It is possible that people identified the constellation of Pisces in these bright stars.
The stars composing the constellation.
There are 75 stars that form this particular constellation, and they can be observed on a clear night in the sky with the help of a basic amateur telescope.
For those who are not interested in astronomy, it is sufficient to know that within the Pisces constellation lies the vernal equinox point. This is where the Sun appears each year, marking the beginning of longer daylight hours in the Northern Hemisphere and shorter ones in the Southern Hemisphere.
Pisces does not astonish observers with its dazzling star brightness. Just like on Earth, the stars in the sky are understated and inconspicuous.
Al pherg
can be paraphrased as
Al ferg
.
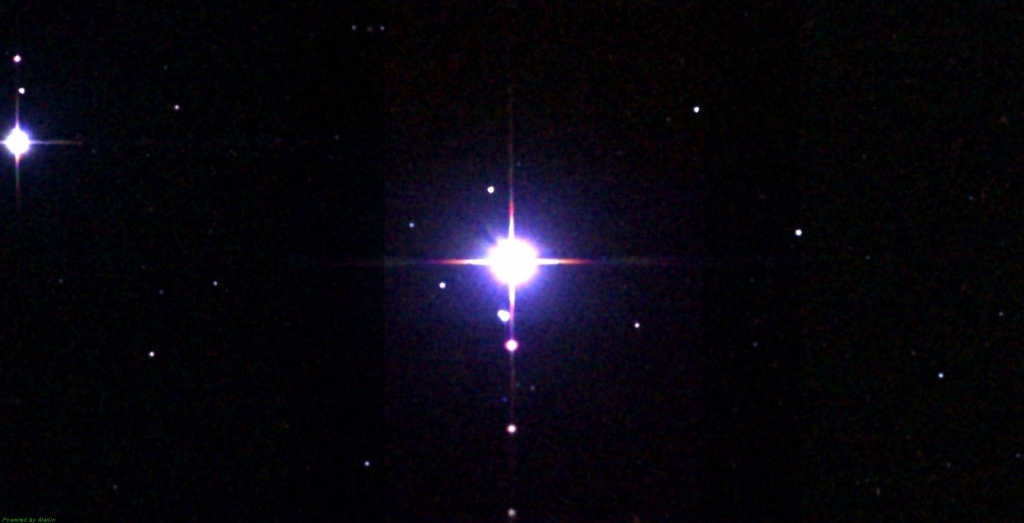

Al pherg, also known as Kullat Nunu, is recognized as the primary luminary of the constellation due to its remarkable brightness. It falls under the fourth classification of stellar magnitude. This colossal star radiates a luminosity that is 316 times more intense than that of our Sun. Situated at a distance of 294 light-years from Earth, it beams a dazzling blue light that captivates our gaze.
Alricia

Photo of HD 12446, also known as the alpha star of the Pisces constellation
The starting point of the constellation is the alpha star of Pisces, which is called Alrisha. This Arabic word can be translated as a rope or twine. Alrisha symbolizes the connection of the mythological rope that binds the Pisces together. This star is the third brightest in the constellation. What makes it interesting is that it represents twins – two white dwarfs.

There is another binary star system in the Pisces constellation known as Omega. It is classified as a dwarf star and is located 106 light years away from Earth.
Other celestial bodies in Pisces
One of the notable stars in Pisces is called gamma. It is the second brightest star in the constellation and is classified as a yellow giant. Its distance from Earth is approximately 130 light years.
Another interesting star in the Western part of Pisces is TX Pisces, which is a carbon star. It emits a dark red color and is quite luminous.
Moving closer to our planet, we have Iota, which is only 45 light years away from Earth. It is a yellow dwarf star and is part of the Pisces constellation.
Finally, the farthest star from Earth in the Pisces constellation is Beta, which is located 492 light years away. It is often referred to as the “mouth of the fish” by Arab astronomers.


The star that is closest to Earth in the Pisces constellation is known as Van Maanen’s star. This star is one of the nearest white dwarfs to the Sun, located approximately 14 light-years away. It was first discovered in the early 20th century by a Dutch astronomer, who named it in his honor. Van Maanen’s star can be found along the path leading to the Western Fish.
M74: The Spiral Galaxy Messier 74
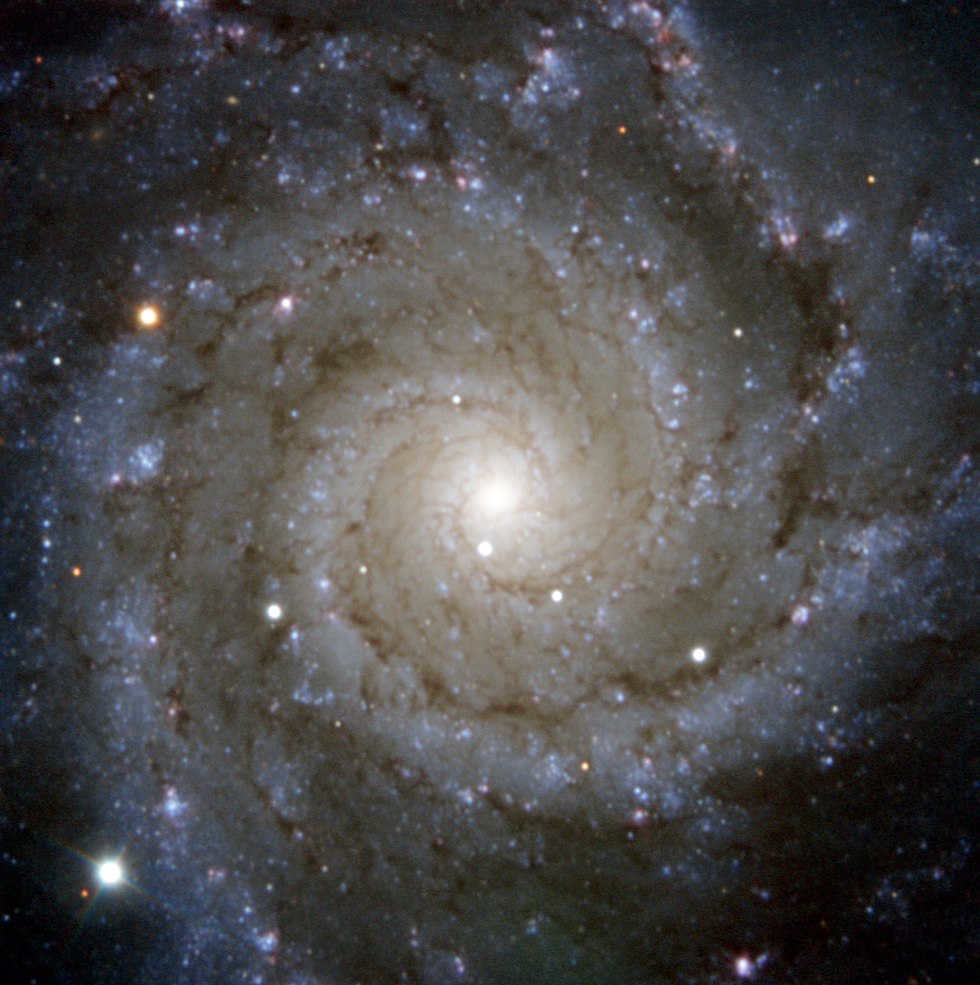

However, the most fascinating entity within the constellation is the spiral galaxy. It goes by the name Messier 74 in the field of astronomy. Its observation is quite challenging for novice stargazers due to its positioning between Etta Pisces and Alpha Aries. The galaxy is currently experiencing active star formation and has given birth to two supernovae in the past decade. Pierre Michener was the first to discover this galaxy in 1780, while modern astronomers have recently uncovered a black hole within M74 that emits an intense X-ray radiation.
In Greek mythology, the stars were perceived by the ancient Greeks as a representation of their deities. Fascinated by these celestial bodies, they invented captivating narratives revolving around them. Among these tales is the story of the Pisces, which involves the goddess of beauty Aphrodite and her son Eros. According to the myth, Aphrodite and Eros transformed themselves into fish to evade the relentless pursuit of the fearsome monster Typhon. This monstrous creature, with its numerous heads and fiery breath, posed a great threat to the divine duo.