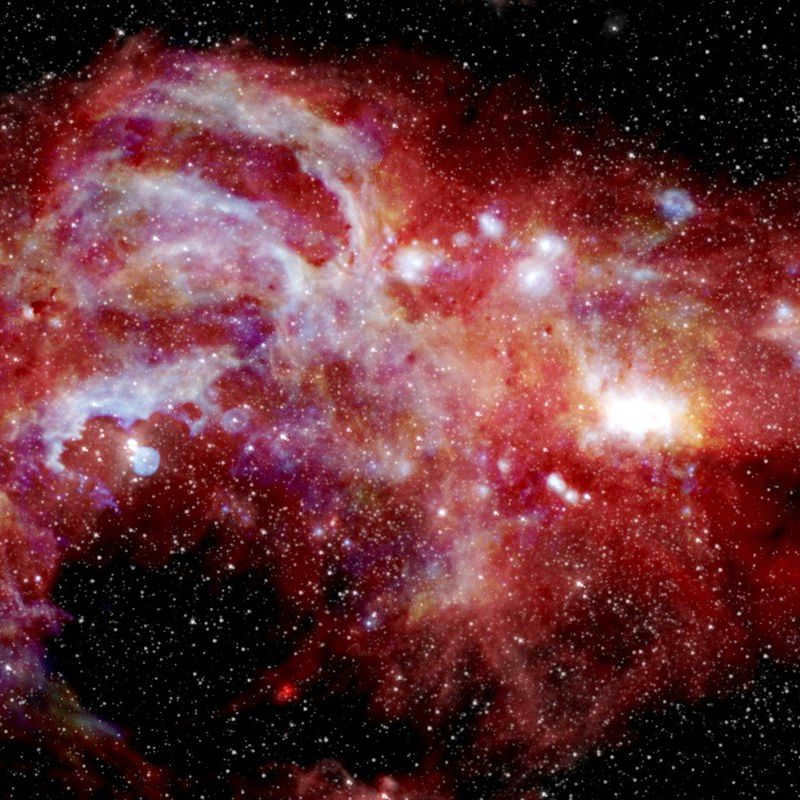
Astronomers recently unveiled a fresh and remarkably detailed snapshot of the central area of the Milky Way galaxy. This captivating image spans an impressive distance of approximately 600 light-years. Discover the significance behind this extraordinary image for scientists and researchers.
What is depicted in the new image?
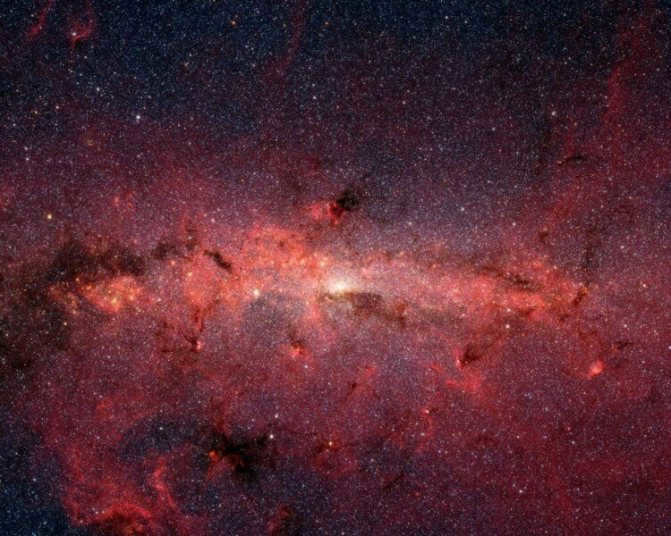
The new image showcases the Arca cluster, which is the most densely populated region of stars within the Milky Way galaxy. Positioned in the center of the image, there is a supermassive black hole that emanates a radiant white glow. Surrounding the black hole is a faint, shimmering halo of silver light.
It is worth mentioning that this is the first instance in which scientists have been able to observe the core of our galaxy with such precision. The data obtained from the SOFIA telescope has provided significant insights, filling numerous gaps in our understanding. With just a bit more information, we will be able to construct a comprehensive representation of the Milky Way.

What was the method used to obtain this image?
Utilizing a unique camera capable of capturing infrared radiation, astronomers were able to capture this image. This camera is situated on board the NASA SOFIA airborne observatory. The resulting panoramic image is a combination of the most recent data and previously gathered information.
What is the intended purpose of the image?
Astronomers will utilize the intricate depiction of the Milky Way in their upcoming investigations. This valuable data will enhance their comprehension of the formation of massive stars and the driving force behind the supermassive black hole situated at the heart of the galaxy. It is worth noting that previous images were unable to capture certain celestial objects that hold significant explanatory potential. Presently, there has been a notable shift in this situation.

Bread basket with the design “Prairie”, measuring 30×30 cm, featuring a terracotta color with printed stripes


Flask “Best Hunter”, 250 ml.

The Season of Autumn.

Tropicano – mirror painting

What do Easter eggs look like from space?


View of our galaxy from space.

Painting on a mirror: The Danaida Butterfly


Landscape painting on a mirror.
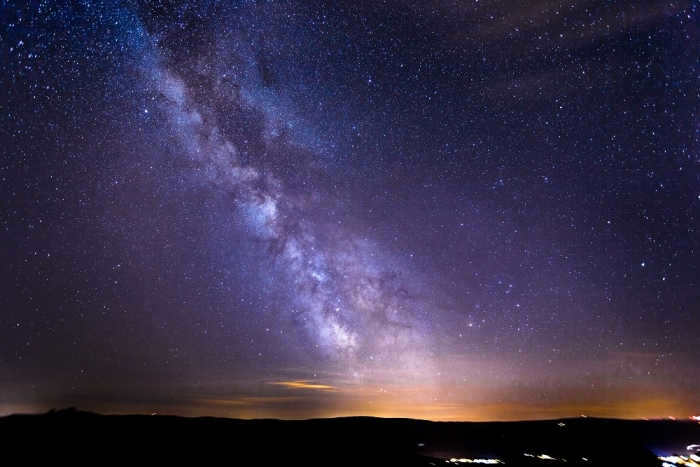

Images of the Milky Way have always captivated nighttime skywatchers and those interested in studying the universe. It can be a challenge to find the perfect location to fully appreciate the beauty of our galaxy. To cater to such individuals, Canadian Dave Achuk has created an incredible video that allows anyone to immerse themselves in the mesmerizing depth and splendor of the Milky Way.
This Canadian astronomy enthusiast compiled 400,000 photographs captured by the orbiting Spitzer Space Telescope and transformed them into a high-quality video lasting approximately 8 minutes. The entire process took him about 5 months, but the end result was well worth the effort! Thanks to his work, the Milky Way galaxy is now accessible to anyone online, regardless of their location on our planet!
Milky Way: fascinating photos and intriguing information
The Milky Way, a mesmerizing spiral galaxy, serves as the home to our beloved planet Earth and the entire solar system. We have meticulously gathered a collection of 12 captivating facts that will truly astound you:
– According to the consensus among scientists, our esteemed galaxy boasts an impressive age of approximately 10 billion years;
– The formation of our solar system took place an astonishing 4.57 billion years ago;
– The Milky Way, a vast expanse, is believed to contain a staggering number of stars ranging from 100 to 400 billion;
– Situated at its core, akin to numerous other galaxies, lies a formidable and enigmatic black hole;
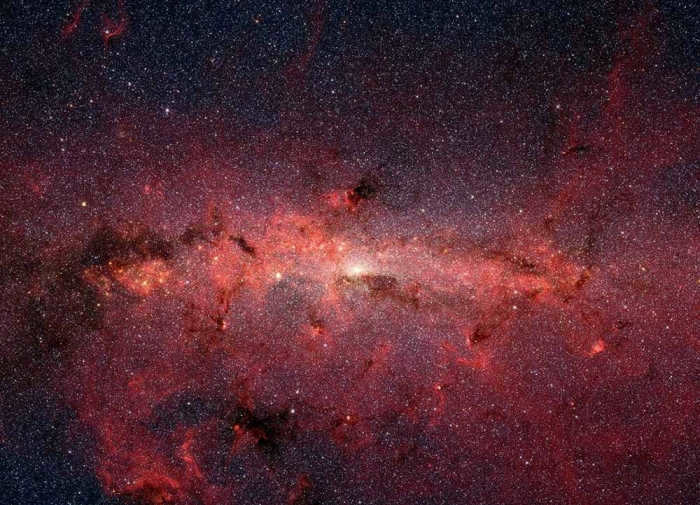

– Our galaxy, known as the Milky Way, is a member of a local cluster of galaxies that also includes the Andromeda Galaxy and the Triangle Galaxy. This cluster is further comprised of approximately 50 smaller galaxies;
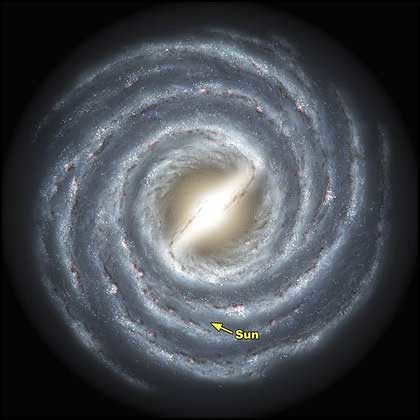
– The solar system is located approximately 7.5-8.5 kiloparsecs away from the center of the Milky Way;
– The ancient Greek astronomer Claudius Ptolemy, who lived during the 1st and 2nd centuries AD, provided the first detailed description of our galaxy;
– The term “Milky Way” is derived from Greco-Roman mythology, and the word “galaxy” itself means “Milky Circle”;
– As our planet Earth is situated within the Milky Way, its exact appearance remains unknown to us. However, scientists have studied similar galaxies and believe that, given the similarities in parameters, our galaxy should have a similar appearance.
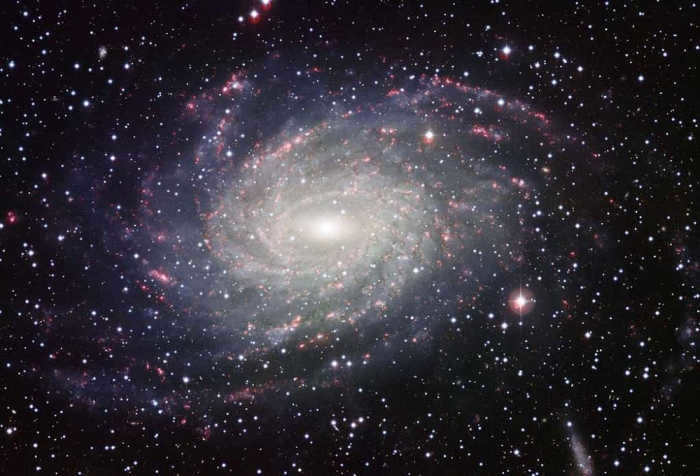

– The Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way Galaxy are on a collision course, approaching each other at a speed of 120 kilometers per second. This cosmic collision is predicted to occur in approximately 4 billion years, and their merger will take place after an additional 2 billion years.
– Scientists also speculate that the Triangle Galaxy may also be involved in this galactic collision.
– It is even possible that the Milky Way will collide with the Triangle Galaxy before it collides with Andromeda.
In general, humankind’s understanding of the structure of the Universe and our own Galaxy is still limited. However, advancements in technology are continually uncovering new facts for scientists worldwide.
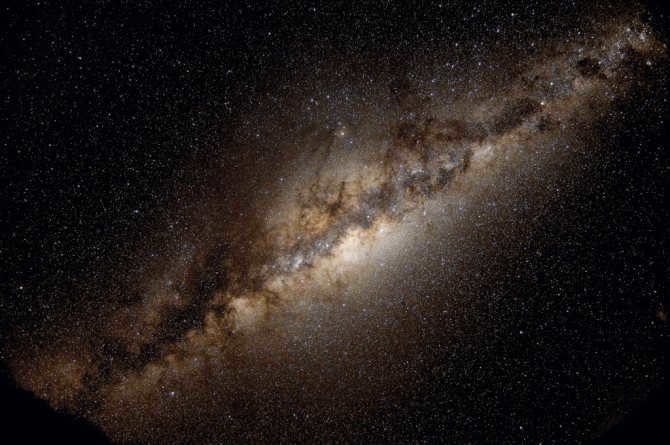



When it comes to our galaxy, one cannot help but ponder what lies at the heart of the Milky Way.
The nucleus of the Milky Way is the central region where stars are born. It is the activity within the nucleus that gave birth to the entire galactic system. In fact, the center of the Milky Way is a relatively compact area, measuring approximately 1,000 parsecs in radius. In the vast expanse of the universe, this size is comparatively small.
The naked eye or even a telescope cannot provide us with a view of the center of the galaxy due to the immense presence of interstellar gas and dust, which diminishes the brightness of the light emitted by the central area of the Milky Way.
Related Materials

The Milky Way, our home, remains an enigma to most people. Although we are familiar with many details about it, there are still numerous unresolved mysteries waiting to be unraveled.

On our starlit island, there is a lighthouse in the distance.
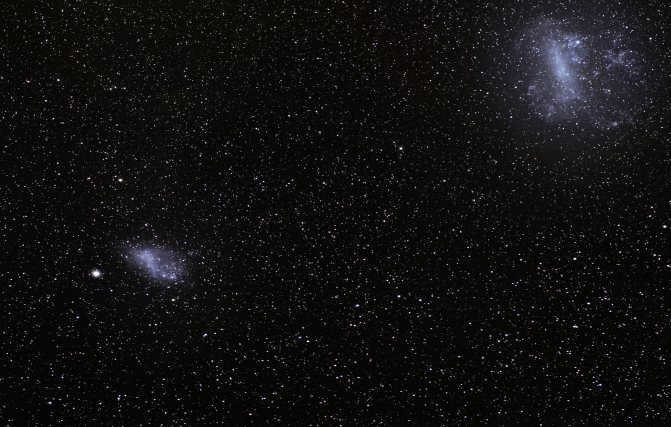
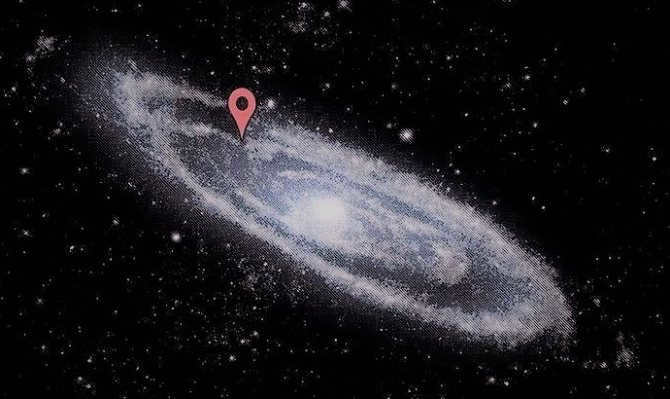



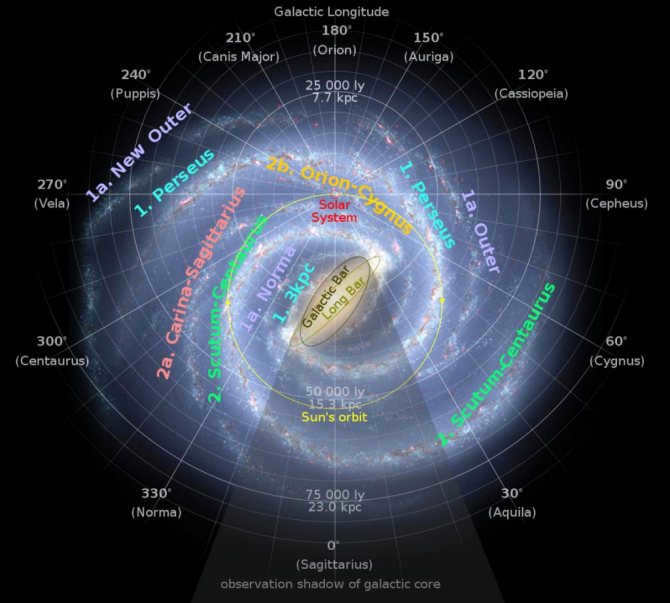

The Milky Way has been extensively studied, with numerous ground and space missions dedicated to understanding its characteristics. Through these efforts, scientists have discovered that the galaxy contains over 400 billion stars, each of which could potentially harbor planets similar to Earth in terms of size, mass, and habitability conditions.
Approximately 90% of the Milky Way’s mass is comprised of dark matter, a phenomenon that has yet to be fully explained by scientists. While dark matter cannot be directly observed, the rapid rotation of galaxies provides evidence for its existence and serves as a protective mechanism against galactic destruction.
Resources about the subject
The general structure of the Galaxy has a resemblance to a disk with a measurement of 80,000 light-years (or 25,000 parsecs) in diameter, and a thickness of approximately 1,000 light-years. Positioned at the center of the galaxy is the Bulge, which consists of aged stars that move in elongated orbits around a supermassive black hole called Sagittarius A. Our Bulge spans a length of 8,000 parsecs.
Due to the spiral shape of the Milky Way, there exist spiral arms within the disk plane. It is challenging for us to observe the shape of these arms due to our solar system’s location. Specifically, we are situated 8,500 parsecs away from the galactic center, positioned on the inner boundary of the Orion arm. Recent findings indicate that there are two additional arms originating from the junction within the galaxy’s inner region.
Furthermore, within the inner part of the galaxy, there are a few more arms, contributing to the formation of a four-arm structure. The galaxy’s disk is encompassed by a sphere known as the Galactic Halo, which extends beyond the galaxy by 5,000 to 10,000 light years. This halo is comprised of hot gas, stars, and dark matter.
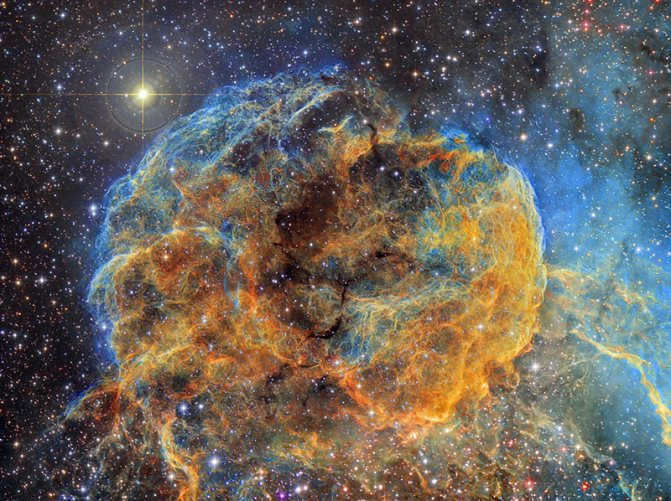
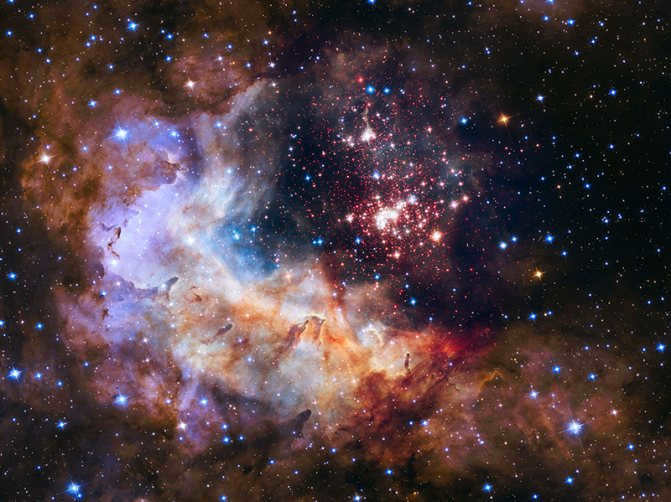
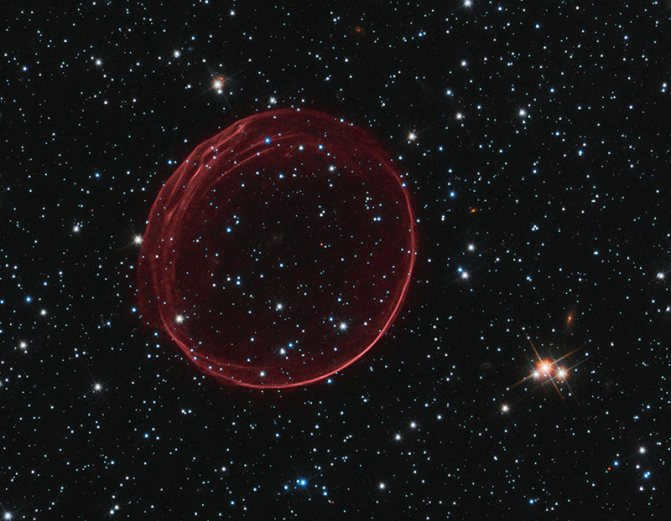
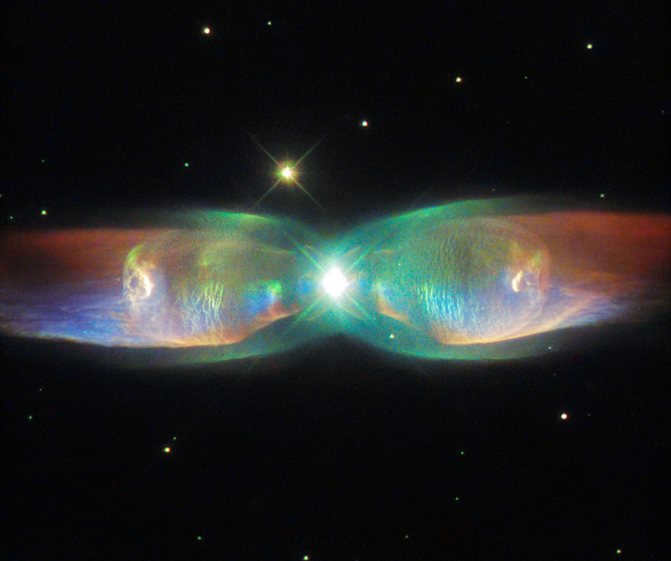










The central region of the galaxy is known for its enigmatic and perplexing characteristics. Unlike the surrounding areas of space, it possesses unique physical properties that have puzzled scientists for years.

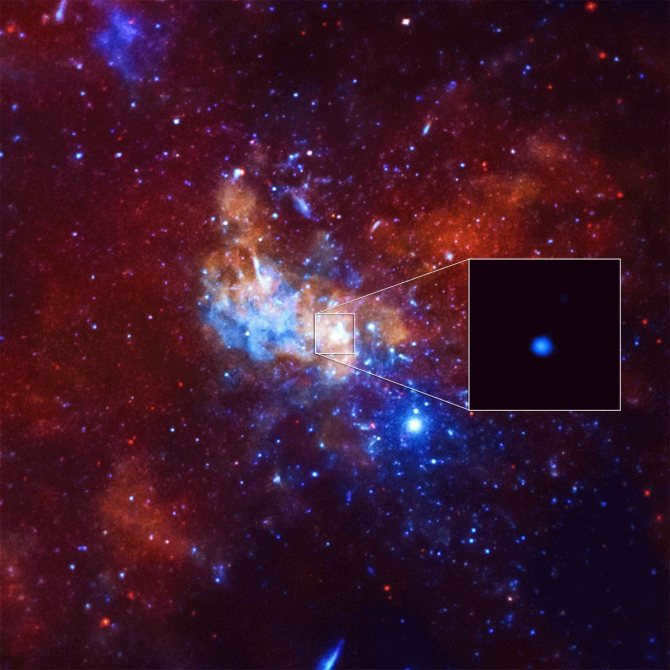
Recently, scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery: the central region of our galaxy is home to a black hole – a space area with altered characteristics.
Our galaxy is relatively young, with an age of approximately 12 billion years, and the process of star formation in its core is still actively ongoing. Within this core, numerous white dwarfs – youthful stars, massive clusters of glowing gas, black holes of varying strengths, and neutron stars have been observed.
All of these elements come together to create an immense, incomprehensibly vast cosmic “kitchen” that continues to produce new stars at an astonishing rate.
Unique Image Collection
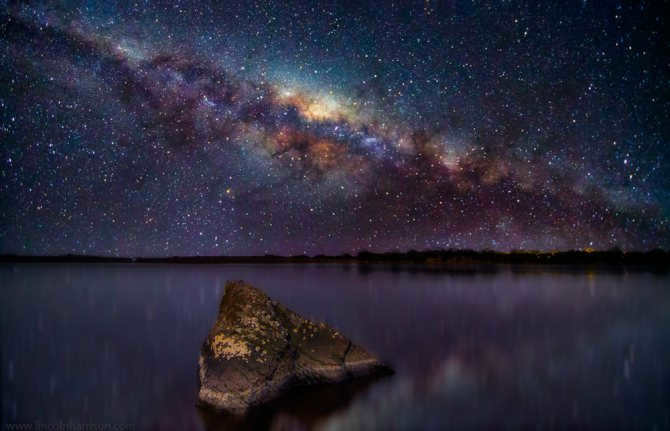
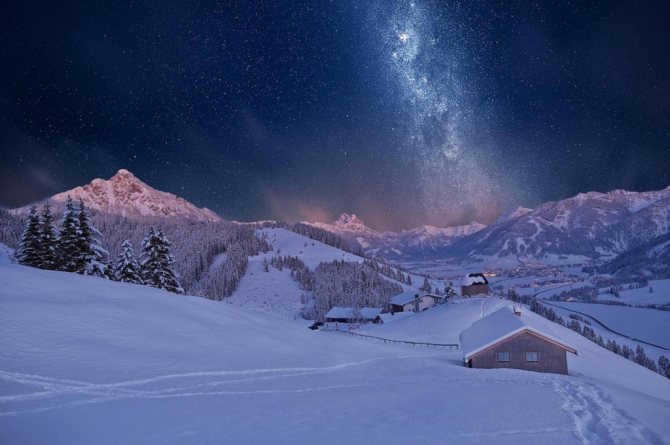
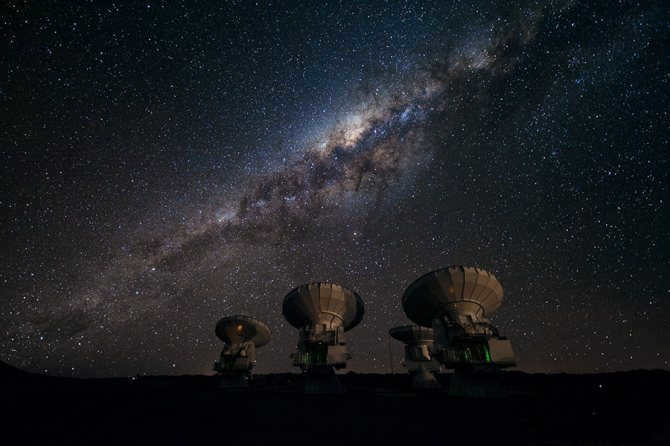
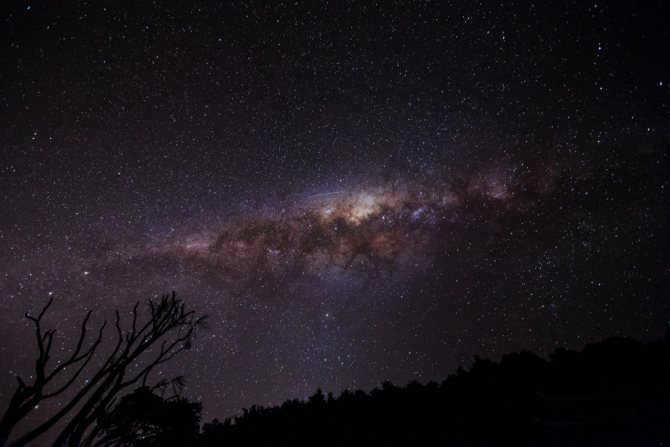
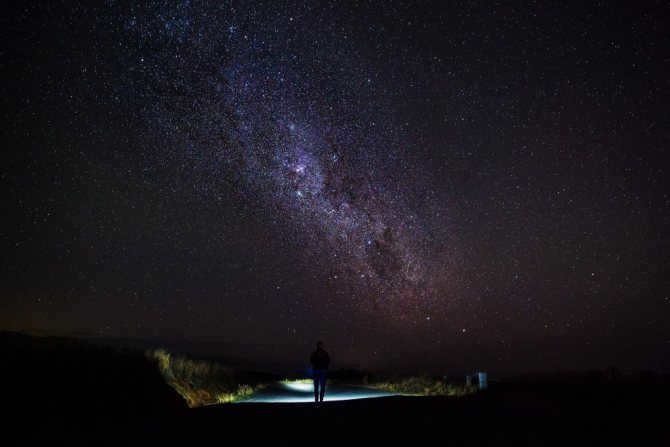
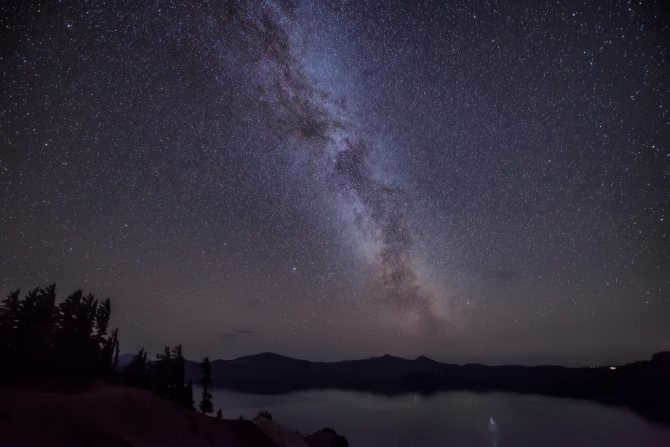
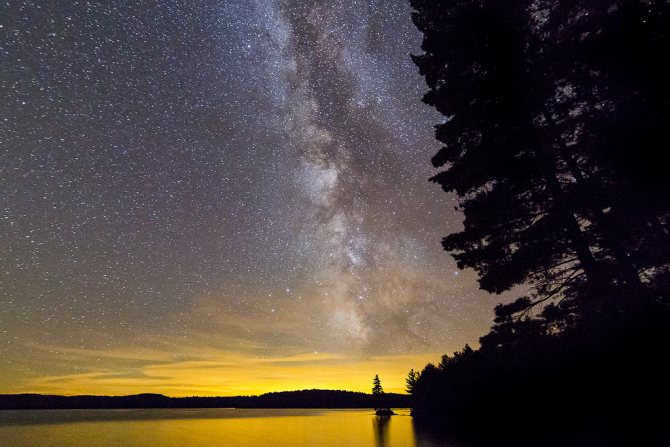
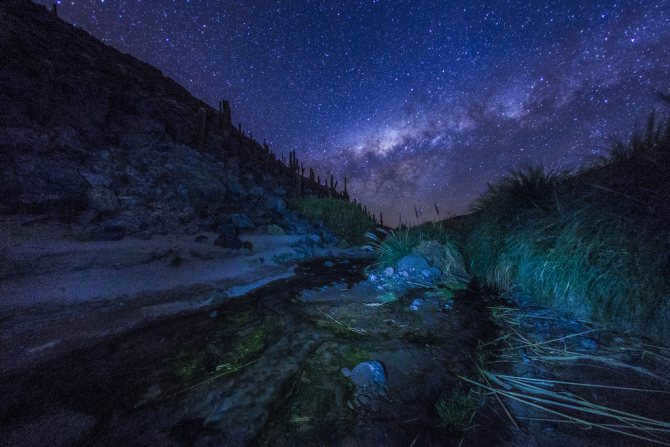
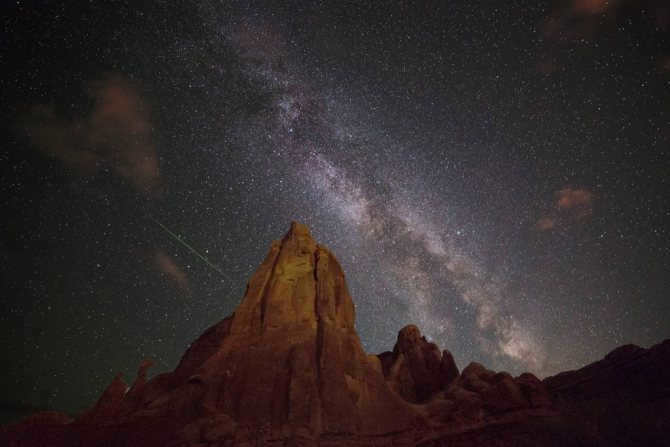
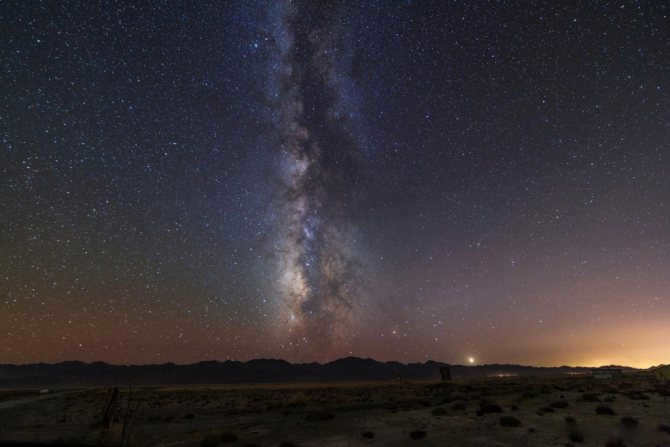
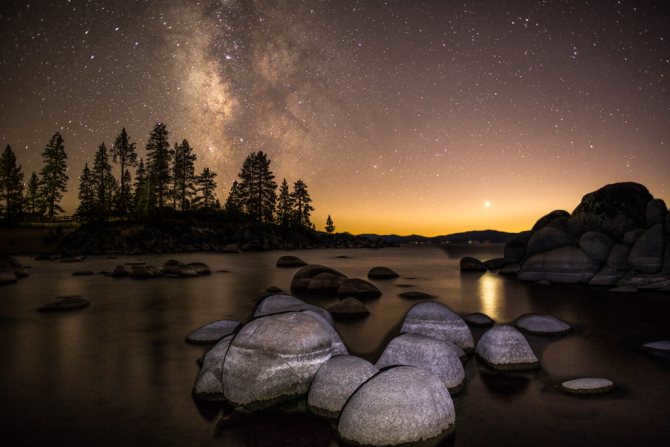
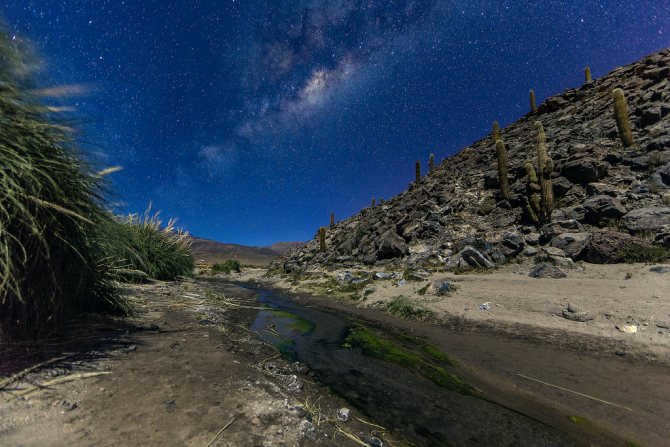
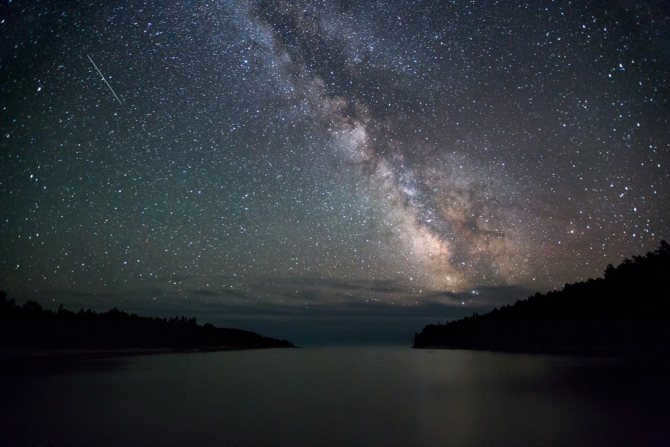
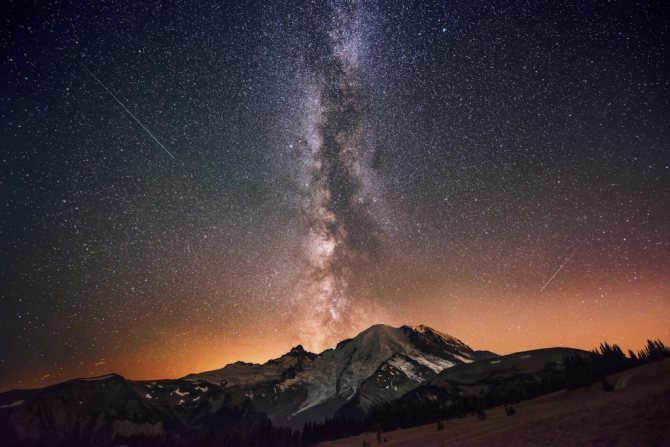
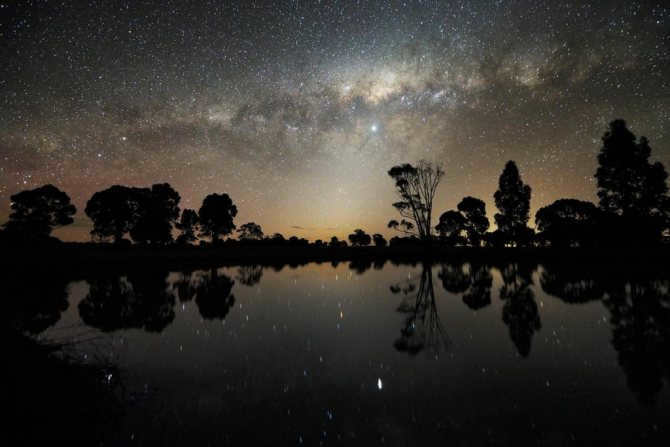
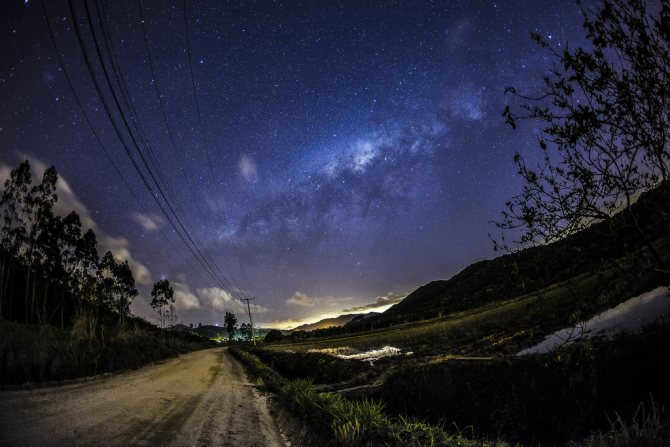
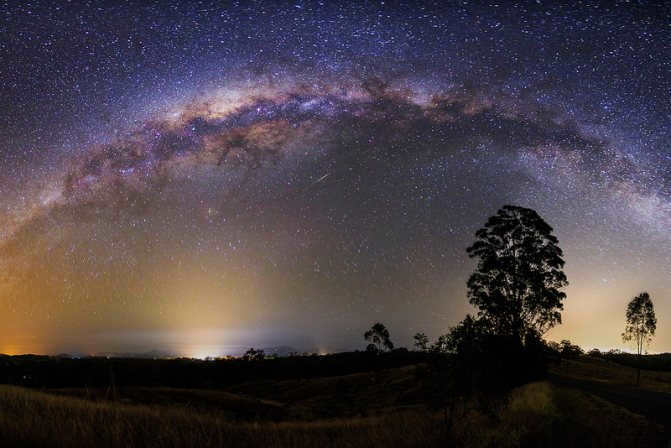
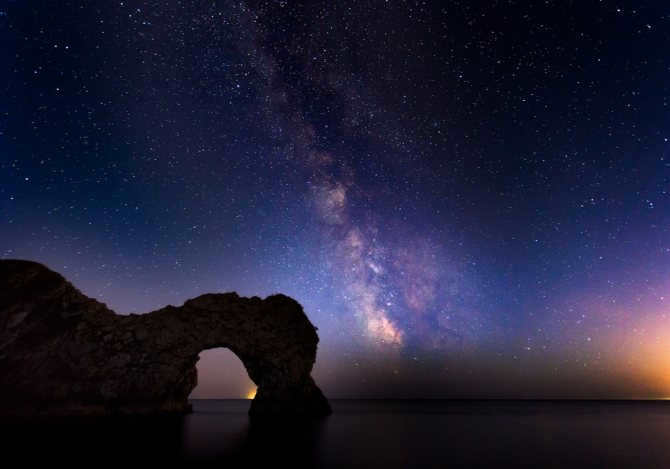
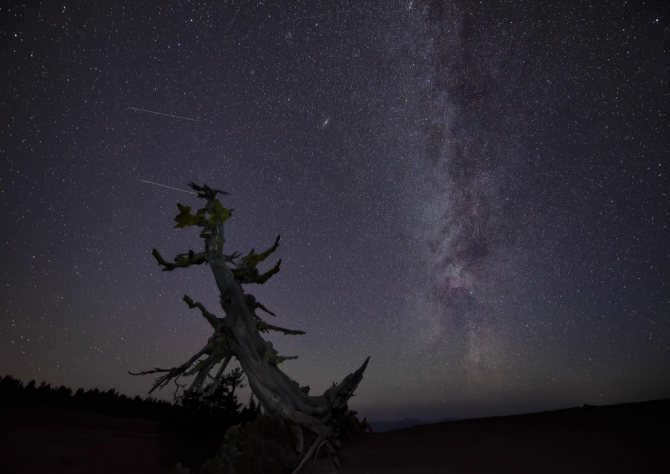
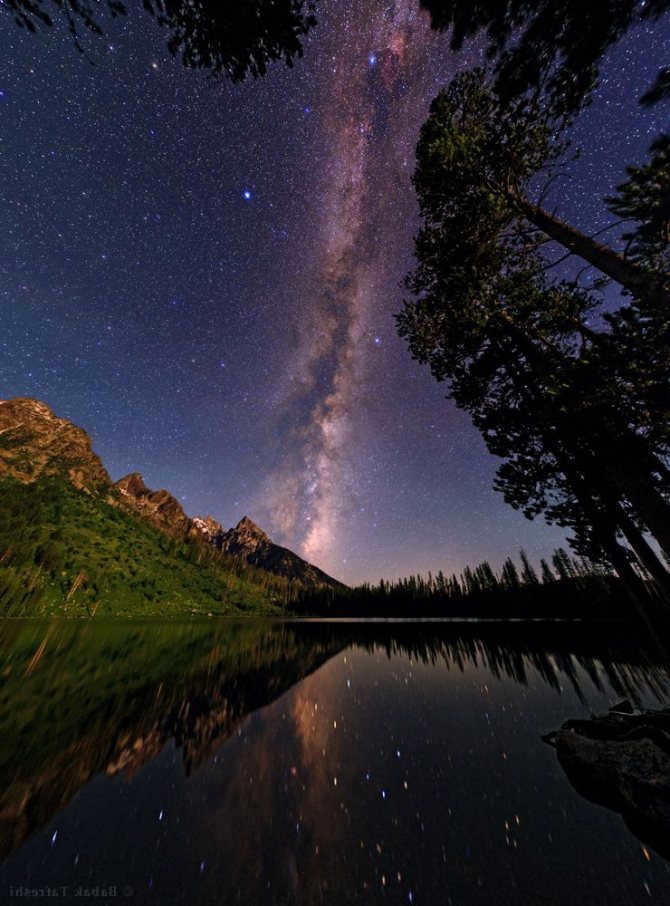
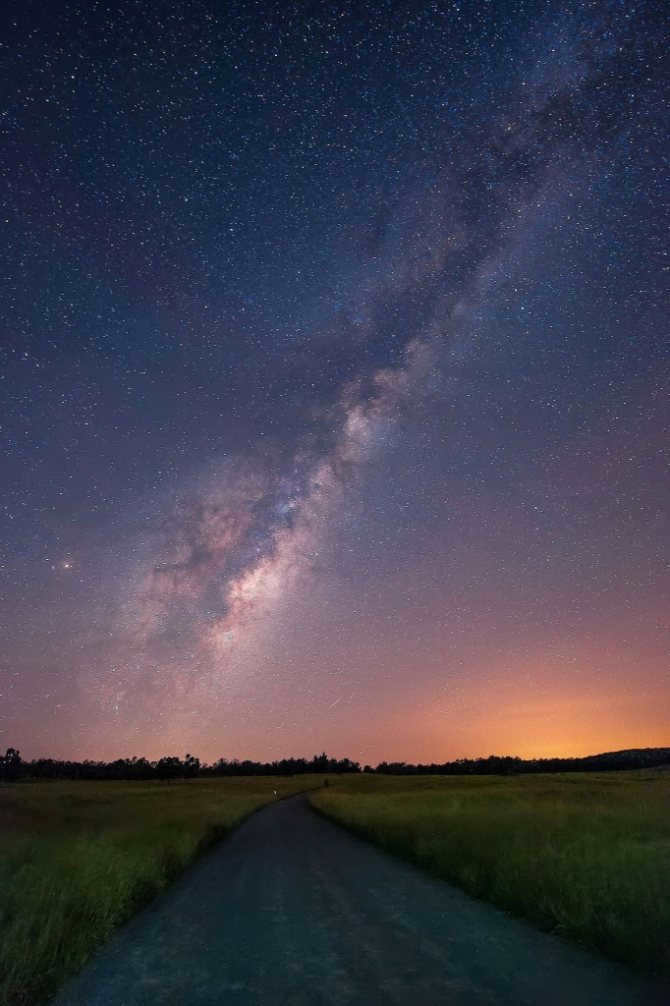
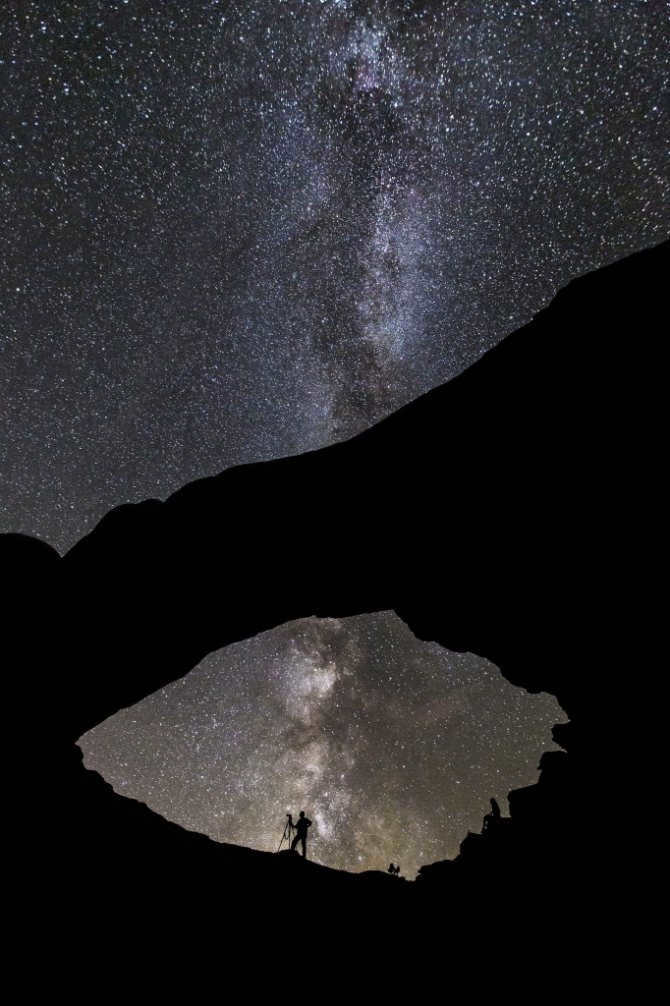




























Similar to numerous others, there exists a gargantuan black hole known as Sagittarius A at the heart of our galaxy, the Milky Way. Positioned at a distance of 26,000 light-years away from our planet, this vast entity spans an impressive size of 22.5 million kilometers.

The biggest star
14. A distance is the Sun from the surface of Mars
15. According to the renowned astronomer Carl Sagan, the number of stars in space exceeds the number of sand grains
16. There exist countless stars that surpass our sun in size
. Just observe how minuscule the Sun appears.
17. VY in the constellation Canis Major is the largest star.
It is a billion times more massive than our Sun.

Additional Resources


According to scientific observations, it has been determined that the Sun travels at a velocity of 220-240 km/s around the center of the Galaxy, completing one revolution every 200 million years. Consequently, our Sun has completed no more than 30 revolutions throughout its entire existence. Simultaneously, the solar system resides within a corotational circle. This means that the Sun’s rotational speed around the center of the Galaxy aligns with the speed of the spiral arm’s compression wave. Within these arms, there are vigorous processes accompanied by intense radiation, with no possibility of escape. Fortunately, the Sun’s position allows us to avoid the detrimental effects of these processes.
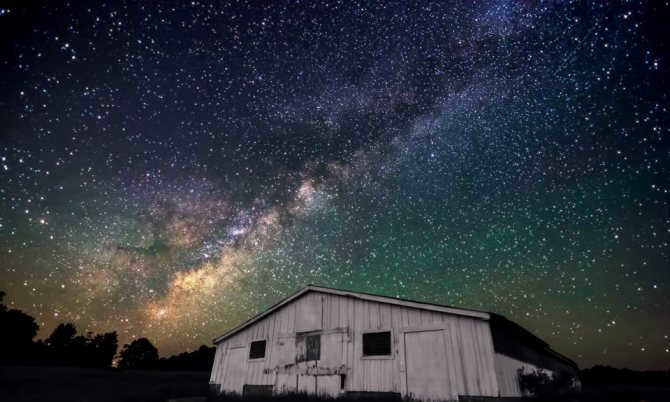

Nevertheless, when observing from our planet, we are only able to perceive a minuscule portion of the vast multitude of stars that exist within the Milky Way. Our galaxy takes the form of a spiral and conceivably possesses a junction.
Present calculations regarding the overall quantity of stars indicate a range of 200 to 400 billion. These are merely a few of the particulars.
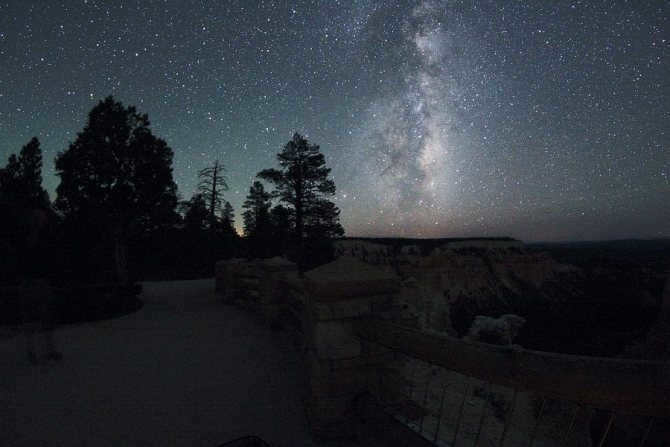

It is possible to capture images of our galaxy, the Milky Way, by using a regular SLR camera and dedicating some time and patience.
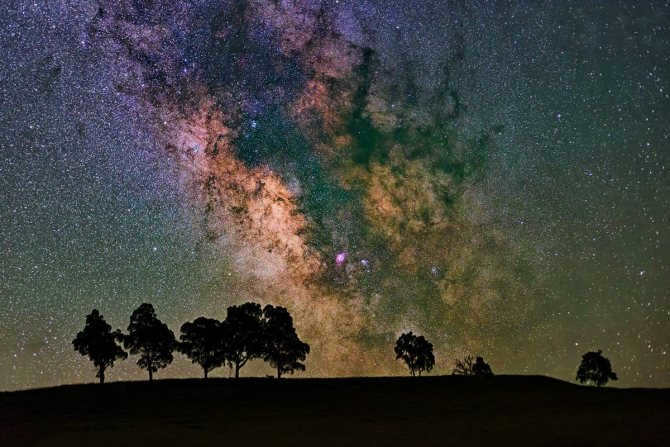

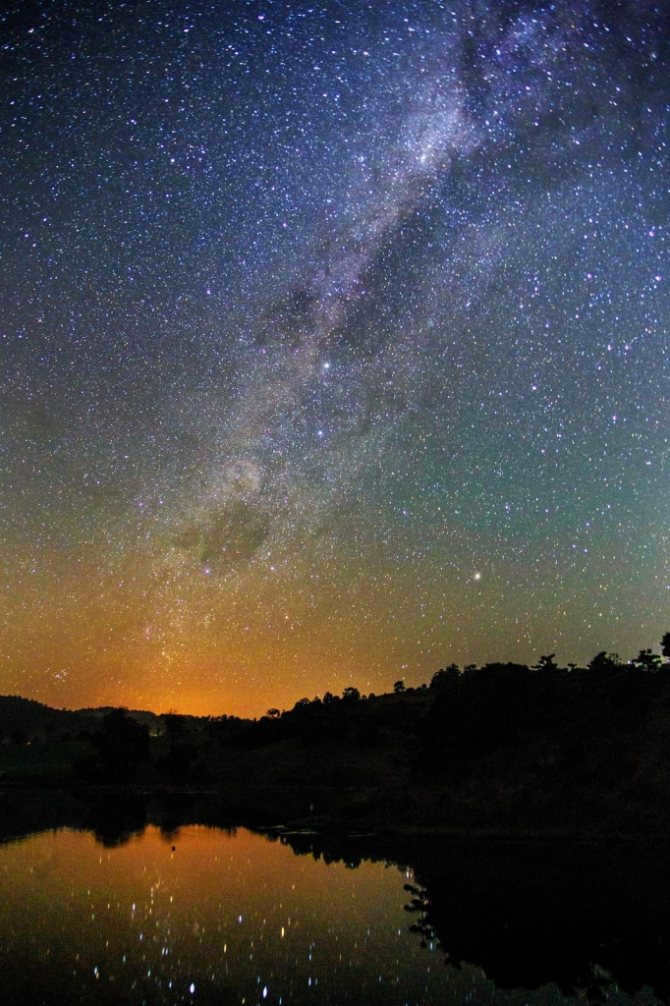
Our shared abode, far from the hustle and bustle of cities and artificial lights
Exploration and nomenclature
The current designation of our galaxy, the Milky Way, has a fascinating origin. It boasts a rich historical background and derives its name from the Latin phrase “via lactea,” meaning “the way of milk,” which has been referenced in various ancient scientific works. One such work observed that the galaxy consists of a vast number of closely clustered small stars. These stars are positioned in such proximity to one another that they resemble spots, and their color characteristics bear resemblance to the appearance of milk.
In the beginning, scientists hypothesized that the Milky Way was teeming with stars. However, this was merely a conjecture that persisted until 1610. It was during this period that Galileo Galilei aimed his inaugural telescope at the celestial heavens and had the ability to observe individual luminous bodies. As a result, humanity uncovered the reality: there exists an abundance of stars, all of which are integral components of the aforementioned galaxy.

The Milky Way
In 1755, I. Kant proposed the idea that the Milky Way Galaxy is composed of stars that share a mutual gravitational force. This gravitational force is what drives the rotation of objects within the galaxy. Ten years later, W. Herschel attempted to map out the shape of the galaxy, but was unaware that a large portion of it was obscured by dust and gas.
It wasn’t until the 1920s that this understanding changed drastically. E. Hubble managed to convince scientists and the general public that what they were observing were not spiral nebulae, but individual galaxies. It was during this time that the true shape of the Milky Way was realized – a spiral galaxy with a central bar.
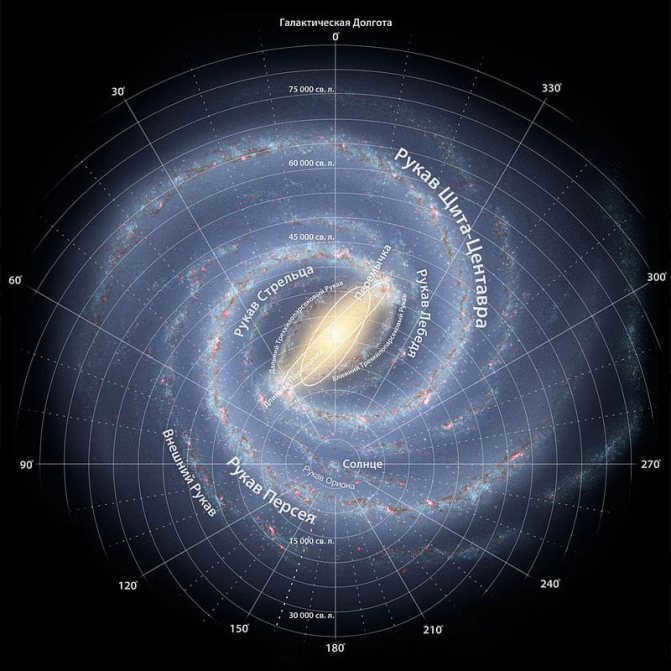
The arrangement of our galaxy
Another enigma of the cosmos
Shortly following the occurrence of the Big Bang, the cosmos was filled with gas, predominantly hydrogen. As time progressed, pockets of gas began to merge due to the force of gravity, eventually forming galaxies in which stars were birthed. Do you comprehend the reason behind stars glowing? It is all connected to the process of thermonuclear fusion involving hydrogen – those stars that eventually transform into supernovae and perish after the explosion “drive” the gas out of the galaxies.
In the enigmatic expanse of intergalactic space, the gas undergoes a cooling process, resulting in increased density. This densified gas lingers in this vastness until the irresistible force of gravity tugs it back towards the galaxy, where it serves as the building blocks for the birth of new stars. This cyclical process persists, as gravity works its magic to condense the gas into galaxies and stars, which subsequently explode and release the gas, only for gravity to once again beckon it forth, giving rise to the creation of fresh celestial bodies.
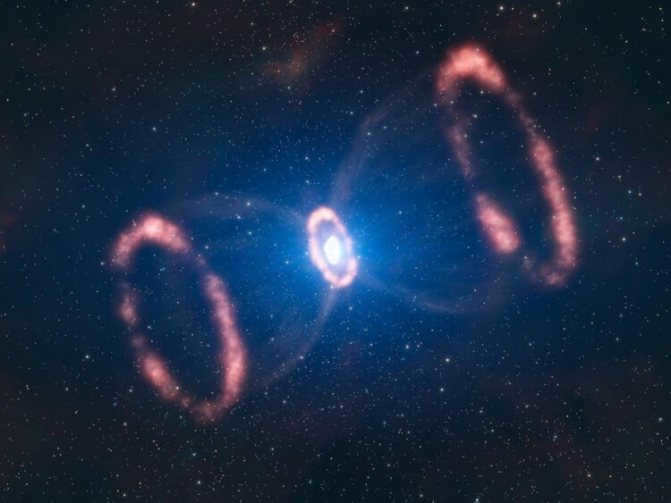

The supernova explosion has been captured in an image by the Hubble telescope
Over time, every galaxy eventually exhausts its supply of recyclable gas. And without gas, new stars cannot form in the universe; old stars reach the end of their lives and perish, leading to the eventual demise of the galaxy. Galaxies exist in what is known as a gas bath, the medium from which they originated and which sustains them. Galaxies inhale and exhale this gas, while the stars continue to burn until the gas is depleted. It’s truly a magnificent process, isn’t it?
Discover even more fascinating facts about the universe on our Yandex.Zen channel
Latest News on Our Galaxy
Topics: Technology " Science

Through the utilization of the Spitzer telescope, space scientists have carried out an all-encompassing structural examination of the Milky Way. This has allowed them to acquire detailed visuals of the elongated cluster located at the core, which sets our galaxy apart from other spiral galaxies. The strip separates the spiral of the galaxy, with a colossal black hole situated at its center, as stated by Ed Churchwell, a professor at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
The examination has revealed that the central portion of the galaxy is longer than anticipated. “This provides the most compelling evidence for a lengthy central strip,” Churchwell commented. Astronomers have long been debating the shape of the galactic center – whether it is elliptical or striplike. However, the most recent investigation clearly demonstrates a striplike structure.
The band, composed of relatively aged red stars, stretches over a distance of approximately 27,000 light-years, which is 7,000 years longer than previously estimated. Furthermore, the band is positioned at an inclination of 45 degrees in relation to the imaginary line connecting the Sun and the galactic center.
New observations made by astronomers have revealed that our galaxy exhibits some unexpected characteristics.
Using the Spitzer telescope, space researchers have conducted a comprehensive analysis of the Milky Way’s structure. This has provided detailed images of the elongated cluster at the core, setting our galaxy apart from other spiral galaxies. The band divides the spiral structure, with a massive black hole residing at its center, according to Ed Churchwell, a professor at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
The examination revealed that the central part of the galaxy is larger than initially anticipated. “This is the most compelling evidence supporting the presence of an elongated central band,” commented Churchwell. For a long time, astronomers have been debating whether the shape of the galactic center is elliptical or streak-like. However, the most recent investigation unequivocally demonstrates a band-like structure.
Comprised of relatively aged red stars, the band spans approximately 27,000 light-years, surpassing the previous estimate by 7,000 years. Moreover, it is positioned at a 45-degree angle in relation to a direct line connecting the sun and the galaxy’s center.





