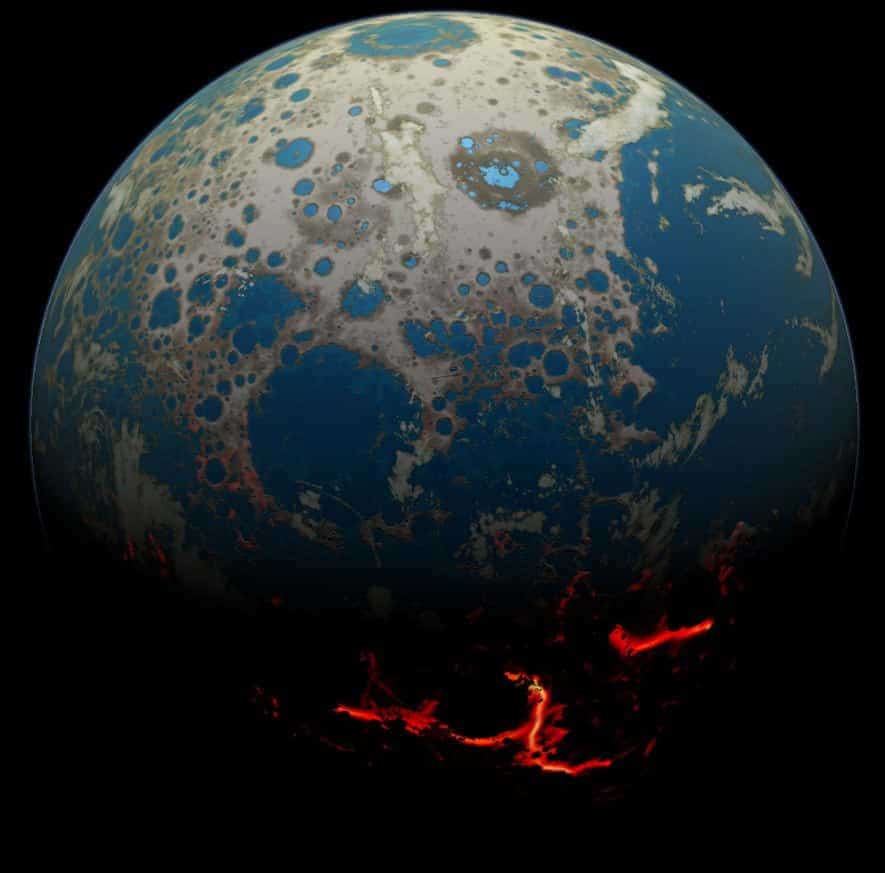
The earth has been in existence for approximately 4.54 billion years. However, it is important to note that this age refers to the entire solar system. It is not a mere coincidence. All of these celestial bodies originated from a single diffuse cloud.
Our universe was once filled with remnants from the formation of the solar system. These remnants, such as rocks, pebbles, and other particles, collided and merged over time, eventually taking the form of the planets we see today. At some point, a large celestial body collided with Earth, causing the detached material to form our satellite, the Moon.
However, determining the age of planet Earth is a complex task for scientists. It is challenging to make accurate assessments based solely on surface observations, as the planet’s constantly changing tectonic activity continuously reshapes its outer layer. The Earth’s older tectonic plates lie concealed beneath the surface, and the oldest rocks discovered so far have been estimated to be around 4-4.2 billion years old.

The scientists believe that all the substances in the system originated simultaneously. The decay of chemical elements occurs at a specific pace, enabling us to ascertain their duration of existence. Additionally, we had the opportunity to study ancient meteorites, which further aided in the calculation of time.
Unsuccessful approaches to determining the Earth’s age
It is important to remember that prior to accurately establishing the age of the Earth, humanity made unsuccessful efforts that did not consistently yield correct results.
Decline in Sea Levels

Benoit de Maillet hypothesized that the existence of high-altitude remains suggested that the Earth had once been entirely submerged by an extensive ocean. Over a span of 2 billion years, this ocean gradually evaporated, leaving the Earth in its current state.

In accordance with William Thompson, the Earth had previously been in a state of intense heat, similar to that of the sun. Following a particular incident, it took between 20 and 400 million years for the Earth to cool down. Regrettably, the scientist had inaccurate information concerning both the temperature and composition of the sun.
The Sun’s Cooling Process

In 1856, Hermann von Helmzgold attempted to estimate the age of the Earth by studying the cooling of the Sun. Although his findings were not entirely accurate, he speculated that the heat source was due to gravitational contraction and determined that it took approximately 22 million years for the star to shrink to its current state.
A skilled tarot reader can provide answers to the following questions:
What does the future hold for you? How will your relationships develop? What is the best decision to make?

Erosion of rocks

Charles Darwin had a belief that the examination of the erosion of sediments from the Cretaceous period could provide insight into the initial age of Earth. One particular sample indicated an age of 300 million years.
The path of the moon’s orbit

George Darwin came to the conclusion that the Moon could have formed from material found on Earth, and the Moon’s fast rotation might have resulted in its ejection. According to his calculations, it took approximately 56 million years for the satellite to form. However, we now understand that the actual cause was a collision with a massive object.
The Origins of Oceanic Salt

In 1715, Edmund Halley proposed the idea of using the level of salt in the ocean for calculations. He observed that the ocean receives salt through streams that become trapped due to water evaporation. Geologists utilized this observation and estimated the age of the Earth to be between 80-150 million years.
The breakthrough came with the development of radiometric dating. Antoine Becquerel discovered radioactivity in 1896, which occurs when materials decay and release energy. Scientists realized that there were significant amounts of radioactive deposits stored deep underground. This discovery led to the development of a new method for age calculation.
A skilled tarot reader can provide answers to the following questions:
What does the future hold for you? How will your relationships unfold? What is the right decision to make?

It was discovered that the process of decay occurs at a consistent rate. Some decayed quickly, while others took billions of years.
In order to determine the half-life, scientists devised a measurement scale. They chose to use the uranium process. By determining the volume of 3 isotopes of lead, the original amount of uranium can be inferred.
If the entire system originated from a single source, the objects will exhibit a uniform sum of isotopes. The higher the uranium-to-lead ratio, the more the isotopes’ values will change. The source for the system is evenly distributed, allowing for the creation of a data line that shows a graph of uranium input and time elapsed.
During testing conducted by Bertram Boltwood, a range of 250 million to 1.3 billion years was determined. The discovery of the oldest materials was of great significance, with stones dating back 2.5-3.8 billion years being found in Canada, Africa, and Australia. The discovery of the oldest fragment occurred in Canada in 1999, revealing an astonishing age of 4 billion years.
This finding set the minimum estimate for the age of the Earth. However, it is important to consider that this number decreases over time due to weathering and tectonic activity.
- What is the number of satellites orbiting Earth?
- Is the shape of Earth spherical?
- What is the reason behind Earth’s round shape?
- Does Earth possess any rings?
- What is the size of Earth?
- What is the age of Earth?
- What is the mass of Earth?
- What is the gravity of Earth?
- How much does Earth weigh?
- How does Earth’s weight compare to other objects?
- What is the size of Earth?
- What is the diameter of Earth?
- What is the circumference of Earth?
- What is the density of Earth?
- What is Earth’s magnetic field?
- What is geomagnetic reversal?
Position and motion of Earth
- Earth, Sun, and Moon
- What causes the change in day and night?
- What are Milankovitch cycles?
- What is a solar day?
- How long does it take for sunlight to reach Earth?
- The Earth’s rotation around the Sun;
- What is the rotation of the Earth?
- Why does the Earth rotate?
- What would happen if the Earth stopped rotating?
- Why is the Earth tilted?
- The magnetic north pole
- Earth’s orbit;
- Precession of the equinoxes
- Distance from the Earth to the Sun;
- Nearest star to Earth;
- Closest planet to Earth;
- How long does a day last on Earth;
- Winter Solstice
- How long is the Earth’s year;
- Earth’s rotational speed;
- Earth’s axis of rotation;
- Tilt of the Earth;
The Earth came into existence approximately 4.567 billion years ago through the process of accretion from the protoplanetary disk. This disk-shaped mass of gas and dust was left over from the formation of the Sun and played a crucial role in the formation of our solar system.

Table of Contents
- When did life on Earth first begin?
- What occurred two million years ago?
- When did humans first appear?
- What is the age of our planet according to the Quran?
- In what year was life invented?
- How did animal life come into existence?
- Who inhabited Earth before the dinosaurs?
- When did life come into existence?
When did life on Earth originate?
The emergence of the first living organism on Earth occurred approximately 3.7 billion years ago (some sources suggest it to be at least 4.1 billion years ago), marking the beginning of the evolutionary process that has continued ever since. The existence of a common ancestor among all present-day organisms indicates their shared evolutionary lineage.
What is the age of the Earth prior to the current era?
The Earth is estimated to be 4.54 billion years old, with a margin of error of ±1%. This calculation is based on the radioisotope dating of meteorites (chondrites) that formed prior to the formation of the planets.
How much time do we have left on Earth?
What could be found on Earth a billion years ago?
Researchers reveal that approximately 1.1 billion years ago, the Earth possessed an exceptionally strong magnetic field. Geologists have recently discovered the initial proof indicating that during this period, the Earth’s magnetic field reached an unprecedented intensity in comparison to both earlier and later eras. This groundbreaking finding has been documented in a report published in the journal PNAS.
What happened two million years ago?
Around two million years ago, homo erectus, also known as the upright man, emerged on Earth. This marked a significant advancement in the evolution of early humans.
When was the world created?
According to James Asher, planet Earth is approximately 6010 years old, with the date of creation being determined as October 22, 4004 BC. Originally, Asher determined the date as October 23, but upon closer examination of the Bible’s statement that “both evening and morning were one day,” he adjusted the date to be a day earlier.
Around 4000 years BC, the first ancient civilizations began to emerge, marking the start of the Bronze Age. This period of time saw the development of bronze mastery and the advent of writing, which ushered in the age of civilized life.
Why does our era begin with the birth of Christ?
In the eighth century AD, Europe adopted a new system for counting the years. Instead of using the reign of the Roman Emperor Diocletian as the starting point, which was a pagan and persecutor of Christians, Dionysius the Lesser decided to use the supposed year of Jesus Christ’s birth as the reference point in the early Middle Ages.
When was the first appearance of Homo sapiens?
The earliest known representatives of the Homo sapiens species, also known as modern man, emerged in Africa approximately 200,000 years ago. Prior to that, it is believed that only Homo habilis, or man of skill, existed, with the first appearances dating back around 2.8 million years.
What is the age of our planet according to the Koran?
If one considers scientific evidence, the age of our planet is estimated to be billions of years. However, according to the Universe Matrix (a program created by the Most High or Architect) or the teachings of the Torah, Bible, and Koran, the planet’s age is believed to be no more than 6,500 years. This information is preserved in all sacred books, along with specific chronologies of historical events.
How long has mankind been in existence?
The likely destiny of the planet in the future is its eventual consumption by the Sun in approximately 5 billion years, once it transitions into a red giant and expands enough to intersect with the Earth’s orbit.
What type of planet could sustain life?
Why is Earth the lone planet with life? To the best of our knowledge, our home planet is the only one within our solar system capable of supporting life as we understand it.
When was life first created on Earth?
According to current scientific models, life originated on Earth approximately 4.1-3.8 billion years ago, shortly after the formation of the planet itself around 4.5 billion years ago. The oldest known evidence of life comes from fossil stromatolites that are estimated to be 3.7 billion years old.
What existed on Earth 500 million years ago?
About 500 million years ago, there were remarkable organisms on Earth that formed complex multicellular structures. Some of the earliest animal life on our planet consisted of interconnected networks of filamentous threads. Researchers from Cambridge and Oxford have discovered evidence of these ancient organisms.
What was the Earth like 4 billion years ago?
A recent study published in Science and Health G1 suggests that 4 billion years ago, Earth resembled one of Jupiter’s moons, Io. Our planet had a similar environment with intense volcanic activity. Tubes within the planet’s interior circulated heat and materials between the core and the surface.
How was the animal kingdom formed?
According to Agência FAPESP, the animal kingdom originated from the evolution of single-celled organisms into multicellular organisms over a span of approximately 3 billion years, primarily in the ocean.
Which countries have the highest population?
China and India are the most populous countries, with China having a population of 1.4 billion people and India having a population of 1.4 billion people. These two countries combined account for nearly 18% of the world’s population.
Who inhabited the Earth prior to the dinosaurs?
Prior to the existence of dinosaurs, there were reptiles that were significantly smaller than the Tyrannosaurus. These creatures are referred to as dinosauromorphs. They were approximately the size of domestic cats and lived approximately 242-244 million years ago.
When did life first appear?
According to current theories, life originated on Earth approximately 4.1-3.8 billion years ago, with the formation of the planet itself occurring around 4.5 billion years ago. The oldest documented stromatolite fossils date back 3.7 billion years.
What occurred in 10,000 B.C.?
Around 10,000 B.C., the last ice age came to an end, resulting in the majority of the Earth becoming habitable once again. Around 9600 B.C., the Late Dryas period concluded, which traditionally marks the boundary between the Pleistocene and Holocene epochs, as well as the Paleolithic and Mesolithic periods.
Did our responses provide assistance?
Recent favorites

What is the ideal number of megapixels for a good camera?
When it comes to megapixels, a good camera should have a range of 10 to 15 megapixels, with an ideal range of 12 to 13 megapixels. Additionally, the size of the pixels is also important – the larger the number, the better the image quality.

How is the image quality determined?
The image quality is determined by the resolution of the image, which is the number of pixels (dots) per unit area. This parameter is denoted as p.

What subjects can I capture using an 85mm lens?
The versatility of 85mm lenses goes beyond shooting portraits. With their sharpness and high-quality optics, these lenses can be used for a wide range of subjects and photography genres.

Is there a way to determine if a lens is compatible?
To identify which lenses are compatible with your camera, you can refer to the crepe index.

What is the process of selecting a lens for a surveillance camera?
By opting for a lens with a longer focal length, you can achieve a more intricate image, albeit at the expense of a narrower field of view.


How to select a lens for capturing photos at night?
Many photographers who specialize in night photography tend to opt for a wide-angle lens rather than a standard lens. Wide angle lenses provide a wider field of view, allowing you to capture more of the night sky and surrounding environment in your shots.
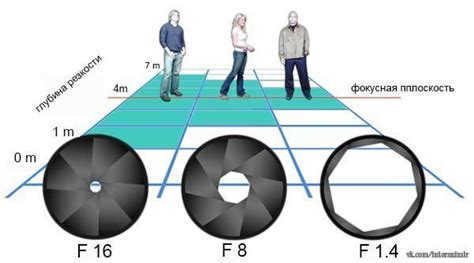
What is the factor that influences the depth of field?
The principle is straightforward: as the aperture size decreases (i.e. the f-number increases), the depth of field increases.


How can I improve the sharpness of a photo?
Why do all photos appear blurry in low light conditions? It is more challenging for cameras to achieve proper focus in dark environments.
The concept of photo sharpness refers to the ability of a photograph to clearly capture and display fine details. It is an essential aspect of photography that can greatly impact the overall quality of an image.

What does photo sharpening mean?
It is a method of enhancing an image that improves the distinction between specific elements.

Planet Earth
The rocks on Earth bear the evidence of its history. In locations such as the Grand Canyon, the erosion caused by water reveals the layers of rock that compose its walls.
By analyzing these layers, geologists can gain a better understanding of the formation of the Earth’s crust. However, the relative age of the deeper layers does not provide information about their absolute age, or how long ago they were formed.
What was the method used to determine the age of the Earth in the past?
In the 19th century, scientists attempted to estimate the age of the Earth by examining the timing of rock formation in recent history. However, these calculations were largely speculative. Their findings suggested that the Earth could be anywhere between 3 million and 1.5 billion years old, a range that is 500 times wide and far from accurate. It became clear that a different approach was needed. Scientists sought to discover a clock-like mechanism that had been set in motion at the moment of the Earth’s creation and had continued to tick until the present day. By examining such a clock, it would be possible to determine the precise age of our planet.
It appears that there are indeed such clocks: within the earth’s crust, within the plant kingdom, and even within the vast depths of the ocean. These organic timekeepers are comprised of radioactive elements that gradually break down and transform into other elements over the course of time. The process of determining the age of rocks or fossils through the use of these radioactive elements is known as radiometric dating. A specific fraction of the radioactive material decays consistently over a given unit of time. This decay rate remains constant regardless of the initial mass of the radioactive material.
The Radiocarbon Dating Technique
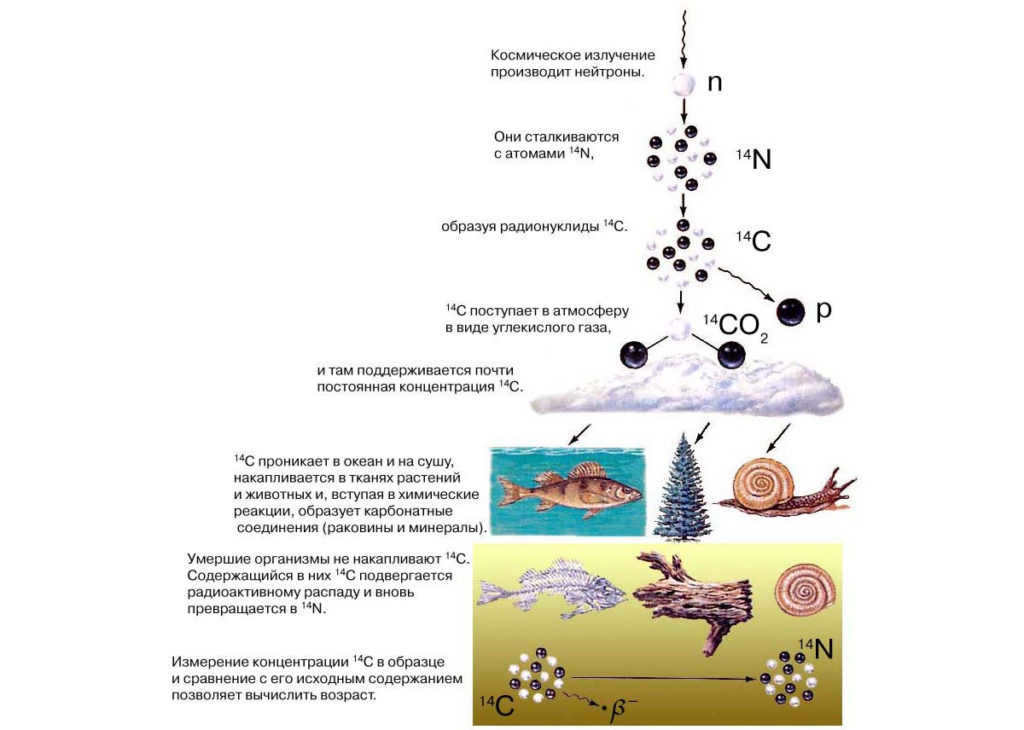
Let’s consider the radiocarbon dating technique as an example. It relies on the fact that living organisms absorb both normal carbon-12 and its radioactive isotope, carbon-14, from the atmosphere and water. It is assumed that the proportion of these two isotopes in water and air remains constant.
This proportion of carbon isotopes is found in living organisms. When an organism dies, the amount of normal carbon in its remains remains unchanged from the time of death, while the radioactive isotope decays (carbon-14). This isotope undergoes half-life decay within 5730 years. Therefore, by measuring the ratio of the two carbon isotopes in the remains of a once-living organism, scientists can determine the age of those remains.
Fascinating fact: Radioactive elements have the ability to function as a natural timekeeper due to their adherence to precise patterns of radioactive decay.
Evaluation of findings
Naturally, none of the dating techniques can be deemed entirely dependable. Consequently, geologists scrutinize multiple radioactive elements, including uranium and thorium, in addition to carbon-14, in order to ensure accuracy. Scientists corroborate their findings by conducting duplicate tests utilizing various radioactive isotopes on the same substance. At times, the two methods yield disparate outcomes. For instance, geologists collected samples of a coral reef located off the shores of Barbados.
Reliability of methods for measuring age
The accuracy of radiometric dating methods is not entirely dependable. As a result, scientists are exploring two different radioactive elements found within the same substance. This is due to the possibility that, for instance, the concentration of carbon-14 in the atmosphere may have fluctuated in recent times, potentially altering its historical levels. If the ratio of carbon-14 to carbon-12 has indeed changed, the radiocarbon method cannot be deemed a reliable means of determining the age of ancient organisms’ remains. This is because the method is based on the assumption that the levels of radioactive carbon in the atmosphere and water have remained constant.
Age of the Earth, Moon and Solar System
The age of the Earth, Moon, and solar system has been determined through the study of uranium’s half-life, which is approximately 4.5 billion years. By using the uranium-thorium method, scientists have measured the age of certain rocks on Earth to be around 3.8 billion years old. This information provides insight into the formation of our planet.
In addition to studying Earth’s rocks, scientists have also examined lunar soil samples obtained from astronaut missions to the moon. These samples have been found to be approximately 4.6 billion years old, similar to the age of meteorites that have reached Earth from neighboring regions of the solar system. Based on these findings, scientists believe that the entire solar system, including the Moon and the Sun, formed approximately 4.6 billion years ago.
If you come across any errors, please select the text and press Ctrl+Enter.

It is common knowledge that our Earth has a long history. However, precisely how old is our planet and how do scientists determine its age?
There exist a group of people known as creationists who assert that our planet is a mere 6,000 years old. They even claim that humans coexisted with dinosaurs in recent history, compressing our entire history into a short span of time. These individuals, along with others of their kind, make these assertions without offering any scientific evidence. This lack of empirical support is a defining trait of such individuals. This is merely our opinion, and we welcome any evidence to prove us wrong.
The age of our planet
There is substantial evidence from scientists that suggests the Earth is far older than 6000 years. They believe that the estimated age of our planet is around 4.5 billion years old.
Acasta gneisses, which are located near the Great Slave Lake in northwestern Canada, have been discovered to be the oldest rocks on Earth. These rocks have an estimated age of 4.03 billion years. It is quite common to find rocks older than 3.5 billion years in various locations across the globe.
In Australia, researchers have made a remarkable discovery – the oldest mineral grains ever found on Earth. These minute crystals made of zirconium silicate have been dated to be 4.3 billion years old, making them the oldest known materials on our planet.
The age of zircons, which are minerals, is determined through a process known as radioisotope dating. This particular type of analysis is conducted using a device called a mass spectrometer. The combination of these methods enables scientists to ascertain the age of historical rock formations, thus offering insights into the geological and evolutionary processes that occurred during that time period, as well as the impact on the organisms that have been preserved as fossils.
So, how does this method actually work? Scientists use a technique that involves measuring the rate of decay of uranium in zircons, which used to be composed of uranium. Uranium has a half-life of 704 million years, meaning that after 704 million years, one gram of uranium will have decayed into half a gram. Then, over the next 704 million years, it will decay again, leaving behind a quarter of a gram. This process continues, with the amount of uranium decreasing by half with each 704 million year period. At the same time, the amount of the element it decays into, in this case lead-207, will increase proportionally. By measuring the ratio of lead to uranium in a rock, scientists are able to calculate its age.
Creationists often conflate radioisotope dating and radiocarbon dating. They frequently assert that carbon dating is the evidence that scientists are deceiving about the Earth’s age. This is because this particular method can only determine ages up to 50,000 years old. Nonetheless, radiocarbon dating still refutes their assertion that “the Earth is 6,000 years old”. Only radioisotope dating can accurately gauge the age of the most ancient rocks and therefore, the Earth.
When did scientists first ascertain the age of our planet? It was in 1926, when the U.S. National Academy of Sciences adopted a radiometric time scale. And we can now consider the controversy settled since then.
However, the oldest zircons are merely 4.3 billion years old! So why was the age of the Earth set slightly higher?
Importance of Meteorites in Determining the Age of the Earth
Scientists have utilized the technique of radioisotope dating to analyze fragments of the Diablo Canyon meteorite, which descended upon our planet approximately 40,000 years ago. Through this method, they established that the meteorite is 4.5 billion years old, providing the most precise estimate for the age of the Earth. But why do scientists turn to meteorites to ascertain the age of our planet? The answer is quite straightforward. The Earth functions as a colossal recycling system, continuously assimilating and transforming old rocks into new ones. However, this recycling process does not extend to meteorites. These celestial bodies, composed of rock and metal, have been drifting within our solar system since its inception.
Presently, the age of 4.5 billion years represents the most accurate figure determined by scientists.

Meteorites Strike
The Earth had an eventful childhood. Approximately 3.9 billion years ago, it experienced a relentless assault from debris during the formation of the solar system. Many scientists believe that these meteorites brought water to the planet. Although each meteorite contains only a small amount of water, they have been bombarding our planet for over 20 million years. This continuous bombardment has gradually led to the formation of Earth’s oceans. So, the next time you enjoy a refreshing sip of mineral water, remember that every droplet, every puddle on Earth is billions of years old.
Bacteria
3.8 billion years ago, the Earth was completely submerged in water. However, upon closer inspection, small patches of land can be observed – these are molten rocks, volcanoes erupting from the ocean. Over time, these lava formations will solidify, giving rise to volcanic islands. Eventually, these islands will merge, forming the very first continents. Nevertheless, during this period, the atmosphere remains toxic and the temperatures are unbearably high, making it an inhospitable destination for vacations.
Since the birth of our planet, meteorites have been bombarding the Earth. However, 3.8 billion years ago marked a particularly intense phase. Evidently, some force disrupted the path of these meteorites, causing them to shower the Earth like hail.
However, our planet did not suffer in vain – meteorites have already brought water here, but scientists believe that they also brought minerals, basic proteins, and amino acids. Now that the storms have subsided and the Earth has cooled, it is likely their time to shine.
One popular theory suggests that life on Earth originated near hydrothermal vents in the ocean. At depths where sunlight can barely reach and temperatures drop to just above freezing, these vents release something resembling blue smoke. It is not actually smoke, but rather hot liquid. Even at the bottom of the ocean, seawater is capable of seeping through cracks in the crust, collecting gases and minerals along the way. This heated mixture is then expelled back into the ocean. There, it combines with a “broth” of minerals and chemicals left behind by meteorites, creating the perfect conditions for life to emerge.
According to numerous researchers, life emerged from this biochemistry. In some way, these substances came together to create single-celled bacteria, which were the earliest life forms on Earth. There are, however, indications that life originated multiple times on our planet before eventually taking on the familiar forms we know. Life emerged. And what followed? Despite the passage of millions of years, there was no significant change – it seemed as though evolution was in no rush to generate more intricate organisms.
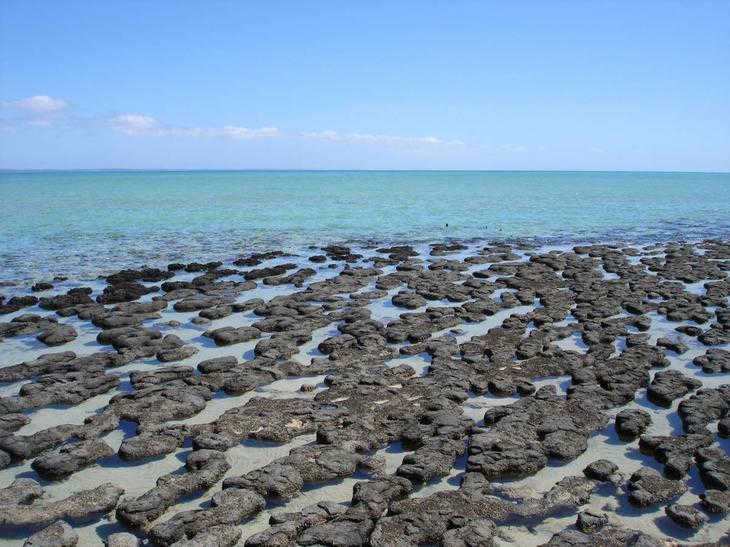
Stromatolites
Approximately 3.5 billion years ago, in the vast expanses of the ocean, a remarkable phenomenon emerged. It appeared as if there were rocks scattered beneath the water’s surface, but in reality, these formations were much more than meets the eye. These structures were, in fact, communities of cyanobacteria, which are groups of living bacteria that have come together to form conglomerates. These ancient mats, known as stromatolites, played a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s history.
The stromatolites thrived by harnessing the power of photosynthesis, a process that converts sunlight and water into glucose, a simple form of sugar. As a result of this process, oxygen is produced as a byproduct. Over millions of years, these seemingly unremarkable “rocks” had a profound impact on the planet, filling the oceans and atmosphere with an abundance of oxygen. Without them, life on Earth as we know it, including ourselves, would likely not exist.

“The Ice Age of the Earth”
As a result of intense geological activity, a vast number of volcanoes were formed, giving rise to a unique phenomenon known as the “Snowball Earth”. These volcanic eruptions released copious amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which then combined with water and transformed into acid rain. However, instead of accumulating in the atmosphere and causing a greenhouse effect, the rocks on Earth’s surface absorbed this carbon dioxide, effectively preventing it from trapping heat. This natural process has been further enhanced by the collision of continents, which has exposed even more of these carbon-absorbing rocks. Concurrently, the Earth has been experiencing natural climate fluctuations and changes in solar radiation, leading to a gradual cooling of the planet. Despite the continuous release of greenhouse gases, the balance between the amount of heat entering the atmosphere and the ability of these gases to retain it has been disrupted, resulting in a cooling effect on Earth.
It is possible that the formation of the supercontinent Rodinia resulted in the obstruction of equatorial waters that carried warm currents. As a result, the polar regions experienced glaciation and began reflecting an increasing amount of sunlight. This, in turn, caused the ice to expand to other areas. Consequently, the surface temperature of the Earth dropped to -40 degrees Celsius. The ice was so extensive that it bound the oceans to depths exceeding 1 kilometer.
This may have been one of the lengthiest and coldest ice ages in the Earth’s history. Supporters of this hypothesis refer to it as the “Snowball Earth” era. It is believed that our planet was completely covered in ice during parts of the Cryogenian and Ediacaran periods of the Neoproterozoic era, and potentially during other geological epochs as well.
The Cambrian Explosion
Despite all odds, the Earth’s core continues to generate immense heat beneath its icy surface. Hidden beneath the thick layer of ice, volcanoes lie dormant, waiting to awaken one by one as the accumulated heat gradually thaws the frozen landscape. However, the rocks that absorb carbon dioxide from these volcanic eruptions still remain concealed beneath the ice, allowing the greenhouse gas to accumulate in the atmosphere. As a result, the trapped heat from the sun steadily melts the glacier, giving rise to cracks, fractures, and irregularities in the Earth’s crust. These disturbances pave the way for the emergence of even more volcanoes. Furthermore, the melting process triggers a series of chemical reactions that release vast quantities of oxygen, which has been trapped within the ice for millions of years. The accumulated heat also plays a role in the fragmentation of the supercontinent Rodinia, an event that took place approximately 750 million years ago.
The duration of a day has already reached approximately 22 hours. The oxygen concentration in the atmosphere has reached unprecedented levels. At this juncture, around 540 million years in the past, the renowned Cambrian explosion occurs: seemingly out of nowhere, a vast array of intricate marine organisms emerge.
The theory of the Cambrian explosion was originally proposed to account for the abrupt appearance of animal fossils in the lower Cambrian strata, while their absence in earlier sediments puzzled scientists. However, recent research has revealed that numerous sophisticated animal species, resembling those of the present, emerged long before the onset of the Cambrian period. Nevertheless, the majority of contemporary organisms appear to have first emerged during the Cambrian period, and this process seems to have occurred at a rapid pace. The proliferation of larger organisms and the emergence of a diverse array of species can likely be attributed, at least in part, to an increase in oxygen levels.
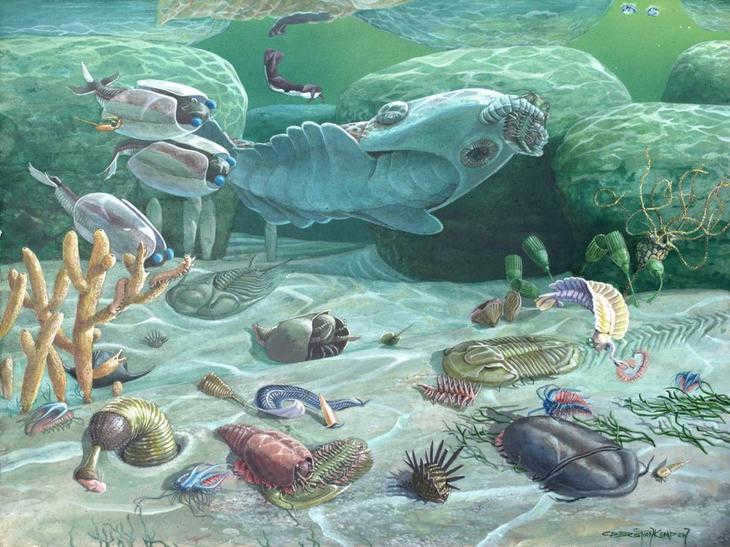

Pangaea
Around 250 million years ago, the Earth once again becomes nearly devoid of life. After a span of fifty million years, the continents come together once more to create a solitary landmass known as Pangaea. During the Permian extinction event, a staggering 70% of all land-dwelling vertebrate species perish, leaving ample space for a novel species that will dominate the planet like no other – not before, nor after it – the dinosaurs. These fearsome reptiles are believed to have evolved from a small population of reptiles that managed to survive the Permian extinction.
As they grow in strength and adapt, restless tectonic plates rend the Earth apart once more: 190 million years ago, Pangaea breaks apart. And 180 million years ago, the world assumes its familiar form, with the emergence of the Atlantic Ocean.
Approximately 65 million years in the past, it appeared that the dinosaurs, a ruling dynasty, would reign over the Earth indefinitely. However, a colossal asteroid hurtling through space serves as a force capable of disrupting this monopoly. This asteroid is currently on a trajectory towards the Yucatan Peninsula’s coastline. The present-day Gulf of Mexico exists solely due to the massive impact of this celestial body.
There is a dinosaur apocalypse occurring. An asteroid arrives and obliterates everything within a vast expanse, instantly vaporizing it. The force of impact is equivalent to the detonation of millions of atomic bombs. Fragments of the asteroid and the Earth’s crust are propelled thousands of kilometers away. Meteor showers ensue, earthquakes rock the land, and tsunamis batter the coasts. The Earth’s surface becomes intensely hot, causing vegetation to spontaneously ignite. For several months, smoke and ash envelop the planet, forming a formidable barrier that blocks the sun’s rays. The dinosaurs, who have reigned for 165 million years, are about to meet their demise. Fortunately, this catastrophe presents an opportunity for small, unassuming mammals known as shrews, who can now rise to prominence.