Dawn is the time at which twilight begins before sunrise.  In the late summer, dawn breaks over the Mojave Desert in California. Dawn can refer to the start of morning twilight, the period of twilight, or the time of sunrise. At dawn, the horizontal skyline of Kaohsiung, Taiwan is visible.
In the late summer, dawn breaks over the Mojave Desert in California. Dawn can refer to the start of morning twilight, the period of twilight, or the time of sunrise. At dawn, the horizontal skyline of Kaohsiung, Taiwan is visible.  The skyline of Prague is also visible at dawn.
The skyline of Prague is also visible at dawn.  In Serra dos Orgaos National Park in Rio de Janeiro state, Brazil, dawn unveils its beauty.
In Serra dos Orgaos National Park in Rio de Janeiro state, Brazil, dawn unveils its beauty.
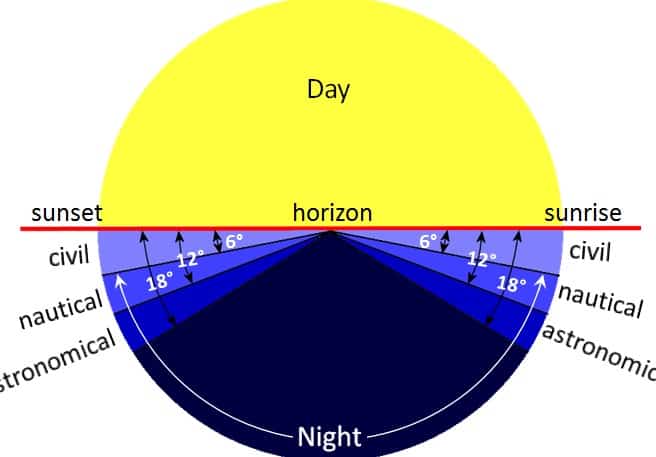
Dawn (on Earth) refers to the period of time that marks the beginning of twilight before sunrise. It occurs when the center of the Sun’s disk is 18° below the observer’s horizon, resulting in the appearance of scattered indirect sunlight in the Earth’s atmosphere. This morning twilight period lasts until sunrise, when the top of the Sun rises above the horizon and direct sunlight overtakes the scattered light.
Civil, maritime, and astronomical dawn are different ways to define the start of the respective twilight periods.
- 1 Etymology
- 2 Types of dawn
- 2.1 Astronomical dawn
- 2.2 Sea dawn
- 2.3 Civil dawn
- 3.1 Equator
- 3.2 Polar regions
- 3.2.1 Example
Origin
The term “Dawn” is derived from the Old English word dagian, which means “to become day”.
Varieties of Dawn
Dawn commences with the initial appearance of brightness in the early morning and continues until the sun rises above the horizon. This pre-sunrise period is divided into three classifications based on the amount of sunlight present in the sky, determined by the angular distance to the center of the Sun (measured in degrees below the horizon) during the morning. These classifications are known as astronomical, nautical, and civil dawn.
Astronomical Dawn
The start of astronomical dawn is signaled when the sun is positioned 18 degrees below the horizon during the early morning hours. This event is commonly referred to as “first light.” Shortly after, astronomical twilight ensues as the sun descends to 12 degrees below the horizon. At this stage, a small portion of the sun’s rays cast a faint glow upon the sky, causing the less bright stars to gradually disappear. In areas with excessive artificial lighting, distinguishing astronomical dawn from nighttime can be challenging. The commencement of astronomical dawn signifies the onset of astronomical twilight, which persists until sea dawn.
Daybreak on the ocean

Sea dawn in Joshua Tree, California, USA
The commencement of nautical twilight occurs when there is sufficient illumination for mariners to discern the horizon at sea, while the atmosphere remains too dim for outdoor activities. In technical terms, nautical twilight commences when the Sun descends 12 degrees below the horizon in the morning. The sky brightens enough to be clearly distinguished from the surrounding land and water. Sea dawn signifies the initiation of nautical twilight, which persists until civil dawn.
The start of morning civil twilight in southern California, USA
Civil twilight commences when there is sufficient illumination to discern most objects, allowing for certain outdoor activities to commence. From a technical perspective, civil dawn occurs when the Sun is positioned 6 degrees below the horizon in the morning.
If the atmosphere is clear, the sky appears blue, but if there are clouds or haze present, it may exhibit hues of bronze, orange, and yellow. Some prominent stars and planets, such as Venus and Jupiter, can be observed with the naked eye during civil dawn. This particular moment signifies the onset of civil twilight, which persists until sunrise.
The Impact of Latitude
The length of the twilight period, such as the time between astronomical dawn and sunrise, varies significantly based on the latitude of the observer. At the equator, this period lasts just over 70 minutes, while in polar regions it can extend for many hours.
Twilight at the Equator
At the equator, the duration of twilight is the shortest. During the equinox, the Sun rises directly in the east and sets directly in the west, forming a right angle with the horizon. Each phase of twilight (civil, nautical, and astronomical) lasts only 24 minutes. Regardless of location on Earth, the twilight period is shortest during equinoxes and longest during solstices.
Polar Regions
As the summer solstice approaches, the daytime in polar regions becomes longer, while the nighttime becomes longer as the winter solstice approaches. This change in daylight hours may have an impact on the timing and duration of dawn and dusk. The effect is more noticeable the closer you are to the poles, where the Sun rises at the spring equinox and sets at the fall equinox, resulting in a prolonged period of twilight that lasts for several weeks.
The polar circle, which is located at a latitude of 66° 34′ north or south, marks the lowest latitude at which the Sun does not set during the summer solstice. The angular radius of the polar circle is determined by the angle between the Earth’s equatorial plane and the ecliptic plane. As you move closer to the pole, the length of time without a sunset increases.
At latitudes higher than 54° 34′ during the summer solstice, it never gets darker than nautical twilight. The level of darkness during the night can vary significantly at these latitudes.
At latitudes higher than 60° 34′, summer nights never get darker than civil twilight. The duration of these “bright nights” is longer at higher latitudes.

Dawn at La Silla Observatory, Chile
During the summer solstice, cities like Glasgow, Scotland (at 55° 51′ N latitude) and Copenhagen, Denmark (at 55° 40′ N latitude), experience a few hours of what feels like nighttime. Oslo, Norway (at 59° 56′ N latitude) and Stockholm, Sweden (at 59° 19′ N latitude), also appear very bright when the Sun is below the horizon. At latitudes 57° 30′ – 57° 00′, when the Sun drops 9.0-9.5 degrees below the horizon, the zenith darkens even on clear nights (except during a full moon), allowing the brightest stars to be visible across most of the sky.
Mythology and religion
In Islamic tradition, the first light of dawn is known as the false morning (Subhe-Kadhib, Arabic صبح اذب), while the light that appears over the sea is called Sehr (سحر) or True Morning (Subhe-Sadiq, Arabic صبح صادق). This time marks the beginning of the daily fast during the holy month of Ramadan and the first prayer of the day.
Within various Indo-European mythologies, there exists a distinct dawn goddess who is separate from the male solar deity. Her name is derived from the PIE root *h2ausos-. Examples include Greek Eos, Roman Aurora, and Indian Ushas. Another related figure is the Lithuanian goddess Aušrinė, and there may also be a connection to the Germanic term *Austrn- (which gave rise to the term Easter). In Sioux mythology, there is a being known as Anpao, who possesses two faces.
The Hindu goddess Ushas is the embodiment of the dawn, while Surya, the Sun, and Aruna, the charioteer of the Sun, are male figures. Ushas holds a significant role in the Rigvedic tradition. The period of sunrise is commonly referred to as Brahmamuhurtham, which is considered the optimal time for engaging in spiritual practices such as meditation and yoga. In certain regions of India, both Usha and Pratyusha (twilight) are revered alongside the Sun during the Chhat festival.
Prime is the designated time for prayer in the traditional Divine Office (Canonical Hours) within the Christian liturgy. It is recited at the first hour of daylight.
The Talmud raises the question of how to calculate the dawn (Hebrew Alos / Alot ha-Shahar, or Alos / Alot) in Judaism, as it has various implications for Jewish law, such as determining the starting time of certain daily commandments like prayer. According to a straightforward interpretation of the Talmud, dawn occurs 72 minutes before sunrise. However, some scholars, like the Vilna Gaon, understand that the Talmud’s timeframe for dawn specifically applies to the equinox day in Mesopotamia. Therefore, they advocate for the calculation of dawn on a daily basis, starting when the sun is 16.1 degrees below the horizon. The longstanding tradition among most Sephardic Jews is to follow the first opinion, while many Ashkenazi Jews adhere to the second opinion.
 L'Aurore by William-Adolphe Bouguereau
L'Aurore by William-Adolphe Bouguereau Mer du Nord by Guillaume Vogels
Mer du Nord by Guillaume Vogels
Literature
- Homer often uses the epithet “Pink Dawn” in the Iliad and Odyssey
- An aubade (also known as Alba in Occitan and Tagelied in German) is a song about lovers parting at dawn
- Aurora Musis amica (Dawn is a friend of Muse) is mentioned in Epigrammata Disticha Poetarum Latinorum, Veterum Et Recentum, Nobiliora (1642) by Barthold Nyhus
- Dawn is the first volume of Jean-Christophe, a novel written by Romain Rolland
- Dawn is a novel written by Henry Rider Haggard and published in 1884
- “Dawn” is a poem written by Rupert Brooke and published in The Collected Poems of Rupert Brooke
- “Dawn,” a poem penned by Richard Aldington.
- “Dawn,” a poem composed by Emily Dickinson.
- “Dawn,” a poem authored by Francis Ledwidge.
- “Dawn,” a poem written by John Masefield.
- “Down,” a poem written by William Carlos Williams.
- I Greet the Dawn: Poems, a compilation of verses authored by Paul Lawrence Dunbar, released on January 1, 1978 by Atheneum Books.
- “I Greet the Dawn,” a concise four-line poem from the anthology A Lyric of Modest Life, authored by Paul Lawrence Dunbar and initially published in 1896. This particular poem was subsequently included in The Complete Poems of Paul Lawrence Dunbar, a collection of his works published in 1913.
Related Information.
Sources
Useful Links
| Dawn-related content can be found on Wikimedia Commons. |
A solar day refers to the period between two consecutive upper culminations of the Sun. The culmination occurs when the Sun passes through the meridian at the observation point. The length of a true solar day varies due to the uneven speed at which the Sun moves along the ecliptic and the tilt of the ecliptic in relation to the celestial equator.
Determining the Duration of Sunrise and Sunset, Solar Day, Time Zones, and Civil Twilight
The measurement of time in civil society is determined by the average duration of a solar day. This time interval is based on the consecutive uppermost points reached by the theoretical Sun as it moves uniformly along the celestial equator. The average solar time begins at midnight and is measured until the moment when the theoretical Sun reaches its lowest point in the sky.
Time Zones.
Time Zones are a system used to measure time, which is based on dividing the Earth into 24 zones in a north-south direction. Each zone represents one hour. In each time zone, all points have the same time, which is the average solar time of the central meridian of the zone. This time is commonly referred to as local time in everyday life. In astronomy, local time is determined by the longitude of each point.
The local time and mean solar time will vary for points located to the west and east of the central meridian. The differences are greatest at the edges of the time zone. The time in adjacent zones differs by exactly one hour.
Decretal time.
Decretal time, also known as daylight saving time, is the official time that is adjusted by adding one hour. This practice was introduced in the Soviet Union through a decree issued by the Council of People’s Commissars on June 16, 1930. As per this decree, the clock hands in all time zones were moved one hour forward. Some other countries also adopted this practice, where the official time differs from the standard time by one hour.
Duration of daylight.
The duration of daylight refers to the period of time between sunrise and sunset. It varies depending on the specific date (month and day) and the latitude of the location. In order to calculate the duration of daylight, specific tables are published that provide the precise times of sunrise and sunset for various locations.
Civil twilight: a unique period of illumination
Civil twilight is an extraordinary time of day that occurs before sunrise and after sunset. It is a period when the natural light allows for various activities such as orientation, target designation, and firing, using the same methods as during daylight. The start and end of civil twilight are determined by the moment when the Sun descends below the horizon line by 6 degrees.
The length of morning and evening twilight depends on factors like the location’s latitude, date, weather conditions, and terrain characteristics. In areas with dense cloud cover, low cloud cover, forests, or deep gorges, the duration of twilight is often shortened. On average, at mid-latitudes, both morning and evening twilight last for approximately 40 minutes.
Calculating the Time of Sunrise and Sunset based on Location and Date
To determine the time of sunrise and sunset, use the latitude of the location and the date (month and day) along with a graph. The latitude can be obtained by digitizing the degrees on the topographic map frame that corresponds to the area of interest.
To find the time of sunrise, locate the corresponding date on the upper part of the graph where the months and numbers are labeled. From this point, draw a straight line parallel to the vertical lines until it intersects with the curve that corresponds to the latitude of the location. If the digitized curve on the graph does not match the latitude of the location, interpolate to find the accurate time.
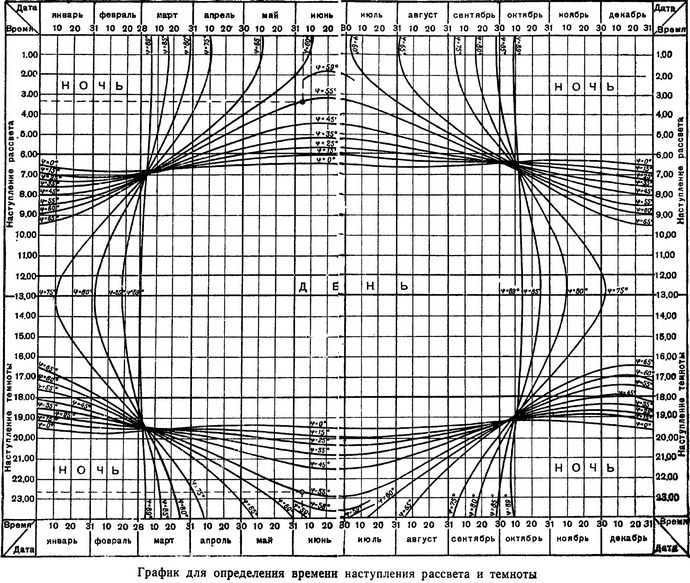
Starting from the point where the date line intersects with the curved line of latitude, draw a horizontal line to the nearest side of the chart. This will help you determine the time of dawn. The hours can be determined by looking at the signatures on the chart, while the minutes can be estimated visually. In the top left part of the chart, you will see a dotted vertical line representing the date June 5. The point where the date line intersects with the latitude curve for 55 degrees is marked with a circle. From this circle, draw a dotted horizontal line to the left side of the chart, and you will find that the time of dawn is 3 hours and 20 minutes.
This is the time of dawn on June 5 at latitude 55 degrees. Similarly, in the bottom part of the chart, you can determine the time of sunset. In the bottom left corner of the chart, you will see a dotted line indicating the countdown to darkness (22 hours and 40 minutes) for the point with latitude 55 degrees on June 5.
When creating a schedule, you need to calculate the average solar (decreasing) time. To convert to the zone time, you need to adjust the data you have. The correction value is calculated by finding the difference between the longitude of the time zone’s central meridian and the longitude of the specific location, measured in hours. If the location is to the east of the central meridian, the correction is subtracted. If it is to the west, the correction is added. The longitude of the location can be determined using a map, while the zone number and the longitude of the central meridian can be found in a table.
Example.
The latitude of the given location is 35 degrees, and according to the chart, the time of sunrise is 3 hours and 20 minutes. To determine the correction, we need to consider the following factors. The time zone number is 2, the longitude of the middle meridian in the time zone is 30 degrees, and the difference between the longitude of the middle meridian and the longitude of the given location is 5 degrees (35-30). The correction in terms of hours will be 20 minutes (1 hour corresponds to 15 degrees). Therefore, the adjusted time of sunrise for this time zone will be 3 hours (3 hours 20 minutes – 20 minutes).
This information is based on the content provided in the book “Handbook of Military Topography” by A. M. Govorukhin, A. M. Kuprin, A. N. Kovalenko, M. V. Gamezo.

Don’t forget to follow our telegram channel, PIONEERS OF TIME, and stay prepared for the future.
The sunrise on April 13 will mark the arrival of Clean Thursday.
This day is also known as Holy Thursday. What important events occurred on this day? Several events hold great significance for Christians worldwide.
Jesus Christ performed the act of washing His disciples’ feet. In those times, it was the duty of a servant to do so. When the disciples argued among themselves about who was the greatest, Christ exemplified humility and mutual service.
On that same evening, the Son of God foretold that one of His disciples, Judas, would betray Him.
At that moment, the sacrament of the Eucharist was established. Jesus pronounced a blessing over the bread, broke it, and declared: “Take, eat, this is my body.” He then repeated the same actions with the wine, stating: “Drink from it, all of you. This is my blood of the New Covenant, which is poured out for many for the forgiveness of sins.”
Customs of Holy Thursday
In the early morning, Orthodox Christians partake in ablutions, at the break of dawn. It is believed that performing ablutions while standing and using flowing water is more preferable. While bathing, one can offer prayers and seek God’s blessings for good health. Even the sick wash themselves with water from silverware, even if it’s just a spoon. Our ancestors believed that this ritual helps to maintain good health throughout the year.
It is recommended to trim nails, shave, and cut hair, while women can also dye their hair. These hygienic practices help to rid oneself of any lingering concerns from the past days.
Following the ablutions, people commence a thorough cleaning of their homes: washing windows, floors, walls, and any other areas that require attention. It is best to use “money” water for this task, which is water that contains coins and salt.
Maundy Thursday is an opportune time to begin the process of baking cakes and coloring eggs. The dough is prepared in the morning, and later in the evening, we commence the baking process, ensuring that we have offered our prayers and eliminated any negative thoughts beforehand. According to tradition, the quality of the kulich cake we produce on this day is said to foreshadow the year ahead. If our kulich turns out to be rich and sweet, it is believed that we will experience prosperity in various aspects of our lives. However, if the cake is not of the highest quality, it is advised not to set our expectations too high for the year to come.
Customs on Holy Thursday
In order to attract prosperity, it is customary to perform the ritual of counting money three times – before dawn, at midday, and at dusk. In modern times, this ritual requires withdrawing cash from a bank card on the eve.

On this particular day, a newborn is traditionally cleansed with holy water and blessed with the words: “May you bathe in water and remain healthy”. It is widely believed that individuals born on this day are less prone to melancholy and despair in adulthood, and tend to have a large circle of friends.
According to folklore, if a young woman desires to find a suitable partner for marriage, she should make preparations by creating space for her future husband. This involves leaving an empty shelf in her closet, as well as placing a spare toothbrush and razor in the bathroom. These actions are believed to increase the chances of finding a compatible soul mate.
If a marriage has lost its spark and has become mundane, it is suggested that the wife examine all the dishes in the household and discard any that have chips or cracks. Additionally, during Easter, the wife can nurture her husband by baking a homemade kulich, a traditional Easter cake.
Weather Signs on Maundy Thursday
- If it rains, we can expect inclement weather to persist until the end of spring.
- If it snows, we can anticipate a hot summer ahead.
- If it is cloudy, it is a favorable indication for a good harvest.
- If it is warm and windless, the weather will remain consistent until the start of summer.
Approximately how long does it take for the sun to fully set behind the horizon?
When the sun sets, how much time does it take for the entire sun to cross the horizon line? The sun’s diameter is about half a degree, so at the equator, it takes approximately 2 minutes for the sun to completely set.
As we move closer to the poles, the sun sets at a shallower angle to the horizon, resulting in a longer duration. For instance, in Moscow during the equinoxes, it takes around 3 minutes and 40 seconds for the sun to fully set, while during the solstices, it takes approximately 5 minutes.
At the North Pole, the time is further extended, lasting a whole day or even longer due to the change in declination.
Every day, the Earth experiences the phenomenon of sunset and sunrise at varying times, solely because of its rotation around the Sun. If this were not the case, the Sun would constantly be at its zenith, resulting in the absence of both sunrises and sunsets. Moreover, this would render life on our planet impossible.

Sunset and sunrise
The occurrence of sunset and sunrise is determined by the moment when the upper edge of the Sun aligns with the horizon line. The path that the celestial body takes across the sky varies depending on the observer’s location on the planet and the time of year. At the equator, the Sun rises and sets perpendicular to the horizon, regardless of the season.

What is the direction of sunrise?
Most individuals are aware that the Sun emerges from the east and sets in the west. However, this is a simplification. Actually, this only occurs on two specific days – during the spring and autumn equinoxes. On the remaining days, the Sun rises from north to south. Every day, the exact locations of sunrise and sunset shift slightly. On the summer solstice, it reaches its maximum point to the northeast. From that point onwards, the celestial body rises a bit further south each day. On the fall equinox, the Sun strictly rises in the east and sets in the west.

Throughout history, humans have long been fascinated with monitoring the precise timing and characteristics of sunrise and sunset. In ancient times, individuals were able to determine the time of day by observing the jagged peaks of mountains on the horizon or by aligning specially placed standing stones.

Sunset and sunrise mark the start and end of the daylight period. It’s worth mentioning that these events are fleeting moments. Twilight refers to the period when the transition from day to night or vice versa occurs. Morning twilight is the time between dawn and sunrise, while evening twilight is the time between sunset and nightfall. The length of twilight varies depending on the location and date.

As an illustration, in regions near the Arctic and Antarctic, there is never complete darkness during winter nights. The sunrise occurs when the upper part of the Sun becomes apparent above the eastern horizon in the morning. On the other hand, sunset marks the time when the trailing part of the Sun is no longer visible and descends below the western horizon in the evening.

Duration of Daylight
The duration of daylight, along with the timing of sunset and sunrise, is not constant. In the northern hemisphere, the length of days varies, with longer days in summer and shorter days in winter. Additionally, the length of daylight saving time also changes depending on the geographic latitude, with shorter days at higher latitudes. Typically, this occurs during the winter season. It is worth noting that due to the gradual slowdown of the Earth’s rotation, the days are becoming slightly longer over time. Approximately 100 years ago, a day was on average 1.7 milliseconds shorter than it is today.

What Makes Sunrise and Sunset Different?
Sunrises and sunsets have distinct visual characteristics. Can we visually differentiate between the two simply by observing the sun as it rises above the horizon, without any prior knowledge of whether it is the start or end of the day? Is there an objective way to distinguish between these two similar phenomena? All periods of twilight are symmetrical, which means there isn’t a significant optical distinction between them.
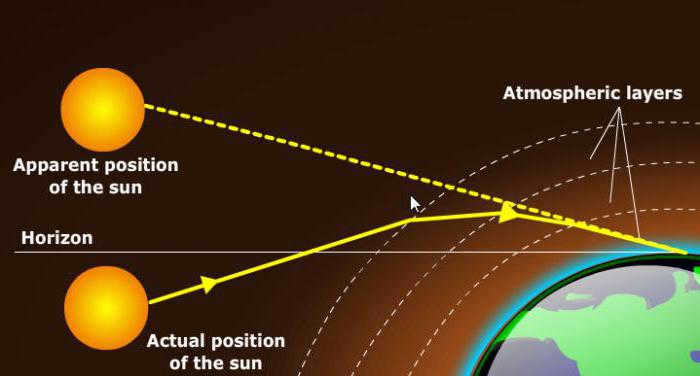
Nevertheless, there are two factors related to humans that nullify their similarity. As evening approaches, eyes that are accustomed to daylight start to fatigue. The light gradually fades away, the sky grows darker, and humans are unable to adapt as rapidly as these changes occur. Certain shades become indiscernible. In contrast, at daybreak, a completely different scenario unfolds.

The obscurity of the night adjusts the eyesight to an incredibly acute and distinct vision, and any slight detectable alteration of hue in the atmosphere becomes immediately noticeable. As a result, at daybreak, more shades are perceived compared to the twilight of the evening. This period poses the highest risk to motorists due to reduced visibility, hence the necessity for artificial illumination. It is imperative to switch on your headlights as darkness descends.
How long does it take for it to get dark after sunset?
So, how much time is needed for darkness to settle in after sunset? In brief, it typically takes around 70 to 140 minutes for the Sun to descend 18º below the horizon and for nightfall to commence.
Therefore, is it possible for twilight to occur in the morning?
The start of morning astronomical twilight (astronomical dawn) occurs when the sun’s geometric center is 18º below the horizon in the morning and concludes when the sun’s geometric center in the morning is 12° below the horizon.
With this in mind, what are the three categories of sunsets?
Professional photographers prefer the hour before sunset and the hour after sunrise. This special time, known as the “golden hour” or “magic hour,” offers the ideal lighting for capturing breathtaking photos. Mastering the art of the golden hour is a valuable skill for any photographer.
If you are located near the equator, darkness can descend in as little as 20 or 30 minutes. However, on average, it takes approximately 70 minutes for the sky to fully darken after sunset. In certain areas, it may take slightly longer for nightfall to truly set in.
(The sunset is the point at which the upper part of the sun’s disk has crossed the horizon.) Just like twilight, there are different types of twilight, including civil twilight, nautical twilight, and astronomical twilight. These occur when the center of the sun’s disk is 6°, 12°, and 18° below the horizon, respectively.
What is the distinction between twilight and twilight?
Twilight refers to the period between sunset and dusk, during which the sky remains illuminated. On the other hand, twilight represents the specific moment when the sun is positioned 18 degrees below the horizon, resulting in the absence of sunlight in the sky.
What is the blue hour?
The blue hour typically spans a duration of 20 to 30 minutes immediately following sunset and just before sunrise. For instance, if the sun sets at 5:5, the blue hour will extend from approximately 10:5 to 30:5. Similarly, if the sun rises at 4:00 am, the blue hour would persist from around 30:4 to 50:XNUMX.
When does the blue hour occur?
The blue hour typically occurs for a duration of 20 to 30 minutes immediately following sunset and just before sunrise. For instance, if sunset is at 5:5, the blue hour will start around 10:5 and end around 30:5. Similarly, if sunrise is at 4 am, the blue hour will begin around 30:4 and conclude around 50:XNUMX.
The general guideline is that the golden hour occurs approximately one hour after the sun rises and one hour before it sets.
Which country experiences the earliest sunrise in the world?
Witness the world’s initial sunrise.
What region of the world is the first to greet the morning sun? It’s right here in New Zealand. Cape East Cape, located just north of Gisborne on the North Island, is the first spot on Earth to witness the sunrise each day.
What is the definition of the blue hour?
The blue hour is a period of time that typically occurs for about 20 to 30 minutes immediately following sunset and immediately preceding sunrise. To provide an example, if the sun sets at 5:50 PM, the blue hour would begin around 6:10 PM and end around 6:40 PM. Similarly, if the sun rises at 4:00 AM, the blue hour would start around 3:30 AM and conclude around 4:20 AM.
That’s the duration until the sun sets. Is it a sight to behold?
One of the most crucial aspects that often goes unnoticed when capturing a sunset is that sometimes the enchantment doesn’t unfold until approximately 15-20 minutes post-sunset. It’s advisable to scout the area 45 minutes prior to sunset, arrange your gear, and then unwind while you wait.
How much time is left until sunset?
Twilight, in its most general sense, refers to the period of time before sunrise and after sunset when the atmosphere is partially illuminated by the sun, but is neither completely dark nor completely illuminated.
When will the sun explode?
Scientists have conducted numerous studies to estimate when the sun will experience its explosive event, but they have determined that it will not occur again for approximately 5-7 billion years. When the Sun does reach the end of its life cycle, it will first expand in size and consume all the hydrogen in its core. Eventually, it will shrink and transform into a dying star.
It appears that in areas with a high population density, the duration of sunset typically ranges from two to five minutes.
What is the duration of the golden hour?
The golden hour, also known as the “magic hour” among movie enthusiasts, is characterized by the sky’s brightness matching that of streetlights, signs, car headlights, and illuminated windows. Surprisingly, this period actually lasts for approximately twenty or thirty minutes.
How do you refer to the time before sunset?
Twilight, in its broadest sense, is the interval of time occurring before sunrise and after sunset when the atmosphere is partially illuminated by the sun but is not completely dark or fully illuminated.
What is the definition of twilight?
In British English, twilight is defined as the period when a gentle diffused light emerges because the sun is positioned just below the horizon, particularly after sunset.
What happens first: sunset or twilight?
Twilight takes place after sunset. It occurs when the upper part of the Sun has crossed the horizon. … Twilight is the time between dawn and sunrise, or between sunset and sunset, when there is still light in the sky because of sunlight being scattered by the atmosphere.
What is the name for the period between day and night?
The period between daylight and darkness, whether after sunset or before sunrise, is known as twilight. Twilight is characterized by diffuse and often pinkish light in the sky. During this time, the sun is below the horizon, but its rays are scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere, resulting in the various colors of twilight.
What is the golden hour? The period of time that professional photographers prefer, which includes the last hour before sunset and the first hour after sunrise, is commonly known as the golden hour or magic hour. During this time, the lighting conditions are ideal for capturing breathtaking photographs.
When does the golden hour happen?
As a general guideline, the golden hour typically takes place approximately one hour after sunrise and one hour before sunset..