The zodiacal constellations are renowned for being intersected by the ecliptic – the path of the Sun across the sky amidst the backdrop of the stars. Moreover, the planets and the Moon also traverse through these constellations. As a result, the Zodiac constellations hold a special fascination for amateur astronomers. Among the thirteen constellations, we will now focus on Capricorn. In this article, we will explore how to locate the constellation Capricorn in the night sky, its appearance, and its observable periods.
When is the best time to observe the constellation Capricorn?
Before attempting to locate the constellation Capricorn, it is important to determine the most suitable time for doing so.
Each year, from January 20th to February 16th, the Sun resides in Capricorn. Consequently, it would be fruitless to search for the constellation during this period. (However, it is quite simple to find it during this time frame: just look at the Sun at any point during the day, and you will automatically be looking at the constellation Capricorn. Of course, constellations are not visible in the sky during daylight.)
As we are aware, the Sun moves from west to east (right to left) in relation to the stars. As a result, by the end of February, the constellation Capricorn will be positioned to the right of the Sun. Consequently, its boundary will be visible in the morning sky before our sunrise.
In the latter part of March, Capricorn can be spotted ascending early in the morning in the southeast amidst the backdrop of daybreak. Despite the fact that, by this time, the Sun has shifted far enough eastward from this constellation, making it somewhat challenging to observe. This is simply because, during springtime, the darkness of night fades away, and daybreak arrives earlier and earlier.
For the same reason, Capricorn is hard to see in the central region of Russia during the latter half of spring and the first half of summer. (And nothing can be seen during the phenomenon of white nights!) In southern Russia, however, Capricorn can be observed in the mornings starting in mid-April.
During mid-summer, the Capricorn constellation no longer rises in the morning, but rather around midnight and can be observed until dawn. And starting from August, when the period of short nights concludes, it becomes accessible to the public.
In the autumn, the optimal period for observing the Capricorn constellation presents itself. The daylight hours are gradually diminishing, which contributes to the prolonged visibility of the constellation across the celestial expanse. When venturing outside the urban areas, under the cloak of the moonless night, the Capricorn constellation becomes clearly discernible during the evening hours. Even during the month of December, one can still catch a glimpse of Capricorn adorning the evening sky. At present, the Sun resides to the right of the constellation, causing it to be observable in the southwestern direction, shortly after the conclusion of twilight.
How to locate the constellation Capricorn in the night sky?
Despite their popularity, not all zodiac constellations are easily recognizable. Many lack a prominent star that stands out. In fact, some constellations like Cancer or Pisces are composed of faint stars.
However, if we were living a century ago, it would have been much easier to spot even the faintest constellations. Nowadays, most people reside in cities that are illuminated at night. The bright street lights hinder our eyes from adjusting to the darkness, while city smog scatters the light, obscuring the majority of stars in the sky.
Regrettably, the constellation Capricorn does not have any notable stars. As a result, it is nearly undetectable in urban skies. On a moonless and cloudless evening, shielded from the glow of street lamps, it might be possible to spot 5 – 7 stars of Capricorn in the celestial expanse. However, it is advisable to venture outside the city limits, far from the glare of urban illumination, for a better chance of observing this elusive constellation.
- In the autumn season, the best time to discover and observe this constellation is during the fall. In case you are not well acquainted with the night sky, keep an eye out for Capricorn during the fall!
- The primary formation visible in the evening sky during autumn is a large triangle created by the bright stars Vega, Deneb, and Altair. This formation is commonly referred to as the summer-fall triangle (or the Great Summer Triangle). Following sunset, the summer-fall triangle can be found in the southern region of the sky. Locate it!
- Nestled within the summer-fall triangle is the relatively dim yet notable star Albireo. (By the way, it’s a stunning double star!) If you mentally draw a line connecting Albireo and the star Altair, and extend it downwards towards the horizon, it will guide you towards the stars alpha and beta Capricorn.
- The visibility of the α and β of Capricorn in the city is extremely low, but the rest of the stars in this constellation are even harder to see! The only star that stands out is the delta (δ) of Capricorn, which is located 20° to the east of this pair.
- This constellation lacks a distinct pattern; instead, it appears as a jumbled series of faint stars that, with some imagination, can be arranged into a shape vaguely resembling a necklace.
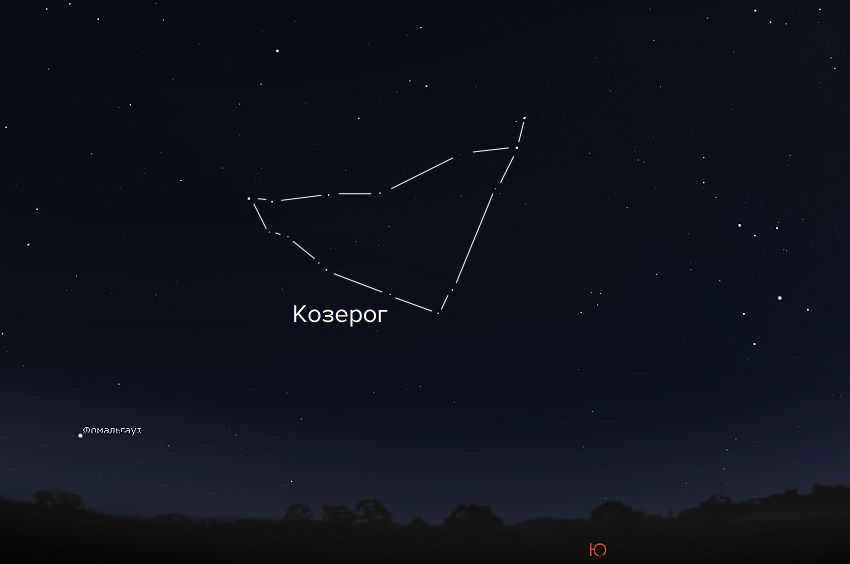
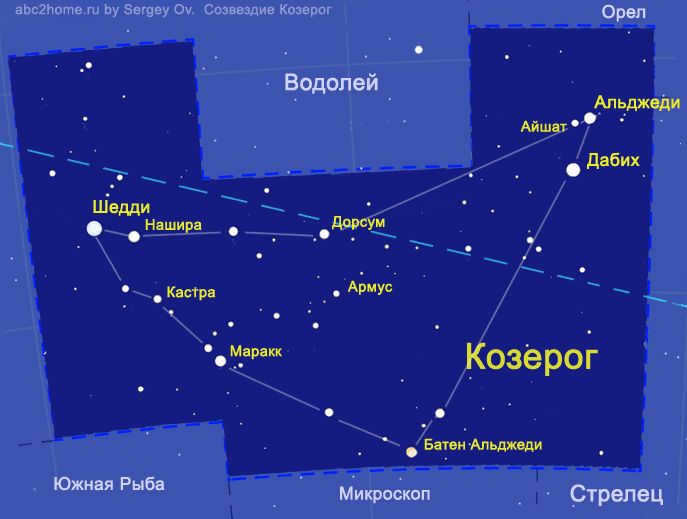
The Capricorn constellation can be observed in the southern sky of Russia. If you are located at the latitude of Voronezh or further south, make sure to look out for the bright star Fomalgaut, which can be found southeast of Capricorn. See the image below for reference.
During the autumn season, the Capricorn constellation can be seen in the southeast after sunset, and later in the evening, it will be positioned in the south and southwest. However, it should be noted that the constellation does not rise very high above the horizon, similar to how the Sun appears low in the January sky.
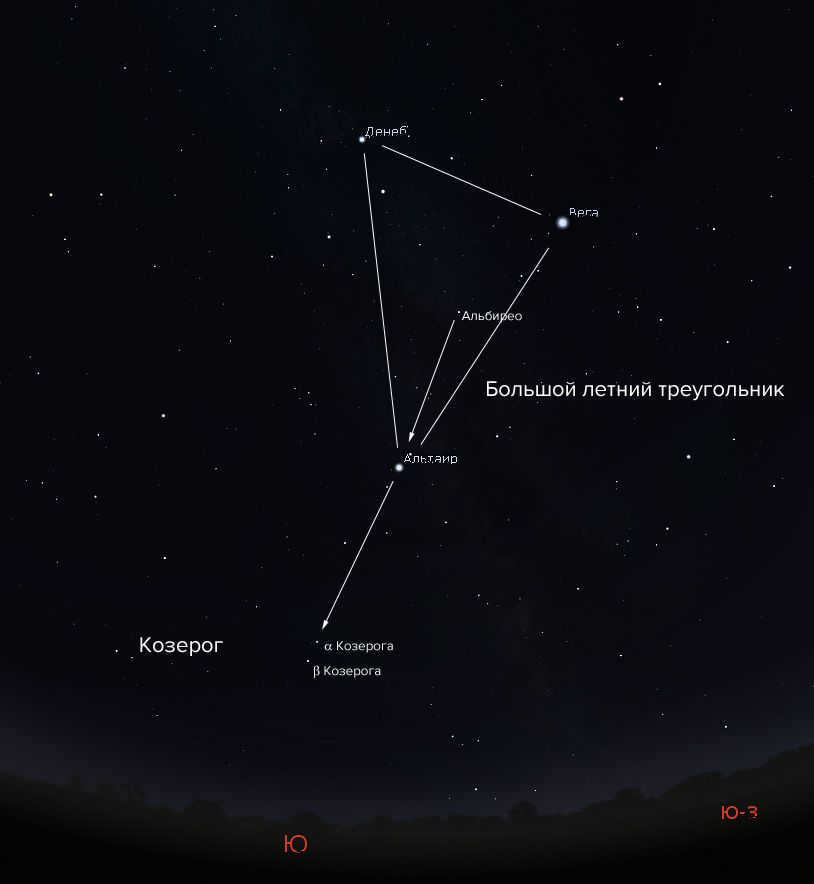
The Great Summer Triangle, which is the main feature of the summer and fall sky, is located south and slightly east of the Capricorn constellation. To locate Capricorn, you can look for the stars Albireo and Altair, which are positioned in the middle of the triangle. Figure: Stellarium
The position of Capricorn constellation and its celestial bodies
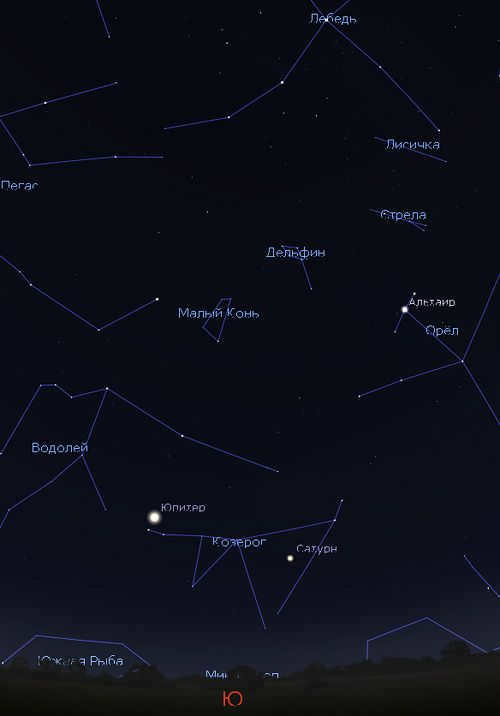
In the autumn of 2021, the constellation Capricorn plays host to the remarkably luminous planet Jupiter and the prominent planet Saturn. They are easily identifiable, even in an urban setting. Image: Stellarium
For those seeking to locate and observe Capricorn in the celestial sphere, there is encouraging news. As a zodiacal constellation, the Moon and planets traverse its region. The Moon appears in this constellation on a monthly basis and spends approximately two days within it. Although planets appear less frequently, they remain visible for longer durations. With their visibility in urban areas, planets and the Moon facilitate the identification of the constellation’s precise position in the sky with minimal effort.
During the fall of 2021, there is an excellent opportunity to spot Capricorn. This is because two bright planets, Jupiter and Saturn, can be observed in the constellation at the same time.
In autumn, Jupiter can be found at the eastern boundary of Capricorn, while Saturn is located at the western boundary. However, in December, Jupiter will transition into Aquarius, while Saturn will remain in Capricorn throughout 2022.
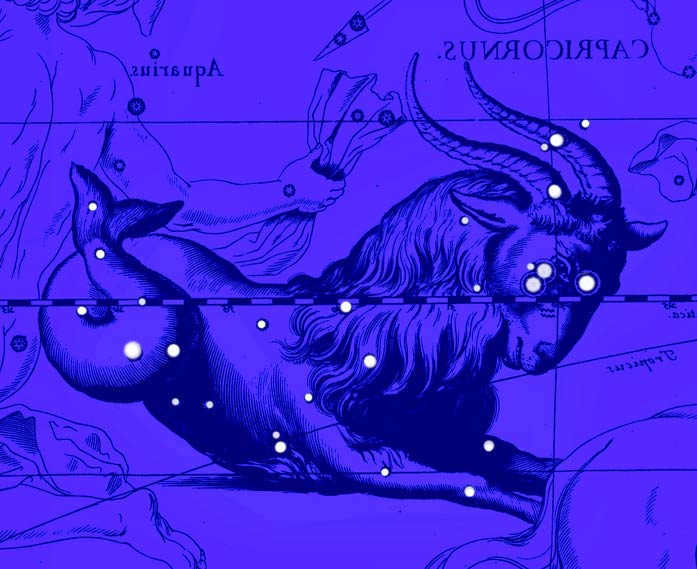
The constellation Capricorn forms a small curved pattern in the sky near Sagittarius. The best time to observe the stars of Capricorn is during summer in the northern hemisphere (or winter in the southern hemisphere). It is one of the oldest constellations known to humanity and has long been associated with the mythical sea goat.
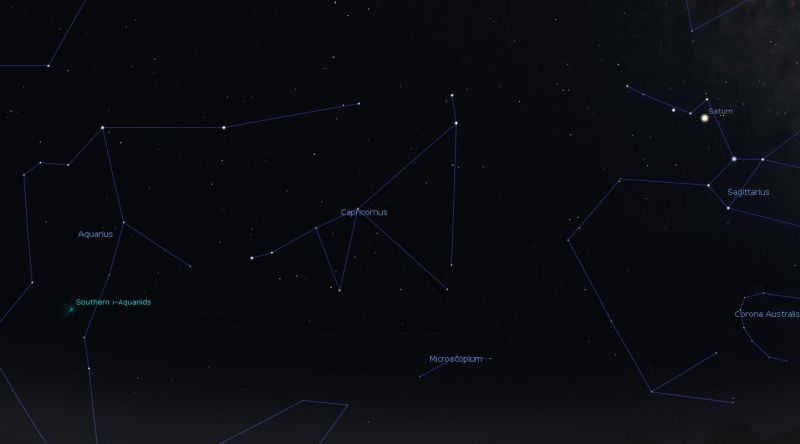

Locating Capricorn
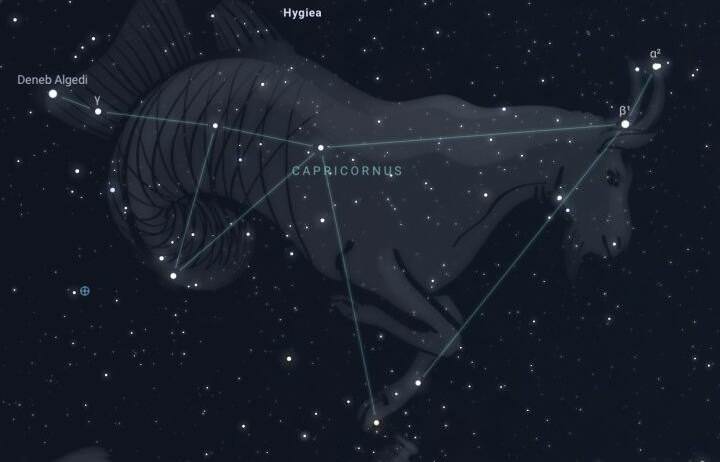
To locate the constellation Capricorn, you can simply search for the constellation Sagittarius. For observers north of the equator, it can be found in the southern sky, while for those south of the equator, it will be higher in the northern sky. Capricorn has a distinct shape that resembles a flattened triangle. Some charts depict it as two triangles along a long line, as shown in the image above. It is situated along the ecliptic, which is the path that the Sun takes as it moves across the sky throughout the year. The Moon and planets also generally follow this path.
The constellation known as Capricorn has been recognized by human civilizations for thousands of years, dating back to the Middle Bronze Age around 2000 BCE. The Babylonians referred to this constellation as the Goat-Fish, while the ancient Greeks associated it with Amalthea, the goat that rescued the infant god Zeus. Over time, Capricorn came to be known as the sea goat. However, in China, it was depicted as a turtle, and in the South Pacific, it was seen as a cave.
Capricorn Constellation
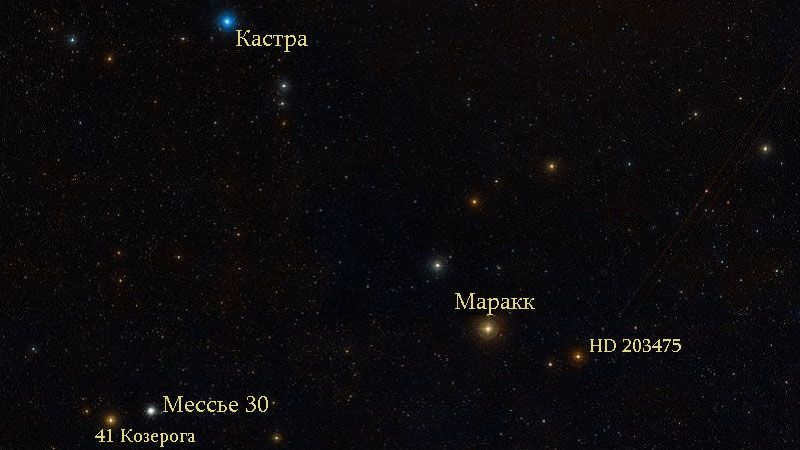
The constellation Capricorn is comprised of approximately 20 stars. The most luminous star, known as Algedi, is part of a multiple star system and is situated a little over 100 light-years from Earth.
The second brightest star, referred to as Dabih or β Capricorn, is a giant yellow star located approximately 340 light-years away. One of the more unique stars in the Capricorn constellation is Delta Capricorn, also known as Deneb Algedi, which translates to “the tail of a sea goat.”
The Multiple star system δ Capricorn has one particular star that stands out as the brightest. Astronomers have classified this star as an eclipsed double star, which means that one of the stars in the system occasionally passes in front of the other, causing the brighter star to temporarily dim. Apart from this unique characteristic, scientists are also fascinated by the unusual chemical composition of this star. It deviates from the typical chemical composition of other stars in the same category. Additionally, this star displays a remarkably fast rotation.
Capricorn’s Collection of Deep Space Objects
While Capricorn may not be the most prominent constellation in the vast expanse of the Milky Way Galaxy, it still offers a glimpse into the wonders of deep space. With the aid of powerful telescopes, keen observers can catch a glimpse of a handful of incredibly distant galaxies residing within the boundaries of this celestial formation.
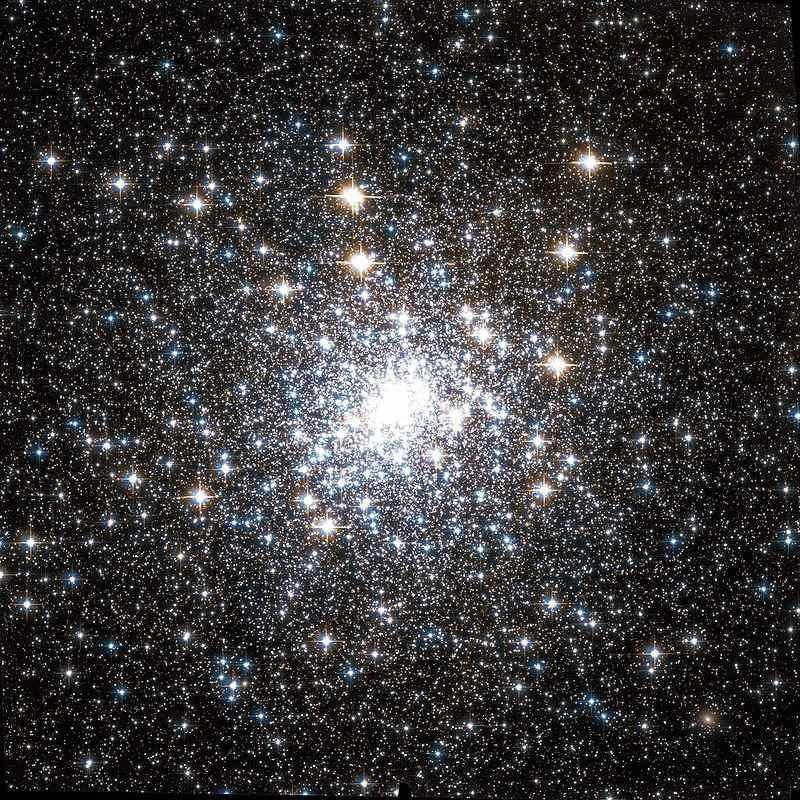

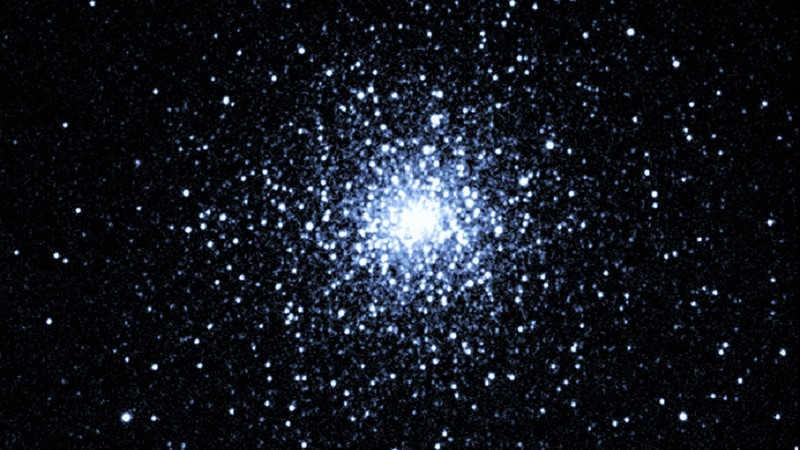
M30 is a type of globular cluster that orbits around the Milky Way galaxy and is home to ancient stars. These stars are actually older than the galaxy itself, suggesting that they formed many billions of years ago, predating the Milky Way by a significant amount of time. The stars in globular clusters like M30 are referred to as “metal-poor” by astronomers due to their lack of heavier elements in their atmospheres, aside from hydrogen and helium. By studying the metallicity of a star, scientists can gauge its age, as stars that formed early in the universe’s history are not influenced by the metals produced by subsequent generations of stars.
The characteristic of Capricorn is primarily associated with moisture, although its initial segment is characterized by high temperatures and can be detrimental, the middle section is moderate, and the final portion brings about rainfall. Both the northern and southern regions of the sign are damp and destructive.
Claudius Ptolemy – On the Weather – “Mathematical Treatise in Four Parts”

Figure 1
The representation of Capricorn ♑
The astrological sign known as Capricorn ♑ originally referred to the tenth 30-degree section of the zodiac belt when measured from the vernal equinox point (Fig. 2 and 3). It now encompasses the entire meridian sector with ecliptic coordinates of 270 °, ±90 °; 300 °, ±90 °.
In the time period of 2022-2023, the Sun will be in the sign of Capricorn from December 22, 2023 06:27 to January 20, 2024 17:07 MSK (Moscow time). The usual dates for the Sun being in this zodiacal sector are December 22 – January 20.
Capricorn represents the winter solstice and in the Northern Hemisphere, its arrival is marked by the longest nights.
This sign derives its name from the constellation Capricorn (Fig. 4), which was entirely within this segment during our era’s beginning. However, due to the precession* phenomenon – the cyclic change in the Earth’s axis direction in relation to the stars – the Sun is now only in the constellation of Capricorn and the sign of Capricorn simultaneously on January 19 and 20 (Fig. 2):
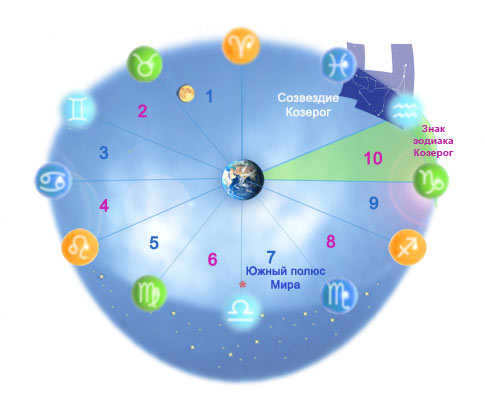
Figure 2 The zodiac sign Capricorn, the constellation Capricorn and their relative position in a spherical projection (according to ancient beliefs, the celestial realm was composed of multiple concentric spheres encircling the Earth).
In our current astronomical era, the region of the sky associated with the zodiacal belt of the Capricorn zodiac sign appears as follows:
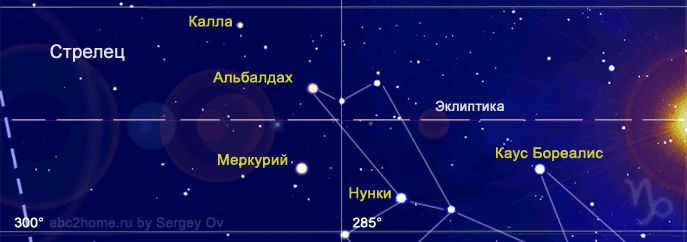
Figure 3. The zodiac sign Capricorn represents a portion of the zodiac belt that corresponds to the sign Capricorn, as of December 22, 2015:
The Sun enters the sign on the right, and the area of the Capricorn sign includes some of the brightest stars of the Sagittarius constellation, as well as the planet Mercury.
In the winter of 2022-2023, Saturn, the most influential planet, will be in the sign of Aquarius starting from December 17, 2020. This sets the stage for cold winters and a higher likelihood for “winter children” (children born in winter) to be mostly Aquarians, according to Ptolemy.
The ancient philosophers attributed the following properties to the sign of Capricorn:
– Capricorn, derived from the constellation Capricornus, is a feminine zodiac sign (in accordance with the principle of alternation and the oldest legend of the constellation). It is considered the first “earthly” abode of Saturn.
– Capricorn symbolizes the birth and development of the Earth element, emphasizing its characteristics of coldness and dryness. Individuals born under this sign often exhibit a dominant phlegmatic temperament, reflecting the influence of these primary elements.
– In ancient times, Capricorn was characterized by several distinct traits and properties: it was located in the southern part of the celestial equator, making it a winter sign. Capricorn is associated with certain elements such as lead (from Saturn) and copper, as well as precious metals like gold. It is also linked to precious stones like onyx and garnet, along with other red transparent and black stones.
Moreover, one important feature of the sign Capricorn is that the Sun often does not play a dominant role in determining the temperament of individuals born during daylight hours in this sign. Instead, Saturn and the interactions of other planets take precedence, as believed by ancient philosophers (according to ancient beliefs).
The Influence of Capricorn Sign, the Sun, and the Planets
Ancient philosophers believed that the Sun, the Moon, and other planets have specific influences on earthly processes within the zodiacal sector of Capricorn. Here are the approximate possibilities of influence:
☉ Sun: Capricorn, being the sign of the winter solstice, has minimal power over earthly life (ranging from 0 to 1/3 of a conditional point – with 1 point representing the power of influence at the moment of exaltation or fall). It is considered the “darkest” winter sign.
☽ Moon: The Moon’s influence on earthly processes diminishes in Capricorn, falling below one (ranging from 1/3 to 0).
♃ Jupiter in the zodiac sign of Capricorn represents the start of Jupiter’s powers waning (1/point power);
☿ Mercury in Capricorn is a highly influential planet (from 1 2/3 to 1 1/3 points);
♂ Mars. Capricorn is the exaltation point of Mars, and its influence is significant (1 point);
♄ Saturn in Capricorn is at home, and its influence is stronger than ever, showcasing its cold nature to the fullest extent (up to 3 points).
Characteristics of the Capricorn Zodiac Sign, their Environment and Botanical Interests
Although Capricorn is traditionally associated with winter, it is interesting to note that ancient civilizations in the tropics and subtropics of Eurasia and North Africa found it suitable to sow many crops that are not well-suited for hot climates during this sign’s season. The people of ancient times had to carefully observe and understand the complex relationship between celestial bodies, weather patterns, and the optimal timing for planting. Ptolemy, for instance, believed that the weather characteristics of January in ancient Alexandria were connected to the sign of Capricorn. This understanding is highlighted in the epigraph on this page.
Determining the favorable conditions for working with plants was crucial for ancient farmers, as their livelihoods and even their lives depended on successful harvests. In addition to the Sun, the Moon and its phases, as well as their interaction with the zodiac signs, held great importance in determining the optimal timing for agricultural activities. The ancient Greeks had a wealth of knowledge on this subject, built upon thousands of years of observations. A separate article will delve into the topic of the Moon in Capricorn, the Capricorn zodiac sign, and their influence on plants. For those who are not currently interested in agricultural matters related to this sign, it is worth noting that Capricorn is not considered one of the most fertile signs. In terms of fertility rankings, it falls in sixth place.
Capricorn Zodiac Sign and Individuals
“People born under the Capricorn zodiac sign are known for their unwavering determination and perseverance when it comes to achieving their goals. They are logical thinkers who prioritize rationality over emotions.”
A person born under the Sun in the sign of Capricorn is commonly known as a “Capricorn”. However, this may not always be the case. According to ancient Greek beliefs, the Sun in this sign is considered to be “relatively powerless”, and the determining factor for the newborn’s patron sign is often indicated by other planets, with Saturn being the most frequent choice.
Ancient philosophers primarily believed that a person’s character is shaped by their life experiences, and the zodiac sign only determines the dominant temperament and resilience (Ptolemy: “resistance to fate”) for those born under it:
The dominant temperament type for those born under the sign of Capricorn is phlegmatic, with a high strength of mind. They prioritize reason over emotions, which makes them persistent and determined in achieving their goals. Capricorn is known as the most ambitious sign. In ancient Greek medicine, the most crucial organs for the health of Capricorns were considered to be the joints and the musculoskeletal system as a whole.
The question of compatibility between Capricorns in relationships with each other and with individuals born under other zodiac signs is of great interest to many people and is discussed in a dedicated article: Compatibility by Zodiac Sign and Temperament. Types of temperament according to Hippocrates.
Important occurrences that took place throughout Russia’s history during the period when the Sun was positioned in the Capricorn zodiac sign
December 29, 1709 – Elizabeth I Petrovna, Russian Empress, was born;
January 09, 1791 – the Peace of Yassky was signed, marking the end of the Russo-Turkish War of the 18th century;
December 26, 1825 – The Decembrist uprising took place in St. Petersburg;
January 04, 1878 – Russian forces entered Sofia, liberating it from Turkish control;
January 05, 1905 – The surrender of Port Arthur’s fortress occurred during the Russo-Japanese War;
December 30, 1922 – The USSR was officially formed;
January 12, 1903 – I.V.Kurchatov, a nuclear physicist and the creator of the Soviet atomic bomb, was born;
January 12, 1907 – S.P.Korolev, the father of Soviet cosmonautics, was born;
January 11, 1919 – The Council of People’s Commissars issued a decree on the implementation of prodrazverstka;
December 25, 1946 – Europe’s first nuclear reactor was launched in the USSR;
December 31, 1968 – The world’s first supersonic passenger airplane, the Tu-144, was introduced;
December 25, 1979 – The Soviet Union began deploying troops to Afghanistan;
December 25, 1991 – M. Gorbachev resigned, leading to the dissolution of the USSR;
December 31, 1999 – Vladimir Putin assumed the role of acting President.
After Capricorn comes the eleventh sector of the zodiac, known as the Aquarius zodiac sign.
Sergey Ov (Seosnews9)
The article on the “Capricorn zodiac sign” will be continued.
Topics: Characteristics of the Capricorn zodiac sign and individuals. Compatibility of the Capricorn zodiac sign – A closer look.
* Capricornus constellation
The stars situated in the horns of Capricornus are under the influence of Venus and, to some extent, Mars; the stars at the level of the mouth are governed by Saturn and, to some extent, Venus; the stars on the feet and belly resemble Mars and Mercury; the stars on the tail resemble Saturn and Jupiter.
Claudius Ptolemy – On the Impact of the Stars – “A Mathematical Exposition in Four Sections”
Because of the Earth’s axis precession, the constellations change their position over time in relation to the vernal equinox, and the Sun’s visible movement through them occurs with a growing delay. The constellations slowly shift counterclockwise, completing a full circle in the zodiac every 25,776 years.
At present, the Sun transits the constellation Capricorn for 28 days: from January 19 to February 16.
Star chart of the Capricorn constellation by Sergey Ov
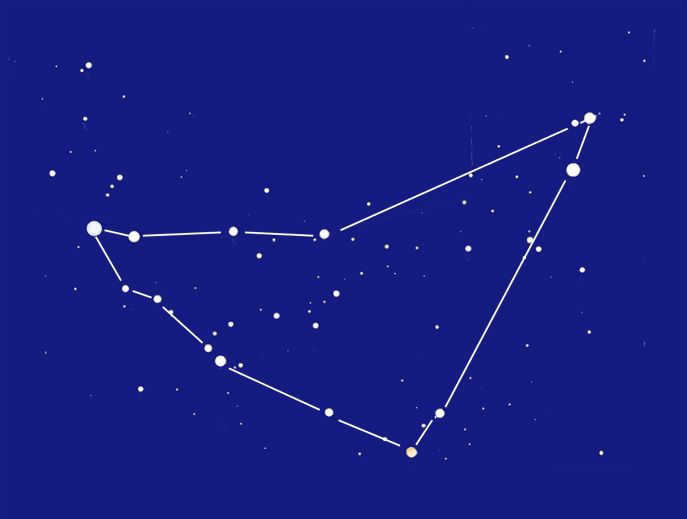
Diagram of the Capricorn constellation created by Sergey Ov, featuring stars that resemble both a “Horn” and a “Fishtail”.
Figure 5 The earliest method of representing the Capricorn constellation involved simplifying the brightest stars into a shape resembling a “Horn” or a “Fishtail”. For those with limited time for contemplation, this asterism served as a quick and recognizable representation (Figure 5). Some may even see a resemblance to a “business tick”, reflecting the modern office environment. This image is also linked to ancient legends of the Horn of Plenty and the Sumerian god with a fish tail.
The ancient Greek myth connected to the constellation Capricorn can be traced back to Homer’s time. It recounts the early years of Zeus, where his mother Rhea had to conceal him from Cronus. Zeus was raised in a cave and nourished with the milk of the goat Amalthea. Following his triumph over Cronus, Zeus immortalized Amalthea by placing her among the stars.
It is possible that in ancient times, individuals envisioned the shape of the Capricorn constellation depicted in Figure 6. 6.
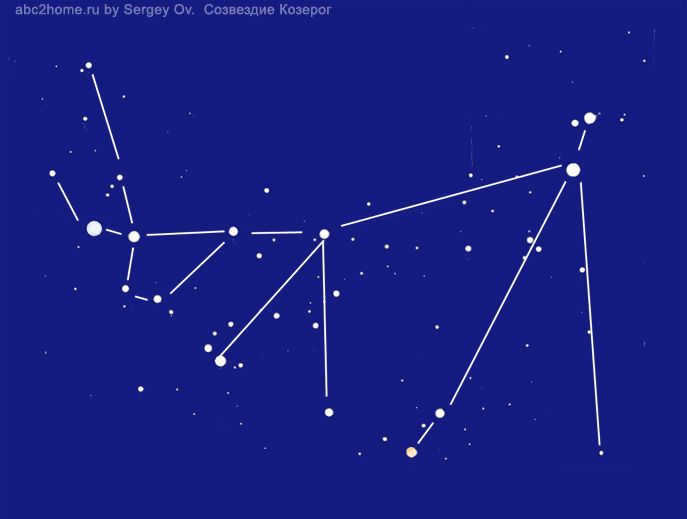
The Capricorn constellation is known for its asterism called the “Goat”. This diagram, created by Sergey Ov, shows the contours of the goat. It is represented by a scheme that includes diagrams of stars. This illustration, labeled as Fig.6, provides a visual representation of the Capricorn constellation.
Inherited from the ancient Greeks, the majority of the recognizable shapes of the constellations that we know today were observed quite differently by them compared to how we see them in our average latitudes. In the Mediterranean, the zodiacal constellations pass near the zenith, and the ecliptic line is nearly perpendicular to the horizon, making the stars appear so bright that they seem within arm’s reach. Gazing at these constellations on warm nights in the south, the ancient astronomers and philosophers were able to let their imaginations roam freely.
During ancient times, the Greeks associated another myth with the constellation Capricorn, which was already included in the zodiacal circle. This myth involved a jolly goat and the horned Pan, the god of shepherding and cattle breeding. During the battle between the gods and the Titans, the goat Pan would warn the gods of danger by blowing his horn. When the head of the Titan Typhon appeared, Pan was able to raise the alarm and then throw himself into the river. As he entered the water, he grew a fish tail and would surface and dive, distracting Typhon’s attention until Zeus struck him with lightning. In gratitude for his bravery, Zeus rewarded Pan with a constellation.
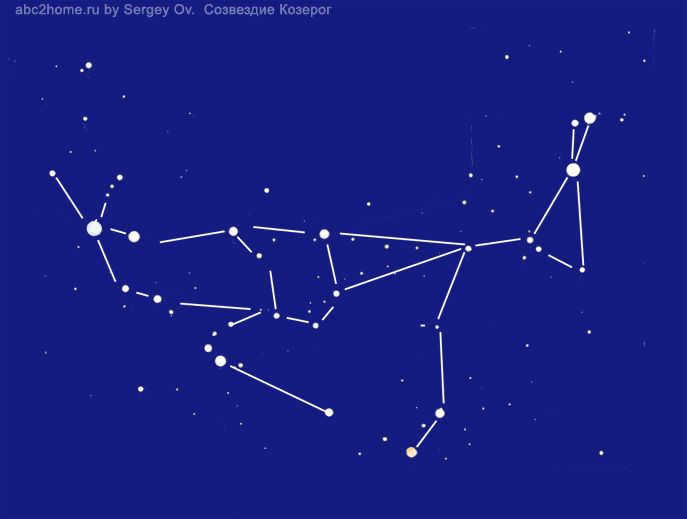
The diagram of the constellation Capricorn, also known as the “Goat”, was created by Sergey Ov. This diagram, labeled as Fig.7, depicts the contours of Capricorn’s various incarnations, which can resemble a kangaroo or even an alien. It also includes a scheme illustrating the stars that make up the constellation. Interestingly, in certain tribes of Australia and Tasmania, Capricorn is referred to as Kunguru.
Sergey Ov
The collage depicting the constellation Capricorn, which was inspired by a drawing in Jan Hevelius’s atlas, provides a visual representation of Ptolemy’s epigraph to the constellation section. This suggests that ancient and medieval astronomers may have viewed the starry sky as a dynamic tapestry of mythical stories. In Figure 8, only the stars recorded by Hevelius in his atlas are highlighted.
ARCHIVE
The Sun’s Journey in the Sign of Capricorn. Years 2000 – 2022
Year The Sun transitions from the sign of Sagittarius to the sign of Capricorn The Sun transitions from the sign of Capricorn to the sign of Aquarius
On December 22, 2023, at 06:27 MSK, January 2024 will begin at 17:07 MSK. On December 22, 2022, at 00:48 MSK, January 2023 will begin at 11:29 MSK. On December 21, 2021, at 18:59 MSK, January 20, 2022 will begin at 05:39 MSK. On December 21, 2020, at 13:02 MSK, January 19, 2021 will begin at 23:40 MSK. On December 22, 2019, at 07:19 MSK, January 20, 2020 will begin at 17:54 MSK. On December 22, 2018, at 01: 23 MSK, January 20, 2019 will begin at 11:59 MSK. On December 21, 2017, at 19:28 MSK, January 20, 2018 will begin at 06:09 MSK. On December 21, 2016, at 12:44 MSK, January 20, 2017 will begin at 00:23 MSK. On December 22, 2015, at 07:48 MSK, January 20, 2016 will begin at 18:27 MSK. On December 22, 2014, at 02:03 MSK, January 20, 2015 will begin at 12:43 MSK. On December 21, 2013, at 21:12 MSK, January 20, 2014 will begin at 07:50 MSK. On December 21, 2012, at 15:12 MSK, January 20, 2013 will begin at 01:52 MSK. On December 22, 2011, at 08:31 MSK, January 20, 2012 will begin at 21:12 MSK. On December 22, 2011, at 05:31 UTC, January 20, 2012 will begin at 18:12 UTC. On December 21, 2010, at 23:40 UTC, January 20, 2011 will begin at 10:14 UTC. On December 21, 2009, at 17:45 UTC, January 20, 2010 will begin at 04:23 UTC. On December 21, 2008, at 12:02 UTC, January 19, 2009 will begin at 22:37 UTC. On December 22, 2007, at 06:08 UTC, January 20, 2008 will begin at 16:43 UTC. On December 22, 2006, at 00:24 UTC, January 20, 2007 will begin at 11:00 UTC. On December 21, 2005, at 18:35 UTC, January 20, 2006 will begin at 05:14 UTC. On December 21, 2004, at 12:39 UTC, January 19, 2005 will begin at 23: 20 UTC. On December 22, 2003, at 07:04 UTC, January 20, 2004 will begin at 17:40 UTC. On December 22, 2002, at 01:14 UTC, January 20, 2003 will begin at 11:52 UTC. On December 21, 2001, at 19:21 UTC, January 20, 2002 will begin at 06:02 UTC. On December 21, 2000, at 13:37 UTC, January 20, 2001 will begin at 00:16 UTC. On January 20, 2000, at 18:23 UTC, a new year will begin.
NAVIGATION AND ADVERTISING
The realm of navigation and advertising is constantly evolving and changing. In this ever-changing landscape, it is important for businesses to stay ahead of the curve and adapt their strategies accordingly. The fusion of navigation and advertising offers a unique opportunity for businesses to reach their target audience in a more immersive and engaging way. By incorporating advertisements into navigation systems, businesses can provide users with relevant and timely information while also promoting their products or services.
One example of this fusion is the use of sponsored locations in navigation apps. Rather than simply providing directions, these apps can now display sponsored locations along the route. For instance, if a user is searching for a nearby coffee shop, the app might display sponsored suggestions or deals from local cafes. This not only helps the user find what they are looking for, but also allows businesses to connect with potential customers at the right time and place.
Another way navigation and advertising can be integrated is through in-car advertising. With the rise of autonomous vehicles, there is an opportunity for businesses to display targeted advertisements to passengers. For example, a ride-sharing service could show ads for local restaurants or attractions based on the passengers’ destination. This allows businesses to reach a captive audience and potentially increase foot traffic to their establishments.
Overall, the fusion of navigation and advertising presents exciting possibilities for businesses to connect with their target audience in a more personalized and interactive way. By leveraging new technologies and strategies, businesses can stay ahead of the competition and create memorable experiences for their customers.

The constellation Capricorn is located in the southern hemisphere and is part of the zodiac. It is not known for its prominent brightness or large size. Capricorn is the 40th largest constellation in the sky and is positioned near other constellations such as Sagittarius, Aquarius, and Eagle.
Myths and legends
Like numerous other groupings of stars, Capricorn was officially documented for the first time in the 2nd century AD in Ptolemy’s catalog. However, its knowledge predates this period. Ancient civilizations referred to it as Fish Goat and simply Goat, Goat, and the Arabs even Goat – “al-Jadi”. Due to the absence of these mammals on their land, Australian aborigines named this constellation Kangaroo.
In accordance with an ancient Greek tale, Capricorn is linked to the goat Amalphea, who nurtured the thunder god Zeus with her milk on the island of Crete. There is also a myth that this constellation symbolizes the woodland deity Pan, the father of the centaur Krotos, who actively supported the Greek gods and was rewarded by being immortalized in the sky.

Constellation Capricorn’s Stars
Interestingly, the most brilliant star in the constellation is neither Alpha nor Beta. It happens to be Delta – Deneb Algedi, which means “the goat’s tail” in translation. It consists of two components: a white giant and its companion.
The second brightest star is Beta. It is called Dabih in Arabic, which means “butcher” or “sacrificer”. When observed through a telescope, Beta appears as a double system. In reality, its primary component is a triple star, and its secondary component is a double star. Additionally, two more stars were discovered in this location, but it remains uncertain if they are part of Beta Capricorn.
Alpha is the third brightest star in the constellation, and its name is derived from the Arabic word al-Jedi, meaning goat, which is also the name for the entire constellation. Unlike Beta, Alpha is visually double but only has one component. The interesting fact is that these stars only appear close together, but in reality, they are actually quite far apart. Alpha, also known as Alpha 2, is located 109 light-years away from Earth and is the third brightest star in the constellation. On the other hand, Alpha 1, the second star in the constellation, is much more distant, with a distance of over 690 light-years from Earth.

Nashira, the alpha star of Capricorn, is the most fortunate celestial body in the entire universe, quite literally. Nashira is derived from the Arabic word for “happy” or “bringing good news”. This star shines brightly and exhibits peculiar variations in its luminosity.
Zeta is a binary system, consisting of a yellow giant and a white dwarf. Although it lacks an individual name, in Chinese astronomy, it is associated with the Twelve States asterism, where it is paired with Nu of the Serpentine to represent the kingdom of Yan.
Theta Capricorni, also known as Dorsum, is appropriately named as it represents the “back of the goat”. This star is a white dwarf that appears visually positioned on the “back” of the constellation.
Baten Algedi, also known as the omega star of Capricorn, symbolizes the “belly of the goat”. This star is a variable red giant.
Psi, along with Zeta, possesses a unique appellation solely in the Chinese language. Within the constellation that you are already familiar with, it embodies the realm of Yue. The star itself takes the form of a yellow-white dwarf.
Iota Capricorn is a fluctuating yellow giant, which also belongs to the Chinese Twelve States asterism. Within this group, in conjunction with the star 37 Capricorn, it represents the kingdom of Dai.
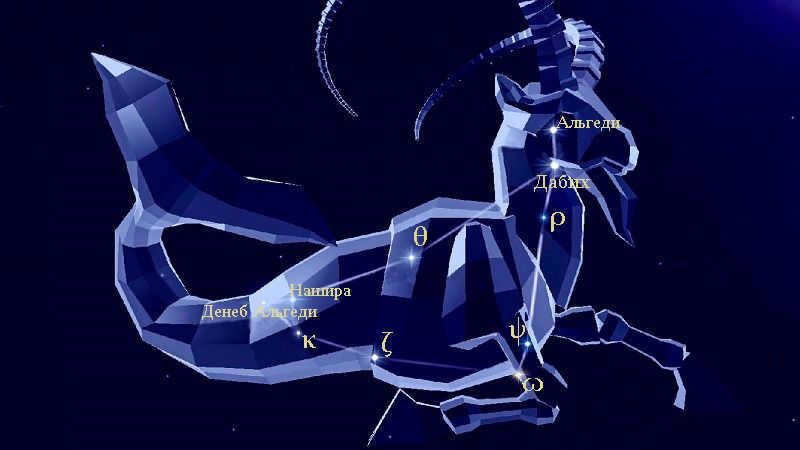
Nu Capricorn is a binary system known as Alshat, which translates to “sheep” rather than “goat.” The primary star is a blue-white dwarf, accompanied by a smaller companion.
Ro Capricorn, on the other hand, represents another star associated with a cloven-hoofed animal resembling a goat but not exactly a goat. Its Latin name, Bos, translates to “cow.” Interestingly, it is also referred to as the Sixth Star of the Bull in Chinese. Rho Capricorn is a binary system consisting of a yellow-white subgiant and a small companion.
Armus, on the other hand, is a binary system known as the “Heart of the Goat.” The primary star in this system belongs to the spectral class A. In the Chinese asterism symbolizing the twelve kingdoms of the Chunzo period, Eta Capricorn represents the Zhou dynasty.
Pi, a double star in the constellation Capricorn, is a celestial object consisting of a blue-white giant and its companion. Known as Oculus, which translates to “eye,” Pi is part of the Chinese asterism Bull, where it represents the Fourth Star of the Bull, alongside Ro.
Phi Capricorn, an orange giant, holds symbolic significance in Chinese astronomy as it represents the kingdom of Chu. However, writer Richard Allen argues that when combined with Hi, Phi symbolizes the kingdom of Wei.
Hee, a white dwarf found in the Chinese asterism, is said to represent either the kingdom of Qi or Wei, according to Allen’s interpretation.
Additional items
The globular cluster M30 or NGC 7099, situated in the Capricorn constellation, gained its notoriety for being the sole entity identified in that region by the renowned astronomer Charles Messier. Recent studies indicate that this cluster experienced a gravitational collapse, leading to a rapid contraction and inward movement of its core. Moreover, the Capricorn constellation houses a remarkable total of five meteor streams.