The Milky Way galaxy can be compared to a sponge, with long, luminous strands consisting of thousands and millions of galaxies interspersed with dark patches, known as howdahs, where star clusters are relatively sparse. It is important to note that no matter where an observer is situated within this vast expanse, the distribution of stars and galaxies will always appear as though they are spread across the inner surface of a sphere, with the observer positioned at the center.

Transitioning from Flat to Three-dimensional
The human visual system has the capability to differentiate between objects that are near and objects that are far, as long as the distance between them is not too great. For example, we can discern a tree that is growing nearby from a mountain that is on the distant horizon. Likewise, we can distinguish a person standing directly in front of us from a crowd of people that are a hundred feet away. This ability to perceive depth is made possible by our binocular vision, although it is also possible, albeit less accurately, with just one eye. Additionally, our brain has the remarkable capacity to estimate parallax, which refers to the apparent shift in the position of an object in relation to its background as we change our viewing angle.
When gazing up at the celestial bodies, all of our clever techniques become irrelevant. By utilizing a powerful telescope, we are able to make an educated estimation of the proximity of the stars nearest to our Sun through the method of parallax. However, our capabilities cease at this point. The pinnacle of achievement in this field occurred in 2007 with the Hipparcos satellite telescope, which successfully determined the distance to one million stars in the vicinity of our Sun. Nevertheless, if parallax is our sole instrument, then anything beyond a few hundred thousand parsecs remains mere specks on the inner curvature of a sphere. Or rather, this was the case until the 1920s.
The Estonian astrophysicist Ernst Epik was the first person to add depth to the flat image of the distant cosmos. He accomplished this by measuring the rotational velocity of a bright star cluster and using that information to calculate its distance. What he discovered was that this distance was much greater than the size of the Milky Way, which had already been accurately determined at that time. Therefore, it was clear that this star cluster could not be part of the Milky Way. This star cluster turned out to be the Andromeda galaxy, which is the closest neighbor to the Milky Way (excluding dwarf satellite galaxies). In situations where the parallax method is ineffective for measuring distances, the property of certain bright stars to change their luminosity allows for an alternative method. The first of these stars were found in the constellation Cepheus, and they are now collectively known as Cepheids. Today, thousands of Cepheids have been instrumental in determining the distances to galaxies that cannot be measured using the parallax method.
Astronomers have made a significant breakthrough by discovering the correlation between the distance to an astronomical object and the red shift of its spectral lines. This important finding, which has often been attributed to Edwin Hubble, was actually the result of the collaborative efforts of several scientists. By accurately measuring redshift, astronomers are now able to determine the distance to even the most remote celestial objects, including galaxy clusters where individual variable stars are indistinguishable and their annual parallax cannot be measured. The development and utilization of advanced tools such as powerful ground-based and space-based telescopes, as well as sensitive spectrometers, has enabled scientists to view the Universe as a vast sponge-like structure, with the majority of matter concentrated in galaxy clusters, filaments, and walls. Additionally, a significant portion (up to 90%) of space is occupied by voids – regions where the density of matter is 15-50% lower than the average.
In 1977, astronomers gathered in Tallinn to exchange data on galaxy groups and their spatial distribution. This event marked a turning point in the understanding of the “large-scale structure of the Universe”. Previously, the Universe was thought to be uniformly filled with galaxies. However, Jaan Einasto, a key figure in large-scale structure research, faced rejection from astronomical journals when he described galactic filaments and the voids between them in his papers. The participants at the Tallinn Symposium, through their numerous papers, shattered the notion of uniformity and introduced the concept of the “cellular structure of the Universe”.
Where is the Milky Way located within the cosmic “sponge”?
In 2013, a team of astronomers made a remarkable discovery: the Milky Way and its neighboring galaxies, collectively known as Laniakea, are situated within an incredibly vast void spanning approximately 1.5 billion light-years. To determine this, scientists compared the levels of radiation emitted by nearby galaxies with those emanating from distant galaxies. The findings revealed a striking image, resembling a small town on the outskirts of a bustling metropolis, where the glow of city lights outshines the dimly lit windows of nearby houses. This colossal expanse of emptiness was aptly named the KVS void, derived from the initial letters of the researchers’ surnames: Ryan Keenan, Amy Barger, and Lennox Cowie.
The KVS void remains a topic of discussion within the astronomy community. Its existence would provide a solution to several fundamental issues. It is important to note that a void is not actually empty, but rather a region where the density of galaxies is 15-50% lower than the average density of the Universe. If the KBC void does exist, this reduced density could explain the discrepancy between the values of the Hubble constant, which measures the rate of expansion of the Universe, obtained through cepheids and relic radiation. This discrepancy poses a significant challenge in modern astrophysics, as the Hubble constant, like other constants, should theoretically remain constant regardless of the method used to measure it. If the Milky Way is located in a massive void, relic radiation encounters less matter on its journey to Earth compared to the cosmic average. By taking this into account, it is possible to reconcile the experimental data and accurately determine the rate of expansion of the Universe.
Theories on the Genesis of Galactic Super-Clusters and Howdahs
Upon the revelation of galaxy and void super clusters, scientists were immediately intrigued by their origins. It soon became evident that the blame could not be placed on an invisible mass within the Universe. The porous structure cannot account for the creation of normal, baryonic matter, which comprises familiar objects and ourselves. According to all calculations, its movement could not have resulted in the macrostructure that is observed today within the timeframe since the occurrence of the Big Bang. Only the redistribution of dark matter, which commenced long before the formation of the first galaxies, could have given rise to galactic super clusters and howdahs.
However, before the concept of the Big Bang was even discussed, the first hypothesis about the presence of filaments and voids emerged. Yakov Zeldovich, a Soviet astrophysicist, along with Jaan Einasto, embarked on an investigation of the macrostructure and initially conducted calculations based on the theory of dark matter as neutrinos, commonly referred to as the hot dark matter theory. Zeldovich proposed that early on in the Universe’s existence, perturbations in the dark matter led to the formation of a cellular structure, often referred to as “pancakes”. Over the course of more than thirteen billion years, these structures attracted baryonic matter through gravitational interactions, resulting in the observed formation of galactic superclusters, filaments, walls, and the empty spaces between them.
TechInsider Network Edition
Founder of “Fashion Press” LLC: 119435, Moscow, Bolshoi Savvinsky per. 12, building 6, 3rd floor, room II. 6, 3rd floor, room II;
Address of the editorial office: 119435, Moscow, Bolshoi Savvinsky per. 12, building 6, street 6, 3rd floor, room II; Address of the editorial office: 119435, Moscow, Bolshoi Savvinsky per. 6, 3rd floor, room II;
Editor-in-Chief: Nikita Vasilenok
Email address of the editorial office: [email protected]
Phone number of the editorial office: +7 (495) 252-09-99
Information product label: 16+
The network edition is registered by the Federal Service for Supervision in the Sphere of Communications, Information Technologies and Mass Media, registration number and date of decision on registration: series EL No. FS 77 – 84123 dated November 09, 2022.
© 2007 – 2023 "Fashion Press" Ltd.
By uploading content to the Website, the User gives "Fashion Press" LLC permission to use, reproduce, distribute, modify, and display the content for free.

Space, a place so distant, enigmatic, and magnificent, has always captivated individuals. In those ancient eras, when humanity lacked the ability to explore the depths of the Universe, they gazed upon the heavens not as mere shining stars, but as divine beings, acknowledging their significance and grandeur.
As science advanced, and the intellectuals and astronomers of antiquity gradually began to comprehend that what we observe is only a small fraction of the vast expanse that extends beyond our planet. Even in those times, scientists had already identified the Sun and planets and observed their movements. Various ancient scientific works positioned the Sun-Earth pair with the luminary in the forefront, but with the rise of Christianity, any allusions to the heliocentric system were deemed as sacrilege.
One’s life could be forfeit for daring to think freely and propagate “heresy”.
Giordano Bruno’s Contributions
Incidentally, the renowned Giordano Bruno, who was publicly executed for his supposed belief in heliocentrism, was in fact condemned for far more thought-provoking transgressions.
Even in his early days as a Catholic priest, the young man possessed a strong skepticism towards religion and allowed himself to question the sacred canons. Furthermore, Bruno had a fascination with literature that was deemed forbidden by the church. Consequently, his superiors had numerous inquiries for their subordinate, but Bruno himself chose to flee, unwilling to wait for the repercussions that may befall his spirit of independence. Subsequently, Bruno became deeply influenced by the ideas of Copernicus and sought to disseminate them wherever he ventured throughout Europe. He also held a keen interest in the realm of magic. Additionally, he developed his own philosophical perspective on the world, vehemently contradicting Catholic doctrines. Ultimately, this determination shaped his destiny, fueling an unwavering desire to convert others to his “faith” and a willingness to defend it until the very end. One fateful day, Bruno’s outspoken beliefs led to accusations and denunciations that reached the ears of the Inquisition. As Bruno refused to renounce his ideas, and the Inquisition had no tolerance for such defiance, the story concluded in the tragic manner that we are familiar with – at the stake.
It has been revealed that the Sun is merely one of countless stars in the Universe, all of which are in perpetual motion, including the Milky Way galaxy, to which it belongs.
But that’s not all. Extensive research and observations have demonstrated the existence of countless galaxies as well. Fortunately, at this point in time, humanity had advanced enough to perceive itself as an all-powerful creator, rather than a feeble insignificance in the vastness of the cosmos.
A brief overview of the Milky Way
The Milky Way is an enormous collection of stars. Scientists estimate that there are between 200 and 400 billion of these celestial bodies. As for the number of planets, it is impossible to determine even an approximate count. When it comes to age, the oldest known star is believed to be 13.2 billion years old. In comparison, our Sun is approximately 4.5 billion years old.
The size of the Milky Way is beyond comprehension for the human mind. The Galaxy’s official diameter is 100,000 light years, but there are indications that it may be twice as large. Its width is estimated to be around 1,000 light years. Despite its vastness, our home galaxy is relatively small compared to its neighbors. The Andromeda Galaxy, which has captivated sci-fi enthusiasts, is at least twice the size of the Milky Way.
The Milky Way is a disk-shaped spiral galaxy with two arms and a central bar. Recent studies have shown that there are actually only two arms, not four, as previously believed. The central bar, also known as the lintel, is not present in all spiral galaxies but is found in about two-thirds of them. This bar contains bright stars that are densely packed together.
The galaxy is constantly in motion, with stars orbiting around the nucleus, similar to how planets orbit around the Sun in our solar system.
At its current speed of 220 kilometers per second, it would take the Sun approximately 250 million years to complete one orbit around the Milky Way.
Where is human habitation located in the Milky Way galaxy?
In the Middle Ages, people were greatly influenced by Copernicus’ heliocentric system and would have been shocked to discover that even within our own Galaxy, which we proudly call “ours”, humans reside on the outskirts.
The center of the Galaxy is approximately 28,000 light-years away.
This means that humanity resides closer to the periphery of this magnificent celestial body. However, it is precisely this placement that has allowed life to thrive on our planet.
The solar system is situated on what is known as the corotational circle. Within this circle, the velocity of the stars corresponds with the velocity of the spiral arms, which in other regions move according to their own individual laws. These arms are an inhospitable environment for life, as they experience periodic outbursts of intense radiation capable of obliterating delicate organisms. The Earth’s atmosphere shields us from solar activity, but in this location, it would be rendered powerless. Therefore, we can conclude that our system is exceedingly fortunate, and scientific evidence shatters any human ambition. If a hypothetical divine origin were to place us at the center, the history of Earth would be incredibly brief.
This is a widely used analogy to illustrate the vastness of the Milky Way and the positioning of our solar system. Let’s envision our Galaxy as a sprawling field, and within it, our system is akin to a tiny grain of sand nestled on one of its borders. The Earth, in this context, would be virtually invisible to the naked eye, requiring a microscope to behold.

Incidentally, there are a plethora of vibrant illustrations depicting the Milky Way – not actual photographs, but rather artistic renderings based on data gathered by scientists. This is to be expected, as current technology does not allow us to peer into the depths of space with telescopes. Furthermore, capturing an authentic photograph of the Galaxy would require venturing beyond its boundaries and attaining a considerable distance.
Why is the Milky Way Called by Such an Unusual Name?
The ancient Greeks bestowed a peculiar name upon our galaxy. According to their mythology, the goddess Hera was unaware that her husband Zeus had secretly given her a baby named Hercules, who was actually the son of another woman. In a twist of fate, Hera discovered the deception and in her fury, milk spilled into the sky, creating a magnificent cluster of stars surrounded by a misty haze.
The name “Milky Way” is more prevalent in Western traditions. In Soviet countries, it was common to refer to our galaxy as “our Galaxy,” a term that is still used today.
In summary, we can state that the vastness of the world that envelops humanity is immense. Despite the immense distances and sizes of celestial bodies, our intellect has the capacity to investigate and harness the powers of nature, gradually navigating through uncharted territories. Hence, it is reasonable to argue that the ancient civilizations were not entirely mistaken in placing Earth at the core of the universe. Our planet possesses distinctiveness, leading one to speculate that it was intentionally crafted, rather than a product of happenstance.

In the Stargate universe, just like in the actual universe, our galaxy (known as Via Lactea in Latin) exists within the Local Group. In the Stargate series, it is alternatively referred to as Avalon, which was the name the Ancients used to identify our galaxy. Within the Stargate universe, our galaxy is home to numerous civilizations that have played significant roles not only within our galaxy, but throughout the entire Local Group as well. These civilizations consist of the Goa’uld, the Tau’ri, and the Replicators.
Within Stargate, our galaxy is just one of several galaxies that possess a functional stargate network. Other galaxies that are known to have stargates include.
Summary [ ]
Basic details [ ]
Interconnection with surrounding galaxies [ ]


It is also possible to journey from the Milky Way to another galaxy (such as Pegasus or Ida) through the use of a stargate. This process necessitates an 8-digit code and a source of powerful energy, such as a ZPM or the energy absorbed by Colonel O’Neill when he possessed the stored knowledge of the Ancients.
Dr. McKay and his team spearheaded the creation of the McKay-Carter intergalactic bridge, a groundbreaking system consisting of 34 Stargates strategically placed between the Milky Way and Pegasus galaxies. Acting as a connecting chain, these Stargates allowed for seamless travel between the two galaxies. At the heart of this chain was the intermediate station known as Midway.
With the help of a software macro developed by Dr. McKay, matter could be transferred through the Stargates without materializing until reaching the intermediate station. It was at Midway that individuals or objects would transition from one galaxy’s Stargate network to the other. The entire journey across this intergalactic bridge typically took around 30 minutes.
However, the discovery of this bridge by the Wraith posed a significant threat to Earth’s safety. In response, the station was self-destructed, rendering the bridge inactive and protecting Earth from potential infiltration.


The Milky Way Galaxy possesses its very own network of stargates. On the outside, the standard Milky Way Stargate appears as a stone gray structure with orange chevrons. Within the inner bezel ring of the Milky Way stargate, there are a total of 39 symbols. With these 38 symbols, the Milky Way stargate network boasts a staggering 1,987,690,320 (38×37×36×35×34×33) potential 7-digit addresses. To input an address into such stargates, one must utilize a dialing device that is connected to the stargate. This involves sequentially pressing the keys that correspond to the characters of the desired address, followed by pressing a large spherical key located in the center of the dialing device’s keyboard. Aside from the stationary dialer, the address can also be entered from any other compatible dialer, whether it be portable or built-in, such as a puddle jumper.
The method of entering the address on a standard Milky Way gate can also involve rotating the inner bezel to select the desired characters. By aligning each character with the upper chevron of the Stargate, it is recognized as part of the address. This manual method of dialing the address allows for greater control and precision. However, on Earth, this process has been automated and is now managed by a computer system.
Stargate Command developed a dialing computer to control the gate after discovering the gate on Earth without a dialer. Unlike a conventional dialer, a dial computer takes longer to input an address on a stargate because the character bezel rotates to select a character. The advantage of using a dialing computer is that it allows for better control and memorization of dialed addresses, although it is not as quick as a dialer in capturing characters without rotating the bezel.
The standard Milky Way stargate is a second generation model. As a result, if a newer version stargate is placed next to it, the second generation stargate loses priority and becomes secondary. The same is true if it encounters an earlier model stargate. On most planets with stargates, they are mounted on a pedestal with steps to facilitate easier access.
Stargate Command has invented a safeguarding mechanism for the gate, a defensive portal. This portal bears a structural resemblance to the aperture found in optical instruments, but with the notable distinction that the plates of the protective portal are crafted from durable metal. Positioned at a distance of three micrometers from the event horizon of the stargate, the defensive portal effectively prevents the rematerialization of atomic particles. Initially, the initial defensive portal was constructed using high-strength steel. However, it was subsequently substituted with a defensive portal composed of trinium.
On the majority of stargate-inhabited planets, the local populace possesses a relatively rudimentary level of technological advancement. Considering the fact that the Goa’uld were portrayed as deities, the inhabitants of these planets associate the stargates with gods, viewing all individuals who traverse through them as divine beings or malevolent entities.
At times, a moving object like the Apophis has the capability to have a gate installed on it. The Apophis, a spaceship utilized for attacking Earth, is constantly on the move, which makes it impossible for the stargate to access it during its journey. Therefore, when the ship is in orbit around a specific planet, the gate’s address is aligned with that planet. The gate’s reference point is directly linked to it.
Historical Background [ ]
Ancient Times [ ]
Ruling Era of the Ancient Civilizations [ ]



Around ten million years ago, a devastating outbreak of a highly contagious and untreatable illness known as the plague swept through the entire Milky Way galaxy. This plague bore a striking resemblance to the one that had previously afflicted Earth.
In the wake of this catastrophic event, the ancient beings who once inhabited Earth made the decision to depart, leaving behind a lone survivor named Ayana.
The origin of the plague is not known definitively, but it bears resemblance to the plague that the Ori Priors used to showcase the might of the Ori. This plague had a profound impact on the Milky Way and caused significant devastation to the Ancient colonies. It is also plausible that other species were affected by this disease. In order to contain the spread of the plague, the Ancients constructed Atlantis. Prior to their departure to Pegasus, the Ancients left behind one of their own on Earth, who was later named Ayana by the Tau’ri. It appears that Ayana was left behind due to being a carrier of the plague. The location where Atlantis launched from still holds a small outpost, equipped with a control chair, a stasis chamber, a database, and a substantial supply of drones. Additionally, prior to their departure, the Ancients utilized the facility on Dakara to reintroduce life to the galaxy and initiate a new phase of intelligent life evolution.
The resurgence of the Ancient Ones. The dominion of the Goa’uld [ ]
By 9177 BC, the second phase of development had given rise to a rudimentary society that existed in seclusion from the rest of the cosmos, as Earth’s stargate, constructed by the Ancient Ones, was ensnared in ice in Antarctica.
Around 8000 B.C., the Lantians made their way back to Earth, fleeing from the Wraith adversaries that arose from their own hubris, only to discover a desolate planet inhabited by savage tribes. Recognizing the absence of civilization, they each chose their own paths, ultimately either ascending and occasionally intervening in galactic affairs, perishing, or, like Moros, entering a state of hibernation to await their time. Civilization faded away, but remnants of its existence endured throughout the cosmos, with the language of the Ancient Ones later influencing the development of Latin.
Everything changed when the System Lord Ra discovered a planet and brought a second gate to it (unaware of the existence of the first gate) in order to transport primitive humans to other planets.
Ra established a mighty and unbeatable empire – enslaving humans to mine the mineral naqahdah, which served as the foundation for his advanced technology. He utilized the stargate system to scatter these humans across the galaxy, thereby giving rise to numerous civilizations modeled after Earth. Additionally, Ra developed an elaborate system for controlling subordinate worlds through the use of Jaffa armies – a genetically modified species of Homo sapiens (sometimes referred to as Homo sapiens jaffus). These Jaffa possess altered immune systems that require sustenance from Goa’uld larvae nurtured in specialized pouches within their bellies, serving as bio-incubators.
By the year 3000 BC, Earth’s inhabitants had revolted against Ra, compelling him to depart from the planet. Subsequently, the gate was concealed beneath the sand, rendering it unattainable.
Contemporary events [ ]
Conflict with the Goa’uld [ ]
Ra’s Stargate stayed hidden until Ba’al, the final surviving System Lord, met his demise, effectively eradicating the Goa’uld menace once and for all.
The Ori Crusade [ ]
The Ori Crusade is an event that has had a significant impact on the galaxy. This event, which occurred in a distant past, was a religious crusade led by the Ori, a powerful ascended race. The Ori believed that they were gods and sought to convert all beings in the galaxy to their religion.
The Ori Crusade began when the Ori discovered the existence of other galaxies and decided to spread their religion to these new worlds. They sent out missionaries to these galaxies, who would preach the teachings of the Ori and attempt to convert the inhabitants.
The Ori Crusade was met with resistance from many civilizations in the galaxy, who did not want to give up their own beliefs and submit to the Ori. This resistance led to a series of conflicts and wars between the Ori and the non-believers.
During the Ori Crusade, the Ori used their advanced technology and powers to devastating effect. They were able to destroy entire civilizations and wipe out entire planets in their quest for dominance. Their followers, known as the Priors, were also formidable warriors who would spread the word of the Ori and enforce their will.
Despite the power of the Ori, there were those who stood against them. One of the most notable groups was the Tau’ri, a race from Earth who had encountered the Ori and their followers. The Tau’ri formed an alliance with other civilizations in the galaxy to fight against the Ori and their crusade.
The Ori Crusade eventually came to an end when the Ancients, another ascended race, intervened. They saw the destructive nature of the Ori and their crusade and decided to stop them. The Ancients used their powers to banish the Ori from the galaxy and sealed off the means of communication between the galaxies.
The Ori Crusade left a lasting impact on the galaxy. Many civilizations were devastated by the wars and conflicts, and the memory of the Ori and their crusade would be remembered for generations to come. It serves as a reminder of the dangers of fanaticism and the power of belief.


In 2006, the Ori, the enemy responsible for the Ancients’ escape into the Milky Way, embarked on a massive crusade throughout the galaxy.
During the same year, the Ori managed to establish a connection between their own galaxy and the Milky Way using a super-gate. They dispatched four teams of SG-1, along with assistance from an Atlantis expedition, to open the super-gate and eliminate one Ori vessel. The remaining three teams, under the leadership of Orisai Adria – an Ori in human form, continued their crusade.
The Ori later discovered the whereabouts of the Sangraal, a weapon designed to combat the ascended beings. Unfortunately, Morgana Le Fey managed to destroy it, but she spared its creator, Merlin, with the intention of having him recreate it. Due to his weakened state, Merlin transferred his memories into Daniel Jackson’s mind, and it was Jackson who successfully crafted the new Sangraal. Eventually, ZV-1 triumphed in delivering the Sangraal to the Alteran Homeworld, ultimately leading to the eradication of all the ascended Ori.
The downfall of the Ori [ ]
Earth remained uncertain for a considerable period about the efficacy of their weapons against the ascended beings. However, a few months later, Adria materialized and admitted that their strategy had been unsuccessful. Concurrently, Baal utilized her physical form as a vessel and discovered that the Ori had indeed perished. (Despite Baal managing to inject her body with poison during his extraction from Adria, Adria’s only means of survival was to ascend.)
Six Ori vessels traversed the supergate and continued their holy war. A year later, ZV-1 embarked on a journey through the super-gate aboard the Odyssey, venturing into the Ori galaxy where they stumbled upon the Ark of Truth. This powerful artifact, capable of revealing the truth to anyone who gazed upon it, served as an anti-Ori weapon. Meanwhile, on Celestis, the Ori’s capital planet, Adria, an ascended being, made her presence known to Daniel Jackson and Vala Mal Doran. Adria claimed to possess the combined power of all the Ori, making her the sole wielder of their might. However, her triumph was short-lived. ZV-1 unveiled the Ark of Truth before Dosai, the High Prior, causing Adria to lose a significant portion of her power. This allowed Morgana Le Fey to render her powerless.
With the destruction of all the Ori, including Adria, ZV-1 returned to Earth while the Ori army retreated back to their own galaxy.
Humans (various populations and races):
- Ashen
- Bedrosians
- Galarans
- Hebridanian Humans
- Orbanians
- Tau’ri
- Tollans
- Galaranians
- Jaffa (including Sodanians)
Jaffa and Ashen constitute a unique breed of humans, created through genetic modification.
Planet Earth, along with the solar system and countless other stars and celestial bodies, is part of our vast Milky Way galaxy, an immense intergalactic structure where the force of gravity governs everything. The precise dimensions of a galaxy remain only approximations. Interestingly, there exist hundreds, perhaps even thousands, of such formations, both large and small, throughout the Universe.

The Milky Way and its surrounding celestial objects.
Every celestial entity within the Milky Way, such as planets, satellites, asteroids, comets, and stars, are in a perpetual state of motion. Originating from the cosmic turbulence of the Big Bang, these objects are all undergoing their own evolutionary processes. While some are more ancient, others are undeniably younger.

Perceiving the boundaries of galaxies visually is an impossible feat. Just a century ago, the scientific community remained oblivious to the fact that our Milky Way galaxy is not the sole one in the vast expanse of the Universe. It was only through the tireless efforts of American astronomer Edwin Hubble that this truth was unveiled – the Universe is replete with a myriad of gravitational formations. These formations range from minuscule galaxies to galaxies of comparable size to ours, and even colossal behemoths. Among these cosmic neighbors, Andromeda stands out as the closest galaxy to the Milky Way, boasting a size 2 to 2.5 times larger. However, not all galaxies are fortunate in their destiny. Dwarf galaxies, in particular, face an unfortunate fate as they are destined to serve as satellites to larger entities, which will eventually engulf them.
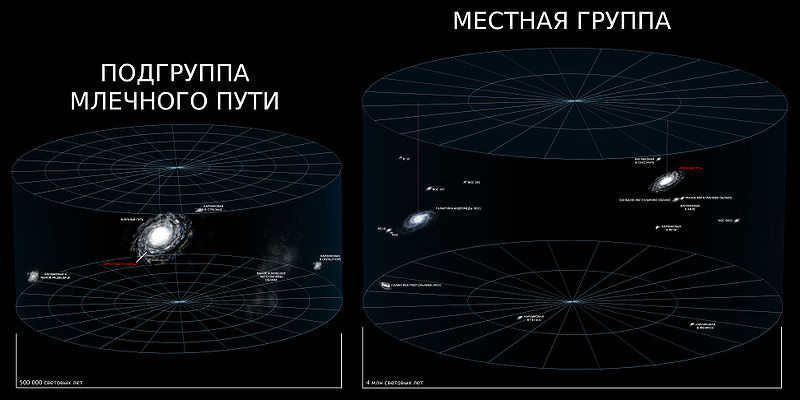

The Local Group, consisting of our intergalactic city along with the Andromeda and Triangle galaxies, is a member of the larger Local Virgo Supergroup formation.
Main features and specifications
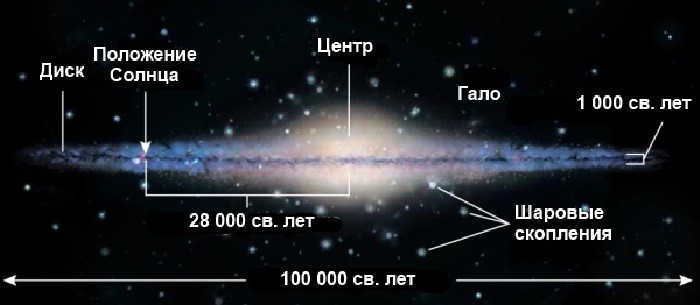
The Milky Way is a classic spiral galaxy classified as SBbc, featuring a central junction. With a diameter of 100 thousand light years, the Milky Way houses between 200 and 400 billion stars of diverse types, each at its own developmental stage. The galactic disk has a varying thickness of up to 1000 light years.
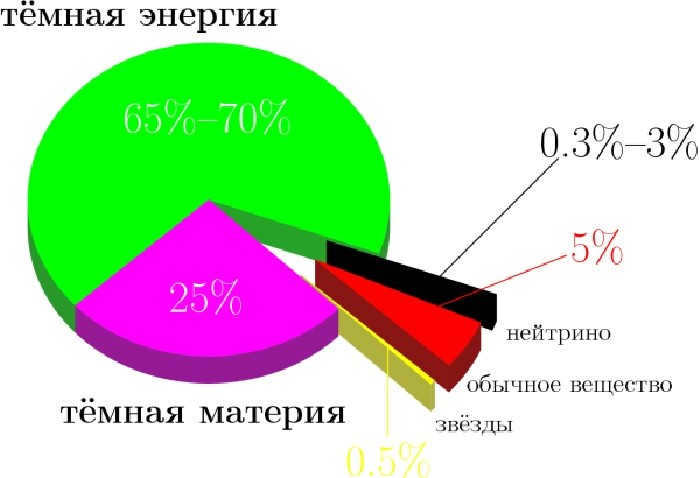
The mass of our Milky Way galaxy is comprised of more than just the mass of its stars. The majority of the galactic disk is composed of dark matter and interstellar gas, resulting in a tremendous weight of 4.8-10¹¹¹ M☉. To put it differently, the Milky Way is a staggering 150 billion times more massive than our Sun.


The galaxy is composed of various parts that rotate at different speeds around the center. While the galactic disk rotates at a moderate speed in the center, the peripheral parts can reach speeds of 200-250 km/s. The Sun is located in one of these peripheral parts, closer to the center of the galactic disk. It is situated at a distance of 25-28 thousand light years from the center of the galaxy. Over the course of its existence, the Sun and the Solar System have made 30 complete revolutions around the central axis of the gravitational formation, which takes approximately 225-250 million years.
The position of the galaxy within the vast expanse of the Universe
There is a noteworthy feature that should be highlighted. The convenience of the position of the Sun and, consequently, the planet Earth is quite remarkable. Within the galactic disk, there is a continuous process of densification taking place. This process is brought about by the disparity between the speed of rotation of the spiral branches and the movement of stars, which abide by their own laws within the galactic disk. During this densification, there are tumultuous events accompanied by powerful emissions of ultraviolet radiation. However, the Sun and the Earth find themselves nestled in the corotational circle, where such turbulent activity is absent. This circle lies between the boundary of the Milky Way arms – Sagittarius and Perseus. This is the reason behind the tranquility we have been experiencing for such a long time. For more than 4.5 billion years, we have remained unscathed by cosmic catastrophes.
The composition of the galactic disk is not uniform. Similar to other spiral gravitational systems, the Milky Way consists of three distinct regions:


- The center of the galaxy is composed of a dense star cluster containing a billion stars of various ages.
- Surrounding the star cluster is the galactic disk, consisting of clusters of stars, stellar gas, and dust.
- Extending beyond the galactic disk is the corona, a spherical halo that contains globular clusters, dwarf galaxies, individual groups of stars, cosmic dust, and gas.
Near the vicinity of the galactic disk, there exists an aggregation of youthful stars in clusters. The density of these star clusters is particularly high at the central region of the disk. Specifically, in this central area, the density amounts to 10,000 stars per cubic parsec. In the region where our solar system resides, the star density is already only 1-2 luminaries per 16 cubic parsecs. As a general rule, the age of these celestial entities does not exceed a few billion years.
Additionally, interstellar gas tends to concentrate around the plane of the disk, under the influence of centrifugal forces. Despite the consistent rate of rotation exhibited by the spiral branches, the distribution of interstellar gas is uneven, leading to the formation of both large and small regions of clouds and nebulae. Nevertheless, the primary building material within the galaxy is dark matter, whose mass surpasses that of all the other celestial bodies present in the Milky Way galaxy.
The bar-like structure known as the jumper can be found in the vicinity of the galactic core. Spanning an impressive distance of 27,000 light-years, it is home to a population of ancient stars, including red giants that derive their stellar material from black holes. This particular region boasts the highest concentration of molecular hydrogen, which serves as the primary ingredient for the formation of new stars.
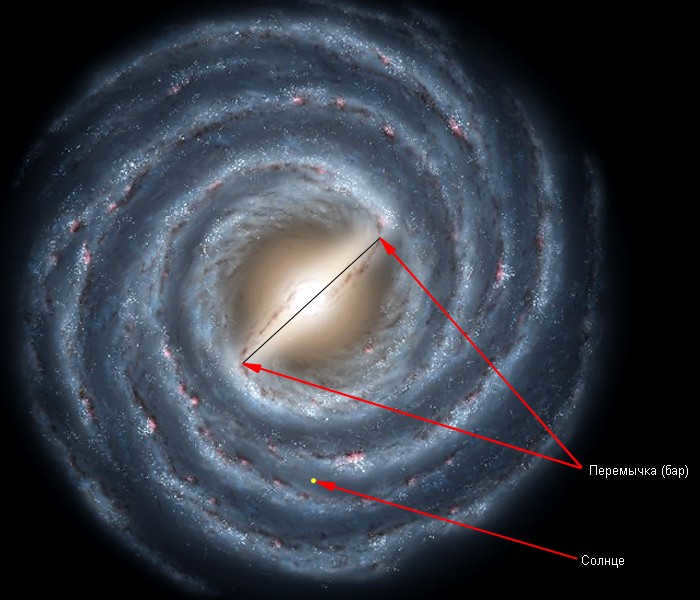
From a geometrical perspective, the structure of the galaxy appears to be quite straightforward. Each spiral arm, of which there are up to four in the Milky Way, originates from a gas ring. The arms spread out at an angle of 20 degrees. At the outer edges of the galactic disk, the dominant component is atomic hydrogen, which extends from the center of the galaxy to the outskirts. The thickness of the hydrogen layer in the outer regions of the Milky Way is significantly greater than in the center, while its density is extremely low. The expulsion of the hydrogen layer is facilitated by the interaction with dwarf galaxies, which have been in the vicinity of our galaxy for billions of years.
Theoretical models for our galaxy
Even ancient astronomers attempted to demonstrate that the visible band in the sky is a constituent of a massive stellar disk that revolves around its center. This claim was substantiated by mathematical computations. It wasn’t until thousands of years later, when instrumental techniques of space exploration came to the aid of science, that we could gain an understanding of our galaxy. A significant breakthrough in unraveling the nature of the Milky Way came from the research conducted by Englishman William Herschel. In 1700, he was able to experimentally prove that our galaxy takes the shape of a disk.

In recent times, scientific research has taken a new direction. Scientists have now turned to comparing the movements of stars at varying distances from each other. By using the parallax method, Jacob Kapteyn was able to make an approximate determination of the galaxy’s diameter, which, according to his calculations, is between 60,000 and 70,000 light years. As a result, the position of the Sun within the galaxy was also determined. It was discovered that the Sun is located relatively far from the active center of the Milky Way and at a considerable distance from its outer edges.

Edwin Hubble, the prominent American astrophysicist, is credited with the fundamental theory concerning the existence of galaxies. It was Hubble who proposed the classification system for all gravitational formations, categorizing them into elliptical galaxies and spiral-type formations. Among these, spiral galaxies form the most extensive group, encompassing formations of various sizes. One such remarkable spiral galaxy is NGC 6872, which has recently been discovered and boasts a diameter exceeding 552 thousand light-years.
The Milky Way Galaxy seems to be a tight and organized gravitational structure. Unlike the surrounding galaxies, our home in the universe is relatively calm. The galactic disk is being gradually diminished by the constant influence of black holes. This phenomenon has been ongoing for billions of years, and its duration remains uncertain. The sole danger looming over our galaxy originates from its closest counterpart. The Andromeda Galaxy is swiftly moving towards us. Experts propose that the convergence of these two gravitational systems might happen in approximately 4.5 billion years.
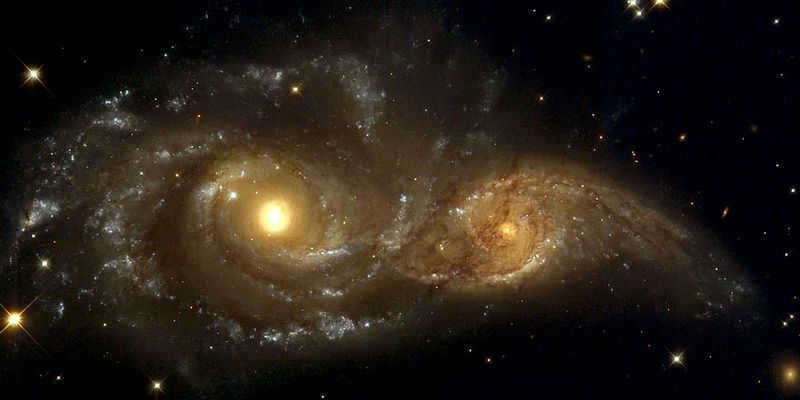


This encounter would signify the demise of the familiar world we inhabit. The smaller Milky Way will be engulfed by a larger celestial body. Instead of two prominent spiral formations, a novel elliptical galaxy will emerge within the cosmos. Prior to this event, our galaxy will assimilate its companions. In approximately 4 billion years, the Milky Way will absorb the two dwarf galaxies – the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds.
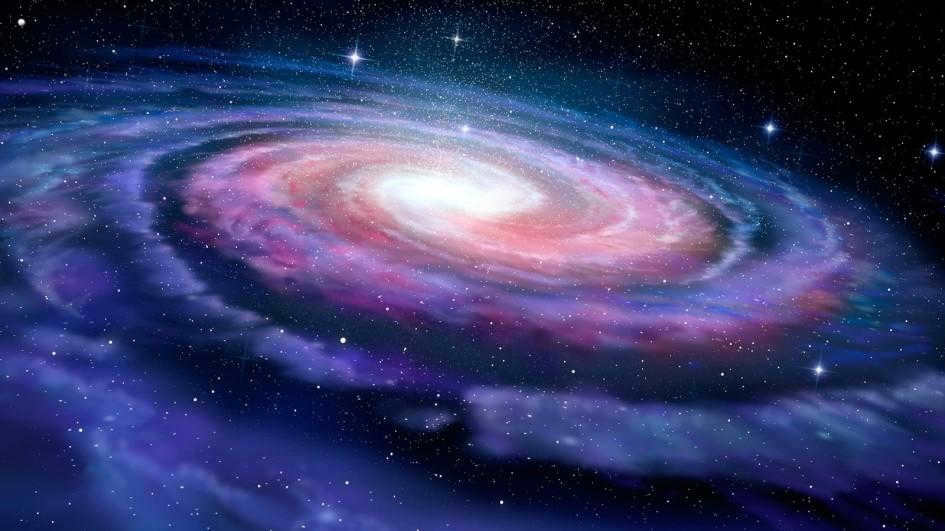

The Milky Way Galaxy is incredibly magnificent and breathtaking. This expansive realm serves as our residence, encompassing our solar system. Every single star and celestial body that we can perceive with our unaided eyes in the nocturnal expanse belongs to our galaxy. Nevertheless, there are certain entities situated in the neighboring Andromeda Nebula, which happens to be the closest neighbor of our Milky Way.
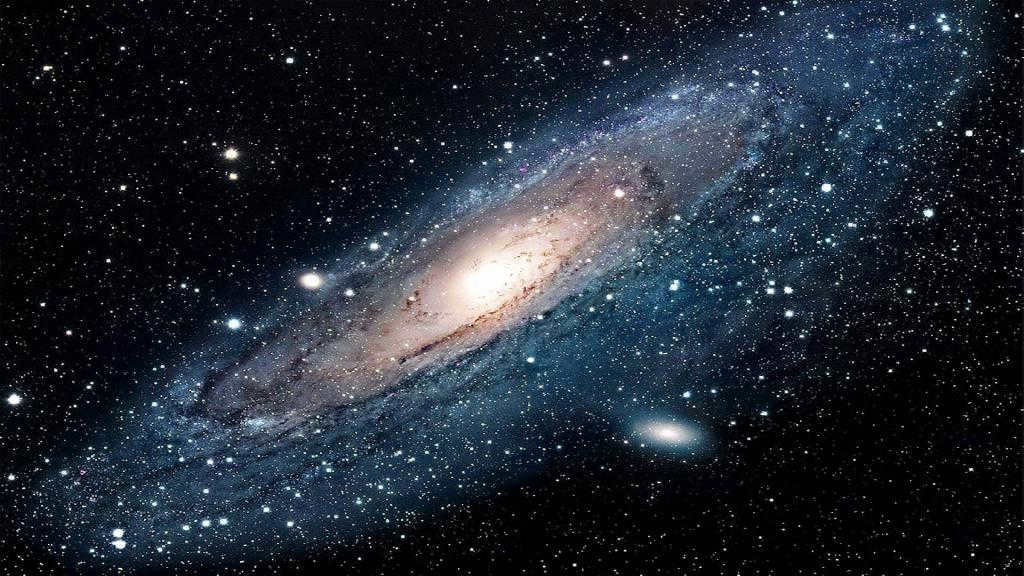

Milky Way’s Description
The Milky Way, also known as our galaxy, is extremely vast, spanning a staggering distance of 100 thousand light years, with each light year equivalent to a mind-blowing 9460730472580 km. Our solar system can be found at a distance of 27000 light years from the galaxy’s center, nestled within one of its spiral arms known as the Orion arm.
Similar to how the Earth orbits around the Sun, our solar system revolves around the center of the Milky Way galaxy. It takes approximately 200 million years for the solar system to complete a full revolution.
The shape of the Milky Way Galaxy is not perfectly symmetrical, resembling a disk with a bulge at its center. It exhibits a unique deformation, with a bend to the north on one side and a downward turn followed by a rightward curve on the other side. This deformation can be visualized as a wave-like pattern. The disk itself is also subject to deformation, primarily due to the presence of the Small and Large Magellanic Clouds. These two dwarf galaxies orbit the Milky Way at a high speed, as observed and confirmed by the Hubble telescope. They are commonly referred to as satellites of our galaxy. The gravitational interaction between the two clouds and the Milky Way forms a heavily weighted and sizable system, owing to the abundance of heavy elements in their mass. This interaction can be likened to a tug of war, resulting in vibrations that deform the Milky Way galaxy. This unique structure of our galaxy is further enhanced by its halo, giving it a distinct identity.
According to scientists, the Magellanic Clouds are expected to engulf the Milky Way in billions of years, and eventually, Andromeda will also consume it.

The Mysterious Halo of the Milky Way
Scientists have embarked on an inquiry to determine the nature of the Milky Way galaxy. Their investigations have revealed that approximately 90% of its mass is composed of dark matter, giving rise to a perplexing halo. In fact, only about 10% of the galaxy, which is visible to the naked eye from Earth, consists of luminous matter.
Multiple studies have substantiated the existence of a halo surrounding the Milky Way. Scientists have constructed various models, accounting for both the visible and invisible components. Through these experiments, it has been postulated that the absence of a halo would result in slower speeds of the planets and other celestial elements within the Milky Way. Consequently, it is hypothesized that the majority of the galaxy is composed of undetectable mass, or dark matter.
The Countless Stars
The Milky Way galaxy is renowned for its extraordinary nature. It possesses a remarkable structure, hosting an excess of 400 billion stars. Remarkably, a quarter of these stars are of significant size. In comparison, other galaxies have a smaller population of stars. For instance, The Cloud is made up of around ten billion stars, while some others consist of a billion. In contrast, the Milky Way houses an astounding 400 billion stars of various types, with only a minute fraction, approximately 3,000, visible from Earth. The exact number of stars within the Milky Way is indeterminable, as the galaxy constantly loses objects due to their transformation into supernovae.

Gases and Particles
Around 15% of the components in our galaxy are particles and gases. Could these be the factors that give our galaxy the name Milky Way? Despite its immense size, we can only observe a distance of about 6,000 light-years ahead, while the actual size of the galaxy is 120,000 light-years. Although it may be larger, even the most advanced telescopes cannot detect anything beyond this distance. This is due to the accumulation of gases and particles.
The density of the particles prevents visible light from passing through, but infrared light can penetrate it, enabling scientists to generate maps of the celestial sky.
What happened before
Scientists believe that our galaxy didn’t always exist in its current form. The Milky Way was formed through the merging of multiple other galaxies. This massive event resulted in the Milky Way capturing other celestial bodies, which greatly influenced its size and shape. Even today, the Milky Way continues to capture planets from other galaxies. One example of this is the dwarf galaxy known as the Big Dog, which is located near our Milky Way. Stars from the Big Dog are periodically assimilated into our galaxy, while some of our stars may move on to other galaxies, creating an exchange of celestial objects with galaxies like Sagittarius.
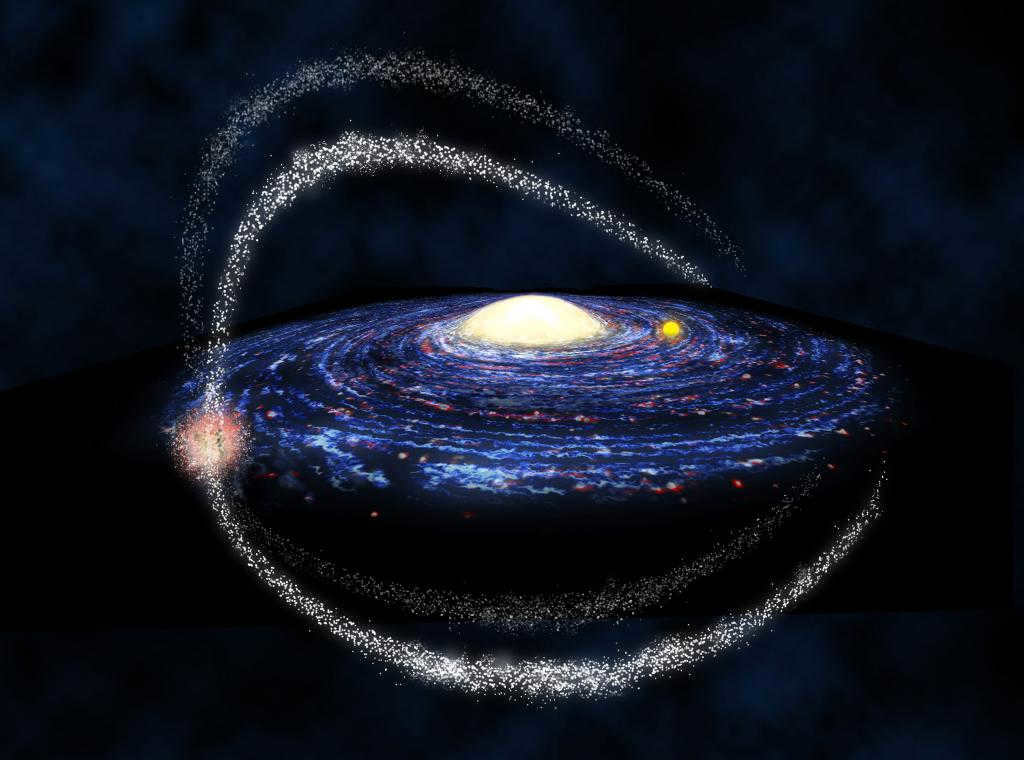

A glimpse of the Milky Way
The true appearance of our Milky Way galaxy when viewed from above remains a mystery to scientists and astronomers. This is primarily because Earth is situated approximately 26,000 light years away from the center of the Milky Way. Due to this positioning, capturing a comprehensive image of the entire galaxy is currently not possible. As a result, any depiction of the Milky Way is either an artist’s rendition or a snapshot of other observable galaxies. Consequently, our understanding of its true appearance is limited, much like how ancient civilizations believed the Earth to be flat.
The nucleus
The core of the Milky Way galaxy is referred to as Sagittarius A*, an immense generator of radio waves that indicate the presence of a massive dark void at its core. It is estimated to measure slightly over 22 million kilometers in diameter, constituting the void itself.
All the substance endeavoring to enter the void accumulates into an enormous disk, nearly 5 million times larger than our Sun. However, even this gravitational pull fails to impede the birth of new stars at the perimeter of the dark void.
Age
By analyzing the structure of the Milky Way galaxy, researchers have been able to make an educated estimate regarding its age, which is believed to be approximately 14 billion years. The oldest known star in the galaxy is slightly over 13 billion years old. Scientists determine the age of the galaxy by studying the age of its oldest star and the processes that occurred prior to its formation. Based on the available data, experts have proposed that our universe is roughly 13.6-13.8 billion years old.
The formation of the Milky Way began with the creation of its central bulge, followed by the development of its inner region where a black hole eventually formed. Approximately three billion years later, a disk with spiral arms started to take shape. Over time, the galaxy underwent various changes, and it was only about ten billion years ago that it started to resemble its current appearance.

We are a component of something greater
All the celestial bodies in the Milky Way galaxy are constituents of a larger galactic structure. We are a constituent of the Virgo Supergroup. The nearest galaxies to the Milky Way, including the Magellanic Cloud, Andromeda, and the other fifty galaxies, form a single cluster known as the Virgo Supercluster. A supercluster is a collection of galaxies that spans a vast expanse. Furthermore, it represents only a fraction of the stellar vicinity.
The Virgo Supercluster encompasses more than one hundred collections of clusters across an area exceeding 110 million light-years in diameter. The Virgo cluster itself constitutes a small portion of the Laniakea supercluster, which, in turn, is a part of the Pisces-Keith complex.
Revolution
As our planet orbits around the Sun, it completes one full revolution in a span of one year. Similarly, the Sun itself rotates within the Milky Way galaxy, revolving around the central axis of the galaxy. Furthermore, our galaxy itself is in motion relative to a unique type of radiation. Known as relic radiation, this serves as a useful benchmark for measuring the velocity of various celestial bodies in the vast expanse of the universe. Extensive research has revealed that our galaxy is rotating at an impressive speed of 600 kilometers per second.
The Origin of the Name
The name of the galaxy originated from its distinctive appearance, which resembles the spilled milk in the night sky. In ancient Rome, it was referred to as “the road of milk.” Even today, it is still commonly known as the Milky Way, as the name is associated with the white band that resembles spilled milk in the night sky.
References to this galaxy can be traced back to the time of Aristotle, who believed that the Milky Way is the point where the celestial spheres connect with the terrestrial ones. This viewpoint remained unchallenged until the invention of the telescope in the seventeenth century, which led to a shift in how people perceived the world.
Our close galactic companion
It is commonly believed that the nearest galaxy to the Milky Way is Andromeda, but this is not entirely accurate. Our closest “neighbor” is actually the Big Dog galaxy, which resides within the Milky Way. It is situated 25,000 light years away from us, and 42,000 light years from the galactic center. Interestingly, the Big Dog is closer to us than it is to the black hole at the center of our galaxy.
Before the discovery of the Big Dog, the closest companion was thought to be Sagittarius, and later it was believed to be the Large Magellanic Cloud. However, when the Big Dog was found at a distance of 70,000 light years, it became the new nearest neighbor. This galaxy is known for its abundance of unique stars with an exceptionally high density of the M-class.
According to scientific theories, the Milky Way consumed the Big Dog, assimilating all of its stars, planets, and other celestial objects.
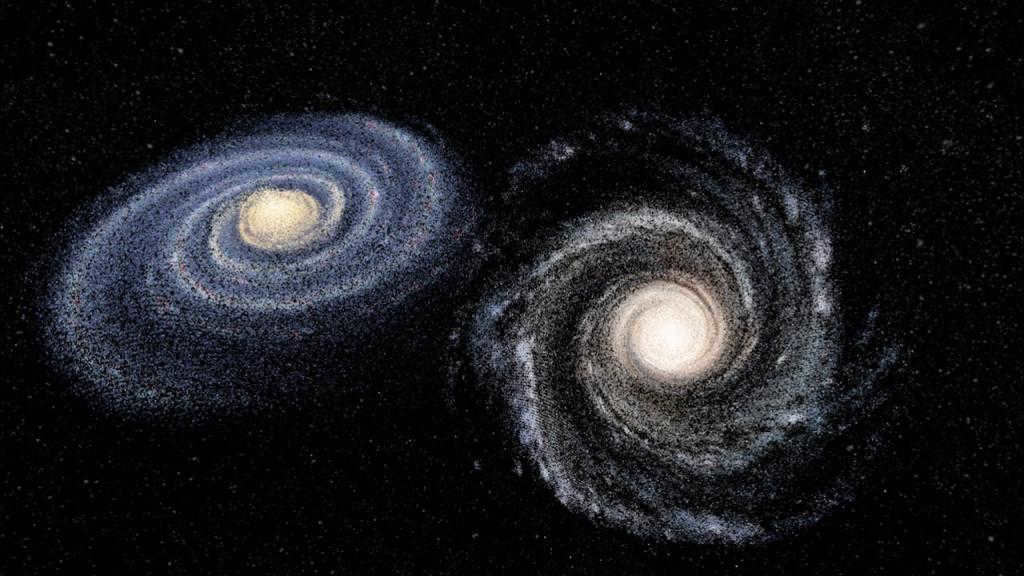

Galactic Clash
In recent times, there has been an increasing speculation that the Andromeda Nebula, the closest galaxy to the Milky Way, will engulf our universe. Both of these colossal entities came into existence approximately 13.6 billion years ago. It is theorized that these behemoths have the capability to merge galaxies, and due to the expansion of the universe, they are expected to move away from each other. However, defying all odds, these celestial objects are moving towards each other at a speed of 200 kilometers per second. It is estimated that the collision between Andromeda and the Milky Way will occur in 2-3 billion years.
Astronomer J. Dubinsky has developed a model of this collision, which is illustrated in the following video:

The collision will not result in a global catastrophe on a massive scale. After a span of numerous billion years, a fresh system will emerge, featuring recognizable galactic formations.
Extinct galaxies
Scientists have conducted an extensive investigation of the celestial expanse, encompassing approximately one-eighth of it. Through the analysis of the star systems within the Milky Way galaxy, they have managed to uncover hitherto undiscovered star streams located on the outskirts of our cosmos. These remnants are all that remain from diminutive galaxies that were once obliterated by the gravitational force.
The telescope installed in Chile has captured a vast collection of images, providing scientists with the means to assess the celestial landscape. Based on these images, it has been estimated that our galaxy is encompassed by a halo composed of dark matter, sparse gas, and a small number of stars. These remnants are believed to be the remains of dwarf galaxies that were once assimilated by the Milky Way. With the abundance of data at their disposal, scientists have been able to reconstruct a “skeleton” of these deceased galaxies. This process is akin to paleontology, where it can be difficult to determine the appearance of a creature based on a few scattered bones. However, with a sufficient amount of data, it becomes possible to piece together a skeleton and make educated guesses about the creature’s characteristics. Similarly, the wealth of information provided by the images has allowed researchers to recreate eleven galaxies that were engulfed by the Milky Way.
Scientists are confident that by observing and evaluating the data they receive, they will be able to discover several additional newly disintegrated galaxies that have been consumed by the Milky Way.
We are under attack
According to scientists, the hypervelocity stars within our galaxy did not originate within it, but rather from the Large Magellanic Cloud. There are many aspects of the existence of these stars that theorists cannot explain. For instance, it is unclear why a significant concentration of hypervelocity stars is found in Sextant and Leo. After reevaluating the theory, scientists have concluded that such high speeds can only be achieved through the influence of a black hole located at the center of the Milky Way.
Recently, there has been an increasing number of observations indicating the presence of stationary stars within our galaxy. Upon analyzing the trajectory of these superfast stars, scientists have made a startling discovery – our galaxy is under attack from the Large Magellanic Cloud.
The Demise of Planets
By closely studying planets within our galaxy, scientists have been able to witness the demise of a planet. This unfortunate planet was devoured by an aging star during its expansion and transformation into a red giant. As the star grew in size, it consumed the planet, causing another planet within the same system to alter its orbit. Based on these observations and the current state of our Sun, scientists have concluded that a similar fate awaits our own star. In approximately five million years, our Sun will transform into a red giant.
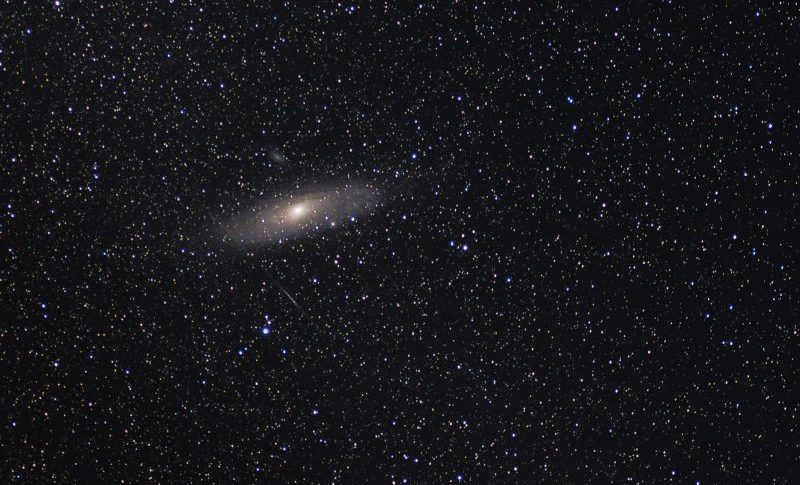

How the galaxy operates
The galaxy we reside in, known as the Milky Way, functions through a complex system of rotating spiral arms. At the very heart of this vast disk lies an enormous black hole.
When gazing up at the night sky, we can observe these galactic arms as they appear as white stripes, resembling a milky pathway adorned with countless stars. These arms, also referred to as branches, are most visible during clear weather in the warmer months when cosmic dust and gases are more abundant.
Within our galaxy, there exist several arms, including:
- The Naugol branch.
- The Orion arm, which is home to our very own solar system. This arm can be seen as our “room” in the greater “house” of the Milky Way.
- The Kiel-Sagittarius arm.
- The Perseus branch.
- The Shield branch of the Southern Cross.





