The recruitment process for astronauts has been conducted by “Roscosmos” for a number of years. Prospective candidates must meet the following qualifications:
- Proficiency in foreign languages;
- No dual citizenship;
- Age under 35;
- A degree in engineering or aviation;
- Good physical and mental health;
- No criminal record.
The selection procedure will assess your suitability based on these key criteria and determine your likelihood of commanding a spacecraft.
Give it a try
Regardless of whether you succeed or not, thanks to the availability of online simulators, games, and physical simulators, anyone can experience the sensation of being an astronaut.
🚀 SpaceX’s online simulator offers the opportunity to dock the Crew Dragon spacecraft with the International Space Station. The interface is designed to be similar to the controls used on the actual spacecraft. NASA’s head managed to do it on the first try – now it’s your turn to see if you can do the same.
🚀 Orbiter is an immersive simulation game that provides a realistic experience. You can explore outer space using both existing spacecraft and fictional ones designed for less experienced users. The simulator was originally released in 2000 and has since seen the development of numerous game models based on real-life ships and space stations, such as “Vostok,” “Mercury,” “Salyut,” and the “Space Shuttle.”
🚀 Space Engine is a unique virtual planetarium and simulation game that features well-known galaxies, stars, and planets. The uncharted space within the game is created using advanced algorithms based on scientific knowledge. Additionally, the surface of the planets is procedurally generated, resulting in exceptionally realistic graphics.
🚀 Kerbal Space Program, a space simulator highly regarded by Elon Musk himself, immerses players in a captivating fictional universe complete with aliens. In this game, you have the opportunity to step into the role of an engineer, designing and building rocket projects to execute a comprehensive space program.
Maximize your knowledge of space and become an astronaut
If you have a deep interest in exploring the vastness of space, there are numerous opportunities to expand your understanding. Attend exhibitions, workshops, and lectures dedicated to space exploration. Many cities have planetariums, space centers, and interactive exhibits where you can immerse yourself in the wonders of the universe. Additionally, consider enrolling in rocket-building courses to further enhance your knowledge and skills.
Discover Moscow’s Space Scene

Saint Petersburg
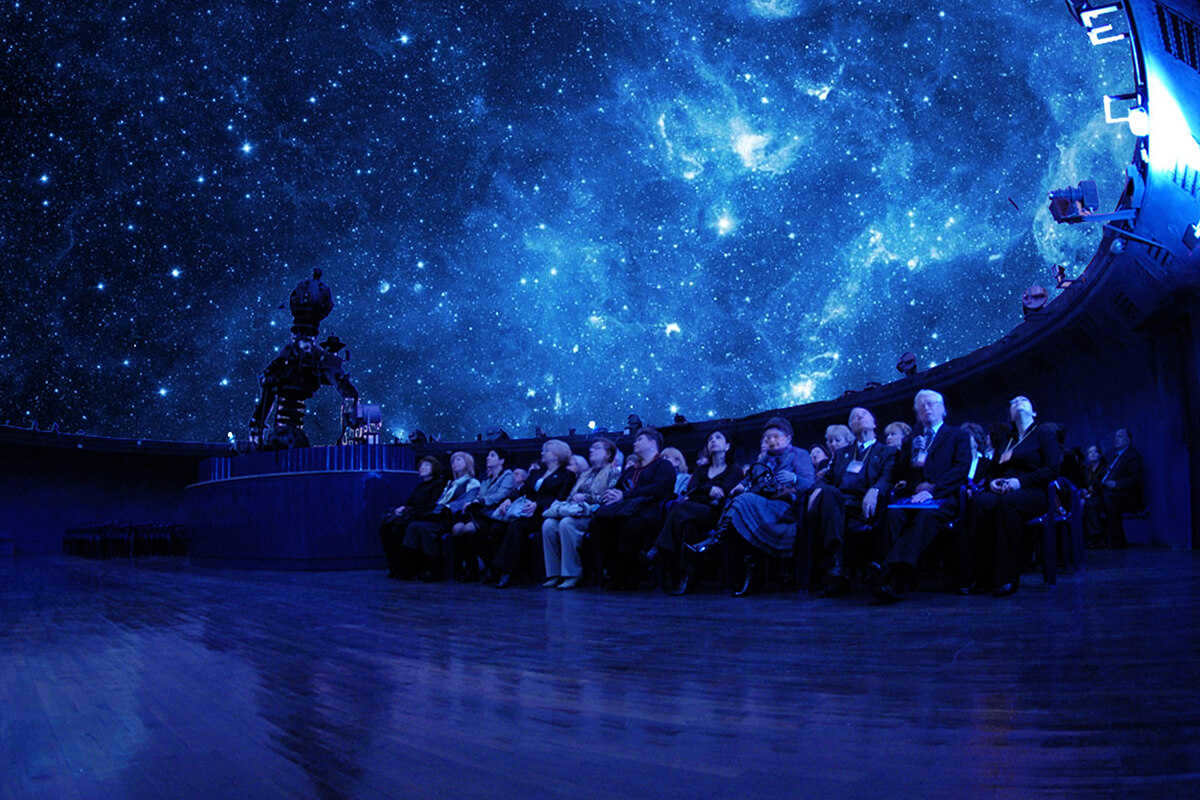

Visitors to the St. Petersburg Planetarium will have the exciting opportunity to embark on a virtual journey through the cosmos. As participants of a space mission, they will have full control over the spacecraft, allowing them to defend our planet from the threat of asteroids and meteorites. Armed with laser cannons, they can engage in intense battles, shooting down incoming space debris and ensuring the safety of Earth.
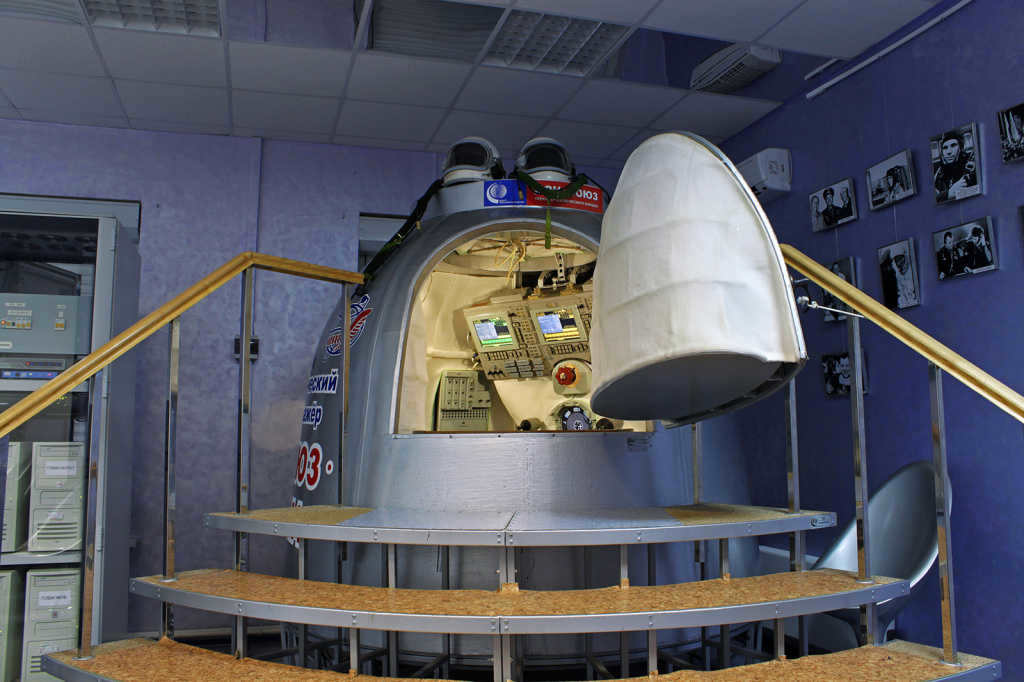

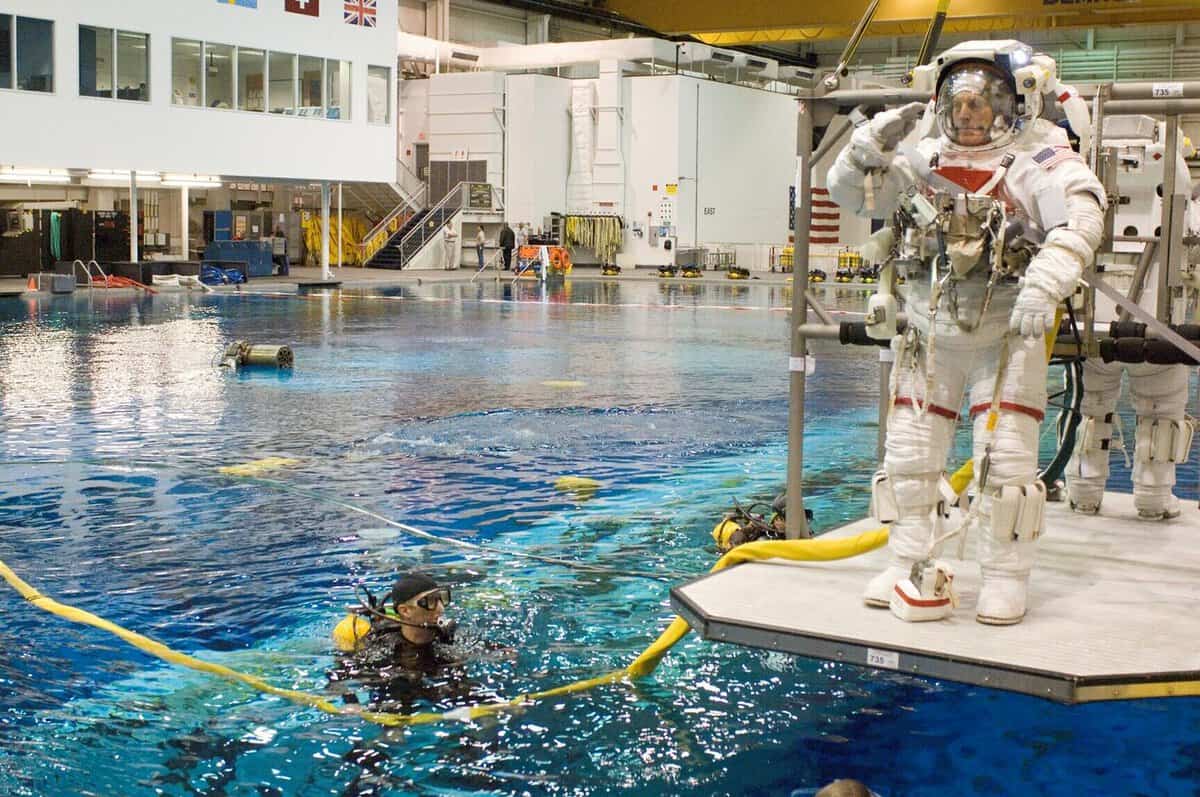
In the "Cosmonautics" hall of the Nizhny Novgorod Planetarium, there is a simulator available for practicing the manual approach and docking of a spacecraft. This simulator is used by real cosmonauts to practice manual docking in the event of equipment failure.
It is the most obvious option, although not the easiest to implement. Astronauts are responsible for managing spaceships, working on the International Space Station, and even venturing into outer space. Their tasks include conducting scientific research and testing various technical devices. There are times when astronauts need to repair equipment on the station. The presence of humans in Earth’s orbit is a biological experiment, and cosmonauts become subjects of study for doctors and biologists back on Earth.
The Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center is responsible for the selection and training of test cosmonauts. Individuals who are under the age of 35 are eligible to apply for admission to the cosmonaut squad. Good health and a higher education are among the primary requirements for prospective cosmonauts. The most sought-after specialties in space are pilot and engineer, and the most straightforward path to becoming a cosmonaut is through a military pilot profession.
Employment Opportunities: Within the Cosmonaut Squadron of Roscosmos.
- Krasnodar Higher Military Aviation School of Pilots named after A.K. Serov;
- Chelyabinsk Higher Military Aviation School of Navigators (branch of the Air Force Academy named after N.E. Zhukovsky and Y.A. Gagarin);
- Syzran Higher Military Aviation School of Pilots (a branch of the Air Force Academy named after N.E. Zhukovsky and Y.A. Gagarin).
Design Engineer
The design engineer is responsible for creating schematics of individual parts and mechanisms for aircraft such as rockets, spacecraft, and satellites. They are involved in developing new technical solutions, participating in the assembly and testing of apparatus and mechanisms, and preparing instructions for equipment operation. Design engineers also design rocket engines, spacecraft, and rocket-space complexes, and patent new designs of units and assemblies.
Work Opportunities: Design engineers can find employment at various organizations, including Ilon Musk’s company 🙂, military-space and defense industry enterprises, research institutes, and design bureaus such as S.A. Lavochkin NPO, Ground Space Infrastructure Operation Center, Space Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences, NPO Energomash named after Academician V.P. Glushko, S.P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation Energia, OAO MNPC Avionics, AO Russian Space Systems.
Robotics engineer
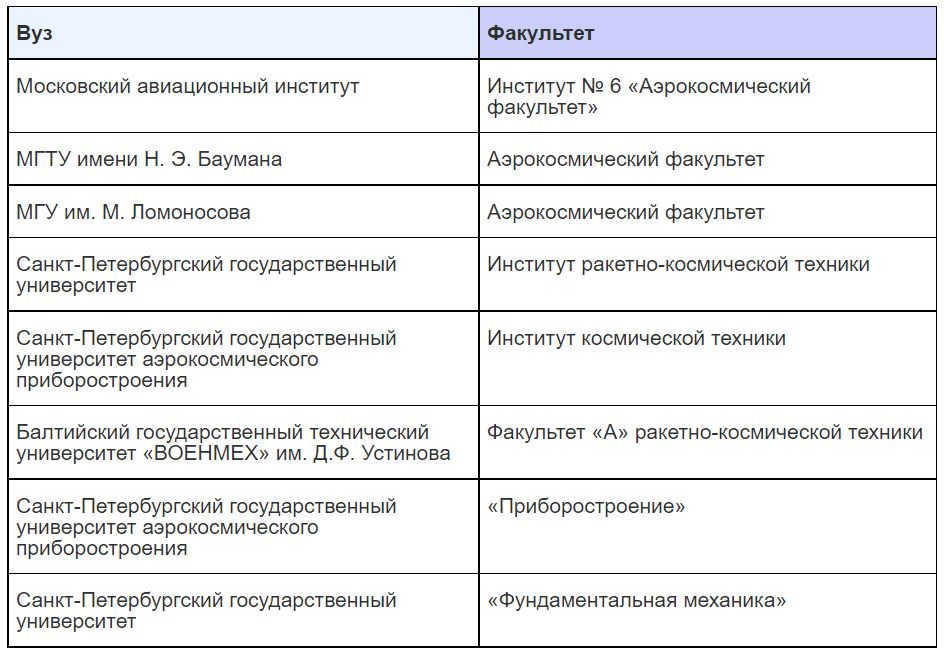
A robotics engineer is responsible for the development of automated systems, specifically those that utilize artificial intelligence technologies. This field is considered to be at the forefront of modern science. In the space industry, robotics engineers are focused on creating and programming vehicles that are capable of exploring space and celestial bodies. Recent advancements in space robotics include the creation of a robot that assists astronauts aboard the space station and a robot designed to handle heavy loads and aid in extreme situations that may arise in orbit. While Russian robotics may currently lag behind other countries, there are plans in place to elevate it to a global standard.
Possible work locations: Aviation and cosmonautics design bureaus, research institutes, and space industry enterprises such as NPO named after M.V. Lomonosov, S.A. Lavochkin, NPO Android Technology, Skolkovo Foundation Space Technologies and Telecommunications Cluster, Institute of Mechanics Problems of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Central Research Institute of Robotics and Technical Cybernetics, Research and Test Center of Rocket and Space Industry, United Rocket and Space Corporation, S.P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation Energia, Center of Ground Space Infrastructure Facilities Operation, and JSC Russian Space Systems.
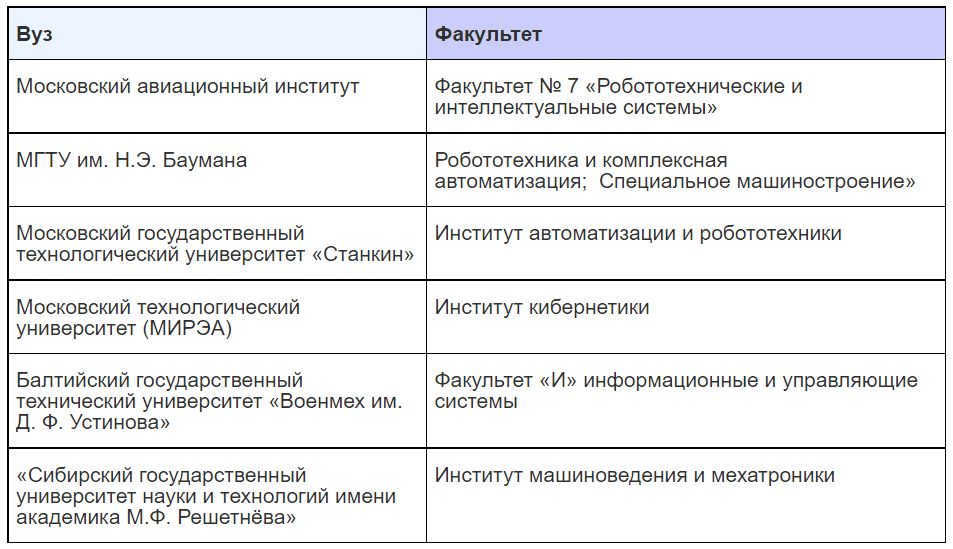
Telecommunications and communications engineer
Communication with the TsUP is crucial for space flights and the exploration of near-Earth space. Telecommunications and communications engineers play a vital role in ensuring the smooth functioning of satellite and spacecraft launch and control equipment. They also design and maintain satellite communications systems that are responsible for transmitting radio and television signals across the globe. Additionally, these engineers are involved in the operation of global satellite navigation systems like GLONASS and GPS.
Those working in the space industry as communication and communications specialists receive training in departments that focus on studying satellite networks, data networks, radio control, radio navigation, and radar.
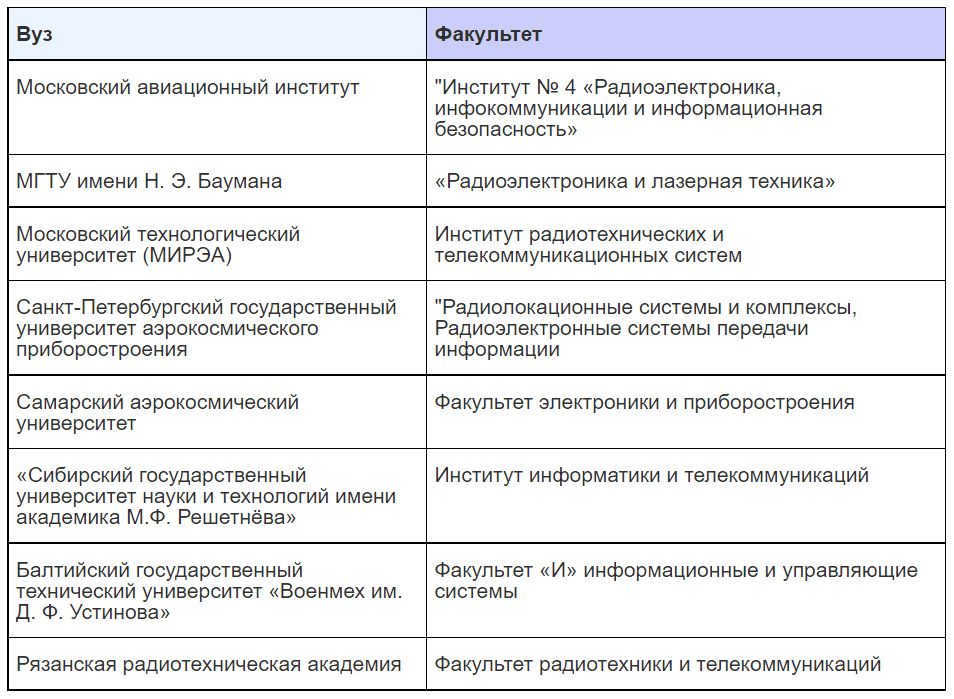
Software engineer
Specialists in information technologies and programming are essential in the space industry. They play a crucial role in programming the on-board computers of satellites and spacecraft. Companies involved in the production of control systems and radio-electronic equipment for space rocket equipment also require programmers. Software engineers are responsible for designing, creating, testing, and maintaining control programs.
Possible job locations: Roscosmos, JSC “Russian Space Systems,” JSC “Information Satellite Systems” named after Academician M.F. Reshetnev, military-space and defense industry enterprises, aviation and cosmonautics design bureaus, research institutes.
Space ballistician
A different title for this occupation is a research engineer specializing in dynamics, ballistics, and spacecraft motion control. Space ballisticians are responsible for calculating the trajectory of orbital vehicles and interplanetary stations, ensuring the safety and precision of spacecraft motion.
Possible work locations: Mission Control Center, air defense forces, specialized companies, research laboratories, and centers.
Stargazer
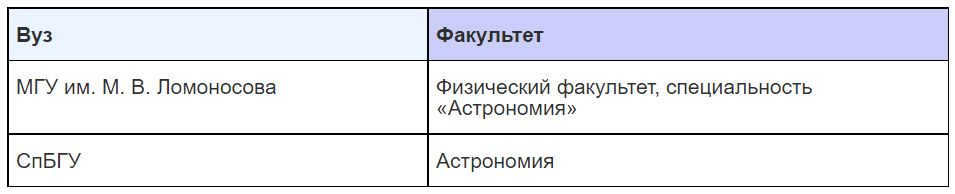
Stargazing is a subdivision of physics and one of the most ancient scientific fields. Contemporary stargazing is divided into astrophysics, astrometry, celestial mechanics, and stellar stargazing. Stargazers are involved in fundamental investigations of outer space and dynamics of stellar systems, explore the Sun and the solar system, individual stars and entire galaxies, comprehend the essence of supernovae and black holes. They accomplish this by means of observations using state-of-the-art telescopes and computer simulation technologies.
Where can you work: There are several places where you can work in the field of astronomy, such as research institutes and observatories. Some notable examples include the Institute of Space Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences, the Astro Space Center of the Physical Institute of the Academy of Sciences, the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, the Astronomical Institute named after V.V. Vakhtangov, the V.V. V. V. Sobolev Astronomical Institute, the Main (Pulkovo) Astronomical Observatory of the Russian Academy of Sciences, and the Special Astrophysical Observatory of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Additionally, the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory of the Russian Academy of Sciences is also a great place to work in this field.
Space Biology Expert
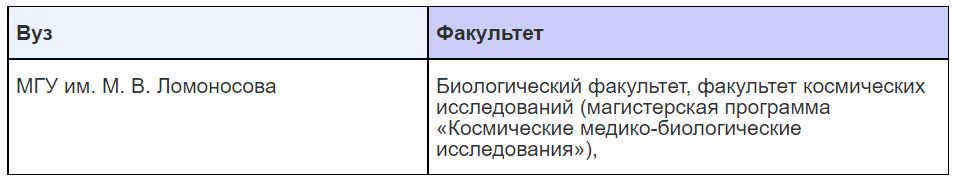
Disciplines that were once only found in the pages of science fiction novels are now becoming a reality. The field of space biology focuses on studying the unique characteristics of living organisms in microgravity, developing life support systems for astronauts, and exploring the possibilities of life on extraterrestrial planets, such as Mars.
Where to work: Opportunities for employment can be found at the Center for Astrobiological Research within the Biology Department of Moscow State University, as well as at the Institute of Medical and Biological Problems under the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Expert in Space Medicine
The field of space medicine involves providing continuous medical support and monitoring for astronauts, developing selection criteria for the astronaut team, and creating specialized rehabilitation techniques to address the effects of weightlessness. As humanity continues to explore space, including missions to the Moon and Mars, there will be a need for new specialists in space medicine to tackle the unique challenges of adapting the human body to reduced gravity.
Possible work location: Yuri Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center
The future holds great ambitions for humanity when it comes to space, including plans for planet colonization and the exploration of the vast reaches of the universe. As a result, the demand for professionals in the “space” field will inevitably rise, requiring individuals with expertise in space tourism management, extraterrestrial structure design, and specialized knowledge in space economics and law. So, if none of the options listed above captivate your interest, don’t let go of your dream just yet!

Individuals are not naturally born as astronauts – rather, they must undergo a transformation to become one. In order to glimpse our planet from the porthole of a spacecraft, individuals must meet a set of criteria pertaining to their health, physical fitness, and education, and successfully pass through an exceptionally rigorous selection process.
If you possess an engineering or scientific background, it is possible for you to undergo the necessary training to become an astronaut. In our article, we will outline the steps and provide an overview of what this training entails.
In Russia, there are no universities specifically dedicated to training astronauts. However, you can pursue an education that closely aligns with the necessary qualifications at the following institutions:
- Moscow Aviation Institute
- Moscow State Technical University, named after Bauman
- Space Research Department of Moscow State University
What are the qualifications needed to become a cosmonaut?
- Being a citizen of the Russian Federation, with no dual citizenship or residency permit
- Holding a master’s or specialist’s degree in engineering, science, or flight-related fields
- Having a minimum of 3 years of experience in the relevant field
- Being under the age of 35
- Possessing at least a B1 level of proficiency in English
- Being physically fit and free from chronic illnesses
- Possessing psychological qualities such as sociability, stress resistance, good memory, attentiveness, punctuality, creative imagination, critical thinking, tolerance, and the ability to learn
- Weighing between 50 and 90 kg
Preparation for a space flight takes six years:
It takes two years for training, passing the State Exam, and obtaining the title of “test cosmonaut”.
Another two years are dedicated to training in groups, where the cosmonauts have to pass various tests and exams.
After being assigned to a crew, there is an additional one and a half to two years of practical training.
Theory and Practice
During the first four years, aspiring astronauts study various subjects such as the structure of the night sky, flight dynamics, and the principles of operating onboard systems and space equipment.
Once they are enrolled in a crew, astronauts undergo training in parachute jumps, experience high G-forces in a centrifuge, and simulate weightlessness during flights. Before being sent into orbit, crew members also train in an underwater simulation of a space station.
In addition, astronauts acquire survival skills in environments such as mountains, deserts, snowy forests, and also learn water rescue techniques, among other things.
During their time in orbit, astronauts engage in scientific research and experiments, including the cultivation of plants in space, the testing of new life support systems, and the utilization of cutting-edge technology.
These endeavors are crucial in our quest to conquer the vast expanse of outer space.
The enigmatic cosmos consistently entices explorers, who go by the names of astronauts or cosmonauts. Brave and resolute individuals persist in their exploration of the depths of space, even in modern times.
What is the definition of an astronaut?
An astronaut is a professional who embodies bravery and courage. Their primary objective is to embark on space missions to conduct scientific and practical investigations. They are accountable for the exploration of undiscovered planets, the examination of celestial bodies, and the development of space technologies. Additionally, astronauts conduct vital experiments in gravity conditions on space stations and spacecraft.
The journey to becoming a cosmonaut starts with a rigorous and challenging selection process at Roscosmos. A key requirement is excellent health, with candidates needing to be under 35 years old and possess high levels of physical and mental fitness. Prospective cosmonauts must also meet specific height and weight criteria, ranging from 150 to 190 cm in height and 50 to 90 kg in weight. Additionally, candidates must possess knowledge in various scientific disciplines and have specialized skills. Many applicants pursue education in fields such as aviation, engineering, or scientific and technical studies before embarking on their cosmonaut career.

Once the selection process is successfully completed, the courses and training sessions commence, focusing on equipping future astronauts with the necessary skills to handle various tasks in space. These include payload delivery to spacecraft, operating rovers, and conducting experiments in a zero-gravity environment. It is mandatory for all new recruits to undergo a 6-month training period before they are eligible to go on space missions. Additionally, astronauts are required to possess multidisciplinary expertise, allowing them to serve as pilots, engineers, biologists, physicists, and chemists simultaneously.
One of the most crucial aspects of the training program is the practice of manual descent from orbit. In the event of an emergency or malfunctioning automation, astronauts must be able to safely bring the spacecraft back to Earth on their own.
The journey of each astronaut is filled with intricate and perilous trials. Their endeavors are dedicated to pushing the limits of what is possible and advancing scientific knowledge, which is why astronauts are revered as heroes. Nevertheless, it takes at least 6 years of training before a specialist can embark on their inaugural spaceflight.
Astronauts can be categorized into:
✔ Pilots who undergo testing
✔ Commanders of crews
✔ Explorers
✔ Instructors
Advantages and disadvantages of the occupation
Advantages of the occupation:
+ Unique work experience. Astronauts have the extraordinary opportunity to travel to space and experience zero gravity.
+ Contributing to scientific progress. Those in this profession work towards the advancement of technology, opening new frontiers for humanity.
+ Prestige. Astronauts are well-known and admired, earning respect in society.

Drawbacks of the occupation:
– Significant hazards. Space flights come with inherent risks, as even modern spacecraft are not immune to malfunctions.
– Extensive training. The demands of the profession necessitate lengthy training and years of preparation. Some astronauts may never actually go to space.
– Physical and mental strain. Space travel is far from an easy task. Intense physical exertion, sleep deprivation, and demanding work can lead to stress and fatigue, which can have a negative impact on emotional well-being and overall health.
Qualities Required for a Cosmonaut
Having only theoretical training is not sufficient for a successful career as a cosmonaut. Certain personal qualities are also crucial for effectively carrying out tasks.
✎ A cosmonaut’s profession does not leave room for mistakes.
✎ The ability to stay focused and remain calm, even in critical situations, are vital qualities for achieving success in this field.
✎ It is necessary to possess problem-solving skills and take responsibility for one’s own actions without relying solely on the team.
✎ Effective interaction with colleagues, being responsive and communicative, is essential for clear understanding on board.
✎ Being able to handle stress and maintain sound judgment while paying attention to detail is of utmost importance.

Where can I study to become an astronaut?
Obtaining a diploma in space science is not possible. The path to becoming an astronaut involves going through a selection process at Roscosmos. To increase your chances of being selected, it is recommended to pursue a degree in engineering or design from the MAI Aerospace Institute.
While a higher education is not mandatory, you can opt for specialized courses offered on online learning platforms like Coursera. For instance, the University of Arizona provides an opportunity to explore the realm of space professions through their course “Astronomy: Exploring Time and Space”.
Where to find employment
The Research and Test Center for Cosmonaut Training named after Yuri Gagarin is the federal state budgetary institution where the training process and professional tasks are conducted.
Salary for cosmonauts
An ordinary cosmonaut earns an average of 65 thousand rubles, even without any flight experience.
► If a cosmonaut is retrained as an instructor, their monthly income increases to 90 thousand rubles.
► The salary level increases with the length of service and position, and can reach up to 170 thousand rubles.
Of course, similar to any profession, there are additional allowances and bonuses that are awarded on an individual basis.
The space sector is experiencing rapid growth, providing a plethora of job prospects for individuals.
Once astronauts finish their time in space, they have the option to explore careers in education, science, or research within the space industry. Additionally, there are employment opportunities available in private space companies that focus on developing, launching, and maintaining a variety of vehicles and systems.

The field of becoming an astronaut offers endless opportunities for personal growth and advancement. The remarkable achievements of renowned astronauts like Yuri Gagarin, Neil Armstrong, and Valentina Tereshkova serve as a testament to the power of determination, inquisitiveness, perseverance, and expertise in paving the way for a successful and fulfilling journey in this profession.
Future of the Profession
As the space industry continues to advance and humanity’s desire to explore new frontiers grows, the demand for astronauts is increasing. Leading countries around the world are already heavily investing in space exploration and the development of new technologies, creating a significant need for professionals in this field.
The rapid growth of private space companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin is also creating new job opportunities for astronauts and aeronautical engineers.
Furthermore, the collaboration between different countries through projects like the International Space Station and planned missions to the Moon and Mars further amplifies the demand for skilled workers in this field.
Source: Humanitarian Technologies Center
If you are interested in staying up to date with the newest information on careers, sign up for our newsletter.

To be involved in the field of space exploration, it is not necessary to possess exceptional physical stamina and endure the gravitational forces of several g. In this article, we will provide information about various occupations that are connected to the realm of space.
Stay connected with us on Telegram: where you can discover a plethora of intriguing content for students from all disciplines. Additionally, make sure not to overlook the exciting discounts and promotions available on our secondary channel.
Occupations in the Space Industry
Within the realm of space-related professions, there is a distinct absence of arbitrary individuals. Consequently, we will provide a concise depiction of these professions, along with the corresponding educational institutions where one can obtain the necessary qualifications.
Cosmonaut (Astronaut)
The first occupation that springs to mind is that of an astronaut. Astronauts play an integral role in space exploration, venturing into outer space, and conducting tests and repairs on specialized equipment.
Where to Study?
Aspiring cosmonauts receive their training at the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center. Presently, anyone has the opportunity to apply and be selected for this esteemed profession. However, this has not always been the case. Historically, the conventional route to becoming a cosmonaut involved pursuing a career as a military pilot, which could be achieved by enrolling in the following:
Engineer
Engineer and pilot are currently the most sought-after professions in the field of space exploration. Additionally, these skilled professionals are also highly valued on the ground. Design engineers play a crucial role in the development and manufacturing of spacecraft components and mechanisms. They are responsible for designing rocket engines, preparing operational instructions for space equipment, and much more.
Where should you pursue your education?
A skilled engineer is always in high demand and can easily find employment opportunities in design bureaus, research institutes, and within the military-space industry. If you’re looking to obtain the necessary education to pursue a career in this field, consider the following options:
Cosmologist
Perhaps this is the most ancient profession related to space. A cosmologist doesn’t venture into space, but instead focuses on the fundamental scientific exploration of the universe. Cosmology is a branch of physics. It is further divided into astrophysics, astrometry, celestial mechanics, and stellar astronomy.
Where can you study?
Are you interested in becoming a cosmologist? Be prepared for the fact that you will not only be observing through a telescope, but also doing a lot of calculations. You can pursue your studies at:
Astronomical Biologist
This field has emerged in recent years. An astronomical biologist is focused on exploring extraterrestrial life, investigating how organisms function in zero gravity, and developing life support systems for astronauts.
Where to pursue this career?
To become an astronomical biologist, one must first complete a degree in Biology from Moscow State University. Afterward, one can apply for the master’s program in “Space Biomedical Research”.
Experts in the field of space medicine are actively involved in monitoring the well-being of astronauts. Typically, they are based at the Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center.
Where can one pursue studies in this field?
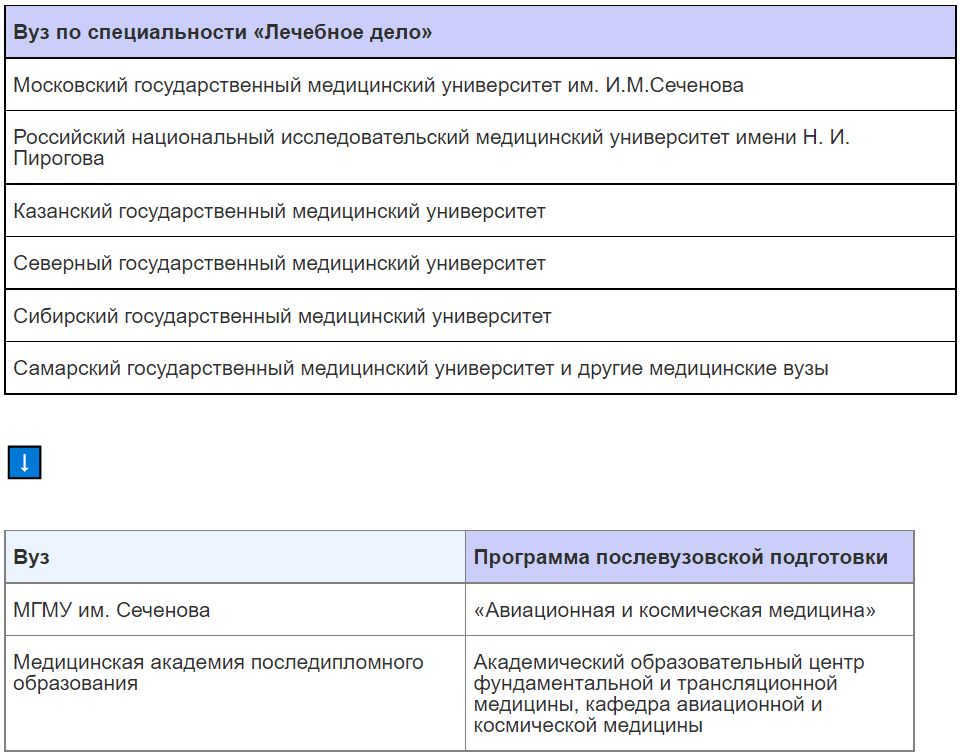
To become a space medical professional, one must complete medical school and then pursue a postgraduate program in “Aviation and Space Medicine” at Sechenov Moscow State Medical University. A similar postgraduate program is also offered at the Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education.
Ballistics Engineer
Ballistics refers to the study of the trajectory of objects, originally focused on the analysis of artillery shell flight. Space ballistics, also known as spacecraft dynamics engineering, involves the calculation of trajectories for artificial satellites, orbital stations, and other vehicles launched into space.
Where Can You Study?
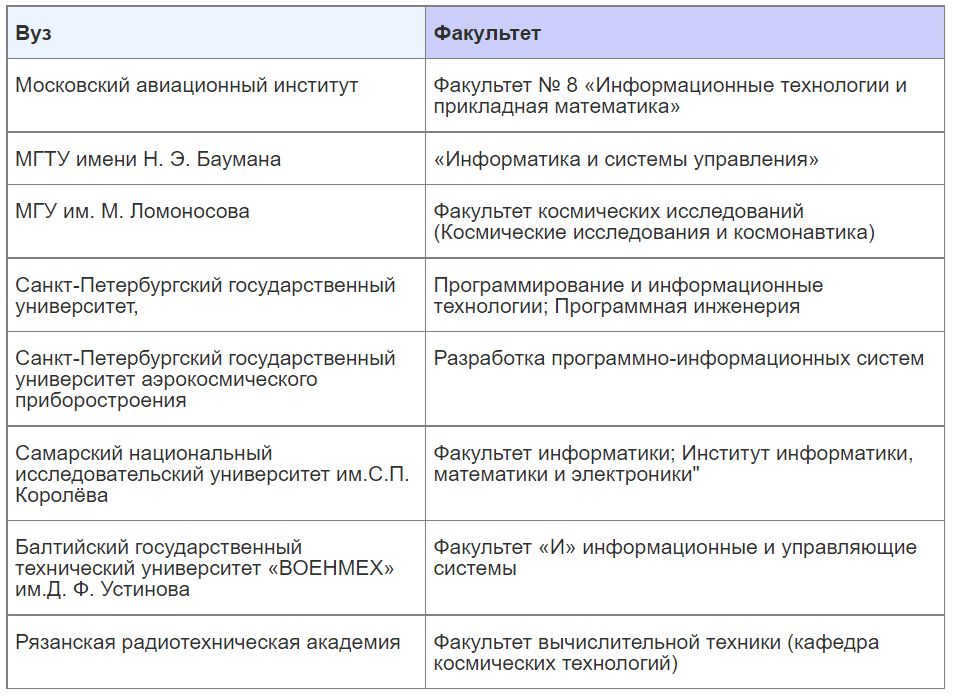
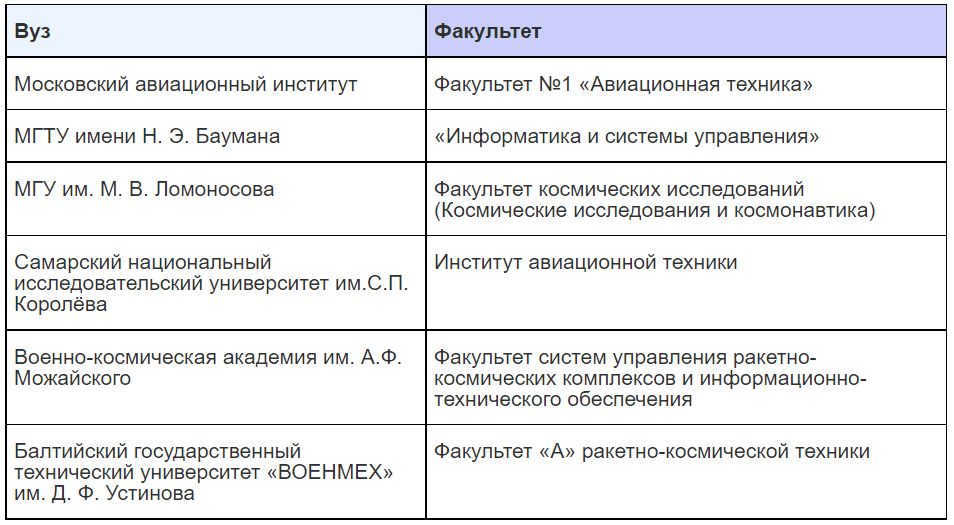
Individuals interested in becoming ballistics engineers can pursue their education at various institutions, including:
- Moscow Aviation Institute (Faculty No. 8, “Information Technology and Applied Mathematics”)
- Bauman Moscow State Technical University (specializing in “Space Research and Cosmonautics”)
- D.F. Ustinov Baltic State Technical University “VOENMEKH” (specializing in “Rocket and Space Engineering”)
Future Space Occupations
It is projected that the number of space professions will grow in the near future. Moreover, these professions won’t necessarily be limited to technical roles. It’s highly likely that the following space occupations will be in demand:
Space Tourism Manager
The inaugural space tourist ventured into space in 2001. Since then, numerous space startups have emerged, with SpaceX being a prominent example. Boeing is also involved in its own space initiatives, while Space Adventure intends to offer lunar tours. Admittedly, none of these ventures have reached full-scale commercial implementation yet, but the potential is evident.
Space Structure Designer
More specifically, a professional who designs the life cycle of space structures. The need for experts in this field is expected to arise in the near future, as the colonization of Mars is already a realistic plan for humanity.
Cosmic Geologist
The profession of cosmic geologist holds great promise for the foreseeable future. Earth’s mineral resources are finite, but they can be extracted from outer space. There are already startups working on extracting mineral deposits from asteroids and the Moon, which is closest to Earth.
An expert in the field of space law
Debates and discussions are a favorite pastime among people. In the event that the colonization of other planets progresses to a point where conflicts arise in space, the expertise of space lawyers will be in demand.
Interested in learning more about the professions of the future? Take a look at our blog!
Remuneration for space industry professionals
Given that space activities in Russia are predominantly managed by the state, professionals in the space industry typically find employment in state research institutes and centers. The salaries offered to individuals in these professions are usually quite substantial, if not astronomical.