Regrettably, your browser does not support JavaScript or it is disabled.
You have the option to either download the clip or obtain a player to play the clip directly in your browser.
Solar eclipse – An astronomical event in which the Moon obscures (eclipses) all or a portion of the Sun as seen from an observer on Earth.
Description
The following is a description of the topic at hand.
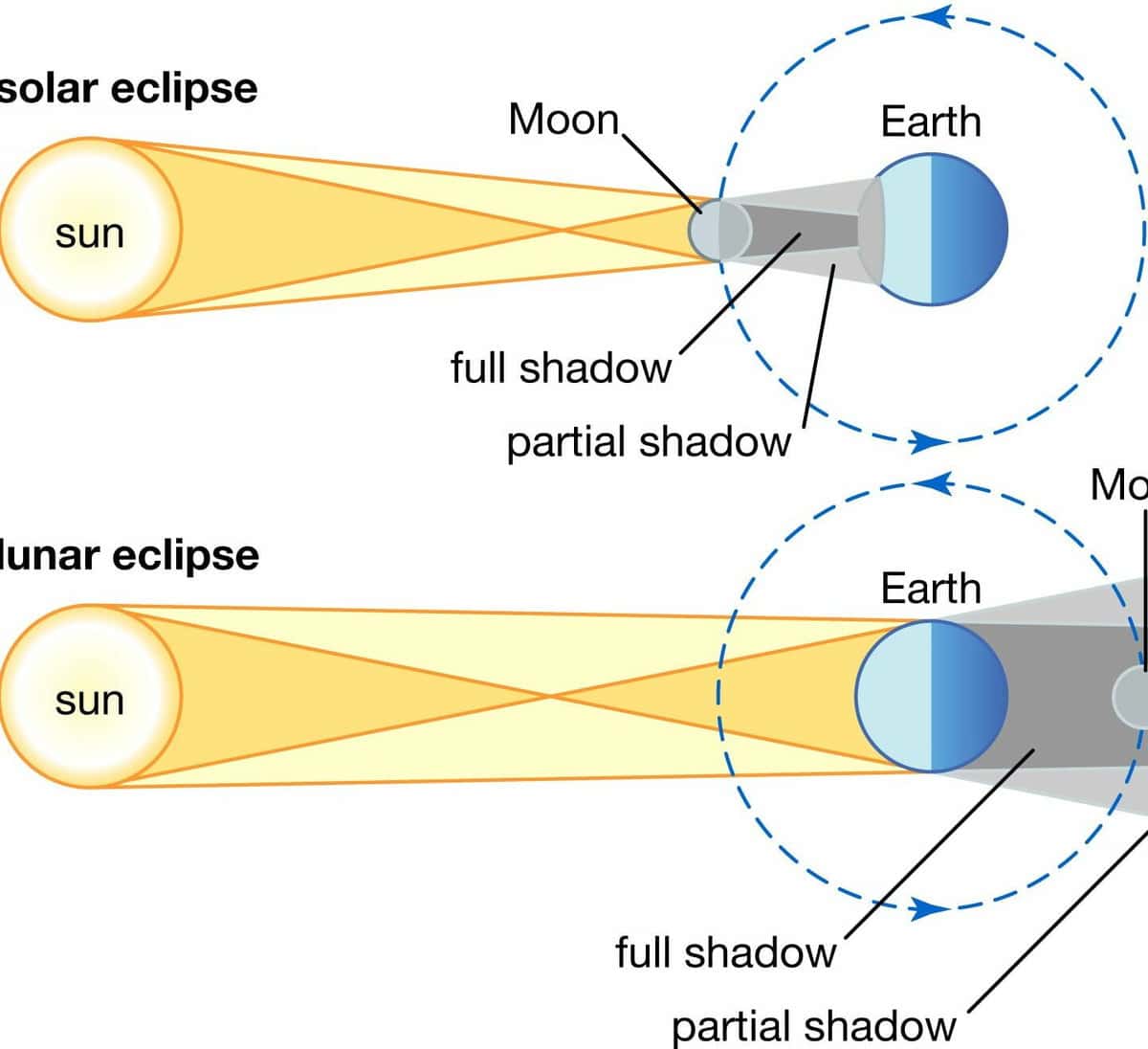
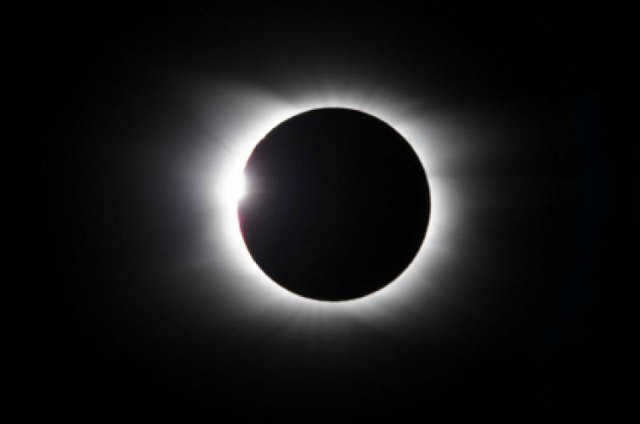
The diameter of the Moon’s shadow on the Earth’s surface is limited to 270 km, resulting in a solar eclipse being visible only within a narrow band along the path of the shadow. Due to the Moon’s elliptical orbit, the distance between the Earth and the Moon during an eclipse can vary, causing the size of the Moon’s shadow spot on the Earth to range from its maximum diameter to zero (when the top of the Moon’s shadow cone does not reach the Earth’s surface). If an observer is located within the shadow band, they will witness a total solar eclipse. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon completely covers the Sun, causing the sky to darken and allowing planets and bright stars to become visible. A solar corona, which is not normally visible in the bright sunlight, can be seen surrounding the Moon’s hidden solar disk. When viewed from the Earth’s surface, the total phase of a solar eclipse lasts only a few minutes. The lunar shadow moves across the Earth’s surface at a minimum speed of slightly over 1 km/s. Astronauts in orbit can observe the moving shadow of the Moon on the Earth’s surface during a total solar eclipse.
Observers located near the path of the total eclipse can witness a unique phenomenon known as a personal solar eclipse. In a partial eclipse, the Moon passes across the Sun’s surface not directly in the center, resulting in only a portion of the Sun being obscured. The darkening of the sky during a partial eclipse is much less pronounced compared to a total eclipse, and no stars become visible. A partial eclipse can be observed from a distance of approximately two thousand kilometers away from the area where the total eclipse occurs.
The total phase of a solar eclipse is also denoted by the phase symbol Φ. The maximum phase of a personal eclipse is usually expressed as a fraction, where 1 represents the total phase of the eclipse. The total phase can also exceed 1, for example, 1.01, if the diameter of the visible lunar disk is larger than the diameter of the visible solar disk. Partial phases have a value less than 1. At the outer edge of the lunar penumbra, the phase is 0.
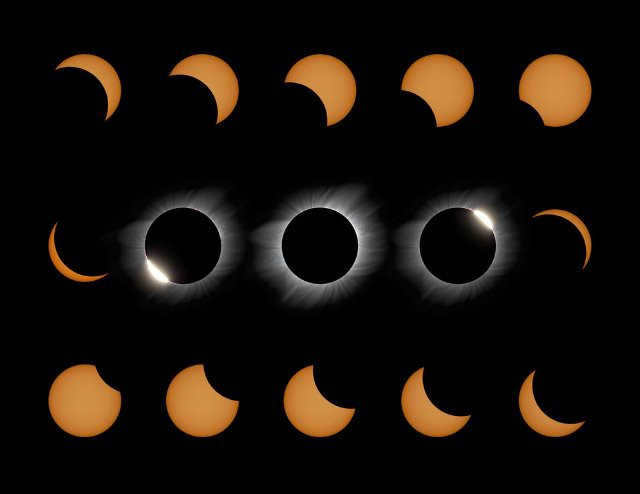
The moment when the leading/trailing edge of the Moon’s circle meets the perimeter of the Sun is known as a touching. The initial touching is when the Moon enters the Sun’s circle (the start of the eclipse, its initial phase). The final tangent (the fourth one in a total eclipse scenario) is the concluding moment of the eclipse, when the Moon exits the Sun’s circle. During a total eclipse, the second tangent is the moment when the front portion of the Moon, after having traversed across the Sun, begins to exit the circle. A total solar eclipse takes place between the second and third touchings. In approximately 600 million years, the Moon will be pushed so far away from the Earth due to tidal deceleration that a total solar eclipse will become unattainable [1].

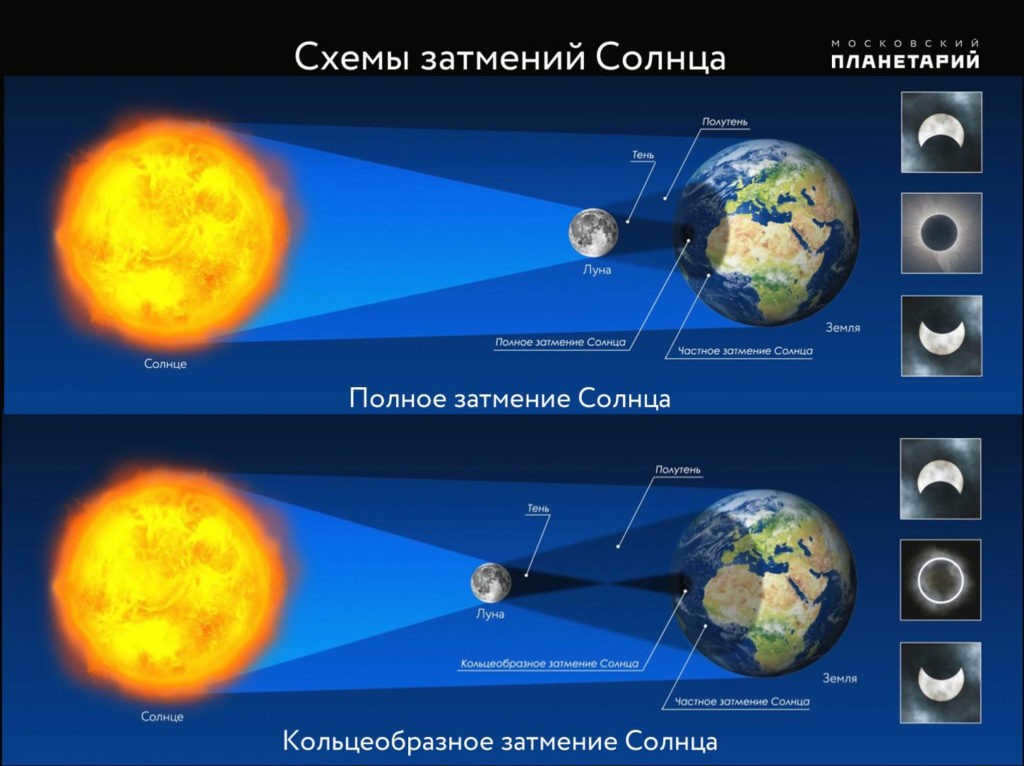
According to the classification in astronomy, a total eclipse is defined as an eclipse that can be observed as total at least somewhere on the Earth’s surface. On the other hand, a partial eclipse occurs when the cone of the Moon’s shadow passes close to the Earth’s surface but does not touch it, thus making it visible as a partial eclipse. When an observer finds himself within the Moon’s shadow, he experiences a total solar eclipse. On the other hand, if he is in the penumbra region, he can witness a partial solar eclipse. Aside from total and partial solar eclipses, there are also annular eclipses.
An annular eclipse occurs when the Moon is situated further away from the Earth during an eclipse compared to a total eclipse. As a result, the shadow’s cone passes over the Earth’s surface without making contact. Visually, the Moon traverses the Sun’s disk during an annular eclipse, but it appears smaller in diameter and cannot completely obscure the Sun. At the peak of the eclipse, the Moon covers the Sun, but a bright ring of the remaining portion of the solar disk is visible around the Moon. The sky remains bright during an annular eclipse, preventing the appearance of stars, and making it impossible to observe the Sun’s corona. The same eclipse can be seen as either a total or annular eclipse in different areas along the eclipse path. Occasionally, this type of eclipse is referred to as a total annular (or hybrid) eclipse.
Frequency of solar eclipses
Earth experiences between 2 and 5 solar eclipses per year, with no more than two being total or annular. Over the course of a century, an average of 237 solar eclipses occur, including 160 partial, 63 total, and 14 annular eclipses [2]. Certain areas of the Earth have a lower frequency of large phase eclipses, and total solar eclipses are even more rare. For example, in Moscow between the 11th and 18th centuries, there were 159 solar eclipses with a phase greater than 0.5 observed, but only 3 were total (occurring on August 11, 1124, March 20, 1140, and June 7, 1415) [3]. Another total solar eclipse was visible in Moscow on August 19, 1887. A ring-shaped eclipse could be seen on April 26, 1827. A very strong eclipse with a phase of 0.96 occurred on July 9, 1945. The next total solar eclipse expected in Moscow will happen on October 16, 2126.
Mentions of eclipses in historical records
Ancient texts frequently make references to solar eclipses. However, the majority of detailed accounts can be found in medieval chronicles and annals from Western Europe. One such account is provided by Maximin of Trier, who documented a solar eclipse occurring on February 16, 538, lasting from the first to the third hour [4].

There are many instances of the solar eclipse happening on the surface of the Earth, where the shade of tree leaves creates a camera obscura effect and allows for the observation of the eclipse.
Phenomena that Occur During a Solar Eclipse
- Shadow waves, also known as shadow bands
- Bailey’s rosary
- Diamond ring
- Sickle shadows, created by the camera obscura effect [5]
- Drop in atmospheric temperature
- Dawn ring
Scientific Discoveries Arising from Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses provide a unique opportunity to observe the Sun’s corona and its nearby surroundings, which is typically challenging under normal circumstances (although astronomers have been able to continuously study the Sun’s neighborhood since 1996, thanks to the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) satellite).
During a total solar eclipse in India on August 18, 1868, French scientist Pierre Jansen made a groundbreaking discovery by studying the Sun’s chromosphere. He managed to obtain a spectrum of a previously unknown chemical element (although it was later discovered that this spectrum could have been obtained without waiting for a solar eclipse, as English astronomer Norman Lockyer demonstrated two months later). This newly discovered element was subsequently named helium, in honor of the Sun.
During a solar eclipse on May 17, 1882, astronomers in Egypt observed a comet passing near the Sun. This celestial object was given the name Comet Eclipse Comet, but it is also known as the Teufik Comet, named after the ruler of Egypt at that time. The comet belonged to the Kreutz family, which includes comets that come very close to the Sun.
Related Links
Notes
- ↑Questions Frequently Asked by the Public About Eclipses. NASA. Archived from the original source on February 4, 2012.Checked March 7, 2010.
- ↑Meeus J. Mathematical astronomy morsels. – Wilmann-Bell, Inc, 1997. – ISBN 0943396.
- ↑Svyatsky D. O. Astronomy of Ancient Russia / Author of the foreword, comments, additions – M. L. Gorodetsky. – Moscow: Russian Panorama, 2007.
- ↑Annals of St. Maximinus of Trier
- ↑Perelman Ya.I.Entertaining astronomy. – 7th ed. – M.: GTTI, 1954. – С. 99-101.
Throughout history, lunar and solar eclipses have held significant meaning for different cultures. Some societies viewed these celestial events with fear and anticipation of an impending apocalypse, while others believed they signaled positive changes to come. The study of solar eclipses began many years ago, as astrologers sought to understand this natural occurrence that happens relatively frequently.
What is the meaning behind it?
Nowadays, every primary school student is familiar with the concept of a solar eclipse. The Earth orbits around the Sun, while the Moon orbits around our planet. When the Moon partially or completely covers the Sun’s disk, it creates an eclipse. During this phenomenon, the Earth, Moon, and Sun align in a straight line. It is important to mention that a solar eclipse can only take place during the new moon phase, when the Moon is completely hidden from view on Earth.


Not every solar eclipse is visible in its entirety. The visibility of the solar disk’s overlap depends on the orbit of Earth’s satellite during a specific time period. In most cases, only a partial eclipse can be observed. People who are preoccupied with their daily activities and fail to pay attention to the sun might completely miss this natural phenomenon. A partial eclipse can be visually similar to twilight, causing a slight darkening of the surroundings during daylight hours, giving the impression that rain is imminent.
Astronomers have already successfully determined the average number of solar eclipses that occur each year. This occurrence is not particularly rare and happens around 5-6 times annually. Typically, the Moon covers the Sun by no more than 70%, resulting in the inability to witness the natural phenomenon from every location on Earth. Additionally, the duration of an eclipse is often quite short, lasting no more than 10 minutes when the solar disk is completely obscured.
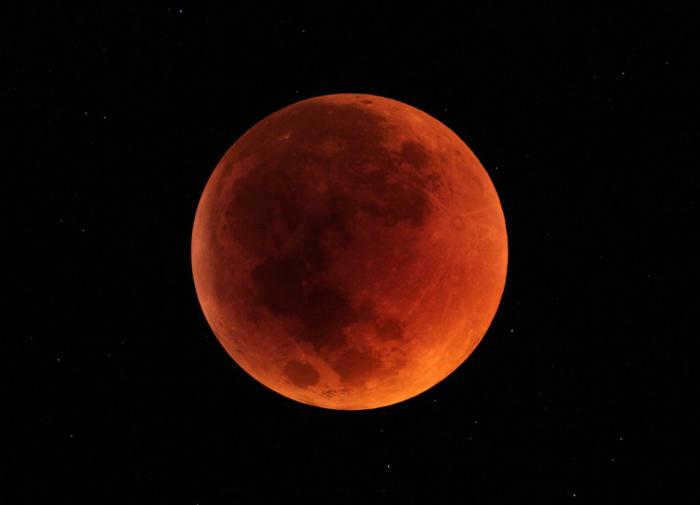
Not only during the daytime, but also at night, it is possible to witness a captivating natural event. Occasionally, a lunar eclipse occurs, which occurs when the lunar disk aligns with the Earth’s shadow. Typically, a total eclipse can be observed in regions where the Moon is above the horizon during this phenomenon. Despite the eclipse, the Earth’s satellite does not vanish entirely. Instead, observers can perceive the moon’s silhouette radiating a vibrant orange hue. This phenomenon is attributed to the Moon’s ability to reflect the sun’s rays with even greater intensity, even during an eclipse.

Solar eclipses are more common than lunar eclipses. You can witness a solar eclipse up to twice a year. A complete alignment of the Earth’s satellite’s disk occurs infrequently. Lunar eclipses are often overlooked and not given much importance. However, every natural phenomenon has an impact on human health and behavior. Therefore, it is advisable for sensitive individuals to prepare in advance for a lunar eclipse.
Various Types of Lunar and Solar Eclipses
Eclipses with identical characteristics occur infrequently. There are two main types of eclipses, depending on which part of the celestial body is obscured by the shadow: partial and total. During a total solar eclipse, darkness falls over only a specific location on Earth. During this time, fortunate spectators can witness the faint outline of the sun’s disk. This phenomenon is considered rare and exceptional. On the other hand, partial solar eclipses occur more frequently when the moon covers only a small portion of the sun’s disk. This natural phenomenon is no longer considered unique. It is important to note that an eclipse can be total for some observers and partial for others, depending on their location on the planet.

There are two types of eclipses: lunar and solar. Lunar eclipses can be total or partial. When the moon is completely in the Earth’s shadow during a lunar eclipse, it is not completely invisible. The moon’s outline can still be seen and it takes on a bright hue due to the sun’s rays illuminating it. A partial lunar eclipse occurs when only part of the moon is covered by the Earth’s shadow, resembling a new moon. In most cases, people are unaware of a lunar eclipse happening in the night sky.
Various natural phenomena have an impact on the overall state of the human body. Individuals who are hypersensitive are particularly affected by these phenomena. They may experience a decline in their health several days prior to a solar eclipse. Elderly individuals may experience headaches, general fatigue, and worsened chronic conditions. Many people find it necessary to reduce their activity levels and prioritize their health during these times. Hypersensitive individuals should plan ahead and find out when the next solar eclipse will occur. On the day of the celestial event, it is advisable for them to remain at home. It is not recommended for perfectly healthy individuals to venture outdoors either.
Expectant mothers are known to be sensitive not just to solar, but also lunar eclipses. Medical professionals advise against exposing oneself to the direct rays of the celestial luminary during such natural occurrences. This can lead not only to poor health, but also to complications in the development of the fetus. When both celestial bodies align, their energy has the most profound impact on an individual. In the best scenario, a pregnant woman may experience a severe headache, while in the worst case, premature labor may ensue. Interestingly, since ancient times, it has been observed that children born during a solar or lunar eclipse tend to enjoy good health and achieve great success in life.

Psychologists also examine the impact of solar eclipses on individuals. It is theorized that during these natural occurrences, people’s minds and emotions become particularly vulnerable. It is advised to avoid tackling complex issues during eclipses, and individuals with mental health conditions should not be left alone. It is during lunar or solar eclipses that suicides are most frequently reported.
Properly Observing a Solar Eclipse: Safety Guidelines
Witnessing a solar eclipse is a truly remarkable experience, but it is crucial to prioritize your health and take necessary precautions. While this natural phenomenon can have negative effects on the human body, it should not be overlooked. To fully enjoy the beauty of a solar eclipse without compromising your well-being, it is essential to adhere to certain guidelines. Never attempt to gaze at the sun during an eclipse without protective eyewear. Unfortunately, many individuals are unaware of the correct methods for observing a solar eclipse and may mistakenly use a telescope or binoculars. These devices are only suitable for viewing the celestial luminary from a closer distance, but eye safety should always be the top priority.

It is not safe to view the eclipse with just sunglasses or smoked glass, as these do not provide full protection from direct sunlight. Prolonged exposure to the sun’s rays during an eclipse can result in damage to the retina. To safely observe this unique celestial event, it is important to use special solar filters. These filters can be purchased at specialized stores that sell photo and video equipment. Without proper eye protection, it is only safe to observe a total solar eclipse, as the direct impact on the eyes is minimized during this phase. However, it takes a trained professional to accurately determine whether the solar disk is completely covered or only partially covered.
Solar filters can be utilized either on their own or in conjunction with binoculars. Opting for the latter option is recommended for individuals seeking to observe all the intricate details of the eclipse. Furthermore, individuals looking to immortalize the moment through photography or videography should also bear in mind the importance of utilizing filters.
The Influence of Eclipses on the Environment
Not many individuals are aware that celestial events have an impact on both human well-being and the environment. Prior to an eclipse, the weather can undergo significant transformations, with frosts sometimes occurring in the midst of warm May days, while unexpected warm spells may emerge during winter. These natural fluctuations, however, pose no threat. Nevertheless, an eclipse can also trigger more perilous changes in nature, such as tsunamis and hurricanes. It has long been observed that the World Ocean experiences heightened activity during lunar and solar eclipses. Therefore, it is crucial for every ship captain to be aware of when the next solar eclipse will occur in order to prevent any potential tragedies. Planning extensive sea voyages on the day of a natural phenomenon is highly discouraged.

Scientists from all over the world are conducting research on the extraordinary natural phenomenon of total lunar or solar eclipses, which are known to be the most dangerous changes in nature. The schedule of celestial events is carefully planned for the next few decades, thanks to the diligent work of astrologers. This meticulous planning allows us to anticipate and potentially prevent various natural disasters such as tsunamis, earthquakes, and hurricanes.
August 11, 1999 marked a momentous occasion with the occurrence of an exceptionally dazzling solar eclipse. The celestial bodies aligned in such a way that the entire disk of the sun was obscured, providing a breathtaking spectacle for nearly all inhabitants of Europe. However, the residents of Bucharest were particularly fortunate, as they were able to witness this extraordinary event in its entirety. It was a remarkable occurrence, as such a natural phenomenon had not been seen in the twentieth century before. The total eclipse, although fleeting, captivated onlookers for a mere duration of three minutes.
Only a partial view of the solar eclipse was visible in Moscow, as the moon covered only 70% of the solar disk. Nevertheless, there was a significant number of individuals eager to witness this extraordinary celestial event. This widespread interest was not coincidental, as national TV channels had been informing the public about the upcoming solar eclipse for several weeks prior. Additionally, entrepreneurs capitalized on the opportunity by selling specialized disposable glasses that allowed viewers to safely observe the sun without damaging their eyesight.
The solar eclipse had a restricted duration. Nevertheless, all individuals had the opportunity to witness the moon overlapping the solar disk. This occurrence was genuinely exceptional. Some artists even depicted the natural phenomenon in their creations. For instance, Elena Voynarovskaya composed an entire poem entitled “Sun, don’t vanish”. The eclipse is also portrayed in the initial segment of the renowned novel “Day Watch”.
Extraordinary solar eclipse in the 21st century
The younger generation is already well aware of the concept of a solar eclipse. However, many schoolchildren have not had the opportunity to witness this phenomenon before. This changed in March 2015, when a remarkable natural event took place that will be remembered for a long time. On March 20, residents of the CIS countries were able to witness a solar eclipse. Astrologers have noted that the most challenging period was from March 16 to April 8. During this time, the solar eclipse had the strongest impact on individuals. Those with chronic illnesses experienced a worsening of their symptoms. However, there was also a positive aspect to it. The eclipse is a time of immense energy release. Those who harnessed this energy wisely were able to make successful deals and form valuable connections.

The Arctic and the north of the Atlantic Ocean were witness to a unique and rare event – a total eclipse. In Russia, the city of Murmansk offered the best vantage point to observe this phenomenon. Meanwhile, in Moscow, the eclipse commenced around 13 o’clock, but unfortunately, it could only be seen partially. Interestingly, many city dwellers were completely oblivious to the fact that the Moon was obscuring the Sun. To catch a glimpse of this celestial spectacle, one needed to rely on specialized equipment.
When is the next opportunity to witness an eclipse?
The study of celestial phenomena has been a long-standing focus for scientists. So, when and where can we expect the next solar eclipse? The answer awaits. Throughout the entire 21st century, a total of 224 solar eclipses are predicted to take place. However, only 68 of these will be of the total variety. There is, however, a different type of eclipse that deserves more attention: annular eclipses. The year 1999 saw one such eclipse, and the next one that will be visible to residents of Europe and CIS countries is set to occur on February 26, 2017. Additionally, in the same year, a total eclipse is scheduled for August 21, lasting a mere 2 minutes and 40 seconds.
What are some important things to remember?
For those interested in witnessing a remarkable natural event, it is crucial to plan ahead. Solar eclipses are brief occurrences, so it is essential to determine the exact times in advance. News outlets and astrological websites often provide information about upcoming total or partial eclipses, typically several weeks in advance.
It is important to note that solar eclipses can have health implications, particularly for the eyes. Looking directly at the sun without proper protective eyewear can be harmful. On March 20th, only those who had access to protective filters were able to safely observe the solar eclipse. Fortunately, these filters are readily available for purchase at specialized stores.
Astronomy is a fascinating field of knowledge that is essential for understanding the world around us. When our thoughts wander, we often find ourselves gazing up at the sky. Sometimes, celestial events can deeply move us. In this article, we will explore two of these events: lunar and solar eclipses.
While the disappearance or partial covering of celestial bodies no longer instills the same superstitious fear as it did in the past, there is still an aura of mystery surrounding these phenomena. Fortunately, modern science has provided us with the facts to explain these events in a simple and accessible way. In today’s article, we will attempt to do just that.

What causes a solar eclipse and how does it occur?
A solar eclipse is a fascinating event that takes place when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, blocking out all or part of the Sun’s surface from the perspective of observers on the ground. This phenomenon can only be witnessed during a new moon, when the side of the Moon facing the Earth is not fully lit up and therefore appears invisible to the naked eye. Now that we have explored the concept of an eclipse, let us delve into the mechanics of how it occurs.
An eclipse occurs when the Moon is not illuminated by the Sun from the side that is visible on Earth. This phenomenon can only happen during the waxing phase, when the Moon is near one of the two lunar nodes. (By the way, a lunar node is the point where the lines of the solar and lunar orbits intersect.) During an eclipse, the shadow of the Moon on Earth has a diameter of no more than 270 kilometers. As a result, the eclipse can only be observed within the path of the shadow strip. Additionally, the distance between the Moon and Earth can vary during the eclipse, as the Moon orbits around the Earth.
When can we witness a complete solar eclipse?
You must have heard about the phenomenon of a complete solar eclipse. Here, we will clarify once again what exactly a complete solar eclipse is and the conditions required for it to occur.
A complete solar eclipse occurs when the Moon’s shadow falls on a specific spot on Earth, with a diameter that can vary. As mentioned before, the diameter of the shadow does not exceed 270 kilometers, and it can even be close to zero. If an observer is located within the dark band at that moment, they have a unique opportunity to witness the Sun completely disappearing. During a complete solar eclipse, the sky becomes dark, revealing the outlines of stars and even planets. Additionally, the previously hidden solar disk is surrounded by the corona, which is normally invisible. The duration of a complete eclipse is typically a few minutes.
The images provided in this article showcase the remarkable occurrence of a solar eclipse, giving you the opportunity to witness and comprehend the nature of this event. In the event that you choose to personally witness this phenomenon, it is imperative to adhere to proper eye safety precautions.
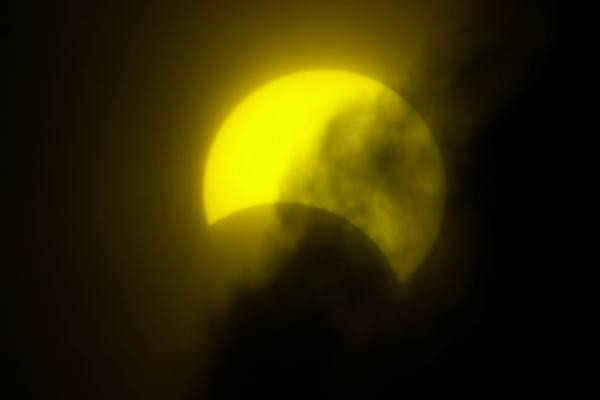

This marks the conclusion of the information section, where we gained knowledge about the concept of a solar eclipse and the necessary conditions for observing it. Now, let us delve into the topic of a lunar eclipse, also known as a lunar eclipse in English.
What is a lunar eclipse and how does it occur?
A lunar eclipse is a celestial event that takes place when the Moon enters the Earth’s shadow. Similar to solar eclipses, lunar eclipses can unfold in various ways.
Based on a variety of factors, a lunar eclipse can be classified as either total or partial. Naturally, we can deduce the essence of each term, which characterizes a specific eclipse. Let us explore the definition of a total lunar eclipse.
When and how does a planet’s moon become hidden?
An eclipse of the Moon occurs when it is positioned above the horizon at the right time. The moon enters the Earth’s shadow, but it is not completely hidden during a total eclipse. Instead, it appears slightly obscured and takes on a dark, reddish color. This is because even though the moon is in shadow, it is still partially illuminated by sunlight passing through the Earth’s atmosphere.
Our understanding of lunar eclipses has grown, but there are other ways in which a planet’s moon can be obscured by the Earth’s shadow. We will discuss these in more detail later on.
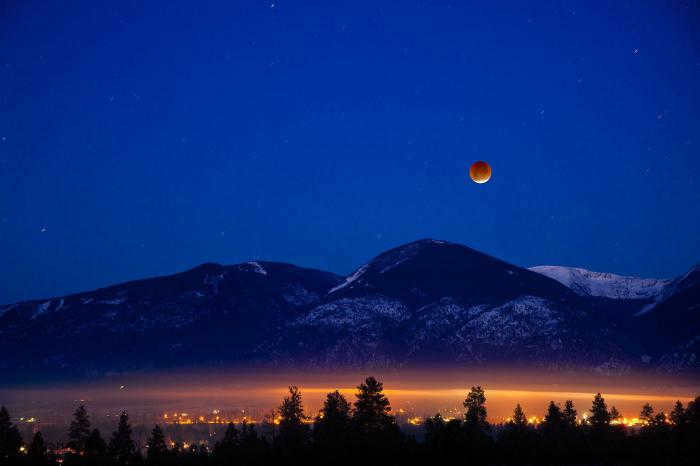

What is a Partial Lunar Eclipse?
Similar to solar eclipses, lunar eclipses can also be partial, where only a portion of the Moon is covered by the Earth’s shadow. During a partial lunar eclipse, one part of the Moon is shaded by our planet while the remaining part remains illuminated by the Sun, making it visible to us.
However, the penumbral eclipse is even more fascinating and unique. Let’s delve into what a penumbral eclipse of the Moon entails.

A Rare Occurrence: Penumbral Lunar Eclipse
Unlike a partial eclipse, a penumbral lunar eclipse occurs in a slightly different manner. It is common knowledge that there are regions on Earth where the sun’s rays are not completely blocked, resulting in the absence of complete shadow. However, these regions do not receive direct sunlight either. They are known as the penumbra. When the Moon passes through this particular area and enters the Earth’s penumbra, a penumbral eclipse can be observed.
Now that we have completed the second primary section of our article, we can delve into the topic of lunar eclipses and their occurrence. However, the realm of solar and lunar eclipses is filled with fascinating facts that are yet to be explored. Let us further explore this subject by addressing several inquiries pertaining to these awe-inspiring phenomena.
Which eclipses occur more frequently?
After acquiring all the knowledge from the preceding sections of this article, one naturally wonders: which type of eclipse are we more likely to witness in our lifetimes? Let’s delve into this topic a bit further.
It may sound unbelievable, but it’s true: the number of solar eclipses surpasses that of lunar eclipses, despite the Moon being smaller in size compared to the Earth’s diameter. One might assume that, based on the understanding of what an eclipse is and why it happens, the shadow of a larger object would be more likely to obscure a smaller one. Following this logic, the Earth’s size should allow it to swiftly conceal the lunar disk. However, there are actually more solar eclipses occurring on our planet. Astronomical data and observations indicate that for every seven solar eclipses, there are only three lunar eclipses, resulting in a ratio of four solar eclipses per lunar eclipse.
The cause of the surprising statistics
The Sun and the Moon, which are the closest celestial bodies to us, have nearly identical diameters in the sky. This is why solar eclipses can occur.
Typically, solar eclipses occur during the new moon phase when the Moon approaches its orbital nodes. Since the Moon’s orbit is not perfectly circular and the nodes of the orbit move along the ecliptic, there are periods when the Moon’s disk on the celestial sphere can be larger, smaller, or even the same size as the solar disk.
The preference is given to a complete solar eclipse in the first scenario. The determining factor is the size of the Moon in relation to the Sun. During its maximum size, a solar eclipse can last for up to seven and a half minutes. In the second scenario, there is only a brief period of complete obscuration. In the third scenario, when the Moon’s diameter is smaller than that of the Sun, a visually stunning annular eclipse takes place. We can observe a bright ring, formed by the edges of the Sun, surrounding the dark disk of the Moon during such an eclipse. The duration of such an eclipse is 12 minutes.
Therefore, we have expanded our understanding of what a solar eclipse is and how it occurs by adding new details that would be of interest to amateur researchers.
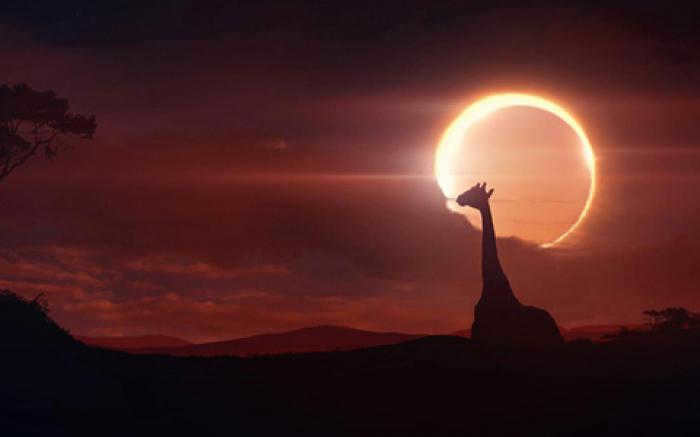

The eclipse factor: the alignment of celestial bodies
Another significant factor contributing to an eclipse is the precise alignment of the celestial bodies. It is uncertain whether the Moon’s shadow will reach the Earth, and at times, only a partial shadow, known as the penumbra, will touch the Earth’s surface. In such cases, we can observe a partial solar eclipse, as we have previously discussed when explaining what a solar eclipse is.
While a lunar eclipse can be seen from any part of the Earth’s night side, providing a view of the entire circumference of the lunar disk, a solar eclipse can only be observed within a narrow strip that is typically 40-100 kilometers wide.
Now that we have an understanding of what an eclipse is and the reasons for their varying occurrences, there remains one more intriguing question: how frequently can we witness these extraordinary phenomena? Throughout our lifetimes, most of us have only experienced news of an eclipse once, or perhaps twice, while some have never encountered one at all.
Although a solar eclipse happens more frequently than a lunar eclipse, it can only be witnessed once in every 300 years in the same location (keep in mind the average width of 40-100 kilometers). However, a total lunar eclipse can be observed multiple times in a person’s lifetime, but only if the observer doesn’t change their place of residence throughout their life. Today, with the knowledge of eclipses, it is possible to travel anywhere and by any means of transportation to witness this phenomenon. Those familiar with lunar eclipses probably wouldn’t hesitate to travel hundreds of kilometers to witness this incredible spectacle. Nowadays, this is not a problem. So if you happen to receive information about another eclipse happening in a particular location, don’t hesitate to make the effort and spend the money to reach the place of maximum visibility at the precise moment when the eclipse is happening. Trust me, no distance can compare to the experiences and impressions you will gain.
The upcoming eclipses within sight
Astronomical calendars provide information on the frequency and timing of eclipses. Additionally, the media will surely cover significant events such as a total eclipse. According to the calendar, the next visible solar eclipse in the capital of Russia is set to occur on October 16, 2126. It’s worth noting that the previous eclipse in this area could be witnessed over a century ago, back in 1887. Therefore, Moscow’s residents will have to wait for many more years to observe a solar eclipse. The only chance to witness this astonishing phenomenon is to travel to Siberia or the Far East, where one can experience a slight darkening of the Sun’s brightness.
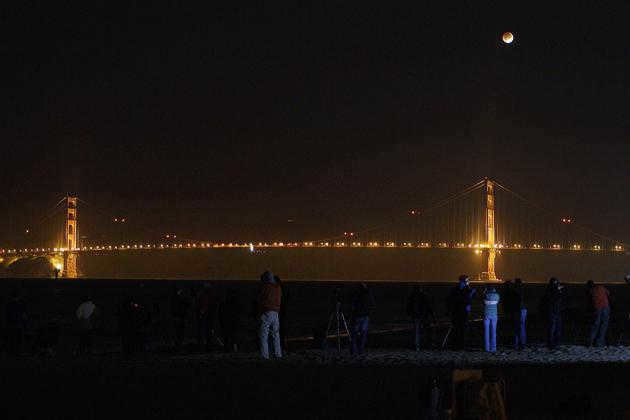

Summary
Our astronomical article aims to provide a clear and concise explanation of lunar and solar eclipses, including their occurrence and frequency. Through our research, we have discovered that eclipses of different celestial bodies follow distinct principles and possess their own unique characteristics. It is crucial for individuals to grasp these details in order to develop a comprehensive understanding of our environment.
In this modern era, with the advancements in science and technology, the once terrifying phenomenon of an eclipse has now become intriguingly mysterious. We now have a clear understanding of what a lunar eclipse and solar eclipse are, and the knowledge of what they bring us. Let our curiosity towards these celestial events be purely cognitive, as we now view them as rare and fascinating occurrences. Lastly, we hope that you have the opportunity to witness at least one eclipse with your own eyes!
Check out the articles titled “Craters!” and “Solar eclipses” for more information.
Not every full moon is accompanied by a lunar eclipse. This is because the lunar orbit is tilted 5° in relation to Earth’s orbit. During most full moons, the Moon either passes above or below Earth’s shadow. The points where the Moon’s orbit intersects with the plane of Earth’s orbit are known as nodes. In order for a solar or lunar eclipse to occur, the Moon must be located at one of these two points, and the points themselves must align along a line connecting the Earth and the Sun.
What causes the rarity of eclipses?
What is the reason behind the infrequency of eclipses? During its orbit around the Earth, the Moon occasionally aligns directly between the Earth and the Sun, resulting in the Moon’s shadow being cast upon the Earth’s surface. This phenomenon, known as a solar eclipse, occurs when the Moon is in a new moon phase and positioned over a specific region of the Earth.
Irish Moon Dogs
In ancient Irish legends, it was believed that the entrance to Emania, also known as the Moon Kingdom, was protected by a pair of dogs. It was warned that mourners should refrain from crying too loudly, as the restless guardian dogs could potentially pose a threat to the departing soul.
Which type of eclipse occurs more frequently – solar or lunar?
Which type of eclipse is more commonly observed – solar or lunar? Throughout the year, there can be anywhere from two to five solar eclipses (with the highest recorded number of five occurring in 1935, and the next occurrence projected for 2206). In contrast, there may be no lunar eclipses within a given year.
What is the definition of lunar seas?
Exploration of the Moon’s surface, known as selenography, originated from Galileo’s initial telescopic observations in August 1609. These observations led him to speculate about the existence of seas and oceans on the Moon.
Solar eclipses occur when the Earth, Sun, and Moon align with each other. During a solar eclipse, the Moon’s shadow partially covers the Earth’s surface.
What is the cause of solar eclipses?
Solar eclipses are caused by the alignment of three celestial bodies: the Moon, the Earth, and the Sun. The Moon orbits the Earth, and the Earth orbits the Sun. Occasionally, these orbits align in such a way that a solar eclipse occurs.
Lunar phases
The different stages of the moon’s appearance in the sky are known as lunar phases. These phases include the first quarter, when the moon is half illuminated; the full moon, when the moon is fully illuminated; and the last quarter, when the moon is once again half illuminated.
Lunar days
Each day of the moon’s cycle, known as a lunar day, holds its own symbolic meaning and has a unique impact on our psyche. From the moment of the moon’s birth, or new moon, these lunar days influence us in various ways. When the moon transitions between phases, there is a disturbance or activation of the astral matter that has an immediate effect.
Complex periods, lunar and solar eclipses
Complex periods, lunar and solar eclipses Mysterious scattering of constellations, mysterious movement of planets, rapidly changing phases of the Moon – all of these can be observed in the night sky by those who are willing to sacrifice their sleep. However, there are certain celestial events that
During its orbit around the Earth, the Moon occasionally positions itself directly between the Earth and the Sun, causing a shadow to be cast on the Earth’s surface. This phenomenon is known as a solar eclipse.
An eclipse takes place during a new moon, when the Moon is positioned above the section of the Earth that is facing the Sun. However, it is not possible for a solar eclipse to occur during every new moon due to the misalignment between the Moon’s orbit around the Earth and the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. As the Moon completes its rotation around the Earth in approximately 29 days, it occasionally moves above or below the Earth’s orbital plane.
An eclipse of the Moon happens only when the Moon is in its full phase and positioned on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun. When the Earth comes between the Moon and the Sun, the Moon moves into the shadow of the Earth and becomes invisible. A partial eclipse takes place when the Moon enters the shadow of the Earth only partially.
In certain years, there are no lunar eclipses, while in other years there can be anywhere from one to three. On the other hand, there are typically two to five solar eclipses each year. In specific regions of the Earth, a complete solar eclipse can be observed once every 360 years.
What is the reason behind choosing this particular tale?
Why have I chosen to write a novella, and why have I chosen to write this specific novella? The question of WHY is the most challenging and significant one, even if the answer may not be readily available. However, it is still worth pondering upon because it encompasses other crucial inquiries, such as determining the appropriate form for my writing.
First “Why?”: why do I need to write about it?
The initial “Why?”: why should I write about it? Let’s commence with the fundamental question: why do I desire to pen down this specific book? In case you have multiple projects ongoing concurrently, implementing the “Why?” approach to each of them will aid you in determining which one to initiate with. It’s quite straightforward:
28. What is the function of codes? Why is the indicator light for “OD OFF,” “Hold,” “S,” or “Check AT” flashing? Why is there a lack of gear shifts?
28. What is the purpose of codes? Why is the indicator light for “OD OFF,” “Hold,” “S,” or “Check AT” flashing? Why is there a lack of gear shifts? In this discussion, we will focus on electronically controlled automatic transmissions. The operation of these automatic transmissions is regulated by a transmission computer installed on the vehicle.
Why are gemstones so rare? The rarity and high value of gemstones are connected, but they have different causes. Rarity is always a result of specific origin conditions. Value, on the other hand, is determined by people. According to Russian law, precious stones are considered
What is the nature of solar eclipses?
What are solar eclipses like? Solar eclipses can be classified into partial, total, and annular based on the observed image. As we know, the Moon orbits around the Earth in a path that is inclined at an angle of approximately 5 degrees to the ecliptic plane.
Are solar or lunar eclipses more frequent?
Do solar or lunar eclipses occur more frequently? There can be anywhere from two to five solar eclipses per year (the most solar eclipses in one year was five, which happened in 1935, and the next time this will occur will be in 2206). It is possible for there to be no lunar eclipses in a given year.
What Are Lunar Eclipses?
Lunar eclipses occur when the Earth, Sun, and Moon are perfectly aligned. During a lunar eclipse, the Moon passes through the Earth’s shadow, creating a breathtaking celestial event. This phenomenon occurs when the Moon is directly opposite the Sun from the perspective of the Earth.
Understanding Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses, on the other hand, occur when the Earth, Sun, and Moon are in perfect alignment. During a solar eclipse, the Moon comes between the Earth and the Sun, causing the Moon’s shadow to partially cover the Earth’s surface. This creates a mesmerizing sight in certain areas on Earth.
What is the reason behind solar eclipses?
Solar eclipses occur due to the interaction of three celestial bodies: the Moon, the Earth, and the Sun. As we are aware, the Moon revolves around the Earth, and the Earth orbits the Sun. Consequently, there are moments when these three entities align in such a way that a solar eclipse takes place.
What caused the fall of Rome? For nearly four centuries, the Roman Empire held dominion over the Mediterranean lands and a significant portion of Europe. The territories that encompass present-day England, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Spain, Portugal, Switzerland, Austria, Hungary, parts of Germany, Romania, Bulgaria, and Greece were all under Roman rule.
In my employ, I have a limited number of individuals who are not related to me by blood. The majority of them are my sisters, nieces, and nephews.
In my service, there are very few individuals who are not part of my family. The majority of them are my sisters, sisters-in-law, and their children. This statement is taken from A.S. Griboyedov’s comedy “Woe from Wit” (1824). These words spoken by Famusov in act 2, scene 5 serve as a representation of nepotism and favoritism. For more on this topic, refer to the article “How not to please a native.”
Elaborate Intervals, Lunar and Solar Eclipses
Elaborate Intervals, Lunar and Solar Eclipses Enigmatic dispersal of constellations, enigmatic motion of the planets, swiftly shifting phases of the moon – all of this can be observed in the celestial sphere every cloudless evening for those who are unafraid to forgo their slumber. However, there exist certain astronomical occurrences that
It is evident in my opinion. The thickness of the shadow cone originating from the Earth is significantly greater than that of the cone from the Moon. The Moon experiences eclipses more frequently, while the Earth tends to avoid them more often. The duration of these celestial events further supports this observation, with solar eclipses lasting only a few minutes and lunar eclipses lasting over an hour.
New inquiries in Other subjects
If nails on 505 kluts were previously overlapped, can they be glued together? Please let me know.
Could you provide a brief summary of the Baptism of Russia and the spread of Christianity in the Moscow region?
In your interpretation of the Old Russian bilinovyTerminovo, who opposes Ilya Muromtsy to Solovyja rozbynik? I am offering 25 points for a detailed response.
Could you give a succinct account of the Baptism of Russia and the spread of Christianity in the suburbs?
What is the distinction between the “Line of Comparison” table and the outcomes of utilizing various types of survey plans on the same location? The survey route… … is a detailed comparison. Where is the survey conducted from? How are the terrain objects recorded? Create a plan in your notebook and sketch a map of the area.
7. Associate the characters with the given names below:
Character Character
1. Vladimir a) Cordelia
2. Aganippe b) Kunigunda
3. Delorge c) Apraxia
4. Huntingdon d) Marie
5. Honorella e) Honorella

A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon enters the Earth’s large shadow. The Moon remains in this shadow for approximately ninety minutes. The eclipsed Moon can be viewed from any location on Earth that is facing the Moon during this hour and a half. On the other hand, a solar eclipse happens when a small shadow of the Moon moves across the Earth’s surface. This type of eclipse is only visible from a narrow strip of land and lasts for a very short time, usually around one minute, as the small shadow quickly passes the observation point. It is easy to deduce that the opportunity to observe each type of eclipse varies.
There is one conduction electron for every copper atom. What is the average speed of the conduction electrons if a current of 10 A is flowing through a copper wire with a diameter of 2.10 m?
When painting a wing with an area of 0.4 square km, 40 ml of paint was used. What is the thickness of the paint layer on the wing?
What is the volume of the beaker when an iron cube with an edge of 2 cm is immersed and the water level increases by 4 divisions?
The figure shows the trajectory of a body moving from point M to point N. What is the distance traveled and the displacement of the body, respectively? Cf … in person
Immediately award 50 points for the accurate response. Necessary materials: 1. Fill the initial beaker with water and position it in a cold environment … carefully repeat the process for the second beaker, placing it in a warm location. 2. Without agitating the water in the glasses, add potassium permanganate crystals to each. 3. Observe the change in water color twice daily (measuring the millimeters the top edge has risen). 4. Utilize the formula D- to calculate the diffusion rate based on your observations (where h represents the height of the red-colored liquid due to diffusion, and 1 represents time). 5. Document your findings.
Can you please help me urgently? I need to calculate the amount of heat released by hot water and absorbed by cold water in teblobiliya, and explain the obtained result.
The mass of hot water, m, is 0.1 kg and the mass of cold water, m, is also 0.1 kg.
The initial temperature of the hot water, c, is 61°C and the initial temperature of the cold water, m, is 17°C.
The temperature of the mixture, t2, is 39°C.
We need to find the amount of heat released by the hot water, Q, in joules, and the amount of heat absorbed by the cold water, Q1, also in joules.
The formula to calculate the amount of heat, Q, is Q = c * m * (t2 – t1).
Now, let’s solve the problem:
Q = c * m * (t2 – t1)
Q = 4200 * 0.1 * (39 – 61)
Q = 4200 * 0.1 * (-22)
Q = -9,240 joules
The amount of heat released by the hot water, Q, is -9,240 joules.
To find the amount of heat absorbed by the cold water, Q1, we can use the fact that the total amount of heat in a closed system is conserved.
Q1 = -Q = 9,240 joules
Therefore, the amount of heat absorbed by the cold water, Q1, is 9,240 joules.
If you have any further questions, please let me know!
Masses 0.5 kg, temperature 20°C. How much energy is required to melt (silver) at this temperature? (The melting temperature of silver is 960°C, and the heat of fusion is 88 kJ/kg).

The Solar System.
If we don’t delve into the essence of the phenomenon, we can state that an eclipse is a temporary vanishing of the Sun or the Moon from the celestial sphere. How does it occur?
Solar eclipse
For instance, in this case, the Moon, traversing between the Earth and the Sun, completely or partially obscures the Sun from the Earth observer. That’s what we call a solar eclipse. Alternatively, the Moon, orbiting around the Earth, aligns itself in such a way that the Earth lies on a direct line connecting the Moon and the Sun.
The phenomenon of a lunar eclipse
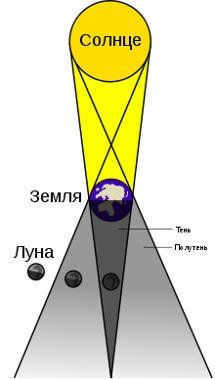
When the Earth’s shadow covers the Moon, causing it to vanish from the sky, a lunar eclipse occurs. Eclipses occur due to the constant movement of celestial bodies. As the Earth orbits the Sun and the Moon orbits the Earth, these processes occur simultaneously. If the Moon, Earth, and Sun align for a brief period, an eclipse occurs. A total solar eclipse is an incredibly rare and captivating phenomenon.
Here’s a fascinating piece of information: When a total solar eclipse occurs, there is a noticeable decrease in the air temperature, the sky becomes darker, and stars become visible in the sky.
What takes place during a solar eclipse
In the past, ancient Chinese artists used to portray a solar eclipse as a majestic dragon devouring the Sun. In reality, though, the Sun eventually emerges from its temporary hiding place, transforming the dark night back into a bright day. This mystical dragon is actually the Moon, moving in between the Earth and the Sun. To gain a deeper understanding of what unfolds during an eclipse, you can perform a simple experiment. Just switch on a table lamp and observe it closely.
Grab a cardboard and gradually slide it in front of your eyes until the cardboard is positioned between your eyes and the lamp. The instant the cardboard obstructs your view of the lamp signifies the commencement of the solar eclipse. Despite being physically distant from the lamp, the cardboard effectively shields the light emanating from it. If you relocate the cardboard further away, the lamp becomes visible once again.
Total and partial solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon, while moving across the daytime sky, positions itself between the Sun and the illuminated surface of the Earth, causing the Sun’s light to be blocked. In the event that the Moon only partially obscures the Sun, a partial solar eclipse takes place.
During a partial solar eclipse, a section of the Sun’s surface is covered by the Moon, resulting in a brief period of twilight. However, if the Moon aligns perfectly between the Earth and the Sun, a total solar eclipse happens. In this case, the Moon completely covers the Sun’s disk. Total solar eclipses are extremely uncommon, as the Moon’s orbit typically positions it either above or below the Sun.

Due to these fluctuations, the Moon can only be seen on an imaginary line connecting the Earth and the Sun once every one or two years. To witness a complete solar eclipse, one must be in the right place at the right time. If you remain stationary and inactive, you may be able to observe a partial eclipse of the Sun approximately every two years. However, a total eclipse may require waiting for centuries.
In 1970 and 1972, fortunate individuals in Nova Scotia were able to witness a total solar eclipse. Conversely, the last solar eclipse in London occurred in 1715, and the next one is not expected until the year 2700. Therefore, residents of London will have to be patient. Nonetheless, if you actively seek out eclipses, you can observe total eclipses quite frequently.
A total solar eclipse occurred in Finland on July 22, 1990. The beautiful beaches of Hawaii provided a stunning view of a total eclipse on July 11, 1991. On June 30, 1992, lucky individuals aboard ships crossing the South Atlantic witnessed a total eclipse. Mark your calendars for November 3, 1994, as a total solar eclipse is expected to grace the skies of Chile or Brazil.
In the morning of February 26, 1979, a remarkable total solar eclipse took place in the United States. This event was vividly recounted by writer Annie Dillard in her story “Total Eclipse.” The suburbs of Washington, D.C. were filled with a crowd of people who had gathered on the hillsides to witness this extraordinary phenomenon. As the eclipse commenced, the once blue sky transformed into a mesmerizing indigo hue. The distant mountains turned a fiery red, while the grass on the hillsides shimmered like silver.
Eventually, the Sun was completely consumed by the encompassing darkness. All that remained was a small white hoop suspended in the blackened sky. Just before the Sun disappeared entirely, an unexpected occurrence took place. A rapid and imposing shadow raced across the Earth, engulfing both the landscape and the mesmerized onlookers. The valley was flooded with darkness, as if being swallowed by the monstrous, swift shadow of the moon.
What enables solar eclipses to occur?
Solar eclipses are made possible by a unique coincidence involving the size and proximity of the Moon and the Sun. Although the Moon is significantly smaller than the Sun, it is much closer to Earth, causing their diameters to appear almost equal. This alignment allows for total solar eclipses, where the Moon perfectly aligns with the Sun.
When the Sun started to reappear, another phenomenon occurred – the passing of a shadowy wall. This wall swiftly moved through the sky, rushing eastward at an unimaginable speed before vanishing over the horizon. The abruptness of this event left observers bewildered and astonished, as the shadow’s velocity caused many to scream in terror.