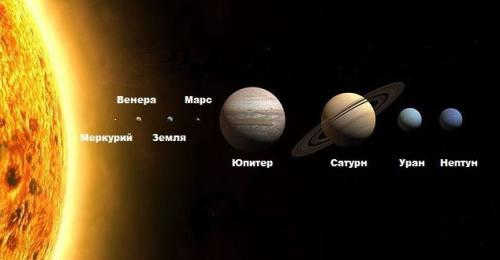
The biggest planet in the solar system. The largest planets in the solar system
There are a total of eight largest planets in the solar system.
There are four inner planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars.
And there are four outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
They are arranged in that order from the Sun:
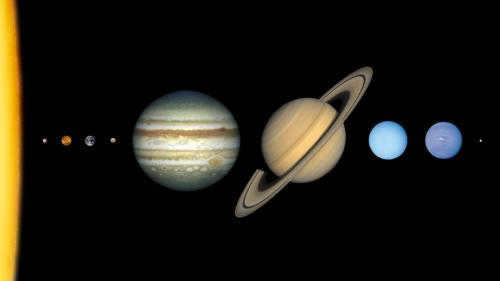
The diagram represents the proportional sizes of the Sun and all eight of the largest planets in the solar system, although their distances from each other differ. It is important to note that the planets are categorized into two groups based on their location and size within the solar system. The outer planets, known as gas and ice giants, are significantly larger than the inner planets in the Earth group. However, even these inner planets are much larger than asteroids, earning them the title of the largest planets in the solar system. Let us now become acquainted with these largest planets in the solar system in descending order:
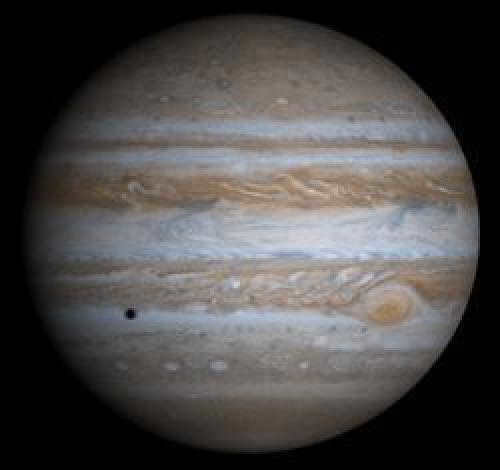
1 Jupiter holds the title for the largest planet with a diameter of approximately 139,822 kilometers.

The most massive planet ever discovered. The largest celestial body in existence
Our cosmos is incredibly vast, and it may seem that nothing can surpass the magnitude of our planet, but this assumption is incorrect. There exist planets that are much larger and more substantial. In the grand scheme of the universe, our Earth is merely a minuscule speck. The solar system is just a single component within the Milky Way Galaxy. The Sun serves as the principal constituent of the Galaxy. Eight planets orbit around the Sun. And only the ninth one, Pluto, was excluded from the list of rotating planets due to its gravitational forces and mass. Each planet possesses its own unique characteristics, such as density and temperature. Some are composed primarily of gas, while others are colossal, minuscule, frigid, scorching, or dwarf-like in nature.

So which planet holds the title for being the largest in the known universe? In the spring of 2006, a groundbreaking discovery was made at the Lovell Observatory in Arizona, USA. Located in the constellation Hercules, scientists stumbled upon a colossal planet that surpassed the size of our very own Earth by a staggering twenty times. To date, this is the largest planet ever discovered in the entire universe. While it may possess sun-like characteristics, it remains firmly classified as a planet. Meet TrES-4, a colossal celestial body that measures 1.7 times the size of Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system. TrES-4 is a massive gaseous sphere composed primarily of hydrogen. This giant planet orbits around a star positioned 1400 units away, and its surface temperature exceeds a scorching 1260 degrees.


If you observe this planet from the ground, it is evident that it orbits its star in a circular path. The exoplanet completes one orbit around its star every 3.55 days. TrES-4, the planet in question, is larger and hotter than the Sun.
The initial discovery of TrES-4 was made by employees of Lowell Observatory. Subsequently, astronomers from Harvard University and W.M. Keck Observatory in Hawaii confirmed the existence of this exoplanet. Researchers at Lowell Observatory speculate that TrES-4 may not be the only planet in its constellation and postulate the possibility of additional planets in the Hercules constellation. It is worth noting that Lowell Observatory is renowned for its discovery of Pluto, the smallest planet in our solar system, back in 1930. However, in 2006, Pluto was reclassified as a dwarf planet, particularly when compared to the massive TrES-4.
Size Comparison of Planets: A Look at Mass and Density
It is a commonly known fact that the planets within the solar system exhibit significant variations in size.
For instance, the planets situated in the inner region of our system are smaller in size but denser compared to the gas giants or ice giants found in the outer region of the solar system. Additionally, in certain cases, planets can even be smaller than certain satellites. However, it should be noted that the size of a planet is not always directly proportional to its mass.
Therefore, while Mercury may be smaller in size compared to Jupiter’s satellite Ganymede or Saturn’s satellite Titan, it actually possesses more than twice the mass of those satellites. Furthermore, while Jupiter is approximately 318 times more massive than Earth, its radius is only 11.21 times that of Earth.
Now, let’s take a closer look at each of the planets and examine their unique characteristics.
Mercury
With a mean diameter of 4,879 kilometers (3,031.67 miles), Mercury is the smallest celestial body in the solar system. It also has the second highest density (after Earth) among all the planets, measuring 5.427 g/cm 3 .
Mercury, similar to other terrestrial planets, is composed of silicate rocks and minerals, along with an unusually large iron core compared to its crust and mantle. As a result, Mercury has a mass of approximately 0.330*10 24 kg, which is only about 0.055 times that of Earth. The gravitational force on Mercury’s surface is a mere 3.7 m/s 2 .

Mercury. Authors and rights: NASA / Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory / Carnegie Institution of Washington.
Venus
Venus, also known as the “sister planet” of Earth due to its similar composition, size, and mass, possesses a density of 5.243 g/cm3. It is positioned as the second planet from the Sun, with an average radius of approximately 6050 kilometers (3759.3 miles). Consequently, the planet’s mass equates to 4.87*10^24 kg, which is 0.815 times that of Earth’s mass. Considering its density and size, the gravitational force on Venus is comparable to that of Earth and measures approximately 8.87 m/s2.

Venus is depicted in its true colors in this photograph taken by the Mariner probe. The original images are in the public domain and the credits go to NASA and Ricardo Nunes.
Earth
Similar to the other planets in the inner solar system, Earth is composed of metals and silicates. It has an average radius of 6,371 kilometers (3,958 miles) and an average density of 5.514 g/m 3 , making it the largest and densest planet in the Earth group. The Earth has a mass of 5.97*10 24 kg and a gravitational force of 9.8 m/s 2 , as you all are aware.
Mars is the third largest planet in our solar system. It shares similarities with Earth and other planets in terms of its composition, consisting of metals and silicate rocks. However, Mars is much smaller than Earth, with an average diameter of 6792 kilometers or 4220 miles. In fact, its mass is only one-tenth that of Earth.
To be more precise, Mars has a mass of 0.642*10 24 kilograms, which is approximately 0.11 times the mass of Earth. Due to its smaller size and density (measured at 3.9335 g/cm 3 ), the gravitational force on Mars is not as strong as on Earth, measuring at a maximum of 3.8 m/s 2 .

The self-portrait featured here was captured by the Mars rover Curiosity on January 23, 2018, while exploring the slopes of Mount Sharp. The credit for this image goes to NASA JPL-Caltech.
Jupiter
Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, boasts an average diameter of 142,984 kilometers. To put it in perspective, Jupiter is capable of containing all the other planets in our system, with the exception of Saturn. It is worth noting that Jupiter’s mass is nearly 2.5 times greater than the combined mass of all the other planets in our solar system, weighing in at a staggering 1,898 x 10^24 kilograms. Despite its massive size, Jupiter’s overall density is relatively low compared to the terrestrial planets. Its average density measures at 1.326 g/cm^3.
Saturn
Saturn is the second largest gas giant in our solar system, and it has an average diameter of 120536 kilometers, making it slightly smaller than Jupiter. Despite its size, Saturn is actually less massive than its counterpart. With a mass of 569*10 24 kg, Saturn is 95 times more massive than Earth. However, what makes Saturn unique is its low density. At only 0.687 g/cm 3 , Saturn is the only planet in our solar system that has a density lower than water (1 g/cm 3 ).

The clouds of Saturn are depicted in this image, which was taken by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft. The rights to this image belong to NASA.
Description of Uranus
Uranus has an average diameter of 120,536 kilometers and ranks as the third largest planet in our solar system. With a mass of 86.8*10 24 kilograms, Uranus is the fourth most massive planet. It has an average density of 1.271 g/cm 3 .
Neptune
Neptune has a diameter of 49528 kilometers, making it about four times larger than Earth. Its mass is 102*10 24 kg, resulting in a density of 1.638 g/cm 3 , which is higher than any other gas giant in the solar system.
The variation in the masses of the planets in the solar system is evident from the information above. However, when it comes to density, size is not always directly proportional. In other words, even though some planets may be only a few times larger than others, they can still have significantly greater mass.
The position of the Sun provides the interstellar medium and ensures the stability of the solar system. It is located within an interstellar cloud that belongs to the Orion-Swan arm, which is part of our galaxy. Scientifically speaking, our Sun is situated on the outer edge, approximately 25 thousand light years away from the center of the Milky Way when considering the galaxy’s diametral plane. The solar system, in turn, orbits around the center of our galaxy. The Sun completes a full revolution around the Milky Way’s center over a span of 225-250 million years, which is considered one galactic year. The Solar System’s orbit is inclined at an angle of 600 relative to the galactic plane. Close by, in our system’s vicinity, other stars and their own solar systems, consisting of both large and small planets, also revolve around the center of the galaxy.

The position of the Sun within the Milky Way galaxy
The solar system is estimated to be around 4.5 billion years old. Similar to most celestial bodies in the universe, our star was created during the Big Bang event. The origin of the solar system can be explained by the same laws of nuclear physics, thermodynamics, and mechanics that govern the universe today. Initially, a star formed and then planets began to form through the interplay of centripetal and centrifugal forces. The Sun emerged from a dense molecular cloud, a cluster of gases resulting from a massive explosion. Through centripetal processes, hydrogen, helium, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and other elements were compressed into a single, compact mass.
The protostar was formed as a result of grandiose and expansive processes, initiating the occurrence of thermonuclear fusion within its structure. This lengthy progression, which commenced considerably earlier, is currently observable as we gaze upon our Sun, which came into existence approximately 4.5 billion years ago. The magnitude of the processes that transpired during the formation of stars can be comprehended by evaluating the density, dimensions, and weight of our Sun:
- The density equates to 1.409 g/cm3;
- The volume of the Sun is nearly identical – 1.40927×1027 m3;
- The mass of the star amounts to 1.9885x1030kg.

The process of the formation of our star can be divided into several stages.
At present, the Sun is a typical astronomical object in the universe. It is not the smallest star in our galaxy, but it is also far from being the largest. The Sun is currently in its mature phase and serves as the center of our solar system. It plays a crucial role in the emergence and existence of life on Earth.
The final formation of the Solar System occurred during the same period, give or take half a billion years. The total mass of the system, including the Sun and all other celestial bodies within it, is approximately 1.0014 M☉. In other words, compared to the mass of our star, all the planets, satellites, asteroids, space dust, and gas particles in orbit around the Sun are relatively insignificant.
The concept of our star and the planets revolving around the Sun is a simplified representation. The mechanical heliocentric model of the solar system, incorporating clockwork, was first introduced to the scientific community in 1704. It is important to note that the planetary orbits within the solar system are not all confined to a single plane; rather, they orbit at various angles.
The Solar System model was developed based on a simpler and older device known as a tellurium, which simulated the Earth’s position and movement relative to the Sun. The tellurium allowed for an explanation of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun and facilitated the calculation of the Earth’s annual duration.
In school textbooks, the solar system is often depicted in its simplest form, with each planet and celestial body having its designated position. It is important to note that the orbits of these objects around the Sun are inclined at various angles to the solar system’s diametral plane. The planets within the Solar System are also situated at varying distances from the Sun, each completing its revolution at a different speed and rotating on its own axis in unique ways.
A solar system map is a visual representation that arranges all celestial objects in a flat plane, allowing us to comprehend their sizes and the distances between them. This depiction enables us to grasp the position of our planet in relation to others, gauge the scale of celestial bodies, and comprehend the vastness of the spaces that separate us from our cosmic counterparts.
Astronomers have recently made a groundbreaking discovery: they have identified the tiniest planet in our solar system.

Astronomers have recently made an exciting discovery – they have potentially identified the tiniest planet in our solar system. This remarkable finding pertains to an object known as Hygeia, which has long been recognized by scientists. However, for a considerable period, it was believed to be an asteroid circling within the asteroid belt located between Mars and Jupiter. Thanks to the latest observations conducted using the Very Large Telescope (VLT), previously unknown characteristics of Hygeia have been unveiled. This breakthrough has allowed researchers to reclassify Hygeia in a novel manner, as reported in Nature Astronomy.
The International Astronomical Union has established the main criteria for dwarf planets. These criteria state that dwarf planets must orbit the Sun and not be satellites of larger bodies. Additionally, they cannot clear the neighborhood of their orbit from other objects and must have enough mass to maintain a spherical shape due to gravity.
Exploring the vastness of our solar system and beyond
Five significant discoveries made by the Hubble Space Telescope
A recent study has revealed that Hygeia may meet all of these criteria. Previously, it was believed to be a elongated fragment of rock, measuring between 350 and 500 kilometers in diameter, with a large impact crater on one side. However, thanks to the advanced imaging system on the Very Large Telescope (VLT), it has now been confirmed that Hygeia is actually spherical in shape.
Scientists have not discovered any evidence of the giant crater. Instead, they found only two small marks on Hygeia from cosmic collisions. This discovery has left the researchers puzzled.
There are approximately 7,000 other celestial bodies with a similar composition that orbit around Hygeia. It is believed that this “swarm” formed around 2 billion years ago when a cataclysm hurled rock fragments into interplanetary orbit.
Following the powerful impacts, it is expected that there would be observable marks on the surface of Hygeia, similar to those found on the asteroid Vesta. However, there are no such traces. Extensive computer simulations were conducted by scientists, leading to the discovery of a plausible scenario. According to their findings, in ancient times, a 75-100 kilometer diameter object collided with a rocky fragment, resulting in the complete pulverization of the latter. Some particles were dispersed, while the majority of the intensely hot and molten debris came together and began to agglomerate. As these materials cooled and solidified, they transformed into nearly perfect spheres. If the scientists’ theory proves to be correct, this event would be the sole known collision of its kind within the entire solar system.
Scientists have observed that Hygeia is approximately half the size of Ceres, previously believed to be the smallest dwarf planet in our solar system. Hygeia may be the tiniest object to have achieved hydrostatic equilibrium, making its study crucial for understanding this phenomenon.
The researchers behind this study have proposed that there could be a significant number of dwarf planets lurking beyond the orbit of Neptune, a discovery that has yet to be made by astronomy.
Earlier, it was announced that Jim Bridenstine, the head of NASA, is advocating for Pluto to regain its planetary status, which was revoked in 2006.
The 9th planet of the solar system. Planet Nine
Planet Nine is a theoretical planet located beyond the orbit of Pluto in the solar system. It was proposed on January 20, 2016 by astronomers Konstantin Batygin and Michael Brown from the California Institute of Technology. Despite extensive research, the planet has not been directly observed.
The validity of the proposed “Planet Nine” as an explanation for the peculiar orbits of certain trans-Neptunian objects, first introduced by Konstantin Batygin and Michael Brown in 2016, has come under scrutiny.
Planet Nine     Kuiper Belt
Astronomers have made a significant discovery: the most remote dwarf planet in our solar system.
Currently, only the distance from the Sun, estimated size, and color of this newly found object are known.
Dwarf planets     Planet Nine     Solar System
A newly found celestial body named “Goblin” has been detected in the outer reaches of our solar system
As scientists continue to search for undiscovered dwarf planets and the mysterious Planet X, they have recently come across an incredibly distant object in space.
Dwarf planets     Oort Cloud      Planet Nine     Solar System
Orbits of “isolated objects” explained by collective gravity, not Planet Nine
A recent study has found that the movements of peculiar entities known as “detached objects” in our solar system are not caused by a mysterious ninth planet, but rather by collisions that occur at the outer edges.
New evidence suggests the presence of an additional celestial body in our solar system
Ongoing debates persist among scientists regarding the potential existence of a ninth planet within the solar system.
Could such a planet truly exist? Planet Nine        Solar System
Recent findings challenge the notion of a ninth planet in our solar system
Inaccuracies in previous observations have cast doubt on the validity of the evidence supporting the existence of Planet Nine.
A revolutionary tool for citizen scientists, which was launched earlier this year, has already resulted in a groundbreaking discovery in the search for new celestial bodies in the outer reaches of our solar system.
This remarkable tool, known as Brown Dwarfs     Planet Nine     Projects, has enabled astronomers to uncover a potential outlier in our solar system.
Astonishing Findings: The Untold Story of Planet Nine
Planet Nine, which may have been an outcast in the past, is a celestial body that originated outside of star systems or was expelled from its original system due to unknown circumstances.
Could this extraordinary phenomenon really exist? The enigma of Planet Nine        Solar System continues to captivate astronomers and scientists alike.
It is possible that Planet Nine has caused a significant alteration in the orbits of all the planets in our solar system, according to a recent collaborative study conducted by Elizabeth Bailey, Konstantin Batygin, and Mike Brown, the researchers who originally discovered the existence of this enigmatic celestial object.
Could this be true?    The influence of Planet Nine on the dynamics of our planetary system is a captivating topic of discussion.
Planet Nine is not responsible for mass extinctions on Earth
There is a theory among some scientists that suggests undiscovered massive icy objects located in the outer regions of our solar system might be the cause of mass extinctions that have occurred throughout Earth’s history. These hypothetical objects are believed to disrupt the Oort cloud, a collection of comets, and redirect some of them towards our planet.
Astronomy video for children: Discovering the planets in our solar system

Cosmos
There are contrasting beliefs regarding the number of planets in outer space. Some argue that Earth is one of the few, while others maintain that there are numerous much larger celestial bodies in the universe. This article will explore the topic of the largest planet in the universe.
Historical Background
Many of us learned about the formation of planetary bodies in school. This captivating process begins with the formation of a cloud composed of dust and gas. Gravity then comes into play, causing compression and heating of the gas in the central region of the future system. As atomic nuclei collide and combine to form more complex structures, a thermonuclear reaction takes place. This leads to the creation of a star and the subsequent birth of new planets.
However, there is still a lingering curiosity among many individuals about the immense size of planetary bodies and the identity of the largest planet in the vast cosmos. Undoubtedly, this question sparks fascination in the minds of adults as time goes by.
When it comes to stars, things are relatively straightforward: the greater the size of the celestial body, the greater the challenges in containing its outer layers, resulting in a shorter lifespan. On the other hand, planets present a more complex scenario, as there are numerous factors to consider before providing a definitive answer.
When exploring the concept of which planet is the largest, it becomes evident that the magnitude of the protoplanetary disk directly impacts the potential number of planets that can form. Conversely, it is also possible for a single object of remarkable magnitude to exist. What makes this topic even more intriguing is the fact that these disks have a finite size, as stars are incapable of capturing all cosmic matter, but only a fraction of it.
Challenges in the Exploration
The largest known planet in the universe is currently setting new records, as affirmed by modern scientists. This extraordinary celestial body goes by the name of HD 106906b. Its characteristics are truly mind-boggling, surpassing those of Jupiter by a factor of 11. It is situated a whopping 650 times farther from its “parent” star than the Earth is from the Sun.
Regarding the entire system to which this record-breaking planet belongs, it is situated at a distance of 300 light-years from our home planet. However, this does not pose any hindrance to its comfortable observation, as this colossal gas giant continues to captivate the imagination of scientists.
The main idea is that the celestial body in question is 11 times bigger than Jupiter. And according to fundamental astronomical principles, such a protoplanetary disk simply does not exist. So how could this extraordinary and enigmatic planet, as well as other celestial bodies larger than the Sun, have formed? The answer to this query will be explored further in the following text.
It’s actually quite straightforward: there exists an alternative hypothesis regarding the genesis of this colossal planet. It proposes that the planet originated from another star system, which is also suggested by its elliptical orbit. It would require approximately 1,500 years for a gas giant to complete one revolution around its host star. While this is a considerable length of time, it is still relatively short on a cosmic timescale.
Therefore, the inquiry concerning the identity of the largest planet in the Universe has been resolved. It turns out to be a celestial body with a captivating alphanumeric designation – HD 106906b. It surpasses Jupiter in size by a staggering factor of 11, thereby evoking immense curiosity among members of the scientific community. Furthermore, despite the extensive array of investigations that have been carried out, this entity still remains shrouded in mystery, giving rise to ongoing research efforts aimed at unraveling its secrets.
Mars and Earth are two celestial bodies within our solar system. Despite their contrasting physical attributes, they share several similarities. Each planet possesses its own distinct qualities due to the various phenomena that take place both internally and on their surfaces.

Is Mars smaller than Earth?
Not only climate and surface characteristics, but also the volumes of these celestial bodies differ. Both Mars and Earth are not the same size. Our planet is significantly larger. Earth is not as small as it may seem. A comparative analysis of these two cosmic bodies demonstrates this.
In order to determine which planet is larger – Mars or Earth, it is necessary to compare their physical characteristics.
For instance, Mars has a diameter of 6.7 thousand kilometers, which is nearly half the size of Earth’s diameter. This difference is quite significant. The total surface area of Mars is approximately equivalent to the land area of the entire globe. From all of this, it can be inferred that Earth is incredibly large, being almost twice the size of Mars.
When comparing the volumes of these planets, the differences are even more significant. Mars has roughly 15% of the volume of Earth. To completely fill Earth’s volume, it would require 6 planets the size of Mars. This is due to the fact that Earth’s volume is 163 billion km³, while Mars’ volume is only 1.1 trillion km³.
By comparing this information about these celestial bodies, it becomes evident that Mars is significantly smaller than our Earth. The imbalance is obvious, with Mars being the little brother of our planet.
There is a lot of interest in the similarities between Earth and Mars. Both planets have a solid structure and their surfaces share common features such as plains, uplands, mountains, volcanoes, and hollows.
Mars is known for its abundance of rocks and craters, with its surface mostly covered in sand or hard rock. Similar to Earth, Mars also has mountains and deserts, as well as canyons.
Comparing Mars and Earth, it is evident that both planets have polar ice caps, although the composition differs. Mars has a rocky surface dominated by dry ice, which is solid carbon dioxide. On the other hand, Earth’s polar ice is made up entirely of water.
The Earth and the Red Planet have a similar internal structure, consisting of a crust, mantle, and core. However, Mars has a partially liquid core, unlike the Earth. In the past, both planets experienced tectonic activity, but currently, only the Earth remains geologically active.
Both the Earth and Mars undergo seasonal changes due to their similar axial tilts. Winter, spring, summer, and fall occur on both celestial bodies, with winter being colder than summer.
While the Earth has one satellite, the Moon, Mars has two satellites, Phobos and Deimos. These satellites orbit their respective planets at specific speeds, influenced by gravitational forces.
Similar to Earth, Mars also experiences twenty-four-hour days. However, the duration of a day on Mars is approximately 24 hours and 37 minutes, making it slightly longer than Earth’s day.
Another similarity between the two planets is the presence of polar lights. Although, on Mars, the aurora borealis is not visible to the naked human eye. Instead, it emits a faint glow in the ultraviolet wavelength range and lasts only for a brief moment.
What sets Mars apart from Earth
When observing Earth and Mars from outer space, one can easily notice the stark differences between these two planets. Earth’s color palette is predominantly comprised of various shades of blue and white. On the other hand, Mars presents itself as a celestial body painted in shades of orange. This distant planet earned the moniker “Red” due to its soil’s high concentration of iron oxide, a substance that bears resemblance to the rust we commonly encounter. Iron rusts when exposed to oxygen, and Mars used to have a significant amount of this gas in its atmosphere. However, over time, the levels of oxygen in the Martian air have drastically decreased, resulting in a critically low presence. As a result, in the sunlight, the dust on Mars, composed primarily of iron oxide, takes on a reddish hue.
Mars is not like Earth’s surface, as it is covered in various formations such as rocks, plains, craters, and sands. The sand dunes on Mars are constantly in motion, driven by the wind across the planet’s surface and even blown upwards. Sometimes, powerful Martian storms can envelop the entire planet in an impenetrable dust cloud.
Unlike Earth, Mars lacks rivers, seas, or oceans. Instead, water on Mars exists primarily in solid form. Some of this water permeates the Martian soil, creating areas of permafrost, while another portion forms polar ice caps.
A Martian year is twice as long as an Earth year, lasting 687 days. Throughout the Martian year, the planet experiences significant changes, including the transition between seasons. Martian winter lasts for 7 Earth months, while summer lasts for 6. During these seasons, the climate and temperature undergo drastic shifts, with winter being much harsher compared to summer.
There exist other disparities between these planets. Mars has a mass that is only 1/10th the mass of Earth. The relatively small size of Mars affects its gravitational force, which is nearly 40% weaker compared to Earth’s. If an individual weighs 50 kg on Earth, they would find that their weight is significantly reduced to only 20 kg when on the Red Planet. Due to the low gravity of Mars, it lost its atmosphere and liquid long ago. The atmospheric pressure on Mars is almost 168 times less than that on Earth.
The Earth is shielded from solar radiation by its magnetic field, which is generated by its liquid core. This magnetic field serves as a protective barrier against radiation from outer space. However, Mars lacks such protection, as its magnetic field is 500 times weaker than Earth’s. This is the distinguishing factor between the two planets.
Mars is home to its very own unique Mount Olympus. Rising nearly 27 kilometers above the planet’s surface, this majestic peak dwarfs Mount Everest in comparison. To reach a similar height, you would need to multiply the length of Earth’s highest peak by three. The diameter of Olympus spans approximately 600 kilometers, which can be traversed in just 6 hours by car, traveling at a speed of 100 km/h. At the base of Olympus, genuine water glaciers can be found, covering an expansive area of several thousand kilometers.
The Mariner Valley never fails to astonish space explorers. Stretching over 4,000 kilometers and reaching depths of approximately 10 kilometers, this vast valley is even visible from space. It appears as a colossal scar on the Martian landscape, spanning a fifth of the planet’s surface.
The thinness of the Martian surface atmosphere is remarkable. The density of the air on Mars is merely 1/100th of the atmospheric density found on our own planet. The presence of oxygen and nitrogen is what allows for the sustenance of life on Earth. These two gases are the predominant components of Earth’s atmosphere. In contrast, the Martian atmosphere consists of nearly 96% carbon dioxide, making it impossible to breathe. Oxygen, on the other hand, only accounts for a mere 0.15% of the Red Planet’s total atmospheric composition.
Earth has something that Mars lacks.
Earth’s atmospheric pressure is suitable for human life, measuring at 101 kPa. On the other hand, Mars has a significantly lower atmospheric pressure, measuring at only 600 Pa, which is 168.33 times less than that of Earth. However, at an altitude of approximately 30 km, the Martian pressure suddenly drops to a mere 30 Pa. Due to this low pressure, the air on Mars is constantly filled with dust. The wind carries particles of sand up to 2 km away and they settle on the planet’s surface for extended periods of time.
The level of radiation on Mars is significantly higher compared to the radiation background on Earth due to the absence of a protective magnetosphere. Unlike Earth, Mars does not have a functioning magnetic field, leaving its surface exposed to high levels of cosmic radiation. The radiation level on Mars is measured at 8 Rad per year, while on Earth, it is only 0.62 Rad per year for individuals residing in large cities.
These elevated radiation levels raise concerns about the possibility of past and present life on Mars. Furthermore, the excessive radiation would pose a threat to the health of space travelers, making it unsafe for prolonged stays on the planet even with the use of protective suits.
The Earth is abundant with rivers, seas, and oceans, covering about 70 percent of its surface. This vast amount of water plays a crucial role in maintaining a moderate temperature on our planet. During the day, the oceans absorb a significant amount of heat, preventing extreme temperature fluctuations. At night, this heat is released back into the atmosphere, ensuring that life on Earth does not freeze. In contrast, Mars lacks such a water presence, with its only representation being in the form of ice.
Another difference between Earth and Mars is the movement of tectonic plates. While our planet experiences slow but continuous movement of these plates, Mars does not. This movement is responsible for various geological activities on Earth, including the presence of active volcanoes. On Mars, however, volcanoes like Olympus Mons have long been inactive. These shield volcanoes are a result of the absence of tectonic plate movement on the Red Planet.
Life exists in various habitats on Earth – from the depths of the oceans to the freezing Antarctic regions and the highest mountain peaks. Every ecological niche is home to some form of living organism. However, on Mars, no conclusive evidence of life has been discovered by scientists.
Perhaps, over time, Mars could transform into a planet similar to Earth. However, there is a more likely possibility. Climate scientists frequently raise concerns, warning that Earth is gradually becoming more like Mars. If humanity fails to recognize the importance of taking care of our planet, it could eventually lose its protective ozone layer and become an uninhabitable wasteland.
Did you find the information helpful? Show your support by giving it a thumbs up on social media!

Jupiter, the colossal celestial object, holds the prestigious title of being the largest planet in our solar system. Its immense size and influence make it an integral part of astronomical studies, especially for high school students. Jupiter’s grandeur extends beyond its physical dimensions, as it played a significant role in the formation of our own planet, Earth. Additionally, its gravitational force acts as a protective shield, safeguarding our planet from potentially catastrophic encounters with wandering meteorites.
The space giant known as Jupiter was officially discovered in 1610 by the renowned Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei. Utilizing a telescope, Galileo not only observed the massive planet but also identified its four prominent satellites.
Fast forward to 1955, when the advent of radio telescopes led to the detection of a powerful radio signal emanating from Jupiter in the form of wide bands.
This discovery indicated that the largest planet in our solar system exhibits electrical activity. Despite advancements in technology that have allowed for more detailed study of Jupiter, it continues to hold numerous enigmatic secrets for humanity to unravel.
When the immense size is simply overwhelming
Not only is Jupiter known for its immense size, but it also surprises astronomers with its mass, which exceeds the combined mass of all the known planets in our solar system. If we were to compare our own planet to this colossal giant, the Earth would be like a tiny pea, while Jupiter would be more akin to a massive soccer ball. What’s even more astounding is the incredible velocity at which this giant planet moves, reaching speeds of up to 45,300 km/h. It completes a full rotation on its axis in just ten hours, while it takes a staggering twelve years for it to complete a single orbit around the sun. This is remarkably fast considering that Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system and is positioned approximately five times farther away from the scorching sun than our own Earth.
Composition of the giant
The largest celestial body in our solar system consists of:
- A core (which astrologers believe to be rocky or icy, although this has not been substantiated),
- Three types of hydrogen: metallic, liquid, and gaseous,
- Clouds.
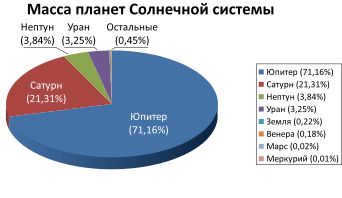

Jupiter is more massive than all the other planets in the solar system combined.
When scientists studied the planet’s gravity, they conducted a thorough examination of its core. There were reports suggesting that the core is as heavy as ten Earth-sized planets and accounts for about 14% of the planet’s total mass. However, the presence of convection currents and the glowing hydrogen within the planet have actually reduced the core’s parameters. It is this combination of the core, interior, and outer atmospheric layers that we now refer to as Jupiter. Besides hydrogen, Jupiter also contains various chemical elements such as phosphine, sulfur, oxygen, ethane, neon, carbon, benzene, ammonia, silicon, and methane. The regions of the planet near the core experience high pressure and temperature.
The question of which planet is the largest in the solar system is no longer a matter of debate. Let’s take a look at the unique aspects of Jupiter. One of the most enigmatic features of this planet has always been the presence of the Big Red Spot on its surface. No other celestial bodies in our solar system possess such vibrant and prominent formations like Jupiter does. Some scientists attribute this phenomenon to the powerful atmospheric storms occurring on the planet. Over the past three centuries, this formation has been observed to consistently maintain its latitude while changing its longitude. At times, the spot shrinks to half its size, while at other times it grows to an impressive scale, which is its distinctive characteristic.
Abundance of loyal companions of the colossal
After perusing this information, there is absolutely no question regarding the identity of the largest planet in our solar system. However, there are an additional 79 moons that reside nearby, serving as its satellites. The brilliant Galileo Galilei was the one to first discover four of these moons, which he aptly named Callisto, Ganymede, Io, and Europa. The subsequent four satellites, known as the Amalthea group, have a diameter of less than 200 km. Among them are Thebes, Amalthea, Adracea, and Metis. The remaining irregular moons are smaller than the initial eight and possess eccentric orbital paths. Furthermore, these moons can be further categorized into families based on their similar size, composition, and orbital trajectories.
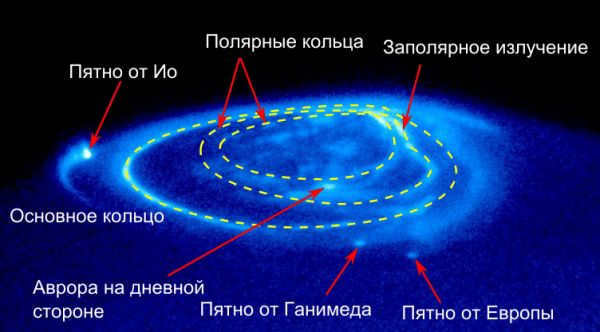

The polar lights on Jupiter have a specific structure, including a main ring, polar emission, and spots resulting from interactions with Jupiter’s natural satellites.
Jupiter’s younger sibling
Saturn is the second largest planet in the solar system, coming after its massive counterpart. Among the celestial bodies in our solar system, Saturn stands out with its remarkable and prominent rings. While similar phenomena can be found on other giant planets in the universe, they lack the same grandeur due to their smaller size, absence of icy particles, and lack of metal and dust impurities. As a result, these rings are not as easily noticeable to us. In terms of composition, Saturn closely resembles Jupiter, with elements such as hydrogen, ammonia, helium, methane, and other impurities. However, the presence of strong winds prevents Saturn from having stable neoplanets like Jupiter.
Interesting Facts to Know
When a student asks, “Which planet is the biggest in our solar system?” the teacher’s response would undoubtedly be Jupiter. However, a knowledgeable educator will also acquaint students with interesting features about this colossal celestial body.
- There are auroras near the north and south poles of Jupiter that are more intense and longer-lasting than the ones here on Earth.
- There are over 300 gas giants in the universe that are larger than Jupiter.
- The name “Jupiter” originates from ancient Roman mythology, paying homage to its principal deity.
The biggest planet in the solar system is Jupiter. Jupiter was first discovered in the early 17th century. The planet is not only massive in size, but also extremely heavy. Its primary components consist of hydrogen and various impurities. Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is a notable feature that has yet to be fully explored, making it even more mysterious. This colossal planet is not alone in space, as its loyal companion Saturn and 67 other moons are nearby.
Ever since our high school days, we have been taught that Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, is a gaseous giant with numerous satellites. These basic facts are likely the extent of what most people remember about Jupiter. However, this magnificent planet is not just massive, it is also incredibly fascinating and there is so much more to learn about it. Who knows, perhaps in the near future, we may uncover new information that is currently unknown to scientists.
How Jupiter was formed
Obviously, nobody can be completely certain about the accuracy of the theory regarding the formation of the solar system as a whole and Jupiter specifically. However, the fundamental theory can be outlined as follows.
Around 4.6 billion years ago, there was no existence of a solar system. It merely consisted of an immense cloud composed of gas and dust. This cloud is now referred to as the solar nebula. Over time, the force of gravity caused the matter to accumulate and the Sun emerged at the center of the nebula.
To prevent the planet-forming gases from being swept away by the solar wind, the gas giant had to form extremely rapidly. Once Jupiter’s solid core reached a mass 10 times that of Earth, its gravitational pull became strong enough to retain light gases without being affected by the solar wind. While Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system, there are even larger planets in the universe. However, very few celestial bodies have been able to form at such a rapid rate.
Another theory for Jupiter’s origin is the instability disk model. The main difference between this model and the conventional model is that its proponents believe that dust and gas were initially bound together. According to this theory, a planet like Jupiter could have formed within a thousand years, whereas the usual timeframe for planet formation is several million years.
The arrival of such an enormous celestial object during the early stages of the solar system’s formation likely had a significant impact on the development of other planets. Jupiter’s considerable mass granted it the power to alter the paths of smaller planets that came into its vicinity. Its gravitational force could have potentially influenced the positioning of certain planets closer to the center of the solar system while pushing others towards its outer regions.
The Unveiling of Jupiter and its Moons
In actuality, there was no unveiling of Jupiter. Indeed, this celestial body can be observed during nocturnal hours without the aid of any optical instrument. Consequently, determining its initial discovery becomes an insurmountable task. Nevertheless, historical records confirm that the planet was recognized in ancient eras. The theological convictions of Greek, Mesopotamian, Babylonian, and various other civilizations were founded, in part, on their awareness of Jupiter’s existence.
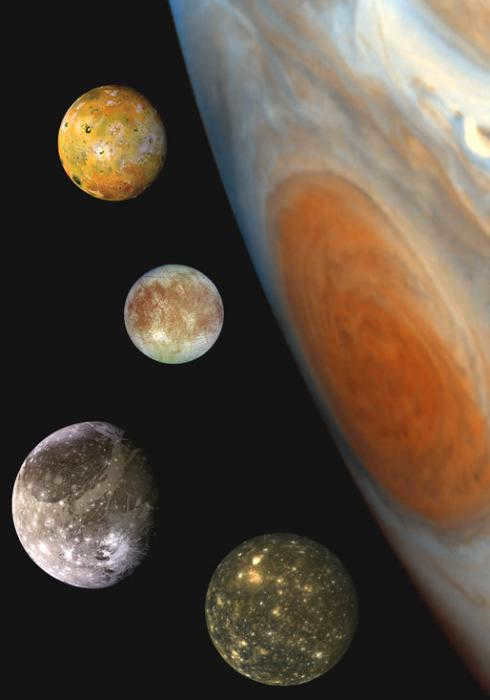

Later on, in 1610, Galileo made a groundbreaking revelation that this celestial entity possesses moons. In our solar system, Jupiter holds the title for being the biggest planet. In the vastness of the galaxy, there exist planets that surpass its size. However, only a handful of planets can claim to have such a vast number of moons. As of now, scientists have identified 67 natural satellites orbiting Jupiter, among which the most prominent and well-known are Io, Ganymede, Callisto, and Europa. These four moons were initially spotted by Galileo, a discovery that solidified the Copernican theory, challenging the notion that Earth was the center of the universe.
Jupiter was given its name in ancient times. It was named after the principal deity of the Romans – a fitting name for the largest planet known even today. Interestingly, the ancient Greeks referred to the same planet as Zeus, drawing a parallel with the Romans, as in Greek mythology, the king of the gods is Zeus. However, this name only survived in ancient Greece, while the Roman name for the planet has endured to this day.
Unique Features
When a child inquires about the largest planet in the solar system, we confidently respond with Jupiter. And our response is not only accurate in a literal sense. Jupiter is not only the largest of all the planets in the solar system, but it also possesses a significantly greater mass than any other planet. Furthermore, Jupiter’s mass is not just greater than that of each individual planet, but it is approximately two-thirds the weight of all the planets combined! Scientists speculate that if Jupiter’s mass were to increase by 80 times, it would have a strong possibility of transforming into a star.
However, it is not just its high mass that gives Jupiter its resemblance to the Sun. Similar to our star, this celestial body is predominantly composed of helium and hydrogen. Furthermore, it possesses four sizable moons and an extensive array of smaller moons. Essentially, Jupiter’s system can be viewed as a miniature version of the entire solar system. Consequently, if a child were to inquire about the largest planet in our solar system, one might not correct them, but instead proudly respond, “Jupiter!”
Upon observing Jupiter through a telescope, one would behold the stunning presence of light and dark stripes adorning its surface. These stripes represent the tumultuous movements of the atmospheric winds, which exhibit speeds of approximately 640 kilometers per hour.

Photographs of Jupiter reveal the extraordinary nature of the Great Red Spot. What makes it truly fascinating is not just its appearance, but its true nature. It is, in fact, a hurricane with wind speeds reaching approximately 360 km/h at its edges. The storm’s size is three times larger than the diameter of Earth. However, this is not the most peculiar aspect of this phenomenon. What is truly remarkable is that the storm has been observed for over 300 years, with only brief periods of interruption. Though the possibility of its cessation remains unconfirmed and is currently just a hypothesis. The spot earned its name “Red” due to the presence of phosphorus and sulfur in the ammonia crystal composition of Jupiter’s clouds.
Dusk
Jupiter is renowned for being the largest planet in our solar system. However, it is also notable for its remarkable “restlessness”. This is due to its exceptionally fast rotation on its axis, which surpasses that of all other known planets. Despite its immense size, a single day on Jupiter lasts less than 10 hours on Earth. Consequently, its rapid rotation has caused the planet to become noticeably more bulging at its equator, resulting in the equator being 7% wider than the poles.
The Atmosphere of Jupiter
Scientists are particularly intrigued by the atmosphere of the largest planet in our solar system. The composition of Jupiter’s atmosphere determines everything in this colossal world. Unlike other planets, Jupiter does not have a solid surface suitable for landing aircraft. Instead, its surface is composed of helium and hydrogen, with a small fraction of other gases present in the air.
The majority of Jupiter’s atmosphere is composed of hydrogen, accounting for approximately 90% of its composition. Helium makes up about 10% of the atmosphere. The remaining fraction, which is incredibly small, includes traces of ammonia, water vapor, methane, and sulfur.
If we were able to descend from the outer shell of Jupiter to its core, we would experience a significant rise in both pressure and temperature. This phenomenon is a result of the gases separating into distinct layers. As we venture deeper into the planet, closer to its center, it is highly probable that hydrogen exists in a liquid state. Furthermore, at even greater depths, it is assumed to transition into a metallic state. The immense quantities of hydrogen and helium contained within Jupiter are what contribute to its status as the most massive planet in our solar system.

The temperature of Jupiter’s atmosphere varies from -150 degrees Celsius in the lower tropospheres to a scorching 725 degrees Celsius at the planet’s surface. As we move higher up, we reach the thermosphere, where a faint glow can be observed. The heating in this region is a result of both solar radiation and particles from the magnetosphere.
Above the thermosphere lies the exosphere, the outermost layer of Jupiter’s atmosphere. Unlike the other layers, the exosphere does not have a defined boundary, allowing gas particles to freely travel into interstellar space.
The heart of Jupiter
Jupiter, the most massive planet in our solar system, is home to a fascinating and enigmatic core. While its exact composition remains a mystery, scientists believe that it is composed of a dense and compact material. Surrounding this core is a layer of metallic hydrogen, a unique form of hydrogen that exists under extreme pressure and temperature conditions. Additionally, this metallic hydrogen is mixed with helium, creating a complex and intriguing environment.
Enveloping the core and metallic hydrogen layer is Jupiter’s immense atmosphere, predominantly composed of molecular hydrogen. This gaseous envelope not only gives Jupiter its iconic appearance but also plays a crucial role in the planet’s atmospheric dynamics and weather systems.
Despite its immense size, the core of Jupiter is surprisingly lightweight compared to Earth, weighing only about one-tenth of our planet’s mass. However, the surrounding hydrogen atmosphere more than compensates for this, making up more than 80% of Jupiter’s overall diameter.
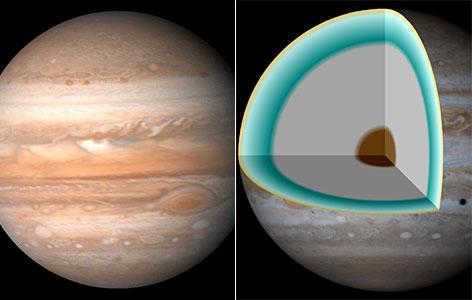
Satellites and rings
Jupiter has a minimum of 63 satellites. The most well-known among them are the Galilean satellites.
The largest planet in our solar system, as expected, possesses the largest satellite in our entire system. Not only is it the biggest satellite, but it is also larger than certain planets, such as Pluto and Mercury. Furthermore, it is the sole known satellite that possesses a magnetic field.
Io is the most volcanically active entity known to the field of science. The sulfur that is released as a result of this activity imparts a yellow-orange hue to the satellite. The gravitational pull of Jupiter generates solid tides on Io, which in turn produce the necessary heat for volcanic eruptions.
Europe is covered with ice throughout. If the ice melts, Europa will have double the amount of water as Earth. Additionally, ice is believed to exist on Callisto and Ganymede.
Callisto has the lowest reflectivity, indicating that its entire surface is likely made up of colorless dark rock.
The largest planet, which surprised scientists in 1979 with its “lands,” also possesses rings. Voyager 1 discovered three rings encircling the gas giant’s equator.
The primary ring features a flat structure, measuring approximately 30 kilometers in thickness and 6400 kilometers in width.

The inner cloud, known as the halo, has a thickness of approximately 20,000 kilometers. It stretches from the primary ring to the outer ring, expanding due to the influence of Jupiter’s magnetic field. Both rings are composed of small, dark particles.
The third ring bears a resemblance to a spider’s web, appearing almost transparent. In reality, it is composed of minuscule fragments from Jupiter’s three moons: Thebes, Amalthea, and Adrasteus. The ring is likely composed of dust particles similar in size to those found in cigarette smoke. This ring boasts impressive dimensions, spanning 129 thousand kilometers in width and over 30 thousand kilometers in thickness.
Jupiter boasts truly astonishing proportions! It is a staggering 318 times more massive than our beloved Earth. In fact, its diameter is a remarkable 12 times the length of our home planet’s equator. Despite its immense weight, this celestial body ranks fifth in terms of density, measuring at 1326 g/cubic centimeter. This can be easily explained by the fact that gas is much less dense than rock. The structure of this gas giant bears a striking resemblance to that of our very own Star. However, for the hydrogen fusion that powers a star to commence, Jupiter would need to increase in size by a whopping 75 times its current dimensions.

Jupiter, located at a distance of 778 million kilometers from the Sun, holds the title of being the largest planet in our solar system. While similar scales can be found in the vast expanse of the Universe, no planet in the neighboring star systems comes close to matching Jupiter’s immense size.
Exploration and Forecasts
The examination of the largest planet in our solar system commenced many years ago, but it was only NASA that conducted comprehensive investigations. The deployment of the Galileo probe into Jupiter’s atmosphere holds particular significance. Additionally, the Pioneer and Voyager spacecraft were dispatched for exploration. The latest transmission of data from Jupiter was received from the New Horizons probe, which was initially sent to Pluto.
As of now, Jupiter does not have any man-made satellites, but the launch of another space explorer to study this gas giant is planned for 2016.
From our planet, Jupiter can be observed using an 80-millimeter telescope. At this level of magnification, one can discern spots, protrusions, and depressions. When employing a telescope with an aperture of 150mm or larger, the Great Red Spot and finer details of the bands become visible.
During the opposition, when observed from Earth, the largest planet in our solar system achieves an apparent magnitude of -2.94. Consequently, Jupiter ranks as the third brightest celestial object in the sky. At other times, its apparent magnitude drops to -1.6.
Ever since the possibility of observing Jupiter became accessible to all inhabitants of Earth, the colossal planet has garnered increasing interest from humanity. Photographs of Jupiter have circulated throughout the Internet and have become a favorite subject among stargazers.
Regrettably, the future remains uncertain. Although it is widely known that Jupiter is the largest planet, its fate remains a mystery. It is hypothesized that in the future, Jupiter may transform into a star, with its moons potentially forming a new planetary system. This could offer an opportunity for humanity to relocate and inhabit this system once the lifespan of our Sun comes to an end.
Amazing facts about Jupiter that everyone should be aware of
- Imagine if the Sun was as small as a door, the Earth would be the size of a coin, and Jupiter would appear as big as a basketball.
- Jupiter is recognized as the fifth planet from the Sun in our solar system.
- A single day on Jupiter only lasts 9 hours and 55 minutes, while it takes the planet almost 12 Earth years to complete one orbit around the Sun.
- Despite being a gas giant, scientists believe that there is a solid core approximately the size of Earth hidden beneath Jupiter’s atmospheric layers.
- The composition of Jupiter’s atmosphere primarily consists of helium and hydrogen.
- Back in 1979, astronomers made a remarkable discovery of faint rings encircling Jupiter.
- Researchers have been conducting extensive studies on Jupiter and its moons for a considerable period. The upcoming Juno mission is scheduled for launch in 2016.