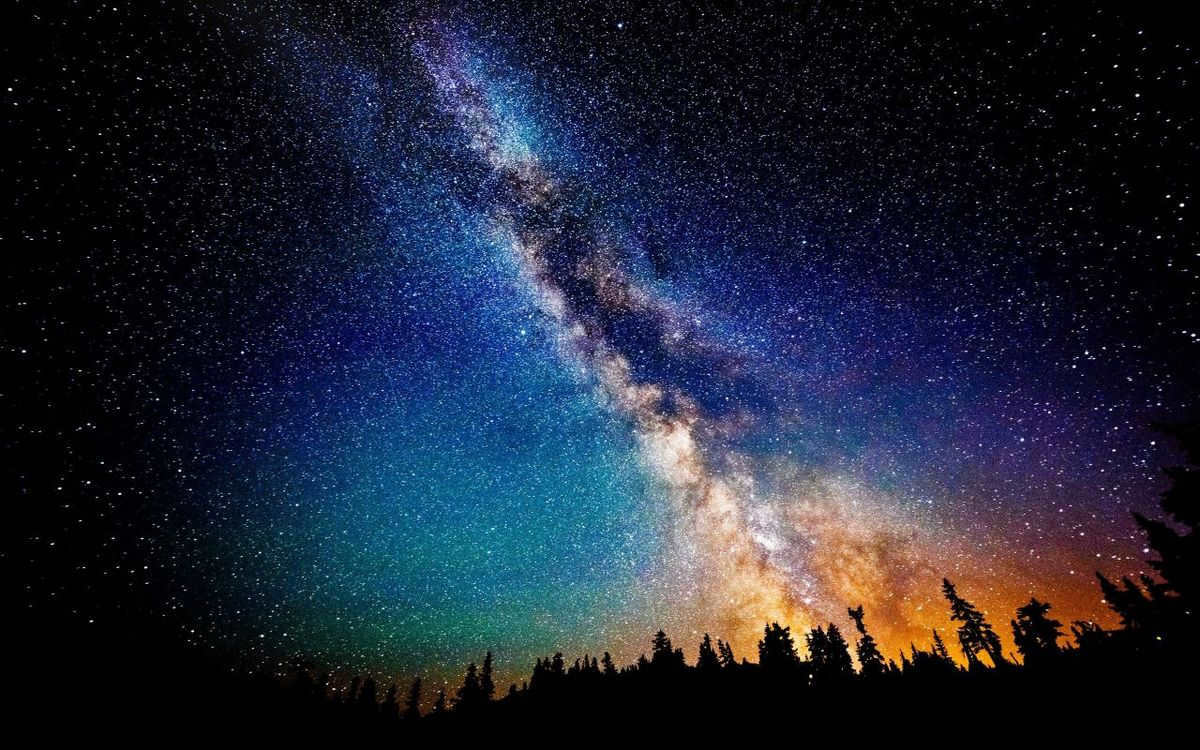
It is common knowledge that our galaxy is named the Milky Way. Specifically, initially, its visible components in the nocturnal firmament were referred to by this moniker – those spiral arms of the galactic structure that are observable from our planet. However, what is the connection between our galaxy and milk, and what is its designation in various other countries? Today, we shall explore this topic collectively.
The Origin of the Name “Milky Way”
In addition to being called the Milky Way in Russia, our galaxy has the same name in most English-speaking, European, and American countries. This name can be traced back to an ancient Greek myth involving Hercules. In the myth, Zeus, who was both the father of Hercules and the supreme god, wanted to bestow divine powers upon his son. The easiest way to do this was to give Hercules the milk of a goddess. One night, Zeus took the infant Heracles to his sleeping wife Hera with the intention of obtaining the goddess’s milk. However, Hera was not pleased with her husband’s idea. She pushed the child away, causing her milk to splash into the sky and leave a bright circular trace. This event ultimately led to the name “Milky Way” for our galaxy.
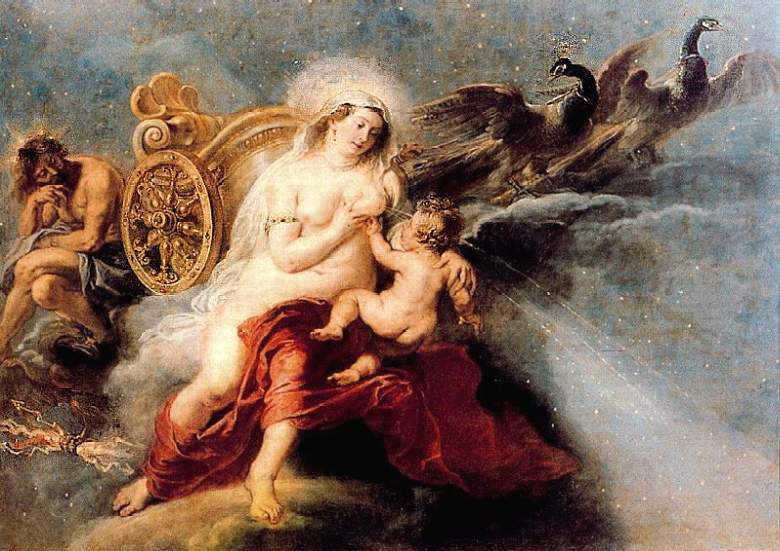


The classification of the Milky Way. Rubens’ portrayal of Hera and Hercules in the Milky Way
Thus, the original designation of our galaxy was “Milky Circle” or “galaxias kyklos” in Ancient Greek. The term “Circle” later transformed into the modern term “path” when it was adopted into Latin. In Latin, the myth underwent reinterpretation, and the streak of the goddess’s milk in the sky became known as “via” – meaning way or road. Interestingly, you may have already observed that the word “galaxy” itself is derived from the Greek term for milk. The Christian Church, along with Latin and Ancient Greek as scientific languages, played a role in disseminating the term “Milky Way” across various languages.
However, the world and history are not limited to the ancient Greek period and Europe – therefore, there are certainly other names for our galaxy. For instance, you may be aware that in Ukrainian, the Milky Way is referred to as “Chumatsky Shlyah (path)”, in homage to the Chumak traders of old. These traders would travel from north to south in search of fish and salt, using the starry streak in the sky as their guide. It wasn’t until Galileo Galilei invented the telescope that it was discovered that the Milky Way is comprised of hundreds of stars. As a result, people from all around the globe have come up with various names for this radiant celestial band.
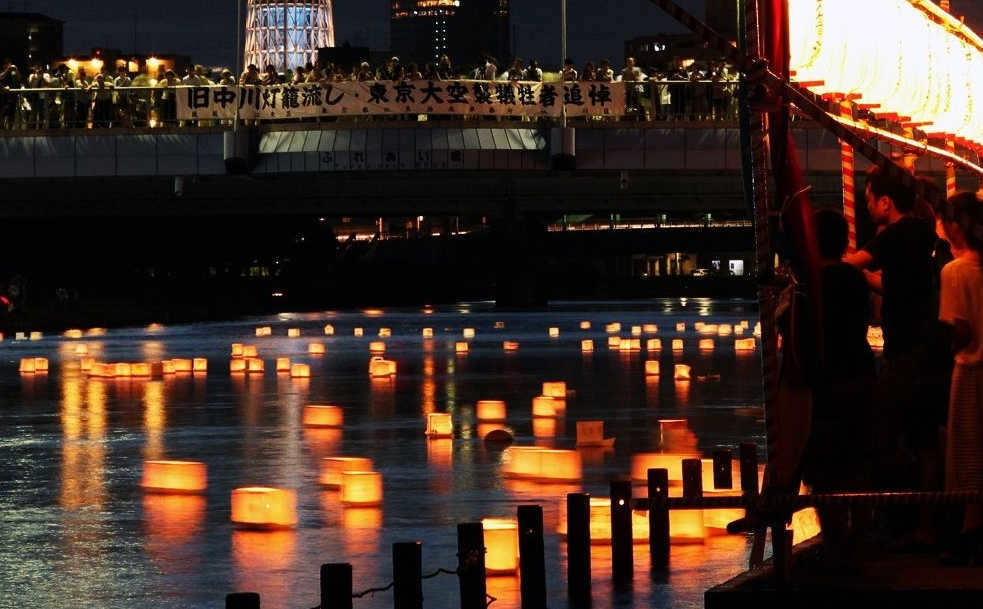


In Eastern countries, lanterns on rivers are not only a symbol of the departed souls, but also a homage to the celestial bodies that form the Milky Way.
As an example, our galaxy was referred to as “The Road to Vyrai” or “God’s Road” by the ancient Slavs. According to their beliefs, birds and the souls of the deceased would fly in the autumn towards paradise, following the path of God’s Road. The supreme god of thunder, Perun, would ride his chariot along this road. With the arrival of Christianity, St. Ilya took the place of Perun. The Finnish name for the Milky Way holds a similar meaning, translating to “bird’s path”. The concept of the Milky Way as a road also existed among the Lithuanians, Armenians, Arabs, Croats, and Spaniards, with each culture attributing a different story to it. For instance, the starry road led pilgrims to Mecca, rescued slaves from Turkish captivity, and reflected the footsteps of Apostle Peter, who would sprinkle straw along his path.
The associations connected with our galaxy don’t end there. The people of Siberia saw in the stars the marks of skis and scars, while the Incas and Mayas envisioned a massive celestial serpent. In Asian cultures, the Milky Way is still associated with a river. For instance, the Japanese use the term “Silver River” to refer not only to our galaxy, but to any galaxy at all. Additionally, the Silver River in the Land of the Rising Sun serves as a symbol of love. During certain holidays, luminous lanterns are launched on the currents of rivers and streams, symbolizing the stars and the souls of the departed.
Did you enjoy the article? Share it with your friends!

Feel free to leave comments or ask any questions about the paragraph on the discussion page.
Galaxies [ edit correct code ]
Categories of galaxies [ edit correct code ]

- Provide instances of every category of galaxy. To which category does our Milky Way galaxy belong?
Elliptical and spherical galaxies are smooth, rounded shapes. They have a gradual decrease in brightness from the center to the outer edges. The level of compression can vary among different elliptical galaxies. In contrast, globular galaxies do not rotate and are not subject to compression. The largest elliptical galaxies have a mass greater than 10^13 solar masses. Their high mass is due to a low presence of gas and dust.
Spiral galaxies consist of a central nucleus and spiral arms. They can have two or more arms that may be equally or unequally developed. Spiral galaxies exhibit a wide range of arm shapes and patterns. Our own galaxy, the Milky Way, is a spiral galaxy. These galaxies are characterized by their rotation and abundant amounts of gas and dust. The mass of spiral galaxies ranges from 10^10 to 10^12 solar masses.
Hypotheses for the origin of quasars [ edit edit code ]
There are multiple hypotheses regarding the genesis of quasars.
One theory suggests that quasars are actually young galaxies in the early stages of development. Numerous astrophysicists subscribe to the belief that the luminosity of these entities is not sustained by thermonuclear processes. Instead, the energy emitted by quasars is gravitational in nature, resulting from the cataclysmic compression that takes place within the core of the galaxy.
One of the most widely accepted theories suggests that quasars are massive black holes that attract surrounding matter. As this matter gets closer to the black hole, its particles accelerate and collide, resulting in powerful radio emissions. If the black hole possesses a magnetic field, it also gathers particles into beams that shoot out from its poles. The gravitational forces exerted by the black hole cause matter to rush towards the center, spiraling faster and faster as it approaches. During these collisions, the energy and speed of the particles decrease, causing them to slowly approach and be absorbed by the black hole. Essentially, the glow observed by astronomers represents the remnants of a galaxy that met its demise in a black hole.
There is another hypothesis that suggests the quasar is actually a black hole that consumes the matter from the galaxy it is forming.
Exploring the Milky Way galaxy [ edit edit code ]
- Can you provide information about the organization of our galaxy, the Milky Way, and the constellations it contains?
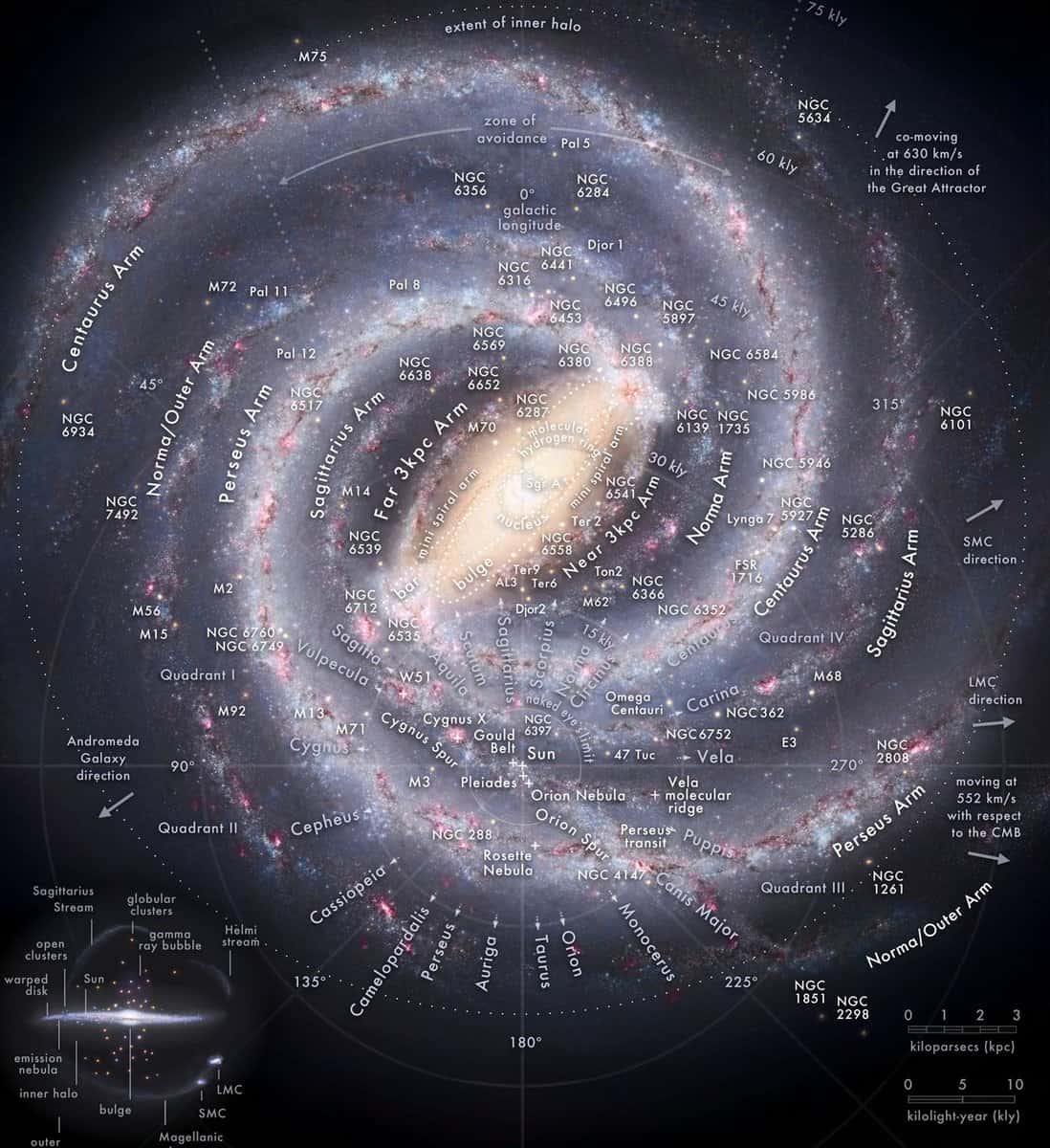
The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy that includes our planet Earth, the Solar System, and all the stars visible to the naked eye. It is known for its distinctive shape.
The Milky Way, along with the Andromeda Galaxy (M31), the Triangle Galaxy (M33), and over 40 smaller satellite galaxies, make up the Local Group of Galaxies, which is part of the larger Virgo Supergroup.
Our solar system is situated in the Orion arm of the Milky Way.
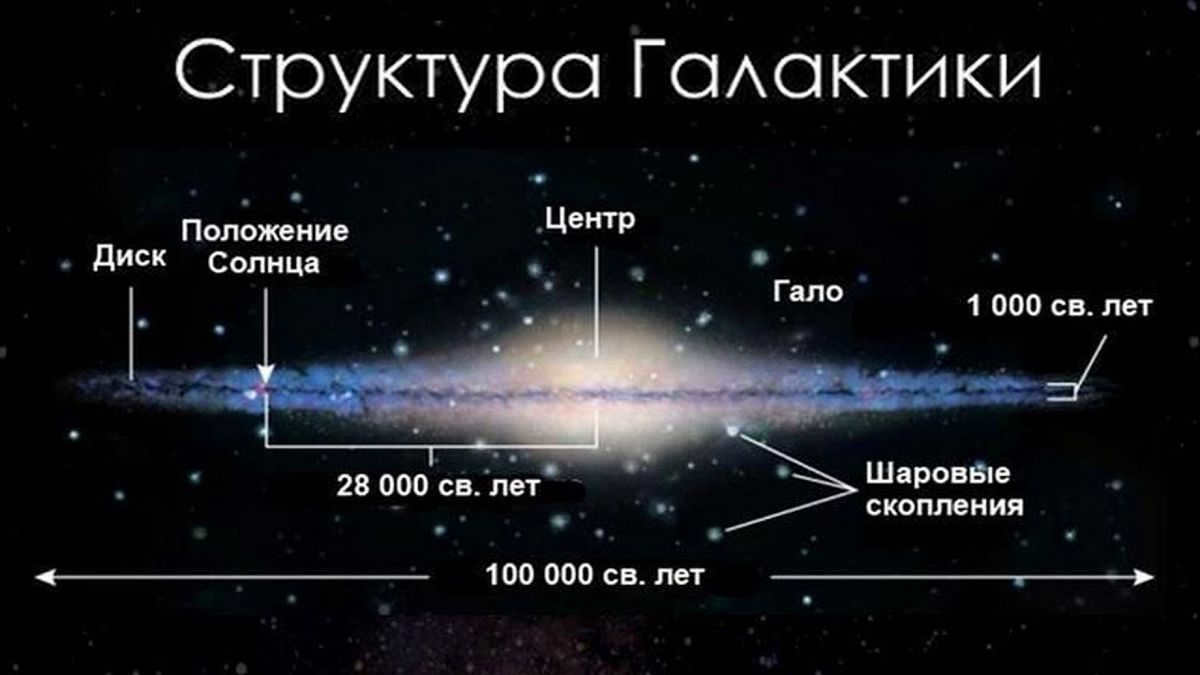
The Milky Way galaxy spans approximately 30,000 parsecs (equivalent to 100,000 light-years or 1 quintillion kilometers) in diameter, and has an estimated average thickness of about 1,000 light-years. It is believed to contain around 200 billion stars, although some modern estimates suggest a range of 200 to 400 billion. The majority of these stars are organized in a flat disk shape.
In the 1980s, astronomers proposed the idea that the Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy rather than a conventional spiral galaxy. This hypothesis was later confirmed in 2005 by the Lyman Spitzer Space Telescope, which revealed that the central bulge of our galaxy is larger than previously believed.
The core – The central part of the galaxy. The central regions of the Galaxy are characterized by a high concentration of stars: each cubic parsec near the center contains numerous stars. The distances between stars are much smaller compared to the vicinity of the Sun.
It is hypothesized that a massive black hole resides in the nucleus.
The Milky Way Galaxy is classified as a spiral galaxy, meaning it has spiral arms situated within the plane of the disk. The solar system is positioned at a distance of 8.5 thousand parsecs from the galactic center, specifically on the inner edge of the Orion arm. This placement prevents the visual observation of the arms’ shape.
The stars and star clusters in the halo exhibit elongated orbits as they orbit around the galactic center. Due to the random rotation of individual stars, with velocities in any direction, the halo itself undergoes a slow rotation as a collective. [1]
Questions regarding additional information [ edit correct code ]
Galileo Galilei’s astonishing finding during his exploration of the Milky Way [ edit correct code ]
- Elaborate on Galileo Galilei’s groundbreaking discovery while observing the Milky Way through a telescope.
In the year 1610, Galileo Galilei made an extraordinary revelation while examining the Milky Way with the aid of a telescope – he ascertained that the Milky Way consists of an immense multitude of dim stars.
The theory of the electromagnetic field was developed by physical scientists who also proved the existence of electromagnetic waves. Please provide the names of these scientists.
- Kindly state the names of the physical scientists who developed the theory of the electromagnetic field and provided evidence for the existence of electromagnetic waves.
Before discussing the discoverer of electromagnetic waves, it is important to note that the first scientist to predict their existence was Faraday, who is credited with founding the theory of the electromagnetic field. In 1832, Faraday put forward his hypothesis. Subsequently, Maxwell took up the task of developing the theory, completing it by 1865. Maxwell then mathematically formalized the theory, providing rigorous evidence for the existence of these phenomena. He also determined the speed at which electromagnetic waves propagate, which coincided with the accepted value of the speed of light at that time. This allowed him to support the hypothesis that light is one type of the radiation being considered. [2]
- Enumerate your most beloved science fiction films and popular scientific television shows that delve into the structure of the universe and its exploration.
Science fiction films that explore the structure of the universe:
- “Cosmos: Space and Time.”
- “How the Universe Works”
- “The Fabric of Space”
- “Hubble Space Odyssey.”
- “The Universe Before the Big Bang.”
- “The Universe.”
Popular scientific television programs on the same subject:
- Through space and time with Morgan Freeman
- BBC: Planets
- Into the Universe with Stephen Hawking
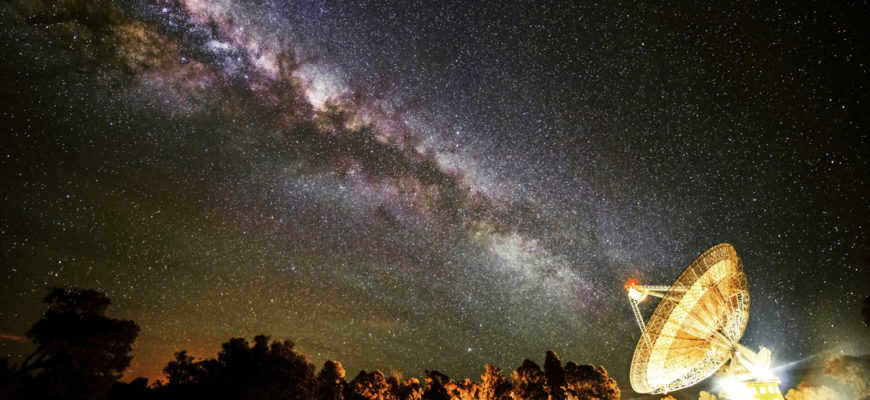

The Milky Way is the official name given to the galaxy that our solar system and Earth are a part of. It falls under the category of a “spiral galaxy” and is characterized by its disk-like shape with a spiral pattern inside.
All of the 200-400 billion stars within this galaxy orbit around a central point in a stretched, curved structure known as a bar or lintel. The name “Milky Way” was given to this galaxy because when observed from Earth’s perspective, it appears as a faint, light-colored band across the sky.
Distinctive Features (dimensions, diameter)
Initially, it was believed that the dimensions of the galaxy were diametrically – 30 thousand parsecs. This equates to approximately 100 thousand light years, or kilometers.
However, in 2018, astronomers from the Canary Institute compiled data from several studies based on spectral analysis. As a result, it was revealed that the diameter of the Milky Way galaxy may exceed expectations by 2 times, reaching 200 thousand light years. The thickness of our disk-shaped galaxy is estimated to be around 1 thousand light-years.
Celestial objects make up only a fraction of the total weight of the galaxy, which is composed of various elements such as planets, stars, interstellar gas, the halo, and dark matter. The invisible components, particularly dark matter, account for the majority of the weight, making it challenging to accurately determine the galactic mass in relation to the mass of the Sun. Currently, astrophysicists estimate that the Milky Way has a mass approximately 1.5 times that of the Sun.
The galaxy known as the Milky Way is composed of several distinct components, including a central core, a surrounding halo, a flat disk, spiral arms, and an outer corona. Of all these regions, the nucleus is widely regarded as the most enigmatic and intriguing.
The Core (Nucleus)
The central region of our galaxy contains a concentration of older stars, forming a dense bulge. There are several thousand celestial bodies per cubic parsec in this area. There are several theories about the exact nature of the central region. According to initial findings, there is a highly massive black hole at the center of the Milky Way, which has been named Sagittarius A. This name is based on its location in the direction of the Sagittarius constellation.
Subsequent to that, astronomers have proposed several hypotheses regarding the composition of the central region of the galaxy. In 2016, a team of Japanese scientists stumbled upon an enigmatic entity in the core, situated approximately 200 light-years from the nucleus. Experts in astrophysics have postulated that this enigmatic object could potentially be a secondary black hole, albeit smaller in size. Fast forward to 2018, and researchers have put forth the notion that within the vicinity of the galactic core, there may exist as many as 20 thousand black holes, possessing a mass akin to that of stars.
Areas of the Milky Way
The structure of our galaxy can be divided into several distinct parts:
The Architrave – This region encompasses the central core and is home to approximately 22 million ancient red stars. Scientists estimate its size to be around 27,000 light-years. Surrounding this central hub is a ring of gas rich in molecular hydrogen, which is believed to contribute to the high level of activity observed in this area.
The Disk – This is a flat region consisting of constellations, gas nebulae, and dust. It rotates at a faster speed than the core. The velocity of rotation varies depending on the distance from the core, ranging from 0 to 250 km/h. As one moves closer to the center, the motion of the galaxy slows down.
The corona is a luminous ring that encircles the outer regions of the galaxy. This celestial halo, stretching 5-10 light years beyond the confines of the Milky Way, exhibits a tumultuous and disorganized rotation of celestial objects, irrespective of their position. It is hypothesized that our galaxy has assimilated smaller galaxies, resulting in the formation of the corona from their remnants. Comprising globular clusters, ionized gas, constellations, and low-mass ancient stars, the corona contributes to the galactic landscape.
Various Models of the Milky Way Galaxy
Extensive research has revealed fascinating insights about our galaxy, debunking the notion that it is a flat structure. In fact, scientists have discovered that the Milky Way galaxy takes on a captivating curved shape resembling the letter S. Below, you can explore an exemplary model representing our galaxy, meticulously crafted by these skilled researchers. If you yearn for a complete visualization of the Milky Way Galaxy’s appearance, we encourage you to explore the remarkable 3D model of our galaxy, as well as other awe-inspiring renditions.
Stars in the Milky Way Galaxy
The exact number of stars in the Milky Way Galaxy remains unknown, but it is estimated to be around 200 to 400 billion. Additionally, scientists have also identified between 25 and 100 billion brown dwarfs within the galaxy.
Nebulae: A Changing Definition
The understanding of what constitutes a “nebula” has evolved significantly since the late 18th century. During this time, astronomers like Charles Messier initially defined a nebula as any celestial cluster that could not be resolved into individual stars. Nowadays, a nebula is defined as an interstellar region composed of dust, gas, and plasma that absorbs, scatters, or reflects light.
The renowned Andromeda Nebula was also discovered to be a galaxy during the scientific investigations of the 1920s. It is located quite a distance away from the Milky Way, approximately 2.52 million light years, yet it remains one of the closest neighboring galaxies. While there are numerous dark and light formations surrounding the Milky Way that are classified as true nebulae, the Horsehead nebula is the most well-known among them.
The galaxies surrounding the Milky Way are situated at an immense distance. Observing them with the naked eye is challenging, if not impossible. To illustrate, the Andromeda galaxy appears as a mere blurry speck, undistinguishable from a star.
In addition to the aforementioned Andromeda galaxy, other recognized galaxies include the Large Magellanic Cloud and the Small Magellanic Cloud. These dwarf galaxies orbit the Milky Way and are separated from it by 170 and 200 thousand light years, respectively. Astronomers have identified closer satellite galaxies around our galaxy, but their size is so minute that they remain imperceptible without specialized equipment.

The Milky Way, also known as the Galaxy, is a collection of two hundred billion stars that includes our own Sun and encompasses our planet.
It is also the designation for the region of the night sky that appears as a bright band, which is the largest concentration of stars within the Milky Way. Viewing individual stars within this whitish, silver streak requires the use of a telescope, as they are so far away from Earth that they blend together, resembling a cloud of cosmic dust.
Galileo was the first to observe the luminous clusters of stars within this celestial “powder” or “milk”. His invention of the telescope completely revolutionized our understanding of the world, despite its initial imperfections.
The ancient Greeks gave the Milky Way a poetic name, which was born out of their mythology. According to the legends, Zeus, in an attempt to immortalize his son Heracles, who was born to a mortal woman, placed him on the breast of his sleeping wife Hera. When Hera woke up, she angrily threw Heracles away, causing the milk from her breast to spill across the vast expanse of the starry sky…
Galaxies and supergalaxies
Galaxies and supergalaxies are celestial structures that captivate the imagination of astronomers and space enthusiasts alike. These vast cosmic systems, comprised of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter, are the building blocks of the universe.
Galaxies come in a variety of shapes and sizes. From spiral galaxies, characterized by their whirling arms of stars, to elliptical galaxies, which appear as smooth and featureless ovals, each type offers its own unique beauty and intrigue. Additionally, there are irregular galaxies that defy traditional classifications, with their chaotic and unpredictable shapes.
Supergalaxies, on the other hand, are even larger and more massive than galaxies. They are formed when multiple galaxies come together in a cosmic dance of gravity, merging and colliding to create something truly awe-inspiring. These colossal structures can span hundreds of thousands of light-years and contain billions of stars.
Studying galaxies and supergalaxies is crucial for understanding the evolution and dynamics of the universe. Astronomers use a variety of tools and techniques, including telescopes, spectroscopy, and computer simulations, to unravel the mysteries of these cosmic giants.
As our understanding of galaxies and supergalaxies deepens, so does our appreciation for the vastness and complexity of the universe. From the intricate spiral arms of a galaxy to the colossal collisions of supergalaxies, these celestial wonders continue to inspire and fascinate us, reminding us of the infinite possibilities that lie beyond our own small corner of the cosmos.

The universe is home to countless galaxies, and the Milky Way is just one of them. While the exact number of galaxies remains unknown to scientists, it is estimated to be in the trillions! These galaxies are organized into clusters known as supergalaxies, with each cluster containing anywhere from tens to several thousand galaxies. To date, researchers have identified 4,073 of these clusters.
Within the vast expanse of the universe, the Milky Way is situated in the Local Group of galaxies. This group consists of three large galaxies and forty dwarf galaxies, and it is a constituent of the Virgo Superscale.
Categories of Galaxies
There are four distinct categories into which all observed galaxies can be classified.
– Elliptical: These galaxies are named for their shape, which resembles a convex lens or an ellipse. They are characterized by a relatively low amount of interstellar dust and gases compared to other types of galaxies. Elliptical galaxies make up approximately 15-20% of the total number of galaxies.

– Irregulars. Each irregular galaxy has a unique shape, making it the most common type of star cluster after dwarf galaxies. All irregular clusters possess distinct characteristics such as size, cluster density, and structure.
– Dwarf. These galaxies are called “dwarf” due to their small size. The closest dwarf galaxy can be found in the Sagittarius constellation and is visible to the naked eye, appearing like one of the stars. In a few billion years, it will merge with the Milky Way and become part of it.
– Spiral. This is the Milky Way. Spiral galaxies are named after their shape, which consists of several “arms” – bands of star clusters that wrap around a central core in a flat body.
The Milky Way: A Spiral Galaxy
The immense size of the Milky Way can be comprehended by considering the dimensions of its flat shape, which spans a diameter of 100,000 light years. Our solar system, including the Sun and its planets, is positioned within the disk of the Milky Way, visible to us as a band of stars across the night sky. The distance from our solar system to the center of the galaxy is estimated to be approximately 28,000 light years, although some sources suggest it may be closer to 25,000 light years.
Surrounding our solar system is a cloud of interstellar dust and gas, known as the “bubble.” This region earned its name due to its extremely low density, essentially making it a vast emptiness. Within our bubble, the density of atoms measures at a mere 0.001 per cubic centimeter.
Similar to all other stars, the Sun completes a full rotation around the galactic core. This rotation, known as a galactic year, spans 250 million Earth years for the Sun.
Within the core of our galaxy reside billions of ancient stars, with a black hole at the center possessing a mass equivalent to 3,000,000 Suns.
The nearest star cluster resembling our own Milky Way is located 2 million light-years away. Scientists are actively studying this cluster to gain insight into the inner workings of our galaxy. Currently, they can only speculate and create virtual models to understand it better.
How many of you can confidently define what a galaxy is?
For most individuals, there exists a general understanding that a galaxy is somehow related to stars and outer space. They envision galaxies as vast entities that can be traversed, much like the protagonists in countless movies and books.
The term “galaxy” is derived from the Greek word “galaktikos”, which means “milky”. It refers to a massive spiral-shaped collection of stars. This is where our Sun is located, known as the Milky Way.
Interestingly, when viewed from Earth, our galaxy appears as a stretched band adorned with stars in the sky. However, it actually has the form of a disk with multiple twisted spiral arms.
While other galaxies can be observed in the sky, distinguishing them from stars and examining these star clusters in detail is only possible with the aid of powerful telescopes.
In ancient times, the Milky Way held great significance and was considered sacred by our ancestors. While each civilization had its own myths and legends surrounding it, the exceptional importance of the Milky Way in the depiction of the universe was widely recognized.

In contemporary times, not many individuals are aware that the Christmas tree symbolizes the World Tree in our physical realm. As per our forefathers, the Milky Way served as its trunk.
What are the components of a galaxy?
A galaxy, including our Milky Way and all other galaxies visible to astronomers through telescopes, is composed of an immense number of stars and star systems. The Milky Way alone contains approximately 200 billion stars.
Among these stars, our Sun is relatively small and not particularly bright. It is located on the outskirts of the galaxy, in one of its arms.
The central region of the galaxy is where the stars are most densely concentrated, creating a luminous spherical cluster. Scientists propose that if viewed from an external perspective, our galaxy resembles the shape of Saturn – a massive glowing sphere surrounded by a broad and relatively thin, uneven ring.
Aside from stars, the galaxy also holds vast formations of gas and dust, some of which produce a vibrant array of colors. The latest scientific discoveries reveal that these nebulas play a crucial role in the formation of new stars and star systems, a process that spans billions of years.
What lies at the heart of the galaxy?

One of the most enigmatic locations in the entire galaxy lies within its central region. However, the physical characteristics of this area differ so greatly from the surrounding regions of space that it took scientists quite a while to comprehend the true nature of this phenomenon.
Only recently has it been definitively determined that the central portion of our galaxy is home to a black hole. This region of space possesses altered properties that make it truly unique.
Our galaxy is relatively young, with an age of approximately 12 billion years. The processes of star formation within its core are still actively occurring, with numerous white dwarfs (young stars) having been discovered. Additionally, there are vast clusters of luminous gas, black holes of varying strength, and neutron stars present.

This massive, incomprehensibly vast cosmic “kitchen” is the source of a constant stream of new stars that are being produced at an astounding rate.
Which is larger, the universe or the galaxy?
By the way, our galaxy is not the only one in the Universe, despite its size. At present, astronomers have confirmed the existence of over a hundred other galaxies.
Some of these galaxies are relatively close to ours and can even be seen without any special equipment, such as the galaxy in the constellation Veronica’s Hair. Others can only be observed using powerful telescopes at observatories. There are also galaxies that can only be seen from space stations, where the presence of the atmosphere does not hinder space observation.