One of the most mesmerizing sights in our world is the view of the starry sky on a dark, moonless night. Countless stars, shining brightly or faintly, in various colors like red, white, and yellow, adorn the celestial expanse. But what exactly are stars? Let me explain it in a simple way that everyone can understand.
Stars are enormous celestial bodies scattered throughout outer space. These objects are held together by gravitational forces, with matter compressed tightly within them. The extreme temperatures within stars cause them to emit light, which is why we can see them. In fact, stars are so hot that even the most solid metals would exist on them in the form of electrically charged gas known as plasma.
What is the reason behind the luminosity of stars?
The emission of light from stars can be attributed to the high temperatures that exist within their core. The temperature inside stars can surpass 10 million degrees Celsius or even higher. These extreme temperatures facilitate thermonuclear reactions, resulting in the conversion of certain chemical elements into different ones. As an example, hydrogen, which is the primary constituent of nearly all stars, undergoes a transformation into helium within their inner regions.
Thermonuclear reactions serve as the primary source of energy for stars, allowing them to emit light and glow for numerous millions of years.
Stars and galaxies
The Universe contains an astronomical number of stars, estimated to be over a billion billion billion. Following the laws of nature, these stars have come together to form massive clusters known as galaxies. Our home lies within one of these galaxies, known as the Milky Way.

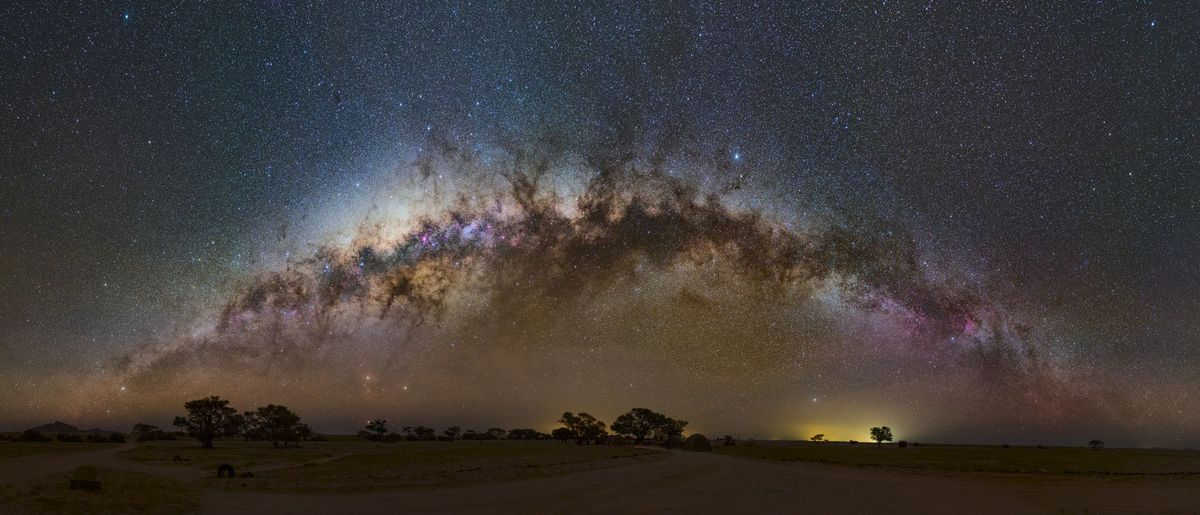
The Milky Way is a galaxy that includes our Sun and all the stars that we can see in the night sky. This stunning photo, captured by Juan Carlos Casado, shows the beauty of our galaxy and the stars that make up its luminous tapestry.
All the stars that are visible to the naked eye or through a small telescope are part of the Milky Way. Although there are other galaxies in the universe, when we observe them through a telescope, they appear as faint, blurry patches of light in the vast expanse of space.
The Sun holds the distinction of being our nearest star. It doesn’t stand out amidst the vast multitude of other stars observable through a telescope. The Sun is neither the most dazzling nor the most faint star, neither the hottest nor the coldest, neither the heaviest nor the lightest. In a sense, one could describe the Sun as a median star. Yet, to us, the Sun plays an incredibly significant role, for this star provides us with both heat and light. It is solely due to the Sun that life thrives on Earth.
The dimensions, weight, and brightness of celestial bodies
The dimensions and weight of even diminutive celestial bodies are immense. As an illustration, the Sun has a diameter that is 109 times that of the Earth and is 330,000 times more massive than our planet! To occupy the same volume as the Sun in outer space, we would require over a million planets the size of Earth!
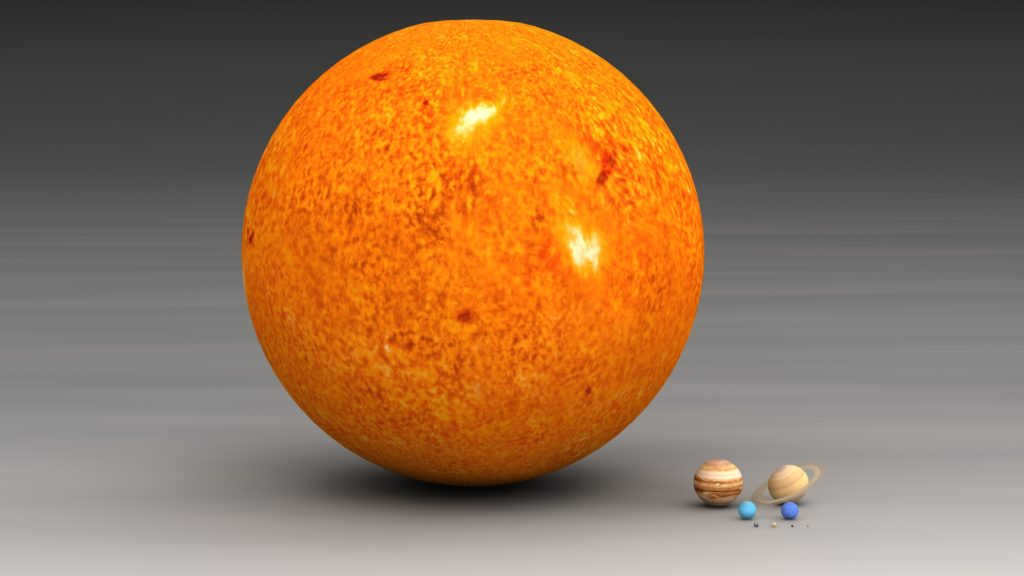

The sizes of the Sun and the planets in our Solar System can be compared. The Earth, depicted as the leftmost planet in the closest row, is just one of the many planets in our vast system.
However, it is important to note that the Sun, despite being an average star, is not the largest star in the universe. For example, Sirius, which is the brightest star in the night sky, is much bigger than the Sun. Sirius is twice as massive as the Sun and has a diameter 1.7 times larger. It also emits 25 times more light than our daytime star!
Another astonishing star is Spica, which leads the constellation Virgo. Spica has a mass 11 times greater than the Sun and a luminosity that is 13,000 times stronger! The sheer power and radiation emitted by this star is truly mind-boggling.
Our galaxy contains approximately 700 billion stars, with at least 500 billion of them being red dwarfs. However, the unfortunate fact is that red dwarfs are so dim that they cannot be seen with the naked eye. To observe these stars, one must use either a telescope or binoculars.
Unique Stars
Aside from red dwarfs, which make up the majority of stars in the Universe, there is also a small percentage of peculiar stars that possess distinct characteristics such as size, luminosity, or density that set them apart from other stars. These unusual stars include sun-like stars, Sirius, and Spica.
White Dwarfs
One particular star that acts as the companion to Sirius.
Many stars do not exist in isolation, like our Sun, but rather in pairs. These stars are known as double stars. Similar to how the Earth and other planets in our solar system orbit around the Sun due to its gravitational force, a companion star can also orbit around the main star.
Double stars consist of a primary star and a smaller companion star that both orbit around a shared center of mass, as depicted by the red cross in the illustration. Source: Wikipedia
In fact, not only do planets orbit around a shared center of mass with the Sun, but the components of a double star also revolve around a common center of mass (as shown in the animated image).
In the 19th century, scientists made a fascinating discovery about the star Sirius, which is the brightest star in the night sky. They found that Sirius had a companion, called Sirius B, that could only be seen through a telescope due to its faintness. What was even more surprising was that despite its faintness, Sirius B had a surface temperature just as hot as Sirius itself. This contradicted what astronomers knew at the time, which was that hotter bodies emit more light. If Sirius B was just as hot as Sirius, why was it so dim?
The answer lies in the size of Sirius B’s surface area. It was much smaller compared to Sirius A. In fact, it was discovered that Sirius B was the same size as Earth, while its mass was equivalent to that of the Sun! This meant that each cubic centimeter of Sirius B contained a staggering amount of matter, weighing 1 ton. The small surface area combined with its massive mass resulted in the satellite appearing dimmer compared to Sirius.
Anomalous stars have been given the name white dwarfs.
Giant red stars
Enormously large and luminous stars have also been discovered in the celestial sphere. One such star, Betelgeuse, has a diameter 900 times that of the Sun and emits 60000 times more light than our daylight! Another star, VY Canis Majoris, has a diameter 1420 times that of the Sun! If VY Canis Majoris were to take the place of the Sun, its surface would extend between the orbits of Jupiter and Saturn, with all the planets from Mercury to Jupiter (including Earth!) contained within the star!

The sizes of the Sun (top left), Sirius (white star), and some massive stars are compared. The UY Shield, a red supergiant that dominates the image, has a diameter 1,900 times larger than that of the Sun.
These stars are known as supergiants. What sets giant and supergiant stars apart is that, despite their immense size, they contain only 5, 10, or 20 times more matter than the Sun. Consequently, the density of these stars is very low. For instance, the average VY density of the Big Dog is 100,000 times lower than the density of room air!
Both white dwarfs and giant stars do not form in that state, but they undergo evolution after the hydrogen within them has transformed into helium.
Stars and the Enigma of the Universe’s Hidden Mass
Not long ago, astronomers held the belief that stars contained the majority of matter in the universe. However, in recent times, it has become evident that the vast majority of the universe’s mass is comprised of enigmatic dark matter and even more perplexing dark energy. Consequently, stars only account for approximately 2% of all matter (and an even smaller proportion for planets, comets, and asteroids!). Nevertheless, it is this minuscule 2% that we are capable of observing, as they emit light! It is hard to fathom just how lackluster the Universe would be without the presence of stars!

The vast expanse of our Universe is composed of countless galaxies, numbering in the trillions. Within this cosmic tapestry, our solar system finds itself nestled within a relatively large galaxy, with the total count of galaxies in the Universe limited to a mere few tens of billions.
What is the reason why we can’t see any stars in the sky during the daytime?

An illustration of the range of apparent brightnesses of different astronomical objects
The scale of stellar magnitudes, which measures the visible brightness of astronomical objects, is logarithmic: a change of one stellar magnitude corresponds to a difference of 2.512 times in the visible brightness, while a difference of five stellar magnitudes corresponds to a difference of 100 times.
What makes stars invisible in urban areas?
Aside from the challenges of observing stars during the day, there is a significant obstacle to observing stars at night in populated regions, such as near large cities and industrial facilities. This obstacle is known as light pollution, which is caused by artificial sources of radiation. Examples of such sources include street lights, illuminated billboards, gas flares from factories, and spotlights used at entertainment events.
In February 2001, John E. Bortle, an amateur astronomer from the United States, developed a light pollution scale to assess the level of light pollution in the sky. This scale, published in the Sky&Telescope journal, consists of nine divisions.
1. A sky devoid of any light
In this nocturnal expanse, not only can one behold the resplendent Milky Way in all its glory, but also witness the distinctive shadows cast by individual Milky Way clouds. The zodiacal light, a phenomenon resulting from the reflection of sunlight off dust particles situated on the opposite side of the Sun-Earth line, can be observed in intricate detail. Stars of up to 8 star magnitudes are discernible to the naked eye, while the overall luminosity of the sky measures at 22 star magnitudes per square angular second.
In this image, the Milky Way and zodiacal light are prominently displayed against the night sky. The antiscia is also visible. When observing with the naked eye, stars with apparent brightness up to 7.5 star magnitudes can be seen, while the background sky brightness measures around 21.5 star magnitudes per square angular second.
3. Countryside sky
In this particular sky, both the zodiacal light and the Milky Way remain easily visible, although with less detail. Stars with a brightness of up to 7 star magnitudes can be observed, while the background sky brightness measures approximately 21 star magnitudes per square angular second.
4. The atmosphere in the space between villages and suburbs
Within this particular airspace, one can still catch glimpses of the ethereal Milky Way and the enigmatic zodiacal light, albeit with limited clarity and only when looking toward the heavens. With the unaided eye, stars of up to 6.5 magnitudes can be observed, while the overall luminosity of the celestial backdrop measures approximately 21 magnitudes per square angular second.
5. The sky above urban areas
Within urban areas, it is rare to catch a glimpse of the zodiacal light or the Milky Way, even under optimal weather and seasonal conditions. The naked eye can only perceive stars with a magnitude of up to 6, while the overall brightness of the sky reaches around 20.5 magnitudes per square angular second.
6. The sky over suburban regions
In suburban regions, the zodiacal light is never visible, regardless of the conditions, and the Milky Way can only be faintly seen when directly overhead. The naked eye can detect stars with a magnitude of up to 5.5, and the background sky brightness measures approximately 19 magnitudes per square angular second.
7. The atmosphere above the region where suburbs meet cities
In this particular region, it is impossible to see either the zodiacal light or the Milky Way no matter the circumstances. Without the aid of a telescope, the human eye can only perceive stars up to a magnitude of 5. The overall brightness of the sky in this area reaches approximately 18 star magnitudes per square angular second.
8. Urban sky
In an urban sky, only a limited number of the most brilliant diffuse star clusters are visible to the unaided eye. The human eye is capable of perceiving stars with magnitudes of up to 4.5, while the overall brightness of the sky is below 18 magnitudes per square angular second.
9. Sky in the heart of cities
In a sky similar to this, only the Pleiades star cluster can be distinguished. The naked eye can only perceive stars with magnitudes up to 4.
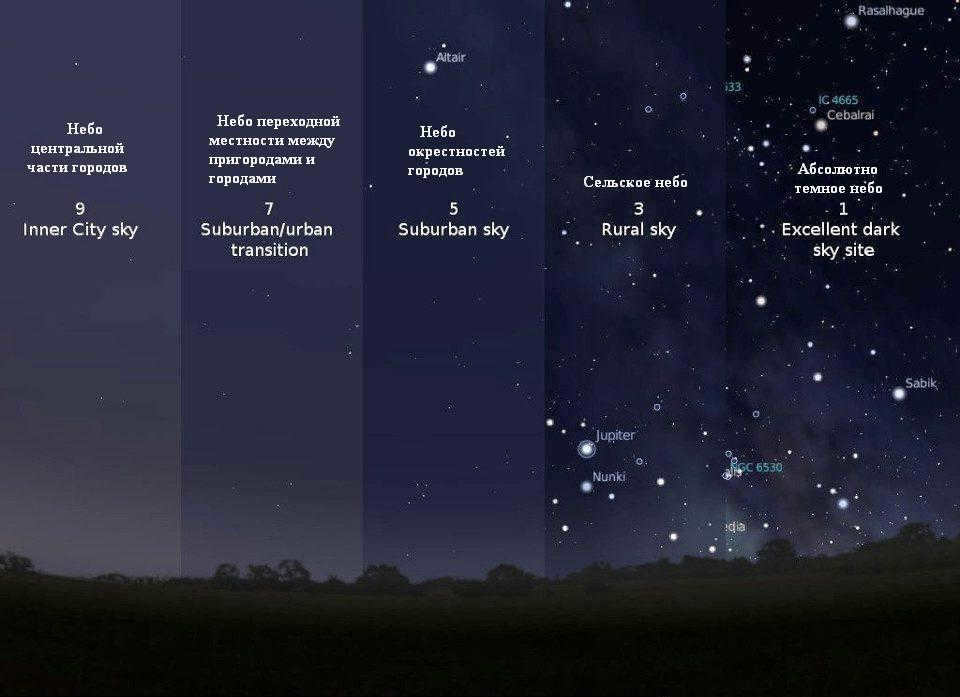
Here is a diagram illustrating the different types of skies based on the Bortle scale.
Due to the impact of light pollution caused by residential, industrial, transportation, and other aspects of modern human civilization, there is a need to establish large-scale astronomical observatories in remote high-mountainous regions far away from human civilization. These areas strictly adhere to specific regulations that limit street lighting, restrict nighttime traffic, and control the construction of residential buildings and transportation infrastructure. Similarly, special protection zones have been designated around the oldest observatories near major cities. For instance, in 1945, a protective park zone was established within a 3 km radius of the Pulkovo Observatory near St. Petersburg, where any large-scale residential or industrial development was prohibited. However, in recent years, there has been an increase in attempts to construct residential buildings within this protective zone due to the high cost of land near one of Russia’s largest megacities. A similar situation can be observed around the astronomical observatories in Crimea, which are situated in an incredibly attractive tourist region.
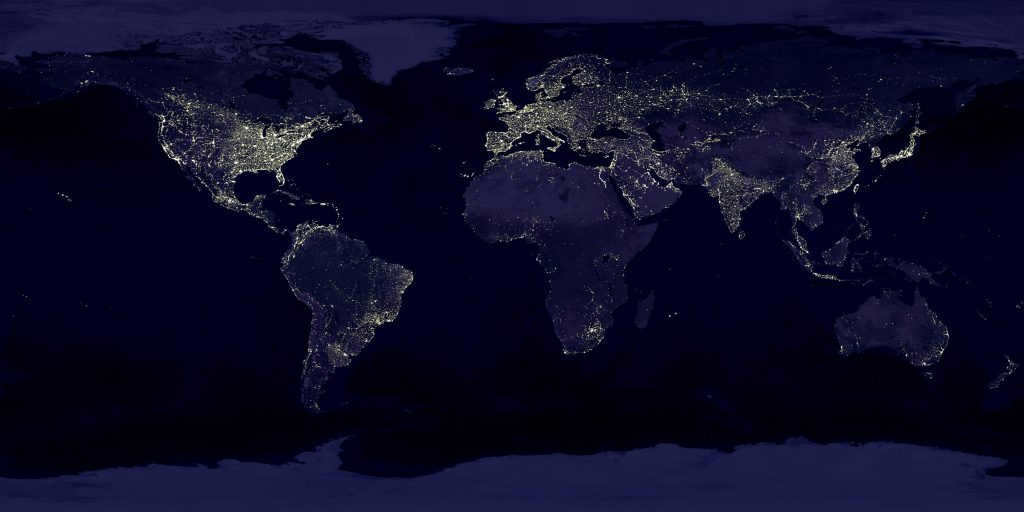

By utilizing night observations from satellites, it becomes possible to create an impartial map of different regions on the Earth’s surface that experience various degrees of illumination.
The NASA picture provides a clear depiction of the regions that are most brightly lit, which include Western Europe, the eastern portion of the continental United States, Japan, coastal China, the Middle East, Indonesia, India, and the southern coast of Brazil. Conversely, the polar regions (particularly Antarctica and Greenland), areas of the World Ocean, the tropical river basins of the Amazon and Congo, the high Tibetan plateau, desert regions of northern Africa, central Australia, northern Siberia, and the Far East exhibit the least amount of artificial lighting.
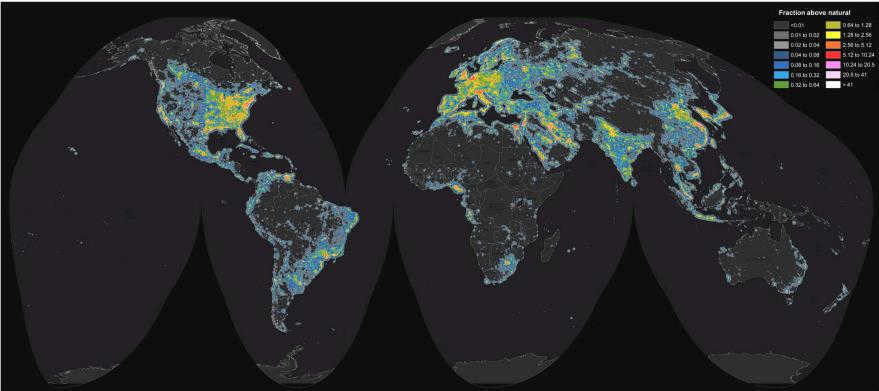
Percentage of natural illumination represented by artificial light pollution on a map
A study has revealed that the highest levels of light pollution can be found in the Nile Delta region of Cairo. This is primarily due to the incredibly dense population of the Egyptian capital, with 20 million people living in an area of just 500 square kilometers. This results in an average population density of 40,000 individuals per square kilometer, which is approximately 10 times higher than the average population density in Moscow. In certain parts of Cairo, the population density surpasses 100,000 people per square kilometer. Other areas with significant light exposure include the metropolitan regions of Bonn-Dortmund (located near the Germany-Belgium-Netherlands border), the Padana Plain in northern Italy, the stretch between Boston and Washington, DC in the United States, and the surroundings of London, Liverpool, Leeds, Beijing, and Hong Kong. In order for residents of Paris to witness a truly dark sky (with light pollution levels below 8% of natural illumination), they would need to travel a minimum of 900 kilometers to Corsica, central Scotland, or the province of Cuenca in Spain. Similarly, for individuals in Switzerland to experience extremely dark skies (with light pollution levels below 1% of natural light), they would have to embark on a journey of over 1360 kilometers to the northwestern part of Scotland, Algeria, or Ukraine.
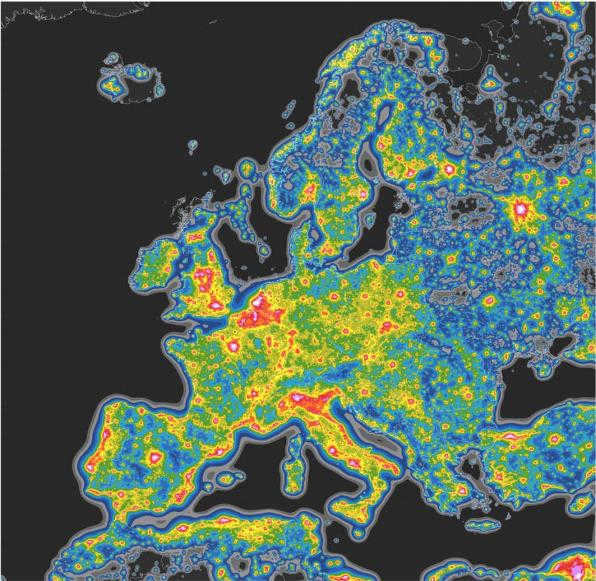
This image displays a map illustrating the extent of light pollution across Europe. It highlights the areas where artificial light sources have contributed to the obscuring of stars in the night sky.
The level of absence of dark skies varies greatly among different countries. Singapore holds the record with 100% of its territory experiencing this phenomenon, followed closely by Kuwait at 98% and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) at 93%. Other countries with high percentages include Saudi Arabia at 83%, South Korea at 66%, Israel at 61%, Argentina at 58%, Libya at 53%, and Trinidad and Tobago at 50%. In these countries, the presence of artificial light pollution obscures the view of the Milky Way, making it impossible for residents to observe it.
In addition to these countries, smaller nations like Singapore, San Marino, Kuwait, Qatar, and Malta also face significant challenges in observing the Milky Way. In Singapore and San Marino, the entire territory is affected, resulting in a 100% obstruction. Similarly, 99% of residents in the UAE, 98% in Israel, and 97% in Egypt are unable to observe the Milky Way due to light pollution.
When looking at the proportion of territory where the Milky Way is not visible, Singapore and San Marino top the list with 100% each. Malta follows closely behind at 89%, while the West Bank experiences a 61% obstruction. Qatar and Kuwait both have 55% of their territory affected, while Belgium and the Netherlands have 51% and 43% respectively. Finally, Israel rounds up the list with 42% of its territory unable to observe the Milky Way.
Paris Earth Hour 2017
While the event has its benefits, such as raising awareness about climate change and promoting energy conservation, there are also drawbacks to consider. One major concern is the potential for increased accidents in global energy systems due to the sudden switch on and off of a large number of electrical appliances. Additionally, studies have shown a clear link between the absence of street lighting and an increase in injuries, street crime, and other emergencies.
What is the reason behind the absence of stars in images captured from the International Space Station (ISS)?
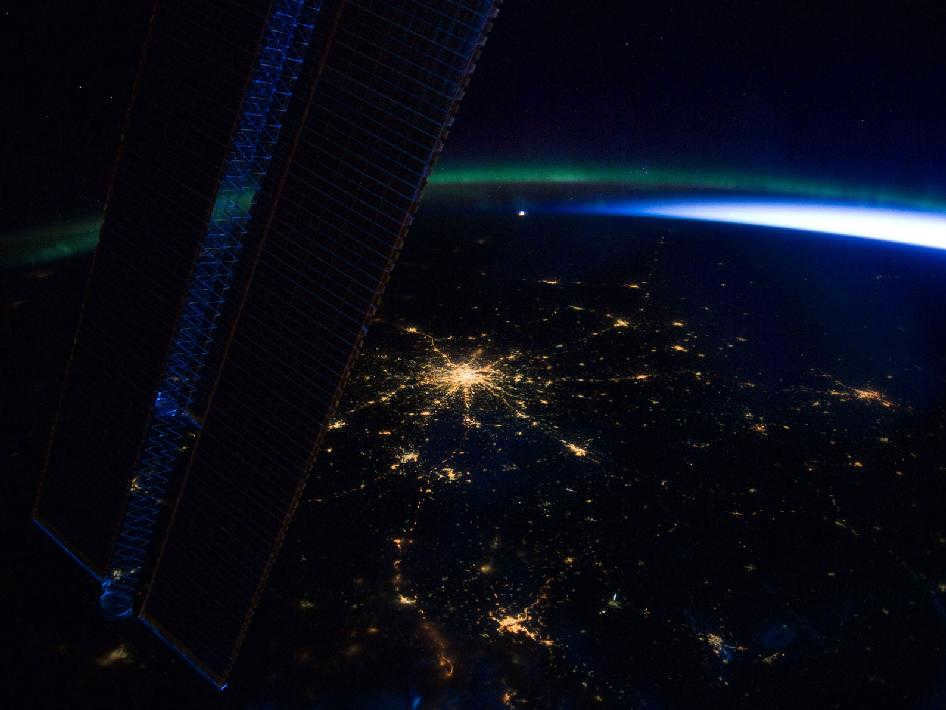


A captured image by NASA while aboard the International Space Station (ISS)
The picture clearly depicts the illuminated city of Moscow, the faint greenish glow of the aurora borealis on the horizon, and the lack of visible stars in the sky. The substantial contrast between the Sun’s brightness and even the most luminous stars renders star observation impossible not only during daylight hours from the Earth’s surface, but also from outer space. This phenomenon effectively highlights the significant impact of “light pollution” from the Sun, relative to the Earth’s atmosphere, on astronomical observations. Nevertheless, the absence of stars in photographs of the sky taken during manned journeys to the Moon has become a central piece of evidence fueling the conspiracy theory that NASA astronauts never actually made it to the Moon.

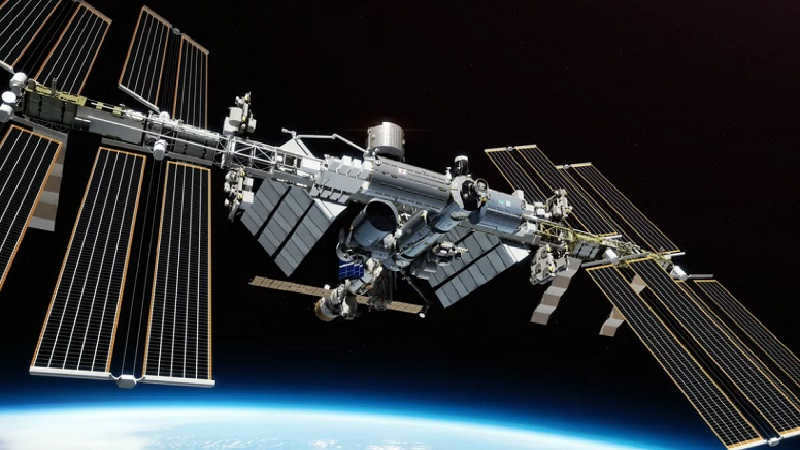
Another picture of the International Space Station (ISS) captured by a spacecraft as it approaches the station.
Why can’t we see any stars in photos of the Moon?
While the Sun appears much brighter than the brightest star, Sirius, in our Earth’s sky with a difference of about 25 star magnitudes or 10 billion times, the apparent luminosity of the full Moon is only 11 star magnitudes dimmer than Sirius, which is roughly 10 thousand times.

Did you enjoy reading this article? Share it with your friends!

It is a frequent occurrence that we, as inhabitants of Earth, are unable to witness the stars that encompass our planet. In fact, it is not always and not in every location that we can behold them. Furthermore, even when we do catch sight of these magnificent gaseous celestial bodies, we are only able to see a fraction of them. For our Universe is truly abundant in such wonders.

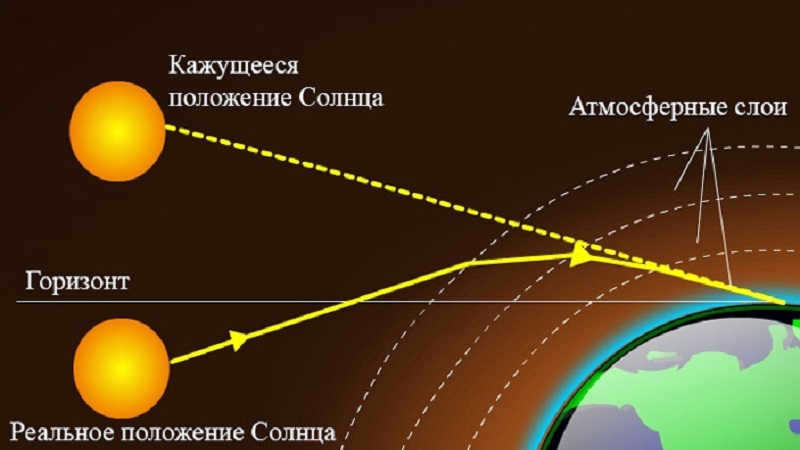
Why is it impossible to observe stars during the day?
There are several factors that contribute to the inability to see stars during daylight:
- Stars emit their own light, unlike other celestial bodies which reflect light.
- The Earth’s atmosphere refracts and scatters sunlight, preventing other sources of light from being visible.
- The color of light is determined by its wavelength. Short wavelengths, such as cyan, blue, and violet, are prevalent during the day, resulting in a blue sky. Longer wavelengths, like red, are dominant during sunset, creating a red sky. This phenomenon limits our ability to see stars during the day.
- The presence of various colors and tints in the sky, as well as the Earth’s atmosphere, prevent starlight from reaching the planet’s surface. Additionally, sunlight during the day scatters in the atmosphere, obscuring the visibility of other stars.
- All stars, excluding the Sun, are located at a significant distance from Earth. Consequently, it becomes impossible to observe them during daylight hours when numerous obstructions arise.
These factors primarily contribute to the exclusive visibility of stars in darkness.
As you are aware, the Sun is not merely a luminous object. It is the nearest and, in fact, the sole star in the solar system. It is the reason behind the existence of life on Earth. Moreover, the Sun influences nearly all the processes occurring in our surroundings, including outer space, particularly within our star system.
Have you longed to create your own website or develop an application but didn’t know where to begin? Online programming courses can provide the assistance you need.
Why stars are more visible in winter
The visibility of stars in the night sky varies throughout the year for observers on Earth. This is due to the movement of the sun and the rotation of our planet around it.
As the Earth and the sun move, the distance between them changes. The closest they come is in January, when most of the sunlight falls on the southern part of the planet, bringing summer. Conversely, the northern part experiences winter. In July, when the Earth is farthest from the Sun, the northern part experiences summer and warmth. This cycle is what brings about the changing seasons.
Due to the planet’s farthest distance from the Sun in the winter months, the nighttime sky appears darker compared to other times. This results in improved visibility and allows for easier observation of objects in the night sky.
It is crucial to note that the visibility of celestial objects is not influenced by the season but rather by the sky’s color, which, in turn, is affected by the time of year and specifically the proximity to the Sun.

Why is it difficult to see stars in the city?
City dwellers are often unable to see a large number of stars, as they are only able to see the brightest ones.
There are a few reasons for this. Firstly, the distance between the stars and the city makes them appear less bright. Secondly, during the daytime, the Sun’s light makes it difficult to see other astronomical objects, except for a few exceptions.
Additionally, light pollution is a major issue in populated areas. The artificial lighting created by human civilization, such as streetlights, advertising signs, and spotlights, obscures the view of the stars in the sky.
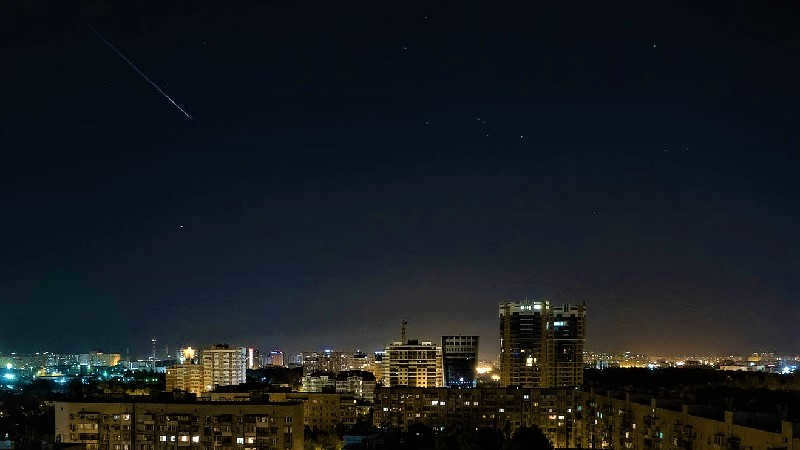

Light pollution refers to the phenomenon of the night sky being illuminated by artificial sources of light, which leads to the scattering of light in the lower layers of the atmosphere and reduces the visibility of celestial objects.
Why are stars not visible in images of the International Space Station?
Interestingly, the images of the International Space Station (ISS) do not capture any stars, despite the fact that this orbital station has helped explore numerous astronomical objects. So, what is the reason behind the absence of stars in ISS images?
It turns out that the brightness of the Sun makes it impossible to observe other luminous celestial bodies. The apparent difference in brightness between the Sun and even the brightest stars affects their visibility. This applies not only to observations from the Earth’s surface but also from space. Therefore, when looking from a spacecraft, the sunlight overwhelms everything else, including the stars.
It is worth noting that images taken on the Moon also do not show stars.

The only celestial body that remains unseen in the nocturnal sky
Curiously, many people often pose this question. In reality, it’s more of a logical inquiry. As one might comprehend, it becomes challenging to perceive celestial bodies under certain conditions. The optimal time for stargazing is during the nighttime.
So, which celestial body eludes our vision during the night? Undoubtedly, it is our very own Sun.
Naturally, numerous stars can be observed through a telescope at any hour of the day. Nevertheless, it is most favorable to observe them after the sun sets. After all, darkness conceals many captivating and beautiful things!
Now you possess the knowledge of where, when, and under what circumstances stars are most visible. I trust this information will prove beneficial in your stargazing endeavors!
From thorns to the Stars….
“Hollywood is heading to the moon.” Once again, the moon scam!
Americans have never set foot on the moon. Evidence and rationale
A conversation with Violet.
10 Comments “Feel free to share your thoughts”

john May 29, 2017 21:21
The reason why stars cannot be seen during the day is due to brainwashing. It might seem like a strange question, but stars are only visible at night because they reflect light from objects when the sun is on the opposite side of the Earth. When you view the Earth from space, it means that the sun is on the same side as the spacecraft. Otherwise, the Earth would appear black, and that’s why the stars cannot be seen. It’s a simple trick – try turning on a flashlight at night and looking sideways through the beam, and you will understand.
Vladimir → john May 30, 2017 4:28 pm.
Have faith in your vision. On clear nights, take a look and you might spot satellites or the International Space Station (ISS) illuminated by the Sun, both of which supposedly fly thousands of miles above the Earth’s surface. They truly shine in the darkness.
It is commonly said that in the vacuum of space, the boiling point of a liquid is not a fixed value; it actually depends on the pressure exerted on the liquid. In fact, in a vacuum, the boiling point of water can be lower than room temperature! This raises the question of how astronauts in their soft suits are able to create and maintain pressure. There is even a video showing an astronaut in outer space wearing boots with laces.
In the past, there used to be a pendulum in St. Isaac’s Cathedral. What was the purpose of this pendulum? And why was it eventually removed?
Interestingly, there are no young individuals among the cosmonauts. Why is that the case? Only older men are selected for space missions! The ISS seems to be full of bespectacled men, just like a medical commission.












john -> Vladimir May 30, 2017 9:04 am
It all relies on the size of the object, if the satellites were at least 1/3 of the size of the moon, it would be visible at this distance. And concerning the spacesuit, it is similar to a diver who dives to a depth of 100 meters, although if from such a depth to raise to the surface of the deep-sea fish, it will explode. I don’t know, I haven’t been there, it’s all speculation. Maybe it is only in the vicinity of the earth works.
Vladimir -> john May 30, 2017 11:15 am
We from the ISS demonstrate how night lighting in cities burns! Depth and space vacuum are different environments, according to YOUR astronauts decompression!? So you are correct to say that everything is a theory. All these theories are disproved.
Igor May 29, 2017 23:17
The research is undeniably captivating, however, our comrade will diligently investigate the accessible information. In order to unearth the truth, one must have a comprehensive understanding, which unfortunately is currently lacking. We can only suggest that he embarks on a cosmic journey himself, if he possesses the necessary “fuel”….)))) May divine gravity guide him.
inquisitive May 30, 2017 3:38 am
curious May 30, 2017 5:34
Ursus May 30, 2017 10:17
?! Amplified reflection of the enigmatic object on the ISS in Dextre’s window. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Jf5SU2Obr7s
Vladimir → Ursus May 30, 2017 11:26 am
This is the countenance of the individual recording in this contrived studio! There is yet another deceitful element in this footage; the dish is rotating, but such antennas do not operate in this mode of rotation! They should be precisely directed.
Anna May 30, 2017 15:27
Thank you so much for sharing the video. It has sparked numerous thoughts and I find it extremely valuable. Your work is greatly appreciated. Keep up the excellent job.
Please feel free to leave a comment
Explore our navigation menu
Discover different headings
Learn more about our site
Pandora’s Box is a comprehensive website that explores a wide range of topics including science, history, religion, education, culture, and politics.
According to legend, the website was once a repository of “secret knowledge” – information that remained hidden and only accessible to those who were initiated. By familiarizing yourself with this information, you could have encountered a source of profound truth and gained a new perspective on the world.
However, it is now widely known that this is merely a myth. Nevertheless, there are rumors that the website still publishes some form of “secret knowledge” within its regular news stream.
It is left to your discretion whether to delve into Pandora’s Box and verify the authenticity of this legend.
Please be aware that the website may contain content unsuitable for individuals under the age of 18. We advise reading the relevant sections before proceeding with browsing:
If you have any questions or suggestions, please contact [email protected].

The proponents of conspiracy theories have increased their efforts. Some are on the lookout for UFOs, while others are promoting the flat Earth theory. There are also those who are “exposing” the U.S. lunar program, providing countless reasons why Americans were not on the Earth’s satellite. It would be easy to dismiss these enthusiasts as fans of REN-TV programs, but their numbers are growing. Experts from NASA have provided an explanation for why the photos taken on the lunar surface do not show any stars.
In the 1960s, two global powers – the Soviet Union and the United States – clashed in a fierce competition for dominance in the realm of space exploration. While the space race was a non-violent endeavor, it was a tense rivalry between Soviet and American engineers, each representing their respective political ideologies of socialism and capitalism.
The Soviet Union emerged victorious in the initial stages of the race. In 1957, they successfully launched the first artificial satellite into orbit, followed by Yuri Gagarin’s historic orbit around the Earth aboard the Vostok-1 spacecraft in 1961. The Americans were unable to surpass the expertise and advancements of their Soviet counterparts. However, the ultimate frontier remained the Moon, and the United States dedicated all its resources and a staggering sum of 135 billion dollars to conquer Earth’s satellite. Finally, in 1969, they achieved the historic feat of becoming the first to set foot on the lunar surface.
Conspiracy Theory
The concept of conspiracy theory has always been a topic of interest and intrigue for many people. It is a notion that suggests secret and hidden plans or actions by powerful individuals or groups, often with malevolent intentions. These theories often challenge the official narratives presented by governments, media, or other authoritative sources.
Conspiracy theories can range from relatively harmless speculations to more extreme and dangerous claims. Some popular conspiracy theories include the notion that the moon landing was faked, that the 9/11 attacks were an inside job, or that powerful organizations control the world’s governments and economies.
While some conspiracy theories have been proven to be true over time, many remain unverified or are widely dismissed as baseless. However, the allure of conspiracy theories persists due to the desire to uncover hidden truths or to find explanations for events that seem inexplicable.
It is important to approach conspiracy theories with a critical mindset and to rely on evidence-based information. While questioning authority and seeking alternative perspectives can be valuable, it is also crucial to discern between fact and fiction.
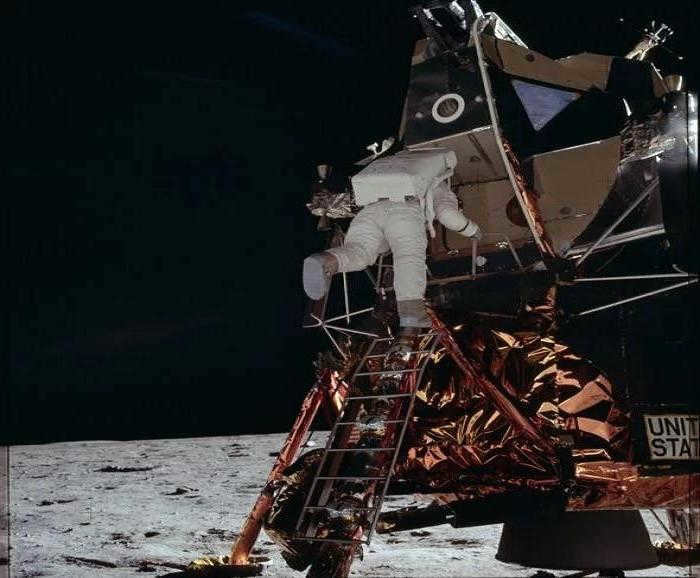

Back in 1968, astronaut William Anders made history by capturing the iconic photograph known as Earthrise during the Apollo 8 mission. This stunning image shows the Earth floating above the moon’s horizon, set against the vast expanse of space.
However, controversy arose shortly after the photograph’s publication, with some people questioning its authenticity. Even in the United States, doubts were raised. How could this be? After all, we see countless stars shining brightly in the night sky. And in space, without the interference of an atmosphere, they should be even more visible. The suspicions were fueled further by images taken by astronauts on the moon’s surface, which also lacked any visible stars.
NASA’s response
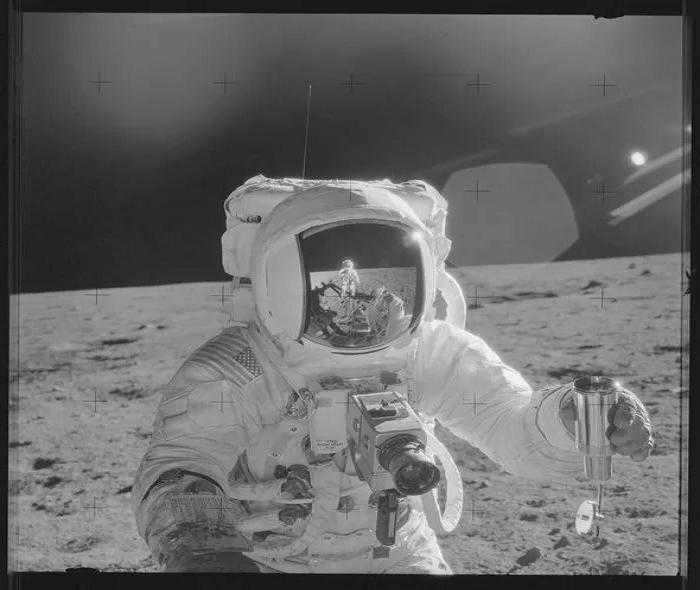


The explanation was quite straightforward and compelling. At least for those who don’t consider the principles of physics to be outdated. In order to achieve clear and defined images, the astronauts used Hasselblad cameras with short exposure times. During the fraction of a second that the camera lens is open, the faint light emitted by stars is not able to be captured on the film. However, if the exposure time is extended, there is a risk of blurring nearby objects due to the movement of the astronauts’ hands holding the camera.





